DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.02.046
氢对X80钢在库尔勒土壤模拟溶液中应力腐蚀开裂行为的影响
谢飞1,王丹1,吴明1,宋嘉良2,张康南1,杨旭1
(1. 辽宁石油化工大学 石油天然气工程学院,辽宁 抚顺,113001;
2. 中国石油天然气运输公司浙江分公司,浙江 杭州,310005)
摘要:采用电化学充氢技术、动电位扫描技术、交流阻抗技术(EIS)和慢应变速率拉伸试验(SSRT)研究库尔勒土壤模拟溶液中氢对X80管线钢应力腐蚀开裂(SCC)行为的影响,并利用扫描电镜(SEM)观察试样断口形貌。研究结果表明:充氢电流密度和充氢时间的增加均能加速金属腐蚀反应;随着充氢量的增大,试样自腐蚀电位呈下降趋势,腐蚀速率逐渐增大,氢促进了X80钢在库尔勒模拟溶液中腐蚀的发展;电化学充氢后,X80钢的应力腐蚀开裂行为主要由氢致开裂(HIC)作用决定,阳极溶解过程只起到辅助裂纹形核的作用,因为氢能引起材料局部塑性变形,促进裂纹尖端形核和扩展。
关键词:X80钢;氢;电化学;土壤模拟溶液;应力腐蚀开裂
中图分类号: TG172.4 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2016)02-0690-07
Effects of hydrogen on stress corrosion cracking behavior of X80 steel in Ku’erle soil simulated solution
XIE Fei1, WANG Dan1, WU Ming1, SONG Jialiang2, ZHANG Kangnan1, YANG Xu1
(1. School of Petroleum Engineering, Liaoning Shihua University, Fushun 113001, China;
2. Zhejiang Branch, CNPC PetroChina , Hangzhou 310005, China)
Abstract: The effects of hydrogen on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) behavior of X80 pipeline steel in simulated Ku'erle soil solution were investigated by electrochemical hydrogen charging, dynamic potential scanning technology, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and slow strain rate test (SSRT). And the fracture surfaces were observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM). The results show that the metal corrosion reaction can be accelerated with the increase of hydrogen current density and time. The corrosion potential of the metal descends and the corrosion rate decreases with the increase of hydrogen concentration. Hydrogen promotes the corrosion development of X80 steel in Ku’erle simulated solution. Hydrogen induced cracking (HIC) plays a decisive role in the SCC behavior of the sample after hydrogen charging. Anodic dissolution process merely plays an auxiliary role in the crack nucleation, because to hydrogen can cause material local deformation, and promote the crack tip nucleation and extension.
Key words: X80 steel; hydrogen; electrochemistry; simulated soil solution; stress corrosion cracking
随着石油天然气工业的发展,长距离高压力的油气管道输送方式正成为当今趋势,这就要求油气输送使用韧性更好、强度更高的管线钢。然而,氢致开裂(HIC)在高强度管线钢上往往体现得更为明显[1-2]。由于石油天然气中的H2S以及油气管线输送过程中外加阴极保护作用等因素,在油气管线服役中环境中的氢进入管线钢中无法避免。故管线钢会产生氢损伤,从而导致材料力学性能指标大幅度下降,加之外力的作用将产生应力腐蚀开裂(SCC),严重影响了油气管网的平稳运行和企业的安全生产[3]。迄今为止,国内外对氢在高强度管线钢发生应力腐蚀开裂行为时所起作用研究多集中在以下2个方面[4-8]:1) 高强钢在H2S环境中的SCC行为;2) 在0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中电化学充氢对高强度管线钢断裂性能的影响。而研究实际土壤环境下氢对高强度管线钢应力腐蚀开裂行为的影响却鲜有报道。目前,大多数研究者[9-11]认为:氢参与了管线钢的应力腐蚀过程,促进了位错的发射、增殖和运动,从而加速了SCC行为的进行。但对氢与应力以及阳极溶解作用之间的具体关系尚不明确。本文作者以X80管线钢为研究对象,库尔勒土壤模拟溶液为腐蚀介质,利用电化学充氢技术、交流阻抗技术、动电位极化技术以及慢应变速率拉伸试验(SSRT),结合扫描电镜(SEM)对试样断口进行观察,研究氢在库尔勒土壤模拟溶液中对X80管线钢应力腐蚀开裂行为的影响及开裂机制。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料及介质
实验材料为西气东输工程中的X80管线钢板材。其化学成分(质量分数,%)为:0.044 C,0.190 Si,1.830 Mn,0.011 P,0.002 S,0.090 Mo,0.230 Ni,0.025 Cr。电化学试样长×宽×高为10 mm×10 mm×2 mm,试样背面点引出Cu导线,利用环氧树脂将试样包封在聚四氟乙烯中。用耐水砂纸按照由粗到细依次从60~ 1 000号对工作电极进行打磨,然后用无水乙醇、去离子水清洗,烘干后备用。拉伸试样为板状试样,按照GB/T 15970.6—2007[12]标准制备,试样示意图如图1所示。拉伸试样的打磨处理方法与电化学试样的相同。
库尔勒土壤取自国家腐蚀环境库尔勒工作站的埋深1 m处的土壤,根据库尔勒土壤的化学成分及pH等理化性质,最终得到其模拟溶液的离子组成为(质量分数,%):0.010 6 HCO3-,0.013 2 NO3-,0.085 2 SO42-,0.231 7 C1-,0.004 4 Ca2+。用分析纯NaHCO3,KNO3,Na2SO4,CaC12,NaCl,MgCl2·6H2O和去离子水配制实验室用库尔勒土壤模拟溶液,并用质量分数为5%的NaOH调节溶液的pH为9.0。电化学实验和慢应变速率拉伸实验所采用的介质均为库尔勒土壤模拟溶液。
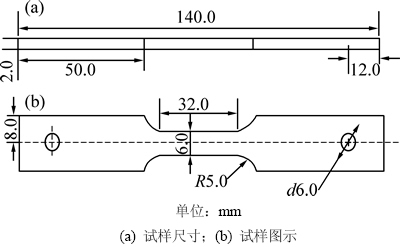
图1 SSRT试样示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of specimen of SSRT
1.2 电化学充氢实验
利用PS-305D型恒电位/恒电流仪进行电化学充氢,充氢溶液采用通氮除氧的0.5 mol/L H2SO4+0.25 g/L As2O3溶液,铂片为阳极,电化学试样为阴极。为了研究不同充氢电流密度和充氢时间对X80钢腐蚀行为的影响,考察6种不同条件对试样进行阴极充氢,具体条件如表1所示。
表1 不同阴极充氢条件
Table 1 Different hydrogen charging conditions

1.3 充氢后电化学测量实验
电化学实验采用3电极体系,充氢后的电化学试样为工作电极,铂片为辅助电极,饱和甘汞电极(SCE)为参比电极。动电位极化和交流阻抗测量在PARSTAT2273型电化学工作站上进行。实验前先将试样极化3 min,极化电位为-1.3 V,待电位稳定后,开始电化学测量。极化曲线的扫描速率为0.5 mV/s,扫描范围为-1.0~0.2 V。交流激励信号为10 mV,EIS测量频率为10-2~105 Hz。
1.4 静态充氢慢应变速率拉伸试验(SSRT)
SSRT在WDML-3型慢应变速率拉伸机上进行,拉伸速率为0.002 mm/min,实验过程一直保持高纯氮氛围。分别测量表1中6种充氢条件下拉伸试样在模拟溶液中的抗拉强度σb和断面收缩率ψ,利用断面收缩率ψ的变化来衡量材料的氢脆敏感性,并采用Cambridge S360型扫描电镜(SEM)对试样在不同充氢条件下的断口形貌进行分析。
本文所有实验均在室温下进行,实验时通入高纯氮以除氧,文中涉及的电极电位均为相对于饱和甘汞电极的电极电位。
2 实验结果与讨论
2.1 动电位极化曲线
X80管线钢在模拟溶液中不同充氢条件下的极化曲线如图2所示。由图2可见:极化曲线呈典型的活化过程,阳极区没有出现活化-钝化转变区,即充氢后的试样电极表面无钝化膜生成,因此,滑移-溶解的膜破裂理论在此条件下不适用。随着充氢电流密度和时间的增加(充氢实验编号1~5),试样的自腐蚀电位越来越低,说明增加充氢量,可以提高试样表面活性,加大局部区域阳极溶解的趋势。这是由于阴极充氢后的部分氢原子通过扩散进入试样表面,落到金属点阵间隙或被氢陷阱(晶界、夹杂、空洞等缺陷处)捕获。而氢原子的进入会使周围晶格发生弹性畸变,产生一定的应变能[13],因此,会导致间隙或氢陷阱处活性升高,电位降低。随着充氢量的增大,这种作用亦会加剧。在相同电极电位下,试样的阳极电流随充氢量的增加而呈上升的趋势,阳极溶解量增大,点蚀坑形成的概率增大,就有利于缩短裂纹尖端形核时间。因此,氢能促进裂纹形核的发展。

图2 X80钢在不同充氢条件下的极化曲线
Fig. 2 Polarization curves of X80 steel under different hydrogen charging conditions
图3所示为充氢电流密度和充氢时间与X80钢腐蚀电流密度Jcorr的关系曲线。由图3可见:当充氢时间为1 h,充氢电流密度从25 mA/cm2增至100 mA/cm2时,X80钢在库尔勒模拟溶液中腐蚀电流密度Jcorr从0.283 mA/cm2增大至0.808 mA/cm2,Jcorr增加幅度很大;当充氢电流密度为100 mA/cm2,充氢时间从1 h增至3 h时,试样的Jcorr从0.808 mA/cm2增大至1.021 mA/cm2,Jcorr仍然增加,但增加幅度有所减小。这表明随着充氢电流密度和充氢时间的增加,金属腐蚀速率呈上升的趋势,说明增大充氢电流密度和充氢时间均会增大氢的渗透量,从而加剧金属腐蚀行为。在不同的充氢条件下,腐蚀速率由小到大的充氢实验编号为1,2,3,4和5。
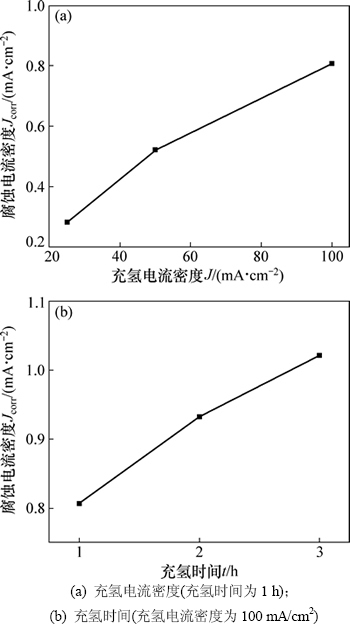
图3 腐蚀电流密度Jcorr与充氢量的关系曲线
Fig. 3 Curves of corrosion current density vs hydrogen charging volume
2.2 交流阻抗
图4所示为X80管线钢在库尔勒模拟溶液中交流阻抗图谱(EIS,其中ZRe为实部,ZIm为虚部)。由图4可知:电化学充氢后试样的EIS只在高频出现容抗弧,在低频段均未出现收缩的实部,说明充氢条件下试样阳极溶解腐蚀后电极表面没有被腐蚀产物膜覆盖。这是因为吸附在电极表面的氢原子能提高材料的活性,并导致阳极溶解处的pH下降,从而抑制了腐蚀产物膜的生成[14]。当充氢量从J=25 mA/cm2,t=1 h增加至J=100 mA/cm2,t=3 h时,试样容抗弧直径呈减小趋势。即金属腐蚀反应阻力的充氢实验编号从大至小分别为1,2,3,4和5。这表明随着充氢量的增大,腐蚀反应速率越来越大,氢促进了腐蚀反应的进行,这与极化曲线结果一致。
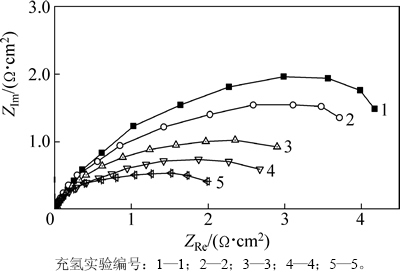
图4 同充氢条件下X80钢的EIS图
Fig. 4 EIS images of X80 steel under different hydrogen charging conditions
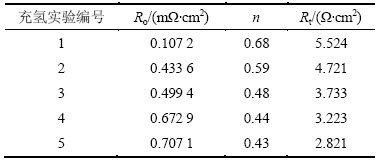
图5所示为试样在模拟溶液中的交流阻抗等效电路,交流阻抗图谱拟合数据结果如表2所示。图5中:Rs为溶液电阻;Rt为电荷转移电阻,它反映了电子在腐蚀反应中的迁移阻力;Cdl为界面双电层电容;Q为电极表面的非理想电容。由于充氢后氢原子进入金属电极表面间隙,导致周围晶格膨胀,以致电极表面不再平整,故这里使用常相位角元件Q代替纯电容C,Q=(jΩ)-n/Y0;Y0为导纳常数(单位为sn·Ω-1·cm-2);jΩ为虚部角频率;n为弥散指数,为与电极表面状态有关的拟合常数;n越大,材料的表面越均匀致密,耐蚀性越好[15-16]。Ro为氢引起的电极表面层电阻。由表2可知:从充氢实验编号1~5,即随着充氢量的增加,金属的弥散系数n逐渐降低,这说明电极表面平整度越来越差,腐蚀趋势越来越严重;随着充氢电流密度的增大,X80钢Rt均大幅度下降;随着充氢时间的增加,试样Rt亦出现逐渐降低的趋势,但下降的幅度有所减小。这表明增大充氢电流密度和充氢时间均能起到增加充氢量及加速腐蚀反应进行的作用。
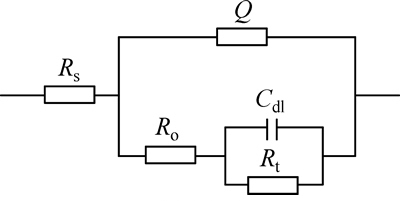
图5 X80钢在模拟溶液中阻抗谱的等效电路
Fig. 5 Equivalent circuit of impedance spectrum of X80 steel in simulated solution
表2 不同充氢条件下的阻抗图谱拟合参数
Table 2 Fitting parameters of EIS under different hydrogen charging conditions
2.3 静态充氢后SSRT
不同充氢条件对X80钢抗拉强度σb和断面收缩率ψ的影响如图6所示。从图6可以看出:试样的抗拉强度σb从未充氢到充氢实验1号,下降幅度最大,说明阴极充氢对材料的σb有显著影响。这可能是因为电化学充氢时试样表层产生了如微空洞或小裂纹的氢损伤,引起了金属的几何软化,从而导致σb大幅度下降;之后随着充氢量的增加,σb变化不大,这表明充氢量的增加对试样σb影响不大。从未充氢到充氢实验5号,随着金属充氢量的增大,试样的断面收缩率ψ呈逐渐下降趋势,氢脆敏感性明显增加,说明材料的氢致塑性损失是由扩散到试样内部的原子氢引起的,而不是由氢损伤造成的。
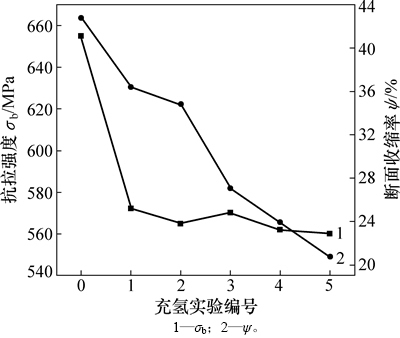
图6 不同充氢条件对X80钢σb和ψ的影响
Fig. 6 Effect of different hydrogen charging conditions on σb and ψ of X80 steel
2.4 断口形貌
图7所示为X80钢在库尔勒模拟溶液中不同充氢条件下断口的形貌特征。由图7可以看出:在未充氢时,断口以均匀韧窝为主,局部地区伴随有撕裂棱,呈现韧性断裂特征,阳极溶解过程对试样的断裂起主导作用。在充氢实验1号中,断口以浅韧窝和带有准解理特征的岩石层断面为主,断裂形貌呈现韧性和脆性混合型断口。与未充氢时相比,充氢实验1号试样断口韧窝数量减少,韧窝直径明显变小。这是因为材料中氢原子的存在加速了裂纹的形核和发展,削弱了阳极的溶解作用。在充氢实验2号中,断口形貌以岩石层断面和解理特征的河流花纹为主,局部有少量浅韧窝出现,且韧窝直径更小。此时,断口表现为脆性断裂。说明随着充氢量的增加,氢致开裂作用机制占主导地位,阳极溶解作用不明显。当充氢电流密度达100 mA/cm2时,试样断面呈明显的河流花样和解理台阶,表现为解理断裂特征,这是典型的脆性断裂。
综上所述,在电化学充氢条件下,X80钢在库尔勒模拟溶液中的应力腐蚀行为过程较复杂,其反应式为:
Fe→Fe2++2e (1)
H+·H2O+e→H+H2O (2)
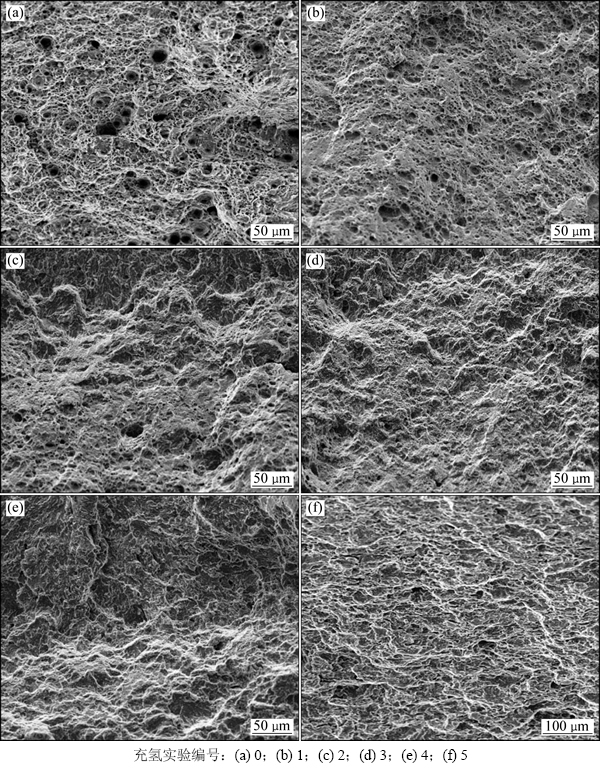
图7 不同充氢条件下X80钢断口SEM图
Fig. 7 SEM images of fracture surface of X80 metal fractured under different hydrogen charging conditions
电化学充氢后的水化的氢离子通过阳极(式(1))提供的电子生成氢原子,见式(2)。氢原子则通过扩散作用进入金属表面及内部。由于外应力和氢应变场的交互作用,产生了应力梯度。在此应力梯度下,原子氢将通过应力诱导扩散向高应力区的陷阱处(位错、空洞、第2相夹杂等缺陷)富集。富集在缺陷处的氢原子会增大所在晶格的活性,降低电位,故缺陷处作为阳极相发生阳极溶解过程,形成点蚀坑。由于应力集中在蚀坑内,因此,裂纹尖端从蚀坑内萌生并扩展[17]。此时,阳极溶解作用有所降低,氢的作用凸显出来。在充氢实验2号富集的氢原子达到一定浓度时,就会在位错线上形成Cottrell气团[18-19],从而产生氢内压。这种内压的剪切分量τH和外应力场引起的剪切分量τs一样,都能使裂纹前端局部区域内的位错增殖和运动。当τH和τs之和大于或等于位错大规模增殖和运动所需克服的阻力τ时,裂纹尖端就会产生局部塑形形变,促进裂纹的萌生和扩展[20-21]。由于室温下氢在金属中的扩散系数较大,氢气团能跟着位错一起运动,不会把位错钉扎住阻碍其运动[22]。故位错迁移就能把氢输送到新形成的裂纹尖端,开始下一个裂纹的萌生和扩展。在此过程中,氢致开裂占主导地位,阳极溶解作用被弱化,所以,试样断口只有局部有浅小的韧窝出现(图7(c))。当充氢电流密度达到100 mA/cm2时,充氢量进一步增大,试样内部原子氢浓度也相应提高,氢内压大大提升,相当于出现1个附加应力,这就有利于裂纹尖端的局部塑形变形,从而促进了裂纹的发展。此时,阳极溶解过程只起到缩短裂纹形核的时间、辅助裂纹形核过程的作用。而氢致开裂作用则更加明显,故试样断口表现为脆性断裂特征(图7(d)~(f))。
3 结论
1) 在库尔勒土壤模拟溶液中,充氢后X80管线钢的极化曲线阳极区呈现活化控制过程,无钝化现象出现。
2) 充氢电流密度和充氢时间的增加均能加速金属腐蚀反应。随着充氢量的增大,试样自腐蚀电位呈下降趋势,腐蚀速率逐渐增大。氢促进了X80钢在库尔勒模拟溶液中腐蚀的发展。
3) 电化学充氢后,X80钢的应力腐蚀开裂行为由阳极溶解和氢共同作用导致,在此过程中氢起到了决定性作用。
参考文献:
[1] MOON J,PARK C,KIM S J. Influence of Ti addition on the hydrogen induced cracking of API 5L X70 hot-rolled pipeline steel in acid sour media[J]. Metals and Materials International, 2012,18(4): 613-617.
[2] LIANG Ping, DU Cuiwei, LI Xiaogang, et al. Effect of hydrogen on the stress corrosion cracking behavior of X80 pipeline steel in Ku’erle soil simulated solution[J]. International Journal of Minerals Metallurgy and Materials, 2009, 16(4): 407-413.
[3] ELBOUJDAINI M,REVIE R W. Metallurgical factors in stress corrosion cracking (SCC) and hydrogen-induced cracking (HIC)[J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2009,13(7): 1091-1099.
[4] CABRINI M, LORENZI S, PELLEGRINI S, et al. Environmentally assisted cracking and hydrogen diffusion in traditional and high-strength pipeline steels[J]. Corrosion Reviews, 2015, 33(6): 529-545.
[5] BUENO A H S, MOREIRA E D, GOMES J. Evaluation of stress corrosion cracking and hydrogen embrittlement in an API grade steel[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2014, 36(1): 423-431.
[6] CHUMALO H V. Influence of hydrogen sulfide on the corrosion-mechanical properties of welded joints of pipe steel[J]. Materials Science, 2012,48(2): 176-179.
[7] CAPELLE J,DMYTRAKH I,PLUVINAGE G. Hydrogen effect on local fracture emanating from notches in pipeline from steel API X52[J]. Strength of Materials, 2009, 41(5): 493-500.
[8] 原佳强, 王莉萍.不同电化学充氢状态下X70,X80管线钢的断裂特性[J]. 金属热处理, 2015, 40(12): 56-58.
YUAN Jiaqiang, WANG Liping. Fracture characteristics of X70 and X80 pipeline steel under different electrochemical hydrogen charging states[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2015, 40(12): 56-58.
[9] 黄一中, 王燕斌, 褚武扬, 等.重轧钢中氢促进位错发射,运动以及氢致裂纹形核[J]. 金属学报, 1998, 34(2): 134-140.
HUANG Yizhong, WANG Yanbin, CHU Wuyang, et al. Hydrogen-facilitated dislocation emission, motion and initiation of hydrogen-induced microcrack in rail steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1998, 34(2): 134-140.
[10] YANG Yongjin, GAO Kewei, CHENChangfeng. Hydrogen-induced cracking behaviors of incoloy alloy 825[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2010,17(1): 58-62.
[11] NAVILLE W, MORASSI A L, LEITE D W, et al. Hydrogen stress cracking in power generator M42 galvanized martensitic carbon steel screws[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2015, 56: 257-264.
[12] GB/T 15970.6—2007, 金属和合金的腐蚀-应力腐蚀试验[S].GB/T 15970.6—2007, Metal and alloy corrosion-stress corrosion test[S].
[13] VENEGAS V, CALEYO F, HALLEN J M, et al. Role of crystallographic texture in hydrogen-induced cracking of low carbon steels for sour service piping[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2007,38(5): 1022-1031.
[14] 陈旭, 何川, 徐杨, 等. 氢对X80钢在土壤模拟溶液中电化学行为的影响[J]. 石油化工高等学校学报, 2011, 24(6): 84-89.
CHEN Xu, HE Chuan, XU Yang, et al. Effect of hydrogen on electrochemical behaviors of X80 steel in simulated soil solution[J]. Journal of Petrochemical Universities, 2011, 24(6): 84-89.
[15] HAMADOU L, KADRI A, BENBRAHIM N. Characterisation of passive films formed on low carbon steel in borate buffer solution (pH 9.2) by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2005, 252(5): 1510-1519.
[16] 谢飞, 吴明, 陈旭, 等. SO42-对X80管线钢在库尔勒土壤模拟溶液中腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(1): 424-430.
XIE Fei, WU Ming, CHEN Xu, et al. Effects of SO42- on corrosion behavior of X80 pipeline steel in simulated Ku’erle soil solution[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(1): 424-430.
[17] SERNA S,CAMPILLO B, J L. Crack growth in microalloyed pipeline steels for sour gas transport[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2005, 14(2): 224-228.
J L. Crack growth in microalloyed pipeline steels for sour gas transport[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2005, 14(2): 224-228.
[18] DONG Chaofang, XIAO Kui, LIU Zhiyong, et al. Hydrogen induced cracking of X80 pipeline steel[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2010, 17(5): 579-586.
[19] 褚武扬. 断裂与环境断裂[M]. 北京:科学出版社, 2000: 108-120.
CHU Wuyang. Fracture and environmental fracture[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2000: 108-120.
[20] 张涛,姚远, 褚武扬, 等. 管线钢氢致附加应力与氢致门槛应力的相关性[J]. 金属学报, 2002, 38(8): 844-848.
ZHANG Tao,YAO Yuan, CHU Wuyang, et al. Relationship between hydrogen-induced additive stress and threshold cracking stress for a pipeline steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2002, 38(8): 844-848.
[21] LV Hong, LI Midan, ZHANG Tiancheng, et al. Hydrogen-enhanced dislocation emission, motion and nucleation of hydrogen-induced cracking for steel[J]. Science in China Series E: Technological Sciences, 1997, 40(5): 530-538.
[22] 孙曙明, 顾家琳, 陈南平. 氢在面心立方金属裂纹尖端变形过程中的作用[J]. 金属学报, 1991, 27(1): 44-48.
SUN Shuming, GU Jialin, CHEN Nanping. Effect of hydrogen on deformation process ahead of crack tip in Ni single crystal[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1991, 27(1): 44-48.
(编辑 刘锦伟)
收稿日期:2015-02-01;修回日期:2015-04-15
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(50771053,51574147);辽宁省教育厅科学研究基金资助项目(L2014156)(Projects (50771053,51574147) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (L2014156) supported by the Liaoning Province Education Science Fund)
通信作者:王丹,博士,讲师,从事油气管道腐蚀与防护技术研究;E-mail:wd841015@163.com