壳聚糖固定化枯草芽孢杆菌水溶液中铜离子的吸附
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2013年第6期
论文作者:刘云国 廖 婷 贺仲兵 李婷婷 王 慧 胡新将 郭一明 何 缘
文章页码:1804 - 1814
关键词:生物吸附;枯草芽孢杆菌;固定化枯草芽孢杆菌;Cu(II);吸附平衡;动力学
Key words:biosorption; Bacillus subtilis; Bacillus subtilis immobilized into chitosan beads (BICB); Cu(II); isotherms; kinetic
摘 要:研究了壳聚糖固定化枯草芽孢杆菌吸附铜离子的性能,分析了pH、吸附剂投加量、温度、铜离子初始浓度和时间对铜离子吸附的影响。结果表明, pH对铜离子的吸附有较大的影响。此外,固定化枯草芽孢杆菌吸附剂比空白吸附剂具有更强的吸附性能。整个吸附过程符合朗缪尔吸附模型(R2=0.994),最大吸附量为100.70 mg/L。动力学模型拟合结果表明,实验符合准二级动力学模型,线性相关指数大于0.999。吸附剂能在0.1 mol/L NaOH溶液中被成功解吸。
Abstract: The ability of Bacillus subtilis immobilized into chitosan beads (BICB) to remove Cu(II) from aqueous solution was studied. The effects of pH, biosorbent dosage, temperature, initial Cu(II) concentration and contact time on removal of Cu(II) were studied using batch adsorption experiments. The results show that the Cu(II) absorption strongly depends on pH and the optimum pH is 6. Compared with chitosan beads (CB), the BICB has higher efficiency and capacity on Cu(II) removal. The Langmuir isotherm model (R2=0.994) is proved to fit the equilibrium data best. The maximum adsorption capacity determined from Langmuir model is 100.70 mg/g. The kinetic data fit well with the pseudo-second-order model and the correlation coefficient is greater than 0.999. The biosorbents are successfully regenerated using 0.1 mol/L NaOH solution.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 1804-1814
Yun-guo Liu 1,2, Ting Liao1,2, Zhong-bing He1,2, Ting-ting Li1,2, Hui Wang1,2, Xin-jiang Hu1,2, Yi-ming Guo1,2, Yuan He1,2
1. College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Environmental Biology and Pollution Control of Ministry of Education, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
Received 10 May 2012; accepted 5 December 2013
Abstract: The ability of Bacillus subtilis immobilized into chitosan beads (BICB) to remove Cu(II) from aqueous solution was studied. The effects of pH, biosorbent dosage, temperature, initial Cu(II) concentration and contact time on removal of Cu(II) were studied using batch adsorption experiments. The results show that the Cu(II) absorption strongly depends on pH and the optimum pH is 6. Compared with chitosan beads (CB), the BICB has higher efficiency and capacity on Cu(II) removal. The Langmuir isotherm model (R2=0.994) is proved to fit the equilibrium data best. The maximum adsorption capacity determined from Langmuir model is 100.70 mg/g. The kinetic data fit well with the pseudo-second-order model and the correlation coefficient is greater than 0.999. The biosorbents are successfully regenerated using 0.1 mol/L NaOH solution.
Key words: biosorption; Bacillus subtilis; Bacillus subtilis immobilized into chitosan beads (BICB); Cu(II); isotherms; kinetic
1 Introduction
Heavy metal pollution has become a serious environmental problem in the last several decades. A large amount of heavy metal ions exist in final industrial effluents which are extremely undesirable due to their toxicity even at low concentrations [1]. Copper is an essential nutrient in trace amount but at a higher level it is toxic to plants, animals and humans [2]. Copper consumption in high doses might bring about serious toxicological concerns because it can be deposited in the brain, skin, liver, myocardium and pancreas [3]. Copper is widely used in various important industrial applications, so its removal and recovery from wastewater is significant for the environmental protection and human health.
Compared with the traditional wastewater treatments [4], biosorption process has been found to be superior to other technologies because of its low cost, high efficiency, convenient operation, regeneration of biosorbent and recovery of metals [5]. Biosorption utilizes a wide variety of microorganisms including bacteria, yeast, algae, protozoa and fungi which could be found everywhere. The mechanisms for removal of heavy metals may involve adsorption, uptake, methylation, oxidation and reduction [6]. Living, dead and immobilized cells can be used in this process. Immobilized cells are usually easier to handle, require less complex separation systems, allow a high biomass density to be maintained and provide a greater opportunity for reuse and recovery [7].
Bacillus subtilis (B. subtilis), as an industry waste, possesses high physiological activity. The structure of cell wall is well-known and consists primarily of peptidoglycan and teichoic acid. Peptidoglycan is a polymer of acetylmuramic and acetylglucosamine acids that display mainly carboxylic and hydroxyl functional groups. Teichoic acid is a polymer of copyranosyl glycerol phosphate that reveals mainly phosphate and hydroxyl groups [8,9].
Natural polymers such as alginate, chitin, chitosan, and cellulose derivatives have been mostly used as the matrix for the immobilization of the microbial cells via entrapment [10]. Chitosan is a product of the partial N-deacetylation of chitin, which has several desirable properties like hydrophilicity, biodegradability and non-toxicity [11]. Chitosan could serve as carriers for enzymes and whole cells, and shows high ability on metal removal. Many studies are available on removal of metals using chitosan [12,13].
The aim of this study was to evaluate the performance of entrapping B. subtilis into chitosan beads for biosorption of Cu(II) from aqueous solution. The influences of experimental parameters such as pH, biosorbent dosage, temperature, initial Cu(II) concentration on Cu(II) removal were studied. In order to better understand the mechanism during the biosorption process, some isotherm and kinetic models were evaluated. Regeneration studies were also carried out to determine the reusability of the biosorbent.
2 Experimental
2.1 Microorganism and materials
The B. subtilis used in this study was provided by Hunan Normal University, China. Chitosan (90% acetylation degree) was supplied by Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. Stock solution (1000 mg/L) of Cu(II) was prepared by dissolving 3.8023 g Cu(NO3)2·3H2O in 1000 mL distilled water. The solutions of different concentrations used in various experiments were obtained by dilution of the stock solution. All reagents were of analytic grade and used without further purification.
2.2 B. subtilis cultivation
Cultivation of B. subtilis was carried out in 250 mL erlenmeyer flasks with 100 mL growth medium on a rotary shaker at 150 r/min with a constant temperature of 37 °C. The growth medium contained 10 g/L peptone, 20 g/L glucose, 4 g/L yeast extract, 5 g/L NaCl and 5 mg/L MnSO4·H2O. The pH of the medium was adjusted to 7.0.
2.3 Preparation of BICB and CB
The Bacillus subtilis immobilized into chitosan beads (BICB) were prepared using the method similar to one described previously [2]: About 2.00 g chitosan was dissolved in 60 mL of 1% (v/v) acetic acid. The chitosan solution was left overnight at room temperature. Then the chitosan solution was mixed with 40 mL B. subtilis suspension. The mixture was slowly dripped into 400 mL NaOH (0.25 mol/L) solution through a syringe with a pinhead to form beads. The spore-immobilized beads were cured for 4 h to enhance their mechanical stabilities. Finally, the beads were filtered, rinsed with sterile water until pH of the washing effluent was up to 7.0. The preparation of chitosan beads (CB) was similar to the above steps except the CB mixed with 40 mL distilled water instead of B. subtilis suspension. The sizes of BICB and CB were measured after the beads were shaped, and the diameter was 2-3 mm.
2.4 Characterization
The BICB before and after biosorption were coated with gold under reduced pressure and the surface morphological images were observed by a scanning electron microscope (QUANTA 200, USA). The existences of the functional groups on BICB before and after biosorption were confirmed by a Fourier-transform infrared spectroscope (Nicolet Nexus 670, USA).
2.5 Batch biosorption and isotherms experiments
Each experiment was carried out in 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 100 mL Cu(II) solution. About 3% (w/v) of BICB/CB were added into this solution, then the solution was stirred on a rotary shaker with 150 r/min at 37 °C for 12 h. The concentrations of Cu(II) before and after biosorption were measured by the atomic absorption spectrometer. Initial pH of the solution was adjusted to the required value by adding 0.1 mol/L HCl and 0.1 mol/L NaOH.
Adsorption isotherm was also performed at optimum conditions with different initial Cu(II) concentrations in the range of 5-300 mg/L. The system was maintained under shaking until adsorption equilibrium was reached. The batch kinetic studies were carried out under three different Cu(II) concentrations (10, 50 and 100 mg/L), and the samples were agitated for designated time periods (0-24 h). Experiments were conducted in triplicate and the average values were taken as result.
The removal efficiency (η) and adsorption amount of adsorbed metal ions (qt) were calculated as follows:
η=(ρi–ρt)×100/ρi (1)
qt=(ρi–ρt)V/m (2)
where ρi and ρt are the Cu(II) concentrations (mg/L) initially and at a given time t, respectively; V is the volume of the Cu(II) solutions; m is the mass of dry biosorbent. The dry masses of both BICB and CB were determined after drying at room temperature for 24 h.
2.6 Desorption
The desorption studies were performed using 3% (w/v) BICB with 100 mL of 50 mg/L Cu(II) solution. After adsorption experiments (12 h), the adsorbed metal ions were eluted with 0.1 mol/L NaOH. The eluted biosorbent was then washed thoroughly with distilled water until the pH of the elute solution reached 7.0 and placed into metal solution for the subsequent adsorption-desorption cycle.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 SEM analysis
The surface areas of BICB before and after Cu(II) biosorption were observed by SEM, and the SEM images are shown in Fig. 1. It can be clearly observed lots of tiny interspace structure distributing on the surface of the biosorbent from Fig. 1(a), thus provided maximum surface area for the biosorption of Cu(II) [14]. Figure 1(b) reveals that the surface of the biosorbent becomes rougher and more protrusions. This may attribute to reactions occurring on the surface of the biosorbent which afterwards changes the structure of BICB. Also, there is a great number of crystal and white granular substances adhered to the surface, which could be the adsorbed copper particles.

Fig. 1 SEM images of BICB before (a) and after (b) biosorption of Cu (II)
3.2 FTIR spectroscopy analysis
The FTIR spectra of BICB before and after Cu(II) biosorption are shown in Fig. 2. Figure 2(a) presents a strong and broad band which appears at around 3309 cm-1 corresponding to the stretching vibrations of N—H and O—H groups. The band at 2860 cm-1 can be assigned to C—H stretching combining with hydroxyls on methylene groups. The peak at 1629 cm-1 due to the secondary amide C=O bond contributed by the remaining acetamido groups. The characteristic absorption band appears at 1579 cm-1 corresponding to N—H bending vibration. The peaks at 1379 cm-1 and 1010 cm-1 attribute to C—H bending and C—O stretching vibration, respectively [10]. Figure 2(b) shows that the FTIR spectrum for Cu(II) loaded onto BICB has some slight changes. The biosorption peak of O—H stretching vibration shifts from 3309 to 3302 cm-1, which suggests the interactions between O—H groups and Cu(II) ions. The intensities of the peaks at 1377 cm-1 and 1022 cm-1 increase after the biosorption process, indicating that C—H and C—O functional groups also play important roles in Cu(II) biosorption.

Fig. 2 FTIR spectra of BICB before (a) and after (b) biosorption of Cu(II)
3.3 Effects of initial pH on Cu(II) adsorption
The pH of the aqueous solution is an important variable during the biosorption progress, because it can affect the protonation of functional groups such as phosphate, carboxyl and amino in the biomass as well as the chemical properties of the metals [15]. Figure 3 presents the effect of initial pH on the removal efficiency of Cu(II) onto BICB and CB by varying pH from 3 to 6.5. The lowest pH designed for this experiment was 3 because chitosan was easily dissolved in acid solution. As can be seen, the removal efficiencies of Cu(II) onto both adsorbents have the same trend, which increases with increasing pH. When the initial pH was adjusted to 3, a little Cu(II) was removed by BICB and CB. On one hand, a large number of H+ and H3O+ in the solution compete with Cu(II) ions for the binding sites on the BICB and CB surfaces and prevent deeper progress of reaction between Cu(II) ions and biosorbent [12]. On the other hand, the electrostatic repulsion exists between the metal cation and the protonated amino group, which prevents the active functional groups from dissociating and reduces the number of binding sites for adsorption of Cu(II) [16,17]. The removal efficiency of Cu(II) increases sharply at the pH range of 3-5 while it increases slightly after the pH is higher than 5. As the pH increases, the negative charge density on the surface of adsorbent increases and the ionic point of ligands such as carboxyl, hydroxyl and amino groups are free so as to promote interaction with the metal cations. When the initial pH is higher than 6.5, precipitation usually occurs with the metallic ions attached to hydroxide ions forming Cu(OH)2 and could lead to inaccurate interpretation of biosorption [2,11]. The cytoderm would dissociate more negatively charged groups in near neutral solution, offering more metal adsorption sites, enhancing the combination and reaction between functional groups and Cu(II). Therefore, pH 6 was chosen as the optimum pH. It is noted that the removal efficiency of Cu(II) on BICB is higher than that on CB at all pH ranges studied. That is because the B. subtilis has several functional groups such as carboxylic and hydroxyl which carry negative charges that allow the cell wall to combine with heavy metals [18]. Similar trend has been reported. WAN NGAH et al [19] investigated pH on chitosan/PVA beads and used pH 6 for further adsorption studies for Cu(II) adsorption. ZHAO et al [16] found that the adsorption amount of Cu(II) on chitosan gel beads increased as the pH increased and pH 6 was chosen as the optimum pH.

Fig. 3 Effects of pH for Cu(II) uptake on removal efficiency by BICB and CB
3.4 Effects of biosorbent dosage on Cu(II) adsorption
The biosorbent dosages of BICB and CB varying from 1.0% to 3.5% (w/v) were used in 50 mg/L Cu(II) solutions under pH 6 to test the effects on Cu(II) adsorption. As shown in Fig. 4, the removal efficiencies of Cu(II) using BICB and CB both increase with increasing biosorbent dose. As the biosorbent mass increases, the surface area of biosorbent also increases. It can be explained that the binding sites remain unsaturated during the adsorption reaction, thus more binding sites are available for the heavy metal ions, which enhances the interaction between Cu(II) ions and the biosorbent [20]. However, the removal efficiency of Cu(II) retains constant when the biosorbent dose continues to increase. This is due to the fact that higher biosorbent dose could produce a “screening” effect on the cell wall, protecting the binding sites, thus resulting in lower Cu(II) ions uptake [21]. Therefore, the optimum biosorbent dosage was taken as 3% (w/v) for further experiments.

Fig. 4 Effects of biosorbent dosage for Cu(II) uptake on removal efficiency by BICB and CB
3.5 Effects of temperature on Cu(II) adsorption
The effects of temperature on adsorption capacity of BICB and CB for Cu(II) are shown in Fig. 5. It can be seen from the figure that the adsorption capacity of BICB for Cu(II) increases as the temperature increases from 28 to 37 °C. The adsorption capacity passed through a maximum at 37 °C and then decreased with the temperature increasing to 43 °C. This small change at 28-37 °C leads to a great change in adsorption capacity (30.6 to 44.7 mg/g), which indicates that B. subtilis is very sensitive to the temperature. The effect of temperature on biosorption process mainly depends on two aspects, the processes of bioaccumulation and the mechanisms of cell metabolism. At lower temperatures, the adsorption capacity is low because of the weak activity and slow metabolism of the cells [22]. The adsorption capacity decreases at higher temperatures, which contributes to the damage of active binding sites in the biomass. Moreover, the high temperatures may reduce the ability of the cell membrane combining with metal ions and inhibit the exchange of Cu(II) ions with the biosorbent. On the other hand, the adsorption capacity of CB increases with increasing temperature, which indicates the endothermic nature of the adsorption process. Metal uptake using immobilized cells is more efficient than that without cells.

Fig. 5 Effects of temperature for Cu (II) uptake on adsorption capacity by BICB and CB
3.6 Effect of initial Cu(II) concentration on Cu(II) adsorption
Initial Cu(II) concentration was adjusted in the range of 5-300 mg/L for adsorption onto the BICB with pH 6 at 37 °C for 12 h. The removal efficiency and adsorption capacity at different Cu(II) concentrations are presented in Fig. 6. At a low Cu(II) concentration of 10 mg/L, the removal efficiency of BICB reaches a maximum of 98.4%, then reduces with the increase of initial Cu(II) concentration. The high biosorption efficiency (close to 99%) at low concentrations indicates the potential application of BICB for removal of a trace amount of Cu(II) from wastewater. The removal efficiency of Cu(II) drops sharply (55.4%) with an increase of initial Cu(II) concentration from 50 to 300 mg/L. This is due to the fact that the saturation of binding sites at high concentrations leads to more Cu(II) ions unadsorbed in solution [4]. In addition, the toxicity of Cu(II) accumulates rapidly in B. subtilis cells at high concentrations, which may reduce the biological activity of BICB and affect the multiplication of B. subtilis during biosorption process. However, the adsorption capacity of BICB grows up with increasing initial Cu(II) concentration, and reaches 97.5 mg/g at the initial Cu(II) concentration of 300 mg/L. This can be attributed to the fact that the higher Cu(II) concentrations increase the overall mass transfer driving force and thus the Cu(II) uptakes onto the biosorbent [21].

Fig. 6 Effects of initial concentration for Cu(II) uptake on removal efficiency and adsorption capacity by BICB
3.7 Effect of contact time on Cu(II) adsorption
The effects of contact time for BICB on the adsorption capacity with different initial concentrations (10, 50 and 100 mg/L) are shown in Fig. 7. It is observed that a rapid uptake occurs within the first 4 h and then followed by a slow increase until the equilibrium state is attained after 12 h at all the initial Cu(II) concentrations. After this equilibrium period, the amount of Cu(II) adsorbed does not change significantly with the time. The fast adsorption of the Cu(II) is probably due to the fact that abundant active binding sites are available on the biosorbents [23], which increases the ion exchange reaction in the aqueous solution. The experiment results support the assumption of two typical steps of biosorption process, which are rapid adsorption (physisorption) and slow accumulation (chemisorption) of heavy metals. It is obvious that the first step plays a major role in the biosorption process. Similar trend was reported in the case of chemically modified chitosan, where the adsorption capacity increased greatly with the contact time up to 9 h and then increased slightly until the equilibrium time was attained at 24 h [24].

Fig. 7 Effects of contact time for Cu(II) uptake on adsorption capacity by BICB
3.8 Adsorption isotherms
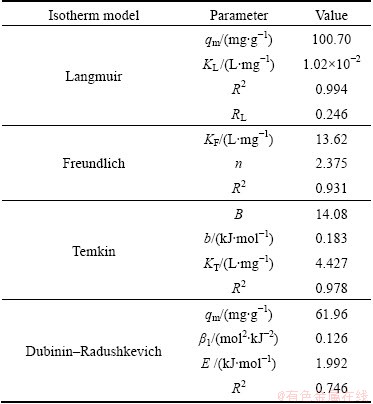
The isotherm studies were carried out at pH 6 with the initial concentrations from 5 to 300 mg/L at 37 °C for 12 h. Adsorption isotherms are significant for explaining the adsorption process and optimizing the use of adsorbent, which indicates how the adsorbate molecules distribute between the liquid phase and the solid phase when the system reaches an equilibrium state [25]. In order to determine the mechanism of Cu(II) adsorption onto the BICB, the experimental data were applied to the Langmiur, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin- Radushkevich (D-R) isotherm equations.
The Langmuir isotherm equation, which is the most commonly used and based on the monolayer adsorption on the active sites of the adsorbent, is represented in linear form as follows :
ρe/qe=KL/qm+ρe/qm (3)
where ρe is the equilibrium concentration in the solution; qm is the maximum adsorption capacity; qe is the amount of Cu(II) adsorbed per unit dry mass of biosorbents at equilibrium; KL is the Langmuir adsorption equilibrium constant.
The Langmuir isotherm experimental data were plotted as ρe/qe vs ρe and its linear fitting results are shown in Fig. 8(a). The Langmuir constants qm and KL were obtained by linear regression method and shown in Table 1. The experimental data exhibited high correlation with Langmuir model under the different concentrations. This result supports the assumptions of Langmuir model that the presence of a limit number of binding sites distribute over the biosorbent surface homogeneously, thus presenting the same affinity for biosorption of a single molecular layer [26]. A good biosorbent is considered to be characterized by a high qm value and a steep initial isotherm slope [9]. The qm and KL obtained in this study represent high affinity between the sorbent and sorbate, which also indicates that the BICB is a good biosorbent.

Fig. 8 Langmuir (a) and Freundlich (b) plots for biosorption of Cu(II) onto BICB
Table 1 Adsorption equilibrium constants obtained from Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin-Radushkevich isotherms in biosorption of Cu(II) onto BICB
The essential feature of Langmuir isotherm can be expressed by separation factor (RL), a dimensionless constant, can be represented as
RL=1/(1+KLρ0) (4)
where KL is the Langmuir constant and ρ0 is the initial concentration of Cu(II).
The calculated dimensionless factor RL is included in Table 1. The RL indicates the shape of the isotherm to be either unfavorable (RL>1), favorable (0
The Freundlich isotherm equation, which is used to explain the adsorption on a heterogeneous surface with uniform energy, is expressed in a linear form as follows:
lg qe=lg ρe/n+lg KF (5)
where KF and n are the Freundlich constants indicating the adsorption capacity and adsorption intensity, respectively.
The Freundlich data were plotted as lg qe vs lg ρe and its linear fitting results are shown in Fig. 8(b). The Freundlich isotherm constants and correlation coefficient (R2) are listed in Table 1. The Freundlich exponent KF and n show facile separation of metal ions from aqueous medium and give an indication of the favorability of adsorption. If n is less than 1, the adsorption intensity is favorable at all concentrations, but if the n is more than 1, the adsorption intensity is favorable at high concentrations but much less at low concentrations [27]. The value of n obtained is greater than 1 which indicates that the adsorption intensity is favorable at high concentrations.
The Temkin isotherm assumes that the heat of adsorption of all the molecules in the layer decreases linearly with coverage due to adsorbent-adsorbate interactions, and the adsorption is characterized by a uniform distribution of the binding energies, up to the maximum energy. It can be described as follows:
qe=[RTln(KTρe)]/b=Bln KT+Bln ρe (6)
where constant B=RT/b, which is related to the heat of adsorption; R is the mole gas constant; T is the temperature; b is the variation of a adsorption energy; KT is the equilibrium binding constant corresponding to the maximum binding energy.
A plot of qe vs ln ρe enables the determination of the isotherm constants B and KT from the slope and the intercept, respectively. Temkin isotherm parameters are listed in Table 1. The high correlation coefficient indicates the biosorbent showing good fitness of the isotherm. Typical bonding energy is reported to be 8-16 kJ/mol for ion-exchange mechanism and less than -40 kJ/mol for physisorption process [13]. The low value of b (0.183 kJ/mol) obtained in the present study indicates rather weak ionic interaction between the adsorbent and adsorbate, and the biosorption process seems to involve both chemisorption and physisorption.
The D-R model, which assumes the characteristic sorption curve is related to the porous structure of the adsorbent. The linear form of the D-R isotherm equation is
ln qe=ln qm-β1ε2 (7)
where β1 is the activity coefficient related to mean biosorption energy and ε is the Polanyi potential which is equal to RTIn(1+1/ρe).
The mean energy of sorption can be calculated as
E=1/(2β1)-0.5 (8)
where E gives the physical and chemical features of adsorption.
The curve was plotted and the values of qm and β1 were calculated from the intercept and slope given in Table 1. The correlation coefficient is lower than other three isotherm values, which indicates that the D-R equation represents the worse fit of experimental data than other isotherm equations. According to the literature, the energy ranges from 1.0 to 8.0 kJ/mol for physical adsorption and from 9.0 to 16.0 kJ/mol for chemical ion-exchange adsorption [24]. The energy for the biosorbent is very low (1.992 kJ/mol), which indicates weak interaction of Cu(II) with the BICB and the biosorption process may be attributed to physical adsorption. This supports the predictions from Temkin isotherm.
From Table 1, it is found that the biosorption process can be best represented by the Langmuir isotherm. The biosorption process involves both chemisorption and physisorption, and the dominant interaction between Cu(II) and the BICB is physical adsorption. The maximum adsorption capacity calculated from the Langmuir isotherm is 100.70 mg/g and it is higher than some other Cu(II) uptake adsorbents reported early. WAN NGAH and FATINATHAN [2] reported the maximum adsorption capacities of Cu(II) were 64.62, 67.66 mg/g onto chitosan beads and Chitosan-alginate beads, respectively. TSEKOVA et al [28] found the maximum Cu(II) uptake was 34.13 mg/g by immobilized Aspergillus niger. Compared with the literatures, the BICB exhibits a good capacity for removal of Cu(II) ions from aqueous solution.
3.9 Kinetics studies
In order to determine the controlling mechanisms of biosorption process, such as mass transfer and chemical reaction, four kinetic models were used to interpret the experimental data. The kinetics studies were carried out at pH 6 and 37 °C using three different initial Cu(II) concentrations (10, 50 and 100 mg/L). The linear form of pseudo-first-order kinetic model is given as
lg(qe–qt)=lg qe–k1t/2.303 (9)
where qe and qt are the amounts of adsorbed Cu(II) on the biosorbent at equilibrium and at time t, respectively, and k1 is the first-order adsorption rate constant.
On the other hand, the linear form of pseudo- second-order model is expressed as
t/qt=qe2/k2+t/qe (10)
where k2 is the pseudo-second-order adsorption rate constant.
The pseudo-first-order experimental data were plotted as lg(qe–qt) vs t while the pseudo-second-order data were plotted as t/qt vs t and the linear fitting results are shown in Fig. 9. The calculated results of these two kinetic equations are given in Table 2. It is found that the pseudo-first-order plot does not adequately describe the adsorption results with a low correlation coefficient. Generally, the pseudo-first-order model is applicable for the initial stage of the biosorption processes and does not fit well to the whole range of contact time [29]. It is observed from Fig. 9(b) and Table 2 that the pseudo- second-order plots are all linear with correlation coefficients higher than 0.999, which indicates that the pseudo-second-order kinetic model fits well with the experimental data. The pseudo-second-order kinetic model assumes that the adsorption capacity of adsorbent is proportional to the number of active sites on its surface, and the rate-limiting step may be chemical adsorption involving valency forces through sharing or exchange of electrons between adsorbent and adsorbate [30] The pseudo-second-order kinetic rate constants (k2) decrease with the increase of initial Cu(II) concentration. This may attribute to more Cu(II) ions existing in solution at high concentrations. They compete against each other and induce a delay in the attainment of equilibrium and lower k2 values. The high applicability of the pseudo- second-order equation of Cu(II) ions onto various adsorbents was also observed [21,24].

Fig. 9 Pseudo-first-order (a) and pseudo-second-order (b) kinetic plots of Cu(II) onto BICB at various initial concentrations
The biosorption data were further analyzed using the Elovich and intraparticle diffusion models. The Elovich equation is suitable to describe the nature of chemical adsorption in the biosorption process and the linear form is given as
qt=(1/β)ln(αβ)+(1/β)ln t (11)
where α is the initial sorption rate constant, and β is related to the extent of surface coverage and activation energy for chemisorption.
The parameters of the Elovich equation were obtained by plotting qt vs ln t and shown in Table 2. The correlation coefficients obtained from this model are lower compared with those of the pseudo-second-order equation, but it can also describe the kinetics of Cu(II) biosorption onto BICB. The value of β increases from 16.710 to 2.9×1060, which shows the correspondingly increasing trend of biosorption rate for Cu(II) ions at higher concentrations. This may be due to the increasing surface coverage on the biosorbent. Similar trend has been found in other studies. ILLANES et al [31] reported that the higher initial sorption rates give smaller α and the parameter β reaches the maximum when it is represented in a lg—lg plot vs the metallic ion concentration with PSf-MS and SAN-MS.
Table 2 Kinetic parameters for adsorption of Cu(II) onto BICB based on different models

In order to investigate whether the biosorption of Cu(II) onto BICB involves multi-step process or not, intraparticle diffusion model is exploited to analyze the experimental data. The intraparticle diffusion equation is expressed as
qt=kit0.5+C (13)
where ki is the intra-particle diffusion rate and constant C is the intercept.
The plots of qt vs t1/2 at different initial Cu(II) concentrations are shown in Fig. 10 and the values of ki are listed in Table 2. It can be seen from Fig. 10 that the plots present a multilinearity, indicating that two or more steps take place during the biosorption process. It is observed that all the plots have an initial curve portion, following by a linear portion and an equilibrium region. The first sharper portion of the plots is due to the external surface biosorption onto BICB, which assumes instantaneous adsorption of this stage. The second linear portion of curves indicates the gradual adsorption stage, where the intraparticle diffusion is rate-controlled. After this space of time, the systems penetrate into the final equilibrium state and the saturation of the biosorbents is observed. Based on the results it may be concluded that the intraparticle diffusion is not only the rate-limiting step for the whole biosorption process [32].

Fig. 10 Intraparticle diffusion kinetic plots of Cu(II) onto BICB at various initial concentrations
3.10 Desorption study
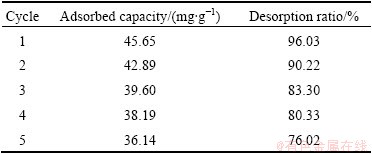
The desorption study is also important because it is useful in the recycling of the adsorbent and recovery of heavy metals. Desorption experiments were conducted with EDTA, HCl, and NaOH. It was observed that the desorption ratio of Cu(II) with EDTA and HCl was much lower than that with NaOH in the first cycle. Perhaps due to the speciation of copper, the surface charge of the adsorbent has changed into the alkaline medium which would weaken the electrostatic interaction between the BICB and the Cu(II) ions, promoting desorption. Hence, further experiments were carried out only with 0.1 mol/L NaOH solution. Table 3 lists the adsorption capacity and desorption ratio of Cu(II) on the BICB in 5 adsorption-desorption cycles. Complete desorption is not possible, perhaps due to the involvement of non-electrostatic forces between the BICB and the Cu(II) ions [13]. It is found that the adsorption capacity and desorption ratio of BICB only decrease by 4.35 mg/g and 3.97% after the first cycle and could still be maintained at 36.14 mg/g and 76.02% at the 5th cycle. The results indicate that the BICB can be successfully regenerate and repeatedly use in Cu(II) ions adsorption study without appreciable losses in their adsorption capacities.
Table 3 Desorption ratio of adsorbed Cu(II) onto BICB
4 Conclusions
1) Cu(II) ions could be effectively adsorbed by Bacillus subtilis immobilized into chitosan beads.
2) FTIR analyses suggest that O—H, C—H and C—O are involved in the removal mechanism of Cu(II).
3) The pH, biosorbent dose, temperature, initial Cu(II) concentration and contact time highly affect the Cu(II) biosorption, and the Cu(II) uptake using BICB is more efficient compared with CB.
4) The equilibrium studies were described by four isotherm models. Among these models, the Langmuir isotherm illustrates the best description of the metal adsorption mechanism and the maximum adsorption capacity of Cu(II) is 100.70 mg/g.
5) The kinetic results show that the pseudo-second- order model agrees best with correlation coefficients higher than 0.999. The mechanism involves both chemisorption and physisorption, and the dominant interaction between Cu(II) and the BICB is physical adsorption.
6) The desorption rate is maintained at 76.02% after 5 cycles. It suggests that the novel BICB is a great potential and low-cost heavy metal biosorbent.
References
[1] Vijayaraghavan K, Yun Y S. Bacterial biosorbents and biosorption [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2008, 26: 266-291.
[2] WAN Ngah W S, Fatinathan S. Adsorption of Cu(II) ions in aqueous solution using chitosan beads, chitosan-GLA beads and chitosan-alginate beads [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2008, 143: 62-72.
[3] Lesmana S O, Febriana N, Soetaredjo F E, SUNARSO J, ismadji s. Studies on potential applications of biomass for the separation of heavy metals from water and wastewater [J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2009, 44: 19-41.
[4] Yang Chun-ping, Wang Jia-qiang, LEI Min, XIE Geng-xin, ZENG Guang-ming, LUO Sheng-lian. Biosorption of zinc(II) from aqueous solution by dried activated sludge [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2010, 22(5): 675-680.
[5] FENG Ning-chuan, GUO Xue-yi, LIANG Sha. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies on biosorption of Cu(II) by chemically modified orange peel [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19(5): 1365-1370.
[6] Zahoor A, Rehman A. Isolation of Cr(VI) reducing bacteria from industrial effluents and their potential use in bioremediation of chromium containing wastewater [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2009, 21: 814-820.
[7] Tsekova K, Todorova D, Ganeva S. Removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewater by free and immobilized cells of Aspergillus niger [J]. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 2010, 64: 447-451.
[8] Ji Yu-lan, Gao Hong, Sun Jin-sheng, FANG Cai. Experimental probation on the binding kinetics and thermodynamics of Au(III) onto Bacillus subtilis [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 172, 122-128.
[9] Frost P C, Maurice P A, Fein J B. The effect of cadmium on fulvic acid adsorption to Bacillus subtilis [J]. Chemistry Geology, 2003, 200: 217-224.
[10] ArIca M Y,  G, YIlmaz M, BEKTAS S, GENC
G, YIlmaz M, BEKTAS S, GENC  . Biosorption of Hg2+, Cd2+, and Zn2+ by Ca-alginate and immobilized wood-rotting fungus Funalia trogii [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2004, B109: 191-199.
. Biosorption of Hg2+, Cd2+, and Zn2+ by Ca-alginate and immobilized wood-rotting fungus Funalia trogii [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2004, B109: 191-199.
[11] Dalida M L P, Mariano A F V, Futalan C M, KAN C C, TSAI W C, WAN M W. Adsorptive removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions using non-crosslinked and crosslinked chitosan-coated bentonite beads [J]. Desalination, 2011, 275: 154-159.
[12] Peng Qing-qing, Liu Yun-guo, Zeng Guang-ming, XU Wei-hua, YANG Chun-ping, ZHANG Jing-jin. Biosorption of copper(II) by immobilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae on the surface of chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles from aqueous solution [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 177: 676-682.
[13] Hu Xin-jiang, Wang Jing-song, Liu Yun-guo, LI Xin, ZENG Guang-ming, BAO Zheng-lei, ZENG Xiao-xia, CHEN An-wei, LONG Fei. Adsorption of chromium(VI) by ethylenediamine- modified cross-linked magnetic chitosan resin: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 185: 306-314.
[14] GANDHI M R, KOUSALYA G N, MEENAKSHI S. Removal of copper(II) using chitin/chitosan nano-hydroxyapatite composite [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2011, 48, 119-124.
[15] WITEK-KROWIAK A, Szafran R G, Modelski S. Biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions onto peanut shell as a low-cost biosorbent [J]. Desalination, 2011, 265: 126-134.
[16] Zhao Fan, Yu Bin-yu, Yue Zheng-rong, WANG Ting, WEN Xian, LIU Zong-bin, ZHAO Chang-sheng. Preparation of porous chitosan gel beads for copper(II) ion adsorption [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 147: 67-73.
[17] LUO Jin-ming, XIAO xiao, LUO Sheng-lian. Biosorption of cadmium(II) from aqueous solutions by industrial fungus Rhizopus cohnii [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20: 1104-1111.
[18] Dundar M, Nuhoglu C, Nuhoglu Y. Biosorption of Cu(II) ions onto the litter of natural trembling poplar forest [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 151: 86-95.
[19] WAN Ngah S W, Kamari A, KOAY Y J. Equilibrium and kinetics studies of adsorption of copper(II) on chitosan and chitosan/PVA beads [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2004, 34: 155-161.
[20] Wang Jing-song, Hu Xin-jiang, Liu Yun-guo, XIE Shui-bo, BAO Zheng-lei. Biosorption of uranium(VI) by immobilized Aspergillus fumigatus beads [J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactive, 2010, 101: 504-508.
[21] Yahaya Y A, Don M M, Bhatia S. Biosorption of copper(II) onto immobilized cells of Pycnoporus sanguineus from aqueous solution: Equilibrium and kinetic studies [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 161: 189-195.
[22] Zhang Jing-jin, Liu Yun-guo, Zhang Wei, ZENG Guang-ming, XU Wei-hua, MIN Zong-yi, PENG Qing-qing, XIAO Yu. Optimization immobilizing activated carbon and bacteria by sodium alginate and its character of adsorption of Pb2+ [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2010, 31(11): 2684-2690. (in Chinese)
[23] Ren Yue-ming, Wei Xi-zhu, ZHANG Mi-lin. Adsorption character for removal Cu(II) by magnetic Cu(II) ion imprinted composite adsorbent [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 158: 14-22.
[24] Kannamba B, LAXMA Reddy K, AppaRao B V. Removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions using chemically modified chitosan [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 175: 939-948.
[25] WAN Ngah W S, Fatinathan S. Pb(II) biosorption using chitosan and chitosan derivatives beads: Equilibrium, ion exchange and mechanism studies [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2010, 22(3): 338-346.
[26] Abu Al-Rub F A, El-Naas M H, Ashour I, AL-MARZOUQI m. Biosorption of copper on Chlorella vulgaris from single, binary and ternary metal aqueous solutions [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2006, 41: 457-464.
[27] Kumar U, Bandyopadhyay M. Sorption of cadmium from aqueous solution using pretreated rice husk [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2006, 97: 104-109.
[28] Tsekova K, Todorova D, Dencheva V, GANEVA S. Biosorption of copper(II) and cadmium(II) from aqueous solutions by free and immobilized biomass of Aspergillus niger [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101: 1727-1731.
[29] Chatterjee S, Woo S H. The removal of nitrate from aqueous solutions by chitosan hydrogel beads [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 164: 1012-1018.
[30]  Y, Aktay Y. Kinetic studies on sorption of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) ions by chitin, chitosan and Rhizopus arrhizus [J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2002, 12: 143-153.
Y, Aktay Y. Kinetic studies on sorption of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) ions by chitin, chitosan and Rhizopus arrhizus [J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2002, 12: 143-153.
[31] ILLANES C O, oCHOA N A, MARCHESE J. Kinetic sorption of Cr(VI) into solvent impregnated porous microspheres [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2008, 136: 92-98.
[32] Subbaiah M V, Vijaya Y, SUBBA Reddy A, YUVARAJA G, KRISHNAIAH A. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies on the biosorption of Cu(II) onto Trametes versicolor biomass [J]. Desalination, 2011, 276: 310-316.
刘云国1,2,廖 婷1,2,贺仲兵1,2,李婷婷1,2,王 慧1,2,胡新将1,2,郭一明1,2,何 缘1,2
1. 湖南大学 环境科学与工程学院,长沙 410082;
2. 湖南大学 环境生物与控制教育部重点实验室,长沙 410082
摘 要:研究了壳聚糖固定化枯草芽孢杆菌吸附铜离子的性能,分析了pH、吸附剂投加量、温度、铜离子初始浓度和时间对铜离子吸附的影响。结果表明, pH对铜离子的吸附有较大的影响。此外,固定化枯草芽孢杆菌吸附剂比空白吸附剂具有更强的吸附性能。整个吸附过程符合朗缪尔吸附模型(R2=0.994),最大吸附量为100.70 mg/L。动力学模型拟合结果表明,实验符合准二级动力学模型,线性相关指数大于0.999。吸附剂能在0.1 mol/L NaOH溶液中被成功解吸。
关键词:生物吸附;枯草芽孢杆菌;固定化枯草芽孢杆菌;Cu(II);吸附平衡;动力学
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (11JJ2031) supported by the Key Project of Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China; Project (2009SK3029) supported by the Plan Science and Technology Department of Hunan Province, China
Corresponding author: Yun-guo LIU; Tel: +86-731-88649208; Fax: +86-731-88822829; E-mail: yunguoliu12@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62664-3

