DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2019.06.009
炉体冷却壁黏结物物相及形成机理
马恒保1,张建良1,焦克新1,周云花2,但家云2
(1. 北京科技大学 冶金与生态工程学院,北京, 100083;
2. 湖南华菱湘潭钢铁有限公司技术中心,湖南 湘潭,411101)
摘要:基于湘钢3号高炉破损调查,对高炉炉腰、炉腹以及炉身下部的黏结物进行取样,通过X线衍射(XRD)以及扫描电镜-能谱分析(SEM-EDS)等手段,系统研究高炉不同位置黏结物的化学成分及微观形貌,分析高炉炉体冷却壁黏结物的物相组成和形成机理。研究结果表明:高炉炉体不同高度部位黏结物的物相组成和沉积行为显著不同,黏结物的物相主要为氧化锌-C和渣铁混合物。结合氧化锌在冷却壁热面沉积行为的热力学条件,分析氧化锌-C型黏结物因氧化锌易被还原而导致黏结物频繁脱落,不利于高炉炉体冷却壁长寿,而形成的高炉渣铁黏结物可以有效地隔离高温物料、煤气与冷却壁的直接接触,延缓物料对冷却壁的磨损等侵蚀,保障高炉冷却壁的寿命。
关键词:炉体;冷却壁;黏结物;长寿技术
中图分类号:TF534 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2019)06-1326-08
Composition and formation mechanism of adhesive in blast furnace cooling stave
MA Hengbao1, ZHANG Jianliang1, JIAO Kexin1, ZHOU Yunhua2, DAN Jiayun2
(1. School of Metallurgical and Ecological Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing,Beijing 100083, China;
2. Hunan Hualing Xiangtan Iron and Steel Co. Ltd., Xiangtan 411101, China)
Abstract: Based on the damage investigation of No. 3 blast furanc(BF) in Xiangtan Iron and Steel Co., the adhesive of the blast furnace belly, bosh and the lower part of furnace shaft were sampled. Through X-ray diffraction(XRD) and scanning electron microscope-energy dispersive spectrometer(SEM-EDS)analysis, the chemical composition and microstructure of the adhesive at different positions of BF were systematically studied, and the phase composition and formation mechanism of the adhesive were investigated. The results show that the phase composition and deposition behavior of the adhesive at different heights of the BF body are significantly different. The main phase of the adhesive is zinc oxide-C and slag-iron mixture. Combined with the thermodynamic conditions of the deposition behavior of zinc oxide on the hot surface of the cooling stave, analysis is made and it is found that the zinc oxide-C adhesive is frequently collapsed due to zinc oxide reduction, which is not conducive to the longevity of the BF body. The formed slag-iron adhesive can effectively isolate the direct contact between high-temperature materials, gas and cooling stave, delay the erosion of cooling stave, thereby ensure the long campaign of the BF cooling stave.
Key words: blast furnace(BF); cooling stave; adhesive; long campaign technology
安全长寿是当代高炉的发展趋势,而炉腰、炉腹及炉身下部区域的寿命是高炉长寿的限制性环节[1-4]。在高炉整体结构中,炉腰、炉腹及炉身下部区域热负荷高[5-6],热流冲击大,工作环境恶劣,而且高炉强化冶炼、炉料结构变化以及操作的不稳定等会加速该区域的侵蚀,导致冷却设备损坏。冷却壁热面形成的黏结物能够隔离高温渣铁和煤气流,避免其受到侵蚀和冲刷,降低自身温度,从而保障冷却设备安全。近年来,高炉渣皮脱落频繁发生,严重影响高炉正常生产[7-9]。张芳等[10]通过包钢1号高炉中修,对5~8段冷却壁渣皮取样,并通过半球法与相图分析初渣及中间渣的软熔性质。梁南山[11]通过涟钢1号高炉解剖发现其冷却壁渣皮主要是氧化锌,并含有少量金属颗粒及铅氧化物或硫化物、砷化物、锡酸钙等。然而,目前并未明确冷却壁黏结物的形成和脱落机理。本文作者以湘钢3号高炉冷却壁黏结物为研究对象,从黏结物的化学成分、物相组成以及微观形貌并结合热力学阐述冷却壁黏结物的形成和脱落机理,以便为研究高炉冷却壁长寿的长效机制提供依据。
1 研究内容与方法
1.1 高炉概况
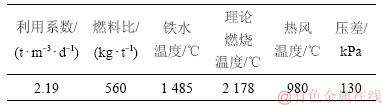
本文以湘钢3号高炉为研究对象,其有效炉容为1 080 m3,于2005年建成投产,产量为2 360 t/d,2015年停炉,其炉役后期主要生产技术指标如表1所示。湘钢3号高炉炉缸直径为8 m,炉腰直径为9.1 m,炉身角为83.71°,炉腹角为79.26°,其炉腹、炉腰部位(6~7段)采用双层铸铁小块冷却壁,炉身下部(8~13段)采用铜冷却板加小块铸铁冷却壁,炉腰、炉腹部位内衬为高铝砖,炉身下部采用喷涂黏土耐火泥的铝炭砖作为内衬。
表1 湘钢3号高炉炉役后期主要生产技术指标
Table 1 Main production indexes of No. 3 BF in Xiang steel at later stage of furnace operation
1.2 取样方案
在湘钢3号高炉破损调查期间,勘察炉腰、炉腹以及炉身下部,发现高炉6~8段冷却壁出现破损,其中炉腰部位(7段)和炉身下部(8段)冷却壁破损较严重,部分未破损冷却壁热面存在一定厚度的黏结物和镶砖。在冷却壁拆除过程中,分别对高炉炉腹、炉腰及炉身下部冷却壁的黏结物取样,取样位置如图1所示。
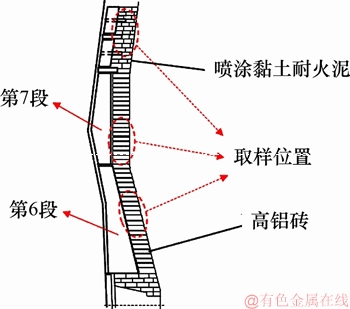
图1 湘钢3号高炉黏结物取样示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of sampling cement in No.3 BF of Xiang steel
图2所示为湘钢3号高炉炉体铜冷却壁热面不同高度部位的氧化锌黏结物和渣铁黏结物的宏观形貌。由图2可以看出:氧化锌黏结物呈现的颜色主要为黑色和黄绿色相间,物相结构松散,极易粉碎;炉腰及炉身下部氧化锌黏结物厚度约10 mm,炉腹氧化锌黏结物厚度约70 mm。图2(d)中黏结物与镶砖具有明显的分层结构,热面为结构致密的渣铁层;中间为黄绿色结构稀疏的氧化锌层;靠近冷却壁处为高铝砖砖衬。炉腹渣皮主要为黑色多孔较为坚硬渣相黏结物,厚度为60~70 mm。

图2 湘钢3号高炉黏结物宏观形貌
Fig. 2 Macroscopic morphology of adhesive in No.3 BF of Xiang steel
1.3 研究方法
使用玛瑙研钵将黏结物样品研磨至粒径小于0.074 mm,利用X线荧光分析(XRF)和X线衍射分析(XRD)分别检测分析黏结物粉末的化学成分和物相。使用切割机把样品切割成长×宽×高为15 mm×10 mm×5 mm的电镜试样,并采用环氧树脂固定,磨样、喷金后通过扫描电子显微镜-能谱仪(SEM-EDS)分析黏结物的微观形貌及物相分布。
2 黏结物化学成分及物相组成
2.1 高炉冷却壁黏结物化学成分
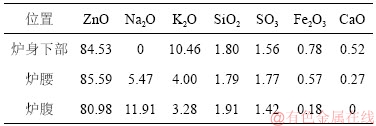
高炉炉体不同部位黏结物的化学成分如表2所示。由表2可以看出:不同部位氧化锌黏结物化学成分主要为氧化锌,质量分数在 80% 以上,碱金属氧化物(Na2O和K2O)质量分数为4%~12%。高炉炉腰、炉腹及炉身下部不同高度部位黏结物的质量分数有较大差异。
表2 不同位置氧化锌黏结物的化学成分(质量分数)
Table 2 Chemical composition mass fraction of zinc oxide adhesive at different positions %
高炉炉腹部位黏结物除了含锌黏结物外,还含有大量的渣铁黏结物。表3所示为炉腹渣铁黏结物化学成分与高炉终渣的化学成分。由表3可以看出:高炉炉腹黏结物渣相的二元碱度R2为0.95,并含有少量的氧化钾、含铁氧化物以及氧化锌等,成分与高炉终渣成分存在显著差别。
2.2 黏结物的物相组成
不同高度位置黏结物的XRD图谱如图3所示。由图3(a)可见:通过MDI Jade 6.4 分析,发现炉腰、炉腹及炉身下部氧化锌黏结物的特征峰一致,不同位置的氧化锌黏结物的物相均为ZnO(PDF #36-1451),黏结物中含有一定质量分数的钾和钠元素,但在XRD图谱中并未检测到碱金属的特征峰,主要是氧化锌含量高,特征峰强度高,碱金属难以表征。由图3(b)可以看出:炉腹部位渣皮的主要矿相为镁黄长石相(Ca2Mg0.75Al0.5Si1.75O7 PDF #79-2424)以及少量的六方钾霞石(KAlSiO4)和硫化锌(ZnS)。
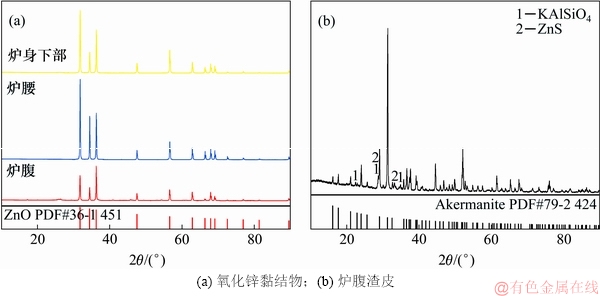
图3 湘钢3号高炉冷却壁黏结物的XRD图谱
Fig. 3 XRD pattern of cooling stave adhesive in No. 3 blast furnace of Xiang steel
3 黏结物形成机理分析
3.1 氧化锌黏结物的形成机理
锌在高炉原燃料中是一种微量元素,主要以硫化锌(ZnS)、氧化锌(ZnO)、铁酸锌(ZnO·Fe2O3)以及硅酸盐(2ZnO·SiO2)的形式存在[12-15]。在1 100~1 500 ℃的高温区内,含锌化合物被还原为单质锌[16],到达温度较低区域时冷凝再氧化,部分随煤气排出,部分随炉料下降,在高炉内形成锌的循环富集。经高炉解剖发现:锌在高炉内的富集倍数达到80[17],湘钢3号高炉炉役后期锌负荷在0.75 kg/t以上,处于较高水平,在冷却壁热面形成大量的氧化锌黏结物。

图4 炉身下部氧化锌黏结物微观结构
Fig. 4 Microstructures of Zinc Oxide adhesive at lower shaft of blast furance
图4、图5和图6所示分别为炉身下部、炉腰以及炉腹部位氧化锌黏结物的微观结构。由图4可见:炉身下部黏结物中氧化锌以网络状结构分布在碳基体中,钾元素均匀分布在碳中。由图5可见:炉腰部位氧化锌黏结物表面覆盖一层片状氧化钾,碳主要以颗粒状存在于氧化锌基体中。由图6可见:炉腹部位氧化锌黏结物中氧化锌以团簇的形状分布在黏结物中。高炉不同部位氧化锌黏结物含量和形态的变化表明氧化锌在高炉中沉积行为不同。
表3 炉腹渣铁黏结物与终渣的化学成分(质量分数)对比
Table 3 Comparison of chemical composition mass fraction of slag skin and final slag %
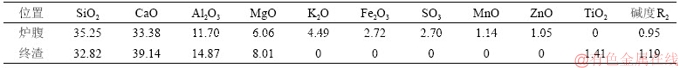
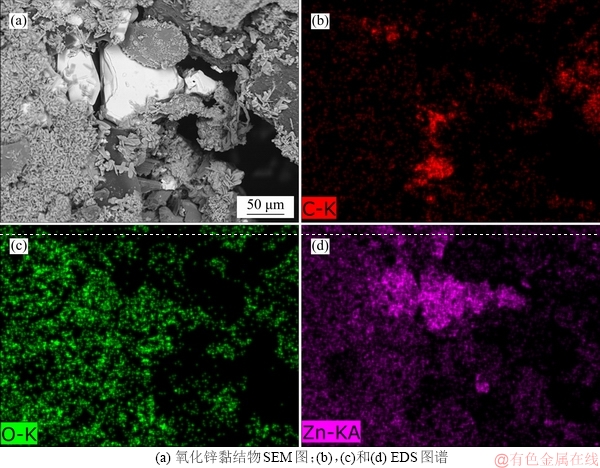
图5 炉腰氧化锌黏结物微观结构
Fig. 5 Microstructures of zinc oxide adhesive in belly
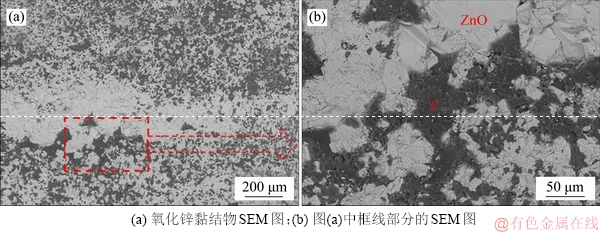
图6 炉腹氧化锌黏结物微观结构
Fig. 6 Microstructure of zinc oxide adhesive in bosh
氧化锌黏结物在高炉内形成和脱落过程如图7所示。在高炉炉腹高温区,氧化还原主要受CO2+C=2CO反应的控制[14],锌蒸气被CO氧化,发生以下反应:
Zn+CO=ZnO+C, △Gθ=-183 683.1+114.993T (1)
计算表明:标准态下当温度小于951 ℃时,锌蒸气开始被CO氧化沉积,而实际高炉冶炼条件下,炉腹冷却壁热面温度相对较低,锌能够被氧化形成氧化锌-C黏结物。
在中温区氧化还原位主要受FeO+CO=Fe +CO2反应的控制[18],锌蒸气的氧化反应如下:
图7 湘钢3号高炉黏结物的形成和脱落机理
Fig. 7 Formation and shedding mechanism of adhesives in No.3 BF of Xiangsteel
Zn+CO2=ZnO+CO, △Gθ=-356 374.3+291.098T (2)
随着煤气中CO2含量的增加,锌蒸气主要由CO2氧化,黏结物中碳元素沉积减少,形成的黏结物主要为氧化锌。
在低温区,CO会发生析碳反应,形成的黏结物主要是碳,少量的氧化锌沉积在碳中,形成网络状结构。
在高炉实际冶炼条件下,氧化锌的还原温度较低,当温度大于锌的沸点(908 ℃)时,氧化锌即能被还原。因此,在高炉内形成的氧化锌黏结物稳定性差,容易脱落,黏结物脱落部位炉衬和冷却壁温度急剧升高,且形成的锌蒸气会侵蚀炉衬,导致炉衬减薄,缩短冷却壁运行寿命。
3.2 渣铁黏结物的形成机理
图8为高炉炉腰高铝砖及其热面黏结物的微观结构。从图8(a)和图8(c)可以看出:镶砖热面黏结物具有明显的分层现象,主要分为渣铁层和氧化锌层。由图8(b)中P1和P2微区的EDS结果可见:渣相和铁中都含有一定质量分数的锌,主要是煤气流中锌和钾的进入造成的。
P1微区渣相的EDS结果按照100%折算后的结果如表4所示。由表4可知:渣相二元碱度为0.37,并含有一定质量分数的氧化亚铁,是一种典型的高炉初渣。图8(d)所示为高铝砖内部微观形貌,砖衬内部出现大量的氧化锌沉积,砖衬产生裂纹和粉化现象。锌在高炉内的循环富集导致砖衬破裂,减少高炉冷却壁的使用寿命,而热面渣铁层的形成会阻止氧化锌的侵蚀,从而保护砖衬。
图9所示为炉腹部位渣皮的微观结构。由图9(a)可见:金属铁与渣之间润湿性较好,且尺寸较小。由图9(b)可见:金属铁尺寸较大,且与渣之间存在明显缝隙。
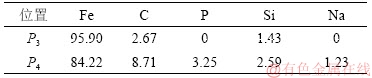
通过EDS对炉腹渣皮中P3和P4微区金属铁分析化学成分,其结果如表5所示。由表5可知:2种金属铁的化学成分明显不同,P3微区金属铁主要是Fe,C和Si,P4微区金属铁C含量明显增加,且含有少量的P和Na元素,表明渣皮中金属铁的来源不同。
在炉腹部位渣皮形成过程中,图9(a)中金属铁主要是由于渣相中FeO被边缘煤气流中的CO还原形成;另一部分主要是在炉渣凝固过程中,少量的从上部滴落的金属铁未从炉渣中分离。通过Factsage热力学软件计算炉腹渣皮的固相线温度为1 180 ℃,当砖衬热面温度低于该温度时,渣皮能够稳定存在。
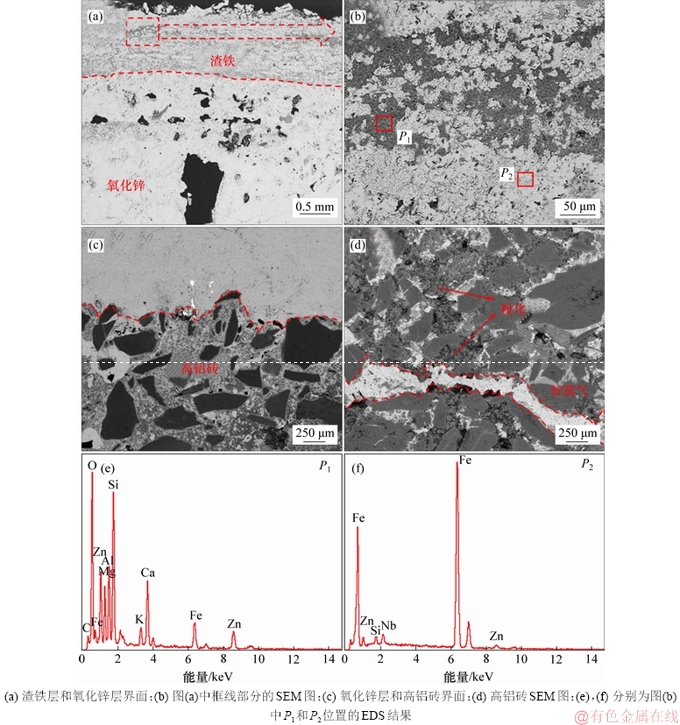
图8 炉腰高铝砖及其热面渣皮的微观结构
Fig. 8 Microstructures of high aluminum brick and hot surface slag skin in belly
表4 渣铁层中渣相的化学成分(质量分数)
Table 4 Chemical composition mass fraction of slag phase iniron layer %

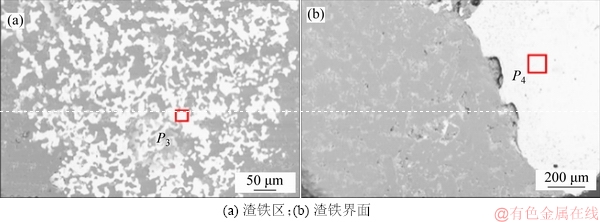
图9 炉腹渣皮微观结构
Fig. 9 Microstructures of slag skin in bosh
表5 渣皮中金属铁的化学成分(质量分数)
Table 5 Chemical composition mass fraction of metallic iron in slag skin %
4 结论
1) 湘钢3号高炉破损调查发现,高炉冷却壁黏结物主要有2种,即氧化锌-C黏结物和渣铁黏结物。
2) 高炉不同温度区间内,氧化锌-C黏结物的沉积行为不同,且氧化锌易还原,稳定性差,氧化锌-C黏结物频繁出现脱落现象,且脱落形成的锌蒸气会侵蚀炉衬,不利于冷却壁的长寿。
3) 在一定冶炼强条件下,渣铁黏结物能够稳定存在,隔离煤气、渣铁及物料与冷却壁的直接接触,实现高炉冷却壁长寿。
参考文献:
[1] 张寿荣. 以科学发展观审视21世纪的中国高炉炼铁[J].钢铁, 2008, 43(11): 1-8.
ZHANG Shourong. On chinese blast furnace ironmaking in the 21st century from the viewpoint of scientific development[J]. Iron and Steel, 2008, 43(11): 1-8.
[2] REINOUD V L, E. VAN STEIN C, MAARTEN G, et al. Blast furnace hearth management for safe and long campaigns[C]//ISSTECH International Technology Conference Proceedings. Indianapolis, Indiana, 2003, 30(8): 123-130.
[3] 魏丽.我国高炉使用铜冷却壁10年来的回顾[J]. 炼铁, 2012, 31(3): 13-15.
WEI Li.Comments on 10 years application of copper cooling stave[J]. Ironmaking, 2012, 31(3): 13-15.
[4] 蒋玲. 高炉铜冷却壁的应用及分析[J]. 钢铁研究, 2003, 31(4): 1-5, 29.
JIANG Ling. Application and analysis of copper stave used in blast furnace[J]. Research on Iron & Steel, 2003, 31(4): 1-5, 29.
[5] 张恒, 张建良, 焦克新, 等. 高炉板壁结合冷却器破损原因解析[J]. 钢铁, 2018, 53(8): 28-37.
ZHANG Heng, ZHANG Jianliang, JIAO Kexin, et al. Analysis on damage cause to stave-plate compound cooling system of a commercial blast furnace [J]. Iron and Steel, 2018, 53(8): 28-37.
[6] WU Lijun, XU Xun, ZHOU Weiguo, et al. Heat transfer analysis of blast furnace stave[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2008, 51(11/12): 2824-2833.
[7] 刘云彩. 高炉渣皮脱落分析[J].中国冶金,2014, 24(12): 32-35.
LIU Yuncai. Analysis of blast furnace slag fall-off[J]. China Metallurgy, 2014, 24(12): 32-35.
[8] 丁德刚, 李刚, 张华伟, 等. 宁钢2号高炉渣皮脱落的应对措施[J]. 炼铁, 2017, 36(5): 35-37.
DING Degang, LI Gang, ZHANG Huawei ,et al. Measures for slag skin shedding of No.2 blast furnace in Ning steel[J]. Ironmaking, 2017, 36(5): 35-37.
[9] 范崇强, 王飞, 李永胜. 鞍钢3号高炉控制渣皮脱落措施的研究[C]. //中国金属学会. 2014年全国炼铁生产技术会暨炼铁学术年会论文集. 郑州: 中国金属学会, 2014: 174-176.
FAN Chongqiang, WANG Fei, LI Yongsheng. The study of control measures on slag crust fall off for No.3 blast furnace in An steel[C]. //The Chinese Society for Metals. 2014 Annual National Ironmaking Technology and Academic Conference. Zhengzhou: The Chinese Society for Metals, 2014: 174-176.
[10] 张芳, 安胜利, 罗果萍, 等. 高炉初渣及中间渣软熔性质的研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2014, 35(5):98-102.
ZHANG Fang, AN Shengli, LUO Guoping, et al. Study on softening melting properties of BF primary slag and medium-term slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014, 35(5): 98-102.
[11] 梁南山. 关于涟钢高炉渣皮形态的研究[J]. 涟钢科技与管理, 2013(3): 21-27.
LIANG Nanshan. Study on the shape of slag skin of BF [J]. Lianyuan Science Technology & Management, 2013(3): 21-27.
[12] 周传典. 高炉炼铁生产技术手册[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社,2002: 115-116.
ZHOU Chuandian. Blast furnace ironmaking production technical manual[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2002: 115-116.
[13] 张芳, 张世忠, 罗果萍, 等.锌在包钢高炉中行为机制[J]. 钢铁, 2011, 46(8): 18-23.
ZHANG Fang,ZHANG Shizhong,LUO Guoping,et al.Behaviors of zinc in blast furnace of Baotou iron and steel (Group) Co.[J]. Iron and Steel, 2011, 46(8): 18-23.
[14] 李肇毅. 宝钢高炉的锌危害及其抑制[J]. 宝钢技术, 2002, 19(6): 18-20, 24.
LI Zhaoyi. Damage of element of Zinc to blast furnace and its inhibition[J]. Bao Steel Technology, 2002, 19(6): 18-20, 24.
[15] 焦克新, 张建良, 左海滨, 等.锌在高炉内渣铁中溶解行为计算分析[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 35(3): 383-387.
JIAO Kexin, ZHANG Jianliang, ZUO Haibin, et al. Calculation analysis of zinc dissolution behaviors of the slag-iron in blast furnaces[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2014, 35(3): 383-387.
[16] DAVID E, SANMBO B. Zinc accumulation during recycling of iron oxide wastes in the blast furnace[J] Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2006, 33(5): 419-425.
[17] JIAO Kexin, ZHANG Jianliang, LIU Zhengjian, et al. Circulation and accumulation of harmful elements in blast furnace and their impact on the fuel consumption[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2017, 44(5): 344-350.
[18] 宋建成, 董一诚. 钾、钠化学物在高炉冶炼过程中行为的热力学计算与分析[J]. 北京钢铁学院学报, 1983(2) :1-10.
SONG Jiancheng,DONG Yicheng.Thermodynamic calculation and analysis about the behavior of potassium, sodium and their chemical in blast furnace process[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Iron and Steel Technology, 1983(2): 1-10.
(编辑 秦明阳)
收稿日期: 2018 -12 -06; 修回日期: 2019 -02 -10
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(517904019) (Project(517904019) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:焦克新,讲师,从事高炉长寿技术研究;E-mail: jiaokexin_ustb@126.com