Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 1633-1639
Thermodynamic model of lead oxide activity in PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3 slag system
Jin-liang WANG1,2, Xiao-chun WEN1, Chuan-fu ZHANG2
1. School of Metallurgy and Chemical Engineering, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou 341000, China;
2. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 20 June 2014; accepted 28 December 2014
Abstract: According to the ion and molecule coexistence theory, a thermodynamic model of lead oxide activity in PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3 slag system was established at the temperature of 1273-1733 K. The activities of PbO in slag were calculated, and their equal activity curves were plotted. The influences of slag basicity Q, iron oxide rate R and temperature T on activity NPbO and activity coefficient γPbO were also investigated. Results show that the calculated values of γPbO are in good agreement with the reported experimental data, showing that the model can wholly embody the slag structural characteristics. NPbO departures positively from Raoult values, and increases with increasing PbO content in slag but changes little with T. γPbO increases with increasing Q, and goes through the maximum with increasing R for basic slag (Q>0.3). Results can be applied to the thermodynamic research and operational optimization of modern lead smelting technologies.
Key words: ion and molecule coexistence theory; thermodynamic model; lead oxide; activity
1 Introduction
Nowadays, some novel technologies, such as QSL, Kivcet and Ausmelt/Isamelt, are replacing conventional lead-making methods [1-3]. The activity of lead oxide is an important parameter that can be widely applied to lowering lead content in slag as well as to optimizing operational parameters of lead smelting process. Several articles have been published on the phase equilibria in lead smelting slags [4-6]; however, only limited data on activity of PbO in CaO-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3 slags have been reported [7].
The ion and molecule coexistence theory (IMCT) [8,9] has been developed to express the reaction ability of components in a slag by the defined mass action concentration Ni according to the mass action law, like the traditionally applied activity ai of component i. The IMCT has been successfully used to predict sulfur, phosphorus or oxygen distribution at slag-metal interface [10-13], and has been verified as an efficient method to calculate the activities of structural units in various slags [14-17].
In the present work, a thermodynamic model of lead oxide activity in PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3 slag system was established according to the IMCT and verified by reported data [7]. The effects of slag composition and temperature on activity and activity coefficient of PbO were investigated, and the equal activity curves of PbO were plotted.
2 Establishment of PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO- Fe2O3 activity model
2.1 Slag structural units
According to the basic hypotheses of the IMCT [9], the main assumptions in the developed thermodynamic model for calculating the activity (mass action concentration) of PbO in PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3 slag can be simply summarized as follows.
1) Structural units in the studied slag are assumed to be composed of simple ions, such as Pb2+, Fe2+, Ca2+ and O2-, simple molecules SiO2 and Fe2O3, and complex molecules as silicates and ferrates. Every cation and anion can be generated from the basic components and exist in the form of ion-pairs as (Pb2++O2-), (Fe2+ +O2-) and (Ca2++O2-).
2) The ion-pairs, simple molecules and complex molecules are under chemically dynamic equilibrium, by taking (Ca2++O2-) and Fe2O3 to form CaFe2O4 as an example as (Ca2++O2-)+Fe2O3=CaFe2O4, and the chemical reactions of forming complex molecules obey the mass action law.
These hypotheses imply the relation between the mole number of basic components and the defined mass action concentration of each structural unit in slag, and connect the defined mass action concentrations of basic components and complex molecules with the chemical reaction equilibrium constant.
According to the IMCT, it can be reasonably obtained that there are four simple ions as Pb2+, Fe2+, Ca2+ and O2-, two simple molecules as SiO2 and Fe2O3in PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3 slag. Meanwhile, according to phase diagrams of CaO-SiO2, FeO-SiO2, FeO-Fe2O3, SiO2-PbO, CaO-FeO-Fe2O3 and CaO- FeO-SiO2, 13 kinds of complex molecules can be possibly formed in PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3 slag in the temperature range from 1273 to 1733 K. The structural units are listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Structural units of PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3 slag system
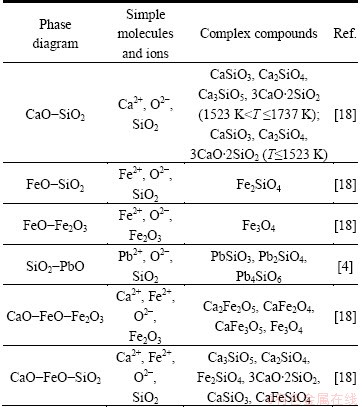
2.2 Chemical reactions between units
The mole numbers of five components in 100 g PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3 slag are assigned as  ,
,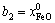 ,
, 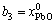 ,
, 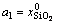 and
and 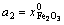 to represent the chemical composition of the slag. The defined equilibrium mole number xi and mass action concentration (activity) Ni of all structural units in PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3 slag are listed in Table 2.
to represent the chemical composition of the slag. The defined equilibrium mole number xi and mass action concentration (activity) Ni of all structural units in PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3 slag are listed in Table 2.
Table 2 Definition of unit’s activity and mole number

The total equilibrium mole number  can be expressed as
can be expressed as
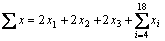 (1)
(1)
According to the IMCT, the mass action concentration (activity) of ion couples in the form of ion-pairs, i.e. (Pb2++O2-), (Fe2++O2-) and (Ca2++O2-), should be represented as
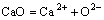
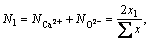
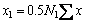 (2)
(2)
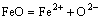
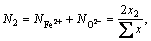
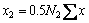 (3)
(3)

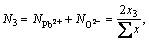
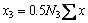 (4)
(4)
Meanwhile, the activity of other independent structural units can be calculated by
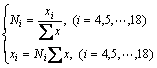 (5)
(5)
The chemical equations between the units of the PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3 slag system are shown as follows:
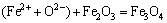

 (6)
(6)

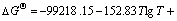
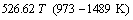 ,
,

 ,
,

 (7)
(7)

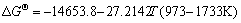 ,
,

 (8)
(8)
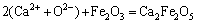
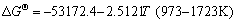 ,
,

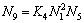 (9)
(9)
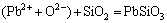
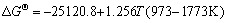 ,
,

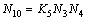 (10)
(10)
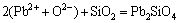
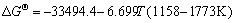 ,
,
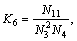
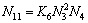 (11)
(11)
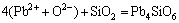

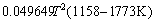 ,
,

 (12)
(12)

 ,
,

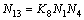 (13)
(13)
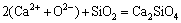
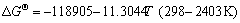 ,
,
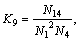
 (14)
(14)
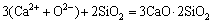
 ,
,
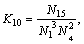
 (15)
(15)

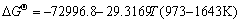 ,
,
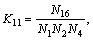
 (16)
(16)
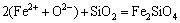
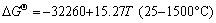 ,
,
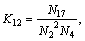
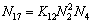 (17)
(17)
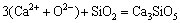
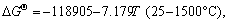
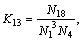
 (18)
(18)
The equilibrium constants 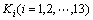 in Eqs. (6)-(18) can be calculated by ΔGΘ of each reaction obtained from Ref. [19].
in Eqs. (6)-(18) can be calculated by ΔGΘ of each reaction obtained from Ref. [19].
2.3 Activity calculation model
According to the conservation law of mass, the following equations can be deduced.
1) For the mole number of CaO
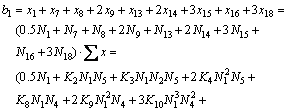
 (19)
(19)
2) For the mole number of FeO
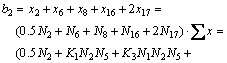
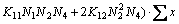 (20)
(20)
3) For the mole number of PbO
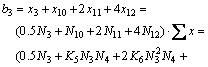
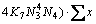 (21)
(21)
4) For the mole number of SiO2

 (22)
(22)
5) For the mole number of Fe2O3
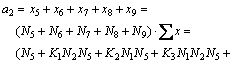
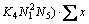 (23)
(23)
6) For the sum of all activities

 (24)
(24)
The following equations can be obtained when  in Eqs. (20)-(23) was eliminated using Eq. (19):
in Eqs. (20)-(23) was eliminated using Eq. (19):
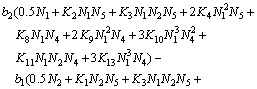
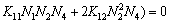 (25)
(25)
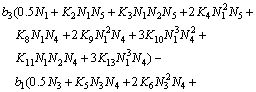
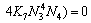 (26)
(26)
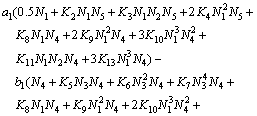
 (27)
(27)
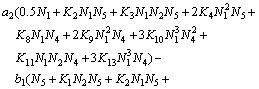
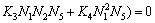 (28)
(28)
By transforming Eq. (24), the following equation can be obtained:

 (29)
(29)
Equations (25)-(29) are the activity models for the PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3 slag system.
3 Calculation flowchart
The activity model is a set of higher order equations and its calculation process is a typical solving process of nonlinear equations. The calculation flowchart of the activity model is shown in Fig. 1.
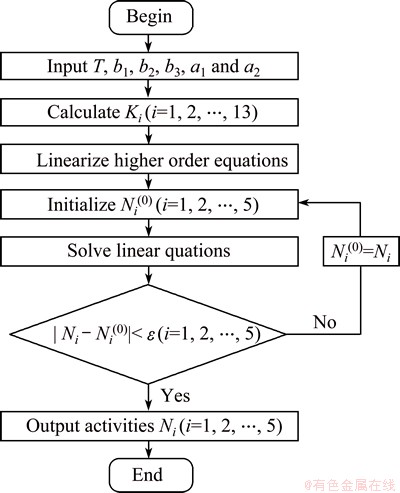
Fig. 1 Calculation flowchart of activity model
For the calculation process, the temperature T and the compositions (b1, b2, b3, a1 and a2) of the PbO-CaO- SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3 slag system were inputted at the beginning. The equilibrium constants of each chemical reaction  then can be calculated. After being linearized, the higher order equations of the activity model were transformed to linear equations about activities
then can be calculated. After being linearized, the higher order equations of the activity model were transformed to linear equations about activities  , which can be solved by the Newton iterative method. To control the iteration process, a precision parameter ε was adopted.
, which can be solved by the Newton iterative method. To control the iteration process, a precision parameter ε was adopted.
In this work, an activity calculation program was developed using Delphi 7.0 based on the activity model above. ε was set to be 1×10-4, because the activities can be regarded as the desired values when all of them changed less than 1×10-4 in the iteration process.
4 Results and discussion
The PbO activity NPbO and the PbO activity coefficient γPbO (γPbO=NPbO/fPbO, fPbO is the mole fraction of PbO in slag) were calculated for slags with different compositions at different temperatures (T).
The slag basicity (Q) and the iron oxide rate (R), defined by Eqs. (30) and (31), are introduced to simplify the description of the slag composition.
Q=w(CaO)/[w(CaO)+w(SiO2)] (30)
R=w(FeOx)/[w(FeOx)+w(CaO)+w(SiO2)] (31)
4.1 Effect of slag composition on activity and activity coefficient of PbO in slag
Figure 2 shows the model calculated values of the activity coefficient of PbO (γPbO) in PbO-CaO-SiO2- FeO-Fe2O3 slag with different Q at 1573 K when the mass ratio of FeO to Fe2O3is 5.0:1 and the mass fraction of PbO in slag is 1%. The corresponding measured data by KUDO et al [7] are also shown in Fig. 2.

Fig. 2 Comparison of calculated values and measured data of PbO activity coefficient in slag
As shown in Fig. 2, the model calculated values of γPbO are in good agreement with the measured data, showing that the activity calculation model can reflect the structural characteristics of the PbO-CaO-SiO2- FeO-Fe2O3 slag system.
It can also be seen from Fig. 2 that γPbO in the slag, varying from 0.5 to 2.5 depending on the slag composition, increases with increasing Q. At a fixed R, the higher the Q value is, the higher the γPbO is. The effect of Q on the activity coefficient is stronger for R=0.31 than for R=0.60, because the slag with R=0.31 is less diluted with iron oxide than the slag with R=0.60. This means that CaO can reduce the solubility of PbO in the slag system, but SiO2 can improve it. Therefore, in order to reduce the lead content in smelting slag, slags with high CaO content are usually adopted in modern lead smelting process.
Figure 3 shows the effect of R on the PbO activity coefficient γPbO at 1573 K when the mass ratio of FeO to Fe2O3 is 5.0:1, the mass fraction of PbO is 15%, and Q is equal to 0.1, 0.3 and 0.5.

Fig. 3 Effect of R on PbO activity coefficient at 1573 K
As shown in Fig. 3, in acidic slag with Q values less than 0.3, γPbO increases with increasing R, owing to a dilution of the acid component of silica by iron oxide. The activity coefficient in basic slag, with Q value over 0.3, goes through the maximum with increasing R. Slag with Q value of 0.5 has the maximum γPbO at R=0.3-0.4. The acid-base reaction may give a good explanation for the relation between the activity coefficient of PbO or lead solubility in slag and the slag composition. For modern lead smelting adopting basic slag, the iron oxide rate (R) is vital to decrease the lead content in the final smelting slag.
Figure 4 shows the relationship between PbO activity NPbO and PbO mole fraction fPbO in PbO-CaO- SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3 slag at 1573 K when the mass ratio of FeO to Fe2O3 is 5.0:1 and Q is equal to 0.4.
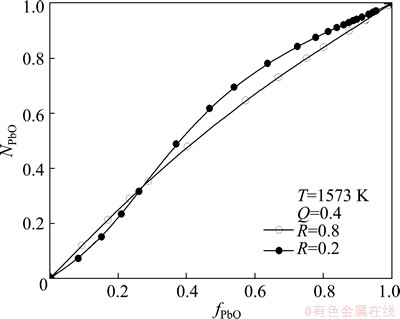
Fig. 4 Effect of mole fraction of PbO in slag on PbO activity at Q=0.4 and T=1573 K
As shown in Fig. 4, NPbO departures positively from Raoult values regardless of R values. The Raoult deviation increases first and then decreases with increasing fPbO, and reaches the maximum at fPbO=0.4 when R=0.8, but at fPbO=0.6 when R=0.2.
4.2 Effect of temperature on activity coefficient of PbO in slag
Figure 5 shows the effect of temperature T on the PbO activity coefficient γPbO at 1373 K and 1573 K when the mass ratio of FeO to Fe2O3 is 5.0:1, the mass fraction of PbO is 15%, and Q is equal to 0.1 and 0.5.
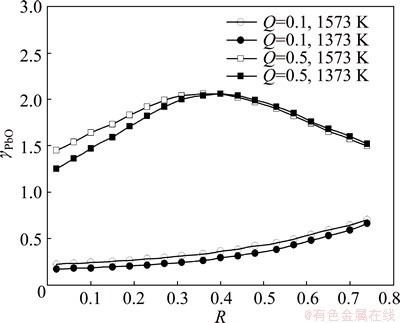
Fig. 5 Effect of temperature on activity coefficient of PbO at Q=0.1 and 0.5
As shown in Fig. 5, the activity coefficients change little with temperature. Accordingly, the effect of temperature on the activity coefficient of PbO is not significant within the temperature range from 1373 K to 1573 K at Q=0.1 and Q=0.5.
4.3 Equal activity curves
Figures 6 and 7 show the equal activity curves of PbO in PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3 slag at Q=0.5 and FeO/Fe2O3 mass ratio of 5.0:1, which is the popular slag composition of modern lead smelting, at 1423 K and 1523 K respectively. For these ternary diagrams, CaO and SiO2 were bound as one coordinate point, named CaO+SiO2, and FeO+Fe2O3 was regarded as another coordinate point, named FeOx.
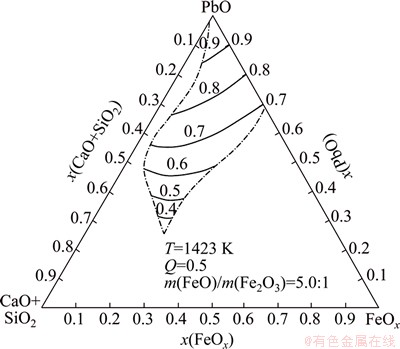
Fig. 6 Equal activity curves of PbO in PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO- Fe2O3 slag at 1423 K
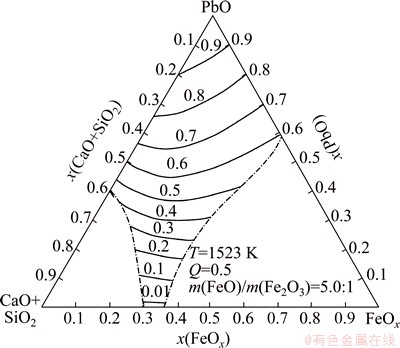
Fig. 7 Equal activity curves of PbO in PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO- Fe2O3 slag at 1523 K
As shown in Figs. 6 and 7, the equal activity curves are almost parallel. PbO activity increases with increasing PbO content in slag, but the activity curves near the PbO-CaO+SiO2 line vary larger with the changing PbO content in slag than that near the PbO-FeOx line for the reason that PbO can combine with SiO2 more strongly than with FeO or Fe2O3.
5 Conclusions
1) Calculated values of the activity model are in good agreement with the reported experimental data, showing that the thermodynamic model can reflect the structural characteristics of the PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO- Fe2O3 slag system.
2) NPbO departures positively from the Raoult values regardless of R values, and increases with increasing PbO content in slag but changes little with T.
3) γPbO varies from 0.5 to 2.5 depending on the slag composition and increases with increasing Q value. CaO can reduce the solubility of PbO in the slag system, but SiO2 can improve it.
4) γPbO in basic slag with Q values over 0.3 goes through the maximum with increasing R value. Slag with Q value of 0.5 has the maximum γPbO at R=0.3-0.4.
References
[1] WANG Jin-liang, WU Yan-xin, ZHANG Wen-hai. Development status of lead smelting technology and the lead vortex flash smelting process [J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2011, 2(1): 14-18. (in Chinese)
[2] SLOVIKOVSKII V V,GULYAEVA A V.Effective linings for Kivcet furnaces [J]. Refractories and Industrial Ceramics, 2014, 54(5): 350-352.
[3] GU H L, SONG X C, LAN X, BALDOCK R, ANDREWS R, REUTERM. Design and commissioning of the Ausmelt TSL lead smelter at Yunnan Tin Company Limited [C]//International Smelting Technology Symposium: Incorporating the 6th Advances in Sulfide Smelting Symposium. Orlando, Florida, USA: The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, 2012: 11-21.
[4] JAK E, ZHAO B J, LIU N, HAYES P C. Experimental study of phase equilibria in the system PbO-ZnO-SiO2 [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1999, 30(1): 21-27.
[5] JAK E, HAYES P C, LIU N G. Experimental study of phase equilibria in the system PbOx-CaO and PbOx-CaO-SiO2 [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1998, 29(3): 541-553.
[6] PEREZ-LABRA M, ROMERO-SERRANO A, HERNANDEZ- RAMIREZ A,ALMAGUER-GUZMAN I, BENAVIDES-PEREZ R. Effect of CaO/SiO2and Fe/SiO2ratios on phase equilibria in PbO-ZnO-CaO-SiO2-“Fe2O3” system in air [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(3): 665-674.
[7] KUDO M, JAK E, HAYES P, YAMAGUCHI K, TAKEDA Y. Lead solubility in FeOx-CaO-SiO2 slags at iron saturation [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2000, 31(1): 15-24.
[8] ZHANG Jian. The coexistence theory of slag structure [J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 1984, 6(1): 21-29. (in Chinese)
[9] ZHANG Jian. Computational thermodynamics of metallurgical melts and solutions [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2007: 241-245. (in Chinese)
[10] WU C C, CHENG G G, TIAN J. A thermodynamic model for evaluation of mass action concentrations of La2O3-Al2O3-CaF2- CaO-MgO slags for electroslag remelting based on the ion and molecule coexistence theory [J]. High Temperature Materials and Processes, 2013, 32(6): 541-550.
[11] YANG Xue-min, ZHAO Wei-jie,CHAI Guo-ming,GUO Han-jie, ZHANG Qiang. A universal thermodynamic model of calculating mass action concentrations for structural units or ion couples in aqueous solutions and its applications in binary and ternary aqueous solutions [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(3): 626-641.
[12] YANG X M, ZHANG M, ZHANG J L, LI P C, LI J Y, ZHANG J. Representation of oxidation ability for metallurgical slags based on the ion and molecule coexistencetheory [J]. Steel Research International, 2014, 85(3): 347-375.
[13] LI P C, ZHANG J L. Representation of dephosphorization ability for CaO-containing slags based on the ion and molecule coexistence theory [J]. ISIJ International, 2014, 54(3): 567-577.
[14] ZHANG Jian. Applicability of law of mass action to distribution of manganese between slag melts and liquid iron [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2001, 11(5): 778-783.
[15] WANG Jin-liang, ZHANG Chuan-fu, ZHANG Wen-hai. Activity calculation model for slag system of CaO-Cu2O-Fe2O3 [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(5): 955-959. (in Chinese)
[16] WANG Jin-liang, ZHANG Chuan-fu, TONG Chang-ren, ZHANG Wen-hai. Action concentration calculation model for slag system of CaO-FeO-Fe2O3-SiO2-Cu2O [J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2009, 40(2): 282-287. (in Chinese)
[17] YANG X M, SHI C B, ZHANG M, ZHANG J. A thermody-namic model for prediction of iron oxide activity in some FeO-containing slag systems [J]. Steel Research International, 2012, 83 (3): 244-258.
[18] Association of Germany Iron and Steel Engineer. Schlackenatlas slag atlas [M]. WANG Jian, PENG Yu-qiang, MAO Yu-wen, trasl. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1989: 41-81. (in Chinese)
[19] LIANG Ying-jiao, CHE Yin-chang. Inorganic thermodynamic data manual [M]. Shenyang: Northeastern University Press, 1993. (in Chinese).
PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3渣系氧化铅活度热力学模型
汪金良1,2,温小椿1,张传福2
1. 江西理工大学 冶金与化学工程学院,赣州 341000;2. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083
摘 要:基于炉渣结构分子和离子共存理论,建立1273~1733 K下的PbO-CaO-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3渣系氧化铅活度热力学模型,计算PbO活度并绘制等活度曲线,考察炉渣碱度Q、氧化铁比率R和温度T对活度NPbO和活度系数γPbO的影响。结果表明,活度系数γPbO的模型计算值与文献测定值吻合程度高,说明该模型能较好地反映该渣系结构本质;NPbO呈拉乌尔正偏差,且随渣中PbO含量的升高而增大,但受温度的影响不明显;γPbO 随Q的升高而增大;对于Q>0.3的碱性渣,γPbO随R的升高而出现极大值。该研究结果可用于现代炼铅工艺的热力学研究和操作优化。
关键词:分子和离子共存理论;热力学模型;氧化铅;活度
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (2013BAB03B05) supported by the National Key Technology R&D Program of China during the 12th Five-Year Plan Period, China; Project (20133BCB23018) supported by the Foundation for Young Scientist (Jinggang Star) of Jiangxi Province, China; Project (2012ZBAB206002) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, China
Corresponding author: Jin-liang WANG; Tel: +86-797-8312337; E-mail: simwjl@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63768-2