考虑流变效应的软黏土地基大应变固结研究
谢新宇1, 2,李金柱1,刘开富2
(1. 浙江大学 软弱土与环境土工教育部重点实验室,浙江 杭州,310058;
2. 浙江理工大学 建筑工程学院,浙江 杭州,310018)
摘要:软黏土压缩性高,在固结过程中变形较大时需要考虑大应变的影响。同时,软黏土具有明显的流变效应,对地基的长期沉降有着重要影响。为此,基于通用有限元软件ABAQUS平台编制土体流变模型UMAT子程序,进行软黏土地基大应变流变固结分析。比较大应变与小应变固结过程中超静孔压消散与沉降发展的差别,并分析模型参数对计算结果的影响。采用半对数经验公式考虑渗透系数随孔隙比的变化,分析渗透指数对固结过程的影响。研究结果表明:大应变固结最终沉降比小应变小,超静孔压消散比小应变快;土体固结对模型中Hooke体弹性模量的变化比Kelvin体弹性模量变化敏感;随着渗透指数的增大,土体固结速率增大。
关键词:软黏土地基;大应变固结;流变;超静孔压消散;沉降发展
中图分类号:TU447 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)11-3472-06
Study on large strain consolidation properties of soft soil considering rheological effect
XIE Xin-yu1, 2, LI Jin-zhu1, LIU Kai-fu2
(1. Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Soft Soils and Geoenvironmental Engineering, Zhejiang University,
Hangzhou 310058, China;
2. College of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou 310018, China)
Abstract: Soft soil often exhibits large settlement during consolidation because of high compressibility, and so the effect of large strain needs considering. Meanwhile, soft soil also has a significant effect of rheology. Therefore, user subroutine of a rheological model was coded on the platform of the FEM software ABAQUS. The study on large strain consolidation of soft soil was performed, based on which the difference of the dissipation of excess pore pressure and the development of settlement between small strain and large strain consolidation were compared, and the effects of the model parameters were analyzed. The variation of permeability was considered by semi-logarithm empirical formula, and the effects of the permeability index were analyzed. The results show that the settlement of large strain is smaller, and the dissipation of excess pore pressure is more rapidly. The consolidation process is more sensitive to the change of modulus in Hooke spring than that of modulus of Kelvin spring, and the consolidation rate increases with the increase of the permeability index.
Key words: soft soil; large strain consolidation; rheology; pore pressure dissipation; settlement development
固结是土力学的基本课题之一,按几何假设的不同,固结理论可以分为小应变固结理论和大应变固结理论。太沙基1925年提出了饱和土的一维固结理论,奠定了现代土力学的基础。太沙基理论假设土体变形是微小的,属于小应变的范畴。然而,研究表明:深厚软土层在固结过程中表现出很大的压缩性,变形甚至达到80%,远远超出了小应变的范围[1-2]。针对这一问题,一些学者进行了大应变固结理论的研究。Mikasa[3]和Gibson等[4]分别得到了以自然应变和孔隙比为变量的一维大应变固结方程,他们被认为是大应变固结理论的开拓者。随后,一系列学者对大应变固结理论进行了长期而深入的研究,取得了许多重要成 果[5-13]。由于大应变固结是高度非线性的问题,获得其解析解很困难,目前的解析解一般建立在一维条件下以及若干假定基础上,难以推广至多维问题,使其应用受到限制。Olson等[5]通过分析土体的材料非线性和几何非线性问题指出,对于大应变固结问题,数值解法具有更广的适应性。Cater[6]基于欧拉描述建立了一般形式的饱和土体三维大应变固结理论,开创了有限元法分析大应变固结问题的先河。有限元技术的不断发展,使得考虑各种复杂条件影响的大应变固结研究成为可能。迄今为止,大应变固结理论研究仍然不够完善,不同研究者得到的结论很不一致,其主要原因在于不同的学者采用了不同的本构模型和计算方 法[10]。同时,软黏土具有明显的流变性,流变性对固结过程中超静孔压消散和沉降发展均有重要影响,但考虑流变效应的大应变固结研究尚不多见。为此,本文作者考虑了土体的流变性,采用平面应变有限元法,基于通用有限元软件ABAQUS编制用户材料子程序,分析大应变固结过程中超静孔压消散和地基沉降发展的规律。
1 大应变固结有限元理论
土体大应变固结问题的控制方程主要包括平衡方程和连续性方程。对于考虑流变的大应变固结分析,采用修正的拉格朗日法(U.L.法)是合理的选择。ABAQUS具有强大的非线性分析能力,能够进行几何非线性分析,ABAQUS/Standard在计算几何非线性问题时,采用的正是U.L.法。对于实体单元,ABAQUS/ Standard均采用Jaumann应力率。
U.L.格式的平衡方程为:
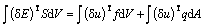 (1)
(1)
式中:S,E,u,f和q分别为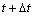 时刻的Kirchhoff应力张量矩阵、Green应变张量矩阵、位移矢量、单位体力矢量和面力矢量。不同于完全的拉格朗日法(T.L.法),以上各量均是以时刻t为参考构形表述的。
时刻的Kirchhoff应力张量矩阵、Green应变张量矩阵、位移矢量、单位体力矢量和面力矢量。不同于完全的拉格朗日法(T.L.法),以上各量均是以时刻t为参考构形表述的。
将式(1)离散后,有
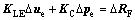 (2)
(2)
式中:KLE,KC,?ue,?pe和?RF分别为单元刚度矩阵、耦合矩阵、节点位移增量矢量、孔压增量和等效节点荷载增量矢量。
U.L.描述的连续性方程为:
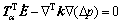 (3)
(3)
式中: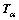 为选项矢量;k为定义在t时刻构形的渗透系数矩阵;?p为孔压增量。
为选项矢量;k为定义在t时刻构形的渗透系数矩阵;?p为孔压增量。
对式(3)进行空间离散和时域离散后有
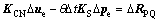 (4)
(4)
式中:KCN,KS,RPQ和 分别为单元渗流矩阵、耦合矩阵、等效节点流量增量矢量和孔压差分系数。
分别为单元渗流矩阵、耦合矩阵、等效节点流量增量矢量和孔压差分系数。
结合式(2)和(4),可得U.L.法土体大应变固结方程为:
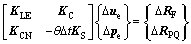 (5)
(5)
2 流变模型及其UMAT实现
2.1 流变模型
考虑采用如图1所示的三元件流变模型,该模型由Hooke体和Kelvin体串联而成,应变可分为Hooke体应变和Kelvin体应变2个部分:
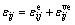 (6)
(6)
式中: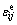 和
和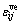 分别为Hooke体和Kelvin体的应变,
分别为Hooke体和Kelvin体的应变,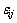 为总应变。
为总应变。
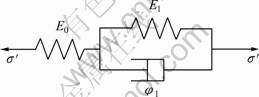
图1 三元件流变模型
Fig.1 Three-component rheological model
图1中E0,E1和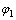 为模型参数。对三维应力状态下的Hooke体和Kelvin体,分别有:
为模型参数。对三维应力状态下的Hooke体和Kelvin体,分别有:
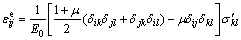 (7)
(7)
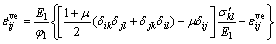 (8)
(8)
假定材料为各向同性体,根据式(7)和(8)可得
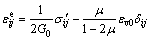 (9)
(9)
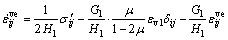 (10)
(10)
式中: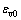 和
和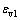 分别为Hooke体和Kelvin体的体应变,
分别为Hooke体和Kelvin体的体应变,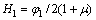 为三维应力状态下的黏弹性系数。联立式(6),(9)和(10),并假定土体体积变形呈弹性,即体积变形由弹性体产生,Kelvin体中只产生剪切变形,不产生体积变形,可得模型在三维应力状态下的微分型本构模型为:
为三维应力状态下的黏弹性系数。联立式(6),(9)和(10),并假定土体体积变形呈弹性,即体积变形由弹性体产生,Kelvin体中只产生剪切变形,不产生体积变形,可得模型在三维应力状态下的微分型本构模型为:
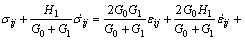
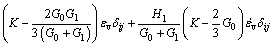 (11)
(11)
式中:令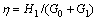 ,
,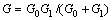 ,
,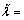
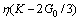 ,
,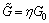 ,
,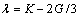 ,可得
,可得
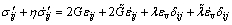 (12)
(12)
2.2 UMAT的实现
除了本身提供的材料模型外,ABAQUS还提供了若干用户子程序(User Subroutines)和实用程序(Utility Routines),以便用户自行定义符合自己问题的模型。利用ABAQUS平台开发子程序,用户仅需少量代码就可以建立自定义的有限元模型,避免了开发整个有限元程序,从而大大减少了工作量。在ABAQUS提供的用户子程序中,与用户材料本构模型相关的子程序是UMAT。按照ABAQUS用户子程序的约定,UMAT子程序开发需定义材料单元积分点的Jacobian矩阵,即材料本构关系的刚度系数矩阵D,如下式所示:
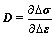 (13)
(13)
式中: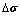 和
和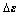 分别为应力增量矢量和应变增量矢量。
分别为应力增量矢量和应变增量矢量。
对于本文模型,从时间t到t+?t时间间隔内的黏弹性应变增量可取为:
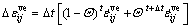 (14)
(14)
式中: 为差分系数,0≤
为差分系数,0≤ ≤1。当
≤1。当 =0时,为显示法;
=0时,为显示法; =1时,为隐式法;当
=1时,为隐式法;当 =1/2时,为隐式梯形法。本文取
=1/2时,为隐式梯形法。本文取 =1/2。
=1/2。
由式(6)得
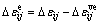 (15)
(15)
对本文研究的固结问题,本构关系是土骨架的应力-应变关系,故有
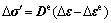 (16)
(16)
式中:De为弹性矩阵。
将式(12)代入式(16),有
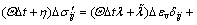
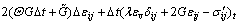 (17)
(17)
由式(13)和(17)可得
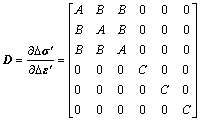 (18)
(18)
式中: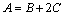 ,
,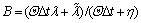 ,
,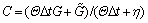 。
。
3 模型应用研究
3.1 计算模型
本文算例如图2所示,土层为均匀饱和的软黏土,在自重应力作用下保持平衡,底面固定,侧面限制x方向的位移,上表面单面排水,假定荷载一次瞬时施加并维持恒定。此外,在计算中考虑了固结过程中渗透性的变化,Tavenas等[14]的研究表明,半对数经验关系能较好地反映黏性土渗透性随孔隙比的变化,如式(19)所示:
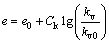 (19)
(19)
式中:e0和kv0分别为初始时刻土体的孔隙比、渗透系数;e和kv分别为固结过程中某一时刻土体的孔隙比、渗透系数;Ck为土体的渗透指数。
土体参数及模型参数如表1所示。
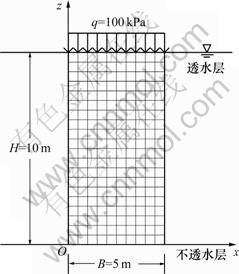
图2 计算模型及网格划分
Fig.2 Calculation model and mesh generation
表1 计算参数
Table 1 Calculation parameters

3.2 大应变效应对固结形状的影响
图3所示为大应变效应对土体超静孔压消散及地基顶部变化发展的影响。从图3(a)可以看出:同一时刻大应变固结理论计算的孔压小于小应变理论计算结果,且在固结初期随着时间的变化差距增大,即考虑大应变后超静孔压消散得更快。图3(b)所示为土层顶部沉降的变化过程。由图3(b)可知:相同荷载下大应变计算的沉降小于小应变计算的沉降,并且当荷载较小时,二者差距不大;随着荷载的增大,二者差距逐渐增大。
3.3 渗透系数变化对固结形状的影响
随着固结过程的变化,土体孔隙比减小,渗透性将降低,式(19)反映了这一过程,其中渗透指数Ck是重要参数,为此本文计算了Ck取不同值时固结过程的差异,如图4所示。由图4可知:尽管Ck取不同的值时土层最终沉降一致,但Ck对超静孔压消散速率和沉降变化速率的影响都很大,Ck越大,固结越快。固结初期,随着时间的增大,超静孔压和沉降的差距均逐渐增大。
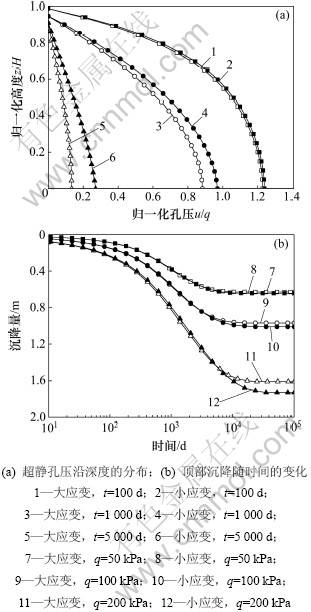
图3 大应变与小应变计算结果对比
Fig.3 Results comparison of large strain and small strain
3.4 压缩性变化对固结形状的影响
除软黏土渗透性及其变化对固结过程有影响外,由于固结过程中土骨架变形和超静孔隙水压力之间存在耦合作用,软黏土压缩性的大小及变化对固结过程也有影响。为计算地基压缩性变化对计算结果的影响,假定本文模型E0和E1随土层深度呈线性变化,即在深度h处有
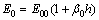 (20a)
(20a)
 (20b)
(20b)
式中:E00和E10分别为地表处E0和E1的值;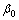 和
和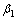 为比例系数。
为比例系数。
图5显示了E0和E1的变化对地基超静孔压消散及沉降变化的影响。由图5可知:当E0和E1沿深度增加时,地基超静孔压消散速率和沉降变化均加快,地基顶部沉降减小。其中,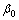 =0,
=0,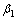 =0.1与
=0.1与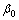 =
=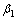 =0时计算结果相差较小;而
=0时计算结果相差较小;而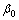 =0.1,
=0.1,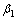 =0与
=0与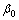 =0.1,
=0.1,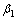 =0.1时计算结果较为接近,固结过程远快于前2种情况。这一结果表明:固结速率和最终沉降主要取决于E0,固结过程对E0的变化非常敏感,而对E1变化则相对不敏感。
=0.1时计算结果较为接近,固结过程远快于前2种情况。这一结果表明:固结速率和最终沉降主要取决于E0,固结过程对E0的变化非常敏感,而对E1变化则相对不敏感。
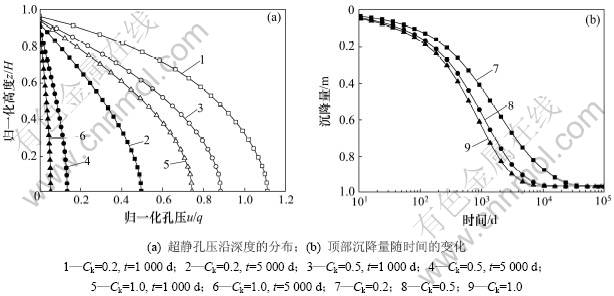
图4 Ck对计算结果的影响
Fig.4 Effects of Ck on calculated results
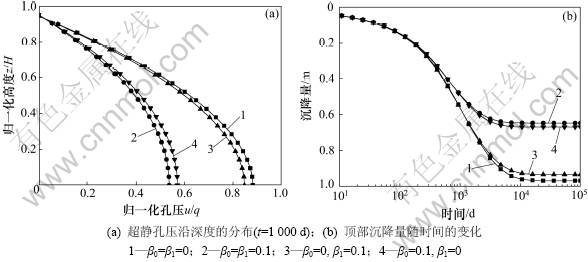
图5 E0和E1对计算结果的影响
Fig.5 Effects of E0 and E1 on calculated results
4 结论
(1) 对于软黏土地基的固结问题,当荷载较大或土体压缩性较大时,大应变理论与小应变理论的计算结果相差较大,需考虑大应变的影响;同一时刻大应变理论计算的超静孔压小于小应变理论计算结果,大应变理论计算的最终沉降小于小应变理论计算结果。
(2) 当采用半对数经验关系考虑软黏土渗透性变化时,渗透指数Ck对固结过程有重要影响,Ck越大,超静孔压消散越快,沉降发展也越快,但最终沉降 相同。
(3) 地基压缩性的变化将显著影响固结过程。对于本文流变模型,E0和E1沿深度增大使超静孔压消散和沉降变化更快,最终沉降减小,固结过程对E0的变化比E1的变化更为敏感。
(4) 本文大应变固结理论和小应变固结理论计算分析的软黏土地基固结过程中超静孔压消散和沉降变化的规律及其差异,可供排水固结法处理深厚软土地基时参考。
参考文献:
[1] Weber W G. Performance of embankments constructed over peat[J]. Journal of Soil Mechanics and Foundations, ASCE, 1969, 95(1): 53-76.
[2] Cargill K W. Prediction of consolidation of very soft soil[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, 1984, 100(6): 125-157.
[3] Mikasa M. The consolidation of soft clay—A new consolidation theory and its application[J]. Civil Engineering in Japan, JSCE, 1965, 1(1): 21-26.
[4] Gibson R E, England G L, Hussey M J L. The theory of one-dimensional consolidation of saturated clays Ⅰ: Finite nonlinear consolidation of thick homogeneous layers[J]. Geotechnique, 1967, 17(2): 261-237.
[5] Olson R E, Ladd C C. One dimensional consolidation problems[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, 1979, 105(1): 11-30.
[6] Cater J P. Finite deformation theory and its application to elastoplastic soil[D]. Sydney, Australia: University of Sydney, 1977: 26-45.
[7] 谢新宇, 朱向荣, 谢康和, 等. 饱和土体一维大变形固结理论新进展[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1997, 19(4): 30-38.
XIE Xin-yu, ZHU Xiang-rong, XIE Kang-he, et al. New developments of one-dimensional large strain consolidation theories[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1997, 19(4): 30-38.
[8] 谢永利. 大变形固结理论及其有限元法[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 1998: 43-58.
XIE Yong-li. Large strain consolidation theory and its finite element method[M]. Beijing: China Communication Press, 1998: 43-58.
[9] 谢康和, 郑辉, Leo C J. 变荷载作用下饱和软黏土一维大应变固结解析理论[J]. 水利学报, 2003(10): 6-13.
XIE Kang-he, ZHENG Hui, Leo C J. Analytical solution for 12D large strain consolidation of saturated soft clay under time2depending loading[J]. Shuili Xuebao, 2003(10): 6-13.
[10] 张继发. 一维大应变固结问题的解析理论研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学岩土工程研究所, 2002: 4-5.
ZHANG Ji-fa. Studies on the analytical theory of one dimensional large strain consolidation problem[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University. Institute of Geotechnical Engineering, 2002: 4-5.
[11] 郑辉, 谢康和, 杨晓强. 双层饱和软土地基一维大应变固结研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2004, 25(11): 1770-1774.
ZHENG Hui, XIE Kang-he, YANG Xiao-qiang. Study of one dimensional large strain consolidation of double layered saturated soft soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2004, 25(11): 1770-1774.
[12] 丁洲祥, 龚晓南, 谢永利. 欧拉描述的大变形固结理论[J]. 力学学报, 2005, 37(1): 92-99.
DING Zhou-xiang, GONG Xiao-nan, XIE Yong-li. Finite strain consolidation theory with Eulerian description[J]. Acta Mechanical Sinaca, 2005, 37(1): 92-99.
[13] 陈敬虞, 龚晓南, 邓亚虹. 软黏土层一维有限应变固结的孔压消散研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2009, 30(1): 191-195.
CHEN Jing-yu, GONG Xiao-nan, DENG Ya-hong. Research on dissipation of excess pore water pressure in one-dimensional finite strain consolidation of soft clays[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(1): 191-195.
[14] Tavenas F, Jean P, Leblond P, et al. The permeability of natural soft clays (part Ⅱ): Permeability characteristics[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1983, 20(4): 645-660.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2010-12-09;修回日期:2011-02-15
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51079126);教育部科学技术研究重点资助项目(210089);浙江省自然科学基金资助项目(Y1090971)
通信作者:刘开富(1977-),男,山东费县人,博士,副教授,从事软黏土力学及地基处理研究;电话:0571-86843376;E-mail: kaifu.liu@gmail.com