Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28(2018) 1329-1333
Significant influence of sharp grain boundary corner on tensile elongation of copper bars with columnar grains and its mechanism
Zhang-zhi SHI1, Hai-peng WANG1, Xue-feng LIU1,2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China;
2. Beijing Laboratory of Metallic Materials and Processing for Modern Transportation, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China
Received 9 March 2017; accepted 18 September 2017
Abstract: The reason why elongation of copper bars with columnar grains drops significantly after small cold-drawing was explored. The copper bars were prepared by warm-mould continuous casting. Tensile test was interrupted at various tensile strains in order to detect crack origin. Electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD) was used to analyze dislocation slip bands. It is found that the as-cast microstructure contains sharp grain boundary (GB) corners nearly parallel to the solidification direction (SD). Elongation of the copper bars drops significantly from 68.8% in as-cast state to 18.8% in as-drawn state. It is revealed that plastic deformation becomes severer in the vicinity of sharp GB corners. Locally accumulated internal stress even activates a slip system with very low Schmid factor of 0.17. The localized plastic deformation near sharp grain boundary corner promotes crack initiation and propagation, which eventually leads to the significant drop of elongation.
Key words: copper; fracture; grain boundary corner; elongation; columnar grain
1 Introduction
An as-cast polycrystalline copper ingot usually has equiaxed grains or columnar grains or both, depending on its specific casting process [1-8]. Its tensile elongation is influenced by trace elements, strain rate, grain shape, grain size, and grain orientation [9-16]. An as-cast copper rod with continuous columnar grains exhibits an extraordinary ability of elongation along the direction of continuous casting. Such a copper rod with 17.3 mm in diameter can be reduced to 19.7 mm in diameter through a series of cold forming processes without annealing [17]. Stress state of a cold forming process is usually different from that of a tensile test. Metals often exhibit larger elongation in cold forming process than that in tensile test. As shown in Fig. 1, the tensile elongation of copper varies widely. Cold drawing results in a decrease of tensile elongation due to the well-known work-hardening effect, which is lowered by about 20% through a small area reduction of 20% (Fig. 1).
Intragranular dislocation slip behavior, interaction between dislocations and grain boundaries (GBs), and interaction between dislocations and defects are main causes of the drop of tensile elongation [18-21]. Previous studies on influence of GB corners on ductility mainly focus on GB triple junctions. In modelling, a GB corner ending at a triple junction is supposed to have an angle of 120° [21-26]. However, in practice, a polycrystalline copper usually contains GB corners with various angles. Sharp GB corners should have a significant influence on the ductility of copper.
2 Experimental
Copper bars with 99.9% Cu were prepared by a self-developed warm-mould continuous casting technology. They have a uniform size of 20 mm×8 mm×1000 mm. The transverse, normal and solidification directions of the as-cast copper bars are designated as TD, ND and SD, respectively. A sketch of warm-mould continuous casting is shown in Fig. 2(a). The temperature of the graphite mould is controlled between 900 and 1000 °C, which is lower than the melting temperature of pure copper (i.e., Tm=1083 °C).
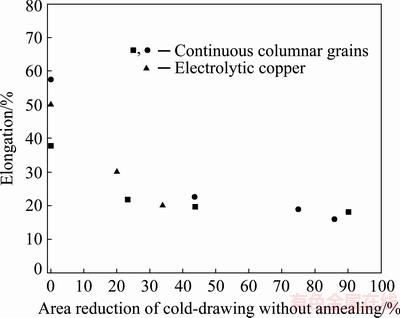
Fig. 1 Decrease of tensile elongation of polycrystalline copper with accumulated area reduction after cold drawing without annealing [3-5]
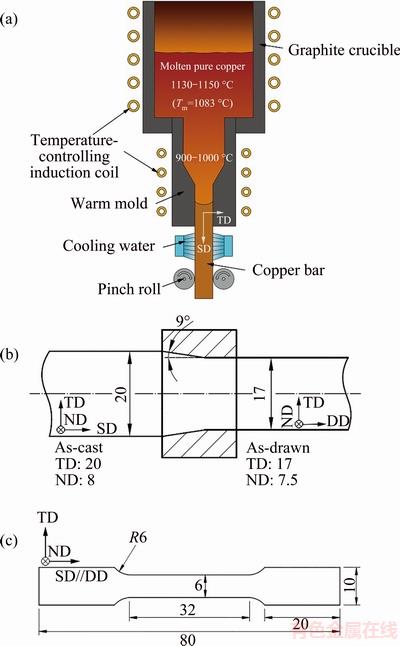
Fig. 2 Sketch of copper bar produced by self-developed warm-mould continuous casting (a), sketch of cold drawing of copper bars (b) and specimens of as-cast and as-drawn copper bars for tensile tests (c) (unit: mm)
Out of the exit of the graphite mould, water is used for strong cooling. As shown in Fig. 2(b), the as-cast copper bars were cold drawn along the SD through a single pass with an area reduction of 20.3%. Their size changes to be 17 mm × 7.5 mm × 1254.9 mm. The transverse, normal and drawing directions of the as-drawn copper bars are designated as TD, ND and DD, respectively. The semi-angle of the drawing die is 9°, with mineral oil as lubricant.
Specimens for tensile tests are shown in Fig. 2(c). In order to observe slip bands, their surfaces were ground, mechanically polished, and then electro-polished. The electro-polishing was conducted at room temperature, 10 V for 15 s, with a solution of 100 mL H3PO4, 100 mL C2H5OH, 200 mL H2O, 2 g NH2CONH2 and 20 mL CH3CH(OH)CH3. Tensile tests were performed using a WDW-10E electronic universal testing machine. The tensile loading direction (LD) was parallel to the SD or the DD, with a strain rate of 1×10-3 s-1. Specimens were etched for 5 s by a solution of 5% FeCl3 and 95% ethanol for microstructure observation using a Zeiss Axio Scope A1 optical microscope. Grain orientations were measured by a Zeiss Auriga field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) equipped with a detector of electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD). The measured EBSD data were post-processed using Matlab MTEX toolbox [27].
3 Results and discussion
A representative microstructure of the as-cast copper with columnar grains is shown in Fig. 3(a). The lengths of the grains are about parallel to the SD, which vary widely from 1 to more than 17 mm. There exist sharp GB corners about parallel to the SD with GB angles ranging from 10° to 90°, locating at triple junctions or at GBs, as pointed out by arrows in Fig. 3(a). After the cold drawing along the SD, the GB corners become sharper. Meanwhile, they should produce stress concentration as can be expected from the theory of elasticity [28,29]. Engineering stress-strain curves of the as-cast and the as-drawn copper specimens are given in Fig. 3(b), showing a prominent work-hardening effect. The as-cast copper has a high elongation of 68.8%. However, after a single pass cold drawing with an area reduction of 20.3%, its elongation drops significantly to 18.8%. The drop is as large as 50%, which is considerably larger than that previously reported, as can be seen from Fig. 1.
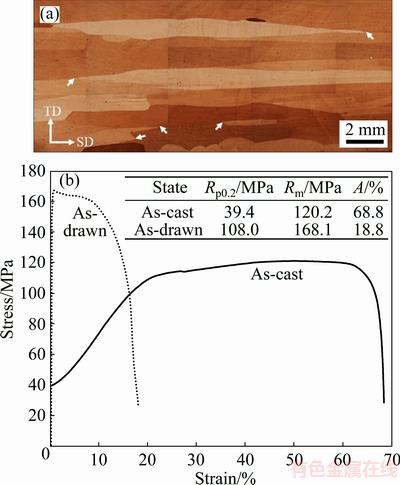
Fig. 3 As-cast microstructure with sharp GB corners pointed out by arrows (a) and engineering stress-strain curves (Rp0.2, Rm and A refer to yield stress, maximum tensile stress and elongation, respectively) (b)
At a tensile strain of 16.0% before final fracture, cracking is detected around sharp GB corners, a representative one is shown in Fig. 4(a). In the figure, boundaries with misorientations larger than 10° are outlined in black. Kukuchi patterns in black regions cannot be indexed due to the absence of the material in cracks or severe lattice distortion caused by plastic deformation [30]. The EBSD image in Fig. 4(a) is colored according to inverse pole figure (IPF) along the DD. It can be seen that the DD is about parallel to 〈001〉 of Grain 1, while it is about parallel to 〈111〉 of Grain 2. With measured Euler angles provided in the upper right part of Fig. 4(a), the average misorientation between Grains 1 and 2 is calculated to be 42.4°. The GB angle of the sharp GB corner of Grain 2 is about 38°. Crack at its tip is much larger than that at its base, indicating that stress concentration is much more serious at the tip.
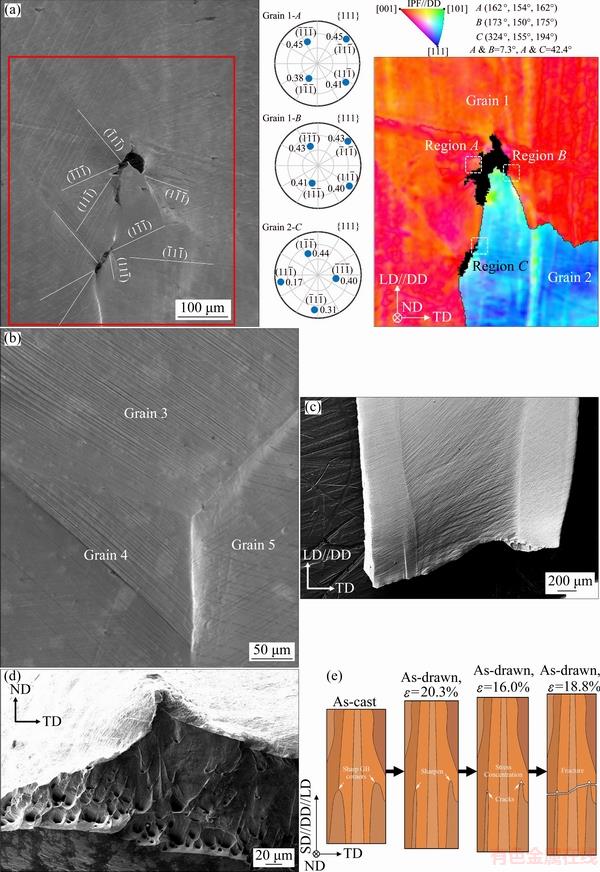

Fig. 4 SEM image and its correspoding EBSD image of sharp GB corner at tensile strain of 16.0% (In EBSD image, boundaries with misorietations larger than 10° are outlined in black. Pole figures and the maximum Schmid factors of slip systems are calculated using measured Euler angles) (a), SEM image of triple junction formed by three grains with three GB corners of obtuse angles larger than 100° at tensile strain of 16.0% (b), fracture morphology viewed from ND at tensile strain of 18.8% (c), fracture morphology viewed from DD (d) and sketch of fracture mechanism of as-drawn copper with columnar grains (e)
Combining the SEM image with its corresponding EBSD image in Fig. 4(a), the slip systems corresponding to the slip bands on the surface of the tensile test specimen can be determined. The measured Euler angles of Region A in Grain 1 are 162°, 154° and 162°. Accordingly, its {111} pole figure and the maximum Schmid factors (SFs) of each {111}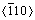 slip system can be calculated, as given in Fig. 4(a). According to the geometry of pole figure, a line normal to the line connecting the center of a pole figure and the pole of a plane is the trace of the plane on the observed surface [31]. So, it can be determined that
slip system can be calculated, as given in Fig. 4(a). According to the geometry of pole figure, a line normal to the line connecting the center of a pole figure and the pole of a plane is the trace of the plane on the observed surface [31]. So, it can be determined that  ,
, 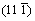 and
and  slip bands appear in Region A, the SFs of which are larger than 0.40. However, only
slip bands appear in Region A, the SFs of which are larger than 0.40. However, only  and
and 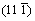 slip bands appear in Grain 1 in regions far away from the crack. Dense
slip bands appear in Grain 1 in regions far away from the crack. Dense  slip bands appear in a narrow region starting at the crack, indicating severer plastic deformation due to stress concentration.
slip bands appear in a narrow region starting at the crack, indicating severer plastic deformation due to stress concentration.
Inhomogeneous plastic deformation is common in a large grain, resulting in misorientation between regions within the grain [32]. For example, in Grain 1, the misorientation between Region B and Region A is 7.3°. So, slip band trace in Region B deviates from that in Region A. Such a deviation is obvious for  slip band, as can be seen from the pole figures in Fig. 4(a). In Region B near the crack, additional
slip band, as can be seen from the pole figures in Fig. 4(a). In Region B near the crack, additional  slip bands with SF of 0.41 are observed due to stress concentration. Similarly, in Grain 1 close to the crack through Region C,
slip bands with SF of 0.41 are observed due to stress concentration. Similarly, in Grain 1 close to the crack through Region C,  ,
, 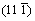 and
and  slip bands with high SFs are also observed (Fig. 4(a)). While in Grain 2 nearby,
slip bands with high SFs are also observed (Fig. 4(a)). While in Grain 2 nearby,  ,
,  and
and 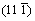 slip bands are observed, SFs of which are 0.44, 0.31 and 0.17, respectively. Comparatively, in Grain 2 far away from the crack, only
slip bands are observed, SFs of which are 0.44, 0.31 and 0.17, respectively. Comparatively, in Grain 2 far away from the crack, only  slip band with the highest SF is observed. Therefore, the abnormal appearance of
slip band with the highest SF is observed. Therefore, the abnormal appearance of 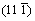 slip band with a rather low SF is due to stress concentration around the crack.
slip band with a rather low SF is due to stress concentration around the crack.
At the same tensile strain of 16.0%, a triple junction formed by Grains 3-5 with three blunt GB corners is shown in Fig. 4(b). The angles of GB corners of Grains 3-5 in the figure are measured to be 112.6°, 110.2° and 137.2°, respectively. In the vicinity of the triple junction, no cracks are detected. Such kind of blunt GB corner is common in copper with equi-axed grains or continuous columnar grains. Compared Fig. 4(b) with Fig. 4(a), it is clear that sharp GB corners promote the formation of cracks.
The cracks that preferentially formed around sharp GB corners propagate rapidly under the applied tensile loading, resulting in fracture at a strain of 18.8%. The fracture morphology viewed from the ND is shown in Fig. 4(c). A large section of the fracture orients about 68° from the LD, while the rest is about normal to it. The fracture morphology viewed from the DD is shown in Fig. 4(d), in which many dimples are observed, indicating a ductile fracture. The mechanism of the dramatic elongation drop is sketched in Fig. 4(e). Sharp GB corners about parallel to the SD exist in an as-cast copper bar with columnar grains. After cold drawing along the SD, they are sharpened and concentrate stress. Since the LD of the tensile test is also along the SD, the stress concentration becomes more serious, resulting in severe plastic deformation around the sharp GB corners. Therefore, cracks preferentially form around them and propagate rapidly, which eventually causes fracture.
4 Conclusions
1) Copper bars with columnar grains, prepared by a self-developed warm-mould continuous casting technology, have a high elongation of 68.8%. However, after a single pass cold drawing with an area reduction of 20.3%, their tensile elongation drops significantly to 18.8%.
2) Sharp grain boundary corners are found in the as-cast copper bars, which are about parallel to the solidification direction. After the cold drawing along this direction, they are sharpened and concentrate stress. Since the tensile loading is also applied along this direction, the stress concentration becomes more serious. Different from the regions far away within a grain, those close to the sharp grain boundary corners deform more seriously, in which more types of slip bands are observed, with smaller spacing or even with a rather low Schmid factor. Therefore, cracks preferentially form around the sharp grain boundary corners and propagate rapidly until fracture happens eventually. The sharp grain boundary corners greatly enhance inhomogeneous plastic deformation, which contributes greatly to the significant elongation drop.
References
[1] HANAZAKI K, SHIGEIRI N, TSUJI N. Change in microstructures and mechanical properties during deep wire drawing of copper [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527: 5699-5707.
[2] KAYALI E S, EL-SAYED M, FUNKE P. Deformation behaviour during drawing of copper rods produced using various processes [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1990, 6: 872-882.
[3] GAO K W, LIU M Y, ZOU F L, PANG X L, XIE J X. Characterization of microstructure evolution after severe plastic deformation of pure copper with continuous columnar crystals [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527: 4750-4757.
[4] WANG Y H, XIAO L R, ZHAO X J, HU W, SONG Y F, ZHANG W, ZHOU H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of columnar- grained copper produced by the Ohno continuous casting technique [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 639: 122-130.
[5] CAMPOS H B, CETLIN P R. The influence of die semi-angle and of the coefficient of friction on the uniform tensile elongation of drawn copper bars [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1998, 80-81: 388-391.
[6] OHNO A. Continuous casting of single crystal ingots by the O.C.C. process [J]. The Journal of the Metals, 1986, 38: 14-16.
[7] TSAI D C, HSU M S, HWANG W S, JIANG C S. Mathematical modeling of solidification microstructure of pure copper by vacuum continuous casting and its experimental verification [J]. The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan International, 2010, 50: 1843-1850.
[8] LIU X F, LUO J H, WANG X C. Surface quality, microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-Sn alloy plate prepared by two-phase zone continuous casting [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 1901-1910.
[9] CARREKER R P, HIBBARD W R. Tensile deformation of high-purity copper as a function of temperature, strain rate, and grain size [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1953, 1: 654-655, 657-663.
[10] LU L, SUI M L, LU K. Superplastic extensibility of nanocrystalline copper at room temperature [J]. Science, 2000, 287: 1463-1466.
[11] KAMLER F, NIESSEN P, PICK R J. Measurement of the behaviour of high-purity copper at very high rates of strain [J]. Canadian Journal of Physics, 1995, 73: 295-303.
[12] MEYERS M A, ANDRADE U R, CHOKSHI A H. The effect of grain size on the high-strain, high-strain-rate behavior of copper [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1995, 26: 2881-2893.
[13] NIEH T G, NIX W D. Embrittlement of copper due to segregation of oxygen to grain boundaries [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1981, 12: 893-901.
[14] ZHANG Z F, LIN G Y, ZHANG S H, ZHOU J. Effects of Ce on microstructure and mechanical properties of pure copper [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 457: 313-318.
[15] LI H H, ZHANG S H, CHEN Y, CHENG M, SONG H W, LIU J S. Effects of small amount addition of rare earth Ce on microstructure and properties of cast pure copper [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2015, 24: 2857-2865.
[16] MA X, LAPOVOK R, GU C, MOLOTNIKOV A, ESTRIN Y, PERELOMA E V, DAVIES C H J, HODGSON P D. Deep drawing behaviour of ultrafine grained copper: Modelling and experiment [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2009, 44: 3807-3812.
[17] ZHANG H, XIE J X, WANG Z D. Fabrication of pure copper rods containing continuous columnar crystals by continuous unidirectional solidification technology [J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2004, 11: 240-244.
[18] KIENER D, GROSINGER W, DEHM G, PIPPAN R. A further step towards an understanding of size-dependent crystal plasticity: In situ tension experiments of miniaturized single-crystal copper samples [J]. Acta Materialia, 2008, 56: 580-592.
[19] FRANCIOSI P, BERVEILLER M, ZAOUI A. Latent hardening in copper and aluminium single crystals [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1980, 28: 273-283.
[20] ZHANG Z F, WANG Z G. Effects of grain boundaries on cyclic deformation behavior of copper bicrystals and columnar crystals [J]. Acta Materialia, 1998, 46: 5063-5072.
[21] JIA W P, LI S X, WANG Z G, LI X W, LI G Y. Cyclic deformation behavior of non-isoaxial copper tricrystals and bicrystals [J]. Acta Materialia, 1999, 47: 2165-2176.
[22] LI S X, REN D B, JIA W P, CHEN C R, LI X W, WANG Z G. On the stress distribution around a triple junction [J]. Philosophical Magazine A, 2000, 80: 1729-1741.
[23] KOBAYASHI S, TSUREKAWA S, WATANABE T. Grain boundary hardening and triple junction hardening in polycrystalline molybdenum [J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53: 1051-1057.
[24] BOLLMANN W. The stress field of a model triple-line disclination [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1991, 136: 1-7.
[25] UPADHYAY M, CAPOLUNGO L, TAUPIN V, FRESSENGEAS C. Grain boundary and triple junction energies in crystalline media: A disclination based approach [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2011, 48: 3176-3193.
[26] REN D B, JIA W P, LI S X, WANG Z G, PENG Z X. Finite element analysis of elastic stress and the resolved shear stress in the primary slip system of a copper tricrystal [J]. Physica Status Solidi, 1999, 171: 453-466.
[27] BACHMANN F, HIELSCHER R, SCHAEBEN H. Texture analysis with mtex-free and open source software toolbox [J]. Solid State Phenomena, 2010, 160: 63-68.
[28] NAKASONE Y, NISHIYAMA H, NOJIRI T. Numerical equivalent inclusion method: A new computational method for analyzing stress fields in and around inclusions of various shapes [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 285: 229-238.
[29] ESHELBY J D. The determination of the elastic field of an ellipsoidal inclusion, and related problems [J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, 1957, 241: 376-396.
[30] BARNETT M R, NAVE M D, BETTLES C J. Deformation microstructures and textures of some cold rolled Mg alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 386: 205-211.
[31] SHI Zhang-zhi, LIU Xue-feng. Characteristics of cross grain boundary contraction twin pairs and bands in a deformed Mg alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 692: 274-279.
[32] LYCHAGIN D V, TARASOV S Y, CHUMAEVSKII A V, ALFYOROVA E A. Strain-induced folding on 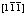 copper single crystals under uniaxial compression [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 371: 547-561.
copper single crystals under uniaxial compression [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 371: 547-561.
尖锐晶界角对柱状晶铜排伸长率的显著影响及机理
石章智1,王海鹏1,刘雪峰1,2
1. 北京科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,北京 100083;
2. 北京科技大学 现代交通金属材料与加工技术北京实验室,北京 100083
摘 要:研究柱状晶铜排在小变形量冷拉拔后伸长率显著下降的原因。通过温型连铸技术制备铜排,在多个应变量停止拉伸测试以探测裂纹源,采用电子背散射衍射(EBSD)技术分析位错滑移带。研究发现,铸态铜排中存在与连铸方向近平行的尖锐晶界角,拉拔后铜排的伸长率由铸态的68.8%骤降至拉拔态的18.8%。在尖锐晶界角附近发生更剧烈的塑性变形,局部应力集中甚至使Schmid因子低至0.17的位错滑移系启动。尖锐晶界角附近塑性变形的集中促使裂纹萌生和扩展,最终导致拉拔态铜排伸长率的显著降低。
关键词:铜;断裂;晶界角;伸长率;柱状晶
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (2016YFB0301300) supported by the National Key R&D Program of China; Project (51674027) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2152020) supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation, China; Project (2015AA034304) supported by the National High-Tech Research and Development Program of China
Corresponding author: Xue-feng LIU; Tel: +86-10-62333627; E-mail: liuxuefengbj@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64770-3