文章编号:1004-0609(2009)02-0353-07
铝及铝合金在南疆沙漠大气环境中的腐蚀行为
郑弃非,孙霜青,温军国,李德富
(北京有色金属研究总院,北京 100088)
摘 要:将铝及铝合金L3、LF21和LY12置于在南疆沙漠大气环境下进行现场暴露试验,利用扫描电镜(SEM)、能谱仪(EDS)和红外光谱仪(FTIR)分析腐蚀形貌、元素分布和腐蚀产物组成。结果表明:在南疆沙漠大气环境中,铝及铝合金发生较严重的大气腐蚀,主要腐蚀产物为Al2O3和水合Al(OH)3;铝及铝合金的腐蚀质量损失随暴露时间的变化遵循幂函数C=Ktn,短期内随着暴露时间的延长腐蚀速率会不断下降;地表浮土中的MgCl2 等成分的存在增加了金属表面的湿润时间,浮土中较高的pH值以及氯离子和硫酸根离子等的共同作用促进了铝及铝合金在南疆沙漠大气环境下的腐蚀。
关键字:铝;铝合金;大气腐蚀;沙漠;腐蚀形貌;腐蚀产物
中图分类号:TG172.3 文献标识码: A
Atmospheric corrosion behaviors of aluminium and aluminium alloys in desert atmosphere of southern Xinjiang Province, China
ZHENG Qi-fei, SUN Shuang-qing, WEN Jun-guo, LI De-fu
(General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals, Beijing 100088, China)
Abstract: Atmospheric corrosion behaviors of typical aluminium and aluminium alloys L3, LF21 and LY12 were investigated in the desert atmosphere of southern Xinjiang Province, China. The corrosion morphologies, elemental distribution and corrosion products were observed and analyzed by SEM, EDS and FTIR, respectively. The results demonstrate that the aluminium and aluminium alloys suffer more serious atmospheric corrosion in the atmosphere of desert saline soil, and the main products are Al2O3 and hydration Al(OH)3. The mass loss data of specimens with exposure time obey well with the power function of C = Ktn, and the corrosion rates are with the extension of time in short term. The surface dust contains MgCl2 that increases the wetness time of the metallic surface. Higher pH value, chloride ion and sulfate ion in the surface dust act as a stimulus to atmospheric corrosion of aluminium and aluminium alloys.
Key words: aluminium; aluminium alloys; atmospheric corrosion; desert; corrosion morphology; corrosion product
铝及铝合金由于其优异的性能,广泛应用于建筑、食品、电子以及航空航天等领域,已成为继钢铁之后用量最大的金属材料。铝及铝合金在大多数大气环境中具有较好的耐蚀性,但在某些严酷的大气条件下会发生较严重的腐蚀[1?2]。CORVO等[3]进行了铝在热带海洋大气环境下的暴露试验,研究表明在高温高湿的大气环境中,铝的腐蚀速率受到Cl?及SO2 的沉积速率的影响。王振尧等[4]通过LC4在格尔木盐湖大气环境中的暴露试验,认为空气中悬浮较高浓度的盐分和Cl?会导致LC4发生较严重的腐蚀。朱红嫚等[5]研究了L3和LD2在近海大气不同距海点的腐蚀行为,发现距海岸线越近Cl?浓度越高,L3和LD2的腐蚀速率也越快。
我国西部的南疆沙漠,降雨稀少,蒸发量大,年平均相对湿度只有47%,但是在考察中却发现该地区铝及铝合金发生了较严重的大气腐蚀[6],初步分析认为,由于扬尘及沙尘暴作用而沉积在金属表面的沙漠盐渍土可能是造成铝等金属材料发生较严重大气腐蚀的主要原因。对于铝及铝合金在南疆沙漠大气环境中的腐蚀行为还未见研究报道。研究铝及铝合金在南疆沙漠大气环境中的腐蚀行为和规律,对于深入认识我国南疆沙漠大气环境对于铝及铝合金腐蚀的影响,为西部地区建设选材用材提供科学依据具有重要意义。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料
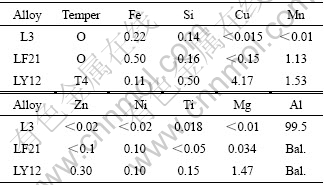
实验材料为3种常用铝及铝合金:纯铝L3、防锈铝LF21和硬铝LY12,其化学成分和热处理状态见表1。试样尺寸为100 mm×50 mm×2.5 mm。其中LY12表面包覆纯铝LB2。
表1 实验材料的化学成分和热处理状态 (mass fraction, %)
Table 1 Chemical compositions and temper of test materials (mass fraction, %)
1.2 暴露方法和暴露地点
所有试样实验前经过丙酮除油,蒸馏水冲洗,无水乙醇脱水,干燥后用分析天平称量,称量精度为0.1 mg。试样朝南暴露,试样平面与水平面成45?固定在暴晒架上,并于0.25、0.5、1、和2 a后分批回收。暴露地点位于塔克拉玛干沙漠北沿的库尔勒市,该地区年平均气温11.0 ℃,年平均相对湿度47%,年平均降水量48.9 mm,年蒸发量2 800.0 mm,浮尘年平均32次,扬沙年平均35次,沙尘暴年平均8次。属于南疆地区典型的沙漠盐渍土大气环境。
1.3 实验分析
回收试样浸入到溶液(50 mL H3PO4+20 g CrO3+1 L H2O,80 ℃,5 min)去除腐蚀产物,用失重法评定其腐蚀速率。用数码相机微距功能观察记录试样表面的宏观形貌。用(HITACHI S4800)扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察腐蚀表面和截面腐蚀形貌,用SEM附带的能谱仪(EDS)分析了腐蚀产物的元素和截面元素的面分布。刮下表面的腐蚀产物与溴化钾混合压片,利用(Nicolet Magna-IR 750)Fourier变换红外光谱仪分析其组成。收集地表浮土,通过理化检验和X射线荧光光谱分析研究其理化性能和组成成分。
2 实验结果
2.1 腐蚀质量损失和腐蚀速率
2.1.1 腐蚀质量损失随暴露时间的变化
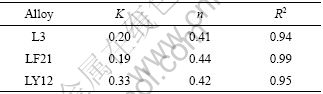
图1所示为3种铝及铝合金在库尔勒的腐蚀质量损失数据随暴露时间的变化曲线,其中曲线是用幂函数C=Ktn进行拟合得到的曲线[7?8]。式中C是腐蚀质量损失,g/m2;t是暴露时间,a;K和n都是常数。从图1中可以看出,在南疆沙漠大气环境中,LY12的腐蚀质量损失明显高于L3和LF21的腐蚀质量损失,LF21的腐蚀质量损失与L3的腐蚀质量损失相近。拟合得到的腐蚀动力学参数K、n和相关系数R2见表2。从表2 中可以看出相关系数R2都大于0.94,表明铝及铝合金在南疆沙漠大气环境中的腐蚀质量损失随暴露时间的变化趋势符合幂函数规律。n值最大为0.44,说明在南疆沙漠大气环境中,铝及铝合金在短期2 a内随着暴露时间延长的腐蚀速率不断下降。
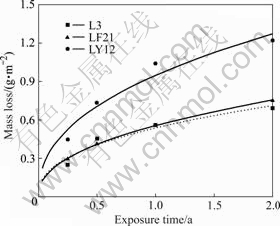
图1 3种铝及铝合金在南疆沙漠大气环境中的腐蚀质量损失随暴露时间的变化曲线
Fig.1 Mass loss data of specimens versus exposure time in desert atmosphere of southern Xinjiang Province, China
表2 3种铝及铝合金的动力学参数K、n和相关系数R2
Table 2 Corrosion kinetic parameters K, n, and correlation coefficient R2 for specimens
2.1.2 腐蚀速率
3种铝及铝合金在库尔勒暴露1 a的腐蚀速率见表3,其平均腐蚀速率为0.27 μm/a。 图2所示为3种铝及铝合金在库尔勒和我国其它典型大气环境中暴露1 a时间平均腐蚀速率的对比图[11]。从图中可以看出,3种铝及铝合金在库尔勒的平均腐蚀速率仅次于江津市(工业酸雨大气)和青岛市(海洋污染大气)的平均腐蚀速率,明显高于其它地区的平均腐蚀速率。可见在干燥少雨的南疆沙漠大气环境中,铝及铝合金发生了比较严重的大气腐蚀。
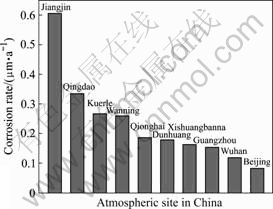
图2 3种铝及铝合金在典型大气环境中暴露1 a的平均腐蚀速率
Fig.2 Average corrosion rates of specimens exposed for 1 a at test sites in China
2.2 腐蚀形貌分析
2.2.1 宏观腐蚀形貌分析
随着暴露时间的延长,3种铝及铝合金表面腐蚀形貌由微小腐蚀点发展到小片腐蚀斑,再发展到大量腐蚀麻点。图3所示为3种铝及铝合金在库尔勒暴露0.5和2 a时的表面宏观腐蚀形貌。暴露0.5 a时试样表面开始出现小片腐蚀斑(见图3点A),并覆盖有一层浮尘。暴露2 a时试样表面开始出现大量腐蚀麻点(图3点 B),并且有大量的浮土附着并聚集在这些腐蚀麻点上(见图3点C)。可见表面浮土参与了铝及铝合金的大气腐蚀过程。
表3 3种铝及铝合金在南疆沙漠大气环境中暴露1 a时的腐蚀速率
Table 3 Corrosion rates of specimens exposed for 1 a in desert atmosphere of southern Xinjiang Province, China (μm/a)
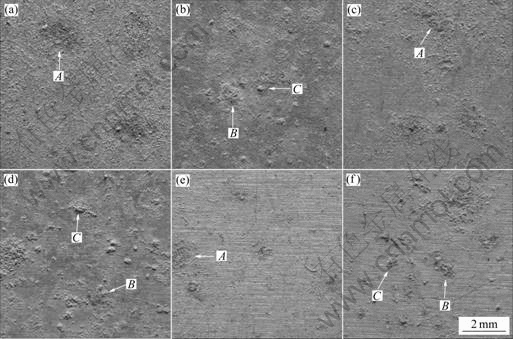
图3 3种铝及铝合金在南疆沙漠大气环境中的表面宏观形貌
Fig.3 Appearances of specimens in desert atmosphere of southern Xinjiang Province, China: (a) L3 for 0.5 a; (b) L3 for 2 a; (c) LF21 for 0.5 a; (d) LF21 for 2 a; (e) LY12 for 0.5 a; (f) LY12 for 2 a
2.2.2 微观腐蚀形貌分析
图4所示为3种铝及铝合金在库尔勒暴露0.5和 2 a时的表面微观腐蚀形貌的(SEM)。从图中可以看到暴露0.5 a后,腐蚀产物中就能观察到龟裂纹,并且表面带有很多浮土。暴露2 a后,表面附着层明显增厚,腐蚀产物和大量浮土凝聚在一起,从LY12表面还能观察到扩展到附着层表面的大片龟裂。表明由浮土和腐蚀产物构成的表面附着层对基体的保护性很差。
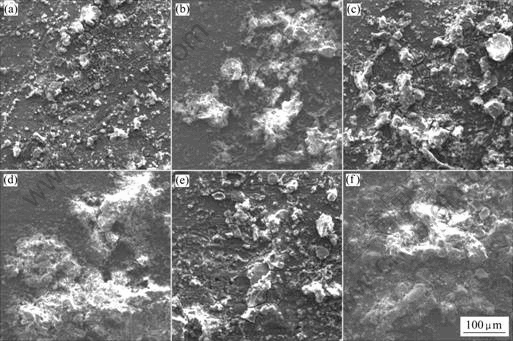
图4 3种铝及铝合金在南疆沙漠大气环境中的表面微观腐蚀形貌(SEM)
Fig.4 Surface morphologies (SEM) of specimens in desert atmosphere of southern Xinjiang Province, China: (a) L3 for 0.5 a; (b) L3 for 2 a; (c) LF21 for 0.5 a; (d) LF21 for 2 a; (e) LY12 for 0.5 a; (f) LY12 for 2 a
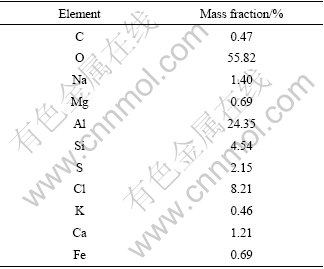
对LY12表面腐蚀产物的EDS分析结果见表4。腐蚀产物中主要为O、Al、Si、Cl和S等元素。其中O和Al主要来自表面生成的氧化铝或氢氧化铝,而其他元素主要来自浮土中的盐在表面的沉积。
表4 LY12在在南疆沙漠大气环境中暴露2 a后表面腐蚀产物的化学成分
Table 4 Chemical compositions of corrosion products of LY12 exposed for 2 a in desert atmosphere of southern Xinjiang Province, China
2.2.3 截面腐蚀形貌分析
图5所示为3种铝及铝合金在库尔勒暴露0.5和2 a的截面腐蚀形貌(SEM)。从图中可以看出,暴露0.5 a后,3种铝及铝合金表面出现比较浅的点蚀坑;暴露2 a后,表面的点蚀坑变深。LF21暴露2 a后基体还出现裂纹,有剥落腐蚀倾向。LY12暴露0.5 a后就点蚀坑外出现比较厚的腐蚀产物,腐蚀产物中存在龟裂,露2 a后点蚀坑变深,坑外附着一层疏松的腐蚀产物及浮土。
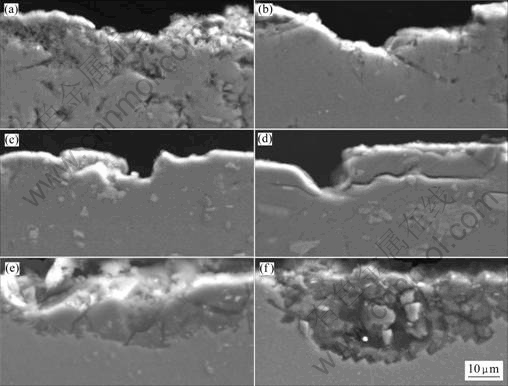
图5 3种铝及铝合金在南疆沙漠大气环境中的截面腐蚀形貌(SEM)
Fig.5 Cross-section morphologies (SEM) of specimens in desert atmosphere of southern Xinjiang Province, China: (a) L3 for 0.5 a; (b) L3 for 2 a; (c) LF21 for 0.5 a; (d) LF21 for 2 a; (e) LY12 for 0.5 a; (f) LY12 for 2 a
图6所示为LY12在暴露2 a后截面的元素的面分布。从元素的面分布可以看出,在附着层中主要有Al和O元素,对应铝表面生成的腐蚀产物氧化铝或氢氧化铝。附着层中还存在粒状分布的Si、Mg和Ca等元素以及弥散分布的Cl和S等元素,对应浮土中的Si、Mg、Ca等元素的氧化物及它们的氯化物和硫酸盐等。截面元素面扫描的结果和表面腐蚀产物的EDS结果相吻合。
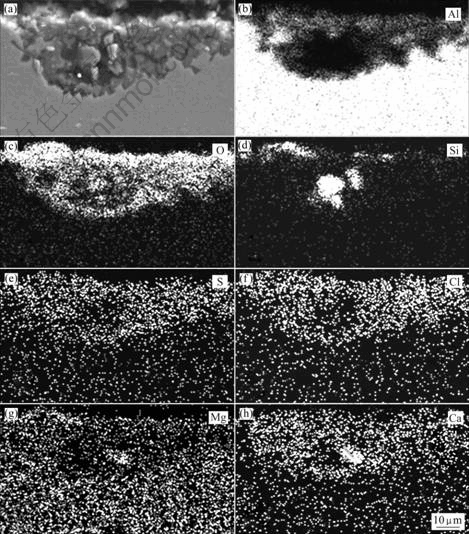
图6 在南疆沙漠大气环境中暴露2 a后LY12截面元素面分布
Fig.6 Cross-section planar elemental distributions of LY12 exposed for 2 a in desert atmosphere of southern Xinjiang Province, China: (a) Substrate morphology; (b) Al; (c) O; (d) Si; (e) S; (f) Cl; (g) Mg; (h) Ca
2.3 腐蚀产物分析
图7所示为LY12暴露2 a后腐蚀产物的Fourier变换红外光谱(FTIR)。根据红外吸收峰位确定其腐蚀产物主要是水合Al(OH)3、Al2O3及 SiO2等,确认了表面 EDS分析和截面元素面分析判断的结果。在一般大气环境中,当铝暴露于大气中时,表面可迅速生成一层致密的惰性氧化膜(γ-Al2O3),在大气中放置几个月后,γ-Al2O3外层将转化为一薄层γ-AlOOH,最后转化为水合Al(OH)3[9?11]。分析结果表明在南疆沙漠大气环境中,铝表面生成的腐蚀产物与在一般大气环境生成的腐蚀产物基本相同。
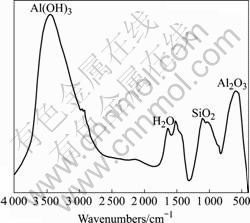
图7 LY12在南疆沙漠大气环境中暴露2 a后腐蚀产物的红外光谱
Fig.7 FTIR spectrum of corrosion products of LY12 exposed for 2 a in atmosphere of desert saline soil of southern Xinjiang Province, China
3 分析和讨论
在库尔勒沙漠大气环境下,含盐量高的地表土在大风扬尘及沙尘暴的作用下,可大量沉积于试样表面。对地表浮土的理化检验表明其可溶性盐的含量高达6.6%, pH值达到9.2。虽然盐渍土的pH值已超出了铝的钝化区间(pH值4.5~8.5),但库尔勒的平均相对湿度只有47%,大部分时间内,铝表面的相对湿度应不会大于发生大气腐蚀的临界相对湿度(70%),铝及铝合金不会发生严重的大气腐蚀。
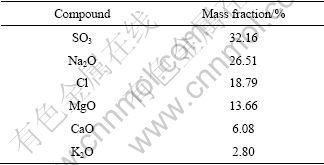
但是,从地表浮土可溶性盐的X射线荧光光谱结果可知(见表5),可溶性盐中主要含有Na、Mg、Cl和S等元素,故浮土中有NaCl、MgCl2、Na2SO4和MgSO4等盐分。而对应MgCl2、NaCl、MgSO4和Na2SO4潮解点的相对湿度分别为33%、75%、86%和93%[12],其中MgCl2的潮解点已远小于库尔勒大气的平均相对湿度47%,因此在南疆沙漠大气环境,由于MgCl2的潮解作用会有效增加了铝表面大于临界相对湿度的时间,为铝发生大气腐蚀创造了必要条件,再考虑到浮土较高pH值的影响,铝及铝合金在相对干燥的南疆沙漠大气环境也会发生较严重的大气腐蚀。
表5 可溶性盐的X射线荧光光谱分析
Table 5 X-ray fluorescence analysis of soluble salts
在南疆沙漠大气环境下,铝及铝合金能够发生严重腐蚀的另一个主要原因是地表浮土中存在Cl?和SO42?。浮土中的Cl?通过沉积的方式进入到腐蚀产物中。而Cl?能够穿透和破坏铝表面的天然氧化层,使得氧化膜失去保护性[13]。也有人认为Cl?和表面的腐蚀产物Al(OH)3发生连续的结合反应而形成可溶的AlCl3或羟基氯化铝,使得氧化膜失去保护性[14?15]:

从而减弱Al(OH)3的保护作用。
4 结论
1) 在南疆沙漠大气环境中,含盐量高的地表浮土沉积于金属表面会造成铝及铝合金发生较严重的大气腐蚀。铝及铝合金的腐蚀失重随暴露时间的变化遵循幂函数C=Ktn,短期(2 a)内,随着暴露时间的延长腐蚀速率会不断下降。
2) 南疆沙漠浮土中的MgCl2 等成分的存在增加了试样表面的湿润时间,沙漠浮土中较高的pH值以及氯离子和硫酸根离子等的共同作用促进了铝及铝合金在南疆沙漠大气环境下的腐蚀。
3) 在南疆沙漠大气环境中,随着暴露时间的延长,铝及铝合金表面由微小腐蚀点发展到腐蚀斑,再发展到大量腐蚀麻点,并且有大量的浮土附着并凝聚在腐蚀产物上。主要腐蚀产物为Al2O3和水合Al(OH)3。
REFERENCES
[1] FUENTE D, OTERO-HUERTA E, MORCILLO M. Studies of long-term weathering of aluminium in the atmosphere[J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(7): 3134?3148.
[2] 朱祖芳. 有色金属的耐腐蚀性及其应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 1995: 20?23.
ZHU Zu-fang. Resistance to corrosion of nonferrous metal and their application[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 1995: 20?23.
[3] CORVO F, PEREZ T, DZIB L R, MARTIN Y, CASTA?EDA A, GONZALEZ E, PEREZ J. Outdoor-indoor corrosion of metals in tropical coastal atmospheres[J]. Corrosion Science, 2008, 50(1): 220?230.
[4] 王振尧, 李巧霞, 汪 川, 韩 薇, 于国才. LC4 铝合金在格尔木盐湖大气环境中的腐蚀行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(1): 24?29.
WANG Zhen-yao, LI Qiao-xia, WANG Chuan, HAN Wei, Yu Guo-cai. Corrosion behaviors of Al alloy LC4 in Geermu salt lake atmosphere[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(1): 24?29.
[5] 朱红嫚, 郑弃非, 谢水生. 万宁地区铝及铝合金不同距海点的大气腐蚀研究[J]. 稀有金属, 2002, 26(6): 456?459.
ZHU Hong-man, ZHENG Qi-fei, XIE Shui-sheng. Study on atmospheric corrosion of aluminium and its alloy at different distance away from sea shore in Wanning marine environment [J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2002, 26(6): 456?459.
[6] 萧以德, 王光雍, 李晓刚, 林 安, 张三平, 秦晓洲, 王振尧, 梁彩凤, 郑弃非, 毛海荣. 我国西部地区大气环境腐蚀性及材料腐蚀特征[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2003, 23(4): 248?255.
XIAO Yi-de, WANG Guang-yong, LI Xiao-gang, LIN An, ZHANG Shan-ping, WANG Zhen-yao, LIANG Cai-feng, ZHENG Qi-fei, MAO Hai-ping. Corrosion behavior of atmospheric environment and corrosion feature of materials in our western area[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2003, 23(4): 248?255.
[7] NATESAN M, VENKATACHARI G, PALANISWAMY N. Kinetics of atmospheric corrosion of mild steel, zinc, galvanized iron and aluminium at 10 exposure stations in India[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(11): 3584?3608.
[8] POURBAIX M. The liner bilogarithmic law for atmospheric corrosion[C]// AILOR W H. Atmospheric Corrosion. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1982: 107?122.
[9] SOWINSKI G, SPROWLS D O. Weathering of aluminum alloys[C]// AILOR W H. Atmospheric Corrosion. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1982: 297?328.
[10] 曹楚南. 中国材料的自然环境腐蚀[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005: 108?124.
CAO Chu-nan. Material natural environmental corrosion of China[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005: 108?124.
[11] LEYGRAF C, GRAEDEL T. Atmospheric Corrosion[M]. 韩恩厚等, 译. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005: 201?209.
LEYGRAF C, GRAEDEL T. Atmospheric Corrosion[M]. HAN En-hou et al, transl. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005: 201?209.
[12] Bengtsson Blücher D, SVENSSON J E, JOHANSSON L G. The influence of CO2, AlCl3?6H2O, MgCl2?6H2O, Na2SO4 and NaCl on the atmospheric corrosion of aluminum[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(7): 1848?1866.
[13] ELOLA A S, OTERO T F, PORRO A. Evolution of the pitting of aluminum exposed to the atmosphere[J]. Corrosion, 1992, 48(10): 854?863.
[14] PYUN S I, MOON S M, AHN S H, KIM S S. Effects of Cl?, NO3? and SO4? ions on anodic dissolution of pure aluminium in alkaline solution[J]. Corrosion Science, 1999, 41(4): 653?667.
[15] GRAEDEL T E. Corrosion mechanisms for aluminium exposed to the atmosphere[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1989, 136(4): 204?12.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50499331_3);国家科技部基础条件平台建设资助项目(2005DKA10400-cj-2)
收稿日期:2008-07-14;修订日期:2008-11-10
通讯作者:郑弃非,教授,博士;电话:010-82241291;E-mail: zhengqf@grinm.com
(编辑 何学锋)