液相氧化处理对炭纤维表面结构的影响
徐先锋1, 2,肖 鹏1,许 林1,熊 翔1
(1. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 华东交通大学 机电工程学院,江西 南昌,330013)
摘 要:对去胶聚丙烯腈炭纤维(PAN-CF)分别进行不同时间的硝酸液相氧化处理,采用N2等温(77.35 K)吸附及SEM观察的方法,分析氧化处理对纤维表面结构的影响。研究结果表明:氧化处理会使纤维表面产生大量的孔洞,增加BET比表面积和BJH累积孔体积,提高表面吸附能力;在氧化初期,伴随着纤维表面大量活化点的迅速氧化,纤维表面微孔、中孔数量、表面粗糙度、比表面积和累积孔体积迅速增加,使纤维表面吸附能力大大增强,但在氧化5 min以后,由于纤维表面尖锐突起处发生氧化,从而减少了纤维表面微孔,比表面积和累积孔体积降低,表面吸附能力减弱。
关键词:聚丙烯腈炭纤维;液相氧化处理;孔结构;等温吸附
中图分类号:TP332 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2008)03-0512-05
Influences of liquid oxidation treatment on surface structure of
carbon fiber
XU Xian-feng1, 2, XIAO Peng1, XU Lin1, XIONG Xiang1
(1. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, East China Jiaotong University, Nanchang 330013, China)
Abstract: PAN carbon fibers (PAN-CF) without adhesion agent were treated with nitric acid for different time. By means of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and isotherm absorption of N2 at 77.35 K, the effects of nitric acid liquid phase oxidation treatments on the surface structure of carbon fiber (CF) were investigated. The results show that these treatments lead to many micro-pores and increase BET surface area (TSA) and BJH cumulative adsorption pore volume (BPV). Surface absorption capability is also improved. At the first stage of oxidation treatments, lots of activation points are oxidized. In addition, the quantity of micro-pore and meso-pore, roughness, TSA and BPV increase rapidly, which enhances the surface absorption capability of CF efficiently. However, during the successive oxidation procedures, the parameters above decrease due to the oxidation of acute points.
Key words: PAN-carbon fiber; liquid oxidation treatment; pore structure; isotherm absorption
聚丙烯腈炭纤维(PAN-CF)是一种新型的特种纤维,具有抗张强度大、抗张模量高、密度小、耐腐蚀、耐磨损、耐高温等优异性能[1],已作为复合材料的增强体广泛应用于航天航空[2-3]、新型纺织机械、石油化工、汽车、机械制造和文体用品等高新技术领域[4]。但是,未经处理的PAN-CF表面呈惰性,与基体结合状态不佳,影响了复合材料的力学性能,限制了PAN- CF的实际应用[5]。因此,炭纤维表面处理技术与炭纤维增强复合材料性能密切相关。目前,国内外对炭纤维表面处理常用的方法有:气相氧化法[5]、液相氧化法[6]、电化学阳极氧化法[7]、等离子体处理[5]、表面化学涂层[8]等。其中,采用液相氧化法不易使纤维产生过度的刻蚀和裂解,而且在一定条件下含氧基团数量比采用气相氧化法的多,在实践中应用广泛[8]。但是,研究表明,若选择的氧化剂与氧化工艺欠佳,则无法达到理想效果[9-10]。因此,研究液相氧化法对炭纤维表面改性的影响对获得最佳的材料性能具有重要意义。杜慷慨等[11]研究了炭纤维含氧基团随液相氧化条件的变化规律,在此,本文作者通过对PAN-CF进行硝酸氧化处理,采用低温氮吸附解析多孔固体表面结构的方法,在分析其对力学性能影响[12]的基础上,探讨不同氧化处理后表面微观结构特别是微孔结构的变化,以解释处理前后纤维性能改变的原因,并用于改进纤维表面处理技术。
1 实 验
1.1 材 料
材料为:PAN-CF,为日本东邦公司的HTA纤维(平均直径为6 μm);硝酸(含量为65%~68%),湖南省株洲开发区石英化玻有限责任公司试剂厂生产,分析纯;丙酮,湖南师大化学试剂厂生产,分析纯。
1.2 实验设备
实验设备为:日本制造的JSM-6360LA型电子扫描仪,观察炭纤维表面形貌;美国QUANTACHROME公司制造的Autosorb-1静态体积吸附分析仪,测量炭纤维在77.35 K时的N2吸附等温线。
1.3 实验方法
将上胶炭纤维在丙酮溶液中浸泡24 h后,取出,在去离子水中浸泡30 min,用超声波清洗10 min,在473 K干燥箱中干燥4 h,得到去胶纤维(试样记为a样),以去胶纤维作为表面液相氧化处理的原始纤维。原始纤维在室温下、硝酸原液中分别氧化5,10,15和20 min,氧化后用去离子水、超声波清洗,干燥并分别记为b,c,d和e样。氧化前、后的炭纤维在773 K时脱气7 h,再采用高纯氮(99.99%)为吸附 质,由Autosorb-1静态体积吸附分析仪测出77.35 K时N2的吸附等温线,比表面积由标准的BET方法进行计算;运用Horvath-Kowazoe方程计算平均微孔直径;运用Doubinin方程,计算平均微孔直径;运用密度函数理论表征炭纤维样品的整体孔径分布。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 实验结果
HTA纤维硝酸氧化前、后的表面SEM形貌如图1所示。由图1可以看出,炭纤维的表面形貌随氧化时间延长呈由粗糙到光滑的趋势。氧化前、后炭纤维在77.35 K时的吸附等温线如图2所示。图2中没有脱附等温线,总的趋势是:随着吸附压力的升高,各试样的吸附量加大,未经氧化处理的吸附线在最下方,硝酸氧化5 min时试样的吸附线在最上方。
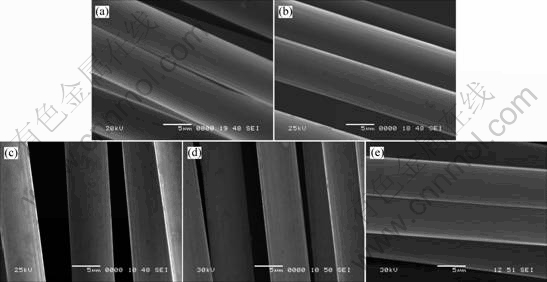
氧化时间/min:(a) 0;(b) 5;(c) 10;(d) 15;(e) 20
图1 氧化时间不同时的炭纤维SEM照片
Fig.1 SEM images of treated and untreated carbon fibers for different oxidation time
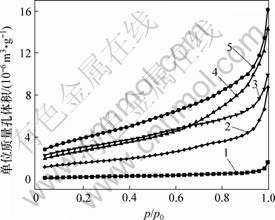
氧化时间/min:1—0;2—20;3—15;4—10;5—5
图2 氧化时间不同时的CF等温吸附曲线
Fig.2 Isotherm absorption curves of treated and untreated carbon fibers for different oxidation time
2.2 分析与讨论
图1表明,未氧化及不同氧化程度的炭纤维表面形貌有所差异,未氧化及硝酸氧化15 min和20 min后的纤维表面较光滑,经硝酸氧化5 min和10 min的纤维表面相对粗糙,但差别并不明显[13]。王成忠等[14]采用AFM的研究方法研究沥青基炭纤维的氧化处理,也得出了类似的结论。
国际纯理论和应用化学联合会(IUPAC)将多孔固体的细孔分为3类:孔径小于2 nm的微孔;孔径为2~50 nm的中孔;孔径大于50 nm的大孔。图2中氮吸附等温线均不包含脱附分支,故在一些存在中孔的纤维中并不能看到滞后回线[15]。这表明炭纤维中除了微孔以外,还出现了大量的中孔。未氧化及不同氧化程度的炭纤维的N2等温吸附曲线表明,未氧化炭纤维的吸附能力弱;而在硝酸氧化5 min后,其吸附能力大大增强;氧化10 min后吸附能力降低;氧化15 min后低压吸附能力稍加强,而高压吸附能力降低;在氧化20 min后吸附能力进一步降低,但仍然高于未氧化炭纤维的吸附能力。通过对经不同时间氧化处理炭纤维的等温吸附曲线进行分析,得到了各纤维的BET比表面积及BJH法累积孔体积与时间的关系曲线,如图3所示。密度函数理论表征的炭纤维样品的整体孔径分布曲线见图4。在等温吸附实验中,假设所有的孔均为球形孔,将孔径与体积关系转换为孔径和孔数量关系,结果见图5(其中,n为CF单位质量的孔数)。图3中,未处理炭纤维的BET比表面积及BJH法累积孔体积最小,而氧化5 min后的BET比表面积及BJH法累积孔体积最大,约为未经处理前的7倍。此后,随着氧化程度的加强,BET比表面积及BJH法累积孔体积均呈下降趋势。
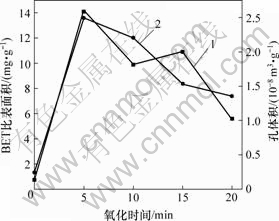
1—BET比表面积;2—BJH累积孔体积
图3 氧化前后CF的BET比表面积及累积孔体积
Fig.3 BET surface area and total pore volume of treated and untreated carbon fibers for different oxidation time
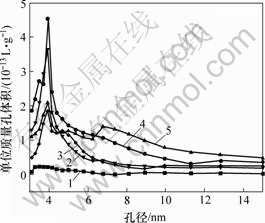
氧化时间/min:1—0;2—15;3—20;4—5;5—10
图4 氧化时间不同时的CF孔径分布曲线
Fig.4 Micro-pore diameter distributions of treated and untreated carbon fibers for different oxidation time
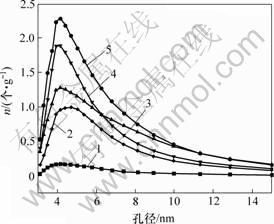
氧化时间/min:1—0;2—20;3—10;4—15;5—5
图5 氧化时间不同时的CF微孔数分布曲线
Fig.5 Micro-pore quantity distributions of treated and untreated carbon fibers for different oxidation time
分析图4可知,氧化前后纤维表面均以孔径在6 nm以下的微孔和中孔数目居多,因此,在扫描电镜下经不同氧化时间后纤维表面的差别并不明显。此外,在相对压力较低时,主要发生单分子层吸附,因此,纤维的孔径越小,其相对压力较低时氮气等温吸附能力越强;而在相对压力较高时,发生多层吸附,即中孔和大孔占主导地位,故尽管d样和c 样的比表面积相差不大(见图3),但因为d样微孔和中孔数目比c样的多,大孔数比c样的少(见图5),故其低压吸附能力比c样的强,而高压吸附能力比c样的低(见图2)。
由图4可知,氧化处理后炭纤维表面累积孔体积大大增加,在前5 min内增加明显,而后逐渐下降。经转换后的图5更清楚地表明,氧化处理后的纤维与未处理纤维相比,表面微孔和中孔数量大大增加,且在前5 min的氧化时间内增加最显著,此后经历了先降低后增加再降低的过程,而大孔数量则一直降低。其原因是本实验所用HTA纤维在出厂前经过适当的氧化处理,表面光滑,微孔少,故BET比表面积及BJH法累积孔体积很小;经过去胶处理,脱去了大部分表面含氧基团,并产生大量的不饱和键。在氧化初期,这些不饱和键和纤维表面的细小石墨微晶晶界、微晶外表面、微晶中的缺陷及纤维表面的孔洞一起,为硝酸氧化提供了大量的活性点,氧化反应进行的速度很快,使得原始的活性点被迅速氧化成微孔。同时,大量的原始孔洞及后续氧化产生的孔洞被进一步氧化成中孔,即孔的扩宽和孔的形成是同步发生的,故纤维表面的微孔和中孔数迅速增加。此时,纤维表面不如原始纤维光滑,其凸凹度增加,高低不平。因此,炭纤维吸附能力大大增强,其BET比表面积及BJH累积孔体积大大增加。进一步延长氧化时间,由于氧化在纤维表面产生的基团对纤维的进一步氧化起阻碍作用,初期的活性点处氧化速度减缓;而完全暴露在硝酸中的纤维表面突起部分的活性增加,会逐渐被氧化,因此,纤维表面的凸凹度降低,纤维趋于平滑,微孔迅速减少,同时,BET比表面积及BJH累积孔体积也降低。
炭纤维经氧化处理后其抗拉强度有所改变[12-13]。硝酸处理5 min后纤维抗拉强度降低,在随后的10,15和20 min处理后抗拉强度逐渐增加[12]。结合图5中纤维表面气孔的变化发现,炭纤维硝酸氧化处理氧化5 min时,形成了很多大孔,造成应力集中,形成Griffith裂缝,故降低了纤维的抗拉强度。经10,15和20 min处理后,大孔减少,同时形成大量的微孔,增加裂纹扩展面积或延长扩展路径,从而提高了材料的断裂韧性[16]。由以上分析可知,氧化处理所产生的微孔会提高炭纤维的抗拉强度。
3 结 论
a. 硝酸氧化处理可以改变HTA纤维的表面结构,产生大量的表面微孔,使比表面积和累积孔体积增加,从而提高其表面吸附能力。
b. 在氧化的初始阶段,纤维表面大量活化点迅速氧化,纤维表面微孔、中孔迅速增加,比表面积和累积孔体积迅速增加,表面吸附能力大大增强;延长氧化时间至5 min后,含氧基团的阻碍作用和随后对纤维表面尖锐突起处的进一步氧化减少了纤维表面微孔和中孔数,比表面积和累积孔体积降低,表面吸附能力减弱。
c. 结合氧化处理对纤维力学性能和气孔结构的影响,适当进行氧化处理能够增加炭纤维表面微孔,提高纤维的抗拉强度。
参考文献:
[1] 贺 福. 碳纤维及其复合材料[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004.
HE Fu. Carbon fiber and composites[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004.
[2] 李丽娅, 黄启忠, 张红波. 聚丙烯腈基炭纤维的组织结构及力学性能[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2005, 36(2): 193-197.
LI Li-ya, HUANG Qi-zhong, ZHANG Hong-bo. Microstructure and properties of polyacrylonitrile carbon fiber[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2005, 36(2): 193-197.
[3] Miller A G, Lovell D T, Seferis J C. The evolution of an aerospace material: Influence of design, manufacturing and in-service performance[J]. Composite Structures, 1994, 27(1/2): 193-206.
[4] 巩前明, 黄启忠, 黄伯云. 炭/炭复合材料浸渍用沥青的性能分析[J]. 中南工业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2000, 31(6): 536-539.
GONG Qian-ming, HUANG Qi-zhong, HUANG Bai-yun. Analysis of the properties of two kinds of coal tar pitches used for impregnation of C/C composite[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology: Natural Science, 2000, 31(6): 536-539.
[5] Bismarck A, Kumru M E, Song B, et al. Study on surface and mechanical fiber characteristics and their effect on the adhesion properties to a podqcarbonate matrap tuned by afodac carbon fiber oxidation[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 1999, 30(12): 1351-1366.
[6] Figueiredo J L, Serp P H, Nysten B, et al. Surface treatments of vapor-grown carbon fibers produced on a substrate Part Ⅱ: atomic force microscopy[J]. Carbon, 1999, 37(11): 1785-1796.
[7] Vijay K K. Surface characterization of KMnO4 treated carbon fiber precursors using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy[J]. Polym Test, 2000, 19(1): 17-25.
[8] Fukunaga A, Ueda S, Nagumo M. Anodic surface oxidation mechanisms of PAN-based and pitch-based carbon fibers[J]. Mater Sci, 1999, 34(12): 2851-2854.
[9] 张晓鸥, 张爱波. 液相氧化碳纤维增强韧化聚苯硫醚复合材料的性能研究[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2000(4): 30-36.
ZHANG Xiao-ou, ZHANG Ai-bo. Performance investigation of liquid phase oxidation carbon fiber rein-forced and toughened polyphenyl enesulfide composite[J]. Fiber Reinforced Plastics/ Composite, 2000(4): 30-36.
[10] Choi M H, Jeon B H, Chung I J. The effect of coupling agent on electrical and mechanical properties of carbon fiber/phenolic resin composites[J]. Polymer, 2000,41(9): 3243-3252.
[11] 杜慷慨, 林志勇. 碳纤维表面氧化的研究[J]. 华侨大学学报: 自然科学版, 1999, 20(2): 136-141.
DU Kang-kai, LIN Zhi-yong. Oxidation on the surface of carbon fibers[J]. Journal of Huaqiao University: Natural Science, 1999, 20(2): 136-141.
[12] 徐先锋, 肖 鹏, 许 林, 等. 炭纤维表面氧化处理对其力学性能的影响研究[J]. 材料导报, 2007, 21(5): 121-124.
XU Xian-feng, XIAO Peng, XU Lin, et al. Investigation on the effect of CF’s surface oxidation treatment on the mechanical properties[J]. Materials Review, 2007, 21(5):121-124.
[13] 信春玲, 王培华. 电解氧化刻蚀提高抗拉强度的研究[J]. 炭素技术, 2002, 21(5): 14-19.
XIN Chun-ling, WANG Pei-hua. Study on improvement of PAN-based carbon fiber by electrolysis oxidation etching[J]. Carbon Techniques, 2002(5): 14-19.
[14] 王成忠, 杨小平, 于运花, 等. XPS, AFM研究沥青基碳纤维电化学表面处理过程的机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2002, 19(5): 28-32.
WANG Cheng-zhong, YANG Xiao-ping, YU Yun-hua, et al. Study on the mechanism of electrochemical oxidized pitch-based carbon fiber by XPS and AFM[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2002, 19(5): 28-32.
[15] Rouquerol F, Rouquerol J, Sing K. Adsorption by powders and porous solids: principles, methodology and applications[M]. London: Academic Press, 1999.
[16] 仲亚娟, 李东风, 华 中. PAN基炭纤维微孔缺陷的表征及其对力学性能的影响[J]. 吉林师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006(2): 16-18.
ZHONG Ya-juan, LI Dong-feng, HUA Zhong. Pores in PAN-based carbon fiber and effects on mechanical properties[J]. Journal of Jilin Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2006(2): 16-18.
收稿日期:2007-06-30;修回日期:2007-09-08
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2006CB600904)
通信作者:徐先锋(1971-),男,湖北罗田人,博士研究生,讲师,从事炭纤维表面改性、C/C和C/SiC复合材料的研究;电话:0731-8836864;E-mail: xu-xianfeng@163.com