文章编号:1004-0609(2013)S1-s0029-06
激光冲击对高温钛合金组织及性能的影响
贾蔚菊,洪 权,赵恒章
(西北有色金属研究院,西安 710016)
摘 要:采用激光冲击强化工艺对近α型Ti834高温钛合金进行表面处理,研究激光冲击前后合金表层组织结构及显微硬度的变化,测试合金的室温拉伸性能及疲劳寿命,并采用扫描电镜分析合金激光冲击前后的疲劳断口特征。结果表明,激光冲击后合金表层位错密度显著增加,晶粒细化。合金室温拉伸强度略有升高,疲劳寿命提高约1~1.5倍。观察疲劳断口发现,未经冲击处理的试样疲劳源区位于试样表面,而冲击后疲劳源区位于试样的中心位置。激光冲击处理后合金表面形成的硬化层可延缓疲劳裂纹的萌生与扩展。
关键词:高温钛合金;激光冲击强化;显微组织;拉伸性能;疲劳
中图分类号:TG 146.4 文献标志码:A
Effect of laser shock processing on microstructure and properties of high-temperature titanium alloy
JIA Wei-ju, HONG Quan, ZHAO Heng-zhang
(Northwestern Institute for Nonferrous Metal Research, Xi’an 710016, China)
Abstract: The near α titanium alloy Ti834 was shock-processed by the high intensity laser. The surface microstructures of specimens were characterized and the micro-hardness was measured before and after shock processing. The room-temperature tensile properties and the fatigue life of the alloy were tested. The fractographs of fatigue specimens were observed by SEM. The results show that, after the laser shock processing (LSP), the dislocation density is enhanced and the microstructure is refined in the surface layer of the alloy. The room-temperature tensile strength has a little increase and the fatigue life increases by about 1-1.5 times. The characteristics of the fatigue fractographs are changed after LSP. The fatigue crack initiates on the surface of the specimens without shock-processing, while the crack initiates at the center of the specimens after LSP. It is believed that the formation of the hardened layer after laser shock processing can delay the initiation and growth of the fatigue crack.
Key words: high-temperature titanium alloy; laser shock processing; microstructure; tensile properties; fatigue
钛合金由于具有密度小、比强度高、耐腐蚀性好等优点而广泛应用于航空航天领域[1-2]。近年来,随着航空航天技术的不断发展,对航空发动机的推重比及飞机的机动性能提出了更高的要求。高温钛合金因其在高温服役条件下具有优异的热强性能,而被广泛应用于制造发动机叶盘和叶片等重要零部件[3]。这些部件在使用过程中承受反复的循环载荷,常因应力腐蚀开裂和疲劳等造成其达不到设计使用时限。因此,如何提高钛合金构件的疲劳强度,延长其服役寿命,提高其工作可靠性,已受到人们的广泛关注。
激光冲击强化(LSP)是一种新的表面处理技术。该技术通过功率密度为GW·cm-2量级、脉宽为ns量级的激光束辐照材料表面所产生的高强度冲击应力波引起材料表面改性,能够产生数百MPa的残余压应力,从而大幅提高材料的表面硬度、强度和疲劳性能[4-6]。目前,国内已将该技术广泛的应用于钢铁、铝合金及镁合金等材料[7-8]。在钛合金方面的应用主要集中在常用的TC4合金上。毛青松等[9]用工作频率为1 Hz、脉冲宽度为10 ns、能量值为15.6 J、光斑直径为3 mm的参数对TC4合金进行激光强化表面处理,处理后在试样表面形成了约10 μm的变形层,且发现冲击处理后试样疲劳寿命是未经处理的试样疲劳寿命的9~l0倍。张永康等[10]采用ABAQUS有限元分析软件对激光冲击强化TC4钛合金的残余应力场进行了分析,试验与有限元分析结果均表明,激光冲击可使TC4钛合金表层产生较大幅度的残余压应力,并获得较深的残余压应力层,可使材料的疲劳寿命和工作可靠性得到大幅提高。
Ti834合金是一种Ti-Al-Sn-Zr-Mo-Si系近α型高温钛合金,目前对该合金的激光冲击强化研究报道较少,本文作者将研究激光冲击工艺对该合金显微组织及力学性能的影响,并探讨其影响机制。
1 实验
实验用Ti834合金取自d 150 mm的棒材,其化学成分如表1所示。合金经反复锻造后获得均匀细小的双态组织结构,如图1所示。
表1 Ti834高温钛合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of Ti834 titanium alloy (mass fraction, %)
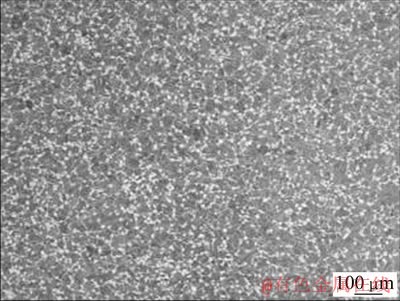
图1 Ti834合金显微组织
Fig. 1 Microstructure of Ti834 alloy
激光冲击试验在Nd:YAG高功率激光冲击强化装置上进行,其实验装置由激光系统、试件和夹具组成。根据国内外对LSP在钛合金方面的相关研究,本次试验选用激光能量4 J、脉宽20 ns,光斑直径2.6 mm,约束层2 mm的流动水介质,吸收层0.1 mm的碳黑胶带。疲劳试验在PLG-20C高频疲劳试验机上进行,试验应力为630 MPa,应力比R= -1,频率为120 Hz。疲劳寿命测试分为未经冲击处理的试样,经过一次冲击处理的试样和经过二次冲击处理的试样。疲劳试样断口采用丙酮进行超声波清洗后,在SUPRATM55型扫描电子显微镜下进行断口形貌观察和分析。激光冲击后试样表面硬度采用401MVD型显微维氏硬度计进行测量,选取测量载荷为1 N,加载时间为30 s。
2 结果与分析
2.1 显微硬度
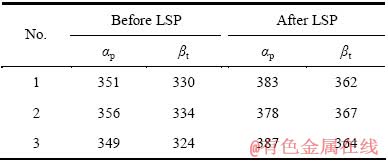
本文中采用的Ti834合金由等轴初生α相(αp)及β转变组织(βt)构成,这两种不同的相结构之间存在硬度差,本文中分别测试αp及βt的硬度值,分别测试3个点,激光冲击前后试样表面显微硬度测试结果见表2。由表2可见,激光冲击处理后αp及βt的硬度均得到了提高。分别将3个点的硬度值取平均值后计算可得,冲击后αp的硬度提高了约8%,而βt的硬度提高了约11%。这可能是在激光冲击波作用下,βt更易发生塑性变形的缘故。
表2 Ti834合金激光冲击前后的表面显微硬度
Table 2 Micro-hardness of Ti834 before and after LSP
2.2 组织结构
激光冲击前后试样表面及横截面组织形貌如图2所示。对比图2(a)和(b)可见,试样经过激光冲击后,组织中原始β晶粒略有减小,等轴α相变化不明显。图2(c)所示为经冲击处理试样的横截面组织,可以看到在试样表面附近β转变组织中的条状α相被打断,细小的球状α相增多,组织明显细化。激光冲击前后试样的透射电子显微镜照片(TEM)如图3所示。由图3(a)可见,组织由初生等轴α相、次生条状α相及残余β相组成,在α/β界面处存在位错塞积。而经激光冲击处理以后,在次生α条中可以观察到大量的位错线,同时在等轴α相中可观察到大量的胞状结构。由此可以推断,在激光冲击过程中,材料表面发生了剧烈的塑性变形,组织内部产生了大量的位错,并在冲击力的作用下位错发生滑移,相互缠结,形成胞状结构。
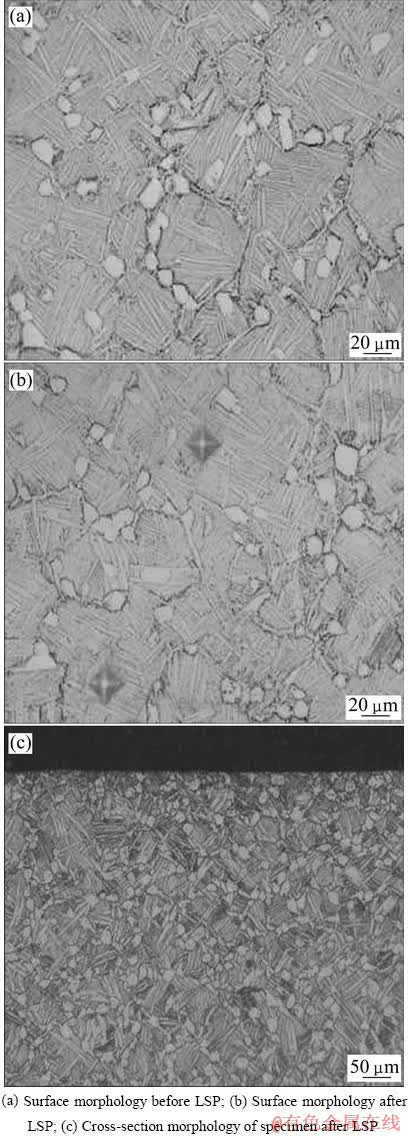
图2 激光冲击前后试样显微组织
Fig. 2 Microstructures of specimens before and after LSP
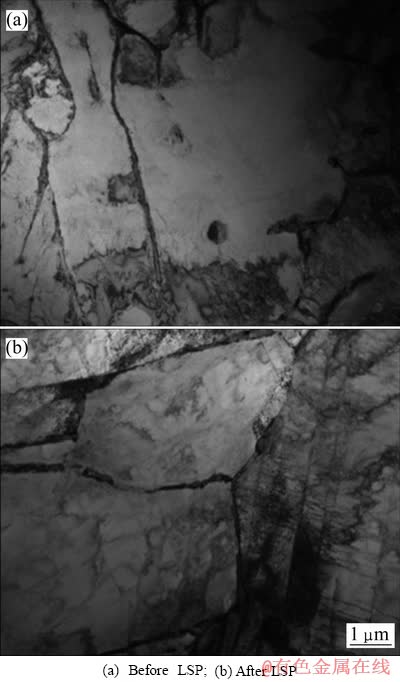

图3 激光冲击前后试样的TEM照片
Fig. 3 TEM micrographs of specimens
2.3 室温拉伸性能
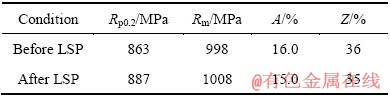
表3列出了Ti834合金激光冲击前后的室温拉伸性能。由试验结果可见,冲击后试样的抗拉强度和屈服强度均略有提高,塑性变化不大。
表3 Ti834合金激光冲击前后的室温拉伸性能
Table 3 Tensile properties of Ti834 alloy before and after LSP at room temperature
2.4 疲劳寿命
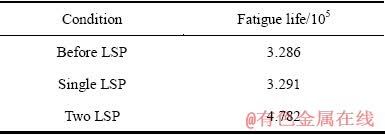
为了对比激光冲击强化对试样疲劳寿命的影响,本文中选择3组试样进行对比,分别为未冲击试样,一次冲击试样和二次冲击试样,每组试样疲劳寿命的平均值列于表4。试验结果表明,经一定的工艺参数处理后,Ti834合金的疲劳寿命延长1~1.5倍。
表4 激光冲击对Ti834合金疲劳寿命的影响
Table 4 Effect of LSP on fatigue life of Ti834 alloy
2.5 疲劳断口分析
图4所示为Ti834合金未经激光冲击处理试样的疲劳断口形貌。从宏观形貌可以看出,疲劳断口存在明显的3个区:疲劳源区(A),疲劳裂纹扩展区(B)和瞬断区(C)。疲劳源是疲劳破坏的起点,疲劳源一般起源于试样内部的缺陷,如孔洞、夹杂等处,这些缺陷都起着尖缺口的作用,促使应力集中,促进疲劳裂纹的萌生。由图4(a)可见,未经激光冲击试样的疲劳裂纹源位于试样表面附近,以源区为起点向外辐射的放射状纹路是疲劳裂纹扩展区,整个扩展区比较平坦。当疲劳裂纹扩展到材料剩余面积不足以承受外载荷的拉应力时,材料断裂,形成疲劳扩展区外侧的瞬断区。源区微观形貌由扇形的小平面组成,呈台阶状向外扩展,如图4(b)和(c)所示。裂纹扩展区由长条状的小平面和韧窝组成,如图4(d)所示。
图5所示为经过激光冲击后试样的疲劳断口形貌。与未冲击试样相比,冲击后试样的宏观断口发生了显著的变化。疲劳源区位于试样的中心位置,裂纹以源区为中心向四周发散,扩展区表面凹凸不平,颗粒粗大。源区仍由解理小平面组成,但可以观察到大量的二次裂纹(图5(b),(c)),这些二次裂纹的形成和扩展释放了裂纹尖端的应力,消耗了更多能量,从而降低了疲劳裂纹扩展速率。扩展区也是由长条状小平面和韧窝组成,只是与未冲击试样相比,长条状小平面比例减小(图5(d))。可见,激光冲击对试样的疲劳裂纹萌生和扩展有明显的抑制作用。这主要是由于在激光冲击过程中,材料受到激光诱导的冲击波作用,在高应变率下发生塑性变形,变形过程中位错发生运动,引起大量位错交割和增值,并且增加空位、间隙原子等结构缺陷,从而阻碍位错的进一步运动,引起加工硬化[11]。另一方面,冲击波使材料产生剧烈塑性变形,表层残留很大的压应力,这些压应力可以平衡疲劳载荷中的部分拉应力,即有效拉应力降低,从而提高疲劳裂纹萌生的临界应力水平,阻碍疲劳裂纹源在表面萌生,从而提高试样的疲劳寿命。
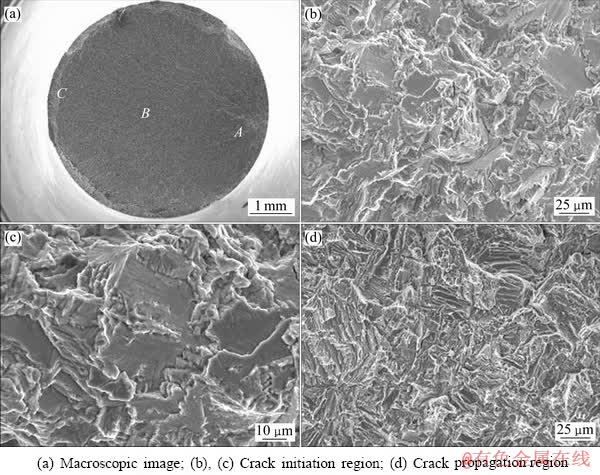
图4 未经激光冲击试样的疲劳断口形貌
Fig. 4 SEM fractographs of fatigue specimens without LSP
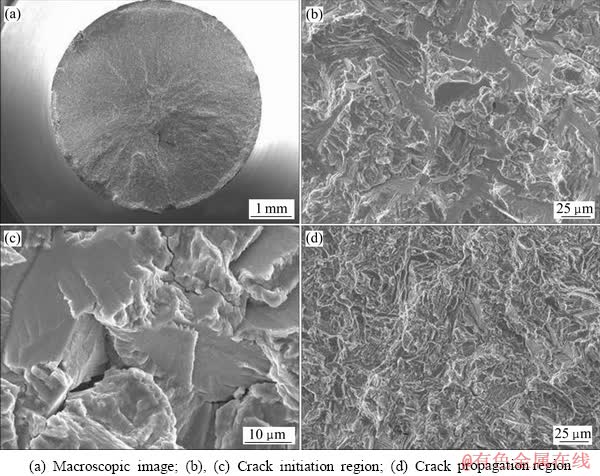

图5 激光冲击试样的疲劳断口形貌
Fig. 5 SEM fractographs of fatigue specimens with LSP
3 结论
Ti834高温钛合金经激光冲击处理后,试样表层位错密度显著增加,晶粒细化,显微硬度提高约8%~11%。冲击处理后合金室温拉伸强度略有升高,高周疲劳寿命提高约1~1.5倍。疲劳断口观察发现,未经冲击处理的试样疲劳源区位于试样表面,而冲击处理后疲劳源区位于试样的中心位置。激光冲击处理后合金表面形成的硬化层可延缓疲劳裂纹的萌生和扩展。
REFERENCES
[1] 陶春虎, 刘庆瑔, 曹春晓, 张卫方. 航空用钛合金的失效及其预防[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2002: 11-13.
TAO Chun-hu, LIU Qing-quan, CAO Chun-xiao, ZHANG Wei-fang. Failure and prevention of aeronautical titanium alloy[M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 2002: 11-13.
[2] BOYER R R. An overview on the use of titanium in the aerospace industry[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1996, 213(1/2): 103-114.
[3] 赵永庆. 高温钛合金研究[J]. 钛工业进展, 2001(1): 33-39.
ZHAO Yong-qing. The research of high temperature titanium alloy[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2001(1): 33-39.
[4] 赵恒章, 杨英丽, 洪 权, 冯 亮, 奚正平. 激光冲击强化技术研究及其在钛合金中的应用[J]. 钛工业进展, 2011, 28(6): 34-37.
ZHAO Heng-zhang, YANG Ying-li, HONG Quan, FENG Liang, XI Zheng-ping. Study on laser shock processing and its application for titanium alloys[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2011, 28(6): 34-37.
[5] MONTROSS C S, WEI T, YE L, G.C. b, MAI Y W. Laser shock processing and its effects on microstructure and properties of metal alloys: A review[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2002, 24(2): 1021-1036.
[6] 何卫锋, 李应红, 周章文, 张永康, 汪 诚. 激光冲击工艺对GH742镍基高温合金疲劳性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2009, 30(3): 42-45.
HE Wei-feng, LI Ying-hong, ZHOU Zhang-wen, ZHANG Yong-kang, WANG Cheng. Effects of laser shock processing on fatigue property of GH742 Ni-based superalloy[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2009, 30(3): 42-45.
[7] REN X D, ZHANG T, ZHANG Y K, JIANG D W, YONGZHUO H F, GUAN H B, QIAN X M. Mechanical properties and residual stresses changing on 00Cr12 alloy by nanoseconds laser shock processing at high temperatures[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528(4/5): 1949-1953.
[8] ZHANG X C, ZHANG Y K, LU J Z, XUAN F Z, WANG Z D, TU S T. Improvement of fatigue life of Ti-6Al-4V alloy by laser shock peening[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(15): 3411-3415.
[9] 毛青松, 高满屯, 杨宝红, 赵 丽. 激光冲击表面处理及疲劳性能有限元分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2011, 11(13): 2930-2934.
MAO Qing-song, GAO Man-tun, YANG Bao-hong, ZHAO Li. Finite element analysis of laser peening surface treatment and fatigue properties[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2011, 11(13): 2930-2934.
[10] 张永康, 周立春, 任旭东, 李 杨, 鲁金忠. 激光冲击TC4残余应力场的试验及有限元分析[J]. 江苏大学学报, 2009, 30(1): 10-13.
ZHANG Yong-kang, ZHOU Li-chun, REN Xu-dong, LI Yang, LU Jin-zhong. Experiment and finite element analysis on residual stress field in laser shock processing TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University, 2009, 30(1): 10-13.
[11] 聂祥樊, 龙霓东, 刘海雷, 何卫锋, 李启鹏. 激光冲击强化对TC17表面硬度的影响[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2012(1): 198-200.
NIE Xiang-fan, LONG Ni-dong, LIU Hai-lei, HE Wei-feng, LI Qi-peng. Effect of Iaser shock peening on surface hardness of TC17 titanium alloy[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2012(1): 198-200.
(编辑 杨 兵)
基金项目:陕西省重点科技创新团队计划资助项目(2012KCT-23)
收稿日期:2013-07-28;修订日期:2013-10-10
通信作者:贾蔚菊,工程师,博士;电话:029-86231078;E-mail: diana19811025@hotmail.com