文章编号:1004-0609(2015)-01-0119-06
LiSi和LiB负极材料的自放电性能
袁光明,高文秀,李 成,赵小玲,郑 奕,刘 波
(上海航天技术研究院 空间电源研究所,上海 200245)
摘 要:熔盐电解质锂电池在激活后由于自放电导致容量发生衰减,采用LiF-LiCl-LiBr低温共熔盐电解质,以二硫化铁为正极材料,分别以锂硅合金和锂硼合金作为负极材料制备单体电池,在500 ℃的温度下进行恒流放电试验。通过改变单体电池的工作电流可控制电池放电时间,并得到单体电池在经历不同工作时间后获得的可利用电容量。并将单体电池的工作时间和可利用电容量经一次线性回归分析。结果发现,使用锂硅合金作为负极材料时,电池的容量衰减率为40.6 C/min;而使用锂硼合金作为负极材料时,电池的容量衰减率仅为15.5 C/min。
关键词:熔盐电解质锂电池;自放电;锂硼合金;锂硅合金
中图分类号:TQ125.18 文献标志码:A
Self-discharge of LiSi and LiB anode materials
YUAN Guang-ming, GAO Wen-xiu, LI Cheng, ZHAO Xiao-ling, ZHENG Yi, LIU Bo
(Shanghai Academy of Space Lighted Technology, Institute of Space Power Sources, Shanghai 200245, China)
Abstract: The capacity decay occurs due to the self-discharge after activation in the molten salt electrolyte lithium batteries. Using LiF-LiCl-LiBr molten salts as electrolyte and FeS2 as cathode material, the lithium-silicon alloy and lithium-boron alloy as anode material to prepare single cells, which was then discharged at constant currents and 500 ℃. The working time of the single cells can be adjusted simply by varying the discharge current, the change of the available capacity is obtained. The working time and the measured capacity were analyzed by unary linear regression. The results show that the rate of the capacity loss is 40.6 C/min when lithium-silicon alloy is used as anode material, which is only 15.5 C/min when lithium-boron alloy is used as anode material.
Key words: molten salt electrolyte lithium battery; self-discharge; lithium-boron alloy; lithium-silicon alloy
熔盐电解质锂电池属于一次性贮备电池,其电解质在贮存状态下为不导电的固体,在激活后受热熔融形成的离子液体却具有高电导率,因此,该电池具有贮存时间长、放电倍率性能好等优点[1-5]。然而,由于电池在较高温度下工作,电极材料在熔融盐中会溶解并迁移,同时也发生一定的热分解,这些因素导致熔盐电解质锂电池在激活后产生严重的自放电,容量快速衰竭[6-8]。GUIDOTTI等[9]曾详细研究过LiSi/FeS2体系的自放电现象,发现其容量衰减率与所使用的电解质、工作温度以及正极材料的处理方法有关。近来,LiB合金由于锂含量高、比容量大、热稳定性好等优点,在熔盐电解质锂电池中被越来越多地作为负极材料使用[10-18],但是对于LiB体系的自放电研究还未见报道。本文作者以FeS2为正极材料、LiF-LiCl-LiBr共熔盐为电解质,分别使用LiSi合金和LiB合金作为负极材料,对二者在500 ℃下的自放电情况进行了 比较。
化学电池的自放电行为一直是电池工作者关注的重点之一。文献中一般先将电池搁置一段时间,然后再测试电池容量的保有率,以此计算电池的自放电率。如樊红敏等[19]利用该方法测试了空间用氢镍蓄电池的自放电率,宋清山等[20]测试了碱性圆柱蓄电池在搁置28 d内的自放电,发现样品蓄电池的自放电速度基本上固定不变。从严格意义上来讲,电池的自放电容量(C′)应该与搁置时间(t1)和放电时间(t2)之和有关,即C′=η(t1+t2)(其中η为自放电率)。文献[19-20]中报道的电池的自放电率相对较低,电池搁置时间常以天为单位计,容量测试则在1 h内完成,t1 2,因此,电池的自放电容量通常被简化C′=ηt1,所以可采用将电池搁置一段时间后再进行容量测试的方法。而本论文研究的高温熔盐锂电池自放电非常严重,若搁置几小时,电池容量完全损耗,为了获得准确的实际容量,容量测试通常需要十几分钟,t1与t2差别不大,因此二者皆不能被忽略,采用搁置的方法并不能真实地反映高温熔盐锂电池的自放电行为。本文作者曾经详细研究过高温熔盐锂电池在搁置状态和放电过程的自放电率,发现高温熔盐锂电池在搁置状态和放电过程下的自放电率几乎一致。因此,本研究中采取了简化方法,舍去了搁置时间(t1),而研究自放电容量与放电时间 (t2)的关系:C′=ηt2。
2,因此,电池的自放电容量通常被简化C′=ηt1,所以可采用将电池搁置一段时间后再进行容量测试的方法。而本论文研究的高温熔盐锂电池自放电非常严重,若搁置几小时,电池容量完全损耗,为了获得准确的实际容量,容量测试通常需要十几分钟,t1与t2差别不大,因此二者皆不能被忽略,采用搁置的方法并不能真实地反映高温熔盐锂电池的自放电行为。本文作者曾经详细研究过高温熔盐锂电池在搁置状态和放电过程的自放电率,发现高温熔盐锂电池在搁置状态和放电过程下的自放电率几乎一致。因此,本研究中采取了简化方法,舍去了搁置时间(t1),而研究自放电容量与放电时间 (t2)的关系:C′=ηt2。
1 实验
1.1 粉料准备
熔盐电解质锂电池的所有粉料均在干燥房中进行处理。负极材料采用锂合金,分别为含锂量44%(质量分数)的LiSi合金和含锂量60%(质量分数)的LiB合金;电解质使用LiF-LiCl-LiBr三元全锂电解质,共熔点为430oC ;将电解质与经高温焙烧的氧化镁混合后制备得到电池用隔离粉;二硫化铁首先经真空干燥处理,然后加入氧化锂和电解质,按一定比例混合后制得正极材料。
1.2 材料分析
采用PANalytical公司生产的EMPYREAN型X射线衍射仪对负极材料进行物相分析,Cu靶,管电流40 mA,管电压40 kV;采用NETZSCH公司生产的DSC 200F3仪器对材料进行热分析,高纯氩为载气,升温速率10 ℃/min。
1.3 单体电池制备
单体电池的制备采用冷压法。依次将正极粉、隔离粉放在模具中刮平,然后平铺上负极,放在油压机上恒压一定时间,压制成一个圆片,圆片直径为44 mm。
1.4 电性能测试
本研究采用自制熔盐电解质锂电池单体放电测试设备以及H&H PL312型直流电子负载器控制恒温恒流放电,数据采集使用DEWETRON DEWE-3020型数据采集仪。单体电池分别在不同电流0.76、1.52、3.04和4.56 A(对应于放电电流密度分别为50、100、200和300 mA/cm2)下放电,并以同一电流密度下初始放电电压的66%作为截止电压,以此来确定单体电池的工作时间,并计算可释放容量。本研究中所有单体电池放电温度均控制在(500±5) ℃。
2 结果与分析
2.1 负极材料的表征
当LiSi合金中的锂质量分数为44%时,合金的主要成分可以用化学式Li3.25Si表示,但由于工艺控制的差别,也有可能存在诸如Li4.4Si、Li3.75Si以及低锂含量的化合物。这些高锂含量化合物的存在会导致LiSi合金的热稳定性变差,加剧电池自放电,因此,并不适合用作熔盐电解质锂电池的负极。通过X射线衍射法对所使用的LiSi合金进行物相分析,其XRD衍射结果如图1所示。从图1中可以看出,LiSi合金的主要衍射峰与Li3.25Si物质(PDF:03-065-1337)衍射峰的位置以及强度很好地吻合,表明该合金可作为负极材料使用。
LiB合金的XRD衍射结果如图2所示。由图2可看出,衍射峰位置(2θ)在25°、42°、45°、52°、72°左右分别对应于LiB0.88化合物的(100)、(101)、(110)、(200)、(210)衍射峰(PDF:01-070-5171);而衍射峰位置(2θ)在36°、52°、65°左右可归为金属Li的(110)、(200)、(211)衍射峰(PDF:00-001-1131)。以上结果表明:LiB合金实际上是一种复合材料,含有LiB0.88和金属Li两种物相。当作为负极材料使用时,主要由金属Li参与放电。LiB合金中金属Li的含量可通过热分析法获得。图3所示为LiB合金在惰性气体保护下以10 ℃/min的升温速率测试得到的DSC图。从图3可见,LiB合金在200 ℃左右出现一个尖锐的吸热峰,这与金属锂的熔点一致;根据该合金测得的熔化焓(151 J/g)以及金属Li的熔化焓(430 J/g),可以计算出该LiB合金中金属Li的含量为35.1%(质量分数)。
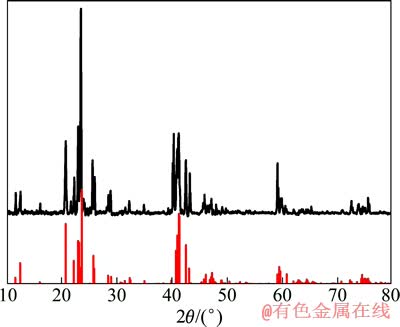
图1 LiSi合金的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of LiSi alloy

图2 LiB合金的XRD谱
Fig. 2 XRD pattern of LiB alloy

图3 LiB合金的DSC谱
Fig. 3 DSC spectrum of LiB alloy
2.2 放电特性
LiSi合金、LiB合金以及FeS2作为电极材料发生的主要电极反应列于表1中。对于实用型熔盐电解质锂电池,电压精度一般要求高于75%,因此,仅有电极的第一步半反应可以应用。LiSi合金、LiB合金以及FeS2第一步半反应的理论比容量分别为1764、4860和1206 C/g。在设计时,通过材料的合理配比使得正负极材料的理论容量处于最佳匹配状态。本研究中的单体电池的理论容量设计为1800C(0.5Ah)。
表1 不同电极材料的电极反应以及理论比容量
Table 1 Electrochemical reactions and their theoretical specific capacity of the electrode materials
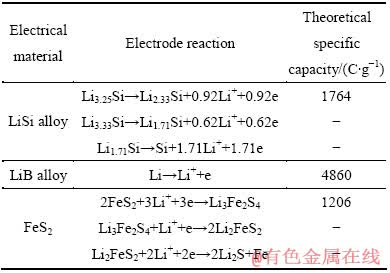
图4所示为LiSi/FeS2和LiB/FeS2两种体系在500 ℃温度下以100 mA/cm2的电流密度放电时的放电曲线。在整个放电过程,LiB/FeS2体系的放电电压均要高于LiSi/FeS2体系的,且放电时间也明显延长。LiB/FeS2体系初始放电电压在2.01 V,随后缓慢下降至第二放电平台,第一放电平台结束时的电压为1.33 V,为初始放电电压的66%。LiSi/FeS2体系初始放电电压仅为1.88 V,并在1.25 V的时候进入第二放电平台,第一平台结束时的电压亦为初始放电电压的66%。因此,本研究中的放电截止电压均设定为同一放电电流密度下初始放电电压的66%。根据上文分析,第一个放电平台的出现是由于电极材料的第一步半反应引起的;随着反应的进行,活性物质逐渐消耗,伴随着产物的积累,导致电池的内阻越来越大,表现出电池的放电电压缓慢下降。当第一步半反应需要的活性物质完全消耗,开始形成第二个放电平台。对图4进行分析,LiSi/FeS2体系的在第一平台放电结束时共释放容量1240C,LiB/FeS2体系有所增加,达到1562C,但均比理论容量(1800C)少,这主要是由于电池的自放电引起的。
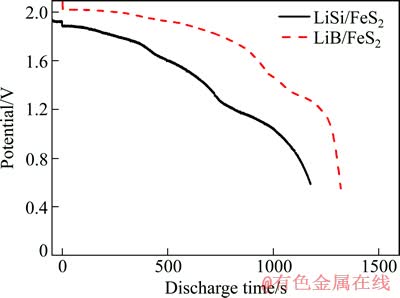
图4 LiB/FeS2与LiSi/FeS2体系放电曲线比较
Fig. 4 Comparison of discharge curves for LiB/FeS2 and LiSi/FeS2
高温熔盐锂电池在贮存时自放电几乎可以忽略,但一旦被激活,由于高温熔盐对正负极材料的强溶解能力以及正负极材料的热分解,就会存在自放电现象,从而导致电池释放的容量下降。通过改变单体电池的放电电流,可以控制单体电池的工作时间;电池工作时间越短,由于自放电而损耗的电容量少,电池可释放的容量越多。图5所示为LiSi/FeS2电化学体系在不同电流密度下的放电曲线。LiSi/FeS2的空载电压为1.92 V;加载后,随着放电电流密度的增加,放电电压下降:当放电电流密度在50、100、200和300 mA/cm2时,初始放电电压分别降为1.90、1.88、1.83和1.80 V。根据不同放电电流密度下的电压降,可计算出LiSi/FeS2体系的初始内阻为0.027 W。
当以同一电流密度下初始放电电压的66%作为截止电压时,从图5中可以得到单体电池在不同放电倍率下的工作时间,并可计算出电池在不同电流密度下放电时可释放的电容量,并将其结果列于表2。以可释放的电容量为纵坐标,相应的放电时间为横坐标,得到放电时间与可释放电容量的关系图(见图6)。经一元线性回归分析,发现LiSi/FeS2体系可释放电容量(C)与放电时间(t)存在以下关系:
 (1)
(1)
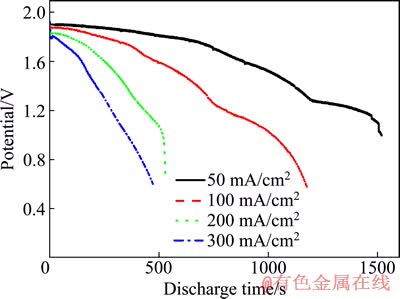
图5 LiSi/FeS2体系在不同电流密度下的放电曲线
Fig. 5 Discharge curves of LiSi/FeS2 at different current densities
表2 不同电化学体系可释放的容量
Table 2 Available capacity of different electrochemical couples


图6 放电时间对LiSi/FeS2体系可释放电容量的影响
Fig. 6 Effect of discharge time on available capacity for LiSi/FeS2
同样,将LiB/FeS2体系在不同电流密度下放电,其放电结果如图7所示。LiB/FeS2的空载电压为2.06 V;当放电电流密度在50、100、200和300 mA/cm2时,初始放电电压分别降为2.04、2.01、1.98和1.95 V。根据不同放电电流密度下的电压降,可计算出LiB/FeS2体系的初始内阻为0.023 W。LiB/FeS2体系在不同放电倍率下的工作时间以及由此计算得到的可释放电容量也列于表2中。根据以上分析结果,做出LiB/FeS2体系可释放电容量与放电时间的关系图,见图8。经一元线性回归分析,发现LiB/FeS2体系可释放电容量(C)与放电时间(t)存在以下关系:
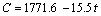 (2)
(2)
综上所述,LiB/FeS2与LiSi/FeS2的电性能差异主要有以下几点。
1) LiB/FeS2单体电池的初始内阻(0.023 W)小于LiSi/FeS2单体电池(0.027 W)。一方面是由于两种锂合金本身的电导率差异;另一方面可归因于负极层厚度的差异。由于LiB合金的理论比容量比LiSi合金高的,相应地,LiB合金的用量少于LiSi合金的,而二者的密度差别不大,因此,使用LiB合金作为负极材料,负极层较薄,由负极层引起的欧姆内阻小。

图7 LiB/FeS2体系在不同电流密度下的放电曲线
Fig. 7 Discharge curves of LiB/FeS2 at different current densities
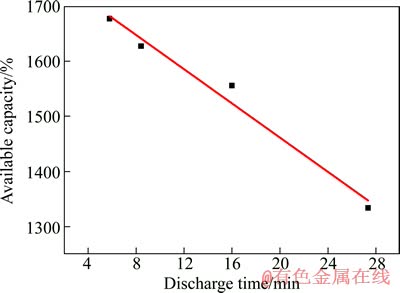
图8 放电时间对LiB/FeS2体系可释放电容量的影响
Fig. 8 Effect of discharge time on available capacity for LiB/FeS2
2) LiB/FeS2单体电池的空载电压(2.06 V)高于LiSi/FeS2单体电池的(1.92V)。这是由于Li3.25Si的电动势比纯Li的电动势高0.15V左右所引起。根据两种单体电池的内阻差异,LiB/FeS2电化学体系的工作电压应高于LiSi/FeS2的,与观测结果吻合。
3) LiB/FeS2电化学体系的容量衰减率(15.5 C/min)小于LiSi/FeS2电化学体系的(40.6 C/min)。因此,对于容量设计相同的两种电池,LiB/FeS2体系表现出来的工作时间要长于LiSi/FeS2体系的。
3 结论
1) 采有LiF-LiCl-LiBr低温共熔盐电解质和FeS2正极材料,分别以LiB合金和锂硅为负极材料制备高温熔盐单体电池,发现在500 ℃的工作温度下单体电池的可利用电容量随着工作时间的延长而降低,说明高温熔盐锂电池在激活后存在严重的自放电。
2) 作为高温熔盐锂电池的负极材料,LiB合金的理论比容量高于LiSi合金的,LiB/LiF2体系的空载电压高、内阻小。因此,能以较高的工作电压对外放电。
3) LiB/FeS2体系由自放电引起的容量衰减率比LiSi/FeS2体系低,因此,在相同理论容量的设计状态下,LiB/FeS2体系表现出的工作时间长。
4) 高温熔盐锂电池在工作状态下的容量衰减率可通过改变电池负极材料而得以抑制,在制备需要长时间工作的高温熔盐锂电池时,LiB合金负极材料的优势较明显。
REFERENCES
[1] GUIDOTTI R A, MASSET P J. Thermally activated (“thermal”) battery technology – Part Ⅰ: An overview[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 161(2): 1443-1449.
[2] GUIDOTTI R A, MASSET P J. Thermally activated (“thermal”) battery technology - Part Ⅱ: Molten salt electrolytes[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 164(1): 397-414.
[3] 陆瑞生,刘效疆. 热电池[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2005: 80-280.
LU Rui-sheng, LIU Xiao-jiang. Thermal battery[M]. Beijing: National Defence Industrial Press, 2005: 80-280.
[4] LINDEN D, REDDY T B. 电池手册[M]. 3版. 汪继强, 译. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007: 362-378.
LINDEN D, REDDY T B. Handbook of batteries[M]. 3rd ed. WANG Ji-qiang, transl. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2007: 362-378.
[5] 李国欣. 新型化学电源技术概论[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2007: 219-259.
LI Guo-xin. Novel chemical power-sources techniques[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science & Technology Press, 2007: 219-259.
[6] MASSET P J, GUIDOTTI R A. Thermal activated (“thermal”) battery technology—Part Ⅲ: FeS2 cathode material[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 177(2): 595-609.
[7] SHARMA R A, SEEFURTH R N. Equilibrium concentrations of FeS2 and FeS in LiCl-KCl eutectic melts[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1984, 131(5): 1084-1089.
[8] BURROW B J, NEBESNY K W, ARMSTRONG N R, QUINN R K, ZURAWSKI D E. Characterization of the materials comprising the reactive interfaces in the Li(Si)/FeS2 primary battery[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1981, 128(9): 1919-1926.
[9] GUIDOTTI R A, REINHARDT F W, SMAGA J A. Self-discharge study of Li-alloy/FeS2 thermal cells[C]// Proceedings of the 34th International Power Sources Symposium. Cherry Hill, NJ(USA): DOE, 1990: 132-135.
[10] RAYMOND A S, FREDERICK E W. Battery with boron-lithium alloy anode: US, 4162352 [P]. 1979-07-24.
[11] SANCHEZ P, BELIN C, CREPY G, de GUIBERT A. Preparation and characterization of lithium-boron alloys: Electrochemical studies as anodes in molten salt media, and comparison with pure lithium-involving systems[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1992, 27: 240-246.
[12] LIU Zhi-jian, DUAN Wei, LI Zhi-you, HUANG Ying-hua, QU Xuan-hui, HUANG Bai-yun. Effects of cathode materials on discharge characteristics of LiB alloy/FeS2 thermal battery[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 1999, 9(3): 530-534.
[13] LIU Zhi-jian, QU Xuan-hui, HUANG Bai-yun, LI Zhi-you. Crystal structure and morphology of a new LiB compound[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2000, 311(2): 256-264.
[14] LIU Zhi-jian, LI Zhi-you, DUAN Wei, QU Xuan-hui, HUANG Bai-yun, ZHANG Si-qi. Preparation of Li-B alloy and study of its microstructure and discharge characteristics[J]. Journal of Material Science & Technology, 2000, 16(6): 581-584.
[15] LIU Zhi-jian, YIN Jian, MENG Zhen-qiang, CHONG Jin, ZHOU De-bi. Electrochemical behavior and morphology of LiB compound anode materials[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16(1): 127-131.
[16] 段 伟, 章四琪, 刘志坚. 预处理对热电池阳极材料LiB合金结构和性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(2): 273-278.
DUAN Wei, ZHANG Si-qi, LIU Zhi-jian. Effect of pretreatment procedures on structure and performance of thermal battery anode LiB alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(2): 273-278.
[17] GUIDOTTI R A, MASSET P J. Thermally activated (“thermal”) battery technology Part Ⅳ: Anode materials[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 183: 388-398.
[18] 种 晋, 马越军, 郝津臣, 赵宝兴, 刘志坚, 董 静, 董树本. Li(B)合金负极在热电池中的应用研究[J]. 电源技术, 2007, 31(3): 220-224.
CHONG Jin, MA Yue-jun, HAO Jin-cheng, ZHAO Bao-xing, LIU Zhi-jian, DONG Jing, DONG Shu-ben. Study on application of lithium boron alloy anode in thermal battery[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 31(3): 220-224.
[19] 樊红敏, 王 淼, 范梅梅, 王树强, 檀立新, 傅晓晴. 空间用氢镍蓄电池自放电率研究[J]. 电源技术, 2012, 138(8): 1122-1124.
FAN Hong-min, WANG Miao, FAN Mei-mei, WANG Shu-qiang, TAN Li-xin, FU Xiao-qing. Self-discharge rate research on space NiH2 cell[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 138(8): 1122-1124.
[20] 宋清山, 邹 英. 碱性圆柱蓄电池自放电搁置时间的探讨[J]. 电源世界, 2003(3): 41-43.
SONG Qing-shan, ZOU Ying. Discuss self-discharge place time of columnar alkaline storage battery[J]. The World of Power Supply, 2003(3): 41-43.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:上海市科学技术委员会浦江人才基金资助项目(13PJ1432200)
收稿日期:2014-05-04;修订日期:2014-09-20
通信作者:刘 波,高级工程师,博士;电话:021-24187657;传真:021-24188008;E-mail:liu_ripple@163.com