Corrosion resistance of 91W-6Ni-3Fe refractory metal, TiAl compound and iron based alloys in molten aluminum
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2012年第9期
论文作者:肖华强 陈维平 柳哲
文章页码:2320 - 2326
关键词:腐蚀行为;熔铝;金属间化合物
Key words:corrosion behavior; molten aluminum; intermetallic compound
摘 要:采用静态浸没腐蚀试验研究91W-6Ni-3Fe难熔合金(91W)、TiAl金属间化合物和两种常用铁基合金(QT700和H13钢)在750 ℃铝液当中的腐蚀性能。通过3D光学显微镜、SEM、EDS和XRD研究样品的表面形貌,腐蚀界面和相组成。结果表明:91W具有最好的耐铝液腐蚀性能,QT700次之,H13再次之,TiAl合金的耐铝液腐蚀性能最差。四种金属材料的腐蚀失重均符合抛物线规律,材料在经过一开始的加速腐蚀阶段后,腐蚀速率趋于稳定。材料在铝液当中溶解遵循扩散-反应机制,91W材料在铝液当中的腐蚀主要由扩散这一速控步骤所决定,而TiAl合金的腐蚀性能差主要是由于TiAl-(TiAl3)-Al扩散偶反应具有较低的激活能。
Abstract: The corrosion behaviors of 91W-6Ni-3Fe (91W) refractory alloy, TiAl intermetallic compound and two types of iron based alloys (QT700 and H13 tool steel) in a liquid aluminum were investigated. Corrosion experiments or static immersion-tests were carried out in pure molten aluminum at 750 ℃. The surface micro-topographies, corrosion interfaces and phase compositions of the immersed samples were investigated by 3D optical microscopy, SEM, EDS and XRD. The results show that 91W exhibits the best corrosion resistance, followed by QT700, H13 and TiAl alloy, consequently. The corrosion mass loss of the four metallic materials adheres to parabolic criterion, and the corrosion rate trends to be stable after initial acceleration. The diffusion-reaction mechanism is proposed for the dissolution of materials in molten aluminum, and the diffusion process is the rate-determining step during the dissolution of 91W in molten aluminum, while the low activation energy for the reaction between TiAl-(TiAl3)-Al couple results in poor corrosion resistance of TiAl alloy in molten aluminum.

![]()

Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 2320-2326
XIAO Hua-qiang, CHEN Wei-ping, LIU Zhe
National Engineering Research Center of Near-Net-Shape Forming for Metallic Materials,
South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
Received 6 September 2011; accepted 19 March 2012
Abstract: The corrosion behaviors of 91W-6Ni-3Fe (91W) refractory alloy, TiAl intermetallic compound and two types of iron based alloys (QT700 and H13 tool steel) in a liquid aluminum were investigated. Corrosion experiments or static immersion-tests were carried out in pure molten aluminum at 750 ℃. The surface micro-topographies, corrosion interfaces and phase compositions of the immersed samples were investigated by 3D optical microscopy, SEM, EDS and XRD. The results show that 91W exhibits the best corrosion resistance, followed by QT700, H13 and TiAl alloy, consequently. The corrosion mass loss of the four metallic materials adheres to parabolic criterion, and the corrosion rate trends to be stable after initial acceleration. The diffusion-reaction mechanism is proposed for the dissolution of materials in molten aluminum, and the diffusion process is the rate-determining step during the dissolution of 91W in molten aluminum, while the low activation energy for the reaction between TiAl-(TiAl3)-Al couple results in poor corrosion resistance of TiAl alloy in molten aluminum.
Key words: corrosion behavior; molten aluminum; intermetallic compound
1 Introduction
Molten aluminum corrosion is one of the major problems in the aluminum-production industry. As very important examples, this corrosion behavior is usually in crucibles, pumps and dies of aluminum die-casting [1-3]. Most of the structures for the production of aluminum components in the casting industry are made of ferrous alloys. Therefore, the corrosion behavior of cast iron and steel in molten aluminum has been widely investigated [4-9]. In these cases, an intermediate zone, consisting of successive layers of iron aluminates, always forms between substrate and molten aluminum [4,5]. Meanwhile, the formation and the growth of these successive intermetallic layers are governed by reaction diffusion laws [7-9]. Based on the above research results, many technological solutions are nowadays provided to improve the liquid aluminum corrosion resistance of iron based materials, such as surface engineering processes (e.g. nitriding, PVD and CVD) and alloying treatment [10-14]. At the same time, many efforts have been attempted to develop new materials with higher corrosion resistance to liquid aluminum.
Refractory metals are potential candidate materials for aluminum die-casting systems. For example, tungsten based alloys are reported to have good corrosion resistance in molten aluminum [15,16]. Besides, some intermetallics, such as aluminides, have attractive mechanical properties and good corrosion and oxidation resistance. However, little research focuses on obtaining the quantitative corrosion resistance associated with these alloys subjected to molten aluminum. ZHU et al [17] investigated the failure of some advanced metal materials for aluminum die-casting dies. They found that the Anviloy 1150 showed the best soldering, washout and thermal fatigue resistance. LUO et al [13] selected γ-TiAl as a reference sample to study the corrosion resistance of some iron based alloys in molten aluminum. Compared to the non-boronized iron alloys, γ-TiAl shows better corrosion resistance in molten aluminum.
In the present work, the corrosion behavior of two kinds of heat resistant materials (91W and TiAl intermetallics) as well as two popular iron based alloys (ductile cast iron QT700 and H13 tool steel) was investigated by immersion tests in molten aluminum. The experimental results provide clues to the selection of candidate materials with suitable durability in molten aluminum.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
Ductile cast iron (QT700), hot work tool steel (H13), tungsten heavy alloy 91W and intermetallic TiAl compound were selected as experimental substrate materials. Their chemical compositions are listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Chemical compositions of substrate materials (mass fraction, %)

2.2 Corrosion testing
Figure 1 shows the static immersion-testing apparatus. The specimens for the immersion tests were disks with dimensions of d16 mm × 6 mm, with a center hole of 3 mm in diameter. For each run, 2 kg aluminum ingot in a bath, containing small amount impurities of Fe and Mn (less than 0.2%, mass fraction), was melted in a graphite crucible by heating at 750 ℃ for 45 min. Before corrosion tests, all the surfaces of the specimens were polished to a 2000-grit finish using SiC paper. The specimens without preheating were statically dipped into the molten aluminum liquid and held for different time. Then, the specimens were taken out from the melt and cooled in air to room temperature.

Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of corrosion test apparatus
2.3 Characterization
For mass loss evaluation and surface morphology observation, the immersed specimens were put into a 10% NaOH solution to remove residual aluminum adhering to the surfaces, and then ultrasonically degreased and cleaned in acetone and alcohol to ensure complete removal of the residual aluminum. The calculation of mass loss directly describes the mass change per unit area (g/mm2), while the corrosion rate is expressed in terms of volume loss per square centimeter of the specimen per hour, i.e. (mm3·cm-2·h-1) [13,18]. 3D optical microscopy was used to investigate the surface morphology of the specimens. Meanwhile, several as-immersed specimens under the same immersion condition from each run were used for microstructural analysis. Each as-immersed specimen was cross- sectioned, mechanical polished and then examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). An integrated energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS) was employed to determine the composition of the formed phases within the reaction region between the substrates and residual aluminum. X-ray diffraction (XRD) tests were carried out to confirm the phase structures of the interface.
3 Results
3.1 Examination of etched surfaces
Figure 2 shows the optical micrographs of the 3D microscopic morphology of the etched surfaces of the materials. As seen in Figs. 2(a) and (b), the etched surfaces are uneven, and there are plenty of cracks, indicating the etched specimens are locally broken up and flaked away. Furthermore, there are some small pits on the etched surfaces due to localized attack of aluminum melt. That is to say, those weak areas, such as defects inside material, grain boundaries and phase boundaries are prone to be eroded by molten aluminum, forming microvoids in local. In Fig. 2(b), little holes could also be seen due to the separation of nodular graphite. As for 91W, though the binder phase of Fe and Ni has been etched by molten aluminum, the W-matrix does not flake due to the fine metallurgical bonding. For the TiAl alloy (Fig. 2(d)), tiny particles are dispersively distributed in the whole substrate.
3.2 Characterization of corrosion products
Figure 3 presents the cross-sectional SEM micrographs of the etched samples, revealing intermetallic layers formed between molten aluminum and substrate. Table 2 lists the composition of phases formed in different diffusion layers.
Figures 3(a) and (c) show the respective microstructures of etched interfaces of H13 steel and QT700. It is found that tongue-like intermetallic compound grows towards the inner matrix and fuses gradually to forming continuous intermetallic compound, hindering the contact between aluminum melt and matrix metal. Simultaneously, besides some particles of intermetallic compound flaking from the matrix, there are some acicular intermetallic compounds which precipitate in the process of the melt solidification. The tongue-like intermetallic compounds formed in the immersion process of H13 steel (Fig. 3(a)) in molten aluminum grow perpendicularly to the interface, the thickness of which is about 150 μm. Meanwhile, there are small cracks near the interface, and many irregular cavities form inside the intermetallic compound layer because of the big difference in diffusion coefficient of atoms of Al and Fe. For QT700, however, Fig. 3(c) reveals that the tongue is not always vertical to the interface, it deflects or separates when meeting nodular graphite. The thickness of formed continuous intermetallic layer reaches about 80 μm, with a number of nodular graphite floating in molten aluminum near the interface. By analyzing Figs. 3(b), (d) and the EDX results in Table 2, the intermetallic compound formed in iron-based material on the immersion interface is mainly Fe2Al5, accompanying with a small quantity of FeAl3 near the interface of molten aluminum.

Fig. 2 3D optical micrographs of sample surfaces immersed in Al melt at 750 ℃ for 8 h: (a) H13; (b) QT700; (c) 91W; (d) TiAl
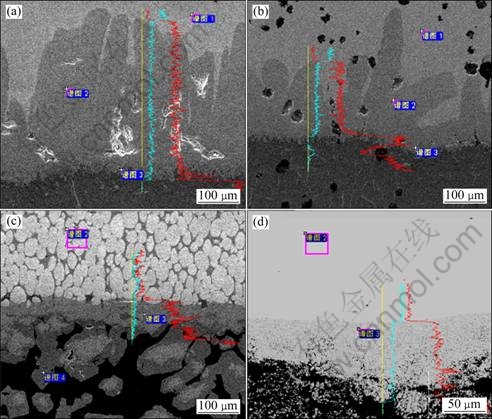
Fig. 3 SEM micrographs and EDX analysis of samples by dipping at 750 ℃ for 8 h in Al liquid: (a) H13; (b) QT700; (c) 91W; (d) TiAl
For 91W, it can be seen from Fig. 3(e) that on the surface of material immersed in molten aluminum, there is a continuous intermetallic compound layer formed with a plane interface of 50 μm in thickness. Furthermore, a lot of intermetallic compounds flake from the matrix in the molten aluminum near the interface. By analyzing Fig. 3(f) and the EDX analysis, the grayish intermetallic compound near the matrix is WAl5, and the dark grey region close to molten aluminum is WAl12.
As for immersed TiAl alloy in molten aluminum, the thickness of the intermetallic layer is about 100 μm (Fig. 3(g)). The intermetallic compound layer is not compact but with a lot of holes. Therefore, there are plenty of broken particles of the intermetallic compound in the aluminum melt near the interface, and there are even big blocks of loose intermetallic compound spalling as a whole. So, as shown in Fig. 2(d), the immersed interface presents a loose and porous structure. Analyzing from Fig. 3(h) and the EDX analysis in Table 2, it is concluded that there is just one kind of reaction product of TiAl3 after TiAl alloy is corrupted by molten aluminum.
To ascertain the phase composition of the interfaces, Fig. 4 presents the XRD analysis of the corrosion interfaces of the materials mentioned above. The XRD analysis results are identical to the former discussion. However, the phase of FeAl3 is difficult to identify in the XRD spectrum of the corrosion interfaces of H13 and QT700, because both the thickness and the quantity of FeAl3 phase are quite small.
3.3 Corrosion rate
Corrosion mass loss can visually describe the material loss after different time of etching in molten aluminum. Figure 5 shows the relationship of corrosion mass loss and square root of the corrosion time after the sample is etched in molten aluminum at 750 ℃ for different time. As expected, it is observed that the mass of all the four materials degrades progressively when immersed in molten aluminum. It is seen that the corrosion mass losses of the four materials have obvious linear relationship with the square root of the corrosion time, that is to say, the corrosion mass loss follows the equation of y=kt1/2+c, where t is dipping time, k and c are constants. After 1 h of etching, the mass losses of the four materials are almost the same. After 4 and 8 h, the mass losses of 91W and H13 are larger, while that of TiAl alloy is the least. Table 3 lists the related constants of corrosion mass loss curve of the different materials. At 750 ℃, the kinetic constants k of corrosion mass losses of H13 steel, QT700, 91W and TiAl alloy are 3.43, 2.47, 3.66 and 1.54, respectively.
As the corrosion rate of a material in molten aluminum is concerned, many researchers take the relation of the thickness of corrosion-formed intermetallic compound layer and corrosion time as the corrosion rate. While, it is not fit for the situation of long time corrosion, because long time corrosion leads to the the formed intermetallic compound breaking up and flaking away. Figure 6 gives the relationship of time and material volume loss per unit time per unit area. Though the corrosion mass loss of 91W is far higher than that of TiAl alloy (Fig. 5), from Fig. 6, it is indicated that the corrosion rate of TiAl alloy is much greater than that of 91W, the maximum of the four materials. That is the reason that corrosion mass loss is visually describing the mass loss of a material through corrosion, while corrosion rate, in fact, shows the thickness loss of a material per unit time, considering the density difference of various materials. In fact, the thickness loss of a material per unit time is taken as the average corrosion rate of the material in this research. It is seen that, from the beginning, materials show an accelerated corrosion stage. After this stage, the corrosion rates of H13 steel and 91W tend to be stable, while, that of TiAl alloy even shows a drop, and the increasing trend of the corrosion rate of QT700 has slowed down slightly. During each corrosion time, TiAl alloy and H13 steel have higher corrosion rates, and the average corrosion rate of 91W is around 5.2 mm3/(cm2·h) after being stable, which is the least one.
Table 2 Compositions of phases formed in different interface layers (point numbers refer to labels in Fig. 3, molar fraction, %)

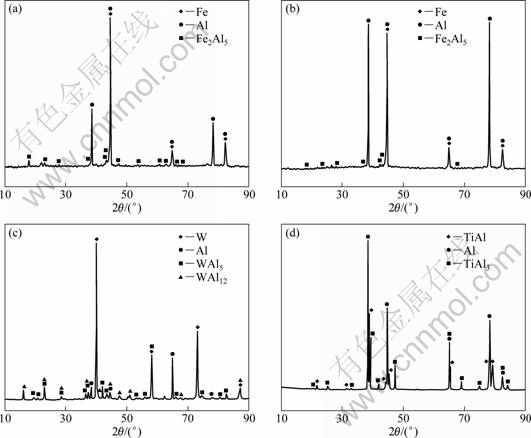
Fig. 4 XRD patterns of interfaces between Al and substrates: (a) H13; (b) QT700; (c) 91W; (d) TiAl
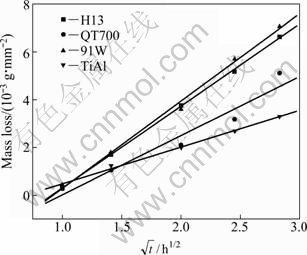
Fig. 5 Relationship between mass loss per unit area and square root of dipping time
Table 3 Constants of equation y=kt1/2+c for mass loss of materials

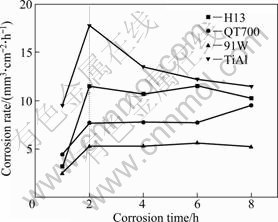
Fig. 6 Corrosion rate of different materials dipping in molten aluminum at 750 ℃
4 Discussion
The selection of materials with suitable durability in molten aluminum requires an understanding not only on the thermodynamic principles and kinetics of the chemical interaction, but also on the interface structure and characteristics of corrosion products. According to the research results, those materials should possess the following characteristics: 1) low solubility in molten aluminum; 2) limited thickness of the interfacial layer; 3) the interfacial compound layer should be dense and well bonded to the substrate; 4) the dispersed second phase acts as a diffusion barrier.
The dissolution of a solid metal into a liquid metal can be described by the Nernst-Shchukarev equation as [19]:
![]() (1)
(1)
where c is the concentration of the dissolved metal in bulk of the melt at time t; cs is the saturation concentration; k is the dissolution rate constant; s is the specimen surface area and v is the melt volume.
![]() (2)
(2)
where D represents the diffusion coefficient of the dissolved metal and δ is the thickness of the diffusion boundary layer. Based on Eqs. (1) and (2), it can be obtained:
![]() (3)
(3)
Actually, Dybkov’s diffusion-reaction model can well explain the dissolution process of materials in molten aluminum [20,21]. Metal atoms Me and Al atoms diffuse reciprocally through intermetallic compound layer, at the same time, new corrosion products (MexAly) will be formed by their respective reactions on the two interfaces of intermetallic compound layer. The diffusion process is one of the rate-determining steps during the dissolution. In view of the diffusion coefficient D, that is hardly found. However, it is believed that the diffusion coefficient D of Fe is much higher than those of Ti and W at 750 ℃ in this case. The solubility of materials in molten aluminum is listed in Table 4. The satisfactory performance of 91W in molten aluminum is primarily due to the low solubility of W in molten aluminum and good bond between the substrate and dense corrosion products (Figs. 3 and 6). The reaction process is another rate-determining step during the dissolution. As shown in Fig. 3, TiAl3 is formed on the boundary between TiAl alloy and Al melt, and then acts as a diffusion barrier. The activation energy for the reaction between TiAl-(TiAl3)-Al couple (95 kJ/mol) is much less than that between Ti-(TiAl3)-Al couple (180 kJ/mol) [22]. This causes the high loss rate of the TiAl alloy in liquid aluminum (Fig. 6). Moreover, the spallation of the porous TiAl3 layer accelerates the dissolution process.
Table 4 Solubility of elements in pure liquid aluminum at 750 ℃ [1,17]
![]()
For the two iron-based alloys investigated in the present work, QT700 exhibits better corrosion resistance in molten aluminum (as shown in Figs. 5 and 6). It is commonly believed that the graphite can decrease the corrosion of the matrix by molten aluminum through preventing aluminum atoms diffusion. From Fig. 3(b), it is obviously seen that the tongue of the corrosion product Fe2Al5 has branched or separated when meeting nodular graphite, which is attributed to the hindering effect of graphite to the diffusion of aluminum atoms; while on the corrosion interface of H13, Fe2Al5 grows perpendicularly to the interface. Therefore, the corrosion of iron matrix is decreased due to the diffusion barrier of graphite (Fig. 6). However, for long corrosion hours (8 h), the corrosion rate of QT700 increases slightly, while the corrosion behavior of H13 trends to be stable, which indicates that the contribution of graphite to corrosion resistance of QT700 has decreased slightly.
5 Conclusions
1) A comparison of the materials gives the following rank with respect to increasing corrosion resistance in molten aluminum: TiAl alloy, H13, QT700 and 91W, respectively.
2) A continuous intermetallic layer forms on the matrix as a result of molten aluminum attack. The mass loss y of materials increases with dipping time t following y=kt1/2+c, and the corrosion rate trends to be stable after the initial acceleration period.
3) The diffusion-reaction mechanism is proposed for the dissolution of materials in molten aluminum. The diffusion process is the rate-determining step during the dissolution of 91W in molten aluminum, while the low activation energy for the reaction between TiAl-(TiAl3)-Al couple results in poor corrosion resistance of TiAl alloy in molten aluminum.
4) The characteristics of the corrosion products and interfaces between substrate and Al melt influence the performance of materials in molten aluminum, and the dispersed graphite can decrease the corrosion of QT700 by molten aluminum through preventing aluminum atoms diffusing.
References
[1] YAN M, FAN Z. Durability of materials in molten aluminum alloys [J]. J Mater Sci, 2001, 36(2): 285-295.
[2] SHANKAR S, APELIAN D. Die soldering mechanism of the interface reaction between molten aluminum alloy and tool steel [J]. Metall Mater Trans B, 2002, 33(3): 465-476.
[3] LOU Ben-zhuo. Corrosion characteristics of several kinds of cast iron and steel materials in high temperature aluminum melt [J]. Corrosion and Protection, 2009, 30(7): 488-490. (in Chinese)
[4] BOUCH? K, BARBIER F, COULET A. Intermetallic compound layer growth between solid iron and molten aluminium [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1998, 249(1/2): 167-175.
[5] ZHANG N X, WOSIK J, FRANGER W, SONNLEITNET R, NAUER G E. Three-dimensional analysis of the growth of intermetallics phases between solid steel and molten aluminium [J]. Intermetallics, 2010, 18(2): 221-225.
[6] GAO Zhan-yong, ZHANG Jing-long, WU Wen-xia, FAN Bing-yuan, ZHAO Tuan. Effect of graphite morphology on erosion resistance of cast iron in molten aluminum [J]. Foundry, 2009, 58(9): 937-939. (in Chinese)
[7] BALLOY D, TISSIER J C, GIORGI M L, BRIANT M. Corrosion mechanisms of steel and cast iron by molten aluminum [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2010, 41(9): 2366-2376.
[8] BOUAYAD A, GEROMETTA CH, BELKEBIR A, AMBARI A. Kinetic interactions between solid iron and molten aluminium [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2003, 363(1-2): 53-61.
[9] SHAHVERDI H R, GHOMASHCHI M R, SHABESTARI S, HEJAZI J. Microstructural analysis of interfacial reaction between molten aluminium and solid iron [J]. J Mater Process Technol, 2004, 124(3): 345-352.
[10] PENG Cheng-zhang, ZHU Ling-ling. Tribological properties and erosion resistance of electroplated Ni-P/nano-Al2O3 composites coatings to aluminum liquid [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(6): 1177-1182. (in Chinese)
[11] NAZARI K A, SHABESTARI S G. Effect of micro alloying elements on the interfacial reactions between molten aluminum alloy and tool steel [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2009, 478(1-2): 523-530.
[12] HWANG S H, SONG J H, KIM Y S. Effects of carbon content of carbon steel on its dissolution into a molten aluminum alloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 390(1-2): 437-443.
[13] LOU D C, AKSELSEN O M, ONS?IEN M I, SOLBERG J K, BERGET J. Surface modification of steel and cast iron to improve corrosion resistance in molten aluminium [J]. J Surf Coat Technol, 2006, 200(18-19): 5282-5288.
[14] WANG De-qing, SHI Zi-yuan, ZOU Long-jiang. A liquid aluminum corrosion resistance surface on steel substrate [J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2003, 214(1-4): 304-311.
[15] TUNCA N, DELAMORE G W, SMITH R W. Corrosion of Mo, Nb, Cr and Y in molten aluminum [J]. Mater Trans A, 1990, 21(11): 2919-2928.
[16] YATSENKO S P, SABIRZYANOV N A, YATSENKO A S. Dissolution rates and solubility of some metals in liquid gallium and aluminum [C]//POPEL P S. 13th international conference on liquid and amorphous metals. Bristol: IOP, 2008: 1-7.
[17] ZHU Yu-long, SCHWAM D, WALLACE J F, BIRCEANU S. Evaluation of soldering, washout and thermal fatigue resistance of advanced metal materials for aluminum die-casting dies [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, 379(1-2): 420-431.
[18] XU J, BRIGHT M A, LIU X B, BARBERO E. Liquid corrosion of 316L stainless steel, 410 stainless steel, and 1015 carbon steel in a molten zinc bath [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2007, 38(11): 2727-2736.
[19] YEREMENKO V N, NATANZON YA V, DYBKOV V I. The effect of dissolution on the growth of the Fe2Al5 interlayer in the solid iron-liquid aluminium system [J]. J Mater Sci, 1981, 16(7): 1748–1756.
[20] DYBKOV V I. Reaction diffusion in heterogeneous binary systems [J]. J Mater Sci, 1986, 21(9): 3078-3090.
[21] DYBKOV V I. Interaction of 18Cr-10Ni stainless steel with liquid aluminium [J]. J Mater Sci, 1990, 25(8): 3615-3633.
[22] Van LOO F J J, REICK G D. Diffusion in the titanium-aluminum system [J]. Acta Metall, 1973, 21(1): 61-71.
肖华强,陈维平,柳 哲
华南理工大学 国家金属材料近净成形工程技术研究中心,广州 510640
摘 要:采用静态浸没腐蚀试验研究91W-6Ni-3Fe难熔合金(91W)、TiAl金属间化合物和两种常用铁基合金(QT700和H13钢)在750 ℃铝液当中的腐蚀性能。通过3D光学显微镜、SEM、EDS和XRD研究样品的表面形貌,腐蚀界面和相组成。结果表明:91W具有最好的耐铝液腐蚀性能,QT700次之,H13再次之,TiAl合金的耐铝液腐蚀性能最差。四种金属材料的腐蚀失重均符合抛物线规律,材料在经过一开始的加速腐蚀阶段后,腐蚀速率趋于稳定。材料在铝液当中溶解遵循扩散-反应机制,91W材料在铝液当中的腐蚀主要由扩散这一速控步骤所决定,而TiAl合金的腐蚀性能差主要是由于TiAl-(TiAl3)-Al扩散偶反应具有较低的激活能。
关键词:腐蚀行为;熔铝;金属间化合物
(Edited by FANG Jing-hua)
Foundation item: Project (51271080) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (S2011010002227) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China; Project (20100172110033) supported by the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education
Corresponding author: CHEN Wei-ping; Tel: +86-20-87113832; E-mail: mewpchen@scut.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61466-0

