压力对挤压铸造Mg-Zn-Y准晶增强AZ91D镁基复合材料显微组织和力学性能的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第12期
论文作者:杨玲 侯华 赵宇宏 杨晓敏
文章页码:3936 - 3943
关键词:镁基复合材料;挤压铸造;准晶;显微组织;力学性能
Key words:magnesium matrix composite; squeeze casting; quasicrystal; microstructure; mechanical properties
摘 要:采用挤压铸造工艺制备Mg-Zn-Y准晶增强AZ91D镁基复合材料,研究挤压压力对此复合材料显微组织和力学性能的影响。研究结果表明:挤压铸造工艺是细化晶粒的有效方法,复合材料由α-Mg基体、β-Mg17Al12相以及二十面体Mg3Zn6Y准晶相(I相)组成,且随着挤压压力的增大,β-Mg17Al12相以及Mg3Zn6Y准晶颗粒含量增加,基体晶粒进一步细化,α-Mg树枝晶向等轴晶转变;当挤压压力为100 MPa时,极限抗拉强度和断后伸长率达到最大值,分别为194.3 MPa和9.2%,拉伸断口出现大量韧窝;准晶增强AZ91D镁基复合材料的强化机制主要为细晶强化和准晶颗粒强化。
Abstract: The Mg-Zn-Y quasicrystal-reinforced AZ91D magnesium matrix composites were prepared by squeeze casting process. The effects of applied pressure on microstructure and mechanical properties of the composites were investigated. The results show that squeeze casting process is an effective method to refine the grain. The composites are mainly composed of α-Mg, β-Mg17Al12 and Mg3Zn6Y icosahedral quasicrystal phase (I-phase). With the increase of applied pressure, the contents of β-Mg17Al12 phase and Mg3Zn6Y quasicrystal particles increase, further matrix grain refinement occurs and coarse dendritic α-Mg transforms into equiaxed grain structure. The composite exhibits the maximum ultimate tensile strength and elongation of 194.3 MPa and 9.2% respectively when the applied pressure is 100 MPa, and a lot of dimples appear on the tensile fractography. Strengthening mechanisms of quasicrystal-reinforced AZ91D magnesium matrix composites are chiefly fine-grain strengthening and quasicrystal particles strengthening.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 3936-3943
Ling YANG, Hua HOU, Yu-hong ZHAO, Xiao-min YANG
College of Materials Science and Engineering, North University of China, Taiyuan 030051, China
Received 6 February 2015; accepted 26 July 2015
Abstract: The Mg-Zn-Y quasicrystal-reinforced AZ91D magnesium matrix composites were prepared by squeeze casting process. The effects of applied pressure on microstructure and mechanical properties of the composites were investigated. The results show that squeeze casting process is an effective method to refine the grain. The composites are mainly composed of α-Mg, β-Mg17Al12 and Mg3Zn6Y icosahedral quasicrystal phase (I-phase). With the increase of applied pressure, the contents of β-Mg17Al12 phase and Mg3Zn6Y quasicrystal particles increase, further matrix grain refinement occurs and coarse dendritic α-Mg transforms into equiaxed grain structure. The composite exhibits the maximum ultimate tensile strength and elongation of 194.3 MPa and 9.2% respectively when the applied pressure is 100 MPa, and a lot of dimples appear on the tensile fractography. Strengthening mechanisms of quasicrystal-reinforced AZ91D magnesium matrix composites are chiefly fine-grain strengthening and quasicrystal particles strengthening.
Key words: magnesium matrix composite; squeeze casting; quasicrystal; microstructure; mechanical properties
1 Introduction
Magnesium alloys have wide application prospect to be utilized as the lightest metal structural materials in aerospace, electronic communication and automotive fields, etc [1-4]. However, the application of most magnesium alloys has been greatly restricted due to their poor strength, oxidation and creep resistance [5]. For example, AZ91D alloy is the most widely used die casting magnesium alloy, which possesses predominant castability and mechanical properties. However, it cannot be used at elevated temperatures beyond 393K due to the low melting point of intermetallic β-Mg17Al12 phase. To accelerate a wide-range application of magnesium alloys as structural materials allowing the maximum mass reduction, properties should be further enhanced by improving the alloy composition and optimizing the fabricating factors.
I-phase has attractive mechanical properties such as high thermodynamic stability, high hardness and high strength, which is attributed to its unique atomic structure [6,7]. Recently, it has been reported that magnesium alloys containing I-phase as a secondary solidification phase exhibit good mechanical properties, which provides a new approach for magnesium alloy strengthening [8-15]. However, monolithic I-phase materials have poor ductility to inhibit structural applications. A reasonable solution for improving structural application is fabricating composites comprising I-phase and a ductile phase, the study of which is rarely reported.
Compared with other manufacturing methods of magnesium matrix composites, squeeze casting is one of the most cost-effective methods, which leads to the microstructure refinement and alleviation of casting defects due to the abrupt heat transfer and the squeezing- pressure effect. This process can be easily adopted for conventional die-casting devices. Now, it is increasingly being used as a practically effective method to produce more densified products [16,17]. The main squeeze casting parameters that affect the cast microstructure are mould preheating temperature, applied pressure level, time delay between pouring of the metal in the die and application of pressure, pouring temperature and duration of pressure application. The applied pressure during solidification prevents the formation of both shrinkage and gas porosity in the solidifying alloy. The necessary pressure for eliminating shrinkage defects varies from alloy to alloy, which mainly depends on the freezing range of the alloy, the growth morphology of the material and the flow stress of the casting when the material is nearly solid [18-22].
Most studies on the effects of alloying elements on microstructure and properties of squeeze casting magnesium alloys have been carried out [23], but very few investigations have been focused on squeeze casting quasicrystal-reinforced magnesium matrix composites until now. This research aimed to present the effects of quasicrystal and applied pressure by investigating the correlation between microstructure and mechanical properties of squeeze casting magnesium matrix composites. For this purpose, Mg-Zn-Y quasicrystal master alloy was fabricated by conventional casting. Then, Mg-Zn-Y quasicrystal-reinforced AZ91D magnesium matrix composites were prepared by squeeze casting process. The effect of applied pressure on microstructure and mechanical properties of composites was investigated. Moreover, the strengthening mechanism was discussed. The study provides a new kind of quasicrystal strengthening phase and squeeze casting technology for preparing magnesium matrix composites.
2 Experimental
The quasicrystal-containing master alloy with the nominal composition of Mg-45Zn-10Y (mass fraction, %) was prepared by using Mg-30%Y master alloy, pure Mg and Zn (>99.9%) raw materials in electric resistance furnace employing a steel crucible under a gas mixture of tetrabromofluoroethane (1% in volume fraction), carbon dioxide (24% in volume fraction) and compressed air atmosphere (75% in volume fraction). AZ91D melt was held at 700 °C for 15 min, followed by adding 5% quasicrystal-containing Mg-45Zn-10Y master alloy into AZ91D melt, and then the melts were held at the same temperature for homogenization. Later, the melts were poured directly into a preheated steel die and composite ingots were prepared by squeeze casting. The applied pressures were 0, 50, 100 and 150 MPa, respectively. The die preheating temperature and pouring temperature were 200 and 700 °C, respectively. Squeeze pressure was applied to the casting within 10 s of pouring and the duration of applied pressure was 20 s.
Phase identification was performed by X-ray diffraction (XRD, D/Max-RB) using monochromatic Cu Kα radiation. Microchemical-analysis was examined by energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS). For microstructure observations, the as-cast specimens were etched with a solution of nitric acid (4 mL) and ethanol (96 mL). The microstructures were observed by optical microscopy (OM, LEICA DM2500M), scanning electron microscopy (SEM, SU-1500) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEM-2010). The ultimate tensile strength and elongation were evaluated using cylindrical test specimens machined from the squeeze casting samples. The shape and size of the specimen are shown in Fig. 1. The tensile fracture surfaces were observed by SEM.
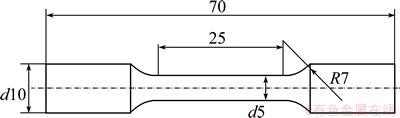
Fig. 1 Shape and size of tensile specimen (unit: mm)
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure of squeeze casting magnesium matrix composites
The microstructure and XRD pattern of Mg-45Zn- 10Y quasicrystal master alloy are displayed in Figs. 2 and 3, respectively. It can be seen that the as-cast Mg- 45Zn-10Y alloy mainly consists of α-Mg phase, I-phase and Mg7Zn3 phase. The dark dendrite, gray matrix, lamellar eutectic structure and petal-like or polygon-like particles are identified as α-Mg, Mg7Zn3, (α-Mg+I-phase) and I-phase, respectively. It is shown clearly in Fig. 2 that large quantity of petal-like and polygon-like quasicrystals are distributed homogeneously in Mg- 45Zn-10Y master alloy. Figure 4 exhibits bright-field TEM image of petal-like quasicrystal and selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern of I-phase with typical 5-fold symmetry, which is a distinctive characteristic of I-phase.

Fig. 2 Microstructure of Mg-45Zn-10Y quasicrystal master alloy
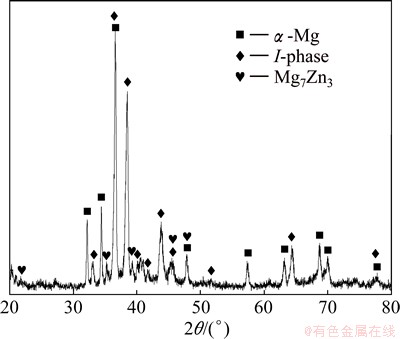
Fig. 3 XRD pattern of Mg-45Zn-10Y quasicrystal master alloy
The as-cast microstructures of quasicrystal- reinforced AZ91D magnesium matrix composites under different applied pressures are illustrated in Fig. 5. It can be concluded that the composites consist of gray-white α-Mg dendrites while the interdendritic spaces are occupied by β-Mg17Al12 phase. Several Mg3Zn6Y quasicrystal particles appear inside the dendrites near the interdendritic regions. The amount and morphology of the phases vary with the applied pressure. Figure 5(a) shows the microstructure of gravity casting (without applied pressure) quasicrystal-reinforced magnesium matrix composite, in which α-Mg appears as coarse dendrites and β-Mg17Al12 phase is inhomogeneously distributed at grain boundaries. With the increase of applied pressure, the contents of β-Mg17Al12 phase and Mg3Zn6Y quasicrystal phase increase and the morphology of α-Mg changes from dendrite structure to equiaxed grain structure. Thus, for the 50 MPa composite sample, some β-Mg17Al12 phases appear at grain boundaries, while for the 100 MPa sample, the amount of β-Mg17Al12 phase increases and for the 150 MPa sample, grain boundaries are dominated by β-Mg17Al12. It is also shown that squeeze casting process is an effective method to refine the grain size. The dendrites of composites are smaller for squeeze casting than those of gravity casting due to high rate of solidification. The grain sizes of squeeze casting composites for 50, 100 and 150 MPa are around 50, 30 and 30 μm, respectively.
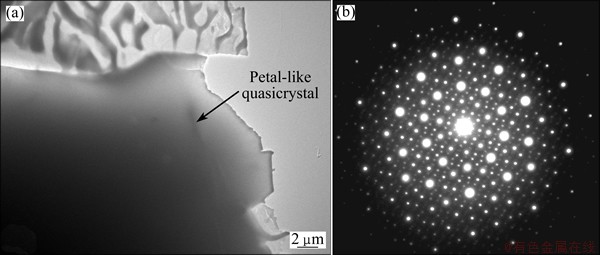
Fig. 4 Bright-field TEM image of petal-like quasicrystal (a) and SAED pattern of I-phase with 5-fold symmetry (b)

Fig. 5 Microstructures of quasicrystal-reinforced AZ91D magnesium matrix composites under different applied pressures
With the increase of applied pressure, the content of β-Mg17Al12 phase increases which is due to solid solubility decrease of Al in α-Mg matrix. On the one hand, the melting point variation of β-Mg17Al12 is greater than that of Mg under pressure, with increasing applied pressure, the eutectic point shifts to the Mg-rich direction, as shown by the arrow in Fig. 6, which leads to lower solubility of Al in α-Mg. On the other hand, with the increase of applied pressure, the cooling rate increases and pseudo eutectic reaction occurs [24], which also cause the same eutectic point change to the Mg-rich direction and solid solubility decrease of Al in α-Mg. The change of equilibrium phase diagram is the basic reason to cause the increase of β-Mg17Al12 content in the alloy. For AZ91D alloy, the content of Al atoms is fixed, with the increase of applied pressure, less Al atoms solute in α-Mg matrix and more Al atoms involve in the formation of β-Mg17Al12 phase. As a result, the content of β-Mg17Al12 phase increases. Similarly, increasing applied pressure leads to solid solubility decrease of Zn and Y in α-Mg matrix, which benefit to forming more Mg3Zn6Y quasicrystal particles.
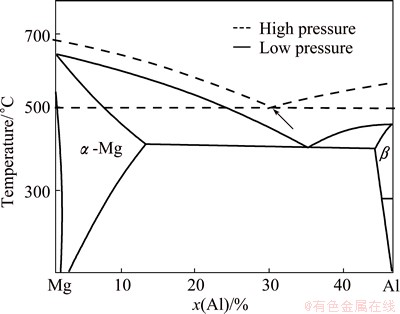
Fig. 6 Effect of pressure on Mg-Al alloy phase diagram
The grain size is also influenced by applied pressure. The solidification of AZ91D alloy during squeeze casting process is carried out under non-equilibrium condition. Al atoms in primary α-Mg cannot diffuse homogeneously which leads to the enrichment of Al atoms in liquid and the formation of more eutectic structure. Increasing applied pressure contributes to obtaining higher cooling rate, and the larger the cooling rate is, the more serious the segregation of Al in primary α-Mg is [24], which results in smaller grain sizes of α-Mg and β-Mg17Al12. Compared with gravity casting, squeeze casting is beneficial to refine grain size. Firstly, heat transfer across the interface between the casting and die is improved, which is ascribed to intimate contact of crystalline layer with die wall under external force. Secondly, the liquidus temperature increases to produce high undercooling degree in front of the crystallization and promote nucleation rate and grain refinement. Finally, when pressure is applied to the material, alloy liquid can feed shrinkage and porosity to make plastic deformation occur. Meanwhile, dendrites are broken and new crystal nuclei are formed to reduce grain size.
It can be found from Fig. 5(b) that microstructure is unhomogeneous and exhibits distinct regions of fine and coarse structure (bi-modal structure) as the applied pressure is 50 MPa. The possible reasons are as follows: Firstly, at the beginning of solidification, the grain size is small, which is attributed to high cooling rate. With the process of solidification, recalescence phenomenon occurs to make grain size increase and appears as bi-modal structure. Secondly, after nucleation and growth of initial grains, small grains will form during the solidification of the remaining alloy melts between initial grains with increasing the cooling rate, which leads to the existence of bi-modal structure. Thirdly, solute elements gather together in melts to form macro-segregation and larger constituent undercooling, which results in small grain size and finally distinct bi-modal structure exhibits.
To confirm the existence of I-phase, SEM, EDS and TEM observations were performed for the composite sample of 100 MPa, as shown in Fig. 7. The results indicate that Mg3Zn6Y I-phase exists indeed in the composite. Figure 8 shows XRD pattern of the sample at an applied pressure of 100 MPa, which reveals that the composite consists of α-Mg, β-Mg17Al12 and I-phase.
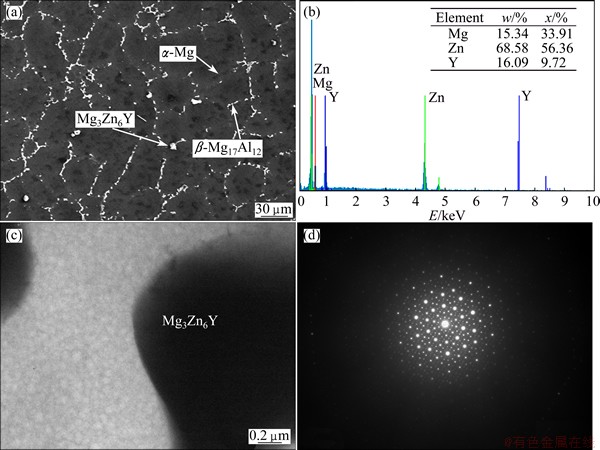
Fig. 7 SEM image of sample with applied pressure of 100 MPa (a), EDS pattern of I-phase (b), bright-field TEM image of I-phase (c), SAED pattern of I-phase with 5-fold symmetry (d)
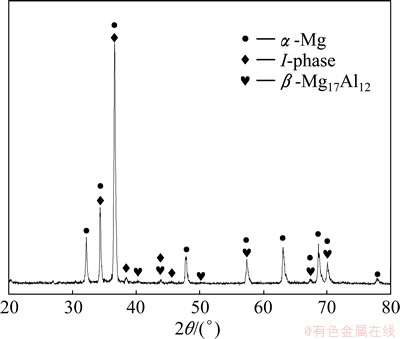
Fig. 8 XRD pattern of sample at applied pressure of 100 MPa
3.2 Mechanical properties of squeeze casting magnesium matrix composites
Figure 9 shows the tensile properties of squeeze casting quasicrystal-reinforced AZ91D magnesium matrix composites under different applied pressures. It is observed from the results that an increase in applied pressure levels between 0 and 100 MPa brings a significant improvement in ultimate tensile strength and elongation. The tensile strength and elongation of composite at 100 MPa both reach the maximum values of 193.4 MPa and 9.2%, respectively, which increase by 83% and 109% compared with those of the sample under gravity casting. Since no obvious microstructure change is observed under applied pressures of 0 and 50 MPa, the improvement in tensile properties by the increase of pressure should be attributed to shrinkage and porosity reduction [25]. However, the best tensile properties for 100 MPa might be mainly ascribed to the grain refinement. It can also be found from Fig. 9 that the tensile properties decrease with the further increase of the applied pressure from 100 to 150 MPa. Firstly, no obvious effect of grain refinement is observed when the applied pressure rises to 150 MPa which leads to a slight increase in properties. Secondly, grain boundaries will be weakened and crack will be promoted because large quantity of β-Mg17Al12 phases are distributed in the vicinity of the grain boundaries under the applied pressure of 150 MPa. The effect of the latter is greater than that of the former and eventually leads to the decrease of tensile properties.
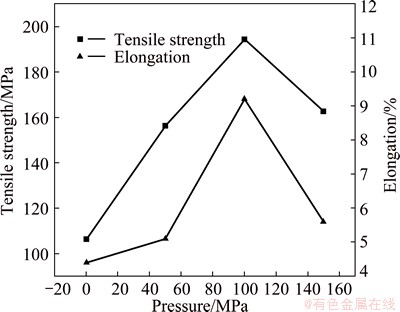
Fig. 9 Mechanical properties of quasicrystal-reinforced AZ91D magnesium matrix composites under different applied pressures
Figure 10 shows the SEM images of tensile fractographs for composites under different applied pressures. It can be observed that the fracture behaviour is somehow influenced by the applied pressure during squeeze casting process. For gravity casting, the fracture surface tends to be smooth and presents a typical brittle fracture. The observed fracture mode of the composites under 50 and 100 MPa is quasi-cleavage fracture and as the applied pressure increases, the fracture mode of composite tends to be more ductile, which is characterized by the presence of more deeper dimples in the 100 MPa specimen compared with 50 MPa specimen. The formation of dimples is due to the coalescence of localized microvoids under a continual rising load. The microvoids nucleate in the areas of localized high plastic deformation such as that associated with β-Mg17Al12 particles, I-phase particles and grain boundaries. With the increase of load on the composite, the microvoids grow, coalesce and eventually form a continuous fracture surface [18]. The less ductile fracture mode of specimen under 150 MPa is attributed to high content of second phases which leads to stress concentration and crack initiation. The SEM observations of the fracture surfaces are in good agreement with the tensile behaviour of the composites.
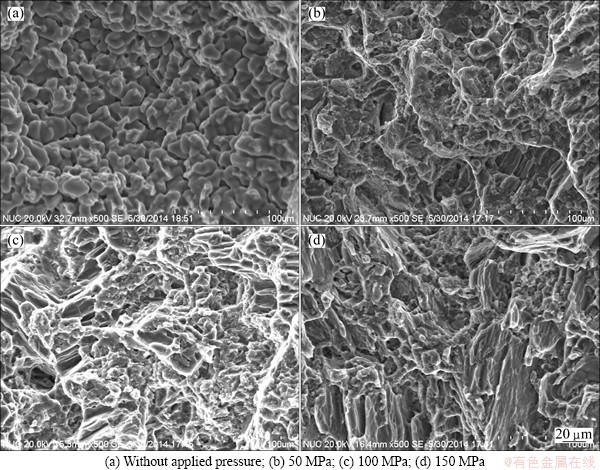
Fig. 10 SEM images of tensile fractographs for quasicrystal-reinforced AZ91D magnesium matrix composites under different applied pressures
3.3 Strengthening mechanism analysis
It is indispensable to add reinforcing phase into magnesium alloys to obtain high strength and toughness. Moreover, the optimization and stability of interface structure between strengthening particles and matrix are important to improve the mechanical properties of magnesium matrix composites.
Fine-grain strengthening is mainly realized by changing grain size of magnesium alloys. Grain boundaries can effectively inhibit dislocation gliding to improve properties. Meanwhile, stress concentrations in front of the grain boundaries activate more slip systems to make uniform deformation and improve the toughness of alloys. The smaller the grain sizes, the larger the strengthening effect of the grain boundaries. In this work, the reasons for grain refinement are as follows. Firstly, squeeze casting process can greatly refine grain size of α-Mg matrix and change the morphology of it into equiaxed grain structure. Secondly, precipitated Mg3Zn6Y quasicrystal particles during solidification effectively prevent the grain growth to exhibit grain refinement effect.
As the reinforcing phase, I-phase particles with smaller size are distributed homogeneously in α-Mg matrix or around β-Mg17Al12 phase. Due to low surface energy of quasicrystals as well as similarity between quasicrystal particles and the matrix, excellent wettability between them can be obtained. Hence, I-phase particles have less rending effect on the matrix and the stress concentration degree in the matrix is much low. Mg3Zn6Y I-phase particles prevent the diffusion of Al and Zn elements, which results in decreasing grain size of the matrix. It can be observed from Fig. 7(a) that there is no interfacial reaction between Mg3Zn6Y quasicrystal particles and α-Mg matrix, meanwhile, there is no brittle phase existing at the interface which results in high interface bonding properties. Mg3Zn6Y quasicrystal particles can effectively pin the grain boundaries and prevent the migration of β-Mg17Al12 phase at grain boundaries. For these composites, the load is mainly undertaken by α-Mg matrix and partly borne by quasicrystal particles. The dispersed distribution of I-phase particles can restrain the matrix deformation, prevent dislocation movement, exhibit the dispersion strengthening effect and finally improve the properties of composites.
4 Conclusions
1) The squeeze casting composites exhibit finer microstructure than gravity casting composite. Squeeze casting process can change the morphology of α-Mg from dendrite structure to equiaxed grain structure. The composites consist of α-Mg, β-Mg17Al12 and dispersed Mg3Zn6Y I-phase. With the increase of applied pressure, the contents of β-Mg17Al12 and Mg3Zn6Y quasicrystal particles increase.
2) The tensile properties of the squeeze casting composites vary with applied pressure. Namely, with the applied pressure increasing from 0 to 150 MPa, the ultimate tensile strength and elongation firstly increase and then decrease. When the applied pressure is 100 MPa, the ultimate tensile strength and elongation reach the maximum values of 194.3 MPa and 9.2%, respectively. The fracture modes of squeeze casting composites transit from brittle cleavage to quasi-cleavage with increasing applied pressure.
3) The strengthening mechanisms are considered as fine-grain strengthening and quasicrystal particles strengthening.
References
[1] CHEN Qiang, YUAN Bao-guo, LIN Jun, XIA Xiang-sheng, ZHAO Zu-de, SHU Da-yu. Comparisons of microstructure, thixoformability and mechanical properties of high performance wrought magnesium alloys reheated from the as-cast and extruded states [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 584: 63-75.
[2] LIU Ke, WANG Qing-feng, DU Wen-bo, LI Shu-bo, WANG Zhao-hui. Failure mechanism of as-cast Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy during tensile test at room temperature [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(11): 3193-3199.
[3] KULEKCI M K. Magnesium and its alloys applications in automotive industry [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2008, 39(9): 851-865.
[4] YANG Ming-bo, WU De-yong, HOU Meng-dan, PAN Fu-sheng. As-cast microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg-4Zn-xY- 1Ca (x=1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 3.0) magnesium alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(3): 721-731.
[5] BAE D H, LEE M H, KIM K T, KIM W T, KIM D H. Application of quasicrystalline particles as a strengthening phase in Mg-Zn-Y alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2002, 342(1): 445-450.
[6] WAN Di-qing, YANG Gen-cang, ZHU Man, XU Quan, ZHOU Yao-he. Solidification of Mg-28%Zn-2%Y alloy involving icosahedral quasicrystal phase [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(3): 586-589.
[7] ZHANG Jin-shan, DU Hong-wei, LU Bin-feng, ZHANG Yan, LIANG Wei, XU Chun-xiang, LU Feng-lei. Effect of Ca on crystallization of Mg-based master alloy containing spherical quasicrystal [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(2): 273-279.
[8] GENG Ji-wei, TENG Xin-ying, ZHOU Guo-rong, ZHAO De-gang. Microstructure transformations in the heat-treated Mg-Zn-Y alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 577: 498-506.
[9] LI Jian-hui, DU Wen-bo, LI Shu-bo, WANG Zhao-hui. Icosahedral quasicrystalline phase in an as-cast Mg-Zn-Er alloy [J]. Rare Metals, 2009, 28(3): 297-301.
[10] ZHAO Xian-feng, LI Shu-bo, WANG Qing-feng, DU Wen-bo, LIU Ke. Effects of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-5Zn-0.63Er alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(1): 59-65.
[11] SINGH A, SOMEKAWA H, MUKAI T. High temperature processing of Mg-Zn-Y alloys containing quasicrystal phase for high strength [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528(21): 6647-6651.
[12] MA Rong, DONG Xuan-pu, YAN Bang-song, CHEN Shu-qun, LI Zhang-bo, PAN Zhang, LING Hong-jiang, FAN Zi-tian. Mechanical and damping properties of thermal treated Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloys reinforced with quasicrystal phase [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 602: 11-18.
[13] WANG Xu-dong, DU Wen-bo, WANG Zhao-hui, LIU Ke, LI Shu-bo. Stable icosahedral phase in Mg44Zn44Gd12 alloy [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2012, 30(5): 503-506.
[14] ZHANG Jin-shan, ZHANG Yong-qing, ZHANG Yan, XU Chun-xiang, WANG Xiao-ming, YAN Jie. Effect of Mg-based spherical quasicrystal on microstructures and mechanical properties of ZA54 alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(7): 1199-1204.
[15] WEI G B, PENG X D, ZHANG B, HADADZADEH A, XU T C, XIE W D. Influence of I-phase and W-phase on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-8Li-3Zn alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(3): 713-720.
[16] KIM B, DO J, LEE S, PARK I. In situ fracture observation and fracture toughness analysis of squeeze cast AZ51-xSn magnesium alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(24-25): 6745-6757.
[17] DO J, KIM B, PARK Y, PARK I. Effects of Ca and Ce addition on tensile and fracture properties in squeeze cast AT42 (Mg-4Al-2Sn) magnesium alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2012, 43(8): 2955-2968.
[18] MASOUMI M, HU H. Influence of applied pressure on microstructure and tensile properties of squeeze cast magnesium Mg-Al-Ca alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528(10-11): 3589-3593.
[19] DONG Pu-yun, ZHAO Hai-dong, CHEN Fei-fan, LI Jun-wen. Microstructures and properties of A356-10%SiC particle composite castings at different solidification pressures [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(8): 2222-2228.
[20] YONG M S, CLEGG A J. Process optimisation for a squeeze cast magnesium alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2004, 145(1): 134-141.
[21] YONG M S, CLEGG A J. Process optimisation for a squeeze cast magnesium alloy metal matrix composite [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2005, 168(2): 262-269.
[22] BIN Shi-bo, XING Shu-ming, TIAN Long-mei, ZHAO Ning, LI Lan. Influence of technical parameters on strength and ductility of AlSi9Cu3 alloys in squeeze casting [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(4): 977-982.
[23] ZHOU M, HU H, LI N Y, LO J. Microstructure and tensile properties of squeeze cast magnesium alloy AM50 [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2005, 14(4): 539-545.
[24] LIPCHIN T N. Alloying capacity for the solid solution of alloys obtained by crystallizing under pressure [J]. Metal Science and Heat Treatment, 1986, 28(4): 282-285.
[25] ZHANG Q, MASOUMI M, HU H. Influence of applied pressure on tensile behaviour and microstructure of squeeze cast Mg alloy AM50 with Ca addition [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2012, 21(1): 38-46.
杨 玲,侯 华,赵宇宏,杨晓敏
中北大学 材料科学与工程学院,太原 030051
摘 要:采用挤压铸造工艺制备Mg-Zn-Y准晶增强AZ91D镁基复合材料,研究挤压压力对此复合材料显微组织和力学性能的影响。研究结果表明:挤压铸造工艺是细化晶粒的有效方法,复合材料由α-Mg基体、β-Mg17Al12相以及二十面体Mg3Zn6Y准晶相(I相)组成,且随着挤压压力的增大,β-Mg17Al12相以及Mg3Zn6Y准晶颗粒含量增加,基体晶粒进一步细化,α-Mg树枝晶向等轴晶转变;当挤压压力为100 MPa时,极限抗拉强度和断后伸长率达到最大值,分别为194.3 MPa和9.2%,拉伸断口出现大量韧窝;准晶增强AZ91D镁基复合材料的强化机制主要为细晶强化和准晶颗粒强化。
关键词:镁基复合材料;挤压铸造;准晶;显微组织;力学性能
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Projects (51204147, 51274175) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Projects (2011DFA50520, 2014DFA50320) supported by the International Cooperation Program from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China; Project (20123088) supported by the Foundation for Graduate Students of Shanxi Province, China
Corresponding author: Ling YANG; Tel: +86-13466805721; E-mail: yangling19810128@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)64041-9

