Fe3O4在铜闪速炉反应塔中的形成热力学
汪金良1, 2,张传福2,张文海3
(1. 江西理工大学 冶金与化学工程学院,江西 赣州,341000;
2. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
3. 中国瑞林工程技术有限公司,江西 南昌,330002 )
摘要:将闪速炉反应塔内部空间视为物料与反应气体不断达到局域平衡的体系,建立铜精矿在闪速炉反应塔内反应的热力学模型,并对Fe3O4在反应塔中的形成热力学进行研究。研究结果表明:随物料在反应塔中的下落,反应塔中的氧势呈先快后缓的下降趋势,其模型计算值与实测值吻合较好,说明模型能较好地反映铜精矿在反应塔内的热力学行为;对于一定成分的物料,反应塔中的温度和氧势对Fe3O4的形成具有显著影响;较低的温度和较高的氧势对Fe3O4的形成有利;反应塔上端较易形成Fe3O4,利于形成内壁挂渣,但下端应加强塔壁水冷保护。
关键词:铜闪速熔炼;反应塔;Fe3O4;热力学;挂渣
中图分类号:TF801 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)12-4787-06
Formation thermodynamic of Fe3O4 in reaction shaft offlash smelting furnace
WANG Jinliang1, 2, ZHANG Chuanfu2, ZHANG Wenhai3
(1. School of Metallurgical and Chemistry Engineering,Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou 341000, China;
2. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. China Nerin Engineering Co. Ltd., Nanchang 330002, China)
Abstract: A thermodynamic model of the copper concentrate reaction in the flash smelting furnace reaction shaft was proposed by treating the shaft interior space as a system where the concentrate and oxygen-rich air achieve local equilibrium continuously while falling to the settler, and then the model was used to analyze the formation thermodynamic of Fe3O4 in the reaction shaft. The results show that the oxygen potential  tends to go down fast first and then slow with the fall of the concentrate in the reaction shaft, and the model calculated
tends to go down fast first and then slow with the fall of the concentrate in the reaction shaft, and the model calculated  is in good agreement with the measured data, showing that the model can wholly embody the thermodynamic behavior of the copper concentrate in the reaction shaft. For the copper concentrate with a certain composition, the temperature T and
is in good agreement with the measured data, showing that the model can wholly embody the thermodynamic behavior of the copper concentrate in the reaction shaft. For the copper concentrate with a certain composition, the temperature T and 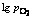 have a significant impact on the Fe3O4 formation, and lower T but higher
have a significant impact on the Fe3O4 formation, and lower T but higher 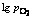 are efficient to form Fe3O4 in reaction shaft. It’s easier to get Fe3O4 and to form frozen slag for the upper part of the shaft than the under part where the shaft wall should be protected more strongly by cooling water.
are efficient to form Fe3O4 in reaction shaft. It’s easier to get Fe3O4 and to form frozen slag for the upper part of the shaft than the under part where the shaft wall should be protected more strongly by cooling water.
Key words: copper flash smelting; reaction shaft; Fe3O4; thermodynamic; frozen slag
自1949年芬兰奥托昆普问世以来,经过不断改进、完善和发展,闪速熔炼已成为当今最具有竞争力的铜镍强化熔炼技术[1],被普遍认为是标准的清洁冶炼工艺[2]。闪速炉及其熔炼过程一直受到广泛关注[3]。反应塔是闪速熔炼炉的最重要部分。在熔炼过程中,反应塔必须能同时承受以下苛刻条件:(1) 含氧体积分数为50%~80%的强氧化性气氛;(2) 速度高达l00 m/s的固体颗粒及熔体的高速冲刷;(3) 强酸性或强碱性炉渣的化学侵蚀;(4) 体积分数为30%~70%的SO2腐蚀;(5) 锍的强烈溶蚀作用。特别是如今高投料量、高铜锍品位、高富氧浓度、高容积热强度的“四高”技术应用[4],不断提高闪速熔炼单炉实际生产能力,也意味着不断提高熔炼炉的热负荷,必然会加速闪速熔炼炉,特别是反应塔内壁的损伤。因此,闪速熔炼反应塔的保护技术成为实现强化冶金的主要“难点”。国内外通常的解决办法是采用在反应塔砌砖之间埋设水套,使得在反应塔内壁形成一层挂渣;也有采用塔外冷水喷淋,使得在无砖反应塔内壁焊接的钢钉上形成一层挂渣层,从而保护反应塔[5]。不管是采用哪种方式,在反应塔内壁形成结构致密、隔热良好、强度一定、厚度适当、分布合理的挂渣,对闪速冶金企业的节能降耗和安全生产都具有重大意义。对于反应塔内壁挂渣,陈卓[6]对从现场获取的内壁挂渣进行了扫描电镜分析,发现挂渣主体为磁铁矿自形晶,此外还包含有玻璃相、铁橄榄石析晶以及少量铜金属和化合物共溶晶粒;Wang等[7]对反应塔内壁挂渣的物性进行了实验研究,发现挂渣中大量的Fe3O4能提高其熔点和黏度,对在反应塔内壁形成挂渣是有利的。由此可见,反应塔中Fe3O4的行为对内壁挂渣的形成至关重要。为此,本文通过建立铜精矿在闪速炉反应塔中反应的热力学模型,对铜精矿在反应塔中熔炼过程进行描述,从而了解Fe3O4在反应塔中的热力学行为,为反应塔内壁挂渣的机理研究提供参考。
1 热力学模型
1.1 物理模型
铜闪速熔炼过程是将铜精矿、富氧空气、熔剂等物料经中央喷嘴高速喷入反应塔内,在2~3 s内完成造锍、造渣和部分吹炼反应,从而得到一定品位铜锍的过程[8]。
然而,虽然铜精矿在反应塔中停留的时间很短,但却经历了非常复杂的反应过程,包括精矿分解、氧化、还原、造锍、造渣等。综合Kemori等[9]对反应机理的研究成果,可以发现铜精矿并不是一进入反应塔就全部反应完全,而是在物料掉入沉淀池的过程中逐步进行的。但由于闪速熔炼采用的精矿喷嘴能将铜精矿、熔剂和反应气体较好地混合,所以,在极短时间内(如1 ms)物料与反应气体应该可以认为达到或接近平衡状态。因此,根据物料在反应塔中不断下落的特征,可将反应塔内部空间视为物料与反应气体不断达到局域平衡的体系。理想状态,当产物到达沉淀池时,所有物料都被反应,从而达到很多研究所描述的闪速熔炼过程多相平衡状态[10-11]。
根据以上分析,得到如图1所示的物理模型。假设闪速炉反应塔沿纵向分为n个足够小的局域,每个局域处于化学平衡状态。当质量为mcon的物料从顶部进入反应塔时,将分成n份逐步与周围的氧气发生反应,即在第1个局域,质量为△m的物料与体积为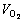 的氧气发生反应并达到化学平衡状态,消耗了氧气△V,于是,在第2个局域,质量为△m的物料将与体积为
的氧气发生反应并达到化学平衡状态,消耗了氧气△V,于是,在第2个局域,质量为△m的物料将与体积为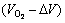 的氧气发生反应并达到化学平衡状态,以此类推,直到反应物到达反应塔底部的沉淀池,此时最后剩下的△m物料将与体积为
的氧气发生反应并达到化学平衡状态,以此类推,直到反应物到达反应塔底部的沉淀池,此时最后剩下的△m物料将与体积为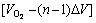 的氧气反应并到达化学平衡。
的氧气反应并到达化学平衡。
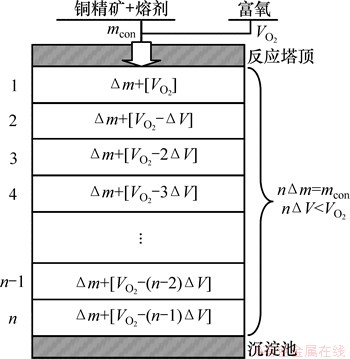
图1 物理模型描述
Fig. 1 Physical model description
因此,可以通过搭建每个局域的多相平衡模型,再利用各局域之间物质的传递,从而建立铜精矿在闪速炉反应塔中反应的热力学模型。
1.2 数学描述
对于反应塔中的每个平衡局域(体系),其总的吉布斯自由能可用式(1)表示:
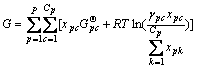 (1)
(1)
其中:P是体系的总相数;Cp是p相中的组分数;xpc是p相中c组分的物质的量;γpc 是p相中c组分的活度系数;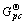 是p相中c组分的标准生成吉布斯自由能。
是p相中c组分的标准生成吉布斯自由能。
由最小吉布斯自由能原理可知:当该体系处于平衡状态时,体系总的吉布斯自由能最小。于是,将式(1)在X(n)处按泰勒级数二阶展开得多项式Q,然后结合质量守恒定律,引入Lagrange因子,构造出 函数(如式(2)所示),将有约束条件的极值问题转换为无约束条件极值问题。
函数(如式(2)所示),将有约束条件的极值问题转换为无约束条件极值问题。
 (2)
(2)
其中:ace为c组分中e元素的数目;be是元素e的总物质的量;m为体系中元素个数,λe 为Lagrange因子。
将L分别对xpc和λe求偏导可得:
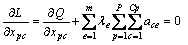
 (3)
(3)
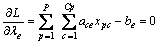 (e=1,…,m) (4)
(e=1,…,m) (4)
由式(3)和式(4)构成的方程组即为各个局域的多相平衡热力学模型,可用Rand算法进行求解,从而得到各局域的相组成。
1.3 求解过程
铜精矿在闪速炉反应塔中反应的热力学模型计算流程如图2所示。
流程中首先设置了一个循环,用于控制计算的进程,以确保n个平衡局域都得以计算。其中n可由式(5)进行计算:
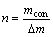 (5)
(5)
式中:mcon为熔炼过程总的进料量;△m为每1 ms掉入沉淀池的物料量。
由于各组分的活度系数与各组分的组成和工艺条件有关,于是当迭代产生新的组成后,必须重新迭代活度系数,以确保组成计算结果的正确性。于是,对每个局域采用双层迭代,分别对组成xpc和活度系数γpc进行迭代,从而得到各局域的稳态平衡组成。当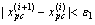 (其中ε1=10-5)时,组成迭代结束;而当
(其中ε1=10-5)时,组成迭代结束;而当 (其中ε2=10-4),活度系数迭代结束。
(其中ε2=10-4),活度系数迭代结束。
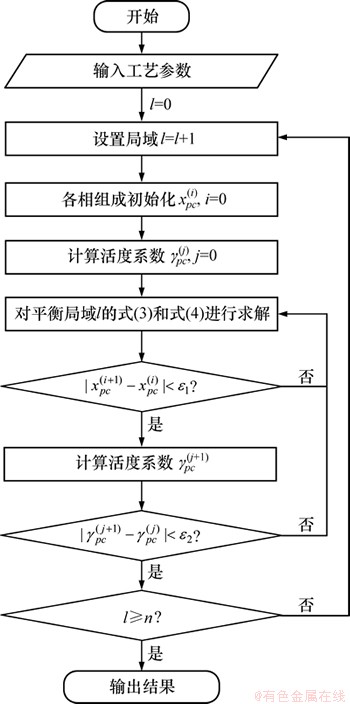
图2 模型计算流程
Fig. 2 Flowchart of model calculation
2 模型验证
2.1 体系各相组分
对于每个平衡局域,可能涉及到5相:铜锍相、炉渣相、磁铁相、二氧化硅相和烟气相。各相组分如下:
(1) 铜锍相:Cu2S,FeS,FeO,Fe3O4,Cu。
(2) 炉渣相:FeO,SiO2,Cu2S,Cu2O,Fe3O4,FeS。
(3) 磁铁相:Fe3O4。
(4) 二氧化硅相:SiO2。
(5) 烟气相:SO2,S2,O2,N2,H2O,H2,CO,CO2。
2.2 热力学数据
计算所需要的各相各组分的标准生成吉布斯自由能为△GΘ=A+B·T·lgT+C·T,其中A,B和C参数见表1。
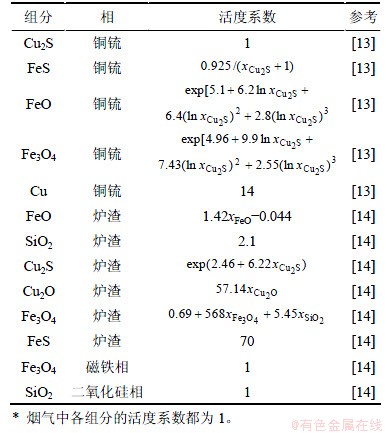
计算所需要的各组分活度系数见表2,其中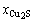 为冰铜中Cu2S的摩尔分数,
为冰铜中Cu2S的摩尔分数,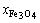 ,
, 和
和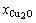 分别为炉渣中Fe3O4,SiO2和Cu2O的摩尔分数。
分别为炉渣中Fe3O4,SiO2和Cu2O的摩尔分数。
表1 各组分的标准生成吉布斯自由能[18]
Table 1 Standard formation Gibbs free energy calculation parameters of components
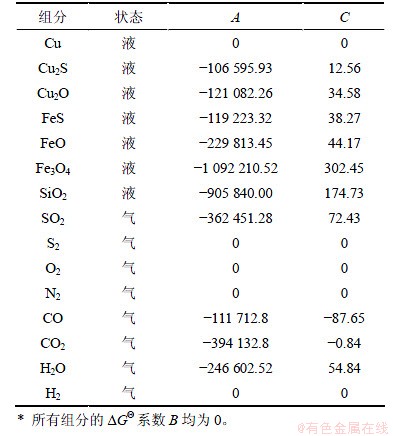
表2 组分的活度系数
Table 2 Activity coefficient of components
2.3 仿真结果
对于如表3所示的物料,在反应塔高度为8 m,温度为1 250 ℃,吨矿氧量为220 m3/t,富氧浓度为60%的情况下,模拟计算了精矿在反应塔中的变化情况,其中氧势变化情况如图3所示。
表3 入炉物料量与物料主要化学成分
Table 3 Quantity and composition of input materials
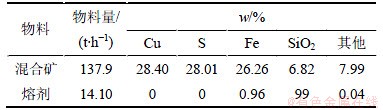
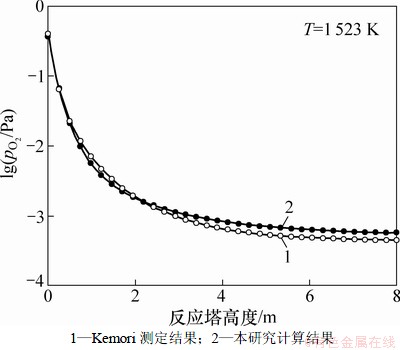
图3 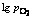 随反应塔高度的变化趋势
随反应塔高度的变化趋势
Fig. 3 Variation of 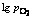 with reaction shaft height
with reaction shaft height
由图3可知:当物料在反应塔中不断下落,体系的氧势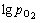 呈先快后缓的下降趋势,表明随着物料在反应塔中的反应不断进行,体系中的氧不断被消耗。模型计算值与实测值吻合较好,说明模型能较好地反映铜精矿在反应塔中的热力学行为,可以用于分析Fe3O4在反应塔内的形成热力学。
呈先快后缓的下降趋势,表明随着物料在反应塔中的反应不断进行,体系中的氧不断被消耗。模型计算值与实测值吻合较好,说明模型能较好地反映铜精矿在反应塔中的热力学行为,可以用于分析Fe3O4在反应塔内的形成热力学。
3 Fe3O4生成热力学
3.1 温度对Fe3O4生成的影响
计算了1 473,1 523和1 573 K温度下,Fe3O4活度 随反应塔高度的变化,结果如图4所示。
随反应塔高度的变化,结果如图4所示。
由图4可知:随着物料在反应塔中不断下降, 不断减小,表明在反应塔上部较易生成Fe3O4,而在反应塔下部不易生成。在其他条件不变的情况下,
不断减小,表明在反应塔上部较易生成Fe3O4,而在反应塔下部不易生成。在其他条件不变的情况下, 随温度的升高而下降,表明较低的温度有利于Fe3O4相的析出。
随温度的升高而下降,表明较低的温度有利于Fe3O4相的析出。
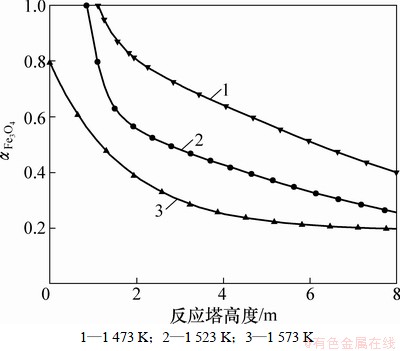
图4 不同温度下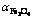 随反应塔高度的变化趋势
随反应塔高度的变化趋势
Fig. 4 Variation of 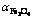 with reaction shaft height at different temperatures
with reaction shaft height at different temperatures
图5所示为1 473 K和1 523 K温度下,Fe3O4析出率 (即析出的Fe3O4质量分数)在反应塔中的变化情况。由图5可知:
(即析出的Fe3O4质量分数)在反应塔中的变化情况。由图5可知: 随着物料的下降和温度的升高而降低,并且Fe3O4在反应塔中析出的空间(高度)随温度的升高而缩小,如从1 473 K时的1.2 m缩小到1 523 K时的0.8 m。
随着物料的下降和温度的升高而降低,并且Fe3O4在反应塔中析出的空间(高度)随温度的升高而缩小,如从1 473 K时的1.2 m缩小到1 523 K时的0.8 m。
因此,要在反应塔中析出Fe3O4,从而形成较好的内壁挂渣,维持较低的温度是有利的,这也是通常使用冷却水套进行反应塔塔壁保护的主要原因。
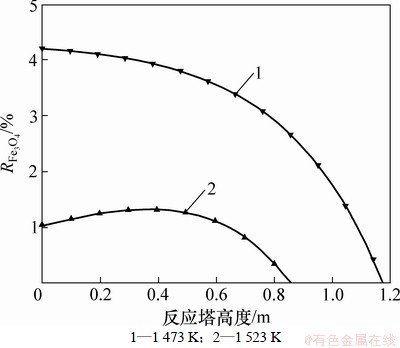
图5 不同温度下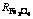 随反应塔高度的变化趋势
随反应塔高度的变化趋势
Fig. 5 Variation of 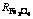 with reaction shaft height at different temperatures
with reaction shaft height at different temperatures
3.2 氧势对Fe3O4生成的影响
在一定温度下,氧势对Fe3O4活度 的影响如图6所示。
的影响如图6所示。
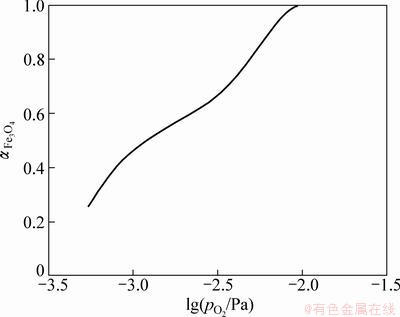
图6 1 523 K时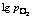 对
对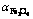 的影响
的影响
Fig. 6 Effect of 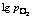 on
on 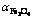 at 1 523 K
at 1 523 K
从图6可知: 总体上随着氧势
总体上随着氧势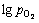 的升高而增大,说明氧势升高有助于Fe3O4的析出。
的升高而增大,说明氧势升高有助于Fe3O4的析出。
结合图3和图6可知: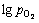 在反应塔的上部空间较高,为Fe3O4的生成创造了有利条件。
在反应塔的上部空间较高,为Fe3O4的生成创造了有利条件。
3.3 温度和氧势对Fe3O4生成的综合影响
图7和图8所示分别为1 473 K和1 523 K时Fe3O4的生成条件。由图7可知:当温度为1 473 K时,Fe3O4析出时的氧势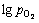 约为-3。由图8可知:当温度为1 523 K时,Fe3O4析出时的氧势
约为-3。由图8可知:当温度为1 523 K时,Fe3O4析出时的氧势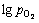 约为-2。这说明Fe3O4析出所需的氧势随着温度的升高而加大,即在较高温度下,需要较高的氧势才有可能析出Fe3O4。
约为-2。这说明Fe3O4析出所需的氧势随着温度的升高而加大,即在较高温度下,需要较高的氧势才有可能析出Fe3O4。
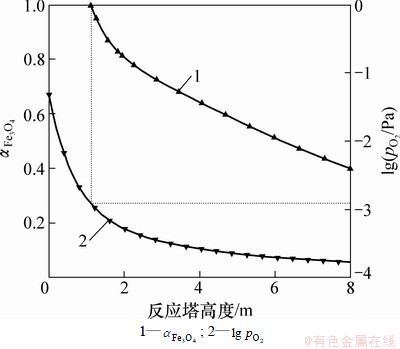
图7 温度为1 473 K时Fe3O4的生成条件
Fig. 7 Formation conditions of Fe3O4 at 1 473 K
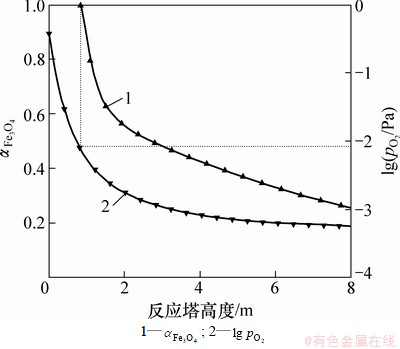
图8 温度为1 523 K时Fe3O4的生成条件
Fig. 8 Formation conditions of Fe3O4 at 1 523 K
4 结论
(1) 模拟计算结果与实测值吻合得较好,表明将闪速炉反应塔内部空间视为物料与反应气体不断达到局域平衡的体系是可行的,所建立的热力学模型能较好地反映铜精矿在反应塔中的热力学行为。
(2) 对于一定成分的物料,反应塔中的温度和氧势对Fe3O4的生成具有显著影响。较低的温度和较高的氧势对Fe3O4的生成有利。
(3) 反应塔上端具有良好的Fe3O4生成条件,较易生成Fe3O4,利于形成内壁挂渣,但反应塔下端氧势较低,不易生成Fe3O4,应加强反应塔内壁的水冷保护。
参考文献:
[1] Moskalyk R R, Alfantazi A M. Review of copper pyrometallurgical practice: Today and tomorrow[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2003, 16(10): 893-919.
[2] Fiscor S. Outokumpu technology makes process improvements possible[J]. Engineering and Mining Journal, 2004, 205(9): 43-45.
[3] 鄂加强, 王春华, 龚金科, 等. 铜火法冶炼热动力学系统实测数据EMD处理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(5): 946-951.
E Jiaqiang, WANG Chunhua, GONG Jinke, et al. Process on measurement data from copper pyrometallurgical heat dynamical system by using of EMD method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(5): 946-951.
[4] 周松林. 闪速熔炼—清洁高效的炼铜工艺[J]. 中国工程科学, 2001, 3(10): 86-89.
ZHOU Songlin. Flash smelting—Clean and efficient smelting technology[J]. Engineering Science, 2001, 3(10): 86-89.
[5] Merry J, Sarvinis J, Voermann N. Designing modern furnace cooling systems[J]. JOM Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, 2000, 52(2): 62-64.
[6] 陈卓. 铜闪速炉系统数值熔炼模型及反应塔炉膛内形在线仿真监测研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学能源科学与工程学院, 2002: 48-54.
CHEN Zhuo. A research on mathematical models of flash smelting system and on-line simulative monitoring of frozen profile of reaction shaft in copper flash furnace[D]. Changsha: School of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University, 2002: 48-54.
[7] WANG Jinliang, WU Yanxin, LIANG Liwei. Evaluation of melting point of the freeze slag in reaction shaft of flash smelting furnace[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 402: 277-282.
[8] 汪金良, 卢宏, 曾青云, 等. 基于遗传算法的铜闪速熔炼过程控制优化[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(1): 156-160.
WANG Jinliang, LU Hong, ZENG Qingyun, et al. Control optimization of copper flash smelting process based on genetic algorithms[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(1): 156-160.
[9] 梅炽, 谢锴, 陈红荣, 等. 闪速炼铜“高效反应区”的形成条件与应用效果[J]. 有色金属, 2003, 55(4): 85-88.
MEI Chi, XIE Kai, CHEN Hongrong, et al. Generating condition and applying results of high efficicency reaction core in copper flash smelting[J]. Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 55(4): 85-88.
[10] Goto S. Equilibrium calculations between matte, slag and gaseous phases in copper smelting[C]//Jones M J. Copper Metallurgy-Practice and Theory. London: Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 1975: 23-29.
[11] 汪金良, 张传福, 张文海. 铅闪速熔炼过程的多相平衡模型[J]. 中南大学学报, 2012, 43(2): 429-434.
WANG Jinliang, ZHANG Chuanfu, ZHANG Wenhai. Multi-phase equilibrium model of lead flash smelting process[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2012, 43(2): 429-434.
[12] 梁英教, 车荫昌. 无机物热力学数据手册[M]. 沈阳:东北大学出版社, 1993: 458.
LIANG Yingjiao, CHE Yinchang. Inorganic thermodynamic data Manual[M]. Shenyang: Northeastern University Press, 1993: 458.
[13] Shimpo R, Watanabe Y, Goto S, et al. An application of equilibrium calculations to the copper smelting operation[C]//Sohn H Y. Advances in sulfide smelting. Utah: Americal Institute of Mining, Metallurgical and Petroleum Engineers, 1983: 295-316.
[14] 谭鹏夫, 张传福. 铜熔炼过程中伴生元素分配行为的计算机模型[J]. 金属学报, 1997, 33(10): 1094-1100.
TAN Pengfu, ZHANG Chuanfu. Computer model of distribution behavior of accessory elements in copper smelting[J]. Acta Metallurgical Sinica, 1997, 33(10): 1094-1100.
(编辑 何运斌)
收稿日期:2012-12-03;修回日期:2013-03-04
基金项目:国家科技支撑计划项目(2013BAB03B05);国家自然科学基金资助项目(50904027);江西省青年科学家(井冈之星)培养对象计划项目(20133BCB23018)
通信作者:汪金良(1976-),男,江西贵溪人,博士,副教授,从事冶金过程数学模拟及反应工程;电话:0797-8312204;E-mail:simwjl@163.com