文章编号:1004-0609(2013)08-2229-06
温度对Ni-金刚石复合电沉积电化学行为的影响
周海飞1,祝郦伟1,钱洲亥1,杜 楠2,田刚强1
(1. 国网浙江省电力公司 电力科学研究院, 杭州 310014;
2. 南昌航空大学 材料科学与工程学院,南昌 330063)
摘 要:在测定Ni-金刚石复合电沉积体系阴极极化曲线、电化学阻抗谱及微分电容曲线等基础上,分析了温度对界面双电层的影响规律,推断出金刚石微粒复合量随温度升高的变化趋势,以此探讨温度在Ni-金刚石复合电沉积中的电化学行为。结果表明:随镀液温度沿30 ℃→40 ℃→60℃升高,Ni-金刚石复合体系的阴极极化减小,法拉第电阻沿17.3 Ω→5.2 Ω→3.0 Ω降低,双电层电容沿40.8 μF→141.2 μF→175.6 μF增加,同时,阴极表面在析出电位附近的负电荷密度逐渐增加。电化学测试结果表明:金刚石微粒复合量将随温度的升高而降低,且工艺实验与电化学测试结果也映证这一点。
关键词:Ni-金刚石;复合电沉积;电化学行为;阴极极化曲线;电化学阻抗谱
中图分类号:TG174.44 文献标志码:A
Effect of temperature on electrochemical behaviors during Ni-diamond composite electrodeposition
ZHOU Hai-fei1, ZHU Li-wei1, QIAN Zhou-hai1, DU Nan2, TIAN Gang-qiang1
(1. Electric Power Research Institute, State Grid Zhejiang Electric Power Company, Hangzhou 310014, China;
2. Institute of Materials Science and Engineering, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China)
Abstract: Based on the study about cathodic potentiodynamic diagrams, electrochemical impedance diagrams and differential capacitance curves, the effect of temperature on diffuse double layer was analyzed, and then the change of particle content in the deposits along with temperature was judged. And the electrochemical action of temperature in Ni-diamond composite electrodeposition was discussed. The results show that, with temperature increasing from 30 ℃, 40 ℃ to 60 ℃, the cathodic potentiodynamic of composite system decreases. At the same time, Faraday resistance decreases from17.3 Ω, 5.2 Ω to 3.0 Ω, the electric double layer capacitance increases from 40.8 μF, 141.2 μF to 175.6 μF. The negative charge density on cathodic surface increases near deposition potential. The electrochemistry testing experiment data indicate that the content of particles in the deposits decreases with the increase of temperature. The technics experiment confirms it well.
Key words: Ni-diamond; composite electrodeposition; electrochemical behavior; cathodic potentiodynamic diagram; electrochemical impedance diagram
复合电沉积是通过电沉积方法使金属与固体微粒共沉积以形成特殊镀层的过程[1],它可根据设计要求改变和调节材料的物理、化学和力学性能[2]。自1920年,德国科学家获得第一个复合镀层以来,由于对特定性能先进材料的需求及对电沉积过程综合模型的需 要[3],复合电沉积技术引起了人们极大的研究热情[4-12],已广泛应用于航空、电子、化工、冶金与核能等工程技术领域。
镀层性能通过微粒复合量调整,温度则对复合量具有重要影响。温度对微粒共沉积的影响虽已有诸多报道,但其影响规律却较为复杂,从而制约其作用机理的研究。HE等[13]在研究Ni-HAP时发现,温度升高使吸附原子团HAP·[Ni2+]n的n值降低,导致阴极过电位降低和HAP·[Ni2+]n量的减少,从而使HAP复合量降低;Watts镀镍液中共沉积Ni-金刚石时,镀液温度由30 ℃升至60 ℃,其复合量降为原来的1/2[14]。但是,ABDEL等[15]研究Ni-聚乙烯体系时发现,随着温度的升高,复合量先升后降,YAO等[8]利用复合电沉积技术制备PbO2-ZrO2纳米复合电极时也发现ZrO2复合量随温度升高呈现相似的变化规律。
在目前复合电沉积的研究中,电化学手段多用于测试复合镀层的性能,如耐蚀性[5, 7, 10, 16]及析氢电催化性能[4, 17]等,用于共沉积过程研究并不多见,更缺少针对温度参数进行的电化学机理研究。复合电沉积过程一般经历复合粒子在电极表面吸附而后被生长金属捕获,这势必改变电极表面状态及附近镀液的对流情况,而极化曲线可直观反映此时电极反应速度与电极电势的关系[18],电化学阻抗测试技术可通过等效电路对界面双电层进行量化分析,微分电容曲线也可获得“电极/溶液”界面的许多重要性质,如表面剩余电荷等[19]。因此,利用电化学手段研究复合电沉积过程具先进性及可行性[20-21]。
已有研究表明[16, 22],作为增强相的金刚石微粒不仅可提高镀层耐磨性,也使镀层在5%NaOH(质量分数)、NaCl及H2SO4溶液中的耐蚀性均有所提高。本文作者利用三电极体系测定了复合体系不同温度下的阴极极化曲线、电化学阻抗谱及微分电容曲线,旨在从机理上探讨温度在Ni-diamond复合电沉积中的电化学行为,并与工艺试验相互映证。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料及方法
工艺试验时,阴极材料用45#钢,阳极材料为Ni-2电解镍,试验用金刚石微粒粒径为30 μm,使用前经稀盐酸浸泡数小时至数十小时,以除去表面的金属杂质,然后用活性剂清洗数遍,使微粒完全被润湿,再经清水清洗后用蒸馏水清洗;为除去基础镀液中的杂质离子如铁离子等,所配镀镍液经0.1 A/dm2处理5 h后使用。通过调速电动搅拌器使微粒悬浮,试验在恒温水浴槽中进行。
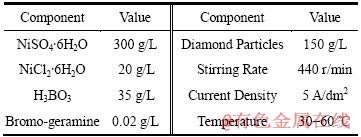
镀液组成及工艺条件如表1所列(药品均为分析纯)。
表1 复合镀液组成及其操作参数
Table 1 Component of compositions electrolyte and its technic parameters
通过三电极体系进行电化学测试,其中研究电极使用45#钢,导电面积为1 cm2,辅助电极使用铂电极,参比电极使用饱和甘汞电极,试验仪器采用荷兰Autolab电化学工作站,电化学阻抗谱及微分电容曲线的测试均在频率响应分析仪(Frequency response analyzer, FRA)模块中进行,所加正弦波电位幅值为10 mV,频率范围为10 kHz~1 Hz,鉴于频率低时测试时间较长,镀液组成可能发生变化,故采用1 Hz的最低测试频率,待测试体系稳定后开始测量;通过调速电动搅拌器使微粒悬浮,搅拌速度为440 r/min,试验在恒温水浴槽中进行;电化学测试装置简图如图1所示。
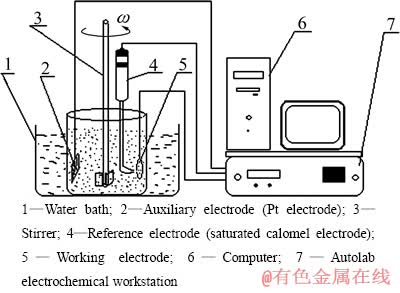
图1 电化学实验装置简图
Fig. 1 Schematic figure of electrochemical experiment setup
1.2 复合量的测定[23]
剥离部分镀层,称量镀层质量(mNi+mdia),在体积比为1:1 HNO3水溶液中加热使复合镀层中的镍完全溶解,待金刚石微粒完全沉淀后分离、烘干,称量镀层中金刚石微粒质量(mdia),由此计算复合量
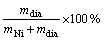 (质量分数)。称量在德国Sartorius 公司的BS210S电子天平上进行,误差为±0.2 mg。
(质量分数)。称量在德国Sartorius 公司的BS210S电子天平上进行,误差为±0.2 mg。
2 结果与分析
2.1 温度对复合电沉积过程的影响
2.1.1 温度对阴极极化的影响
微粒在溶液中的电泳速度(数量级为10~5 cm/s)比搅拌引起的微粒随着液流的运动速度(数量级为l cm/s)小得多,故微粒在镀液中传递时可略去电泳作用[14]。当微粒到达阴极与镀液界面的分散双电层后,电位差降落在以微米计的分散双电层距离内,故场强很高,此时微粒的电泳速度变得比电结晶速度高百倍。如果认为微粒在双电层内的迁移是其进入镀层的关键,那么复合镀层的形成必将受到两个因素的影响,即微粒吸附电荷的种类及大小和外电场的场强[14]。界面间紧密双层的厚度与剩余场强的乘积,在数值上等于过电位[14],故通过研究过电位对微粒与金属共沉积的影响,可了解外电场的重要作用,该影响可通过阴极极化曲线的变化粗略反映。
不同温度时的阴极极化曲线如图2所示。比较发现,当温度沿30→40→60 ℃提高,复合体系的阴极极化逐渐降低,相当于过电位的减小,即电极/溶液界面间场强减弱;极化降低还表明此时镍还原速度的加快。
关于带电质点在电解液中的电泳速度计算公式如下[24]: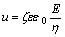 (式中,u表示电泳速度,η为镀液黏度,E为电场场强,ζ表示Zeta电位,ε为相对介电常数,ε0=8.85×10-12 F/m),场强减弱使微粒的电泳速度减缓且与阴极表面的吸附变得脆弱;此外,温度升高促使镀液黏度η升高,也加剧了微粒电泳的减缓。
(式中,u表示电泳速度,η为镀液黏度,E为电场场强,ζ表示Zeta电位,ε为相对介电常数,ε0=8.85×10-12 F/m),场强减弱使微粒的电泳速度减缓且与阴极表面的吸附变得脆弱;此外,温度升高促使镀液黏度η升高,也加剧了微粒电泳的减缓。
有文献报导,瓦特镀镍液中的SiC微粒能吸附Ni2+使表面荷正电[25],TiO2粉末对溶液中金属离子也存在吸附[18],复合镀液中的SiC微粒[26]与PTFE微粒[27]还可吸附稀土离子而使表面呈现较强的正电性。金刚石微粒在溶液中同样能吸附正离子(如H+、Ni2+)形成荷微量正电的吸附原子团[14],有利于微粒进入阴极,但吸附和脱附是同时存在的可逆过程,根据Langmuir 吸附理论,溶液温度的逐渐升高促使可逆过程向脱附方向进行,导致微粒表面正电荷吸附量的降低。
温度的升高导致电极/溶液界面间场强的减弱、镍还原速度的加快及金刚石微粒表面正电荷密度的降低等效果必然使微粒复合量逐渐下降。
图2还显示,各曲线在-0.88 V附近发生明显变化,镍离子在此电位附近还原为金属镍。
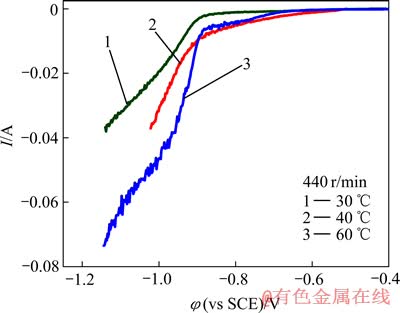
图2 不同温度时Ni-金刚石复合电沉积的阴极极化曲线
Fig. 2 Cathodic potentiodynamic diagrams of Ni-diamond composition electrodeposition at different temperatures
2.1.2 温度对电化学阻抗谱的影响
Ni-金刚石复合体系在不同温度下于-0.88 V处的电化学阻抗谱如图3所示,阻抗谱呈现较好的半圆形容抗弧,则体系的模拟等效电路可用图4表示。
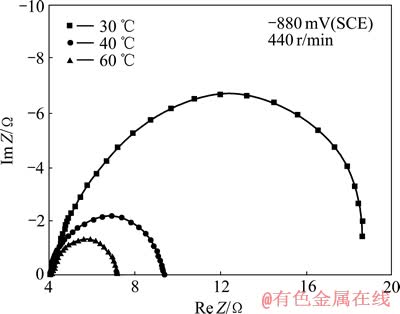
图3 不同温度时Ni-金刚石复合电沉积的电化学阻抗谱
Fig. 3 Impedance diagrams of Ni-diamond composite electrodeposition performed at different temperatures
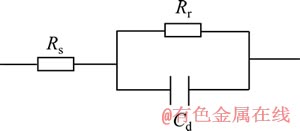
图4 Ni-金刚石复合电沉积电化学阻抗谱的等效电路图
Fig. 4 Electrical equivalent circuit of Ni-diamond composite electrodeposition used for simulating impedance diagrams
图4中,Rs表示体系的溶液电阻,Rr表示氧化还原时因电荷迁移和物质扩散而产生的法拉第电阻,Cd 表示界面区电荷产生的双电层电容。拟合后发现,随着溶液温度由30 ℃→40 ℃→60 ℃变化,法拉第电阻沿17.3 Ω→5.2 Ω→3.0 Ω递减,双电层电容相应沿40.8 μF→141.2 μF→175.6 μF递增。
HE等[16]对Ni-金刚石复合电沉积体系的研究发现,微粒的添加使Ni2+的还原电位更负,意即金刚石微粒在电极表面的吸附与沉积对金属离子的放电具有一定阻碍作用。图3中法拉第电阻的递减,恰与图2中阴极极化随温度升高而降低的趋势相吻合,表明该阻碍作用的减弱,即Ni2+还原速度因温度升高而加快,这必将导致微粒复合量的降低。Ni2+还原速度的加快还意味着电极表面沉积与吸附的惰性微粒减少,致使阴极有效表面积增大,相当于构成双电层的极板面积增大[28],从而导致图3中双电层电容随温度升高而递增。上述分析表明,法拉第电阻及双电层电容随温度升高的变化趋势均是微粒复合量降低的表现。
2.1.3 温度对电极表面荷电种类及密度的影响
Ni-金刚石复合体系于不同温度时的微分电容曲线如图5所示。由图5可知,随着温度沿30 ℃→40 ℃→60 ℃逐渐升高,复合体系的零电荷电位沿-0.844 V→-0.715 V→-0.346 V正移,零电荷电位下的微分电容值沿3.24 μF/cm2→3.35 μF/cm2→ 3.58 μF/cm2渐增,由相应微分电容曲线经Autolab电化学工作站自带软件拟合后发现,电极表面均荷负电,且随温度升高电荷密度由-0.046×10-7 C/cm2→-5.610 3×10-7 C/cm2→-19.227×10-7 C/cm2明显增大。
微分电容值Cd的变化趋势与交流阻抗谱中双电层电容的变化规律完全一致,同样可认为是吸附于电极表面的金刚石微粒减少致使有效极板面积增大造成的。
由极化曲线的分析已知,温度升高使电极/溶液界面间的场强E减弱,表面吸附有正电荷的微粒的电泳及镍离子的电迁移均随之降低,可能导致阴极表面的电子来不及被中和,从而使电极表面在零电荷电位时的负电荷密度越来越高。
2.2 温度对复合量的影响
温度与复合量间的工艺实验结果如图6所示,图中曲线直观显示,在试验温度范围内,金刚石微粒的复合量随溶液温度升高而降低。HE等[13]在研究Ni-羟基磷灰石(Ni-HAP)复合电沉积时同样如此;YAO 等[8]认为温度升高致使微粒的吸附量减少,从而使阳极过电位降低,造成微粒被基质金属捕获的几率下降。当然,基质金属Ni的沉积速度因温度升高而加快也是复合量降低的重要原因,工艺试验映证了电化学测试结果的有效性。
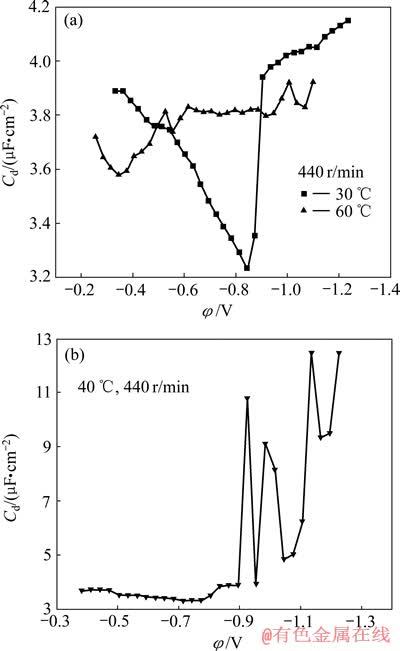
图5 不同温度时Ni-金刚石复合电沉积的微分电容曲线
Fig. 5 Differential capacitance curves of Ni-diamond composite electrodeposition at different temperatures
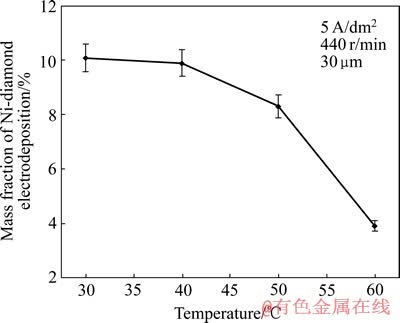
图6 Ni-金刚石复合电沉积温度与金刚石微粒复合量的关系
Fig. 6 Relationship between temperature and mass fraction of Ni-diamond composite electrodeposition
3 结论
1) 温度升高使Ni-金刚石复合体系的阴极极化减小。此时,电极/溶液界面间场强逐渐减弱,微粒电泳速度降低,不利于微粒进入镀层,同时Ni2+还原加速,亦不利于复合量的提高。
2) 温度升高使复合体系的法拉第电阻递减,双电层电容递增,且使阴极表面在析出电位附近的负电荷密度渐增。
3) 复合量随镀液温度升高而降低,工艺实验结果与电化学测试分析结果相互映证。
REFERENCES
[1] 冯秋元, 李廷举, 金俊泽. 复合电镀机理研究及最新进展[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2007, 36(3): 559-564.
FENG Qiu-yuan, LI Ting-ju, JIN Jun-ze. Research on the mechanism of composite electroplating and its latest progress[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2007, 36(3): 559-564.
[2] 周海飞, 杜 楠, 赵 晴. 复合电沉积工艺研究现状[J]. 电镀与涂饰, 2005, 24(6): 41-46.
ZHOU Hai-fei, DU Nan, ZHAO Qing. Status of composite electrodeposition techniques[J]. Electroplating and Finishing, 2005, 24(6): 41-46.
[3] MUSIANI M. Electrodeposition of composites: an expanding subject in electrochemical materials science[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2000, 45(20): 3397-3402.
[4] 张 艺, 王森林, 李彩彩. Ni/LaNi5多孔复合电极的制备及其析氢电催化性能[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2012, 41(3): 457-461.
ZHANG Yi, WANG Sen-lin, LI Cai-cai. Preparation and electrocatalytic performance for hydrogen evolution reaction of the Ni/LaNi5 porous composite electrode[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012, 41(3): 457-461.
[5] 杜宝中, 王 博, 路蕾蕾. 稀土镧对Ni-P-PTFE复合镀层结构和性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2011, 40(s2): 229-232.
DU Bao-zhong, WANG Bo, LU Lei-lei. Effect of LaCl3 on the microstructure and properties of Ni-P-PTFE composite coating[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2011, 40(s2): 229-232.
[6] 李明菲, 彭 晓, 王福会. 新型细晶Ni3Al涂层的高温氧化行为[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2011, 31(6): 414-418.
LI Ming-fei, PENG Xiao, WANG Fu-hui. High temperature oxidation behavior of a novel five-grained Ni3Al coating[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2011, 31(6): 414-418.
[7] RANJAN S, SIDDHARTHA D, KARABI D. Effect of stirring rate on the microstructure and microhardness of Ni-CeO2 nanocomposite coating and investigation of the corrosion property[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2011, 205(13/14): 3847-3855.
[8] YAO Ying-wu, ZHAO Chun-mei, ZHU Jin. Preparation and characterization of PbO2-ZrO2 nanocomposite electrodes[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 69: 146-151.
[9] PIERRE-ANTOINE G, PATRICE B, JACQUES P. Electrodeposition and characterization of Ag-ZrO2 electroplated coatings[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2001, 140(2): 147-154.
[10] ALAIN R, JULIO C P DE S, ANTONIO F S. Co- electrodeposition and characterization of Cu-Si3N4 composite coatings[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2011, 205: 4596-4601.
[11] 李爱昌, 赵 娣, 李 倩. (Ni-Mo)-TiO2纳米薄膜的制备及其光催化降解罗丹明B的性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(2): 526-532.
LI Ai-chang, ZHAO Di, LI Qian. Preparation of (Ni-Mo)-TiO2 thin films and their photocatalytic activity of Rhodamine B[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(2): 526-532.
[12] 李 渊, 蒋良兴, 倪恒发. 锌电积用Pb/Pb-MnO2复合电催化阳极的制备及性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(12): 2357-2365.
LI Yuan, JIANG Liang-xing, NI Heng-fa. Preparation and properties of Pb/Pb-MnO2composite anode for zinc electrowinning[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(12): 2357-2365.
[13] HE Li-ping, LIU Hai-rong, CHEN Da-chuan, CHEN Zong-zhang, BAI Xiao-jun. Fabrication of HAP/Ni biomedical coatings using an electro-codeposition technique[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2002, 160(2/3): 109-113.
[14] 郭鹤桐, 张三元. 复合镀层[M]. 天津: 天津大学出版社, 1991.
GUO He-tong, ZHANG San-yuan. Composite coatings[M]. Tianjin: Tianjin University Press, 1991.
[15] ABDEL H Z, GHAYAD I M. Characteristics of electrodeposition of Ni-polyethylene composite coatings[J]. Material Letters, 2002, 53(4): 238-243.
[16] HE Xiang-zhu, WANG Yong-xiu, SUN Xin, HUANG Li-yong. Preparation and investigation of Ni-Diamond composite coatings by electrodeposition[J]. Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Letters, 2012, 4(1): 48-52.
[17] WU Gang, LI Ning, ZHOU De-rui, KURACHI MITSUO. Electrodeposited Co-Ni-Al2O3 composite coatings[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2004, 176(2): 157-164.
[18] 邓朝阳. Zn-Co、Zn-Co-TiO2电镀工艺及其基础理论研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2000.
DENG Zhao-yang. A study on processes and fundamentals of Zn-Co and Zn-Co-TiO2 electroplating[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2000.
[19] 查全性. 电极过程动力学导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004.
ZHA Quan-xing. Introduction of electrode process kinetic[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004.
[20] 曹楚南, 张鉴清. 电化学阻抗谱导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002.
CAO Chu-nan, ZHANG Jian-qing. An introduction to electrochemical impedance spectroscopy[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002.
[21] 杜克勤, 邹恩义, 王 炜. 铜-氮化硅复合电沉积过程的交流阻抗测试分析[J]. 大连铁道学院学报, 1998, 19(1): 83-87.
DU Ke-qin, ZOU En-yi, WANG Wei. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of Si3N4 particle occlusion during copper electrodeposition[J]. Journal of Dalian Railway Institute, 1998, 19(1): 83-87.
[22] 余 焜, 施智祥. 金刚石颗粒强化银基复合镀层[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2000, 10(S1): 198-204.
YU Kun, SHI Zhi-xiang. Ag-based composite coatings reinforced by diamond particulates[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2000, 10(S1): 198-204.
[23] 杜 楠, 周海飞, 赵 晴, 廖 强. Ni-金刚石复合电沉积的界面作用力及其对复合量的影响[J]. 材料工程, 2008, 2: 23-26.
DU Nan, ZHOU Hai-fei, ZHAO Qing, LIAO Qiang. Interfacial force in nickel-diamond composite electrodeposition and its effect on diamond content in composite plating[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2008, 2: 23-26.
[24] 赵胯国. 胶体与界面化学[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2003.
ZHAO Kua-guo. Colloid and interface chemistry[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2003.
[25] 吴人洁. 复合材料[M]. 天津: 天津大学出版社, 2000.
WU Ren-jie. Composite materials[M]. Tianjin: Tianjin University Press, 2000.
[26] 朱诚意, 郭忠诚. 稀土对电沉积Ni-W-B-SiC复合镀层组织结构及性能的影响[J]. 过程工程学报, 1999, 20(3): 225-228.
ZHU Cheng-yi, GUO Zhong-cheng. Effects of addition of RE on properties and structure of Ni-W-B-SiC composite coatings[J]. Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 1999, 20(3): 225-228.
[27] 唐宏科, 赵文轸, 杨 燕. 稀土在Ni-Co-PTFE复合电镀中的作用机制研究[J]. 稀有金属, 2006, 30(6): 804-807.
TANG Hong-ke, ZHAO Wen-zhen, YANG Yan. Mechanism of Ni-Co-PTFE composite plating with rare earths[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2006, 30(6): 804-807.
[28] LIDIA B, PIER L B, ALBERTO B, STEFANO M, FRANCOIS W, PIERRE P, JACQUES G. Preparation and investigation of nanostructured SiC-nickel layers by electrodeposition[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2002, 151(1/4): 89-95.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家电网公司科技项目(ZDK/GW001-2012, ZDK011-2011);浙江省电力公司科技项目(5211011306V2, 52110113091M)
收稿日期:2012-09-14;修订日期:2013-04-25
通信作者:杜 楠,教授;电话:0791-3863187;E-mail: D_unan@sina.com