文章编号:1004-0609(2008)08-1534-07
脆性岩石高温剪切(Ⅱ型)断裂的微观机理
谢海峰,饶秋华,谢 强,黎纵宇,王 志
(中南大学 土木建筑学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:采用剪切盒和扫描电镜实验研究脆性岩石的高温剪切(Ⅱ型)断裂特征及微观机理,并通过密度、单轴压缩实验研究岩石高温的物性和力学性能。实验表明:在高温加载下,胶结物材料的干脱和岩石内部微裂纹的形成、发育,这两种因素共同影响着岩石的弹性模量、抗压强度、断裂峰值荷载,前者占主导地位起强化作用,后者占主导地位起弱化作用,临界温度为250 ℃。在高温剪切盒加载下,岩石发生沿原裂纹面断裂破坏,裂纹核随着温度增加而增大,断口多为穿晶断裂。晶面上具有多而密的平行线条纹和较多的岩屑等典型的剪切破坏特征,表明岩石破坏为剪切断裂(Ⅱ型)。
关键词:脆性岩石;剪切断裂;高温;断裂机理
中图分类号:TU 452 文献标识码:A
Plane shear (ModeⅡ) fracture experiment analysis of brittle rock at high temperature
XIE Hai-feng, RAO Qiu-hua, XIE Qiang, LI Zong-yu, WANG Zhi
(School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Compression-shear box and scanning electron microscope(SEM) tests were used to study the shear fracture characteristics and mechanism of brittle rock at high temperature. The physical and mechanical properties of brittle rock at high temperature were investigated by density test and uniaxial compressive test. The test results show that, under compression-shear loading and at increasing temperature, both the dry-baking of clay material and the micro-cracks initiation and development have effects on elastic modulus, axial compressive strength and fracture peak load. The former is dominant before a certain critical temperature such as 250 ℃ and can increase the mechanical properties of rock, while the latter is dominant after the critical temperature and can decrease the mechanical properties of rock. The new crack is initiated and propagated almost along its original plane of specimen at high temperature. The radius of crack nucleation zone is increased with the increase of temperature and the fracture morphologies are of trans-granular fracture. The crystal surfaces have many dense parallel patterns and rock fragments, which represents the shear fracture (Mode Ⅱ).
Key words: brittle rock; shear fracture; high temperature; fracture mechanism
在地下基础、深部资源开发、核废料地下处置等工程中,裂隙岩体不仅承受各种加载条件,如:拉抻 (Ⅰ型)、平面剪切(Ⅱ型)、反平面剪切(Ⅲ型)及其复合型加载等,而且承受高温高压等作用。高温对岩石的物性、力学性能及其断裂破坏影响显著[1?4],国内外开展岩石高温断裂的研究较少,主要采用三点弯 (TPB)[5?6]、短棒 (SR)[7?8]等实验研究岩石的高温拉伸(Ⅰ型)断裂,尚未涉及岩石的高温剪切(Ⅱ型)断裂研究。
对于常温下的岩石Ⅱ型断裂问题,国内外学者做了大量的研究工作,主要采用反对称四点弯(AFPB)[9]、紧凑拉剪(CTS)[10]、冲剪(PTS)[11]、中心巴西圆盘 (CCBD)[12]等实验,通过对试样原裂纹面施加纯剪切载荷来获得岩石的Ⅱ型断裂。但结果表明:在纯剪切加载下岩石发生的是Ⅰ型断裂,并非Ⅱ型断裂[13?14]。为了实现真正的岩石Ⅱ型断裂,必须通过对原裂纹面施加压应力来有效地抑制裂纹尖端的拉应力,从而使岩石发生沿原裂纹面的Ⅱ型断裂。因此,剪切盒实验被认为是实现岩石Ⅱ型断裂及测定岩石Ⅱ型断裂韧度KIIC的一种有效方法[15]。
本文作者采用剪切盒实验研究岩石的高温Ⅱ型断裂规律,并利用单轴压缩、密度和扫描电镜等实验研究高温下岩石断裂特征及机理,以寻求一种实现岩石高温Ⅱ型断裂及测定岩石高温Ⅱ型断裂韧度 的有效方法。
的有效方法。
1 实验方案
1.1 石材
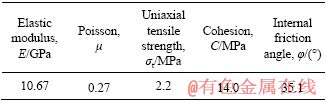
石材选自于云南楚雄的红砂岩。通过偏光显微镜矿物成分鉴定,红砂岩具有粉细砂结构,主要由石英(90%)、长石(4%)、岩屑(4%)等胶结组成,晶体粒度为0.05~0.25 mm。按照国际岩石力学学会测试标准,测得岩石常温下的力学性能如表1所列。
表1 红砂岩常温下的力学性能
Table 1 Mechanical properties of red sandstone at room temperature
1.2 试样
剪切盒和密度实验均采用立方体试样,其中剪切盒试样采用厚度为0.8 mm的金刚石锯片预制双边裂纹加工,裂纹宽t=1 mm。单轴压缩实验采用长方体试样。所有试样尺寸见表2。试样加工时,要求试样表面垂直偏差不超过0.25?,不平行度小于0.05 mm。
1.3 实验方案
在剪切盒实验中,如图1所示,分别在20、60、100、150、200、250和300 ℃对试样加温并恒温2 h后立即进行加载。通过A1、A2面施加平面剪切力Pτ,同时施加侧压力Pσ,Pτ与Pσ之间的比值由压模角决定。由于太大会导致侧压太小且易使试样倾覆,太小会产生试样局部压碎,故本实验选取α=70?。实验中,记录峰值荷载PM,并观察裂纹起裂及断裂轨迹。
表2 岩石试样尺寸
Table 2 Sizes of rock specimens
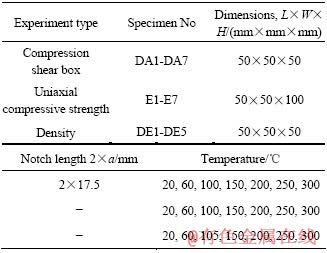
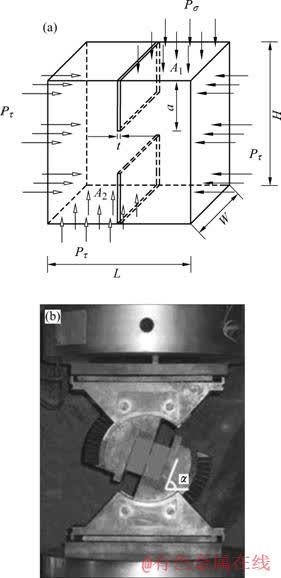
图1 剪切盒实验
Fig.1 Compression-shear box test: (a) specimen; (b) Experi- mental set-up
在单轴压缩实验中,分别将试样加温到20、60、100、150、200、250和300 ℃,恒温2 h后立即进行加载。利用竖向引伸计测量轴向应变,通过不同温度下的应力—应变曲线确定岩石的高温弹性模量及抗压 强度。
以上所有的实验均在中南大学测试中心的Instron1346型电液伺服式实验机上完成。采用位移控制,加载速率为0.05 mm/s。
根据工程岩体实验方法标准[16],在密度实验中,选取20、60、105、150、200、250和300 ℃加温试件,恒温2 h后立即进行体积和质量的测量。体积测量采用游标卡尺,最小刻度值为0.02 mm;称量采用瑞士METTLER TOLEDO生产的PL303精密天平,最小刻度为0.001 g。根据所测得的体积和质量计算不同温度下岩石的密度。
为了分析岩石的微观断裂特征,实验后在裂尖位置分别切取尺寸为10 mm×10 mm×5 mm左右的小块体试样进行扫描电镜实验。由于岩石不导电且孔隙较多、含水率高,实验前先在JFC–1600型喷涂仪上抽真空后喷金才能进行扫描观测。实验仪器为日本JEOL生产的JSM–6360LV扫描电子显微镜,采用二次电子成像方式。
2 结果与分析
2.1 宏观断裂分析
如图2所示,在高温剪切盒加载即压剪加载下,岩石均发生沿原裂纹面的破坏,断裂起裂角几乎为零,裂纹面为平面,宏观表现为Ⅱ型断裂。
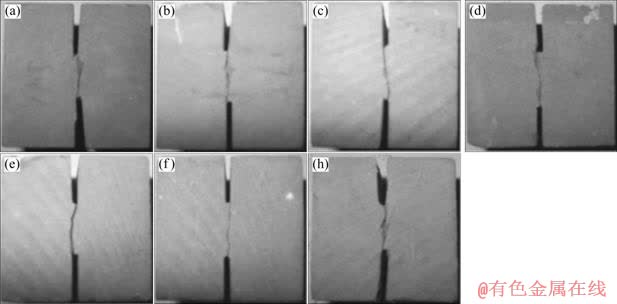
图2 不同温度下岩石剪切断裂轨迹
Fig.2 Shear fracture trajectories of sandstone specimens at different temperatures: (a)20 ℃; (b)60 ℃; (c) 100 ℃; (d) 150 ℃; (e) 200 ℃; (f) 250 ℃; (h) 300 ℃
岩石的剪切断裂峰值荷载随温度的变化曲线如图3所示。峰值荷载随温度的增加而增加,在某个临界温度(如250 ℃)时达到极值后,则随温度的增加反而减少。此外,岩石的弹性模量、抗压强度随温度的变化具有与剪切断裂峰值荷载类似的规律,见图4。
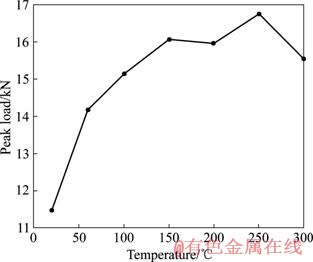
图3 断裂峰值荷载随温度变化
Fig.3 Variation of peak load of Mode Ⅱ fracture with temperature
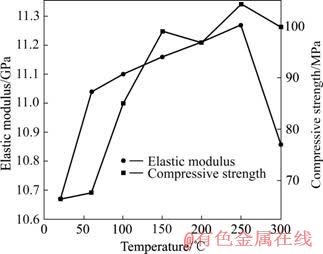
图4 弹性模量、抗压强度随温度变化
Fig.4 Variations of elastic modulus and compressive strength with temperature
岩石的体积、质量、密度随温度的变化曲线如图5所示。砂岩主要为晶体与泥质胶结物、水份组成。胶结物和晶体间孔隙中存在着结晶水和吸附水。由于温度的升高引起岩石内部孔隙和胶结层干脱现象发生,致使岩石的质量减小,其中在100 ℃时岩石质量比常温时减少了1.3%。随着干脱过程的结束,岩石的质量不再变化而趋近一个常数。同时,随着温度的增加,岩石的体积因微裂纹的形成、发育而膨胀增大,其中常温至100 ℃温度段变化最大,岩石体积增加了1%,因此由质量、体积计算得到的岩石密度则随温度的升高反而降低。
可见,在高温加载下,由于温度升高造成胶结物材料的干脱和由于热力耦合效应造成岩石内部微裂纹的形成、发育这两种因素共同影响着岩石的弹性模量、抗压强度、断裂峰值荷载。当温度升高时,由于岩石内部矿物颗粒的热膨胀率不同和胶结物材料的干脱会引起空隙体积减小,原生微裂纹趋于闭合,导致晶体颗粒之间、晶体颗粒与胶结物之间的摩擦因数增大。在达到某个临界温度(如250 ℃)之前,胶结物材料的干脱占主导地位,从而提高了岩石的弹性模量、抗压强度、断裂峰值荷载;在达到该临界温度之后,岩石内部原生微裂纹的发育与新生微裂纹的形成、发育占主导地位,则降低了岩石的弹性模量、抗压强度、断裂峰值荷载。
由图3~5可知,在20~100 ℃之间,岩石的物性(质量、体积、密度)、力学性能(弹性模量、抗压强度)、断裂峰值荷载等变化幅度最大,这是因为在该温度段,胶结层材料烘干致使矿物的结晶水干脱最多最剧烈。可见,结晶水干脱对岩石的物性、力学性能及断裂峰值荷载影响很大。
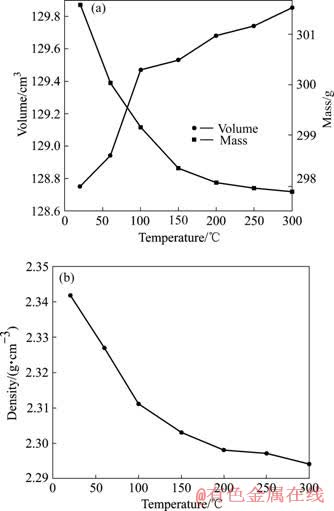
图5 岩石物性与温度的关系
Fig.5 Relationships of properties of sandstone and temperature: (a) Volume and mass; (b) Density
2.2 微观断口分析
为了更清楚地描述岩石断口的微观形貌特征,本研究按断裂面的内部结构来定义细观层次。视红砂岩均为二相材料,第一相为晶体相,第二相为岩屑等组成的胶结物相[17],如图6所示。

图6 红砂岩相分析
Fig.6 Phase analysis of red sandstone
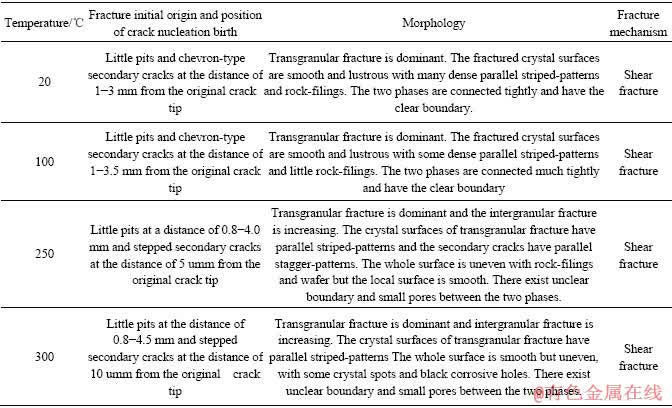
图7所示分别为20、100、250和300 ℃ 4种温度下的岩石断口形貌图。在低倍数(30倍)下,可以观察到断面平整度和损伤情况;局部放大至100倍后可以清晰看到断口岩面的各相分布和光泽情况;进一步放大到850~3 000倍数后,可以看到穿晶晶体面的纹络和坑孔形态。
断口微观特征的详细描述见表3。随着温度的增加,微裂纹的加速形成、发育致使以凹坑、二次裂纹等为特征的裂纹核增大;岩面的平整度变差,光泽度降低,黑蚀坑出现,晶面岩屑增加,两相之间的界线变得模糊。两相间存在小孔隙,主要是由于两相的热膨胀变形不同和外力造成;两相边缘轮廓较模糊且断面光泽较暗,表明第二相胶结层高温干脱较严重。虽然裂纹核的半径随温度加大,但从250和300 ℃时的大倍数断口形貌图(见图7(c)和7(d))可以看到,岩石断口始终为穿晶断裂,晶面光滑且表面具有多而密的平行条状纹和较多岩屑等典型剪切形貌,因此在高温剪切盒加载下岩石发生的破坏为剪断破坏。
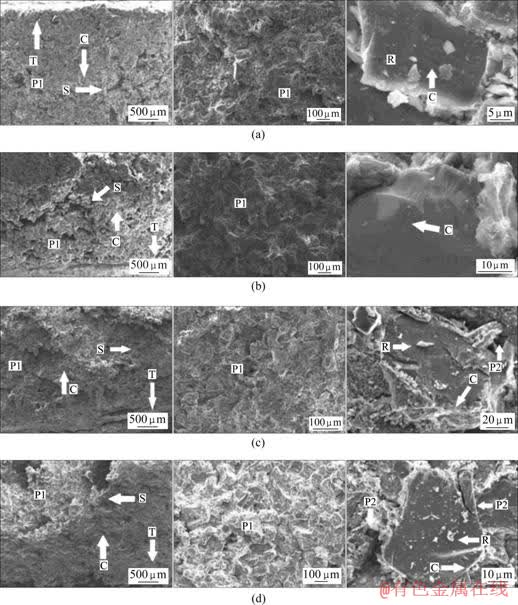
图7 不同温度下岩石剪切断裂的断口形貌
Fig.7 Shear fracture morphologies of compression-shear specimen at different temperatures: (a) 20 ℃; (b) 100 ℃; (c) 250 ℃; (d) 300 ℃ (C: Crack initiation orientation; P1: Pits; P2: Pores; R: Rock cuttings; S: Secondary crack; T: Tip)
表3 断口微观分析
Table 3 SEM analysis
3 结论
1) 在高温剪切盒实验中,脆性岩石的断裂轨迹始终沿原裂纹面,起裂角近似为零,宏观表现为剪切(Ⅱ型)断裂。
2) 高温会同时引起岩石内部胶结物材料的干脱和微裂纹的形成、发育,致使岩石的质量降低、体积增大和密度减小。在高温加载下,胶结物材料的干脱和岩石内部微裂纹的形成、发育这两种因素共同影响着岩石的弹性模量、抗压强度、断裂峰值荷载,前者占主导地位起强化作用,后者占主导地位起弱化作用,临界温度为250 ℃。
3) 随着温度的升高,岩石断口微观特征表现为岩石裂纹核增大,断口多为穿晶断裂,晶面光滑且具有多而密的平行条状纹和较多岩屑等典型的剪切形貌,表明在高温剪切盒加载下岩石破坏为剪切(Ⅱ型) 断裂。
4) 剪切盒实验是实现岩石高温Ⅱ型断裂和测定岩石高温Ⅱ型断裂韧度 的一种有效方法。
的一种有效方法。
REFERENCES
[1] 张晶瑶, 马万昌, 张凤鹏, 金校元. 高温条件下岩石结构特征的研究[J]. 东北大学学报: 自然科学版, 1996, 17(1): 5?9.
ZHANG Jing-yao, MA Wan-chang, ZHANG Feng-peng, JIN Xiao-yuan. On rock structure character under high temperature [J]. Journal of Northeastern University: Natural Science, 1996, 17(1): 5?9.
[2] 赵 鹏, 谢卫红, 王习术, 高 峰. 高温下岩石SEM实时实验研究[J]. 力学与实践, 2005, 28(3): 64?67.
ZHAO Peng, XIE Wei-hong, WANG Xi-shu, GAO Feng. The real time experimental research on rock's SEM under high temperature[J]. Mechanics in Engineering, 2005, 28(3): 64?67.
[3] 张 渊, 万志军, 赵阳升. 细砂岩热破裂规律的细观实验研究[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报, 2007, 26(4): 529?531.
ZHANG Yuan, WAN Zhi-jun, ZHAO Yang-sheng. Meso- experiment of fine sandstone thermal crack laws[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University, 2007, 26(4): 529?531.
[4] 王靖涛, 赵爱国, 黄明昌. 花岗岩断裂韧度的高温效应[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1989, 11(6): 113?119.
WANG Jing-tao, ZHAO Ai-guo, HUANG Ming-chang. Effect of high temperature on the fracture toughness of granite[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1989, 11(6): 113?119.
[5] AYATOLLAHI M R, ALIHA M R M. On determination of mode Ⅱ fracture toughness using semi-circular bend specimen[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures,2006, 43(17): 5217?5227.
[6] FUNATSU T, SETO M, SHIMADA H, MAISUI K, KURUPPU M. Combined effects of increasing temperature and confining pressure on the fracture toughness of clay bearing rocks[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2004, 41(6): 927?938.
[7] BALME M R, ROCCHI V, JONES C, SAMMONDS P R, MEREDITH P G, BOON S. Fracture toughness measurements on igneous rocks using a high-pressure, high-temperature rock fracture mechanics cell[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2004, 132(2): 159?172.
[8] 张宗贤, 喻 勇, 赵 清. 岩石断裂韧度的温度效应[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 1994, 4(2): 7?11.
ZHANG Zong-xian, YU Yong, ZHAO Qing. Effect of temperature on rock fracture toughness[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1994, 4(2): 7?11.
[9] 王桂尧, 孙宗颀, 黎振兹. 岩石Ⅱ型裂纹扩展的一般规律[J]. 中南工业大学学报: 自然科学版, 1994, 25(4): 450?454.
WANG Gui-yao, SUN Zong-qi, LI Zhen-zi. General behaviour of mode Ⅱ crack propagation in rocks[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology: Natural Science, 1994, 25(4): 450?454.
[10] 马世骧, 胡 泓. CTS试件中复合型疲劳裂纹扩展[J]. 力学学报, 2006, 38(5): 698?704.
MA Shi-xiang, HU Hong. The mixed-mode propagation of fatigue crack in CTS specimen[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2006, 38(5): 698?704.
[11] BACKERS T, STEPHANSSON O, RYBACKI E. Rock fracture toughness testing in Mode Ⅱ—punch-through shear test[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2002, 39(6): 755?769.
[12] AL-SHAYEA N A, KHAN K, ABDULJAUWAD S N. Effects of confining pressure and temperature on mixed-mode (Ⅰ-Ⅱ) fracture toughness of a limestone rock[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences 2000, 37(4): 629?643.
[13] RAO Qiu-hua, SUN Zong-qi, STEPHANSSON O, LI Chun-lin, STILLBORG B. Shear fracture(Mode Ⅱ) of brittle rock[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2003, 40(3): 355?375.
[14] 陈 枫. 岩石压剪断裂的理论与实验研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2002.
CHEN Feng. The theoretical and experimental investigation on rock fracture due to shear-compression loading[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2002.
[15] RAO Qiu-hua. Pure shear fracture of brittle rock-A theoretical and laboratory study[D]. Sweden. Lule? University of Technology, 1999.
[16] GB/T50266—99. 工程岩体试验方法标准[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 1999.
GB/T50266—99. Standard for tests method of engineering rock masses[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 1995.
[17] 哈宽富. 断裂物理基础[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000.
HA Kuan-fu. Fracture physical base[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2000.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50374073);中国博士后科学基金资助项目(2002032256);中南大学博士学位论文创新工程资助项目(1343- 77239)
收稿日期:2007-12-03;修订日期:2008-03-18
通讯作者:饶秋华,教授,博士;电话:0731-8836001;E-mail: raoqh@mail.csu.edu.cn
(编辑 何学锋)