Cu2+和Zn2+抗性真菌的分离、鉴定及其富集特性
刘云国,樊 霆,周 娜,何义超,闵忠义,邬思丹
(湖南大学 环境科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410082)
摘 要:从湖南省岳阳市临湘铜锌尾砂坝土壤内分离、纯化得到1株抗铜和锌的菌株CTB430-1,分析该菌株形态和测定菌株ITS基因序列鉴定菌种,研究不同pH值、金属离子初始浓度和金属离子共存对菌体生长量和富集重金属的影响;分别采用考马斯亮兰法和碘量法测定菌体内可溶性蛋白和还原性谷胱甘肽含量。研究结果表明:鉴定该菌株为Aspergillus flavus,其对Cu2+和Zn2+的最低抑菌质量浓度分别为400和800 mg/L;菌株的生长和富集受溶液pH值、金属离子初始质量浓度和金属离子共存的影响,Cu2+和Zn2+的富集量分别在其质量浓度为200和250 mg/L时达到最大,为30.82和40.37 mg/g;菌体内可溶性蛋白和还原性谷胱甘肽含量发生变化,表明菌株对Zn2+具有较强的适应能力和抗性,还原性谷胱甘肽能缓解Cu2+和Zn2+对CTB430-1的氧化损伤。
关键词:真菌;铜;锌;抗性;富集;蛋白质;还原性谷胱甘肽
中图分类号:X51 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2009)01-0060-07
Isolation, identification and its bioaccumulation characteristics of
a fungus strain with resistance to Cu2+ and Zn2+
LIU Yun-guo, FAN Ting, ZHOU Na, HE Yi-chao, Min Zhong-yi, WU Si-dan
(College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China)
Abstract: A fungus CTB430-1 with resistance to copper and zinc was isolated from soil at a copper and Zinc Tailing of Linxiang in Yueyang city, Hunan province. The fungus was identified by analyzing the morphology and measuring the ITS sequence. The effects of pH, initial concentration, co-ions on the growth of CTB430-1 and bioaccumulation of Cu2+ and Zn2+ were studied. The protein and glutathione in the cells were determined by using the coomassie brilliant blue method and iodometric method, respectively. The results show that the strain is identified as Aspergillus flavus. Its minimal inhibitory concentration for Cu2+ and Zn2+are 400 and 800 mg/L, respectively. pH, initial concentration, co-ions in solution can affect the growth of CTB430-1 and bioaccumulation of Cu2+ and Zn2+, and the maximum bioaccumulation capacities of Cu2+ and Zn2+ are 30.82 and 40.37 mg/g at initial concentrations of 200 and 250 mg/L, respectively. Furthermore, the changes of protein and glutathione in the cells show that the strain holds high adaptive abilities and tolerance of zinc, and glutathione can alleviate the oxidation stress of copper and zinc.
Key words: fungus; copper; zinc; resistance; bioaccumulation; protein; glutathione
重金属污染在自然界无法通过自净作用或生物降解去除,其在自然环境中的归宿、迁移、转化以及对生物累积效应等问题,已成为当今环境科学研究的热点[1-2]。目前,国内外主要用化学沉淀法、氧化还原法、离子交换法处理含重金属的废水,成本较高[3-4]。由于微生物尤其是抗性微生物对低浓度含重金属废水的吸附和富集效果好,成本低,因而具有广阔的应用前 景[5-7]。在此,本文作者对Cu2+和Zn2+具有高效抗性的富集菌株CTB430-1,通过分析菌株形态和测定ITS基因序列鉴定菌种。同时,研究菌株对Cu2+和Zn2+的抗性和富集特性、重金属作用下菌体内可溶性蛋白和还原性谷胱甘肽的含量变化,探讨真菌对重金属的抗性机理。
1 实验材料和方法
1.1 实验材料
a. 马丁氏培养基(筛选培养基):葡萄糖 10 g,蛋白胨5 g,KH2PO4 1 g,MgSO4·7H2O 0.5 g,琼脂15~ 20 g,蒸馏水1 L。为了有效抑制细菌和放线菌生长,另加1%孟加拉红水溶液3.3 mL和1%链霉稀释液3 mL。
b. 土豆培养基(固体培养基):去皮马铃薯500 g (土豆洗净去皮,在水中煮至沸腾15 min),葡萄糖20 g,琼脂20 g,蒸馏水1 L。
c. 扩大培养基(液体培养基):葡萄糖20 g,蛋白胨10 g,NaCl 0.2 g,CaCl2 0.1 g,KCl 0.1 g,K2HPO4 0.5 g,NaHCO3 0.05 g,MgSO4 0.25 g,FeSO4·7H2O 5 mg,蒸馏水1 L。
1.2 菌株筛选
从湖南省岳阳市临湘铜锌尾砂坝取土样。将10 g新鲜土样装入含有90 mL无菌水的三角瓶中,用玻璃珠打散、搅匀,制成土壤悬液,用涂布法涂布在马丁氏固体培养基平板上,于28 ℃培养5~7 d,然后,挑选单菌落接入土豆培养基划线分离,经反复培养,找出菌落性状、颜色相同的菌株,初步推断为同一菌种。将筛选出的菌株接入土豆培养基斜面中,于28 ℃培养5 d,放入4 ℃的保温箱中保存备用。
分离菌株的菌落、细胞形态特征判定按文献[8]中方法进行。
1.3 ITS基因序列测定和鉴定
对菌株进行 ITS区域扩增。取适量菌体溶于10 μL裂解液中,于80 ℃变形15 min后,取1 μL作为模版,使用TaKaRa Fungi Indentification PCR Kit(Code No.D317)PCR扩增目的片段,以ITS1 Forword primer/ITS4 Reverse primer为引物扩增出菌株的ITS基因序列,测序由宝生物工程(大连)有限公司完成。
将测定的序列提交到NCBI(美国国立生物技术信息中心)数据库,应用BLAST程序与数据库中已有的基因序列进行同源性比较分析。
1.4 菌悬液制备
在无菌条件下,取菌体5 mg接入装有200 mL无菌水的500 mL锥形瓶中,于温度为28 ℃、转速为120 r/min条件下震荡2 h,于4 ℃的保温箱中保存备用。
1.5 菌株的抗性实验
将1 mL菌悬液接入Cu2+和Zn2+质量浓度不同(0~1 g/L)的液体培养基100 mL中,于28 ℃、转速为120 r/min条件下震荡培养7 d,用密度法测定菌种的生长量,分析菌株的抗性。
1.6 菌株的富集特性
1.6.1 pH值对菌株CTB430-1生长及富集Cu2+和Zn2+的影响
将1 mL菌悬液接入装有100 mL液体培养基(Cu2+和Zn2+质量浓度均为50 mg/L)的锥形瓶中,设初始的pH值范围为2~6,于28 ℃、转速为120 r/min的条件下震荡培养7 d。
1.6.2 不同浓度重金属对菌株CTB430-1生长及富集Cu2+和Zn2+的影响
将1 mL菌悬液接入装有100 mL液体培养基的锥形瓶中,Cu2+和Zn2+质量浓度范围为25~200 mg/L,于28 ℃、转速为120 r/min时震荡培养7 d。
1.6.3 Cu2+和Zn2+共存时对菌株CTB430-1生长及富集Cu2+和Zn2+的影响
将1 mL菌悬液接入装有100 mL液体培养基的锥形瓶中,加入不同质量浓度的Cu2+和Zn2+(0,25,50,100 mg/L),于28 ℃、转速为120 r/min时震荡培养7 d。
1.7 菌株抗性机理特性
将1 mL菌悬液接入装有100 mL液体培养基的锥形瓶中,Cu2+和Zn2+质量浓度范围分别为0~200 mg/L,于28 ℃、转速为20 r/min时震荡培养7 d,测定不同重金属浓度下菌株体内可溶性蛋白和还原性谷胱甘肽的含量变化。
以上每个实验均做3个,结果取平均值。
1.8 测定方法
1.8.1 菌株生长量测定
实验完成后,经过滤的菌体用蒸馏水清洗干净放入温度为60 ℃的烘箱中烘至质量恒定,测定菌株生长量。
1.8.2 菌株Cu2+和Zn2+富集量
实验完成后,对每个样品取1 mL上清溶液测定重金属的浓度,根据重金属的初始浓度计算菌株对重金属的富集量。

1.8.3 重金属浓度测定
用原子吸收分光光度计(PE AA700 U.S.A.)测定反应后剩余溶液的重金属浓度。
1.8.4 可溶性蛋白的提取和测定
取1.0 g经清洗干净的新鲜菌体,加入5.0 mL Tris-HCL(pH7.0)提取液,液氮研磨后于转速为5 000 r/min、温度为4 ℃的条件下离心30 min,得到的上清液用考马斯亮兰法蛋白试剂盒(南京建成生物工程研究所购买)处理后,用紫外分光光度计测定可溶性蛋白浓度。
1.8.5 还原性谷胱甘肽的提取和测定
取1 g烘干的菌体粉末,并按顺序加入4 mL蒸馏水与5 mL沸水,充分混合后放入95~100 ℃水浴锅中水浴10 min,然后,立即放于冰水中速冷,在转速为5 000 r/min时离心10 min,取出的上清液采用碘量 法[9]测定还原性谷胱甘肽的含量。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 菌株的筛选
经多次分离筛选,得到1株对Cu2+和Zn2+具有抗性的菌株,命名为CTB430-1。菌株在土豆培养基中经多次分离划线,于28 ℃培养72 h,菌株布满整个平面皿,菌丝疏松,表面呈黄绿色,背面略呈褐色。透过显微镜观察,菌丝多分枝,具有隔膜,有大量的分生孢子梗,梗端膨大成球形的泡囊,在泡囊表面又生出呈放射状排列的小梗,每个小梗顶端产生成串的分生孢子,呈黄绿色。根据菌落、细胞形态特征,初步判定为曲霉属(Aspergillus)。
2.2 ITS基因序列测定与鉴定
将测定的CTB430-1的ITS基因序列(GeneBank上的注册号为 FJ389893)在NCBI上进行BLAST比较,结果表明,其与Aspergillus属中Aspergillus flavus等多个种的ITS基因序列具有100%的同源性,与Aspergillus oryzae等多个种具有99%的同源性,因此,鉴定该菌株为Aspergillus flavus。
2.3 菌株CTB430-1对重金属Cu2+和Zn2+的抗性
Cu2+和Zn2+对CTB430-1生长和富集的影响分别见图1和图2(其中,m为菌体富集量,g;w为菌体生长量,mg/g)。由图1和图2可知,菌株CTB430-1对Cu2+和Zn2+都具有抗性,在Cu2+和Zn2+质量浓度分别低于50和100 mg/L时,对菌株CTB430-1的抑制作用不明显。Cu2+和Zn2+对CTB430-1菌株的最低抑菌质量浓度分别为400和800 mg/L。Trichoderma atroviride[10]在Cu2+和Zn2+质量浓度分别为400和800mg/L时不能存活,Pseudomonas aeruginosa Asu 6a[11]对Cu2+和Zn2+最低抑菌质量浓度分别为403.2和598 mg/L,可见, CTB430-1菌株对Cu2+和Zn2+具有较强的抗性。

1—Cu2+;2—Zn2+
图1 Cu2+和Zn2+对CTB430-1生长的影响
Fig.1 Effects of Cu2+ and Zn2+ concentration on growth of CTB430-1
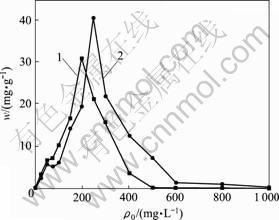
1—Cu2+;2—Zn2+
图2 CTB430-1对Cu2+和Zn2+的富集的影响
Fig.2 Effects of CTB430-1 on accumulation of Cu2+ and Zn2+
随着Cu2+和Zn2+初始质量浓度的增加,菌株CTB430-1的生长量逐渐降低,菌株对金属离子的富集量先增加后减少,Cu2+和Zn2+的富集量分别在其质量浓度为200和250 mg/L时达到最大,为30.82和40.37 mg/g。细胞壁与膜的表面富集是微生物抵抗重金属离子毒性的手段之一。在较高浓度的重金属离子环境中,微生物可先摄入一定量的重金属离子,刺激体内抗性机制运行,促进体内能与重金属作用的酶生成,同时,通过壁膜成分的改变促进重金属离子富集。高浓度的Cu2+和Zn2+对菌株具有一定的毒性,导致菌株新陈代谢活性和富集能力降低。
2.4 菌株CTB430-1生长及对重金属的富集特征
2.4.1 pH值对菌株CTB430-1生长及富集Cu2+和Zn2+的影响
pH值对菌株CTB430-1生长及富集Cu2+和Zn2+的影响分别见图3和图4。由图3和图4可知,当 pH>5时,菌株的生长量和富集能力相对较强,其原因主要是大多数菌类通常适宜于中性和弱碱性环境,pH值过低将抑制菌株的活性和生长。pH值较低时,因溶液中大量H+与金属离子竞争富集于活性位点而抑制菌株对金属离子的富集。大多数真菌表面官能团带负电荷,有助于金属离子的富集,当pH值较低时其功能团带正电荷,不与金属离子发生作用[12]。pH值为5时,菌株在Cu2+和Zn2+溶液的生长量和富集量达到最高,其生长量分别为0.66和0.80 g,富集量分别为5.31和6.07 mg/g。
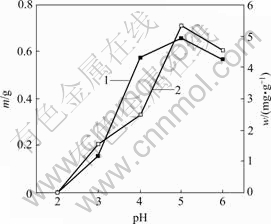
1—菌体生长量w;2—菌体富集量m
图3 Cu2+质量浓度为50 mg/L时pH值对菌株CTB430-1生长及富集Cu2+的影响
Fig.3 Effects of pH value on growth of CTB430-1 and accumulation of Cu2+ when concentration of Cu2+ is 50 mg/L
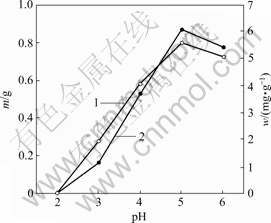
1—菌体生长量w;2—菌体富集量m
图4 Zn2+质量浓度为50 mg/L时pH值对菌株CTB430-1生长及富集Zn2+的影响
Fig.4 Effects of pH value on growth of CTB430-1 and accumulation of Zn2+ when concentration of Zn2+ is 50 mg/L
2.4.2 重金属不同初始浓度对菌株CTB430-1生长及富集Cu2+和Zn2+的影响
重金属离子初始浓度对菌株CTB430-1生长和富集Cu2+和Zn2+的影响分别见图5和图6。由图5和图6可知,Cu2+和Zn2+浓度增加对菌株生长有潜在的抑制作用,导致菌株生长延滞期增加,菌株生长缓慢,这说明菌株富集主要依靠菌株自身的代谢活动进行[13]。Cu2+和Zn2+富集量在菌株生长开始阶段较低,随着时间延长,菌株生长量和富集量逐渐增加,在菌株生长量达到平衡时富集量最大。菌株对Cu2+和Zn2+富集量分别在4 d和5 d时达到平衡。可见,Cu2+对菌株生长抑制作用较Zn2+的大。
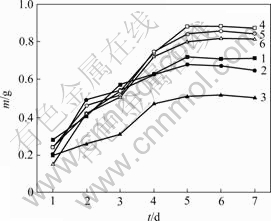
1—Cu2+ 25 mg/L; 2—Cu2+ 50 mg/L; 3—Cu2+ 100 mg/L;
4—Zn2+ 25 mg/L; 5—Zn2+ 50 mg/L; 6—Zn2+ 100 mg/L
图5 重金属离子初始浓度对菌株CTB430-1生长的影响
Fig.5 Effects of initial concentration of Cu2+and Zn2+on growth of CTB430-1

1—Cu2+ 25 mg/L; 2—Cu2+ 50 mg/L; 3—Cu2+ 100 mg/L;
4—Zn2+ 25 mg/L; 5—Zn2+ 50 mg/L; 6—Zn2+ 100 mg/L
图6 重金属离子初始浓度对菌株CTB430-1富集Cu2+和Zn2+的影响
Fig.6 Effects of initial concentration on accumulation of Cu2+and Zn2+ of CTB430-1
2.4.3 Cu2+和Zn2+共存时对菌株CTB430-1生长及富集的影响
Cu2+和Zn2+共存时对菌株CTB430-1生长及富集的影响见图7。由图7可知,Cu2+和Zn2+共存时对菌株CTB430-1生长抑制作用大于单个离子存在的作用,菌株生长量随着2种金属浓度增加递减,菌株对Cu2+和Zn2+的富集能力分别在(100+50) mg/L和(25+100) mg/L时达到最大,为7.65和14.94 mg/g,这说明在共存系统内,金属单离子浓度较高时,其竞争能力较强。即在Cu2+和Zn2+共存时,低浓度Cu2+或Zn2+能促进菌株对高浓度Zn2+或Cu2+菌株的富集;两者共存浓度都较高时,菌株富集能力下降。可见,菌株富集Zn2+能力受到的抑制作用较小。在Cd2+,Zn2+和Pb2+共存时,Penicilium simplicissimum[14]吸附金属离子的能力均小于单离子存在时的吸附能力,且Zn2+的吸附能力受到的抑制作用最小,与本研究结果具有一定的相似性。
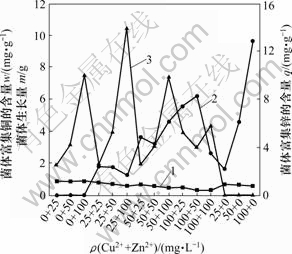
1—菌体生长量;2—菌体富集铜的含量;
3—菌体富集锌的含量
图7 Cu2+和Zn2+共同存在时对菌株CTB430-1生长及富集的影响
Fig.7 Effects of co-ions on growth of CTB430-1 and accumulation of Cu2+and Zn2+
2.5 菌株CTB430-1对重金属的抗性机理
2.5.1 不同浓度重金属对菌株CTB430-1体内可溶性蛋白含量的影响
研究表明,细胞在适应环境胁迫的生理过程中需要调整蛋白质的合成与降解,以适应新的环境[15]。重金属对菌株CTB430-1体内可溶性蛋白含量的影响见图8。由图8可知,在Cu2+和Zn2+作用下可溶性蛋白含量均呈现先下降后增长的趋势,后又略有下降。在Cu2+和Zn2+浓度较低时可溶性蛋白含量有所降低,其原因可能是Cu2+和Zn2+抑制了可溶性蛋白合成并诱导蛋白质的降解,降低了可溶性蛋白含量。随着重金属浓度增加,可溶性蛋白含量增加,这是生物对逆境胁迫的一种生理生化反应,其原因可能是细胞结构和功能遭受破坏时的应激反应;另一方面,生物在逆境下的适应表现即防护反应,可作为鉴定生物相对抗性的指标。随着Cu2+和Zn2+浓度继续增加,对CTB430-1的毒性也逐渐增大,可溶性蛋白含量开始减小,细胞代谢速度减慢,对Cu2+和Zn2+胁迫的适应力增强。Heyser等[16]认为蛋白含量降低可使细胞代谢速度减慢,从而增强微生物细胞对环境胁迫的适应力,这与本实验结果相一致。

1—Cu2+; 2—Zn2+
图8 重金属离子初始浓度对菌株CTB430-1体内可溶性蛋白含量的影响
Fig.8 Effects of initial concentration of Cu2+and Zn2+on soluble protein contents in cells of CTB430-1
总的来说,菌株CTB430-1体内可溶性蛋白含量变化不大,主要是因其对Cu2+和Zn2+具有抗性,且对Zn2+抗性较强。
2.5.2 不同重金属浓度对菌株CTB430-1体内还原性谷胱甘肽的影响
重金属离子初始质量浓度对菌株CTB430-1体内还原性谷胱甘肽含量的影响见图9。由图9可知,随着Cu2+质量浓度的增加,菌株CTB430-1体内还原性谷胱甘肽(GSH)的含量先升高,然后逐渐下降;随着Zn2+质量浓度增加,GSH的含量先增加后降低,在50~150 mg/L内又呈现先增加后降低趋势。该变化与重金属的性质和浓度有关。另外,金属离子存在时菌株体内GSH含量均大于空白时的含量,这表明金属毒性刺激菌株生成GSH,来缓解重金属对细胞的氧化损伤。GSH是生物体内非蛋白硫醇的主要来源,含有巯基,能与重金属直接结合[17],同时,GSH是生物体内重要的抗氧化物质,可清除细胞内活性氧,缓解氧化损 伤[18]。当Cu2+和Zn2+质量浓度为25 mg/L时,GSH含量达到最大,表明胞内活性氧物质大量增加;而当Cu2+和Zn2+质量浓度大于25 mg/L时,GSH含量降低。其原因可能是菌株体内抗氧化系统其他成分的介入,降低了活性氧浓度,或者菌株体内GSH与金属离子发生反应,缓解金属离子的毒性。另外,高浓度金属离子对菌株机能损伤而抑制GSH的产生[19]。
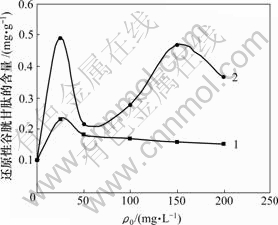
1—Cu2+; 2—Zn2+
图9 重金属离子初始浓度对菌株CTB430-1体内还原性谷胱甘肽含量的影响
Fig.9 Effects of initial concentration of Cu2+and Zn2+on glutathione contents in cells of CTB430-1
3 结 论
a. 从湖南省岳阳市临湘铜锌尾砂坝土壤内筛选得到1株对Cu2+和Zn2+具有高效抗性的菌株CTB430-1,通过对其形态特征和ITS基因序列测定分析,鉴定该菌株为黄曲霉(Aspergillus flavus)。
b. Cu2+和Zn2+对菌株CTB430-1的最低抑菌浓度分别为400和800 mg/L,Cu2+和Zn2+的富集量分别在其质量浓度为200和250 mg/L时达到最大,为30.82和40.37 mg/g。菌株生长和富集金属离子的能力受溶液初始pH值、金属离子初始质量浓度以及金属离子共存的影响。当pH>5时,菌株的生长量和富集能力相对较强;随着Cu2+和Zn2+质量浓度增加,对菌株生长的抑制作用增大,相比而言,Cu2+的抑制作用较大。Cu2+和Zn2+共存时对菌株CTB430-1生长抑制作用大于单个离子存在时的作用,两者共存质量浓度都较高时,菌株CTB430-1富集能力较低。
c. 在Cu2+和Zn2+不同浓度作用下,菌株内可溶性蛋白和还原性谷胱甘肽含量变化趋势说明,该菌株对Zn2+具有较强的抗性,还原性谷胱甘肽能缓解Cu2+和Zn2+对CTB430-1的氧化损伤。
参考文献:
[1] Artola A, Balaguer M D, Rigola M. Heavy metal binding to anaerobic sludge[J]. Water Research, 1997, 31(5): 997-1004.
[2] Malik A. Metal bioremediation through growing cells[J]. Environmental International, 2004, 30(2): 261-278.
[3] Pagnanelli F, Trifoni M, Beolchini F, et al. Equilibrium biosorption studies in single and multi-metal systems[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2001, 37(2): 115-124.
[4] Kadirvelu K, Senthilkumar P, Thamaraiselvi K, et al. Activated carbon prepared from biomass as adsorbent: elimination of Ni(Ⅱ) from aqueous solution[J]. Bioresoure Technology, 2002, 81(1): 87-90.
[5] Lodeiro P, Barriada J L, Herrero R, et al. The marine macroalga Cystoseira baccata as biosorbent for cadmium(Ⅱ) and lead(Ⅱ) removal: Kinetic and equilibrium studies[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2006,142(2): 264-273.
[6] LIU Yun-guo, FAN Ting, ZENG Gung-ming, et al. Removal of cadmium and zinc ions from aqueous solution by living Aspergillus niger[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16(3): 681-686.
[7] Shankar C, Sridevi D, Joonhong P, et al. Biosorption of chromium and nickel by heavy metal resistant fungal and bacterial isolates[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 146(1/2): 270-277.
[8] 魏景超. 真菌鉴定手册[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1979: 129-136.
WEI Jing-chao. Fungi identification handbook[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1979: 129-136.
[9] 安贤惠. 还原性谷胱甘肽提取方法初探[J]. 淮海工学院学报, 2003, 12(2): 49-52.
AN Xian-hui. A preliminary study on the extracting method of glutathione[J]. Journal of Huaihai Institute of Technology, 2003, 12(2): 49-52.
[10] López E E, Vázquez C. Tolerance and uptake of heavy metals by Trichoderma atroviride isolated from sludge[J]. Chemosphere, 2003, 50(1): 137-143.
[11] Hassan S H A, Abskharon R N N, Gad El-Rab S M F, et al. Isolation, characterization of heavy metal resistant strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from polluted sites in Assiut city, Egypt[J]. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 2008, 48(3): 168-176.
[12] Yan G, Viraraghavan T. Heavy metal removal from aqueous solution by fungus Mucor rouxii[J]. Water Research, 2003, 37(18): 4486-4496.
[13] Uslu G, Dursun A Y, Ekiz H I, et al. The effect of Cd(Ⅱ), Pb(Ⅱ) and Cu(Ⅱ) ions on the growth and bioaccumulation properties of Rhizopus arrhizus[J].Process Biochemistry, 2003, 39(1): 105-110.
[14] Ting F, Yun-Guo L, Bao-ying F, et al. Biosorption of cadmium(Ⅱ), zinc(Ⅱ) and lead(Ⅱ) by Penicillium simplicissimum: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 160(2/3): 655-661.
[15] Banerjee B D, SETH V, Bahattacharya A. Biochemical effects of some pesticides on lipid peroxidation and free-radical scavengers[J]. Toxicology Letters, 1999, 107(1/3): 33-47.
[16] Heyser J W, Nabors M W. Growth, water content and solute accumulation of two tobacco cell lines cultured on sodium chloride, dextran, and polyethylene glycol[J]. Plant Physiology, 1981, 68: 1454-1459.
[17] 周文彬, 邱保胜. 藻类对重金属的耐性与解毒机理[J]. 湖泊科学, 2004, 16(3): 265-272.
ZHOU Wen-bin, QIU Bao-sheng. Mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance in algae[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2004, 16(3): 265-272.
[18] Ana I G L, Sofia C C, Etelvina M A P F. Glutathione-mediated cadmium sequestration in Rhizobium leguminosarum[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2006, 39(4): 763-769.
[19] Saint D, Labrot F, Narbonne J F, et al. Glutathione, glutathione-related enzymes, and catalase activities in the earthworm Eisenia fetida andrei[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1998, 35(4): 602-614.
收稿日期:2008-11-10;修回日期:2009-01-05
基金项目:“十一五”国家科技支撑计划项目(2006BAD03A1704;2006BAD03A1706)
通信作者:刘云国(1955-),男,湖南常德人,教授,博士生导师,从事重金属污染水体的生物治理和修复研究;电话:0731-8649208;E-mail: liuyunguo2005@yahoo.com.cn