DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.01.16
准静态拉伸过程中CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金显微组织的演变
蔡小勇1,唐群华2,戴品强1, 3, 4
(1. 福州大学 材料科学与工程学院,福州 350116;
2. 莆田学院 机电工程学院,莆田 351100;
3. 福建工程学院 材料科学与工程学院,福州 350118;
4. 福建工程学院 福建省新材料制备与成形技术重点实验室,福州 350118)
摘 要:采用电子背散射衍射技术,研究室温下CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金在准静态单向拉伸(应变速率为1×10-1 s-1)过程中显微组织的演变。结果表明:合金的变形机制主要是位错的滑移,同时伴随着少量的孪生。当应变约为0.81%时,合金开始出现新的Σ3孪晶界。晶向<001>附近的拉伸轴向<001>方向转动,形成弱的<001>//RD丝织构,符合Toylor模型,晶粒拉伸轴向<001>-<111>连线转动,符合Sachs模型。晶粒尺寸显著影响晶粒的转动速率,小尺寸晶粒转动最快,大尺寸晶粒次之,中等尺寸晶粒转动最慢。晶粒Schmid因子越大,晶粒的转动越快。
关键词:高熵合金;背散射电子衍射;微观组织;准静态拉伸;晶粒转动
文章编号:1004-0609(2018)-01-0135-07 中图分类号:TG115 文献标志码:A
多主元高熵合金由5种或5种以上主元按照等原子比或近等原子比设计的一类新型合金。由于高熵效应,高熵合金倾向于形成简单固溶体结构,而不出现复杂的金属间化合物[1]。传统的合金设计理念认为,合金组成元素越多,越容易形成脆性金属间化合物等复杂相,造成合金分析和应用困难。因此,高熵合金理论的提出,被认为合金化理论的重大突破之一[2]。与传统合金相比,高熵合金具有高硬度、高耐磨性、优异的高温强度和良好的低温韧性等优越性能[3-7]。
近年来,CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金由于具有简单晶体结构和优异的力学性能,吸引了材料研究学者的广泛关注[8-14]。例如,CANTOR等[15]首次报道了CoCrFeMnNi合金,发现这种合金由单一的面心立方结构(fcc)固溶体相组成,且具有良好的热力学稳定性和优秀的延展性;STEPANOV等[16]发现80%轧制后CoCrFeMnNi合金在77和293K的抗拉强度可分别高达1500和1200 MPa;HE等[17]发现CoCrFeMnNi合金在1023~1123 K的实验环境中,高应变速率下的变形机制主要是位错攀移,低应变速率下的变形机制主要是位错滑移;OTTO等[6]发现CoCrFeMnNi合金在77K时,拉伸过程中产生纳米孪晶,合金变形机制由室温下位错滑移变成位错滑移和孪生,合金抗拉强度增加。目前,关于CoCrFeMnNi合金的研究主要集中不同实验条件下的力学性能分析,而对于合金变形过程中微观组织的研究较少涉及。因此,本文作者采用电子背散射衍射(EBSD)技术,对CoCrFeMnNi合金在准静态拉伸过程中微观组织的演变进行研究。
1 实验
选用纯度大于99.9%的Co、Cr、Fe、Mn和Ni金属原料,通过真空悬浮感应熔炼法制备等原子比CoCrFeMnNi合金。从铸锭中切割出15 mm×20 mm×40 mm的试样块,在室温下对试样块进行压下量为90%的轧制,随后进行800 ℃、1 h的再结晶退火。从退火试样中沿着轧制方向切割出如图1所示拉伸试样,标距长10 mm,厚1 mm,宽2 mm。以拉伸试样本身建立参考坐标系,轧制方向为RD,横向为TD,法向为ND。对拉伸试样的ND×RD面进行电化学抛光,获得光滑且无表面应力的区域。
准静态拉伸指应变速率为1×10-4~1 s-1的拉伸。室温下准静态拉伸试验采用Instron1185型万能拉伸试验机,应变速率为1×10-1 s-1。在拉伸应变约为0.81%、4.10%、6.32%和12.01%时,这些应变均属于同一样品上拉伸所得,采用FEI Zeiss supra55场发射扫描电镜配置的EBSD系统对抛光区域进行测量,步长为0.3μm,并采用Channel5.0软件进行分析。采用中心点平均取向差(Kernal Average Misorientation,KAM)法对EBSD数据进行重构。重构出来的KAM图可直接反映晶粒内各个位置的应变(位错)分布。
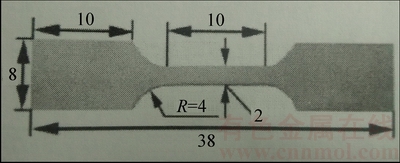
图1 拉伸样品尺寸
Fig. 1 Dimensions of tensile samples (Unit: mm)
2 结果与分析
2.1 变形机制
图2所示为试样不同拉伸应变量下组织的KAM分布图(含Σ3孪晶界分布)。由图2(a)可以看出,拉伸前试样存在大量Σ3孪晶界,这主要是由于CoCrFeMnNi合金具有较低的堆垛层错能,退火后易生成孪晶 [6]。由图2(a)、(b)和(c)左下角白色箭头指示可以看出:拉伸前,该区域没有Σ3孪晶界;当应变为0.81%时,开始出现Σ3孪晶界,即出现变形孪晶;在应变达到4.10%时,Σ3孪晶界贯穿晶粒。同时,箭头指示出现Σ3孪晶界的区域,在拉伸变形前有大量位错堆积,且堆积形状与孪晶相似,均为条状。现有的孪晶形成理论中,认为退火孪晶是在一条迁移的晶界后面,由于生长原因,肖克利不全位错环在连续的(111)面上形核,然后由于不全位错之间互相排斥使层错长大形成了退火孪晶[18]。因此,图2(a)中箭头指示晶粒上的条状堆积位错可能为退火过程中残留的肖克利不全位错,后续拉伸变形可促进肖克利不全位错叠加,从而造成的形变孪晶,见图2(b)和2(c)箭头指示位置。此外,本文作者课题组的前期实验表明,CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金在应变速率为1×10-3 s-1时,合金是通过滑移而非孪生方式协调其拉伸变形[19]。综上所述可知,条状堆积的位错和高的应变速率(1×10-1 s-1)是促进该合金形变孪晶生成的原因之一。如图2所示,在应变量为 0~6.32%时,随着拉伸应变量的增加,晶粒内位错通过滑移在晶界附近堆积,晶粒内部位错减少。这表明CoCrFeMnNi合金在准静态下拉伸变形的机制主要是位错的滑移,同时伴随着少量的孪生。
2.2 晶粒取向变化
图3所示为试样在不同拉伸应变量下取向成像图(OIM)和基于RD方向的反极图。其中,图3(a)、(c)、(e)、(g)和(i)为OIM图,以彩色表征晶粒取向;图3(b)、(d)、(f)、(h)和(j)为反极图。如图3(b)所示,拉伸变形前,晶粒与轧向平行的晶向的极点主要分布于RD反极图的中部,且在<001>-<111>线附近有明显的聚集。比较图3(d)、(f)、(h)和(j)可以看出,随着拉伸应变量的增加中部的极点向<001>-<111>线聚集,这说明拉伸过程中晶粒的拉伸轴是向<001>-<111>线转动,符合Sachs模型。图2(j)中<001>出现等高线,表明晶向<001>附近的拉伸轴向<001>方向转动,形成弱的<001>//RD丝织构,符合Taylor模型。
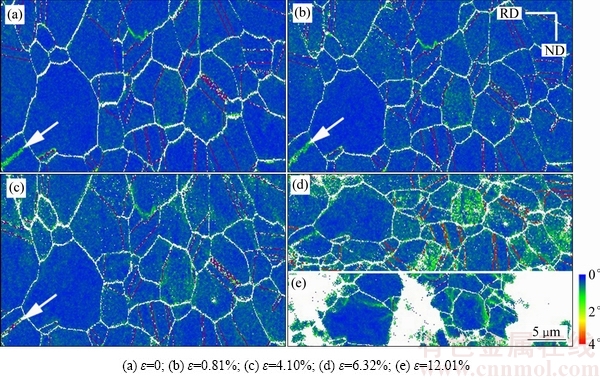
图2 不同拉伸应变量下样品的KAM分布图(含Σ3晶界分布)
Fig. 2 KAM images of samples (including Σ3 twinning boundary) at different tensile strains
从图3(a)、(c)、(e)、(g)和(i)可以看出,随着拉伸应变量的增加,晶粒沿拉伸方向伸长,成扁平状,且各个晶粒取向发生不同程度的转动。图4(a)所示为试样拉伸前的取向成像图,图4(b)所示为试样拉伸前的Schmid因子(取向因子)成像图。为了研究不同尺寸晶粒的转动,从图4(a)中选取6个尺寸不同且Schmid因子接近的晶粒进行观察,为了排除孪晶对晶粒的影响,这些晶粒都不含孪晶。

图3 不同拉伸应变量下样品的OIM和反极图
Fig. 3 OIM images and inverse pole figures of samples at different tensile strains: OIM image
表1和2所示为晶粒1~6在不同拉伸应变量下的晶体学信息,包括欧拉角、Schmid因子、晶粒尺寸和角轴对。其中,中心点欧拉角的获得是基于晶粒在不同拉伸应变量下的中心点取向,即采用晶粒中心点取向代表晶粒的平均取向。为了研究晶粒1~6取向变化,将取向欧拉角变化换算为角轴对(见表2)。另外,通过软件还能获得如表2中各晶粒拉伸前的ms(Schmid因子)和晶粒尺寸。从表2中可以看出,晶粒1的尺寸最大,晶粒2和晶粒3次之,晶粒4、5和6尺寸接近,但比晶粒1~3小很多,为了方便讨论,将晶粒尺寸在10 μm左右的晶粒视为大晶粒(即晶粒1为大晶粒);将晶粒尺寸在6 μm左右的晶粒视为中等晶粒(即晶粒2和3为中等晶粒);将晶粒尺寸在2 μm左右的晶粒视为小晶粒(即晶粒4、5和6为小晶粒)。
比较Schmid因子接近的大晶粒、中等晶粒和小晶粒角轴对,即比较晶粒1~5,发现当拉伸应变量为0.81%时,这3种晶粒转动无明显规律。当拉伸应变量为12.01%时,晶粒转动速率由快到慢依次为小晶粒、大晶粒、中等晶粒;比较3个小晶粒,发现晶粒6 的Schmid因子最小,当应变量为12.01%时,转动角度最小。
为了更加直观判断晶粒转动的快慢,选取晶粒1、2和4来分别表征大晶粒、中等晶粒和小晶粒,获得晶粒在不同拉伸应变量下的反极图,如图5所示。比较图5(a)、(b)和(c)可知,晶粒1、2和4拉伸轴向<001>-<111>连线转动,这与上文所述拉伸轴转动方向相一致,此外,大晶粒1和小晶粒4的拉伸轴转动明显,中等晶粒2的拉伸轴转动较小。根据Hall-Petch公式,多晶体材料的强度随晶粒细化而提高。晶粒越大起始塑变抗力越小,晶粒越大越容易发生变形。但在塑性变形过程中,由于较大晶粒容易变形,小晶粒不易变形,在局部区域可能由于小晶粒阻碍大晶粒变形,大晶粒对小晶粒施加一定的外力,导致小晶粒附近产生应力集中,促进小晶粒变形,晶粒转动加快。
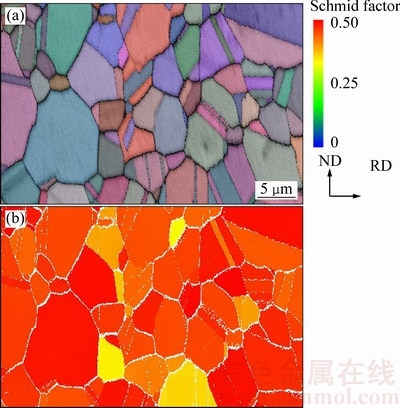
图4 拉伸前样品的取向成像图和Schmid因子成像图
Fig. 4 Orientation micrographs of sample and Schmid factor of sample before tensile strains
表1 不同拉伸应变量下晶粒中心点的欧拉角
Table 1 Midpoint Euler angle of grains at different tensile strains
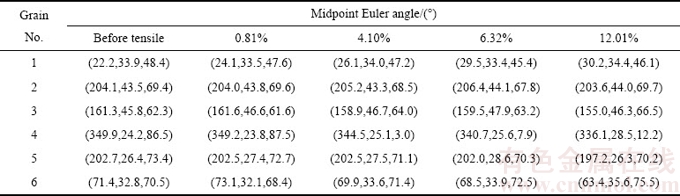
表2 不同拉伸应变量下晶粒的晶体学信息
Table 2 Crystallographic information of grains at different tensile strains
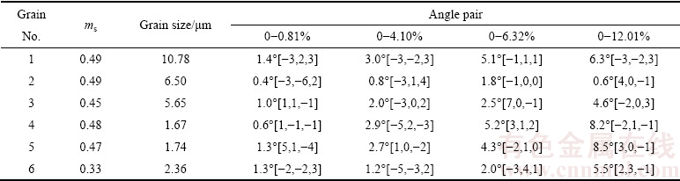

图5 不同拉伸应变量下晶粒1、2和4的反极图
Fig. 5 Inverse pole figures of grains at different tensile strains
综上所述,当Schmid因子大小相当,小晶粒转动最快,大晶粒次之,中等晶粒转动最慢;当晶粒尺寸大小相当且Schmid因子相差较大时,Schmid因子较大的晶粒转动快,Schmid因子较小的晶粒转动慢,符合Schmid定律。
3 结论
1) CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金在准静态拉伸时,当合金的应变为0.81%时,合金开始出现新的Σ3孪晶界。合金的变形机制主要是位错的滑移,同时,伴随着少量的孪生。
2) 当合金的应变为0~12.01%时,晶粒的拉伸轴主要向<001>-<111>连线转动,符合Sachs模型;晶向<001>附近的拉伸轴向<001>方向转动,形成弱的<001>//RD丝织构,符合Taylor模型。
3) 当Schmid因子大小相当时,小晶粒转动最快,大晶粒次之,中等晶粒转动最慢;当晶粒尺寸大小相当时,Schmid因子较大的晶粒转动快,Schmid因子较小的晶粒转动慢,晶粒转动符合Schmid定律。
REFERENCES
[1] YEH J W, CHEN S K, LIN S J, GAN T S, SHUN T T, TSAU C H, CHANG S Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2004, 6(5): 299-303.
[2] 隋艳伟, 陈 霄, 戚继球, 何业增, 孙 智. 多主元高熵合金的研究现状与应用展望[J]. 功能材料, 2016, 47(5): 50-54.
SUI Yan-wei, CHEN Xiao, WEI Ji-qiu, HE Ye-zeng, SUN Zhi. Research progress of high-entropy alloys with multi-principal elements and its prospective application[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2016, 47(5): 50-54.
[3] SENKOV O N, WILKS G B, SCOTT J M, MIRACLE D B. Mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25, and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20, refractory high entropy alloys[J]. Intermetallics, 2011, 19(5): 698-706.
[4] GALI A, GEORGE E P. Tensile properties of high- and medium-entropy alloys[J]. Intermetallics, 2013, 39(4): 74-78.
[5] SENKOV O N, SENKOVA S V, MIRACLE D, WOODWARD C. Mechanical properties of low-density, refractory multi-principal element alloys of the Cr-Nb-Ti-V-Zr system[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2013, 565(5): 51-62.
[6] OTTO F, DLOUHY A, SOMSEN C, BEI H, EGGELER G, GEORGE E P. The influences of temperature and microstructure on the tensile properties of a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61(15): 5743-5755.
[7] KUZNETSOV A V, SHAYSULTANOV D G, STEPANOV N D, SALISHCHEV G A, SENKOV O N. Tensile properties of an AlCrCuNiFeCo high-entropy alloy in as-cast and wrought conditions[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2012, 533(1): 107-118.
[8] MA D, GRABOWSKI B,  F, NEUGEBAUER J, RAABE D. Ab initio, thermodynamics of the CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy: Importance of entropy contributions beyond the configurational one[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 100: 90-97.
F, NEUGEBAUER J, RAABE D. Ab initio, thermodynamics of the CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy: Importance of entropy contributions beyond the configurational one[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 100: 90-97.
[9] WILSON P, FIELD R, KAUFMAN M. The use of diffusion multiples to examine the compositional dependence of phase stability and hardness of the Co-Cr-Fe-Mn-Ni high entropy alloy system[J]. Intermetallics, 2016, 75: 15-24.
[10] 霍文燚. 06Cr19Ni10表面氩弧熔覆CoCrFeMnNi系高熵合金涂层研究[D]. 辽宁: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2015.
HUO Wen-yi. Investigation of CoCrFeMnNi system high-entropy alloy coatings by tungsten inert gas cladding on 06Crl9Nil0 steel[D]. Liaoning: Liaoning Technical University, 2015.
[11] MA D, YAO M, PRADEEP K G, TASAN C C, SPRINGER H, RAABE D. Phase stability of non-equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 98: 288-296.
[12] 刘玉林, 罗永春, 赵 丹, 张国庆, 康 龙. 高熵合金(CoCrFeMnNi)/铜真空扩散连接的界面行为及接头性能研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2017, 53(2): 84-91.
LIU Yu-lin, LUO Yong-chun, ZHAO Dan, ZHANG Guo-qing, KANG Long. Interfacial behavior and joint performance of high-entropy alloy CoCrFeMnNi and pure cu joints obtained by vacuum diffusion welding[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 53(2): 84-91.
[13] OTTO F, HANOLD N L, GEORGE E P. Microstructural evolution after thermomechanical processing in an equiatomic, single-phase CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy with special focus on twin boundaries[J]. Intermetallics, 2014, 54(18): 39-48.
[14] 刘玉林, 罗永春, 石彦彦. 高熵合金CoCrFeMnNi/不锈钢真空扩散焊[J]. 电焊机, 2016, 46(12): 122-127.
LIU Yu-lin, LUO Yong-chun, SHI Yan-yan. Vacuum diffusion welding between CoCrFeMnNi high entropy and stainless steel[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2016, 46(12): 122-127.
[15] CANTOR B, CHANG I T H, KNIGHT P, VINCENT A J. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 375/377(1): 213-218.
[16] STEPANOV N, TIKHONOVSKY M, YURCHENKO N, ZYABKIN D, KLIMOVA M, ZHEREBTSOV S, SALISHCHEV G. Effect of cryo-deformation on structure and properties of CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy[J]. Intermetallics, 2015, 59: 8-17.
[17] HE J Y, ZHU C, ZHOU D Q, LIU W H, NIEH T G, LU Z P. Steady state flow of the FeCoNiCrMn high entropy alloy at elevated temperatures[J]. Intermetallics, 2014, 55(2): 9-14.
[18] MAHAJAN S, PANDE C S, IMAM M A, RATH B B. Formation of annealing twins in f.c.c. crystals[J]. Acta Materialia, 1997, 45(6): 2633-2638.
[19] 唐群华, 戴品强. CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金单向拉伸的组织和取向演变[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2016, 23(1): 99-103.
TANG Qun-hua, DAI Pin-qiang. Microstructure and grain orientation evolution of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy during uniaxial tensile deformation[J].Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2016, 23(1): 99-103.
Microstructure evolution of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy during quasi-static tensile
CAI Xiao-yong1, TANG Qun-hua2, DAI Pin-qiang1, 3, 4
(1. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou 350116, China;
2.School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Putian University, Putian 351100, China;
3. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Fujian University of Technology, Fuzhou 350118, China;
4. Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Advanced Materials Processing and Application, Fujian University of Technology, Fuzhou 350118, China)
Abstract: The evolution of microstructure of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy during quasi-static tensile (strain rate 1×10-1 s-1) were investigated using electron backscatter diffraction technology. The results show that the dominant deformation mechanism is dislocation gliding, which is accompanied with less twinning. The alloy generates new Σ3 twin boundaries when the strains is 0.81%. The tensile axes close to <001> rotate toward <001> and form a weak <001>//RD fiber texture following Toylor model. The tensile axes rotate to the line of <001>-<111> following Sachs model, the grain size influences the rotational speed of grains. The rotational speed of small grain is the fastest than big grains and medium grains, and the medium grain is the slowest than other grains. The bigger Schmid factor of grain is, the faster grain rotation is.
Key words: high-entropy alloy; electron backscatter diffraction technology; microstructure; quasi-static tensile; grain rotation
Foundation item: Project(2014H6005) supported by the Major Industry-academy Cooperation of Fujian Province, China
Received date: 2016-10-12; Accepted date: 2017-04-17
Corresponding author: DAI Pin-qiang; Tel: +86-591-22863456; E-mail: pqdai@126.com
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:福建省高校产学合作项目(2014H6005)
收稿日期:2016-10-12;修订日期:2017-04-17
通信作者:戴品强,教授,博士;电话:0591-22863456;E-mail:pqdai@126.com