医用镁合金表面改性研究进展
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报2011年第1期
论文作者:曾荣昌 孔令鸿 陈君 崔洪芝 刘成龙
文章页码:35 - 43
关键词:镁合金;生物材料;生物涂层;腐蚀;生物相容性
Key words:magnesium alloy; biomaterials; bio-coating; corrosion; biocompatibility
摘 要:由于镁及其合金具有良好的生物相容性和力学相容性,降低镁合金过快的腐蚀速度成为其作为生物材料应用的关键,医用镁合金表面改性已成为新一代生物材料的研究重点。介绍医用镁合金的发展历程,重点讨论镁合金表面生物活性陶瓷(如羟基磷灰石(HA))、阳极氧化膜、可降解高分子聚合物(如聚乳酸(PLA)、PLGA、壳聚糖)、惰性生物陶瓷涂层(如TiO2、Al2O3、ZrO2)、化学转化膜(氟化膜、稀土转化膜)和金属镀层(如Ti、Zn)制备、耐蚀性及其生物相容性,并指出其发展趋势。
Abstract: Magnesium and its alloys have excellent biocompatibility and mechanical compatibility. The reduction in their rapid corrosion rates becomes the key to clinical applications. The current study on magnesium alloys as biomaterials is focused on the surface modification. The history and recent cutting edge researches on the bio-coatings on medical magnesium alloys were predominately reviewed. The emphasis was placed on the recent progress of the preparation, corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of the bio-coatings. These coatings include hydroxyaptite (HA), micro arc oxidation films or plasma electrolyte oxidation coatings, degradable polymers (polylactic acid (PLA), poly (lactide-co- glycolide) (PLGA) and chitosan), inert bio-ceramic coatings (TiO2, Al2O3 and ZrO2) and chemical conversion films (fluoride and rare earth) and ion implanted titanium and zinc films as well. The developmental trends were proposed.
文章编号:1004-0609(2011)01-0035-09
曾荣昌1, 2, 孔令鸿2, 陈 君2, 崔洪芝1,刘成龙2
(1. 山东科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,青岛 266510;
2. 重庆理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,重庆 400050)
摘 要:由于镁及其合金具有良好的生物相容性和力学相容性,降低镁合金过快的腐蚀速度成为其作为生物材料应用的关键,医用镁合金表面改性已成为新一代生物材料的研究重点。介绍医用镁合金的发展历程,重点讨论镁合金表面生物活性陶瓷(如羟基磷灰石(HA))、阳极氧化膜、可降解高分子聚合物(如聚乳酸(PLA)、PLGA、壳聚糖)、惰性生物陶瓷涂层(如TiO2、Al2O3、ZrO2)、化学转化膜(氟化膜、稀土转化膜)和金属镀层(如Ti、Zn)制备、耐蚀性及其生物相容性,并指出其发展趋势。
关键词: 镁合金;生物材料;生物涂层;腐蚀;生物相容性
中图分类号:TG146.22 文献标志码:A
ZENG Rong-chang1, 2, KONG Lin-hong2, CHEN Jun2, CUI Hong-zhi1, LIU Cheng-long2
(1. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266510, China;
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Chongqing University of Technology, Chongqing 400050, China)
Abstract: Magnesium and its alloys have excellent biocompatibility and mechanical compatibility. The reduction in their rapid corrosion rates becomes the key to clinical applications. The current study on magnesium alloys as biomaterials is focused on the surface modification. The history and recent cutting edge researches on the bio-coatings on medical magnesium alloys were predominately reviewed. The emphasis was placed on the recent progress of the preparation, corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of the bio-coatings. These coatings include hydroxyaptite (HA), micro arc oxidation films or plasma electrolyte oxidation coatings, degradable polymers (polylactic acid (PLA), poly (lactide-co- glycolide) (PLGA) and chitosan), inert bio-ceramic coatings (TiO2, Al2O3 and ZrO2) and chemical conversion films (fluoride and rare earth) and ion implanted titanium and zinc films as well. The developmental trends were proposed.
Key words: magnesium alloy; biomaterials; bio-coating; corrosion; biocompatibility
镁合金具有良好的生物相容性和力学相容性[1]、第三代医用材料的可降解性和生物活性特征[2]以及其他金属基生物材料和可降解高分子材料所不具备的性能。因此,镁合金作为新一代医用植入材料具有广泛的发展前景。
近10年来,ZENG等[3]和STAIGER等[4]从不同面报道医用镁合金腐蚀降解、生物相容性和表面改性的研究进展。
1999年,HEUBLEIN等[5]在美国华盛顿输尿管心血管治疗会议上报告了镁的降解和作为心血管介入器械的前景。2001年,HAFERKAMP等[6] 在日本先进镁合金平台科学与技术会议上指出生物材料是镁应用的新领域。2005年,WITTE等[7]在《Biomaterials》上率先发表了4种商用镁合金动物试验研究结果,从而揭开了21世纪镁合金医用研究的序幕。
李龙川等[8]、STAIGER等[4]和ZENG等[3]基于商用镁合金的腐蚀降解及表面改性现状,指出了医用镁合金的应用前景和面临的挑战。基于合金化分析,SONG等[9]于2007年指出可作为医用镁合金的合金化元素,并认为医用镁合金阳极氧化膜具有明显提高耐蚀性的优势和应用前景。
2008-2009年,高家城和乔丽英[10]、WITTE等[11]、黄晶晶和杨柯[12]、陶海荣和蒋垚[13]、郑玉峰等[14]和张佳等[15]综述了镁及镁合金作为骨固定材料、骨组织工程多孔支架材料、冠状动脉支架的腐蚀性能、力学性能、生物相容性和表面改性以及临床医用研究进展,分析了化学成分、加工工艺和合金元素、体内外试验方法以及环境等因素对镁合金腐蚀的影响。
不仅如此,在国际国内会议上,医用镁合金研究也备受关注。2006第年七届镁合金及其应用国际会议(德国)论文集中仅有4篇涉及医用镁合金研究;2009年第八届镁合金及其应用(德国)会议设有镁合金生物材料专题,有5个报告7个墙报,论文集收录相关论文12篇。2009年12月,在广州华南理工大学召开的中国生物医学工程学会生物材料分会首次设有“可腐蚀、降解型医用金属材料”专题,其中,有54个医用镁合金材料研究报告。
由此可见,镁合金已逐渐成为当今生物材料的研究热点[16-18]。动物试验研究结果表明,镁合金作为骨植入材料在动物体内仅存在较短时间(60~90 d)就会降解消失,不能满足骨骼生长对力学性能的要求[5-6]。医用镁合金过快的腐蚀降解速度严重制约着其推广应用,是亟待解决的关键科学技术问题。
1) 商用镁合金耐蚀性还不能满足可降解植入材料要求,镁合金过快的腐蚀速度导致析氢速度较大。纯镁的析氢速度高达10 mL/h 或者40 mL/(cm2?d)[9],医用镁合金BioMag352(0.2%Zn-2.82%Nd-0.19%Ca- 0.21%Y-0.33%Zr, 质量分数)的析氢速度高可达2.5 mL/h或10 mL/(cm2?d)[19],而人体吸收氢的容许度仅为2.25 mL/(cm2?d)[9]。
2) 镁合金过快的腐蚀速度同时导致溶液pH 值的快速升高,对人体骨骼及组织生长产生潜在危害。在镁合金闭塞电池溶液中,pH值在极短时间内迅速增加到10.5以上,即镁合金腐蚀引起局部碱化速度加快。由于材料在使用环境中,pH值发生变化,可能使人体产生异常反应。例如,可能导致人体组织中蛋白质达到等电点而发生蛋白质沉积和炎症,或出现溶血现象和局部溶骨现象[20]。
3) 腐蚀过快还将使人体组织在未充分愈合之前植入体丧失机械整体性,从而引起力学性能(如抗拉强度、抗压屈服强度和疲劳强度)的迅速劣化。
针对上述问题,ERINC 等[21]提出可降解医用镁合金的标准为:在37 ℃模拟体液中的腐蚀速率小于0.5 mm/a,有效服役期90~180 d;室温屈服强度大于200 MPa,伸长率大于15%。
研究结果表明:材料合金化、变形加工、非晶化和表面改性是提高镁合金耐蚀性的主要途径。
1) 添加某些合金元素如Al、In、Mn、Zn、Zr和Y可提高镁合金的耐蚀性[9, 18];
2) 挤压和轧制可细化镁合金晶粒组织,从而提高其耐蚀性[22];
3) Mg-Zn-Ca金属玻璃可改变合金的腐蚀形态,显著降低析氢速度[1];
4) 表面改性更能显著地提高镁合金材料的耐蚀性[23]。
尽管镁的合金化和变形加工工艺都可以明显改善镁合金的耐蚀性,但是,其耐蚀能力还不能满足植入材料的实际要求。非晶态镁合金的塑性远比晶态的差。例如,非晶态Mg60Zn35Ca5的塑性低于2%,晶态的塑性可达10%~27% [1]。因此,表面改性研究成为医用镁合金的应用关键和研究重点。针对以前的文献在分析广度和深度上的欠缺,本文作者旨在深入分析镁合金医用涂层制备的技术方法、原理及特点,比较和评价各种涂层的耐蚀性和生物相容性。
1 镁合金生物涂层
镁合金生物涂层包括生物活性陶瓷(如羟基磷灰石(HA))[23-28]、阳极氧化膜[29-31]、可降解高分子聚合物(如聚乳酸、PLGA、壳聚糖)[32-35]、化学转化膜(氟化膜、稀土转化膜)[36-38]、金属镀层(如Ti、Zn)[39-40]和惰性生物陶瓷涂层(如TiO2、Al2O3、ZrO2)[3, 41]。
1.1 生物活性陶瓷
生物活性陶瓷包括HA和磷酸三钙(Ca3(PO4)2)。HA具有良好的生物相容性,是骨骼的主要成分,其分子式为 Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2,Ca原子与P原子的摩 尔比(n(Ca)/n(P))=1.67。它微溶于水,呈弱碱性(pH为7~9),故易溶于酸而难溶于碱。HA选择性地吸附富有酸性氨基酸和丝氨酸的蛋白质以及磷酸基和羟基含量高的蛋白质[42 -43]。它能诱导骨生长,即新骨可以从HA植入体与原骨结合处沿着植入体表面或内部贯通性空隙攀附生长。WITTE等[17]将 HA加入镁合金制得镁/HA复合材料。研究结果表明,HA可改变镁合金的腐蚀形态,使镁合金从局部腐蚀变为均匀腐蚀。Ca3(PO4)2包括α-Ca3(PO4)2和β-Ca3(PO4)2。后者是应用最广泛的可降解生物陶瓷,其n(Ca)/n(P)=1.5。人们在镁合金表面尝试了多种方法,如电沉积[23-24, 28]、化学沉积[25-26]、激光熔覆[27] 以及离子束辅助沉积(IBAD)[42]来沉积HA或Ca/P涂层。
1.1.1 电沉积
张春艳等[23] 研究了镁合金AZ31 分别经过过饱和Ca(OH)2溶液和阳极氧化预处理后,在Hank’s 溶液、Ca(NO3)2 和NH4H2PO4 混合溶液中制备Ca-P 基生物陶瓷涂层的可能性。将经过过饱和Ca(OH)2溶液和阳极氧化预处理后的镁合金AZ31,分别浸入Hank’s 溶液和pH为5.5的0.042 mol/L Ca(NO3)2和0.025 mol/L NH4H2PO4的混合溶液(Ca-P溶液)中制备Ca-P基生物陶瓷涂层。在Ca-P溶液中浸泡48 h后,两种预处理的镁合金表面均获得了主要为磷酸氢钙(DCPD)和少量磷酸三钙(TCP)的竹叶状或片状结晶体(见 图1)。但是,在Hank’s溶液中,镁合金表面未产生HA结晶,表明无法通过仿生溶液沉积的方法在镁合金表面得到HA涂层。研究结果表明[24]:在Mg-Ca合金表面能够形成与Mg-Al合金表面成分、结构和形貌相似的Ca-P涂层,且Ca-P涂层的耐蚀性与基体的化学成分相关。AZ31基体及其Ca-P涂层的腐蚀电流密度分别小于Mg-1.0Ca合金的基体和涂层的腐蚀电流密度。
郭磊[25]等采用恒电压阴极电沉积法及碱热处理在镁合金AZ31B表面制备Ca-P涂层。合金样品经环氧乙烷消毒处理植入家兔体内28 d后发现,Ca-P涂层表面的磷、镁、氧和钙元素含量较单纯AZ31B合金的明显增高,其表面分布着许多均匀的Ca-P颗粒。经过观察发现,Ca-P/AZ31B植入后有轻度炎症反应,溶血率仅为2.5%,符合生物材料溶血性小于5%的要求。SONG等[28]将AZ91D镁合金置入含有0.1 mol/L Ca(NO3)2、0.06 mol/L NH4H2PO4、10 mL/L H2O2,pH为4.3的电解液,获得一层由磷酸氢钙水合物(CaHPO4·H2O)和β-Ca3(PO4)2组成的涂层。然后,将沉积的涂层浸泡在1 mol/L NaOH 溶液中2 h后转变为HA。结果显示,HA涂层可以提高AZ91D镁合金在SBF中的耐蚀性。
1.1.2 化学沉积
耿芳等[26]采用低温化学沉积法在镁合金表面制
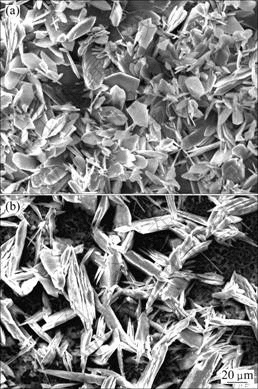
图 1 AZ31试样经过过饱和Ca(OH)2溶液预处理12 h和阳极氧化处理后在pH值为5.5的0.042 mol/L Ca(NO3)2和0.025 mol/L NH4H2PO4的混合溶液中浸泡48 h后的SEM 像[23]
Fig.1 SEM images of AZ31 samples immersed in mixed solution of 0.042 mol/L Ca(NO3)2 and 0.025 mol/L NH4H2PO4 with pH value of 5.5 for 48 h: (a) Pre-soaked in Ca(OH)2 saturated solution for 12 h; (b) After treatment of anodized oxidation process[23]
备具有生物活性的β-Ca3(PO4)2涂层。MTT比色法、单细胞凝胶电泳技术(SCGE)和流式细胞术(FCM)实验证实,经过表面处理后,镁合金支架无细胞毒性,β-TCP表面处理后的镁合金支架浸提液对细胞DNA无损伤,对细胞周期无改变。
将镁合金放入一些碱性溶液中,然后在模拟人体体液中浸泡一定时间,可在镁合金表面形成无定形磷酸钙盐或镁钙磷灰石((Ca1-xMgx)10(PO4)6(OH)2)沉淀。
将纯镁浸入过饱和NaHCO3-MgCO3溶液中,然后再进行热处理,经过SBF浸泡14 d后,处理过的试样表面沉积了一层磷酸钙磷灰石[44]。经过热碱处理后,镁在模拟人体体液和SBF溶液中的耐蚀性均有改善。然而,进一步研究[45]表明,经过碱处理以后镁合金会产生细胞毒性,且会导致明显细胞形态和细胞分裂的变化。而未经碱液处理的镁合金则没有细胞形态的变化或细胞生长受抑制的情况,也没有产生细胞毒性。
1.1.3 激光熔敷和离子束辅助沉积
高亚丽等[27]采用激光熔覆技术在AZ91D镁合金表面制备具有生物活性的羟基磷灰石涂层。结果表明:所制备的涂层和镁合金基体达到了良好的冶金结合;涂层显微结构为致密的胞状晶体,主要由Mg、HA、CaH2P2O7和CaH4(PO3)2·H2O组成,其中,n(Ca)/n(P)= 1.73, 接近理论值1.67。为了获得较高n(Ca)/n(P)的磷酸盐蒸发剂,YANG等[43]将37%的CaO粉末添加到HA粉末中,并采用IBAD方法涂敷在AZ31镁合金基体上,经250 ℃,2 h的退火处理后,在100 ℃的去离子水中浸泡0.5 h,最终获得一层Ca-P涂层。浸泡15 d后,含Ca-P涂层试样的质量损失是裸试样的1/5。这说明Ca-P涂层明显地降低了镁合金的腐蚀速度。
以上研究表明,镁合金羟基磷灰石转化膜是很有应用前景的生物活性涂层。但是,HA在镁合金上应用存在的主要问题是这类涂层脆性较大,结合力差。因此,提高HA与镁合金的基体之间的结合是其能得到应用的关键技术。
1.2 阳极氧化膜
金属或合金的阳极氧化或电化学氧化是将金属或合金的制件作为阳极置于电解液中,在外加电流作用下使其表面形成氧化物薄膜的过程。微弧阳极氧化(Micro arc oxidation, MAO)是通过电解液与相应电参数的组合,在Mg等有色合金表面依靠弧光放电产生瞬时高温高压作用,制备以基体金属氧化物为主的陶瓷膜层。这种膜层也属于陶瓷涂层,具有多孔的特点。
1.2.1 阳极氧化膜对耐蚀性的影响
MAO膜层能显著地提高镁合金基体的耐蚀性。ZENG等[22]采用微弧氧化工艺在挤压态Mg-1.0Ca合金表面制得具有微米级孔隙的阳极氧化膜(见图2)。研究发现,经过微弧阳极氧化的Mg-1.0Ca在Hank’s溶液中的极化曲线大幅度地左移,而微弧氧化前后的电位—时间曲线变化不明显。ZHANG等[30]将具有MAO膜层的AZ91D镁合金在Hank’s溶液中浸泡21 d后,其质量损失仅为基体的1/15。AZ91基体和有MAO膜层的腐蚀速度分别为2.90×10-2和2.05×10-7 A/cm2。该研究表明,具有MAO的镁合金的耐蚀性提高几个数量级。SONG[31]将阳极氧化后的纯镁在Hank’s溶液中浸泡30 d,没有观察到氢气产生。
1.2.2 阳极氧化膜对耐磨性的影响
ZHANG 等[30]对具有MAO膜层的AZ91D进行润滑滑动磨损试验后发现,AZ91D基体的质量损失是微
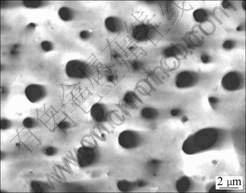
图2 Mg-1.0Ca微弧氧化膜的SEM像[22]
Fig. 2 SEM image of MAO coating on Mg-1.0Ca alloy [22]
弧氧化试样的1.5倍。但是,在腐蚀与磨损环境的交互作用下,结果可能会不同。CHEN等[29]采用微磨粒磨损实验考察有MAO膜的AZ91分别在0.9% NaCl、0.9% NaCl +0.35 g/L NaHCO3及0.9% NaCl +0.7 g/L NaHCO3 3种溶液中的磨损腐蚀行为发现,与基体相比,MAO膜尽管提高了AZ91的耐腐蚀性能,但由于MAO膜层很脆,在磨损过程中会形成微磨粒,反而降低了其耐磨性。因此,还需要进一步的腐蚀磨损实验来评价镁合金表面MAO膜层的耐磨性能。
1.2.3 阳极氧化膜对细胞毒性的影响
郭磊等[46]发现AZ31B阳极氧化膜浸提液的微核率为0.44%,与生理盐水阴性对照组无显著差异,且低于国际药典阳性标准(0.5%),无致突变反应,溶血率为4.3%。通过体外直接接触细胞毒性试验和MTT比色法试验发现,AZ31B有氧化膜和无氧化膜的成骨细胞合成碱性磷酸酶(ALP)的活性与正常组无显著性差异,从而证实氧化膜和AZ31B材料对成骨细胞的增值和成骨活性无毒性作用。这表明,镁合金阳极氧化膜具有良好的生物相容性。
阳极氧化膜的优点是与基体具有良好的结合力和耐蚀性较强。与HA或Ca-P涂层比较,阳极氧化膜的结合力和耐蚀性能均优于Ca-P涂层的结合力和耐蚀性能。这种多孔的膜层可能有助于组织生长和制备载药涂层。但镁合金阳极氧化膜的磨蚀腐蚀机理有待进一步探讨,氧化膜是否可降解以及降解速度等问题还有待进一步研究。
1.3 可降解高分子涂层
高分子生物活性材料不仅具有良好的生物相容性,而且可生物降解和降解产物容易吸收或代谢,并且有利于细胞的粘附、生长、增殖以及基因表达和调控。镁合金医用材料表面改性的高分子涂层主要有两类:聚乳酸(PLA)及其共聚物和壳聚糖。
1.3.1 聚乳酸及其共聚物
PLA的单体是乳酸。乳酸或丙交酯(乳酸的环状二聚体)在一定条件下聚合,都可得到等规、间规、无规的PLA。PLA的结构式[46]为
![]()
医用聚乳酸(PLA)可在人体内降解,最终产物为二氧化碳和水,参与人体代谢循环排出,具有较好的生物相容性。聚乙交酯-丙交酯(PLGA)是目前应用最广泛的一种聚乳酸共聚物,由乳酸与乙醇酸或乙交酯与丙交酯共聚得到。
赵常利等[33]采用浸涂提拉法在Mg-Zn合金表面获得致密的PLGA涂层。PLGA涂层能有效地提高镁合金的耐蚀性。在生理盐水中的阳极极化曲线表明其腐蚀过程存在活化区和钝化区,并且涂层合金的腐蚀电流密度比基体的腐蚀电流密度约小2个数量级。黄晶晶等[35]采用硅烷偶联剂对镁植入材料表面进行预处理,用浸涂法制备镁植入材料表面聚乳酸涂层。处理后的试样在Hank’s溶液中浸泡10 d后,其质量损失明显降低,说明镁表面涂覆聚乳酸涂层可提高其在模拟体液中的耐蚀性。
但医用PLA或PLGA的酸性降解产物会降低组织周围的pH,对人体产生一种非炎症性抗宿主反应,加之其亲水性和机械强度较弱,对组织和细胞的黏附生长将产生一定影响。在聚合物中引入碱性物质如羟基磷灰石,或与呈碱性的壳聚糖混合使用,可弥补聚合物降解引起的pH下降,有利于防止无菌性炎症的发生[47]。聚乳酸涂层降解时的酸性产物反过来可能会加速镁合金的腐蚀。由于PLA呈疏水性,其降解速度比较慢。PLLA在体内完全降解吸收的时间一般为 28 d~8 a [47]。由此可见,PLLA与镁的腐蚀降解速率的匹配是值得关注的一个问题。
1.3.2 壳聚糖
壳聚糖是由N-乙酰-2-氨基-2-脱氧-D-葡萄糖以β-1,4-糖苷键形式连接而成,其分子式为(C8H13NO5)n。它是一种安全无毒的可降解生物材料,由甲壳素在强碱环境下脱乙酰制得,既具有与植物纤维素相似的结构,又具有类似人体骨胶原组织的结构,因此,其生物活性极高。除了具有止血和抗凝血功能外,高活性的功能基团使壳聚糖表现出类似抗生素的特性,能不同程度地抑制多种细菌的生长,同时能分泌多种免疫因子,调节体液免疫,增强机体的抗感染能力,增强机体免疫系统功能,消炎止痛,促进伤口愈合[47]。
许鑫华等[32]在镁合金WE43表面涂覆壳聚糖,研究其在Hank’s模拟体液中的腐蚀性能。试验中涂层与金属基底的结合强度增大,抑制了失粘和起泡,使得自腐蚀电位升高,腐蚀电流密度减小,从而延缓了腐蚀的发生。但总的来说,壳聚糖膜对镁合金的腐蚀性能影响比较复杂。壳聚糖的降解速度同PLA的降解速度一样,也比镁的降解速度慢很多。目前,壳聚糖应用于镁合金表面的研究尚处于起步阶段,与Ca-P涂 层和阳极氧化膜相比,可降解高分子涂层的耐磨性 较差。
1.4 化学转化膜
化学转化膜是采用化学或电化学方法在金属表面形成金属氧化物、铬酸盐、磷酸盐或其他与表面化学结合的化合物。镁合金转化膜类型主要有铬酸盐系、磷酸盐系、锡酸盐系和稀土盐系或氟化镁等[48]。目前,有关人体环境中的化学转化膜层主要有MgF2和稀土转化膜。
1.4.1 MgF2转化膜
HASSEL等[49]和ZENG等[36]等发现,MgF2转化膜在模拟体液中具有一定的耐蚀性。WITTE等[37]在进行挤压态镁合金LAE442家兔体内腐蚀试验时发现,MgF2可显著降低镁合金的腐蚀速率。此外,临床42 d后观察发现,MgF2涂层延缓了金属元素在体内的释放,相邻骨骼中氟浓度没有升高,且没有皮下气泡出现,显示MgF2涂层具有良好的耐蚀性和生物相容性。
1.4.2 稀土转化膜
颜廷亭等[38]使用CeCl3在AZ31B镁合金表面制得主要成分为CeO2和MgO的转化膜。结果表明,处理后的AZ31B镁合金在生理盐水和Hank’s溶液中的耐蚀性得到显著改善,同时表现出较好的抗凝血性能,具有与316L不锈钢相当的、良好的血液相容性。RUDD等[50]和GAO等[51]等应用稀土转化技术在镁表面制备一层保护性膜,处理后的镁合金的耐蚀性能得到了显著提高。GAO等[51]使用CeCl3 和Y(NO3)3 溶液获得转化膜,在纯镁上这层膜分别由Mg(OH)2、Ce2O3、MgO和Mg(OH)2、Y2O3和MgO组成,且后者的耐蚀性优于前者的耐蚀性。
化学转化膜的缺点是它们的厚度都非常薄,不能抵抗任何机械损伤,仅能做打底层使用。且其生物相容性还需要进一步证实。
1.5 金属离子注入涂层
金属离子注入涂层可通过离子注入来制备。离子注入则可在真空条件下往镁合金表面注入任何元素,但注入深度有限,一般为50~500 nm。离子在固溶体中处于置换或间隙位置,形成不能通过平衡相图预见的表面层。
LIU等[40]采用离子注入技术将钛注入AZ91镁合金表面,形成一层混合层和表面氧化膜。其主要成分为二氧化钛与少量的氧化镁。氧化膜有3个层次:外层主要成分为10 nm厚的MgO、TiO2与Mg(OH)2;中间层主要成分为50 nm厚的TiO2、MgO以及少量的MgAl2O4和TiO;第3层为表面富集的金属Mg、Ti、Al及Ti3Al。钛离子的注入显著地提高了AZ91基体的开路电位或自腐蚀电位。这主要是由于形成了更致密的表面氧化膜。ZHANG等[52]在纯镁上通过离子注入获得一层致密的、结合良好的Ti涂层,发现该涂层是一层既没有孔隙,也无明显的互扩散层。涂层改善了镁的耐蚀性。
但离子注入层不一定总能提高合金的耐蚀性。WAN等[39]采用离子注入方法在Mg-Ca合金上制备一层Zn涂层。结果出乎意料,所有Zn注入层的耐蚀性都比空白对比试样的耐蚀性差。这表明Zn对于生物医用Mg-Ca合金来说不是理想的离子注入元素。
镁合金表面离子注入可能存在的风险是镁合金基体的腐蚀速度远远大于表面注入层的腐蚀速度,易出现电偶腐蚀的问题,且Ti注入层不易降解。目前还没有动物试验方面的数据。
1.6 惰性陶瓷涂层
在金属材料表面上喷涂TiO2、Al2O3及ZrO2生物陶瓷材料,可提高植入材料的性能[3, 41, 53]。例如,高纯Al2O3生物陶瓷主要用于关节头和关节臼的制备。Ti的氧化层具有优良的生物相容性,宽禁带N型半导体TiO2层具有抗凝血性、纳米TiO2层具有抗菌性、稳定的TiO2层具有生物惰性和优良的生物相容性[42]。ZENG等[41]采用等离子喷涂法在镁合金AM60上获得多孔的菜花状TiO2陶瓷涂层(见图3)。由于基体和多孔涂层之间的电偶腐蚀,TiO2涂层并没有增强AM60在Hank’s溶液中的耐腐蚀性能。然而,用硅酸钠封闭后,其腐蚀速率明显降低。XIN等[53]采用阴极电弧工艺在镁合金上制得1 ?m厚的Al2O3/Al和1.5 ?m厚的ZrO2/Zr两种具有三明治结构的涂层。Al或Zr中间层用来阻碍氧化物与镁的直接接触,因此可以增加涂层与基体材料之间的结合强度。实验结果表明,这些涂层与基体材料之间具有良好的结合强度,同时也改善了耐蚀性。但由于涂层中存在的孔隙在SBF中长时间浸泡,电解液的渗透会使涂层的保护性能明显降低。此外,采用阴极电弧工艺获得的涂层比等离子喷涂所得的涂层致密,且具有平整的表面以及与母材良好的结合强度。
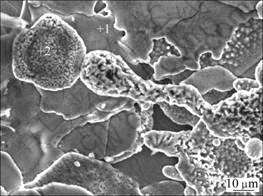
图3 AM60镁合金表面等离子喷涂TiO2 的SEM像[22]
Fig.3 SEM image of plasma sprayed TiO2 coating on AM60 magnesium alloy[22]
热喷涂涂层的一个主要优点是具有粗糙表面与孔隙,可储存缓释药物。缺点是如果没有进行后续封闭处理,在SBF中长时间浸泡后,会降低涂层的腐蚀性能。另外,金属陶瓷涂层为惰性材料,不能降解。对于镁合金来说,此类涂层的研究刚刚开始,有不少问题有待深入探讨。
2 结 语
1) 表面/界面和表面改性一直都是生物材料研究的重点。医用镁及合金表面改性的目的是提高镁合金在人体体液中的耐蚀性能,以减缓体内降解速率,并使材料具备优良的生物相容性。但一般来看,单一涂层难于满足人体环境对于综合性能(如耐蚀、选择性吸附、耐磨和抗腐蚀疲劳)的要求。
2) 表面改性还要赋予医用镁合金表面/界面生物功能化,诱导组织再生和形成(选择性吸附蛋白、构成可激活和调控细胞基因表达的微环境),控释药物和生物活性物质(药物、细胞素、基因),具备抗菌性、抗凝血性和抗组织增生等生物功能。
3) 运用材料学、腐蚀科学、表面工程、生物组织工程、医学和药学等多学科理论,开发具有梯度、可控降解、表面/界面功能的新型医用镁合金生物复合涂层将是研究的方向。
References
[1] ZBERG B, UGGOWITZER P J, LOEFFLER J F. MgZnCa glasses without clinically observable hydrogen evolution for biodegradable implants[J]. Nature Materials, 2009, 8(11): 887-891.
[2] HENCH L L, POLAK J M. Third-generation biomedical materials[J]. Science, 2002, 295(5557): 1014-1027.
[3] ZENG R C, DIETZEL W, WITTEL F, HORT N, BLAWERT C. Progress and challenge for magnesium alloys as biomaterials[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2008, 10(8): 3-14.
[4] STAIGER P M, PIETAK A M, HUADMAI J, DIAS G. Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials: A review[J]. Biomaterials, 2006, 27(9): 1728-1734.
[5] HEUBLEIN B, ROHDE R, NIEMEYER M, KAESE V, HARTUNG W, R?CKEN C, HAUSDORF G, HAVERICH A. Degradation of magnesium alloys: A new principle in cardiovascular implant technology[C]//Annual Symposium of Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics. New York, 1999: 5-10.
[6] HAFERKAMP H, BOEHM R, HOLZKAMP U, JASCHIK C, KAESE V, NIEMEYER M. Alloy development, processing and applications in magnesium lithium alloys[J]. Materials. Transactions, 2001, 42(7): 1160-1166.
[7] WITTE F, KAESE V, HAFERKAMP H. Corrosion of four magnesium alloys and the associated bone response[J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(17): 3557-3563.
[8] 李龙川, 高家诚, 王 勇. 医用镁合金的腐蚀行为与表面改性[J]. 材料导报, 2003, 17(10): 29-32.
LI Long-chuan, GAO Jia-cheng, WANG Yong. Corrosion behaviors and surface modification of magnesium alloys for biomaterial applications[J]. Materials Review, 2003, 17(10): 29-32.
[9] SONG G, SONG S. A possible biodegradable magnesium implant material[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2007, 9(4): 298-302.
[10] 高家诚, 乔丽英. 镁基可降解硬组织生物材料的研究进展[J]. 功能材料, 2008, 39(5): 705-708.
GAO Jia-cheng, QIAO Li-ying. Magnesium-based degradable hard tissue biomaterials[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2008, 39(5): 705-708.
[11] WITTE F, HORT N, VOGT C, COHEN S, KAINER K U, WILLUMEIT R, FEYERABEND F. Degradable biomaterials based on magnesium corrosion[J]. Current Opinion in Solid State and Mater Sci, 2008, 12: 63-72.
[12] 黄晶晶, 杨 柯. 镁合金的生物医用研究[J]. 材料导报, 2006, 20(4): 67-69.
HUANG Jing-jing, YANG Ke. Research on magnesium alloys for bio-medical applications[J]. Materials Review, 2006, 20(4): 67-69.
[13] 陶海荣, 蒋 垚. 可降解镁合金内固定材料研究进展[J]. 国际骨科学杂志, 2008, 29(5): 293-294.
TAO Hai-rong, JIANG Yao. Research progress of degradable magnesium alloy materials for internal fixation[J]. International Journal of Orthopaedics, 2008, 29(5): 293-294.
[14] 郑玉峰, 刘 彬, 顾雪楠. 可生物降解性医用金属材料的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2009, 23(1): 1-4.
ZHENG Yu-feng, LIU Bin, GU Xue-nan. Research progress in biodegradable metallic materials for medical application[J]. Materials Review, 2009, 23(1): 1-4.
[15] 张 佳, 宗 阳, 付彭怀, 袁广银, 丁文江. 镁合金在生物医用材料领域的应用及发展前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 29: 149-152.
ZHANG Jia, ZONG Yang, FU Peng-huai, YUAN Guang-yin, DING Wen-jiang. Application and development prospect of magnesium alloys as biomedical materials[J]. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research, 2009, 29: 149-152.
[16] WITTE F, FISCHER J, NELLESEN J, CROSTACK H, KAESE V, PISCH A, BECKMANNE F, WINDHAGEN H. In vitro and in vivo corrosion measurements of magnesium alloys [J]. Biomaterials, 2006, 27: 1013-1018.
[17] WITTE F, FEYERABEND F, MAIER P, FISCHER J, STORMER M, BLAWERT C, DIETZEL W, HORT N. Biodegradable magnesium-hydroxyapatite metal matrix composites [J]. Biomateials, 2007, 28(13): 2163-2174.
[18] GU Xue-nan, ZHENG Yu-feng, CHENG Yan, ZHONG Sheng-ping, XI Ting-fei. In vitro corrosion and biocompatibility of binary magnesium alloys [J]. Biomaterials, 2009, 30(4): 484-498.
[19] AGHION E E, ARNON A, ATAR D,SEGAL G. Biodegradable magnesium alloys and uses thereof: US, PCT/IL2007/000520[P]. 2007-08-11.
[20] 洪岩松, 杨 柯, 张广道, 黄晶晶, 郝玉全, 艾红军. 可降解镁合金的动物体内骨诱导作用[J]. 金属学报,2008, 44(9): 1035-1041.
HONG Yan-song, YANG Ke, ZHANG Guang-dao, HUANG Jing-jing, HAO Yu-quan, AI Hong-jun. The role of bone induction of a biodegradable magnesium alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2008, 44(9): 1035-1041.
[21] ERINC M, SILLEKENS W, MANNENS R. Applicability of existing magnesium alloys as biomedical implant materials[C]//Magnesium Technology 2009. Warrendale: TMS, 2009: 209-214.
[22] ZENG R C, ZHANG R F, CHEN R S, DIETZEL W, KAINER U K. Corrosion of plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings on Mg-Ca alloy in Hank’s solutions[C]//Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Magnesium Alloys and Their Applications. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2009: 961-966.
[23] 张春艳, 曾荣昌, 陈 君, 杨 惠, 田中青. 镁合金AZ31 表面液相沉积Ca-P 生物陶瓷涂层的研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2009, 38(8): 1363-1367.
ZHANG Chun-yan, ZENG Rong-chang, CHEN Jun, YANG Hui, TIAN Zhong-qing. Study on chemical deposition of calcium phosphate bioceramic coating on AZ31 magnesium alloy surface[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2009, 38(8): 1363-1367.
[24] ZHANG Chun-yan, ZENG Rong-chang, LIU Cheng-long, GAO Jia-cheng. Comparison of calcium phosphate coatings on Mg-Al and Mg-Ca alloys and their corrosion behavior in Hank’s solution[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2010, 204 (21/22): 3636-3640.
[25] 郭 磊, 刘 魁, 张世亮, 高晓宇, 黄晶晶, 杨 柯. CA-P/AZ31B镁合金的生物相溶性研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2009, 38(1): 99-103.
GUO Lei, LIU Kui, ZHANG Shi-liang, GAO Xiao-yu, HUANG Jing-jing, YANG Ke. Biocompatibility of CA-P/AZ31B magnesium alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2009, 38(1): 99-103.
[26] 耿 芳, 谭丽丽, 贺永莲, 杨敬玉, 张炳春, 杨 柯. 多孔镁表面生物活性β-TCP涂层的制备及其细胞相容性研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2009, 38(2): 318-322.
GENG Fang, TAN Li-li, HE Yong-lian, YANG Jing-yu, ZHANG Bing-chun, YANG Ke. Preparation and cytocompatibility of bioactive β-TCP coatings on porous magnesium scaffold surface[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2009, 38(2): 318-322.
[27] 高亚丽, 熊党生, 王存山, 潘学民. 医用镁合金激光熔覆羟基磷灰石涂层初探[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 200929(4): 305-307.
GAO Li-ya, XIONG Dang-sheng, WANG Cun-shan, PAN Xue-min. Laser cladding hydroxypatite coating on magnesium alloy for biomaterials application[J]. Special Casting and Nonferrous Alloys, 2009,29(4): 305-307.
[28] SONG Y W, SHAN D Y, HAN E H. Electrodeposition of hydroxyapatite coating on AZ91D magnesium alloy for biomaterial application[J]. Materials Letter, 2008, 62(17/18): 3276-3279.
[29] CHEN Jun, ZENG Rong-chang, HUANG Wei-jiu, ZHENG Zi-qing, WANG Zhen-lin, WANG Jun. Characterization and wear resistance of macro-arc oxidation coating on magnesium alloy AZ91 in simulated body fluids[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(s1): s361-s364.
[30] ZHANG X P, ZHAO Z P, WU F M, WANG Y L, WU J. Corrosion and wear resistance of AZ91D magnesium alloy with and without microarc oxidation coating in Hank’s solution[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42(20): 8523-8528.
[31] SONG G L. Control of biodegradation of biocompatable magnesium alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(4): 1696-1701.
[32] 许鑫华, 程 静, 张春怀, 闫学良, 朱天兵, 姚康德, 曹 路, 刘 寅. 医用镁合金的生物腐蚀及高分子涂层处理[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2008, 37(7): 1225-1228.
XU Xin-hua, CHEN Jing, ZHANG Chun-huai, YAN Xue-liang, ZHU Tian-bing, YAO Kang-de, CAO Lu, LIU Yin. Bio-corrosion and polymer coating modification of magnesium alloys for medicine[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2008, 37(7): 1225-1228.
[33] 赵常利, 张绍翔, 何慈晖, 李佳楠, 张蓓蕾, 张小农. 生物医用镁合金表面PLGA涂层研究[J]. 功能材料, 2008, 39(6): 987-993.
ZHAO Chang-Li, ZHANG Shao-xiang, HE Ci-hui, LI Jia-nan, ZHANG Bei-lei, ZHANG Xiao-nong. Study on injectable bone repairing porous composite material[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2008, 39(6): 987-993.
[34] 张 萌, 齐 民, 刘洪泽, 杨 璠, 赵 红, 杨大智, 刘 炼. 聚丙交酯-乙交酯聚合物(PLGA)涂层体外降解行为研究[J]. 功能材料, 2006, 37(2): 277-280.
ZHANG Meng, QI Min, LIU Hong-ze, YANG Fan, ZHAO Hong, YANG Da-zhi, LIU Lian. Investigation of degradation of PLGA polymer film in simulated body’s liquid[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2006, 37(2): 277-280.
[35] 黄晶晶, 任伊宾, 张炳春, 杨 柯. 可降解镁植入材料表面涂层的制备及其性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(9): 1465-1469.
HUANG Jing-jing, REN Yi-bin, ZHANG Bing-chun, YANG Ke. Preparation and property of coating on degradable Mg implant [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(9): 1465-1469.
[36] ZENG R C, CHEN J, DIETZEL W, HORTK N, KAINER K U. Electrochemical behavior of magnesium alloys in simulated body fluids[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(S1): s166-s169.
[37] WITTE F, FISCHER J, NELLESEN J, VOGT C, VOGT J, DONATH T, BECKMANNE F. In vivo corrosion and corrosion protection of magnesium alloy LAE442[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, ![]() 2010, 6(5): 1792-1799.
2010, 6(5): 1792-1799.
[38] 颜廷亭, 谭丽丽, 熊党生, 龚明明, 张炳春, 杨 柯. 生物医用AZ31B镁合金表面稀土转化膜的制备及其性能[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2009, 38(5): 918-923.
YAN Ting-ting, TAN Li-li, XIONG Dang-sheng, GONG Ming-ming, ZHANG Bing-chun, YANG Ke. Preparation and properties studies of rare earth conversion coating on bio-medical AZ31B magnesium alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2009, 38(5): 918-923.
[39] WAN Yi-zao, XIONG Guang-yao, LUO Hong-lin, HE Fang, HUANG Yuan, ZHOU Xiao-shong. Preparation and characterization of a new biomedical magnesium-calcium alloy [J]. Materials and Design, 2008, 29(10): 2034-2037.
[40] LIU C L, XIN Y C, TIAN X B, ZHAO J, CHU P K. Corrosion resistance of titanium ion implanted AZ91 magnesium alloy[J]. J Vacuum Sci Technol A-Vacuum Surfurce Films, 2007, 25(2): 334-340.
[41] ZENG R C, DIETZEL W, CHEN J, HUANG W J, WANG J. Corrosion behavior of TiO2 coating on magnesium alloy AM60 in Hank’s solution[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2008, 373/374: 609-612.
[42] 谈国强, 苗鸿雁, 宁青菊, 夏 傲.生物陶瓷材料[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2006: 84-86.
TAN Guo-qiang, MIAO Hong-yan, NING Qing-ju, XIA Ao. Bio-ceramic materials[M]. Beijing: Chemistry Industry Press, 2006: 84-86.
[43] YANG J X, JIAO Y P, CUI F Z, LEE I S, YIN Q S, ZHANG Y. Modification of degradation behavior of magnesium alloy by IBAD coating of calcium phosphate[J]. Surfurce and Coatings Technology, 2008, 202(22/23): 5733-5736.
[44] 高家诚, 李龙川, 王 勇. 镁表面改性及其在仿生体液中的耐蚀行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(9): 1508-1513.
GAO Jia-cheng, LI Long-chuan, WANG Yong. Surface modification on magnesium by alkali-heat-treatmentand its corrosion behaviors in SBF[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(9): 1508-1513.
[45] QIAO L Y, GAO J C, WANG Y. Biocompatibility evaluation of magnesium-based materials[J]. Mater Sci Forum, 2007, 546/549: 459-462.
[46] 郭 磊, 刘 魁, 张世亮, 黄晶晶, 谭丽丽, 杨 柯. 氧化镁膜AZ31B镁合金材料的细胞毒性研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2008, 37(6): 1027-1031.
GUO Lei, LIU Kui, ZHANG Shi-liang, HUANG Jing-jing, TAN Li-li, YANG Ke. Cytotoxicity of AZ31B magnesium alloy covering with magnesium oxide[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2008, 37(6): 1027-1031.
[47] 沈新元. 生物医学纤维及其应用[M]. 北京: 中国纺织出版社, 2009: 132-144.
SHEN Xin-yuan. Biomedical fibers and their applications[M]. Beijing: China Textile Press, 2009: 132-144.
[48] 曾荣昌, 兰自栋, 陈 君, 韩恩厚. 镁合金表面化学转化膜的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报,2009, 19(3): 397-404.
ZENG Rong-chang, LAN Zi-dong, CHEN Jun, HAN En-hou. Progress of chemical conversion coatings on magnesium alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(3): 397-404.
[49] HASSEL T, BACH F W, KRAUSE C, WILK P. Corrosion protection and repassivation after the deformation of magnesium alloys coated with a protective magnesium flouride layer[C]//Magnesium Technology 2005. San Francisco: TMS, 2005: 485-491.
[50] RUDD A L, BRESLIN C B, MANSFELD F. The corrosion protection afforded by rare earth conversion coatings applied to magnesium[J]. Corrosion Science, 2000, 42(2): 275-288.
[51] GAO J C, XUE Y, QIAO L Y. Surface modification of magnesium with rare earth conversion films for biomedical protection[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2007, 546/549: 601-604.
[52] ZHANG Er-lin, XU Li-ping, YANG Ke. Formation by ion plating of Ti-coating on pure Mg for biomedical applications[J]. Scripita Materialia, 2005, 53(5): 523-527.
[53] XIN Y C, LIU C L, ZHANG W J, JIANG J, TANG G Y, TIAN X B, PAUL K C. Electrochemical behavior Al2O3/Al coated surgical AZ91 magnesium alloy in simulated body fluids[J]. Electrochemistry Society, 2008, 155: 178-182.
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2007CB613706);教育部留学回国人员启动基金资助项目;重庆市科技攻关计划资助项目(CSTC, 2009AB4008)
收稿日期:2010-03-15;修订日期:2010-11-01
通信作者:曾荣昌,教授,博士;电话:0532-80681226;E-mail: rczeng2001@yahoo.com.cn

