西昆仑山前甫沙—克里阳地区中新生代构造事件的裂变径迹证据及其地质意义
来源期刊:中南大学学报(自然科学版)2018年第3期
论文作者:王震亮 廖晓 范昌育 YANG You-xing(杨有星) 解巧明 赵子龙
文章页码:642 - 655
关键词:油气聚集;裂变径迹;构造事件;中新生代;甫沙—克里阳地区;西昆仑山前
Key words:hydrocarbon accumulation; fission track; tectonic event; Meso—Cenozoic; Fusha—Keliyang area; piedmont of the western Kunlun Mountains
摘 要:基于甫沙—克里阳地区位于塔里木盆地和西昆仑造山带的盆山结合部位,其构造位置特殊、演化复杂,综合运用锆石、磷灰石裂变径迹测年及磷灰石热演化历史模拟方法,结合野外地质调查和地震资料,对该地区进行低温热年代学研究。研究结果表明:甫沙—克里阳地区中新生代发生5期构造事件,对应地质时代分别为晚三叠世、晚侏罗世、晚白垩世、早中新世和上新世;各期构造事件在本区及周邻均具有明显的地质响应,其中,晚三叠世的构造事件具有长期整体抬升的特征,该事件使得本区烃源岩的热演化程度延缓,为油气的晚期成藏奠定了基础;而上新世的快速抬升事件则使得研究区内烃源岩、断裂输导和圈闭等成藏要素相互耦合,促使油气发生晚期成藏,对该区油气聚集具有重要的控制作用。
Abstract: The Fusha—Keliyang area is located in the conjunction region of Tarim Basin and western Kunlun Orogenic Belt, which has a special tectonic location and complex evolutionary history. Zircon, apatite fission track dating and time-temperature thermal history modeling combined with field geological survey and seismic data were carried out to analyze the uplifting history of the Fusha—Keliyang area.The results show that the Fusha—Keliyang area undergoes five cooling events which occurs in the Late Triassic, Late Jurassic, Late Cretaceous, Early Miocene and Pliocene. The five cooling events have good response relationship with the regional background and field geological characteristics. The Late Triassic uplift event has the characteristics of long-term overall uplift, which lays the foundation for the late hydrocarbon accumulation. The Pliocene uplift event makes the source rock, faults, trap couple with each other in the study area, which leads to oil and gas accumulation in the late stage, and plays an important role in controlling the hydrocarbon accumulation in the area.
DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2018.03.018
廖晓1, 2,王震亮1, 2,范昌育1, 2,杨有星3,解巧明1, 2,赵子龙1, 2
(1. 西北大学 大陆动力学国家重点实验室,陕西 西安,710069;
2. 西北大学 地质学系,陕西 西安,710069;
3. 中国地质调查局油气资源调查中心,北京,100029)
摘要:基于甫沙—克里阳地区位于塔里木盆地和西昆仑造山带的盆山结合部位,其构造位置特殊、演化复杂,综合运用锆石、磷灰石裂变径迹测年及磷灰石热演化历史模拟方法,结合野外地质调查和地震资料,对该地区进行低温热年代学研究。研究结果表明:甫沙—克里阳地区中新生代发生5期构造事件,对应地质时代分别为晚三叠世、晚侏罗世、晚白垩世、早中新世和上新世;各期构造事件在本区及周邻均具有明显的地质响应,其中,晚三叠世的构造事件具有长期整体抬升的特征,该事件使得本区烃源岩的热演化程度延缓,为油气的晚期成藏奠定了基础;而上新世的快速抬升事件则使得研究区内烃源岩、断裂输导和圈闭等成藏要素相互耦合,促使油气发生晚期成藏,对该区油气聚集具有重要的控制作用。
关键词:油气聚集;裂变径迹;构造事件;中新生代;甫沙—克里阳地区;西昆仑山前
中图分类号:P542 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2018)03-0642-13
LIAO Xiao1, 2, WANG Zhenliang1, 2, FAN Changyu1, 2, YANG Youxing3, XIE Qiaoming1, 2, ZHAO Zilong1, 2
(1. State Key Laboratory of Continental Dynamics, Northwest University, Xi’an 710069, China;
2. Department of Geology, Northwest University, Xi’an 710069, China;
3. Oil and Gas Resource Research Center, China Geological Survey, Beijing 100029, China)
Abstract: The Fusha—Keliyang area is located in the conjunction region of Tarim Basin and western Kunlun Orogenic Belt, which has a special tectonic location and complex evolutionary history. Zircon, apatite fission track dating and time-temperature thermal history modeling combined with field geological survey and seismic data were carried out to analyze the uplifting history of the Fusha—Keliyang area.The results show that the Fusha—Keliyang area undergoes five cooling events which occurs in the Late Triassic, Late Jurassic, Late Cretaceous, Early Miocene and Pliocene. The five cooling events have good response relationship with the regional background and field geological characteristics. The Late Triassic uplift event has the characteristics of long-term overall uplift, which lays the foundation for the late hydrocarbon accumulation. The Pliocene uplift event makes the source rock, faults, trap couple with each other in the study area, which leads to oil and gas accumulation in the late stage, and plays an important role in controlling the hydrocarbon accumulation in the area.
Key words: hydrocarbon accumulation; fission track; tectonic event; Meso—Cenozoic; Fusha—Keliyang area; piedmont of the western Kunlun Mountains
西昆仑造山带位于青藏高原的西北缘、塔里木盆地的西南缘,西接帕米尔,东连阿尔金山和东昆仑山,是中央造山带的重要组成部分。其构造线呈近东西向,绵延2 000多km,是1条复合型造山带。西昆仑造山带跨越和衔接帕米尔高原、塔里木盆地西南坳陷、青藏高原、阿尔金断裂、东昆仑造山带等众多性质各不相同的构造单元,自中生代以来先后经历了晚三叠世羌塘地块和塔里木板块碰撞拼贴,古特提斯洋消失[1-4],晚侏罗世构造带深部物质持续汇聚和向上运移引发的北向逆冲扩展[5-8],晚白垩世缓慢隆升和均匀沉 降[9-11],中新世印度板块向欧亚板块俯冲导致西昆仑造山带强烈地北向逆冲扩展[12-14],上新世受青藏高原快速隆起发生快速抬升[15-16],地球动力学背景演化过程复杂,对应的沉积格局经历了由海相到内陆湖盆再到以海湾三角洲为主的局限海盆,最终由海到陆的多期变迁转换[5, 17-18]。地层展布既有古近系在塔西南坳陷全盆分布,也有侏罗系局限分布于西昆仑山前[16-17, 19],逆冲推覆、褶皱变形、三角带构造、不整合、抬升剥蚀现象发育[13, 20-24],发育于不同时期的断裂混为一体[25-26],烃源岩、储集层、盖层、圈闭、输导体系等油气地质条件发育[24, 27],并且陆续不断地有油气发现。独特的大地构造位置、复杂的沉积演化、良好的油气成藏条件使得西昆仑造山带及相邻区域倍受众多研究者的青睐,成为研究的热点地区。甫沙—克里阳地区位于西昆仑造山带北部的中东段,是塔里木盆地西南坳陷重要的构造转折带,多期次叠加的构造作用使得区内现今褶皱、断裂、逆冲推覆等构造发育[24, 26, 28],地层出露分布范围差异大、不整合现象普遍发育[18-19]。柯克亚凝析油气田和柯东1井高产油气流在该区被相继发现,充分显示了该区良好的油气勘探前景。该区在中新生代前陆盆地发展演化阶段时发生了几期构造事件,不同期次的构造事件有何差异,对后期柯克亚、柯东1井等的油气聚集成藏产生了什么影响,这些问题都制约了人们对该区的科学认知和进一步油气勘探,而前人对这方面的研究很少,因此,在研究甫沙—克里阳地区中新生代构造事件发生时间、期次、特征差异的基础上,探讨其对该区油气成藏地质条件的影响,不仅对认识本区复杂的构造演化特征具有重要的科学意义,而且对指导其后续的油气勘探也具有现实价值。为此,本文作者在前人工作的基础上,通过野外地质调查和地震资料,利用裂变径迹热年代学方法并结合区域地质特征对磷灰石裂变径迹的时间 -温度热演化历史进行模拟。通过将磷灰石、锆石裂变径迹测年及磷灰石热模拟结果与区域构造背景和沉积响应相结合,研究甫沙—克里阳地区中生代以来发生的构造事件特征,并探讨其对油气成藏地质条件的影响。
1 地质背景
甫沙—克里阳地区位于塔里木盆地和西昆仑造山带盆山结合带的中东部(见图1(a)),西起造山带山前弧形构造转折处,东至克里阳以东,呈近东西向展布(见图1(b))。该区现存地层主体出露晚古生代和新生代地层,周缘分布少量中生代地层(见图1(b))。古生代地层主要由晚古生代海相沉积组成,沉积了厚层的台地相碳酸盐岩夹陆棚相碎屑岩;中生代地层则为内陆盆地演化时期的滨浅湖、河流和冲积扇相砂泥岩沉积;新生代沉积由古近系海湾三角洲相蒸发岩和碎屑岩建造、新近系陆相碎屑岩建造和第四系陆相磨拉石建造组成(见图1(c))。甫沙—克里阳地区处于盆山结合部位,自中生代以来,随着西昆仑造山带隆升,发生了多期次构造事件,使得区内地层逆冲变形和抬升剥蚀严重,沉积层序间存在叶尔羌群与达里约尔组、英吉莎群与克孜勒苏群、乌拉根组与卡拉塔尔组之间等多期不整合现象(见图1(c))。经过多年勘探,在柯克亚背斜的中新统和柯东1井白垩系获得了高产油气流,相继发现了柯克亚凝析油气田和柯东1井(见图1(b))。
2 样品分布与测试结果
2.1 样品采集与分布
根据甫沙—克里阳地区现今地层总体呈近东西向展布的特征,本次研究的10个样品自东向西方向呈条带状分布,层位为泥盆系、石炭系和白垩系,岩性均为砂岩(图1(b)、表1)。样品XN-1和XN-2采自克里阳东部的泥盆系和白垩系,XN-3,XN-4,XN-5和XN-6采自甫沙—克里阳地区南部的泥盆系,XN-7和XN-8分别采自断裂上盘与断裂带相距约3.0 km和3.2 km的石炭系,XN-9和XN-10采自甫沙西北部的白垩系和石炭系。所有样品均采自野外新鲜露头,采集质量均超过5 kg。本次裂变径迹测试分析在中国科学院高能物理研究所完成。采用外探测器法分析裂变径迹[29]。将采集的样品经粗碎、细碎后,用手工淘洗粗选,应用重液分离和电磁分选挑选出磷灰石和锆石单矿物。将磷灰石颗粒置于玻璃片上,用环氧树脂滴固,经研磨和抛光后制成光薄片,使得矿物内表面露出。在25 ℃下用质量分数为7% HNO3蚀刻30 s揭示自发径迹,将低铀白云母外探测器和矿物一起放入反应堆辐照,然后在25 ℃下用质量分数为40% HF蚀刻20 s揭示诱发径迹;中子注量利用CN5铀玻璃标定。利用AUTOSCAN仪器选择平行C轴的柱面测出自发径迹和诱发径迹密度以及水平封闭径迹长度。根据IUGS推荐的ξ常数法和标准裂变径迹年龄方程计算裂变径迹年龄。本文获得的磷灰石和锆石Zeta常数分别为410±17.6和90.9±2.8。测试分析结果见表1。获得的有效测试裂变径迹年龄样品共10个,其中磷灰石和锆石裂变径迹年龄样品均为5个。
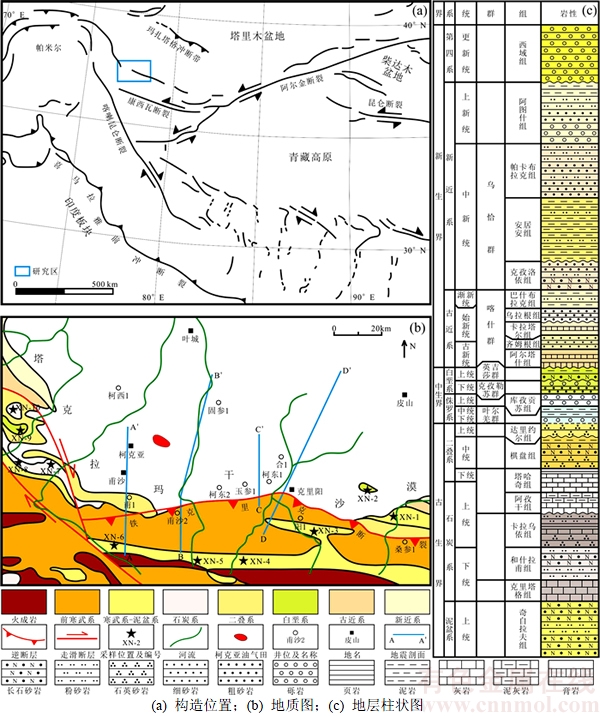
图1 甫沙—克里阳地区构造位置、地质图及地层柱状图(构造位置据文献[7]修改)
Fig. 1 Tectonic sketch map,geological map and stratigraphic column of the Fusha—Keliyang area (Structure location is modified by Ref. [7])
2.2 裂变径迹测试结果
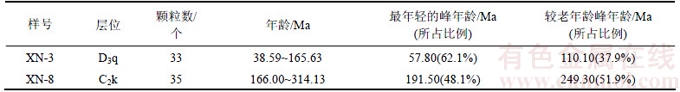
磷灰石和锆石裂变径迹测试结果反映了样品所经历的最高古地温的时间及其热演化历史[30]。从表1可知:甫沙—克里阳地区各样品的裂变径迹年龄分布在65~223 Ma之间,均小于样品所寄地层年龄,说明这些样品都经历了完全退火,其裂变径迹年龄代表了最老的抬升年龄。其中,XN-3样品磷灰石和XN-8样品锆石裂变径迹年龄的检验概率P(χ2)分别为0和0.5%,均小于5.0%,表明这2个样品在地质历史时期经历了复杂的热演化历史。裂变径迹年龄为混合年龄,可利用年龄概率分布和高斯拟合曲线的方法对其进行年龄分解,得出不同的峰值年龄,代表不同时期的冷却年龄[31-32]。现使用BRANDON[33]推荐的方法,通过BinomFit软件对这2组混合年龄进行分解,共得到4个不同的高斯拟合峰值年龄,由此获得其相应的冷却抬升年龄,见表2。XN-3样品的33个磷灰石颗粒裂变径迹年龄为38.59~165.63 Ma。该混合年龄被分解成110.1 Ma和57.8 Ma这2个高斯拟合峰值年龄,表明其在部分退火带时期主要经历了与之对应的早白垩世晚期和古新世晚期这2个期次的冷却抬升事件;XN-8样品的35个锆石颗粒裂变径迹年龄为166.00~314.13 Ma,其混合年龄(219.00±10.00) Ma被分解成249.30 Ma和191.50 Ma这2个高斯拟合峰值年龄,表明其经历了早三叠世和早侏罗世这2个时期的冷却抬升事件。
表1 甫沙—克里阳地区裂变径迹测试结果
Table 1 Test results of fission track in Fusha-Keliyang area
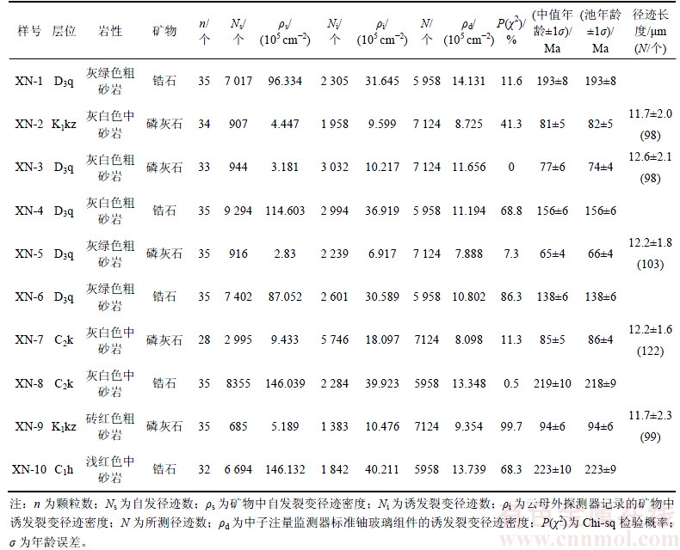
表2 甫沙—克里阳地区裂变径迹年龄分解结果
Table 2 Fission track peak-fitting d results of age in Fusha—Keliyang area
本区测试的XN-2,XN-3,XN-5,XN-7和XN-9样品磷灰石裂变径迹长度(见表1)均比磷灰石裂变径迹的原始长度小,这说明磷灰石裂变径迹在形成之后均受到构造热事件的影响而发生部分退火甚至完全 退火。
3 裂变径迹测试结果所反映的构造事件
3.1 裂变径迹年龄分布
将甫沙—克里阳地区不同层位磷灰石和锆石裂变径迹年龄及其分解所得的高斯拟合峰值年龄投在年龄分布图上,所得结果见图2。从图2可以看出峰值年龄集中分布在3个时间段,分别为191.50~249.30 ,138.00~ 156.00和57.80~110.10 Ma,分别对应地质时代为晚三叠世、晚侏罗世和晚白垩世,反映出该区地层在这3个时期内发生了明显的冷却抬升构造事件。
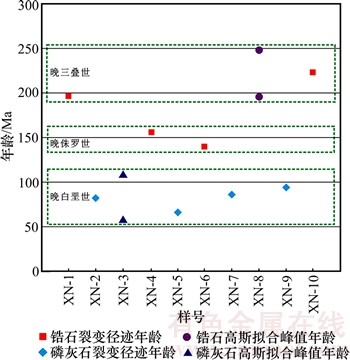
图2 甫沙—克里阳地区样品裂变径迹年龄分布
Fig. 2 Distribution of fission track ages of the Fusha—Keliyang area samples
3.2 磷灰石裂变径迹热模拟
随着温度升高,磷灰石裂变径迹的长度和密度均逐渐减小,每一条径迹记录了低于封闭温度的某一阶段热演化历史信息,因此,可利用磷灰石单颗粒的径迹年龄和长度进行热历史模拟[29, 34-35]。本次研究就是利用KETCHAM等[36]提出的多组分复杂成分Monte Carlo退火模型,运用HeFTy软件对甫沙—克里阳地区磷灰石样品的裂变径迹年龄和长度进行热史反演 模拟。
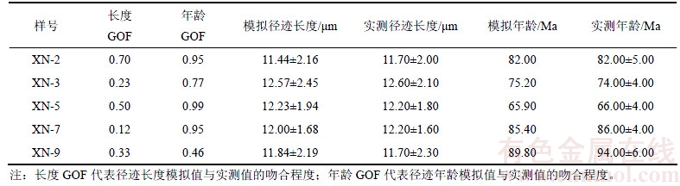
模拟过程中的参数设置如下:原始径迹长度为16.3 μm;现今地表温度为20 ℃;以古沉积温度10 ℃和实际测试样品的地层年龄为初始温度和时间;时间-温度历史曲线中的最大温度为200 ℃;拟合选项选取限制任意搜索项(CRS);拟合曲线数量超过50 000条。另外,热史反演模拟时,最重要的就是根据样品所处的地质背景确定限制约束条件。本区三叠系普遍遭受剥蚀缺失[18],因此,三叠纪地层存在明显的缓慢埋藏甚至温度降低现象;依据本次测试的磷灰石颗粒年龄分布得知早白垩纪为其地层埋藏最高温度时期。实际模拟过程可分为3步:1) 设定时间-温度演化曲线中的参数和约束条件;2) 基于退火模型,使用正演法求出径迹年龄和长度的模拟值;3) 比较模拟值和实测值,评价模拟结果,找出最佳的时间-温度演化曲线。在进行模拟结果质量检验时,一般采用模拟值与实测值的吻合程度GOF进行表征,若GOF大于0.05,则认为模拟过程是比较可信的;若GOF大于0.50,则认为模拟结果是高质量的。
本次的磷灰石裂变径迹热模拟结果如图3所示,其中XN-2和XN-5样品的长度GOF和年龄GOF均大于或等于0.5,表明模拟结果是高质量的。XN-3样品的长度GOF为0.23,年龄GOF为0.77;XN-7样品的长度GOF为0.12,年龄GOF为0.95;XN-9样品的长度GOF为0.33,年龄GOF为0.46,模拟结果检测值均大于0.05,表明模拟结果是比较可信的(见表3)。
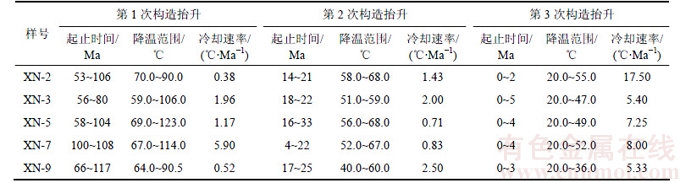
XN-2样品的热模拟结果表明:该样品在距今106 Ma即早白垩世晚期达到最大埋藏古地温90 ℃,在53~106 Ma存在缓慢的地层抬升冷却过程,在53 Ma内温度降低20 ℃,降温速率为0.38 ℃/Ma;自14.00~21.00 Ma和0~2.00 Ma存在2次快速冷却抬升,降温幅度分别为10 ℃和35 ℃,降温速率分别为1.43 ℃/Ma和17.5 ℃/Ma,见表4。
XN-3和XN-5样品自泥盆纪沉积以来经历了相似的热演化历史,分别在80 Ma和104 Ma达到最大埋藏古地温106 ℃和123 ℃,后期均存在着3次抬升冷却过程。XN-3样品的第1次抬升冷却事件发生在80~56 Ma,温度降低46.7 ℃,降温速率为1.96 ℃/Ma;新生代的2次抬升冷却事件发生在18~22 Ma和0~5 Ma,降温幅度分别为8 ℃和27 ℃,降温速率分别为2 ℃/Ma和5.4 ℃/Ma。XN-5样品的3次抬升冷却过程分别发生在58~104,16~33及0~4 Ma,第1次抬升使得样品从123 ℃降低到69 ℃,冷却速率为1.17 ℃/Ma;渐新世的抬升降温幅度为12 ℃,冷却速率为0.71 ℃/Ma;上新世的抬升降温幅度为29 ℃,冷却速率为7.25 ℃/Ma,抬升冷却事件持续至今。
XN-7样品在108 Ma达到最大埋藏温度114 ℃,之后主要经历了3次抬升事件,分别发生在100~108,4~22及0~4 Ma;早白垩世晚期的抬升降温幅度为47 ℃,冷却速率为5.9 ℃/Ma;中新世的抬升降温幅度为15 ℃,冷却速率为0.83 ℃/Ma;从4 Ma开始样品发生强烈抬升冷却,温度从52 ℃降至20 ℃,并持续至今,冷却速率为8 ℃/Ma。
XN-9样品的热历史模拟结果也表明了3次抬升冷却事件:第1次缓慢抬升事件发生在66~117 Ma,降温幅度为26.5 ℃,冷却速率为0.52 ℃/Ma;新生代的2次抬升事件分别发生在17~25 Ma和0~3 Ma,降温幅度分别为20 ℃和16 ℃,冷却速率为2.5 ℃/Ma和5.33 ℃/Ma。
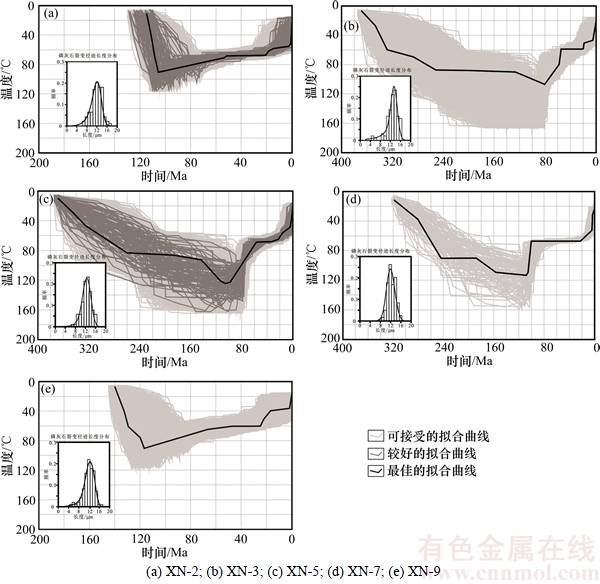
图3 甫沙—克里阳地区磷灰石裂变径迹热史模拟结果
Fig. 3 Simulation results of apatite fission track thermal history of Fusha—Keliyang area
表3 甫沙—克里阳地区磷灰石热史模拟GOF检测值
Table 3 Goodness of Fit value of apatite fission track thermal history simulation in Fusha—Keliyang area
甫沙—克里阳地区5个样品的磷灰石裂变径迹热模拟结果表明白垩纪为地层的最大埋藏古地温时期,之后主要经历了3次抬升冷却事件:第1次发生在晚白垩世,地层冷却速率为0.38~5.90 ℃/Ma;第2次抬升冷却事件发生在中新世,冷却速率为0.71~2.50 ℃/Ma;第3次抬升事件发生在上新世并持续至今,地层冷却速率为5.33~17.5 ℃/Ma,冷却速率与前2次相比明显增大,是快速挤压抬升的结果。
表4 甫沙—克里阳地区磷灰石热史模拟构造抬升事件
Table 4 Tectonic uplift events via apatite fission track modeling in Fusha—Keliyang area
4 中新生代构造事件
甫沙—克里阳地区中生代以来的第1期构造事件发生在晚三叠世,此时羌塘地块和塔里木板块碰撞拼贴,古特提斯洋消失,塔里木板块南缘形成1个弧后前陆变形造山区[37]。强烈的构造挤压作用使得该区三叠系整体被抬升遭受剥蚀,全区普遍缺失三叠纪沉积,这从该区南北向的地质剖面AA',BB'和DD'可以明显看出(图4(a),(c)和(d))。同时造成了下伏石炭系、二叠系与上覆侏罗系之间的广泛不整合接触,例如上石炭统卡拉乌依组厚层灰黑色灰岩与下侏罗统康苏组暗红色、灰绿色砂岩夹薄层泥岩、煤线的高角度不整合(图5(a)),中二叠统棋盘组灰绿色、肉红色砂岩与中下侏罗统叶尔羌群砖红色细砂岩之间的平行不整合接触,并且在不整合面上部发育1.2 m厚的砾岩(图5(b)和(c))。
晚侏罗世西昆仑山以南之前发生的多次碰撞作用使得西昆仑构造带深部物质沿着昆中结合带发生汇聚和向上运移,西昆仑山体发生快速抬升;同时,塔里木地块自北向南开始俯冲,北向的逆冲扩展和南向的陆内俯冲使得该地区处于对冲挤压状态[9, 38]。正是在这种构造背景下,该地区发生隆升事件,上石炭统阿孜干组灰黑色泥晶灰岩逆冲推覆在上白垩统英吉莎群肉红色、灰绿色细砂岩夹薄层泥岩之上(图5(d));中二叠统棋盘组生物碎屑灰岩、粉砂岩、泥岩互层与下白垩统克孜勒苏群砖红色、灰绿色细砂岩夹薄层红色泥岩之间地层缺失,且产状差别很大,形成高角度不整合接触(图5(e))。
甫沙—克里阳地区晚白垩世发育第三期构造事件,此时发生自南向北、近于水平的深层缓慢拆离作用[9],使得该区晚白垩世—古近纪沉积地层以连续整合接触为主,只是在局部存在不整合,如下白垩统克孜勒苏群砖红色、黄绿色细砂岩与古新统阿尔塔什组白色膏岩、上白垩统英吉莎群细砂岩与始新统卡拉塔尔组膏岩之间的角度不整合接触(图5(f)和(g))。本区的5个磷灰石样品热史模拟结果均反映了此期构造事件(见表4)。金小赤等[39]对柯克亚、克里阳和桑株剖面不整合面、沉积界面、沉积环境、沉积物厚度、粒度变化特征进行了综合研究,结果表明西昆仑在晚白垩世发生了明显的隆升。
第4期构造事件发生在早中新世,这与SOBEL等[40-42]对克里阳南部周缘地区所得出的磷灰石裂变径迹年龄相一致。该时期由于印度板块持续向北挤压,造成了西昆仑山体抬升[9, 37]。王永等[43]利用沉积学、地貌学和古地磁学的方法研究认为西昆仑在约25 Ma发生整体隆升。金小赤等[39, 42, 44]从沉积相、地层厚度、岩石成分和粒度分析等沉积学的角度进行分析,发现西昆仑在中新世经历了强烈的抬升剥露。该区普遍发育的古近系卡拉塔尔组厚层白色膏岩与巴什布拉克组砂泥岩互层之间的角度不整合接触(图5(h))以及始新统乌拉根组砂岩逆冲推覆在中新统乌恰群暗红色泥岩之上(图5(i))均表明这次挤压构造抬升剥蚀事件的发生。同时,热模拟结果表明位于甫沙—克里阳地区西部的XN-5和XN-9样品比东部的XN-2和XN-3样品抬升开始时间早,本次冷却抬升事件具有西部发生早而东部发生晚的特征。程晓敢等[28]利用地震资料对该区新生代构造变形特征进行研究,认为西昆仑山前同一排构造带的变形存在着由西向东迁移的特征。
第5期构造事件发生在上新世,热模拟结果表明甫沙—克里阳地区该期抬升开始时间很接近且地层冷却速率均明显加快,这可能是受青藏高原快速隆升的影响。黎敦朋等[41, 45]对该区相邻区域进行了裂变径迹年代学分析,结果表明自4.7 Ma以来西昆仑发生了整体大规模抬升。源自西昆仑造山带的挤压冲断作用使得山前冲断带开始形成,并且表现为由造山带向前陆方向逐渐变新的“前展式”变形[28]。JIN等[17, 44, 42]通过对西昆仑山前盆地新生代沉积序列进行研究,认为西昆仑在中新世晚期—上新世早期发生了快速隆升。中新世晚期—上新世早期塔西南山前盆地沉积环境由相对平静的河湖相转变为快速堆积的山前冲积扇和河流相[39, 44, 46],沉积速率由早期的0.015 mm/a增加到0.950 mm/a[5],古流向也由乌恰群的NEE—SWW方向转变为阿图什组时期的SWW—NEE[47]。ZHENG等[5, 48-49]使用古地磁方法进行研究,认为西昆仑造山带在4.5 Ma开始隆升。以上这些研究均表明甫沙—克里阳地区自上新世至今发生了快速抬升剥蚀事件。
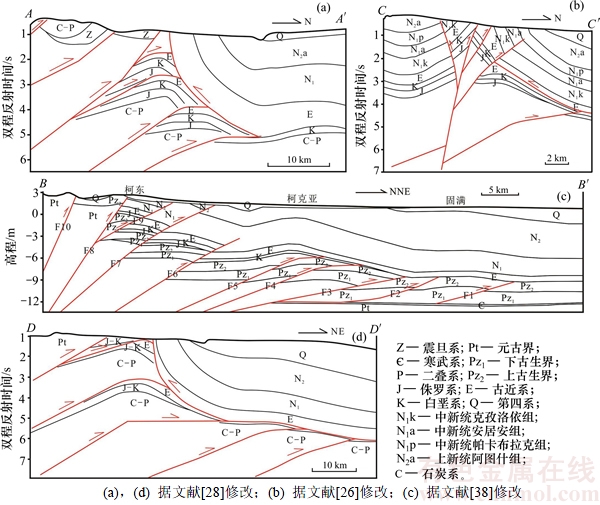
图4 甫沙—克里阳地区地质剖面
Fig. 4 Geological sections of Fusha—Keliyang area
综上所述,甫沙—克里阳地区测试样品的裂变径迹年龄和磷灰石裂变径迹热模拟所反映的构造事件期次、起止时间与其所处的构造背景及构造事件导致的地层分布、接触关系见图6。由图6可知:甫沙—克里阳地区中生代以来主要经历了晚三叠世、晚侏罗世、晚白垩世、早中新世和上新世5期构造事件,并且均具有明显的区域构造背景和沉积响应。晚三叠世的挤压构造持续时间长,抬升幅度大,地层整体被抬升遭受了严重剥蚀;晚侏罗世构造抬升使得该区地层整体被抬升剥蚀,但其持续时间短;在晚白垩世和早中新世,只是本区的局部地区地层被抬升剥蚀,大部分地区沉积地层仍以连续沉积为主,发生了明显的差异抬升剥蚀事件;而上新世则发生整体、快速地挤压抬升,地层冷却速率显著加快。
5 油气地质意义
甫沙—克里阳地区中新生代共发生了5期构造事件。其中,晚三叠世的整体性抬升事件使得该区普遍缺失晚二叠世和三叠纪沉积,下伏石炭系—下二叠统海相泥质烃源岩的热演化程度被延缓降低,该区柯克亚油气田地层埋藏热演化史曲线变化趋势也说明这点[50]。同时,随着该区应力场由挤压向拉张转换,早中侏罗世发育一系列受北西西—南东东走向正断层控制的断陷盆地[46],控制了该区中下侏罗统陆相冲积扇和沼泽煤系地层的沉积展布范围,使其以狭长的条带状平行西昆仑山的走向分布于其山前地带,最终控制了该区另外一套重要烃源岩中下侏罗统地层的分布范围。上新世构造事件对甫沙—克里阳地区油气聚集的影响示意图见图7。

图5 甫沙—克里阳地区野外地质特征
Fig. 5 Field geological photographs of Fusha—Keliyang area
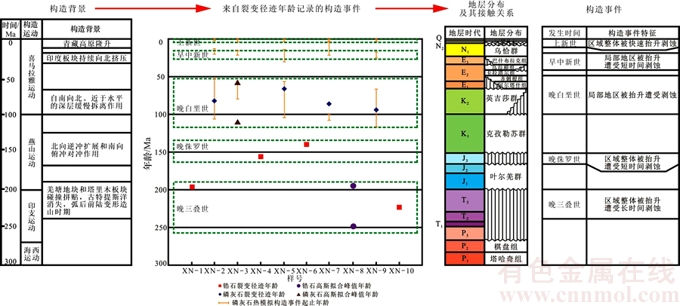
图6 甫沙—克里阳地区中新生代构造事件
Fig. 6 Meso—Cenozoic tectonic event of Fusha—Keliyang area
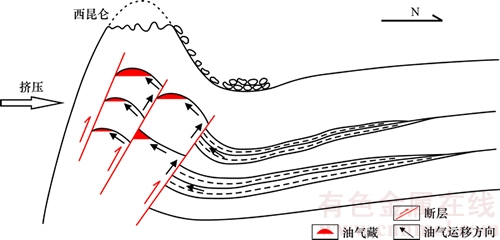
图7 上新世构造事件对甫沙—克里阳地区油气聚集的影响示意图
Fig. 7 Sketch map of Pliocene tectonic event since Pliocene for hydrocarbon accumulation in Fusha—Keliyang area
第2期的构造事件发生在晚侏罗世,持续时间较短。该区普遍缺失上侏罗统,使得下伏中下侏罗统泥岩和煤系烃源岩与其上覆白垩系砂岩地层直接接触,有利于后续中下侏罗统烃源岩生成的油气在白垩系储层中聚集成藏。该套有利的烃源岩和储集层组合已经被柯东1井的勘探结果所证实。
晚白垩世和早中新世的2期差异性构造抬升事件使得本区白垩系、古近系和新近系以连续沉积为主,偶见不整合接触和逆冲推覆构造,构造挤压抬升强度较弱。晚白垩世的挤压构造抬升事件形成了分布范围较广泛的自西昆仑山前向塔里木盆地内部逆冲推覆的低角度断层(图4(c)中断层F1,F2,F3,F4和F5),为下伏油气的向上运移提供了通道。
上新世的快速挤压抬升事件使得中新统乌恰群被抬升剥蚀充当物源,邻近山前区域地层进入到快速埋藏阶段,加剧了该区主力烃源岩石炭系—下二叠统泥岩的热演化程度,油气大量生成。何登发等[50-51]针对本区烃源岩热演化的研究也说明这点。强烈的挤压逆冲推覆作用还使得本区在西昆仑山前形成一系列高角度逆冲断层(图4(b)中断层F6,F7,F8,F9和F10)的同时,发育与断层相关的背斜圈闭(图4)。何登发等[50, 52]运用相态资料和有机包裹体地球化学方法对柯克亚凝析油气田及柯东—柯克亚构造带的油气成藏特征进行了研究,结果表明该区油气的主要成藏时期为上新世晚期,具有明显的晚期成藏特征。以上均说明此期构造事件在促使本区烃源岩热演化程度加剧、形成高角度深层大断裂运移通道和背斜圈闭等油气地质条件发育的基础上,确实发生了油气的聚集成藏作用。
综上所述,晚三叠世和上新世的2期构造事件对甫沙—克里阳地区的油气聚集产生了重要的影响。正是在晚三叠世整体地层被长时间抬升剥蚀、主力烃源岩石炭系—下二叠统热演化程度被延缓的前提下,上新世的整体快速挤压抬升事件促使本区烃源岩、断裂输导、圈闭等油气地质条件相互耦合,使得该区油气能够聚集成藏(见图7)。可以说,晚三叠世的构造抬升事件是该区油气聚集的基础,而上新世的快速挤压抬升作用则是控制该区油气聚集的关键。
6 结论
1) 甫沙—克里阳地区中新生代经历了5期构造抬升事件,主要对应于晚三叠世、晚侏罗世、晚白垩世、早中新世和上新世,并且均具有明显的区域构造背景和沉积响应。
2) 晚三叠世构造事件为整体长时间的冷却抬升事件,晚侏罗世的整体性抬升剥蚀事件持续时间较短,晚白垩世和早中新世两期构造抬升事件在本区表现为差异性隆升剥蚀,并且早中新世构造抬升具有西早东晚的特征,而上新世则整体快速地抬升剥蚀。
3) 晚三叠世的整体性构造抬升事件使得甫沙—克里阳地区烃源岩热演化程度被延缓,生烃潜力被保存,为油气晚期成藏奠定了基础;而上新世以来的快速挤压抬升则促使烃源岩、断裂输导、圈闭等油气地质条件发育,并且各成藏要素能够相互耦合,促进该区油气的晚期成藏,是控制该区油气聚集的关键。
参考文献:
[1] BURTMAN V S. Cenozoic crustal shortening between the Pamir and Tienshan and a reconstruction of the Pamir—Tienshan transition zone for the Cretaceous and Palaeogene[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 319(2): 69-92.
[2] COWGILL E, YIN An, HARRISON T M, et al. Reconstruction of the Altyn Tagh fault based on U-Pb geochronology: role of back thrusts, mantle sutures, and heterogeneous crustal strength informing the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2003, 108(B7): 2346-2373.
[3] 曲国胜, 李亦纲, 李岩峰, 等. 塔里木盆地西南前陆构造分段及其成因[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 2005, 35(3): 193-202.
QU Guosheng, LI Yigang, LI Yanfeng, et al. Tectonic segmentation and its origin of southwestern Tarim foreland basin[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2005, 35(3): 193-202.
[4] WANG Chao, LIU Liang, KORHONEN F, et al. Origins of Early Mesozoic granitoids and their enclaves from West Kunlun, NW China: implications for evolving magmatism related to closure of the Paleo—Tethys ocean[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2016, 105(3): 941-964.
[5] ZHENG Hongbo, POWELL C M, AN Zhisheng, et al. Pliocene uplift of the northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geology, 2000, 28(8): 715-718.
[6] ROBINSON A C, YIN An, MANNING C E, et al. Cenozoic evolution of the eastern Pamir: implications for strain- accommodation mechanisms at the western end of the Himalayan—Tibetan orogeny[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2007, 119(7/8): 882-896.
[7] 潘家伟, 李海兵, JEROME V D W, 等. 西昆仑山前冲断带晚新生代构造地貌特征[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(10): 1368-1379.
PAN Jiawei, LI Haibing, JEROME V D W, et al. Late cenozoic morphotectonic features of the thrust belt in the front of the West Kunlun Mountains[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2007, 26(10): 1368-1379.
[8] BERSHAW J, GARZIONE C N, SCHOENBOHM L, et al. Cenozoic evolution of the Pamir Plateau based on stratigraphy, zircon provenance, and stable isotopes of foreland basin sediments at Oytag (Wuyitake) in the Tarim Basin (West China)[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 44(1): 136-148.
[9] 崔军文, 郭宪璞, 丁孝忠, 等. 西昆仑—塔里木盆地盆-山结合带的中、新生代变形构造及其动力学[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(4): 103-118.
CUI Junwen, GUO Xianpu, DING Xiaozhong, et al. Mesozoic Cenozoic deformation structures and their dynamics in the basin range junction belt of the west Kunlun Tarim basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 13(4): 103-118.
[10] ROBINSON A C, YIN An, LOVERA O M. The role of footwall deformation and denudation in controlling cooling age patterns of detachment systems: an application to the Kongur Shan extensional system in the Eastern Pamir, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 496(1/2/3/4): 28-43.
[11] CAO Kai, WANG Guocan, BERNET M, et al. Exhumation history of the West Kunlun Mountains, northwestern Tibet: evidence for a long-lived, rejuvenated orogen[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 432: 391-403.
[12] 陈汉林, 张芬芬, 程晓敢, 等. 帕米尔东北缘地区构造变形特征与盆山结构[J]. 地质科学, 2010, 45(1): 102-112.
CHEN Hanlin, ZHANG Fenfen, CHENG Xiaogan, et al. The deformation features and basin-range coupling structure in the northeastern Pamir tectonic belt[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2010, 45(1): 102-112.
[13] LUKENS C E, CARRAPA B, SINGER B S, et al. Miocene exhumation of the Pamir revealed by detrital geothermochronology of Tajik rivers[J]. Tectonics, 2012, 31(2): 2014.
[14] THIEDE R C, SOBEL E R, CHEN Jie, et al. Late Cenozoic extension and crustal doming in the India-Eurasia collision zone: New thermochronologic constraints from the NE Chinese Pamir[J]. Tectonics, 2013, 32(3): 763-779.
[15] CAO Kai, WANG Guocan, BEEK P V D, et al. Cenozoic thermo-tectonic evolution of the northeastern Pamir revealed by zircon and apatite fission-track thermochronology[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 589(2): 17-32.
[16] WEI Honghong, MENG Qingren, DING Lin, et al. Tertiary evolution of the western Tarim basin, northwest China: a tectono-sedimentary response to northward indentation of the Pamir salient[J]. Tectonics, 2013, 32(3): 558-575.
[17] JIN Xiaochi, WANG Jun, CHEN Bingwei, et al. Cenozoic depositional sequences in the piedmont of the west Kunlun and their paleogeographic and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2003, 21(7): 755-765.
[18] 方爱民, 马建英, 王世刚, 等. 西昆仑—塔西南坳陷晚古生代以来的沉积构造演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(12): 3396-3406.
FANG Aimin, MA Jianying, WANG Shigang, et al. Sedimentary tectonic evolution of the southwestern Traim Basin and west Kunlun orogen since Late Paleozoic[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(12): 3396-3406.
[19] 程晓敢, 陈汉林, 师骏, 等. 西昆仑山前侏罗—白垩系分布特征及其控制因素[J]. 地球科学, 2012, 37(4): 635-644.
CHENG Xiaogan, CHEN Hanlin, SHI Jun, et al. Distribution characteristics and controlling factors of Jurassic—Cretaceous in the front of West Kunlun Mountains[J]. Earth Science, 2012, 37(4): 635-644.
[20] HUBBARD M S, GREW E S, HODGES K V, et al. Neogene cooling and exhumation of upper-amphibolite-facies 'whiteschistes' in the southwest Pamir Mountains, Tajikistan[J]. Tectonophysics, 1999, 305(1): 325-337.
[21] 肖安成, 杨树锋, 陈汉林, 等. 西昆仑山前冲断系的结构特征[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(增刊): 28-136.
XIAO Ancheng, YANG Shufeng, CHEN Hanlin, et al. Structural characteristics of thrust system in the front of the West Kunlun Mountains[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2000, 7(Suppl): 128-136.
[22] 牟中海, 唐勇, 崔炳富, 等. 塔西南地区地层剥蚀厚度恢复研究[J]. 石油学报, 2002, 23(1): 40-44.
MU Zhonghai, TANG Yong, CUI Bingfu, et al. Erosion thickness restoration in southwest Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2002, 23(1): 40-44.
[23] CAO Kai, BERNET M, WANG Guocan, et al. Focused Pliocene—Quaternary exhumation of the Eastern Pamir domes, western China[J]. Earth and Planetary Sciences Letters, 2013, 363(2): 16-26.
[24] 李世臻, 康志宏, 邱海峻, 等. 塔里木盆地西南坳陷油气成藏模式[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(2): 387-398.
LI Shizhen, KANG Zhihong, QIU Haijun, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation modes of the southwest depression in Tarim Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41(2): 387-398.
[25] COWGILL E. Cenozoic right-slip faulting along the eastern margin of the Pamir salient, northwestern China[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2010, 122(1): 145-161.
[26] 程晓敢, 黄智斌, 陈汉林, 等. 西昆仑山前冲断带断裂特征及构造单元划分[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(8): 2591-2601.
CHENG Xiaogan, HUANG Zhibin, CHEN Hanlin, et al. Fault characteristics and division of tectonic units of the thrust belt in the front of the West Kunlun Mountains[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(8): 2591-2601.
[27] 何登发, 李德生, 何金有, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷和西南坳陷油气地质特征类比及勘探启示[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(2): 201-218.
HE Dengfa, LI Desheng, HE Jinyou, et al. Comparison in petroleum geology between Kuqa depression and southwest depression in Tarim Basin and its exploration significance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(2): 201-218.
[28] 程晓敢, 雷刚林, 陈汉林, 等. 西昆仑山前甫沙—克里阳地区新生代变形特征及油气控制作用[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(1): 83-89.
CHENG Xiaogan, LEI Ganglin, CHEN Hanlin, et al. Cenozoic structural deformation of the Fusha—Keliyang area in the piedmont of the western Kunlun Mountains and its control on hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(1): 83-89.
[29] GLEADOW A J W, BELTON D X, KOHN B P, et al. Fission track dating of phosphate minerals and the thermochronology of apatite[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2002, 48(1): 579-630.
[30] GLEADOW A J W, DUDDY I R, LOVERING J F. Fission track analysis: A new tool for the evaluation of thermal histories and hydrocarbon potential[J]. Appea Journal, 1983, 23: 93-102.
[31] 周祖翼, 毛凤鸣, 廖宗廷, 等. 裂变径迹年龄多成分分离技术及其在沉积盆地物源分析中的应用[J]. 沉积学报, 2001, 19(3): 456-458.
ZHOU Zuyi, MAO Fengming, LIAO Zongting, et al. Estimation of the multi-component fission track age data and its application in the provenance study of sedimentary basins[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2001, 19(3): 456-458.
[32] STEWART R J, BRANDON M T. Detrital-zircon fission-track ages for the “Hoh Formation”: Implications for late Cenozoic evolution of the Cascadia subduction wedge[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2004, 116(1/2): 60-75.
[33] BRANDON M T. Decomposition of mixed grain age distributions using BinomFit[J]. On Track, 2002, 24: 13-18.
[34] 曲少东, 刘池洋, 李健, 等. 吉林省大黑山南段新生代隆升的裂变径迹证据[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 45(11): 3893-3899.
QU Shaodong, LIU Chiyang, LI Jian, et al. Fission track thermochronology evidence for Cenozoic uplifting of the southern Daheishan in Jilin, China[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(11): 3893-3899.
[35] 田涛, 任战利, 吴晓青, 等. 雅布赖盆地萨尔台凹陷中—新生代构造热事件的磷灰石裂变径迹分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 46(8): 2974-2982.
TIAN Tao, REN Zhanli, WU Xiaoqing, et al. Apatite fission track analysis of Meso-cenozoic tectonic-thermal history in Sartai depression, Yabrai Basin[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2015, 46(8): 2974-2982.
[36] KETCHAM R A, DONELICK R A, CARLSON W D. Variability of apatite fission-track annealing kinetics. Ⅲ. Extrapolation to geological time scales[J]. American Mineralogist, 1999, 84(9): 1235-1255.
[37] 贾承造. 中国塔里木盆地构造特征与油气[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1997: 238-242.
JIA Chengzao. Tectonic characteristics and petroleum of Tarim Basin China[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1997: 238-242.
[38] 谢会文, 王春阳, 王智斌, 等. 基底滑脱层分布对褶皱冲断带变形影响的物理模拟研究: 以塔西南西昆仑山前褶皱冲断带为例[J]. 高校地质学报, 2012, 18(4): 701-710.
XIE Huiwen, WANG Chunyang, WANG Zhibin, et al. The effect of spatial distribution of basement detachment on deformation in a fold and thrust belt: an analogue modeling approach an example of West Kunlun fold-and-thrust belt[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2012, 18(4): 701-710.
[39] 金小赤, 王军, 陈炳蔚, 等. 新生代西昆仑隆升的地层学和沉积学记录[J]. 地质学报, 2001, 75(4): 459-467.
JIN Xiaochi, WANG Jun, CHEN Bingwei, et al. Stratigraphic and sedimentologic records of the uplifting of the west Kunlun in the Cenozoic[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2001, 75(4): 459-467.
[40] SOBEL E R, DUMITRU T A. Thrusting and exhumation around the margins of the western Tarim basin during the India—Asia collision[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1997, 102(B3): 5043-5063.
[41] 黎敦朋, 赵越, 胡健民, 等. 青藏高原西北缘高原面与陡坡地貌形成过程的裂变径迹热年代学约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(5): 900-910.
LI Dunpeng, ZHAO Yue, HU Jianmin, et al. Fission track thermochronologic constraints on plateau surface and geomorphic relief formation in the northwestern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(5): 900-910.
[42] 王聪. 西昆仑山铁克里克地区新生代构造隆升及沉积响应[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学地球科学学院, 2015: 38-124.
WANG Cong. Cenozoic tectonic uplift and sedimentary evolution of the Tiklik area, Western Kunlun orogen[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University. School of Earth Sciences, 2015: 38-124.
[43] 王永, 李德贵, 肖序常, 等. 西昆仑山前晚新生代构造活动与青藏高原西北缘的隆升[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(1): 41-47.
WANG Yong, LI Degui, XIAO Xuchang, et al. Late Cenozoic tectonic movement in the front of the West Kunlun Mountains and uplift of the northwestern margin of the Qinghai—Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geology in China, 2006, 33(1): 41-47.
[44] 司家亮, 李海兵, BARRIER L, 等. 青藏高原西北缘晚新生代的隆升特征:来自西昆仑山前盆地的沉积学证据[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(10): 1356-1367.
SI Jialiang, LI Haibing, BARRIER L, et al. Late Cenozoic uplift of the northwestern margin of the Qinghai—Tibet Plateau: sedimentary evidence from piedmont basins of the West Kunlun Mountains[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2007, 26(10): 1356-1367.
[45] 刘函, 王国灿, 曹凯, 等. 西昆仑及邻区区域构造演化的碎屑锆石裂变径迹年龄记录[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(3): 64-78.
LIU Han, WANG Guocan, CAO Kai, et al. The detrital zircon fission-track ages constraint to tectonic processes in west Kunlun and adjacent regions[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(3): 64-78.
[46] 廖林, 程晓敢, 王步清, 等. 塔里木盆地西南缘中生代沉积古环境恢复[J]. 地质学报, 2010, 84(8): 1195-1207.
LIAO Lin, CHENG Xiaogan, WANG Buqing, et al. Reconstruction of Mesozoic sedimentary paleoenvironment in the southwestern Tarim Basin, Northwestern China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(8): 1195-1207.
[47] 裴军令, 孙知明, 李海兵, 等. 青藏高原西北缘晚新生代沉积岩古流向的磁化率各向异性确定及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(7): 1613-1620.
PEI Junling, SUN Zhiming, LI Haibing, et al. Paleocurrent direction of the Late Cenozoic sedimentary sequence of the Tibetan Plateau northwestern margin constrained by AMS and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(7): 1613-1620.
[48] ZHENG Hongbo, HUANG Xiangtong, BUTCHER K. Lithostratigraphy, petrography and facies analysis of the Late Cenozoic sediments in the foreland basin of the West Kunlun[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2006, 241(1): 61-78.
[49] SUN Jimin, LIU Tungsheng. The age of the Taklimakan desert[J]. Science, 2006, 312(5780): 1621-1621.
[50] 何登发, 陈红英, 柳少波. 柯克亚凝析油气田的成藏机理[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1997, 24(4): 28-32.
HE Dengfa, CHEN Hongying, LIU Shaobo. Pool-forming mechanism of Kekeya condensate oil and gas field[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1997, 24(4): 28-32.
[51] 郑涛, 徐耀辉, 王进. 塔西南坳陷二叠系烃源岩热演化及生烃史模拟[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2013, 35(5): 33-37.
ZHENG Tao, XU Yaohui, WANG Jin. Simulation on thermal evolution and hydrocarbon generation history of Permian source rocks in southwestern depression of Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2013, 35(5): 33-37.
[52] 莫午零, 林潼, 张英, 等. 西昆仑山前柯东—柯克亚构造带油气来源及成藏模式[J]. 石油实验地质, 2013, 35(4): 364-371.
MO Wuling, LIN Tong, ZHANG Ying, et al. Hydrocarbon origin and accumulation model of Kedong—Kekeya tectonic belt in piedmont of West Kunlun Mountain[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2013, 35(4): 364-371.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2017-08-08;修回日期:2017-10-09
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(41672121);中国地质调查局项目(DD20160203) (Project(41672121) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(DD20160203) supported by the Program of China Geological Survey)
通信作者:王震亮,博士,教授,从事油气地质学研究;E-mail: mianxnwu@163.com

