文章编号:1004-0609(2007)09-1521-06
急冷条件下Cu-Sn合金的快速枝晶生长
杨 扬,徐锦锋,翟秋亚
(西安理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,西安 710048)
摘 要:研究快速凝固Cu-xSn(x=7%, 13.5%, 质量分数)合金的相结构、组织形态和枝晶生长特性,将金属熔体热传导方程与Navier-Stokes方程相耦合,从理论上计算液态合金的冷却速率。结果表明:在急冷快速凝固条件下,Cu-7%Sn合金形成过饱和的单相a-Cu固溶体组织;Cu-13.5%Sn合金形成以亚稳的Cu13.7Sn相为主相、a-Cu为第二相的快速凝固组织;随着冷却速率的增大,溶质截留效应增强,合金相结构由复相向单相转变;沿垂直于辊面方向上合金的组织形态依次为近辊面细小等轴晶、中部柱状晶及自由面粗大等轴晶;增大冷却速率,晶体形态由柱状晶向等轴晶转变;在急冷快速凝固过程中,a-Cu和Cu13.7Sn相均以枝晶方式生长;随温度梯度的增大,晶体生长速率呈线性增大。
关键词:Cu-Sn合金;单辊法;急冷快速凝固;晶体生长
中图分类号:TG 164.1; TG 113.12 文献标识码:A
Rapid dendritic growth in melt-spun Cu-Sn alloys
YANG Yang, XU Jin-feng, ZHAI Qiu-ya
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an 710048, China)
Abstract: The phase structure and microstructural characteristics of rapidly solidified Cu-xSn(x=7%, 13.5%, mass fraction) alloys were investigated. The cooling rate was calculated theoretically by coupling the heat conduct equation and Navier-Stokes equation. The results show that under rapid solidification condition, the single phase a-Cu solid solution is formed in Cu-7%Sn alloy. The microstructure of Cu-13.5%Sn alloy consists of main phase Cu13.7Sn and a few of a-Cu phase. With increasing cooling rate, the effect of solute trapping is enhanced, and the phase structure changes from multiphase to single-phase. The microstructures of the alloy along the direction vertical to wheel surface are characterized by fine equiaxed, columnar and coarse equiaxed grain, respectively. Both a-Cu and Cu13.7Sn phase grow in the manner of dendritic growth. With increasing temperature gradient, the growth rate of columnar crystals increases linearly.
Key words: Cu-Sn alloy; melt-spun method; rapid solidification; crystal growth
Cu-Sn合金具有优良的导电性及焊接性,被广泛应用于电机、继电器、波导管等电气装置零部件的连接中[1-6]。由于Sn在晶界处偏析严重,传统工艺制备的Cu-Sn合金材料在压应力作用下容易发生动态脆 化[7]。为此,通常采用添加合金元素的方法促进形核,细化晶粒,从而达到减小偏析、消除动态脆化引起的合金表面的热裂倾向[8]。急冷快速凝固可使合金熔体获得106 K/s以上的冷却速率,实现合金熔体的快速形核与生长,获得偏析程度小、合金相固溶度高、成分均匀和组织细小的快速凝固组织,甚至获得与平衡凝固组织不同的亚稳相结构[9]。例如,在快速凝固条件下,Cu-20%Sn形成以亚稳的Cu5.6Sn为主相的快速凝固组织[10]。可见快速凝固技术为改善Cu-Sn亚包晶合金的组织与性能提供了新途径[11]。但有关Cu-Sn合金快速凝固的研究报道尚不多见。本文作者选取Cu-7%Sn和Cu-13.5%Sn两种成分的合金为研究对象,在急冷快速凝固条件下研究了两种合金的相选择、组织演变规律及晶体生长特征,为Cu-Sn合金的制备提供理论依据。
1 实验
Cu-7%(质量分数)Sn和Cu-13.5%Sn母合金用高纯Cu(99.99%)和Sn(99.999%)在超高真空电弧炉中熔炼配制而成,样品质量约为1.2 g。采用单辊法实现快速凝固,实验过程中辊面线速度控制在5~23 m/s范围。获得的合金薄带尺寸为:厚20~40 mm,宽5 mm,长约2 m。
合金薄带经树脂镶嵌、抛光之后,选用5 g FeCl3+ 15 mL HCl+100 mL C2H5OH混合溶液进行浸蚀。使用XJG-05型光学显微镜分析合金的组织形态,用D/MAX-1200型X射线衍射仪(XRD)分析合金的相结构。
2 结果与讨论
Cu-Sn合金二元平衡相图[12]的左侧部分见图1,实验用合金成分用箭头标于图中。在平衡凝固条件下,当合金温度降至液相线时,首先从过冷熔体中析出具有面心立方结构的初生a-Cu相,直至凝固完毕。其中Cu-13.5%Sn合金的成分点位于包晶线的左端,根据杠杆定律,合金在1 071 K下形成的β包晶相含量近乎为0。因此,两种成分的合金其高温凝固组织均由单相a-Cu组成。随着温度的进一步下降,两种合金中的a-Cu相将发生脱溶转变,分别析出少量的ε相和δ相。由于Cu、Sn原子半径差异较大,Sn在Cu中的扩散速度较慢, 623 K下的共析转变往往难以进行,故室温下Cu-7%Sn合金的平衡凝固组织由a-Cu和少量的ε相组成,Cu-13.5%Sn合金则由a-Cu和少量的δ相组成。
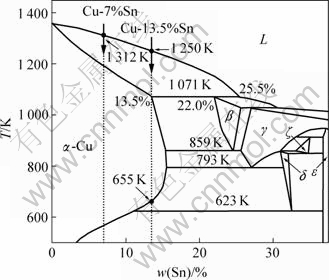
图1 Cu-Sn合金二元平衡相图
Fig.1 Phase diagram of Cu-Sn binary alloy
在快速凝固条件下,冷却速率对合金组织的形成有着显著的影响。为了揭示冷却速率与组织形态之间的相关规律,将热传导方程、Navier-Stokes方程和连续方程相耦合,对液态合金的温度场和冷却速率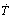 (
(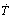 =-dT/dt)进行了理论计算。动量传输和能量传输主控方程如下[13]:
=-dT/dt)进行了理论计算。动量传输和能量传输主控方程如下[13]:
Navier-Stokes方程为
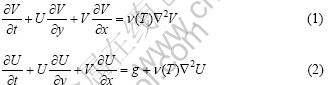
连续方程为

熔体和固体能量方程分别为

Navier-Stokes方程和热传导方程的初始条件和边界条件采用了惠希东等[15]的处理方法,辊轮与熔体接触表面的传热按照牛顿方式进行,即 ,其中,l为热导率,
,其中,l为热导率, 和
和 分别为熔体与辊轮接触面熔体和辊轮一侧的温度,
分别为熔体与辊轮接触面熔体和辊轮一侧的温度,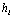 为界面换热系数。合金的物性参数由纯Cu和Sn的物性参数[14]拟合而成。理论计算所用物性参数如表1所列。计算获得的冷却速率与辊速的关系如图2所示。从计算结果可知,随着辊速的增大,冷却速率增大。
为界面换热系数。合金的物性参数由纯Cu和Sn的物性参数[14]拟合而成。理论计算所用物性参数如表1所列。计算获得的冷却速率与辊速的关系如图2所示。从计算结果可知,随着辊速的增大,冷却速率增大。
表 1 理论计算所用物性参数
Table 1 Physical parameters used in calculation

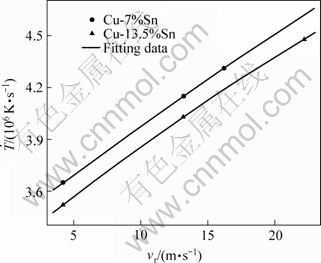
图2 快速凝固条件下液态合金的冷却速率随辊速的变化
Fig.2 Variations of cooling rate with wheel velocity for rapidly solidified alloys
2.1 快速凝固过程的相选择
快速凝固合金的XRD谱如图3所示。由图可见,在急冷快速凝固条件下,溶质截留效应显著增强,Cu-7%Sn合金形成了具有面心立方结构的a-Cu固溶体的单相凝固组织。
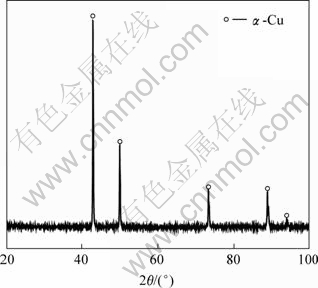
图3 快速凝固Cu-7%Sn合金的X射线衍射谱
Fig.3 X-ray diffraction pattern of rapidly solidified Cu-7%Sn alloy
快速凝固Cu-13.5%Sn合金的XRD谱如图4所示。由图可知,在快速凝固条件下,合金中形成了具有面心立方结构的Cu13.7Sn相和a-Cu固溶体相。大的冷却速率使亚稳的Cu13.7Sn和过饱和的a-Cu相存留下来。冷速较低时(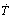 =3.52×106 K/s),凝固组织以Cu13.7Sn为主相,并存在一定量的a-Cu相。冷速升高后(
=3.52×106 K/s),凝固组织以Cu13.7Sn为主相,并存在一定量的a-Cu相。冷速升高后(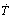 =4.03×106 K/s),Cu13.7Sn相含量增多,a-Cu相含量相应的减少。冷速达到
=4.03×106 K/s),Cu13.7Sn相含量增多,a-Cu相含量相应的减少。冷速达到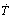 =4.48×106 K/s时,Cu13.7Sn相含量显著增多,a-Cu相含量几乎为0,凝固组织由单相Cu13.7Sn组成。
=4.48×106 K/s时,Cu13.7Sn相含量显著增多,a-Cu相含量几乎为0,凝固组织由单相Cu13.7Sn组成。
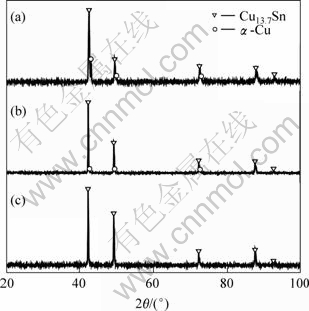
图4 快速凝固Cu-13.5%Sn合金的XRD谱
Fig.4 X-ray diffraction patterns of rapidly solidified Cu-13.5%Sn alloys: (a) 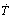 =3.52×106 K/s; (b)
=3.52×106 K/s; (b) 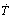 =4.03×106 K/s; (c)
=4.03×106 K/s; (c) 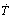 =4.48×106 K/s
=4.48×106 K/s
综上所述,在急冷快速凝固条件下,Cu-7%Sn合金形成a-Cu单相凝固组织。Cu-13.5%Sn合金形成以Cu13.7Sn为主相的快速凝固组织,随着冷却速率的增大,溶质截留效应增强,合金相结构由复相向单相转变。
2.2 快速凝固组织特征
快速凝固Cu-7%Sn合金的组织形态如图5所示。图5(a)、(b)分别为较低冷却速率(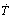 =3.65×106 K/s)和较高冷却速率(
=3.65×106 K/s)和较高冷却速率(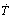 =4.15×106 K/s)条件下的凝固组织形貌。可以看出,在条带厚度方向上大致可分为3个晶区,依次为:靠近辊面的激冷等轴晶区、中间的柱状晶区以及靠近自由面的粗大等轴晶区。激冷等轴晶区离辊面最近,受辊面的激冷作用最强烈,形核率最大,因而形成了细小均匀的等轴晶。两种冷却速率下所形成的激冷等轴晶区的厚度分别为11 μm和4 μm。中部的柱状晶区离辊面稍远,所受激冷作用减弱,在垂直辊面方向上形成了较大的温度梯度,以定向凝固为主,形成柱状晶组织。由于受辊面的剪切作用的影响,柱状晶与辊面约成75?夹角。两种冷却速率下所形成的柱状晶区厚度分别约为18 μm和13 μm。当柱状晶生长延伸到一定厚度时,由于结晶潜热的释放和不断增厚的凝固层热阻的增大,必然造成柱状晶前方冷却速率和温度梯度的降低,从而导致柱状晶生长驱动力减弱,进而导致粗大等轴晶的形成。两种冷却速率下所形成的粗大等轴晶区厚度分别约为15 μm和7 μm。随着冷却速率的增大,柱状晶区厚度趋于减小,凝固组织显著细化。
=4.15×106 K/s)条件下的凝固组织形貌。可以看出,在条带厚度方向上大致可分为3个晶区,依次为:靠近辊面的激冷等轴晶区、中间的柱状晶区以及靠近自由面的粗大等轴晶区。激冷等轴晶区离辊面最近,受辊面的激冷作用最强烈,形核率最大,因而形成了细小均匀的等轴晶。两种冷却速率下所形成的激冷等轴晶区的厚度分别为11 μm和4 μm。中部的柱状晶区离辊面稍远,所受激冷作用减弱,在垂直辊面方向上形成了较大的温度梯度,以定向凝固为主,形成柱状晶组织。由于受辊面的剪切作用的影响,柱状晶与辊面约成75?夹角。两种冷却速率下所形成的柱状晶区厚度分别约为18 μm和13 μm。当柱状晶生长延伸到一定厚度时,由于结晶潜热的释放和不断增厚的凝固层热阻的增大,必然造成柱状晶前方冷却速率和温度梯度的降低,从而导致柱状晶生长驱动力减弱,进而导致粗大等轴晶的形成。两种冷却速率下所形成的粗大等轴晶区厚度分别约为15 μm和7 μm。随着冷却速率的增大,柱状晶区厚度趋于减小,凝固组织显著细化。
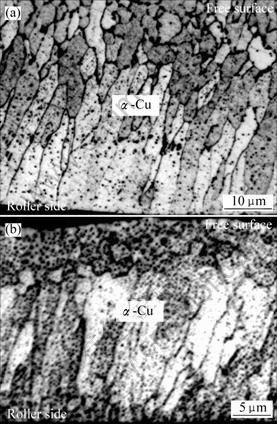
图5 Cu-7%Sn合金快速凝固显微组织
Fig.5 Rapid solidification microstructure of Cu-7%Sn alloy at different cooling rates: (a) 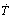 =3.65×106 K/s; (b)
=3.65×106 K/s; (b) 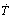 =4.15×106 K/s
=4.15×106 K/s
快速凝固Cu-13.5%Sn合金的组织形态如图6所示。图6(a)所示为低冷却速率(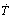 =3.52×106 K/s)条件下的凝固组织。可以看到,在灰白色的主相Cu13.7Sn周围分布着大量黑色点状的第二相a-Cu相。其快速凝固组织沿垂直辊面方向也依次为细小等轴晶区、柱状晶区以及粗大等轴晶区。图6(b)所示为较高冷却速率(
=3.52×106 K/s)条件下的凝固组织。可以看到,在灰白色的主相Cu13.7Sn周围分布着大量黑色点状的第二相a-Cu相。其快速凝固组织沿垂直辊面方向也依次为细小等轴晶区、柱状晶区以及粗大等轴晶区。图6(b)所示为较高冷却速率(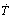 =4.48×106 K/s)条件下的组织形貌。由于冷却速率的增大,溶质截留效应增强,其凝固组织为单相Cu13.7Sn等轴晶。而且,随着冷却速率的增大,辊面的激冷作用增强,凝固组织显著细化,晶体形态由柱状晶转变为等轴晶。
=4.48×106 K/s)条件下的组织形貌。由于冷却速率的增大,溶质截留效应增强,其凝固组织为单相Cu13.7Sn等轴晶。而且,随着冷却速率的增大,辊面的激冷作用增强,凝固组织显著细化,晶体形态由柱状晶转变为等轴晶。
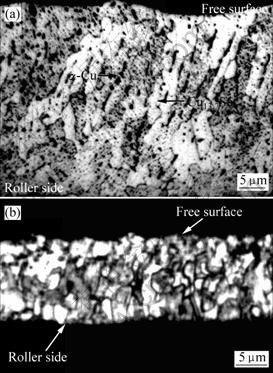
图6 Cu-13.5%Sn合金快速凝固显微组织
Fig.6 Rapid solidification microstructure of Cu-13.5%Sn alloy at different cooling rates: (a) 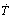 =3.52×106 K/s; (b)
=3.52×106 K/s; (b) 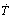 =4.48×106 K/s
=4.48×106 K/s
2.3 柱状晶的快速生长
在快速凝固条件下,由于在液池底部垂直于辊面方向上存在较大的温度梯度,柱状生长成为单相合金快速凝固的主要特征之一。对于Cu-7%Sn合金而言,理论计算获得的温度梯度(GT=dT/dy)随液池高度y的变化如图7所示。由图可知,当y≤90 μm时,温度梯度随液池高度的增加急剧减小;而当y≥90 μm时,温度梯度的变化趋于平稳。计算得出的温度梯度值在(2.5~3.0)×106 K/m范围,高的温度梯度容易导致柱状晶的形成。
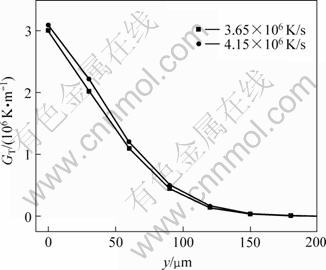
图7 Cu-7%Sn合金的温度梯度随液池高度的变化
Fig.7 Variations of temperature gradient with height of puddle for Cu-7%Sn alloy
在忽略液相过热的条件下,凝固速率(vd)取决于固相中的温度梯度Gs [9]:

计算得到的a-Cu和Cu13.7Sn相柱状晶生长速率vd随温度梯度的变化关系如图8所示。由图可知,随温度梯度的增大,柱状晶生长速率呈线性增大。实验值与理论计算值相符合。
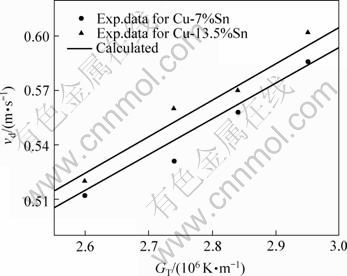
图8 枝晶生长速率随温度梯度的变化
Fig.8 Variations of velocity of dendritic growth with temperature gradient
实验测定的柱状晶生长速度随冷速的变化如图9所示。随着冷却速率的增大,枝晶生长速率也呈线性增大,最大达到60 cm/s。Cu-7%Sn、Cu-13.5%Sn合金枝晶生长速率(vd)与冷却速率之间的函数关系分别为
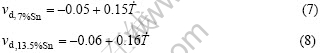
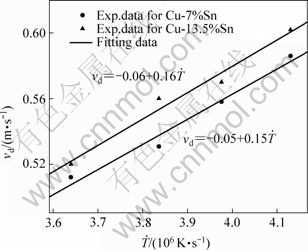
图9 枝晶生长速率随冷却速率的变化
Fig.9 Variations of velocity of dendritic growth with cooling rate
随着冷却速率的增大,柱状晶生长速率呈线性增大,结晶潜热的释放更加集中,固液界面前沿温度梯度波动增强,进而打破柱状晶生长的连续性,导致组织形态由柱状晶向等轴晶转变。
3 结论
1) 在快速凝固条件下,Cu-7%Sn合金形成过饱和的单相a-Cu固溶体组织。Cu-13.5%Sn合金形成以亚稳的Cu13.7Sn为主相的快速凝固组织,随着冷却速率的增大,溶质截留效应增强,合金相结构由复相向单相转变。
2) Cu-7%Sn和Cu-13.5%Sn合金的快速凝固组织沿垂直于辊面方向依次为细小等轴晶区、柱状晶区以及粗大等轴晶区。随着冷速的增大,柱状晶区厚度变小,晶体形态由柱状晶向等轴晶转变。
3) 在急冷快速凝固过程中,a-Cu和Cu13.7Sn相均以柱状晶方式生长。随着温度梯度和冷却速率的增大,柱状晶生长速率呈线性增大。
致谢
作者感谢西北工业大学应用物理系魏炳波教授和空间材料科学与技术实验室提供的实验支持。
REFERENCES
[1] Al-Ganainy G S, Fawzy A, Adb El-Salam F. Transient and steady-state creep characteristics of Cu-2wt%Sn alloy in the solid solution region[J]. Physica B, 2004, 344(1/4): 443-450.
[2] Song J Y, Yu Jin and Lee T Y. Effects of reactive diffusion on stress evolution in Cu-Sn films[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 51 (2): 167-170.
[3] Debiemme-Chouvy C, Ammeloot F and Sutter E M M. X-ray photoemission investigation of the corrosion film formed on a polished Cu-13Sn alloy in aerated NaCl solution[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2001, 174(1/2): 55-61.
[4] MA Xin, QIAN Yi-yu, Yoshida F. Effect of La on the Cu-Sn intermetallic compound (IMC) growth and solder joint reliability[J]. J Alloys and Compound, 2002, 334(1/2): 224-227.
[5] Ammeloot F, Fiaud C, Sutter E M M. Characterization of the oxide layers on a Cu-13Sn alloy in a NaCl aqueous solution without and with 0.1 M benzotriazole Electrochemical and photoelectrochemical contributions[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1999, 44(15): 2549-2558.
[6] MA Xin, WANG Feng-jiang, QIAN Yi-yu, Yoshida Fusahito. Development of Cu-Sn intermetallic compound at Pb-free solder/Cu joint interface[J]. Materials Letters, 2003, 57(22/23): 3361-3365.
[7] Barrera E V, Menyhard M, Bika D, Rothman B, McMahon C J. Quasi-static intergranular cracking in a Cu/1bSn alloy; an analog of stress relief cracking of steels[J]. Scripta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1992, 27(2): 205-210.
[8] Liu X Y, Kane W, McMahon C J Jr. On the suppression of dynamic embrittlement in Cu-8wt%Sn by an addition of zirconium[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 50(5): 673-677.
[9] 周尧和, 胡壮麒, 介万奇. 凝固技术[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1998.
ZHOU Yao-he, HU Zhuang-qi, JIE Wan-qi. Solidification technology[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 1998.
[10] 翟秋亚, 杨 扬, 徐锦锋, 郭学锋. 快速凝固Cu-Sn合金的组织形态及相结构[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(8): 1374-1379.
ZHAI Qiu-ya, YANG Yang, XU Jin-gen, GUO Xue-feng. Microstructual morphology and phase strucrure of rapidly solidified Cu-Sn alloy[J]. The China Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(8): 1374-1379.
[11] XU Jin-feng, WANG Nan, WEI Bing-bo. Microstructural characteristics and electrical resistivity of rapidly solidified Co-Sn alloys[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(21): 2242-2246.
[12] Massalski T B, Murray J L, Bennett L H. Binary alloy phase diagrams[M]. ASM International, 1986: 1481-1482.
[13] 徐锦锋, 魏炳波. 急冷快速凝固过程中液相流动与组织形成的相关规律[J]. 物理学报, 2004, 53(6): 160-166.
XU Jin-feng, WEI Bin-bo. Liquid phase flow and microstructure formation during rapid solidification[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2004, 53(6): 160-166.
[14] Brandes E A. Smithells metals reference book[M]. 6th ed. London: Butterworth, 1983: 14.
[15] 惠希东, 杨院生, 陈晓明, 胡壮麒. 单辊法制备非晶合金中的传热与熔体流动数值模拟[J]. 金属学报, 1999, 35(11): 1206-1210.
HUI Xi-dong, YANG Yuan-sheng, CHEN Xiao-ming, HU Zhuang-qi. Numerical simulation of heat transfer and fluid flow during preparing amorphous alloy by single roller spinning[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1999, 35(11): 1206-1210.
基金项目:陕西省自然科学基金资助项目(2006E134,2006E120);陕西省教育厅科学研究计划资助项目(06JK220)
收稿日期:2006-10-30;修订日期:2007-06-05
通讯作者:徐锦锋,教授;电话:029-82312069;传真:029-82310856;E-mail:xu-zhai@xaut.edu.cn
(编辑 龙怀中)