材料对锂离子电池热稳定性的影响
胡传跃1,2,李新海2,王志兴2,罗文斌2
(1.湖南人文科学技术学院 化学材料科学系,湖南 娄底,417000;
2.中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要: 采用差示扫描量热法研究锂离子电池材料包括导电剂、粘结剂、电解液、Li0.5CoO2与LiC6对锂离子电池热稳定性的影响,并对由这些材料制备的063048型方形锂离子电池进行安全性测试。研究结果表明:锂离子电池的热稳定性受正极、负极及电解液3种因素的影响,电池热反应释放的热量由大到小顺序为:负极、正极、电解液。负极反应热主要来源于LiC6与粘结剂及电解液之间的反应,且与粘结剂的性质、用量及电解液用量有关;正极反应热主要来源于Li0.5CoO2的分解反应及其分解产生的氧气与有机溶剂之间的燃烧反应。聚偏二氟乙烯粘结剂比丙烯酸系水基粘结剂的热稳定性高,导电碳黑导电剂的热稳定性比乙炔碳黑导电剂的热稳定性高。过充实验结果表明,聚偏二氟乙烯粘结剂及导电碳黑能显著提高LiCoO2/石墨型锂离子电池的热稳定性。
关键词: 锂离子电池; 热稳定性; 安全性; 材料
中图分类号:TM912.9 文献标识码:A 文章编号: 1672-7207(2005)04-0587-07
Influence of materials on thermal stability of lithium-ion batteries
HU Chuan-yue1,2, LI Xin-hai2, WANG Zhi-xing2, LUO Wen-bin2
(1.Department of Chemistry and Materials Science, Hunan Institute of Humanities,
Science and Technology, Loudi 417000, China;
2.School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was used to study the influence of materials on the thermal stability of lithium-ion batteries. The materials included conductive carbon black, acetylene carbon back, polyvinylidene fluoride(PVDF) adhesive, acrylic adhesive, Li0.5CoO2 and LiC6. The safety test was carried out on 063048 prismatic lithium-ion batteries. The results show that PVDF adhesive and conductive carbon black exhibit better thermal stability compared with acrylic adhesive and acetylene carbon black. The total reaction heat of each influencing factor responsible for the thermal stability of lithium-ion batteries from large to small is as follows: anode, cathode, electrolyte. The anode reactions mainly take place among LiC6, adhesives and electrolyte. The reaction heat is strongly influenced by the nature and amount of adhesive and electrolyte. The released heat in cathode mainly resulted from organic solvent combustion reaction due to the evolved oxygen from Li0.5CoO2 decomposition at elevated temperature. The overcharging experiments show that the safety of LiCoO2/graphite lithium-ion battery can be improved by choosing PVDF as adhesive and conductive carbon black as conductive additive.
Key words: lithium-ion battery; thermal stability; safety; material
由可逆嵌入与脱嵌的负极材料如石墨、石油焦等取代金属锂制备的锂离子电池,不仅能延长电池循环寿命,提高快速充电能力,而且能提高电池的安全性[1,2]。尽管近来金属锂电池的安全性有所提高,在正常使用条件下,能满足使用要求,但当充电过程在阳极沉积锂枝晶时电池的安全性不能满足使材料对锂离子电池热稳定性的影响 用要求。为了提高锂离子电池的安全性能,人们进行了大量的研究。所研究的内容主要有:电池的耐过充性能[1,3];高温下充电态的正极材料与非水溶剂的反应[4-7];电池的热效应[8-12];电解液的热稳定性[13-18]。在此,作者采用差示扫描碳量热法研究当前商品化锂离子电池中常用乙炔黑、导电碳黑及常用粘结剂如聚偏二氟乙烯(PVDF)、丙烯酸系水基粘结剂对锂离子电池热稳定性的影响,以及电池的正极、负极和电解液对电池热稳定性的影响。
1 实验部分
1.1 仪器和试剂
1.1.1 仪器仪器为:MDSC 2910型差示扫描量热仪;天津Lanlike公司生产的LK2008B型电池综合测试仪;天津天宇技术实业有限公司生产的DZG-404型真空干燥箱;德国MBRAUN公司生产的MB150B-G手套箱;Mettle公司生产的AE160型电子天平(精确度为0.01 mg)。
1.1.2 试剂试剂为:聚偏二氟乙烯(PVDF);丙烯酸系水基粘结剂;导电碳黑;乙炔碳黑;石墨;LiCoO2;碳酸乙烯酯(ethylene carbonate, EC);碳酸二甲酯(dimethyl carbonate,DMC);碳酸甲乙酯(ethylmethyl carbonate,EMC);电解液1 mol/L LiPF6/EC-DMC-EMC(EC,DMC和EMC的质量比为1∶1∶1)等。原料与试剂均为市售电池级。
1.2 样品的制备 将PVDF、导电剂与LiCoO2按质量比7∶5∶88混合,以N-甲基吡咯烷酮为分散剂制备LiCoO2电极,铝箔基体厚度为0.02 mm;将PVDF与石墨按质量比11∶89混合,以N-甲基吡咯烷酮为分散剂制备PVDF型石墨电极;将丙烯酸系水基粘结剂与石墨按质量比11∶89(以丙烯酸系水基粘结剂乳液的固体含量计算) 混合,以去离子水为分散剂制备水基粘结剂型石墨电极,铜箔基体的厚度为0.01 mm,组装成容量为700 mA·h的063048型方形锂离子电池,以不锈钢为外壳。乙炔碳黑、导电碳黑、石墨及LiCoO2在真空箱中于1.3×103 Pa和150 ℃处理15 h;PVDF在真空及120 ℃处理20 h;丙烯酸系水基粘结剂乳液则先在电热鼓风干燥箱中于80 ℃烘干水分,然后在真空干燥箱中于100 ℃处理20 h。在手套箱中以电子天平称量并制备差示扫描量热(differential scanning calorimetry,DSC)样品。纯LiPF6与浓度为1 mol/L LiPF6/EC-DMC-EMC的电解液则在手套箱中直接制备成DSC样品。
1.2.1 不经溶剂浸提的Li0.5CoO2与LiC6的DSC样品的制备以乙炔碳黑为导电剂、PVDF为粘结剂制备LiCoO2电极;以PVDF粘结剂或丙烯酸系水基粘结剂制备石墨电极;以正极膜、负极膜及隔膜等组装成容量为700 mA·h的063048型方形锂离子电池。锂离子电池经充放电模式处理后,LiCoO2电极转变成Li0.5CoO2电极,同时,石墨电极转变成LiC6电极;然后,将电池在手套箱中拆开,用刮刀分别自正、负极刮取Li0.5CoO2与LiC6粉末样品,并迅速制备成DSC样品,整个过程在10 min内完成,制好的DSC样品在20 min内开始测量。
1.2.2 溶剂浸提的Li0.5CoO2的DSC样品的制备将上述Li0.5CoO2电极粉末用DMC浸泡48 h后于1.3×103 Pa和100 ℃处理36 h,在手套箱中制备DSC样品。
1.2.3 电池充放电模式以70 mA恒流充电至4.20 V,以4.20 V恒压充电至下限电流10 mA;以70 mA恒流放电至2.75 V模式进行活化;然后,将电流由70 mA改为700 mA进行5次充放电循环;最后,以70 mA恒流充电至4.20 V,4.20 V恒压充电至下限电流5 mA,以获得稳定的Li0.5CoO2和LiC6电极材料;电池在每次充电与放电之间搁置10 min,以消除极化现象。
1.3 方形锂离电池的过充测试 考察所制备的063048型方形锂离子电池的导电剂及粘结剂对其耐过充性能的影响。电解液为浓度为1 mol/L的LiPF6 /EC-DMC-EMC(EC,DMC和EMC的质量比为1∶1∶1)。电池先以1C倍率、恒流恒压方式充电至电压为4.20 V、下限电流为10 mA终止;然后,以3C倍率、10 V模式对电池进行过充。在测试过程中,当电压达5.00 V前每隔30 s记录1次电压数据;当电压达到5.00 V后每隔5 s记录1次数据。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 材料的DSC分析
2.1.1 导电剂的热稳定性图1所示为导电碳黑与乙炔碳黑的DSC曲线。测量条件为:空气气氛,扫描速率10 ℃/min。结果表明:乙炔碳黑在温度为356 ℃处存在1个放热峰,峰的起始温度为313 ℃,反应热为110.5 J/g;而导电碳黑在温度为371 ℃处存在1个放热峰,起始温度为322 ℃,反应热为22.0 J/g。乙炔碳黑的反应温度较导电碳黑的反应温度略低,但乙炔碳黑的反应热约为导电碳黑的反应热的5倍。因此,以导电碳黑为导电剂,可降低因电池过充时锂钴氧分解释放的氧与导电剂反应释放的反应热。
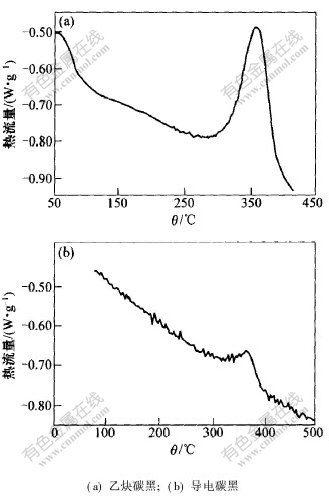
图 1 导电剂的DSC曲线
Fig. 1 DSC profiles of conductive additives
2.1.2 粘结剂的热稳定性图2所示为PVDF粘结剂与丙烯酸系水基粘结剂的DSC曲线。测量条件为:氩气气氛,扫描速率10 ℃/min。可见,丙烯酸系水基粘结剂在温度为105.3 ℃左右存在1个吸热峰,起始温度为67.0 ℃,反应热为-84.2 J/g;217 ℃处存在1个放热峰,起始温度为186.7 ℃,反应热为141.0 J/g; 300 ℃附近存在1个很弱的放热峰,反应热为8.6 J/g。这些数据表明,丙烯酸系水基粘结剂在67℃开始熔解,当温度达到186.7℃时,开始分解并放出大量反应热。对于PVDF粘结剂,仅在167 ℃处存在1个较强的吸热峰,起始温度为157 ℃,反应热为-41.4 J/g,这是PVDF的熔解峰,当扫描至300℃时,仍无PVDF的分解反应发生。因此,PVDF粘结剂的热稳定性较丙烯酸系水基粘结剂的热稳定性高,说明采用PVDF粘结剂的锂离子电池较采用丙烯酸系水基粘结剂的锂离子电池具有更高的热稳定性。
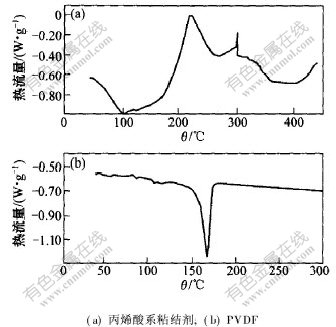
图 2 粘结剂的DSC曲线
Fig. 2 DSC profiles of adhesives
2.1.3 电解液的热稳定性图3所示为纯LiCoO2和LiPF6锂盐与电解液1 mol/L LiPF6/EC-DMC-EMC的DSC曲线。测量条件为:空气气氛,扫描速率5 ℃/min。可见,LiPF6在温度达到180 ℃前仍然稳定,当温度超过180 ℃时出现2个吸热峰,1个出现在温度为180~210 ℃处,反应热约为-20 J/g;另1个在250 ℃以上,其中第1个峰为LiPF6的可逆熔解峰,这与G.B.Gerardine等[13]的研究结果一致;无杂质的分解放热峰存在,是因为LiPF6的纯度很高(纯度高于99.9%,水分含量小于0.003%),且DSC铝罐在手套箱中迅速压紧密封。图3(b)所示为电解液1 mol/L LiPF6/EC-DMC-EMC的DSC曲线,在温度为125~250 ℃时存在3个放热峰,其中,起始2个放热峰的热量很少,可忽略不计;第3个主要的放热峰位于215 ℃左右,释放的热量接近电解液的总热量300 J/g。实际上,锂离子电池体系是贫液体系,即在锂离子电池中相对于电池正极与负极材料含量,电解液的含量很低,因而电解液本身分解所释放的热量较少。
2.1.4 电解液对纯LiCoO2和Li0.5CoO2的热稳定性的影响图4所示为Li0.5CoO2的DSC曲线。测量条件为:氩气气氛,扫描速率5 ℃/min。图4(a)表明,纯LiCoO2很稳定,即使在400 ℃的高温下仍不分解。图4(b)所示为用DMC浸提并真空烘干的Li0.5CoO2的DSC曲线,用DMC浸提Li0.5CoO2的目的是除去电极中残留的电解质LiPF6,以消除LiPF6的热分解反应对Li0.5CoO2的热稳定性的影响。结果显示,在165 ℃左右存在1个吸热峰,为PVDF的熔解峰;Li0.5CoO2在200 ℃左右开始分解,出现第1个放热峰,峰温为228 ℃,反应热为64.8 J/g,在279 ℃处出现第2个放热峰,起始温度为260 ℃,反应热为315.2 J/g。Li0.5CoO2的第1个峰与第2个峰的热分解反应分别如式(1)和式(2)所示。图4(c)所示为未用溶剂浸提的Li0.5CoO2的DSC曲线,该样品中存在残留的溶剂EC,DMC,EMC及锂盐LiPF6。由图4(c)可知,PVDF的熔解吸热峰消失,且Li0.5CoO2自158.4 ℃开始分解,第1个放热峰出现在温度为173.4 ℃处,反应热为74.1 J/g。根据图3所示的结果可判断这个放热峰受Li0.5CoO2样品中残留的电解液的影响;当加热至210 ℃时开始出现第2个放热峰,峰温为273.2 ℃,反应热为370.3 J/g。将图4(b)与图4(c)进行比较可知,当有溶剂和锂盐存在时,Li0.5CoO2的2个DSC放热峰与热分解反应的初始温度均向较低的温度方向漂移,且每个放热峰的反应热更高,表明有机溶剂与锂盐的存在降低了Li0.5CoO2电极的热稳定性,且有机溶剂可能与Li0.5CoO2分解产生的氧发生燃烧反应。这与D.D. Macneil等[7]报道的在高温下Li0.5CoO2与非[CM(22] 水溶剂反应的结果一致。当有碳酸乙烯酯存在时,
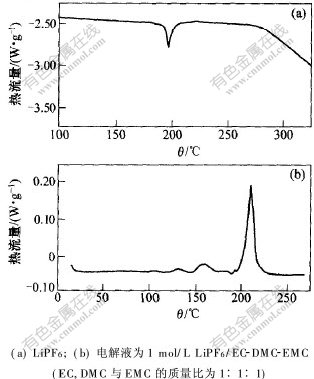
图 3 电解液的DSC曲线
Fig. 3 DSC profiles of electrolytes
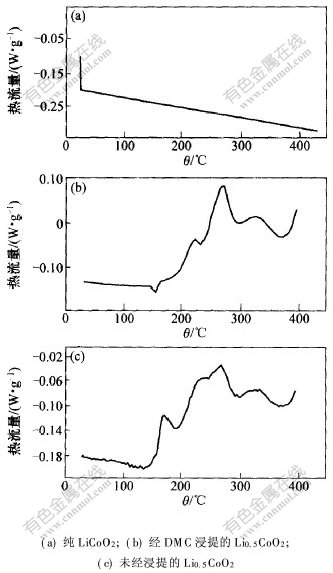
图 4 LiCoO2与Li0.5CoO2的DSC曲线
Fig. 4 DSC profiles of LiCoO2 and Li0.5CoO2
Li0.5CoO2的分解机理为:
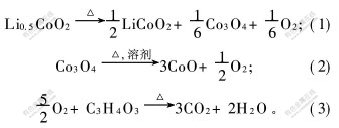
因此,Li0.5CoO2高温分解释放O2,释放的O2与有机溶剂发生燃烧反应,释放大量热量,总反应如式(4)所示。图4(c)中2个放热峰释放的热量较图4(b)相应的2个放热峰释放的热量多,是由于湿润的电极中存在的有机溶剂EC,DMC和EMC与Li0.5CoO2分解释放的氧之间发生燃烧反应释放大量热量。在电池设计时,采用一种合适的电解液溶剂体系以减小溶剂对Li0.5CoO2热稳定性的影响,可提高电池的热稳定性即提高电池的安全性。
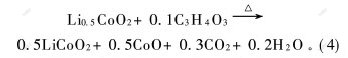
2.1.5 粘结剂对LiC6的热稳定性的影响图5所示为不同粘结剂对石墨电极热稳定性的影响。图5(a)所示为未充电的纯石墨粉的DSC曲线。测量条件为:空气气氛,扫描速率5 ℃/min。图5(a)表明石墨粉在温度为341 ℃处存在1个放热峰,起始温度为256 ℃,反应热为17.38 J/g,即未充电的石墨在温度低于256 ℃时稳定。图5(b)和图5(c)所示分别为以PVDF粘结剂与丙烯酸系水基粘结剂的4.2 V的石墨电极的DSC曲线,测量条件为:氩气气氛,扫描速率5 ℃/min。图5(b)和图5(c)表明,在温度为100~300 ℃范围内均存在2个放热峰,第1个峰为电极表面固体电解质膜(SEI膜)碎裂的反应所致;第2个峰由电极中粘结剂与LiC6反应及LiC6与电极中残留的电解液之间的反应所致,该峰反应总热量的大小受粘结剂的性质、含量以及残留的电解液量的影响。实验时该峰的放热[CM(22] 量可能比实际电池被过充时该峰所放出的热量偏
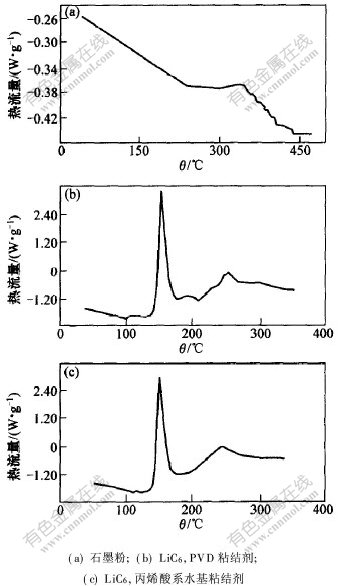
图 5 粘结剂对石墨电极影响的DSC曲线
Fig. 5 DSC profiles for influence of adhesive
on graphite electrode [TS)] 低,主要是因为在手套箱中拆解电池及制备DSC样品过程中,电极中电解液部分挥发,这与S.Hossain等[17 ]对中间相碳微球的研究结果一致。X射线衍射结果表明:负极热分解反应主要发生在石墨的表面,而石墨的晶形结构并没有发生变化,反应受锂在石墨层状结构中迁移的扩散速率控制[1]。在图5(b)中,第1个放热峰峰温为152 ℃,起始温度为132.8 ℃,反应热为750.4 J/g;第2个放热峰峰温为246.8 ℃, 起始温度为219.6 ℃,反应热为257.9 J/g。在图5(c)中,第1个放热峰峰温为150.8 ℃,起始温度为131.4 ℃,反应热为744.7 J/g;第2个放热峰峰温为239.6 ℃, 起始温度为199.2 ℃,反应热为265.5 J/g。比较图5(b)和图5(c)发现,第1个峰形状、峰温及反应开始温度均非常接近,说明粘结剂对SEI膜碎裂反应的影响很小,可以忽略不计;但第2个峰的形状,峰温等存在一定差别,主要是采用不同粘结剂所致。当使用丙烯酸系水基粘结剂时,反应开始温度更低,升温速率更大,释放热量更多,说明当采用丙烯酸系水基粘结剂时,石墨电极的热稳定性比采用PVDF粘结剂时的热稳定性低,这与图2中粘结剂的DSC结果一致。在电池制备工艺上,若采用丙烯酸系水基粘结剂,虽然在一定程度上可以降低电池的生产成本,但同时降低了电池的热稳定性即电池安全性。
2.2 电池的安全性测试 当充电器质量不高或失去功效时,锂离子电池可能因充电控制系统的错误监测而被过充。当电池过充时,锂钴氧正极材料中的剩余锂离子(标准满充电态为Li0.5CoO2)在4.3~4.7 V时迁出,比在标准满充电条件有更多的锂离子被迁移至碳负极[18],其化学反应如式(5)和式(6)所示。如果碳负极的锂嵌入能力小,则锂离子在表面沉积,显著降低电池的热稳定性。当正极材料中的锂被全部迁出后,电解液开始被氧化,这种氧化反应释放大量热量,导致电池温度迅速升高。此外,当电池温度超过230 ℃甚至达300 ℃左右时,充电态的锂钴氧(Li0.5CoO2)可分解释放氧[5,7],并与有机溶剂发生剧烈的燃烧反应,这种有机溶剂的燃烧反应可瞬间释放大量热量与气体,导致电池温度与内压迅速升高甚至电池爆炸。标准满充电:
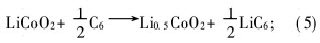
过充电:
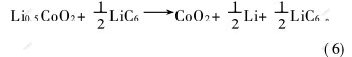
当过充电流较小或电池处于热稳定状态时,电池不会出现冒烟等危险情况,这主要因为隔膜收缩,微孔关闭,限制锂离子的通过。若电池内沉积大量的金属锂,当枝晶化锂导致电池内部短路时,电池温度不会升高,仅因内部短路变成电压为零的电池。当施加高倍率如3C倍率过充电流或电池热稳定性极低时,则可能发生冒烟、燃烧或爆炸等事故。当锂离子电池被过充时,电池电子阻抗产生的焦耳热及电化学极化热等热效应导致电池温度逐渐升高;至5.0 V以上后,电解液开始氧化分解并释放出大量热量与气体,此时材料的热稳定性如导电剂及粘结剂对电池热稳定性的影响发生作用。若使用热稳定性高及热反应时单位质量释放热量较少的导电剂与粘结剂,则电池温度升高的速率相对较小,有利于电池及时启动安全装置。因此,电池被过充时自5.0 V升至10.0 V的时间愈长,表示电池耐过充性能愈好。图6所示为以不同导电剂及粘结剂制备的LiCoO2/石墨型锂离子电池的过充测试结果。表1是电池过充过程中自5.0 V升至10.0 V所需的时间。图6中电池1的正极采用乙炔碳黑导电剂与PVDF粘结剂,负极为PVDF粘结剂;电池2的正极采用导电碳黑导电剂与PVDF粘结剂,负极为PVDF粘结剂;电池3的正极采用乙炔碳黑导电剂与PVDF粘结剂,负极采用丙烯酸水基粘结剂。可见,在电池过充的过程中,在5.0V以下时电池的电压变化速率非常小,这一阶段是锂离子自Li0.5CoO2中脱嵌的过程(如式(5)和式(6)所示)。由于锂离子电池过充时Li0.5CoO2中剩余的锂离子在4.3~4.7 [CM(22]V时脱出,根据高电流下被过充时电池的电化学极化电势,得锂离子自Li0.5CoO2中完全脱嵌的电位约为5.1 V(vs Li/Li+)。由图6及表1可知,当电池正极的导电剂采用导电碳黑,而电池正、负极的粘结剂同时采用PVDF时,电池的耐过充性能最好,说明在提高电池热稳定性方面,导电碳黑较乙炔碳黑好,PVDF粘结剂比丙烯酸系水基粘结剂好,这与P. Biensan等[1]的研究结果一致。在锂离子电池被过充时产生的热量及反应动力学方面,负极较正极的影响大,尽管正、负极材料的比容量差别大,正极材料的质量约相当于负极材料质量的2倍,但电池负极释放的热量最多,而电池中电解液本身的放热量很小。电池中最剧烈的反应为贮锂的碳负极即LiC6与粘结剂之间的反应,反应释放热量的多少与粘结剂的性质及用量有关。氧分别与单位质量的导电碳黑和乙碳炔碳黑反应时,导电碳黑与氧反应释放的热量少得多;并且导电碳黑的导电性优于乙炔黑的导电性,电池正极中导电碳黑和粘结剂的含量较低,从而减弱了导电碳黑、粘结剂分别与Li0.5CoO2分解释放的氧之间的反应,提高电池的热稳定性。
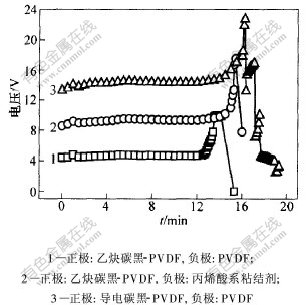
图 6 锂离子电池3C倍率过充测试结果
Fig. 6 Overcharging test results of lithium-ion batteries at 3C rate
表 1 锂离子电池被过充时自5.0 V升至10.0 V的时间
Table 1 Time for lithium-ion batteries from 5.0 V to 10.0 V during overcharging

3 结 论 a. 锂离子电池热稳定性主要由正极、负极及电解液的热稳定性决定,锂离子电池中热反应释放的热量由大到小的顺序为:负极、正极、电解液。b. 负极热反应主要是LiC6与负极中粘结剂以及电解液发生剧烈反应,并释放大量热量。该反应受粘结剂的性质及用量的影响。c. 在提高电池热稳定性方面,PVDF粘结剂较丙烯酸系水基粘结剂好,导电碳黑添加剂较乙炔碳黑添加剂好。高温时电解液与Li0.5CoO2的分解产物反应,释放大量热并降低了Li0.5CoO2分解的起始温度。
参考文献:
[1]Biensan P, Simon B, Peres J P, et al. On safety of lithium-ion cells[J]. J Power Sources, 1999,81-82: 906-912.
[2]Nazri G A, Conell R A, Julien C. Preparation and physical properties of lithium phosphide-lithium chloride: a solid electrolyte for solid sate lithium batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics, 1996,86-88(1): 99-105.
[3]Tobishima S I, Takei K, Sakurai Y, et al. Lithium ion cell safety[J]. J Power Sources, 2000, 90: 188-195.
[4]Maleki H, Deng G, Anani A, et al. Thermal stability studies of Li-ion cells and components[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1999,146(10): 3224-3229.
[5]MacNeil D D, Dahn J R. The reaction of charged cathodes with nonaqueous solvents and electrolytes (Ⅰ.Li0.5CoO2)[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2001, 148(5): 1205-1210.
[6]Macneil D D, Dahn J R. The reaction of charged cathodes with nonaqueous solvents and electrolytes (Ⅱ.LiMn2O4 charged to 4.2 V)[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2001,148(5): 1211-1215.
[7]Macneil D D, Dahn J R. The reactions of Li0.5CoO2 with nonaqueous solvents at elevated temperatures[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2002, 149(7): 912-919.
[8]Yoshiyasu S, Kiyonami T, Akira N. Thermal behaviors of lithium-ion cells during overcharge[J]. J Power Sources, 2001,97-98: 693-696.
[9]Carlos J, Reis R, Thermodynamic analysis of the symmetry factor and the transfer coefficient in electrode kinetics[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1997,144(7): 2404-2409.
[10]Takano K, Saito Y, Kanari K, et al. Entropy changes in lithium ion cells on charge and discharge[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2002, 32 (1): 251-258.
[11]Selman J R, Said A H, Uchida I, et al. Cooperative research on safety fundamentals of lithium batteries[J]. J Power Sources, 2001,97-98: 726-732.
[12]Funahashi A, Kida Y, Yanagida K, et al. Thermal simulation of large-scale lithium secondary batteries using a graphite-coke hybrid carbon negative electrode and LiNi0.7Co0.3O2 positive electrode[J]. J Power Sources, 2002,104: 248-252.
[13]Gerardine G B, Talph E W, Zhang Z M. Thermal stability of LiPF6-EC:EMC electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries[J]. J Power Sources, 2001, 97-98: 570-575.
[14]Kawamura T, Kimura A, Egashira M, et al. Thermal stability of alkyl carbonate mixed-solvent electrolytes for lithium ion cells[J]. J Power Sources, 2002, 104: 260-264.
[15]Yamaki J I, Takatsuji H, Kawamura T, et al. Thermal stability of graphite anode with electrolyte in lithium-ion cells[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2002,148(1): 241-245.
[16]Edstrom K, Andersson A M, Bishop A, et al. Carbon electrode morphology and thermal stability of the passivation layer[J]. J Power Sources, 2001, 97-98: 87-91.
[17]Hossain S, Kim Y K, Saleh Y, et al. Comparative studies of MCMB and C-C composite as anodes for lithium-ion battery systems[J]. J Power Sources, 2003, 114: 264-276.
[18]Reimers J N, Dahn J R. Electrochemical and in situ X-ray diffraction studies of lithium intercalation in LixCoO2[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1992, 139(7): 2091-2097.
收稿日期: 2004-04-06
作者简介:胡传跃(1972-),男,湖南安化人,博士,从事锂离子电池及相关材料研究
论文联系人: 胡传跃,男,博士;电话:0738-8325065(O);E-mail: huchuanyue@vip.sina.com