二代镍基单晶高温合金DD5的组织演化和稳定性
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2016年第8期
论文作者:崔仁杰 黄朝晖
文章页码:2079 - 2085
关键词:单晶高温合金;DD5合金;显微组织演变;热处理;热暴露
Key words:single crystal superalloy; DD5 alloy; microstructural evolution; heat treatment; thermal exposure
摘 要:研究含晶界强化元素碳、硼和铪的第二代镍基单晶高温合金DD5的组织演化和稳定性。利用光学显微镜、扫描电镜、电子探针、能量分散光谱和萃取试验研究DD5合金的铸态、热处理态和热暴露后的微观组织和成分。在铸态条件下,γ相为初生凝固相,枝晶间存在3种偏析相,其形貌取决于元素偏析程度。热处理后,枝晶杆内γ′相细小且立方化程度高,尺寸约为0.5 μm,质量分数为61.685%,枝晶间存在不规则γ′相和MC/M23C6碳化物。经980 °C、1000 h热暴露后,未发现TCP相析出,表明DD5合金在980 °C具有较好的组织稳定性。
Abstract: The microstructual evolution and stability of a second generation single crystal (SC) nickel-based superalloy DD5 with minor grain boundary (GB) strengthening elements (C, B and Hf) were studied as a function of as-cast, heat treatment and thermal exposure. The microstructure and composition of the alloy were investigated by optical microscopy, scanning electron microanalysis (SEM), electron probe microanalysis (EPMA), energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS) and extraction analysis. In the as-cast condition, the microstructure observations and composition analysis showed that γ phase was the primary solidification phase and there were three microsegregations in the metal matrix. The morphology of these microsegregations depended on element segregations. After heat treatment, the dendrite cores contained fine and cuboidal-shaped γ′ particles with an average edge length of about 0.5 μm, while interdendritic regions contained irregularly-shaped γ′ particles and MC/M23C6 carbides. The mass fraction of γ′ phases was 61.685%. After exposure at 980 °C for 1000 h, no TCP phase was observed in both dendritic and interdendritic regions, indicating a good microstructual stability of the DD5 alloy at 980 °C.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26(2016) 2079-2085
Ren-jie CUI, Zhao-hui HUANG
Science and Technology on Advanced High Temperature Structural Materials Laboratory, Beijing Institute of Aeronautical Materials, Beijing 100095, China
Received 22 November 2015; accepted 25 February 2016
Abstract: The microstructual evolution and stability of a second generation single crystal (SC) nickel-based superalloy DD5 with minor grain boundary (GB) strengthening elements (C, B and Hf) were studied as a function of as-cast, heat treatment and thermal exposure. The microstructure and composition of the alloy were investigated by optical microscopy, scanning electron microanalysis (SEM), electron probe microanalysis (EPMA), energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS) and extraction analysis. In the as-cast condition, the microstructure observations and composition analysis showed that γ phase was the primary solidification phase and there were three microsegregations in the metal matrix. The morphology of these microsegregations depended on element segregations. After heat treatment, the dendrite cores contained fine and cuboidal-shaped γ′ particles with an average edge length of about 0.5 μm, while interdendritic regions contained irregularly-shaped γ′ particles and MC/M23C6 carbides. The mass fraction of γ′ phases was 61.685%. After exposure at 980 °C for 1000 h, no TCP phase was observed in both dendritic and interdendritic regions, indicating a good microstructual stability of the DD5 alloy at 980 °C.
Key words: single crystal superalloy; DD5 alloy; microstructural evolution; heat treatment; thermal exposure
1 Introduction
Nickel-based single crystal (SC) superalloys are critical to the continuous development of high- performance turbine engines, because they possess a good balance of the properties required for operation in the severe high temperature conditions. SC superalloy vanes have demonstrated to possess excellent aircraft engines performance and durability benefits compared with polycrystalline vanes [1-5].
At the present stage, the production of SC superalloys vanes is expected to increase as a result of emerging markets, such as utility gas turbine. However, the main factors to limit the manufacture of the mass market SC superalloys components are the high production costs resulting from low casting yields due to rejectable grain defects such as low angle boundary (LAB) and high angle boundary (HAB) [6-11]. Moreover, these grain defects cannot be completely eliminated during casting due to the complex configurations of the vanes. Research so far has revealed that the addition of minor grain boundary (GB) strengthening elements, such as carbon (C), boron (B) and hafnium (Hf), is usually the best solution to increase the maximum allowable angle boundaries, which increase casting yields, and as a result, decrease the production costs [12-14]. In recent years, superalloy developments have focused on making SC vanes to obtain the high manufacturing yields necessary for meeting cost objectives using intentionally adding minor GB strengthening elements to SC superalloys, indicating that an optimum use of these elements and tight control can maintain optimum properties and castability [15-22]. Therefore, it is a tendency to develop SC superalloys containing minor GB strengthening elements as a material for high temperature structural applications in the aircraft engines and utility gas turbine.
DD5 alloy is a C-, B- and Hf-containing second generation nickel-based superalloy, which is driven by the industry call for advanced technology SC vanes at affordable production costs. In comparison with typical second generation SC nickel-based superalloys, e.g., PWA 1484 and CMSX-4, GB strengthening elements are employed in DD5 alloys to enhance GB strength. Besides, these elements also modify matrix properties by forming second phases and adjusting partitioning of elements on solidification. However, there is little information about the microstructure of relatively high GB strengthening elements containing SC nickel-based superalloys. Therefore, it is necessary and instructive to investigate the microstructures of GB strengthening elements containing DD5 alloys as a new material for applications in the aircraft engines and utility gas turbine. In this work, the microstructual evolution and stability of DD5 alloy were studied as a function of as-cast, heat treatment and thermal exposure.
2 Experimental
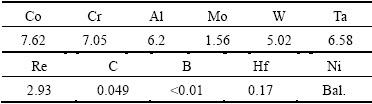
The DD5 master alloys used in this work were produced starting from pure elements in a vacuum induction furnace. The SC bars with dimensions of 15 mm (diameter) × 180 mm (length) were directionally solidified in an industry Bridgeman furnace with a seed technique. The bars were directionally solidified in the [001] direction at a constant withdrawal rate of 3.5 mm/min. The longitudinal orientation of each bar was determined by X-ray diffraction techniques. Only bars with orientations within 10° of [001] and without defects, such as slivers, freckles, low or high angle boundaries, were used in this work. The results of chemical composition analysis of DD5 SC bars are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Chemical composition of DD5 SC bars (mass fraction, %)
In order to study the microstructual evolution as a function of as-cast, heat treatment and thermal exposure, the as-cast bars were experienced the standard heat treatment (SHT) and long-term unstressed thermal exposure. The SHT schedule was described as follows: 1300 °C, 2 h; AC + (1120 °C, 4 h); AC + (1080 °C, 4 h); AC + (900 °C, 4 h); AC. The heat treatment was performed in a vacuum furnace with temperature fluctuations within ±5 °C. The long-term unstressed thermal exposure after SHT was performed in an antivacuum furnace at 980 °C for 1000 h.
The microstructures of the samples were characterized using 10 mm height samples sectioned from the bars by electrical discharge machining (EDM). The microstructures of the as-cast, heat-treated and thermal exposed samples were examined after grinding, polishing and etching with the etchant (100 mL HF +200 mL HNO3 + 100 mL C3H8O3) which dissolves the γ′ precipitates. The microstructures were characterized by optical microscopy (OM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and electron probe microanalysis (EPMA). Energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS) was used to analyze the chemical composition of the samples. The compositions, lattice constants and mass fractions of various phases in the as-cast, heat-treated and thermal-exposed samples were determined by extraction analysis which is frequently applied for identifying precipitates in metallic systems.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructures of as-cast samples
The microstructure and phase composition of the second generation SC nickel-based superalloys were systematically studied, e.g., PWA 1484 and CMSX-4. However, there is little information about the microstructure of relatively high GB strengthening elements containing second generation SC nickel-based superalloys. In comparison with the samples without these additions, there were strong element segregations within the interdendritic regions which are usually observed in high GB strengthening elements containing directionally solidified (DS) superalloys, e.g., DZ406 and IC10 [23,24].
Figure 1 shows typical microstructures of as-cast DD5 samples. The primary dendritic morphology is clearly visible (Fig. 1(a)) and there are three micro- segregations in the two-phase γ+γ′ microstructure (Fig. 1(b)). The first microsegregation is the flower-like phase (Phase A) within the interdendritic regions. It is the typical γ/γ′ eutectic (γ/γ′-segregation, TaAl-rich, Fig. 2(a)) as is usually observed in as-cast SC nickel- based superalloys. The presence of regions of γ/γ′ eutectic phase with relatively large size disrupts the continuity of the γ+γ′ microstructure of samples, as shown in Fig. 1(b). The second microsegregation (Phase B) is a small amount of black regions within the interdendritic regions, surrounded by gray regions consisting of the γ+γ′ microstructure (Fig. 1(b)). The black regions are larger, irregular and rich in Ta and Al (TaAl-rich, Fig. 2(a)), indicating that it is the coarse γ′ phase (γ′c-segregation, plate-like eutectic). The size of the coarse γ′ phase is relatively large, as compared with the γ′ phase within the dendritic regions. Figure 1(c) shows the micrograph of γ′ phase within the dendritic regions. It can be seen that the γ′ phase is irregular and the size is not homogeneous within the dendritic regions (Fig. 1(c)). The last microsegregation (Phase C) is the white/gray particles dispersed in the finally solidified interdendritic regions (Figs. 1(b) and (d)). The EDS analysis reveals that they are MC carbides (MC-segregation, Fig. 2(b)). The morphologies of these particles exhibit two shapes: script/rod-shaped particles (MC(1)) and blocky particles (MC(2)).
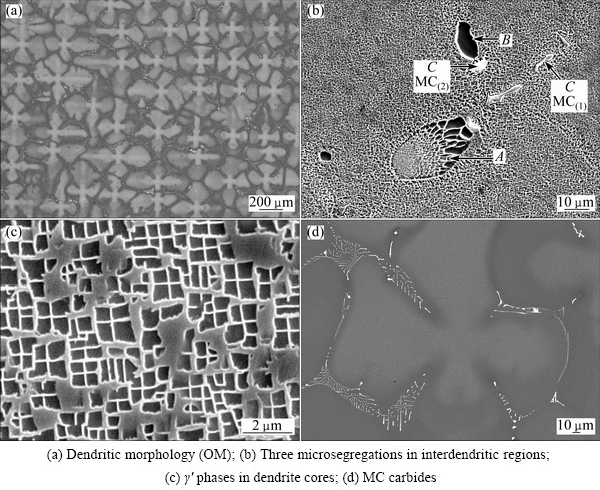
Fig. 1 Microstructures of as-cast DD5 sample
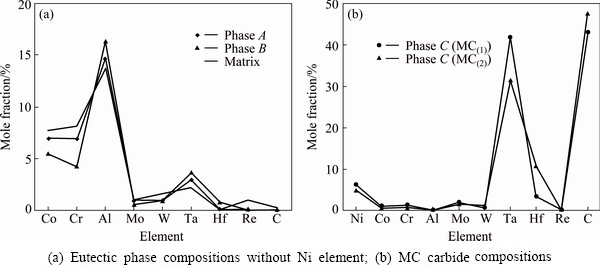
Fig. 2 EDS analysis of phase composition in Fig. 1(b)
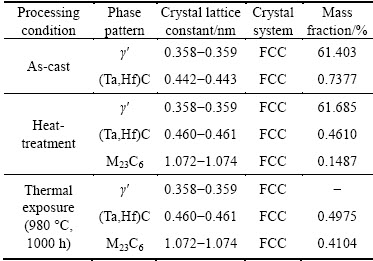
The results of extraction analysis further confirm that the microstructures of as-cast, heat-treated and thermal-exposed DD5 samples consist of γ, γ′ and carbides, as shown in Table 2. Under the as-cast condition, it can be seen that the mass fractions of γ′ phases and MC carbides are 61.403% and 0.7377%, respectively. They have a FCC crystal structure, and their lattice constants are aγ′=0.358-0.359 nm and aMC=0.442-0.443 nm.
Table 2 Phase compositions and crystal structures of various DD5 samples (extraction)
It is known that the γ phase forms as a primary solidification phase in most second generation SC
nickel-based superalloys during directional solidification. The chemical compositions of DD5 alloys used in this work are similar with these alloys, except for additions of GB strengthening elements (C, B and Hf). Thus, it can be deduced that the γ phase is the primary solidification phase for DD5 alloys. This is in line with the microstructural evidence shown in Fig. 1(a) where the secondary dendrite arms are vertical to the primary arms, i.e., fourfold symmetry dendrites, which are typical dendrite morphologies of cubic crystal structure γ phases. As the primary phase, γ dendrite cores are rich in γ stabilizers (Co, Cr, W, Re and Mo) and depleted in γ′ stabilizers (Ta and Al), whereas the interdendritic regions exhibit high Ta and Al concentrations (partition coefficients for elements: 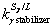 >1 and
>1 and 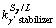 <1), indicating that the MC carbides and eutectic γ/γ′ phase may have formed in these TaAl-rich interdendritic regions. The presence of white/gray particles dispersed in the interdendritic regions confirms the precipitations of MC carbides (MC-segregation, Ta-rich) after the solidification of γ primary phases. The black regions in the interdendritic regions (Fig. 1(b)) were found to consist of the flower-like γ/γ′ microstructure, confirming the occurrence of the eutectic reaction L→γ+γ′. Once the eutectic temperature is reached, the eutectic γ/γ′ phase will form from the interdendritic liquid (γ/γ′-segregation
<1), indicating that the MC carbides and eutectic γ/γ′ phase may have formed in these TaAl-rich interdendritic regions. The presence of white/gray particles dispersed in the interdendritic regions confirms the precipitations of MC carbides (MC-segregation, Ta-rich) after the solidification of γ primary phases. The black regions in the interdendritic regions (Fig. 1(b)) were found to consist of the flower-like γ/γ′ microstructure, confirming the occurrence of the eutectic reaction L→γ+γ′. Once the eutectic temperature is reached, the eutectic γ/γ′ phase will form from the interdendritic liquid (γ/γ′-segregation 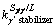 >1) and consume the interdendritic liquid. However, this eutectic reaction is probably incomplete due to the quick cooling rate and low diffusivity of elements. Therefore, the remaining liquid (Lr,) which later transforms to the coarse γ′ phase (γ′c-segregation,
>1) and consume the interdendritic liquid. However, this eutectic reaction is probably incomplete due to the quick cooling rate and low diffusivity of elements. Therefore, the remaining liquid (Lr,) which later transforms to the coarse γ′ phase (γ′c-segregation, 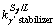 >1), is present in the interdendritic regions (Fig. 1(b)). As cooling proceeds, the γ′ phase precipitates in an irregular form from the γ matrix, resulting in a γ+γ′ microstructure. Besides MC carbides, other precipitated phases resulting from the GB strengthening elements Hf and B were not found in the as-cast sample by both extraction analysis and EPMA, e.g., Ni5Hf and M3B2. These findings indicate that for the processing conditions used in this work, DD5 alloy evolves the following solidification and solid-state transformation path: L→L+γ→L+γ+MC→Lr +γ+MC+γ/γ′→γ′c+γ+MC+γ/γ′→γ′c+(γ+γ′)+MC+γ/γ′.
>1), is present in the interdendritic regions (Fig. 1(b)). As cooling proceeds, the γ′ phase precipitates in an irregular form from the γ matrix, resulting in a γ+γ′ microstructure. Besides MC carbides, other precipitated phases resulting from the GB strengthening elements Hf and B were not found in the as-cast sample by both extraction analysis and EPMA, e.g., Ni5Hf and M3B2. These findings indicate that for the processing conditions used in this work, DD5 alloy evolves the following solidification and solid-state transformation path: L→L+γ→L+γ+MC→Lr +γ+MC+γ/γ′→γ′c+γ+MC+γ/γ′→γ′c+(γ+γ′)+MC+γ/γ′.
The morphologies of the above three micro- segregations (γ/γ′-segregation, γ′c-segregation and MC-segregation) depend on element segregations. It is known that the γ/γ′-segregation or γ′c-segregation is controlled by composition. For most nickel-based superalloys, the eutectic phase formed during directional solidification is the flower-like γ/γ′ morphology (γ/γ′-segregation, Fig. 1(b)). Only in high γ′ stabilizers containing nickel-based superalloys, the single γ′ eutectic phase can be found, which is actually the coarse γ′ primary phase formed from remaining liquid (γ′c-segregation, Fig. 1(b)). In the present study, both eutectic phases were observed in one sample. The reasons for such finding can be attributed to strong element segregations within the interdendritic regions, probably resulting from the higher additions of GB strengthening elements. As discussed above, the eutectic reaction L→γ+γ′ is probably incomplete, resulting in remaining liquid. Therefore, once the γ′ stabilizers concentrations are high enough, the coarse γ′ phase will directly form from remaining liquid (Lr→γ′c). This is in agreement with the present phase composition shown in Fig. 2(a) where the coarse γ′ phase is further enriched in Ta and Al as compared with the eutectic γ/γ′ and interdendritic regions.
Also, the element segregation plays a key role in the MC carbide morphology. It is known that the carbide morphology is controlled by solidification and composition [19-22]. The solidification conditions used in this work are similar. Thus, it can be deduced that the composition is the important factor. It can be seen from Fig. 2(b) that the compositions of two MC carbides are similar, except for the Hf content. If a carbide particle contains a higher Hf level, the lattice constant of the carbide consequently increases, causing the relatively large lattice misfit between matrix and carbide. This will promote the formation of the blocky carbides, because blocky particles have much smaller surfaces than rod-shaped ones. This is in line with the present phase composition shown in Fig. 2(b) where the blocky carbide (MC(2)) is rich in Hf as compared with the rod-shaped one (MC(1)). Therefore, it is indicated that the Hf-segregation is the reason for the carbide morphology change.
The distribution of microsegregations depends on the structure of the primary phase. During primary γ solidification, γ stabilizers are segregated to γ dendrites and Ta and Al are rejected to the interdendritic regions (TaAl-rich). As cooling proceeds, MC carbides rich in Ta are regularly present in these interdendritic regions and the growing γ dendrite as a primary solidification phase rejects the MC particles to the finally solidified interdendritic regions. Similarly, the eutectic γ/γ′ and coarse γ′ phases rich in Ta and Al are also present in these finally solidified interdendritic regions.
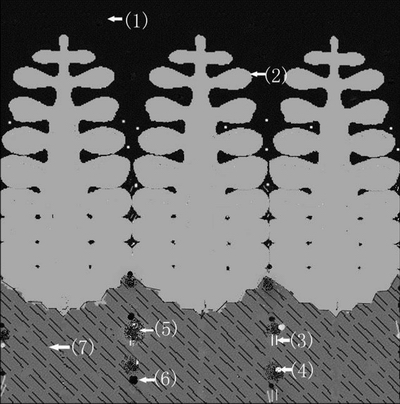
Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of microstructure evolution and microsegregation origin during cooling and directional solidification for DD5 alloy
Figure 3 shows a schematic diagram of the microstructual evolution and microsegregation origin during cooling and directional solidification for a DD5 alloy: “1” represents the liquid present at the solid–liquid interface; “2” represents the growing γ dendrites as a primary solidification phase; “3” represents the script/ rod-shaped carbides formed during cooling to solidification (MC(1)-segregation); “4” represents the blocky carbides in the interdendritic regions (MC(2)- segregation); “5” represents the formation of the flower- like γ/γ′ microstructure in the interdendritic TaAl-rich regions through a eutectic reaction L→γ+γ′ (γ/γ′- segregation); “6” shows the remaining liquid, which later transforms to the coarse γ′ phase (γ′c-segregation); “7” shows the precipitation of the γ′ phase in an irregular form from the γ matrix, resulting in a two-phase γ+γ′ microstructure.
3.2 Microstructures of heat-treated samples
Figure 4 shows typical microstructures of fully heat-treated DD5 samples. The alloy shows an incomplete-solution-treatment and aged microstructure. For the DD5 alloy, the incipient melting temperature decreases due to the additions of the C, B and Hf elements. The reduction in solution heat treatment temperature to avoid incipient melting results in an incomplete solution of the γ′ phase, including a small amount of eutectic γ/γ′ phases. Whilst the dendrite cores contain fine and cuboidal shaped γ′ particles with an average edge length of about 0.5 μm (Fig. 4(c)), interdendritic regions contain irregularly shaped γ′ particles and a small amount of residual eutectic phases with a volume fraction less than 1% (Fig. 4(d)). This microstructure helps to easily recognize the initial dendritic/interdendritic regions using SEM/EPMA (Fig. 4(a)), although the element segregations reduce and microstructures gradually become homogeneous after heat treatment. In the heat-treated condition, the mass fraction of γ′ phases is 61.685% (Table 2).
After heat treatment, most MC carbides maintain their initial shape (Fig. 4(b)). However, it can be deduced that a part of MC carbides will decompose due to the high temperature of the solution treatment. This is in line with the present extraction analysis results shown in Table 2 where the mass fractions of MC carbides decrease from 0.7377% to 0.4610% after heat treatment. The decomposition of MC carbides promotes the precipitation of other carbides. As shown in extraction analysis results, M23C6 carbides form during heat treatment. This carbide is FCC crystal structure with a lattice constant 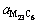 =1.072-1.074 nm (Table 2).
=1.072-1.074 nm (Table 2).
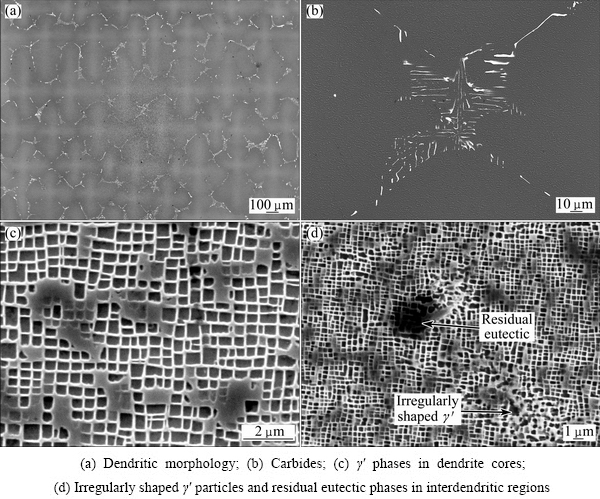
Fig. 4 Microstructures of heat-treated DD5 sample
3.3 Microstructures of thermal-exposed samples
According to the following equation (Eq. (1)) given by aerospace standard [25], the electron-vacancy number (Nv) of the DD5 alloy used in this work is 2.14. The Nv value of the σ phase precipitation is 2.45-2.52, and those of the μ and Laves phases are higher than 2.3. Therefore, it is predicted from the calculated results that no TCP phases will precipitate during thermal exposure of the DD5 alloy. This is in line with the microstructual analysis results where no TCP phase was observed in the samples under 980 °C and 1000 h exposure.
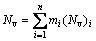 (1)
(1)
where mi is the mass fraction of element i in the alloy composition; (Nv)i is the electron-vacancy number of element i.
The microstructures of the samples subjected to thermal exposure are shown in Fig. 5. In the dendritic regions, there is a slight coarsening of γ′ phases taking place after exposure at 980 °C for 1000 h (Fig. 5(a)). No TCP phase was observed. In the interdendritic regions, most carbides are in discrete/blocky shape. The script/rod-shaped carbides were observed to decompose after exposure at 980 °C for 1000 h (Fig. 5(b)). However, it can be deduced that they are still MC carbides. This is in line with the extraction analysis results shown in Table 2 where the mass fractions of MC carbides in the heat-treated and thermal-exposed samples are similar, i.e., 0.4610% and 0.4975%, respectively. For M23C6 carbides, the mass fraction increases from 0.1487% to 0.4104% after exposure at 980 °C for 1000 h (Table 2), indicating a further precipitation during exposure. In addition, no other new phase was found.
In summary, no TCP phase was observed in both dendritic and interdendritic regions, indicating a good microstructual stability of the DD5 alloy at 980 °C. During exposure, the main microstructual evolutions are the slight γ′ coarsening and the M23C6 carbide precipitation. After exposure, the microsegregations further reduce and microstructures gradually become homogeneous.
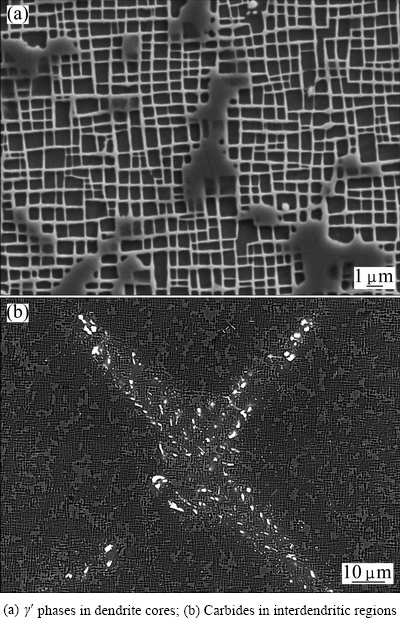
Fig. 5 Microstructures of thermal-exposed DD5 sample
4 Conclusions
1) Under the as-cast condition, γ phase was the primary solidification phase and there were three microsegregations in the metal matrix, i.e., γ/γ′ eutectic phase, coarse γ′ phase and carbide particles. The morphology of these microsegregations depended on element segregations. The microstructural analysis revealed the presence of script and blocky MC carbides in the interdendritic regions. The morphology of the carbides was a strong function of composition, with the presence of significant Hf levels, leading to the blocky morphology. For the processing conditions used in this work, DD5 alloy evolved the following solidification and solid-state transformation path: L→L+γ→L+γ+MC→Lr+γ+MC+γ/γ′→γ′c+γ+MC+γ/γ′→γ′c+(γ+γ′)+MC+γ/γ′.
2) During heat treatment, M23C6 carbides formed and γ′ particles in dendrite cores became fine and cuboidal shaped with an average edge length of about 0.5 μm. The microsegregations reduced and microstructures gradually became homogeneous after heat treatment.
3) During exposure, the main microstructual evolutions were the slight γ′ coarsening and the M23C6 carbides precipitation. After exposure at 980 °C for 1000 h, no TCP phase was observed in both dendritic and interdendritic regions, indicating a good microstructual stability of the DD5 alloy at 980 °C.
References
[1] GEL M, DUHL D N, GIAMEI A F. The development of single crystal superalloy turbine blades [C]//Superalloys 1980, OH: ASM, 1980: 205-214.
[2] CETEL A D, DUHL D N. Second-generation nickel-base single crystal superalloy [C]//Superalloys 1988. Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1988: 235-244.
[3] WALSTON W S, O′HARA K, ROSS E W, POLLOCK T M, MURPHY W H. RenéN6: Third generation single crystal superalloy [C]//Superalloys 1996. Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1996: 27-34.
[4] TIN S, POLLOCK T M, MURPHY W. Stabilization of thermosolutal convective instabilities in Ni-based single-crystal superalloys: Carbon additions and freckle formation [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2001, 32: 1743-1753.
[5] HARRIS K, WAHL J B. Improved single crystal superalloys CMSX-4(SLS)[La+Y] and CMSX-486 [C]//Superalloys 2004. Warrendale, PA: TMS, 2004: 45-52.
[6] POLLOCK T M, MURPHY W H, GOLDMAN E H, URAM D L, TU J S. Grain effect formation during directional solidification of nickel base single crystal [C]//Superalloys 1992. Champion, PA: TMS, 1992: 125-134.
[7] BUSSAC A, GANDIN C. Prediction of a process window for the investment casting of dendritic single crystals [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1997, 237: 35-42.
[8] TAMAKI H, YOSHINARI A, OKAYAMA A, NAKAMURA S. Development of a low angle grain boundary resistant single crhstal superalloy YH61 [C]//Superalloys 2000. Reno, NV: TMS, 2000: 757-766.
[9] NAPOLITANO R E. SCHAEFER R J. The convergence-fault mechanism for low-angle boundary formation in single-crystal castings [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2000, 35: 1641-1659.
[10] D’SOUZA N, NEWELL M, DEVENDRA K, JENNING P A, ARDAKANI M G, SHOLLOCK B A. Formation of low angle boundaries in Ni-based superalloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 413-414: 567-570.
[11] NEWELL M, DEVENDRA K, JENNINGS P A, D’SOUZA N. Role of dendrite branching and growth kinetics in the formation of low angle boundaries in Ni-base superalloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 412: 307-315.
[12] ROSS E W, O′HARA K S. Rene′N4: A first generation single crystal turbine airfoil alloy with improved oxidation resistance low angle boundary strength [C]//Superalloys 1996. Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1996: 19-25.
[13] CHEN Q Z, JONES C N, KNOWLES D M. The grain boundary microstructures of the base and modified RR 2072 bicrystal superalloys and their effects on the creep properties [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 385: 402-418.
[14] CHEN Q Z, JONES C N, KNOWLES D M. The microstructures of base/modified RR2072 SX superalloys and their effects on creep properties at elevated temperatures [J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50: 1095-1112.
[15] ZHOU Y Z, VOLEK A. Effect of carbon additions on hot tearing of a second generation nickel-base superalloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 479: 324-332.
[16] AL-JARBA K A, FUCHS G E. Effect of carbon additions on the as-cast microstructure and defect formation of a single crystal Ni-based superalloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 373: 255-267.
[17] KONG Y H, CHEN Q Z. Effect of minor additions on the formation of TCP phases in modified RR2086 SX superalloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 366: 135-143.
[18] CHEN Q Z, KONG Y H, JONES C N, KNOWLES D M. Porosity reduction by minor additions in RR2086 superalloy [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 51: 155-160.
[19] CUTLER E R, WASSON A J, FUCHS G E. Effect of minor alloying additions on the carbide morphology in a single crystal Ni-base superalloy [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2008, 58: 146-149.
[20] LIU L R, JIN T, ZHAO N R, WANG Z H, SUN X F, GUAN H R, HU Z Q. Effect of carbon additions on the microstructure in a Ni-base single crystal superalloy [J]. Materials Letters, 2004, 58: 2290-2294.
[21] YU Zhu-huan, LIU Lin, ZHANG Jun. Effect of carbon addition on carbide morphology of single crystal Ni-based superalloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 339-345.
[22] HU Qin, LIU Lin, ZHAO Xin-bao, GAO Si-feng, ZHANG Jun, FU Heng-zhi. Effect of carbon and boron additions on segregation behavior of directionally solidified nickel-base superalloys with rhenium [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23: 3257-3264.
[23] HUANG Zhao-hui, TAN Yong-ning, JIA Xin-yun, ZHANG Hong-wei, ZHANG Qiang, ZHANG Jun, TANG Ding-zhong. Study on long-term aging of the second generation DS superalloy DZ406 [J]. Materials Engineering, 2009(S1): 105-109. (in Chinese)
[24] ZHAO Xi-hong, HUANG Zhao-hui, TAN Yong-ning, ZHANG Qiang, JIA Xin-yun, XU Hui-bin. Microstructure of IC10 superalloy [J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2008, 28(3): 28-33. (in Chinese)
[25] Aerospace Standard AS5491. Calculation of electric vacancy number in superalloys [S].
崔仁杰,黄朝晖
北京航空材料研究院 先进高温结构材料重点实验室,北京 100095
摘 要:研究含晶界强化元素碳、硼和铪的第二代镍基单晶高温合金DD5的组织演化和稳定性。利用光学显微镜、扫描电镜、电子探针、能量分散光谱和萃取试验研究DD5合金的铸态、热处理态和热暴露后的微观组织和成分。在铸态条件下,γ相为初生凝固相,枝晶间存在3种偏析相,其形貌取决于元素偏析程度。热处理后,枝晶杆内γ′相细小且立方化程度高,尺寸约为0.5 μm,质量分数为61.685%,枝晶间存在不规则γ′相和MC/M23C6碳化物。经980 °C、1000 h热暴露后,未发现TCP相析出,表明DD5合金在980 °C具有较好的组织稳定性。
关键词:单晶高温合金;DD5合金;显微组织演变;热处理;热暴露
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Corresponding author: Ren-jie CUI; Tel: +86-10-62498312; E-mail: 32269573@qq.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64323-6

