文章编号:1004-0609(2012)02-0485-05
磁场对Sn-9Zn钎料组织、显微硬度及电化学腐蚀的影响
吴 敏1, 2,刘政军1
(1. 沈阳工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,沈阳 110023;
2. 辽宁石油化工大学 机械工程学院,抚顺 113001)
摘 要: 运用X射线衍射仪、扫描电镜、电化学测试系统等研究0.125 T的静态磁场及旋转磁场对Sn-9Zn钎料的组织及性能影响。结果表明:静态磁场及旋转磁场均可促进Sn-9Zn钎料组织细化,其中旋转磁场可使Zn相分布呈旋转状;与未经磁场作用相比,静态磁场和旋转磁场可使Sn-9Zn钎料的显微硬度分别提高7.4%和10.2%,达到18.8 HV和19.3 HV;此外,经静态磁场及旋转磁场作用的钎料的腐蚀电位分别为-1.428和-1.450 V,比Sn-9Zn钎料的有所降低,而腐蚀电流密度分别为1.424×10-8和2.538×10-9 A/m2,相比Sn-9Zn钎料,其腐蚀电流密度明显减小,钎料腐蚀性能得到改善。
关键词:金属材料;Sn-9Zn钎料;锡合金;磁场;组织;显微硬度;电化学腐蚀
中图分类号:TG42 文献标志码:A
Effects of magnetic fields on microstructure,
microhardness and electrochemical corrosion of Sn-9Zn solder
WU Min1, 2, LIU Zheng-jun1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shenyang University of Technology, Shenyang 110023, China;
2. School of Mechanical Engineering, Liaoning Shihua University, Fushun 113001, China)
Abstract: The microstructure and property of Sn-9Zn solder were investigated under static magnetic field and rotary magnetic field of 0.125 T by XRD, SEM and electrochemical detector system. The results show that both static magnetic field and rotary magnetic field can refine the microstructure of Sn-9Zn solder, and Zn phase is rotating as well, the microhardness of Sn-9Zn solder under static magnetic field and rotary magnetic field increase by 7.4% and 10.2%, reaching to 18.8 HV and 19.3 HV, respectively, compared with the solder without magnetic field. While the corrosion potential of the solder under static magnetic field and rotary magnetic field decrease slightly and the corrosion current density obviously declines, which improves the solder corrosion property.
Key words: metallic materials; Sn-9Zn solder; Sn alloy; magnetic field; microstructure; microhardness; electrochemical corrosion
目前,在研究开发的无铅钎料体系中,尽管Sn-Zn系钎料存在易氧化、焊接结合界面强度低等缺点,但仍具有与Sn-Pb共晶合金相接近的熔点、钎焊工艺性好和价格低廉等优点,受到国内外研究人员关注,并在工程生产中得到一定应用[1-4]。针对Sn-Zn系钎料存在的不足,国内外很多学者通过尝试向该钎料添加Bi、Re和Ga等多种元素来改善其性能,效果并不十分理想[5-6]。外加磁场具有电磁作用,可改变液态金属结晶过程中的传质和传热过程,显著细化晶粒、改善凝固组织、提高力学性能,目前已在铝合金、镁合金等合金的制备过程中得到应用[7-8]。鉴于此,本文作者运用X射线衍射仪、扫描电镜和电化学测试系统等探讨外加静态磁场及旋转磁场对Sn-9Zn钎料组织、显微硬度及电化学腐蚀的影响,以期为在磁场作用下金属材料特别是无铅钎料的材料制备及其性质研究提供数据与信息。
1 实验
1.1 钎料制备
采用TG328A型分析天平作为称量工具,将化学纯的金属Sn和Zn分别按指定比例(质量比)置于石墨坩埚中,用石墨粉做覆盖剂,用加热炉加热制备钎料。先将Sn料加热至450 ℃,待熔化后,加入Zn钎料,待完全熔化后,充分搅拌均匀,冷却至300 ℃浇注,凝固得板条块Sn-9Zn钎料,将钎料在室温下放置24 h,进行组织稳定化处理。同时制备Sn-37Pb钎料用于进行对比试验研究。
1.2 磁场作用钎料凝固
将制得的钎料在磁场条件下进行试验,旋转磁场实验装置示意图如图1所示,其中磁场是由两块磁铁产生、中心位置磁场强度为0.125 T(磁铁材质为钕铁硼,磁场强度由两磁铁间距离来控制,其大小由Gaussmeter TM-701仪器测定);首先将钎料在箱式加热炉中重熔,温度250 ℃,保温时间5 min,然后分别在未加磁场、静态磁场和旋转磁场作用下凝固(其中测试条件r=0即静态磁场、r=1 250 r/min即旋转磁 场),制得的钎料试样分别用于微观组织观察与成分分析、显微硬度和耐腐蚀性能测试。
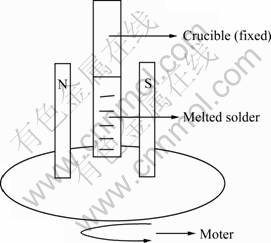
图1 旋转磁场示意图
Fig. 1 Diagram of rotary magnetic field
1.3 微区物相分析及组织观察
分别用日本理学D/max-RB X射线衍射仪和日本岛津公司SSX-550扫描电镜及其附带EDAX能谱仪对Sn-9Zn钎料微观组织的物相、形貌及成分进行观察与测定。其中XRD测定条件为Cu Ka辐射,管电压为40 kV,管流为100 mA,测角仪半径185 mm,采用q-2q步进扫描方式,步长为0.02°(2q),扫描速度为8 (°)/min;扫描电镜测定条件为加速电压为15 kV,样品电流为1.00 nA,工作距离为17 mm。
1.4 钎料显微硬度测试
在室温下,用HXD-1000TMC/LCD显微硬度计对Sn-9Zn钎料进行硬度测试(参照GB 4342—84标准进行,其中F=0.098 N,t=10 s)。钎料分别在不同磁场作用下冷却凝固,制得柱状检测试样(其中圆柱试验直径10 mm,高度10 mm),待检测试样分别经砂纸打磨、抛光机抛光后,进行显微硬度测试,每个试样分别在不同位置随机测试6处,取测试平均试验值进行分析。
1.5 钎料腐蚀性能测试
选择CHI604C型电化学测试系统作为钎料腐蚀性能测试仪器,3.5% NaCl溶液(质量分数)作为腐蚀溶液,试验温度为室温(25 ℃),甘汞电极作为参比电极,利用动电位法测量钎料极化曲线。将钎料制得柱状试样(其中试样直径为10 mm,高度为10 mm),待检测试样分别经砂纸打磨、抛光机抛光后,进行电化学测试,扫描范围-2~0 V,扫描速度0.01 V/s,通过相应的电化学分析软件CHI660B分析腐蚀电位、腐蚀电流密度参数判断其耐腐蚀性能。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 显微组织分析
图2所示为不同磁场作用下Sn-9Zn钎料组织的SEM像及XRD谱,根据Sn-Zn二元合金相图[7]、XRD谱可以确定,未加磁场作用时,Sn-9Zn钎料组织是由粗大的呈长片状富Zn相及灰色富Sn相基体而构成的混合组织,其中部分粗大富Zn相组织尺寸可达80~100 μm,这对Sn-9Zn钎料的性能是十分不利的,而经静态磁场或旋转磁场作用后,钎料的显微组织中已经没有粗大的长片状富Zn相组织出现,表明磁场作用可抑制初生富Zn相的形成与长大,钎料组织尤其是富Zn相得到显著细化,其中在静态磁场作用下,Zn相以短针状较均匀的分布在基体中,尺寸达30~40 μm;而在旋转磁场作用下,Zn相的变为细小的针状组织,数量明显比在静态磁场作用下多,尺寸达20~40 μm,分布均匀,呈一定的旋转状。由相应的X射线衍射分析可知,磁场作用并未改变Sn-9Zn钎料物相的组成,即钎料仍由Sn和Zn两相构成,但Sn、Zn两相特征峰的峰值强度发生较大变化,其中Sn相的(200)、(101)、(211)特征晶面的特征峰峰值强度得到显著增强,而Zn相的(002)、(101)、(100)特征晶面的特征峰峰值强度变化不明显。磁场作用使Sn-9Zn钎料组织发生改变的机理为未经磁场作用时,Sn-9Zn钎料为过共晶成分,且属于在非平衡条件下的冷却凝固,Zn相较Sn相的熔点高[9],因此,Zn相作为领先相首先从液态钎料中凝固析出并长大;而在磁场作用下,尽管仍在非平衡条件下冷却凝固,但一方面,静态磁场或旋转磁场作用是从外部对Sn-9Zn钎料合金熔体输入能量,可加剧结构和能量的变化;同时Sn-9Zn钎料合金熔体与磁场之间由于存在强烈的相互作用而产生电磁力,起强迫对流作用[10];另一方面,根据磁场作用前后的XRD谱可知,外加静态磁场或旋转磁场作用会促进Sn原子在(200)、(101)、(211)面的结晶形核速度加快,同时将Zn原子推向液态金属中,使Zn原子在局部富集,当浓度达到共晶成分时,Sn和Zn原子形成共晶组织,这在很大程度上抑制粗大Zn相作为领先相从钎料中析出,以上两方面均有利于晶核形成,从而细化Sn-9Zn钎料合金组织。特别是液态Sn-9Zn钎料在凝固时施加旋转磁场,液态金属中每一垂直截面与旋转磁场产生相对运动,会产生感应电动势及相应的感应电流,磁场与感应电流间发生电磁作用,会在熔体内产生一个电磁力分量(即Lorentz力),其方向与磁场的旋转方向相同,具有驱动熔体随电磁场旋转的趋势[11-12],致使钎料组织分布呈一定的旋转状。
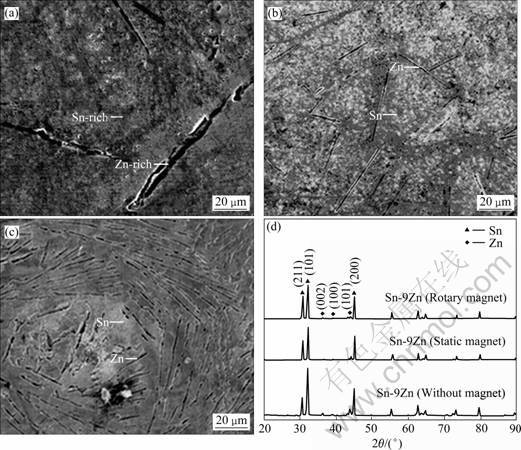
图2 不同磁场对Sn-9Zn钎料组织及XRD谱的影响
Fig. 2 Effect of different magnetic fields on microstructures and XRD patterns of Sn-9Zn solder: (a) No magnetic field; (b) Static magnetic field; (c) Rotary magnetic field; (d) XRD patterns
2.2 显微硬度分析
不同磁场作用方式均对Sn-9Zn钎料显微硬度产生较大影响,结果如图3所示。由图3可以看到,Sn-9Zn钎料的显微硬度明显高于Sn-37Pb钎料的,且静态磁场可使Sn-9Zn钎料的显微硬度提高7.4%,达到为18.8,而旋转磁场可使Sn-9Zn钎料的显微硬度提高10.2%,达到为19.3。在一定程度上,硬度是标志材料综合力学性能的指标,因此,磁场作用对改善Sn-9Zn钎料力学性能是有益的。钎料的显微硬度取决于各种条件,如温度、钎料的化学成分、钎料的显微组织等,像晶粒的尺寸与分布、析出相大小与数量等可对位错运动产生重要影响,因此是决定钎料显微硬度的主要因素[13-14]。基于磁场对钎料显微组织影响分析可以得到,外加磁场作用可使Sn-9Zn钎料显微组织细化,尤其是对于粗大的长片状Zn相组织更为明显,相比静态磁场作用,在旋转磁场下,Sn-9Zn钎料中出现更多细小的Zn相组织出现,且分布更为均匀,这些弥散分布的Zn相会阻碍位错运动,对钎料基体有细晶强化、弥散强化作用,因此,旋转磁场作用更有利于Sn-9Zn钎料显微硬度的提高。
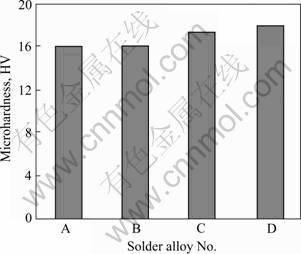
图3 磁场作用下Sn-9Zn及Sn-37Pb钎料的显微硬度
Fig. 3 Microhardness of Sn-9Zn and Sn-37Pb solders under magnetic fields: A—Sn-37Pb (Without magnet); B—Sn-9Zn (Static magnet); C—Sn-9Zn (Without magnet); D—Sn-9Zn (Rotary magnet)
2.3 电化学腐蚀分析
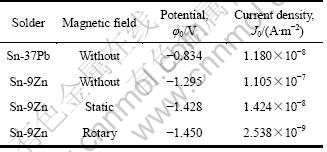
图4及表1所示为不同方式磁场作用前后Sn-9Zn及Sn-37Pb钎料在3.5%NaCl溶液、室温条件下的极化曲线及其相应的腐蚀电位、腐蚀电流密度的测试结果。可以看出,未经磁场作用时,Sn-9Zn钎料的腐蚀电位明显低于Sn-Pb钎料的腐蚀电位,因而其耐蚀性也明显不及Sn-Pb钎料的,其原因如下:一方面,Sn-Zn系钎料组成元素的标准电极电势都很低[15],而电极电势是衡量金属溶解变成金属离子转入溶液趋势的标量,电极电势值越负,金属越活泼,溶入溶液的离子倾向越大,越容易发生腐蚀;另一方面,Sn-9Zn钎料中的Zn相呈片状存在,易发生选择性腐蚀,造成脱锌现象发生,从而降低Sn-9Zn钎料的耐蚀性。经静态磁场或旋转磁场作用后,Sn-9Zn钎料的腐蚀电位(反映钎料腐蚀趋势的指标)略有降低,但腐蚀电流密度(反映钎料实际腐蚀程度的指标)却明显变小,且随着腐蚀电位增加,腐蚀电流密度变化不大,远小于Sn-Zn钎料未在磁场作用下的腐蚀电流密度。腐蚀电流密度越小,表明金属离子溶入溶液的速度越慢,即腐蚀速率越慢,其耐蚀性也越好,因此可以确定,外加磁场作用可使Sn-9Zn钎料的耐蚀性能得到较大提高。基于磁场对Sn-9Zn钎料微观组织及XRD影响分析可知,磁场作用并未从根本上改变Sn-9Zn钎料的物相组成,因此对提高钎料腐蚀电位作用不大。Sn-9Zn钎料在3.5% NaCl溶液中的腐蚀产物主要为ZnO、SnO和Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O等[16],而静态磁场或旋转磁场作用可明显的影响Zn相尺寸及分布方式,Zn相生长得到明显抑制,变为更加细小,且分布更加均匀,这样可降低Sn-9Zn中Zn相的数量及活性。因此,在3.5%NaCl溶液中腐蚀时,不再是完全的Zn相选择性腐蚀,而是整个钎料组织均发生腐蚀,相比Zn相面积,钎料腐蚀面积明显增大,因此腐蚀电流密度显著减小,致使Sn-9Zn钎料的耐蚀性得到提高。
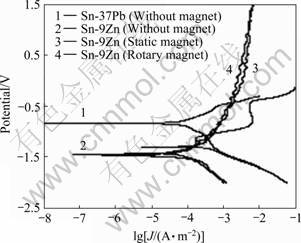
图4 磁场作用下Sn-9Zn及Sn-37Pb钎料的极化曲线
Fig. 4 Polarization curves of Sn-9Zn and Sn-37Pb solders under magnetic fields
表1 不同磁场作用下Sn-9Zn以及Sn-37Pb钎料在3.5%NaCl溶液、室温条件下的腐蚀电位(φ0)、腐蚀电流密度(J0)
Table 1 φ0 and J0 obtained from 3.5%NaCl solution for Sn-9Zn and Sn-37Pb solder at room temperature under different magnetic fields
3 结论
1) 静态磁场及旋转磁场均可促进Sn-9Zn钎料组织明显细化,其中旋转磁场作用可使Zn相的针状组织分布呈旋转状。
2) 静态磁场及旋转磁场均可提高Sn-9Zn钎料的显微硬度,其中静态磁场可使Sn-9Zn钎料显微硬度提高7.4%,达到为18.8 HV,而旋转磁场可使Sn-9Zn钎料显微硬度提高10.2%,达到为19.3 HV。
3) 静态磁场及旋转磁场均可使Sn-9Zn钎料的腐蚀电位有所降低,分别为-1.428和-1.450 V,而腐蚀电流密度分别为1.424×10-8和2.538×10-9 A/m2,远低于Sn-Zn钎料未在磁场作用下的腐蚀电流密度,且随着腐蚀电位增加,腐蚀电流密度的变化不大,改善Sn-9Zn钎料的耐蚀性。
REFERENCES
[1] ZHANG Liang, XUE Song-bai, GAO Li-li, SHENg Zhong, YE Huan, XIAO Zheng-xiang, ZENG Guang, CHEN Yan, YU Sheng-lin. Development of Sn-Zn lead-free solders bearing alloying elements[J]. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron, 2010, 21: 1-15.
[2] ZHAO H, WANG H Q, SEKULIC D P. Spreading kinetics of liquid solders over an intermetallic solid surface (Part 2): Lead-free solders[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2009, 38(9): 1846-1854.
[3] TSAI Ying-ling, HWANG Weng-sing. Pasty ranges and latent heat release modes for Sn-9Zn-xAg lead-free solder alloys[J]. Materials Transactions, 2004, 45(6): 1949-1957.
[4] MAHMUDI R, GERANMAYEH A R, NOORI H, KHANBAREH H, JAHANGIRI N. A comparison of impression, indentation and impression-relaxation creep of lead-free Sn-9Zn and Sn-8Zn-3Bi solders at room temperature[J]. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron, 2009, 20: 312-318.
[5] WANG Hui, XUE Song-bai, ZHAO Feng. Effects of Ga, Al, Ag, and Ce multi-additions on the wetting characteristics of Sn-9Zn lead-free solder[J]. Rare Metals, 2009, 28(6): 600-605.
[6] HUNG Fei-yi, LUI Tuan-sheng, CHEN Li-hui, YOU Ji-ge. Vibration fracture behavior of Sn-9Zn-xCu lead-free solders[J]. J Mater Sci, 2007, 42: 3865-3873.
[7] 刘政军, 吴晓峰, 程明华, 贾 华, 苏允海. 电磁作用对镁合金焊缝金属组织性能的影响[J]. 沈阳工业大学学报, 2008, 30(6): 643-646.
LIU Zheng-jun, WU Xiao-feng, CHENG Ming-hua, JIA Hua, SU Yun-hai. Effect of electromagnetic field on microstructures and properties of magnesium alloy of weld metal[J]. Journal of Shenyang University of Technology, 2008, 30(6): 643-646.
[8] XU Guang-ming, BAO Wei-ping, CUI Jian-zhong. Microstructure and segregation of magnesium alloy solidified under magnetostatic field[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2004, 14(2): 316-320.
[9] 长崎诚三, 平林真. 二元合金状态图集[M]. 刘安生, 译. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2004: 279.
NAGASAKI S, HIRABAYASH I. Binary alloy state atlas[M]. LIU An-sheng, transl. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2004: 279.
[10] 班春燕. 电磁场作用下铝合金凝固理论基础研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2002: 25-30.
BAN Chun-yan. Fundamental study on solidification of Al alloys under electromagnetic fields[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2002: 25-30.
[11] 陈翔燕. 凝固过程中外场对流动控制的研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2007: 14-15.
CHEN Xiang-yan. Study on external field controlling flow during melt solidification[D]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2007: 14-15.
[12] 王晓东. 电磁力对金属熔体驱动及运动形态控制的研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2002: 20-21.
WANG Xiao-dong. Study on electromagnetic force driving and controlling flow modality of molten metal[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2002: 20-21.
[13] ISLAM R A, WU B Y, ALAM M O,CHAN Y C, JILLEK W. Investigations on microhardness of Sn-Zn based lead-free solder alloys as replacement of Sn-Pb solder[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2005, 392: 149-158.
[14] SHEN J, LIU Y C, HAN Y J, TIAN Y M, GAO H X. Strengthening effects of ZrO2 nanoparticles on the microstructure and microhardness of Sn-3.5Ag lead-free solder[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2006, 35(8): 1672-1679.
[15] 魏保明. 金属腐蚀理论及应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2004: 19.
WEI Bao-ming. Metal corrosion theory and application[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2004: 19.
[16] 樊志罡, 马海涛, 王 来. Cu对Sn-9Zn无铅钎料电化学腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(8): 1302-1306.
FAN Zhi-gang, MA Hai-tao, WANG Lai. Effect of Cu on electrochemical corrosion behavior of lead free Sn-9Zn-xCu solder[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(8): 1302-1306.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:辽宁省教育厅科学研究计划资助项目(2008382,20060505)
收稿日期:2011-10-08;修订日期:2011-04-16
通信作者:吴 敏,讲师;电话:0413-6865150;E-mail: Wumin_1@sina.com