地下水源热泵定压差取水方式对含水层渗透性的影响
王松庆,张旭
(同济大学 机械工程学院,上海 200092)
摘要:针对地下水源热泵取水引起含水层颗粒迁移问题建立数学模型,并通过案例计算分析地下水源热泵定压差取水方式对含水层渗透性的影响。研究结果表明,地下水源热泵运行5 a后含水层厚度为20,25和30 m时的孔隙率依次增大到初始值的2.57,1.86和1.59倍,渗透系数依次增大到初始值的156,16和7倍;考虑颗粒迁移时,地下水源热泵定压差取水方式对含水层渗透性影响显著。
关键词:地下水源热泵;定压差;含水层;渗透性
中图分类号:TQ051.5 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)06-1624-05
Influence of constant pressure difference on aquifer permeability induced by groundwater source heat pump pumping
WANG Song-qing, ZHANG Xu
(College of Mechanical Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China)
Abstract: The mathematic model of aquifer particles migration induced by groundwater source heat pump (GWSHP) pumping was theoretically presented. A case which represents the influence of constant pressure difference on aquifer permeability induced by GWSHP pumping was analysed. The results indicate that the hydraulic conductivity increases by 156, 16 and 7 times respectively as aquifer porosity increases 2.57, 1.86 and 1.59 times respectively of initial value 20, 25 and 30 m in five-year operation of GWSHP for different aquifer thicknesses. Considering particles migration, the permeability of aquifer is affected obviously by GWSHP pumping under constant pressure difference.
Key words: groundwater source heat pump; constant pressure difference; aquifer; permeability
地下水源热泵是夏季以地下水为散热源制冷,冬季以地下水为吸热源制热的一种热泵型空调装置。由于土壤的隔热和蓄热作用,地下水温度随季节气温的变化较小,特别是深井水的水温常年基本不变,一般比当地年平均气温高1~2 ℃,是一种十分理想的热泵热源。近几年,在我国部分地区得到较快发展与应 用[1]。许多学者对这一新型空调系统在使用过程中产生的一系列问题进行了研究,如倪龙等[2-3]对同井回灌式地下水源热泵地下水渗流进行理论研究,分析了含水层厚度、渗透系数比和不同含水层对同井回灌地下水源热泵地下水渗流和换热的影响;李旻等[4]对单井回灌地下水源热泵承压含水层渗流解析解进行推导,为分析地下水中的传热问题奠定了基础;刘学玲等[5]对地下水地源热泵夏季运行进行了测试和分析,研究了井水温度变化以及井间距对热泵运行的影响;张远东等[6]应用数值模拟方法对北京某地下水源热泵运行后的地温变化进行了研究,并对5 a后的温度场进行了预测。但是,地下水源热泵在使用过程中仍然存在一些问题如井水含沙问题需要进一步研究。若把含沙的地下水不断地抽到热泵机组中,则会导致热泵机组被损坏,更可能会由于长期抽水而造成取水井井壁坍塌,产生地下水源热泵空调系统无法使用的严重后 果[7]。若不对这些问题进行研究并加以解决,则地下水源热泵的发展将受到制约和限制。目前,地下水源热泵都是按照设计值定流量方式取水,并未考虑颗粒迁移问题,对于定压差取水方式研究较少。在此,本文作者首先建立地下水源热泵取水引起含水层颗粒迁移的数学模型,并通过典型算例,分析地下水源热泵定压差取水方式对含水层渗透性的影响。
1 颗粒迁移问题的数学模型
井水含沙问题产生的主要原因是由于地下水在渗流过程中与含水层相互作用,是一个多孔介质中 流-固耦合的复杂问题。当满足某些条件时,含水层颗粒会脱离含水层骨架随着地下水一起运动,产生井水含沙问题。即使地下水源热泵设有除砂装置,使得脱离含水层的颗粒无法进入机组,但由于颗粒随着地下水进入井孔,仍然会对含水层渗透性产生影响。需要建立合理描述该现象的数学模型,以解决该问题。
1.1 数学模型的建立
颗粒迁移问题数学模型的建立主要依据质量守恒原理,对饱和多孔介质中流体(地下水)、颗粒以及固体骨架三相分别建立各自对应的连续性方程,同时假设固体骨架是刚性的,不发生弹性变形,流体不可压缩。其数学模型如下:
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
式中: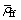 为流体的平均密度,kg/m3;
为流体的平均密度,kg/m3; 为迁移 颗粒的平均密度,kg/m3;
为迁移 颗粒的平均密度,kg/m3; 为固体骨架的平均密度,kg/m3;
为固体骨架的平均密度,kg/m3; 为流体的实际平均流速,m/s;
为流体的实际平均流速,m/s;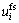 为迁 移颗粒的实际平均流速,m/s;
为迁 移颗粒的实际平均流速,m/s;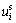 为骨架的移动速度,m/s;m为侵蚀率,kg/(m3?s)。m为孔隙率和颗粒浓度等参数的函数[8-9],
为骨架的移动速度,m/s;m为侵蚀率,kg/(m3?s)。m为孔隙率和颗粒浓度等参数的函数[8-9],
 (4)
(4)
λ为与侵蚀有关的参数,对于同一含水层可看作是常数;vcr为临界渗透速度,m/s,当地下水实际渗透速度大于临界值时,颗粒发生迁移。在连续性方程中,流体、颗粒和骨架的速度的表示是处理方程的关键。目前,国外对于这类问题通常采用如下假设[9-10]:固体骨架不会发生变形,骨架相速度为零,流体速度与颗粒速度相同。假设含水层均质各向同性,地下水源热泵地下取水时,沿着径向方向是渗流的主要方向,可以把地下取水过程看作典型的一维渗流问题。
1.2 基本参数定义与模型简化
本文的数学模型是基于表征体元方法建立的,该方法是求解多孔介质中流动问题一种常用的方法[11]。假设含水层处于饱和状态,在体积为dV表征体元内,存在流体、颗粒以及固体骨架三相介质,其中,颗粒是由地下水渗流与含水层骨架相互作用后从含水层固体骨架中脱离后产生的,随着地下水一起在含水层孔隙中流动,表征体元内各相混合成分如图1所示。流体、颗粒以及固体骨架相的质量分别用mff,mfs和ms表示,体积分别用dVff,dVfs和dVs表示。下面对所建数学模型简化过程中用到的基本参数进行数学定义[8]。
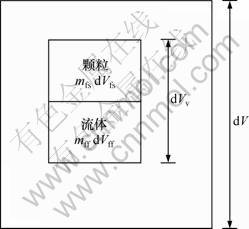
图1 表征体元中混合成分示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of mixing element in representative elementary volume
(1) 孔隙体积:
 (5)
(5)
(2) 含水层的孔隙率:
 (6)
(6)
(3) 颗粒浓度:
 (7)
(7)
(4) 流体、颗粒及固体骨架的密度:
 (8)
(8)
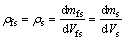 (9)
(9)
(5) 表征体元内流体、颗粒和骨架的平均密度:
 (10)
(10)
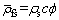 (11)
(11)
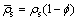 (12)
(12)
(6) 渗透速度与实际平均流速的关系:
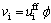 (13)
(13)
式中:ρff为流体的密度,kg/m3;ρfs为颗粒的密度,kg/m3;ρs为固体骨架的密度,kg/m3;vi为渗透速度,m/s。
结合数学模型(1)~(3)和上述定义的参数,对式(1)~(3)进行化简,得:
 (14)
(14)
 (15)
(15)
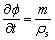 (16)
(16)
2 颗粒迁移对含水层渗透性的影响
地下水源热泵取水井的单井取水量可通过地下水动力学中的相关知识求得[12-13]:
Q=KJA (17)
v=KJ (18)
 (19)
(19)
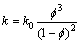 (20)
(20)
式中:Q为取水量,m3/s;K为渗透系数,m/s;J为水力梯度,是地下水流动方向上距离为L的两断面间的压差与L和地下水密度之积的比值,为无量纲数;A为取水面积,m2;k为渗透率,m2;k0为与渗透率有关的常数,可通过已知的孔隙率与渗透率计算得到,m2;μ为地下水的动力黏度,N?s/m2;g为重力加速度,m/s2。
由式(17)~(20)可知:渗透系数是影响渗透速度的重要影响因素。若不考虑地下水回灌后引起地下水的温度变化,即水的密度和动力黏度为常数,则含水层的孔隙率是影响渗透系数的唯一变量。由于地下水源热泵取水会引起颗粒发生迁移,孔隙率的变化进而影响含水层的渗透性。对于上述问题,结合本文建立的颗粒迁移数学模型,通过典型算例对地下水源热泵定压差取水方式对含水层渗透性的影响进行研究。
3 算例
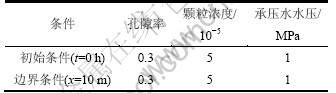
地下水源热泵单井取水问题可看作关于取水井对称的半无限大平面问题。假设地下水100%回灌,同时机组每天间歇运行,远端的水头水压不发生变化,井壁处可维持恒定压力,水泵进水口与井壁处的压力相同,则远端与井壁间的压差不变,地下水源热泵在两端定压差的情况下进行取水。虽然该假定是一种理想状态,但讨论两端压差对含水层渗透性的影响十分重要。地下水源热泵开始运行时,两端压差可以保证机组的取水量满足设计要求,作为压差的选取依据,确定井壁处的渗透速度。地下水渗透速度均大于含水层的临界渗透速度,含水层会发生颗粒迁移,与侵蚀有关的参数λ取为0.1。本文选取的含水层主要由中粗砂组成,假设含水层均质各向同性,为承压含水层,取水井为完整井,含水层厚度分别假设为20,25和30 m(分别用情况1,2和3表示),为了满足取水量的要求,不同厚度的含水层需要的压差不同,但对于相同厚度的含水层,地下水源热泵运行期间压差保持不变,含水层的具体参数如表1所示。
表1 含水层相关参数
Table 1 Aquifer correlation parameter

目前,一些实际工程地下水源热泵的单井取水量主要集中在60~120 m3/h,取水井径为500~600 mm[14-16]。通过对实际工程案例分析可知:目前地下水源热泵应用于公共建筑的较多,如办公楼,剧院等。因此,本文选取的典型算例中地下水源热泵冬夏季每天运行时间为9点至17点,共运行8 h。建筑冬夏季热泵运行时间共计180 d,取水井井径为500 mm,取水量为100 m3/h 。研究范围选取距离取水井中心10 m的区域范围,假设距离井中心10 m处为远端,水头保持不变,初始条件与边界条件的选取如表2所示。对地下水源热泵运行5 a后含水层渗透性的变化进行 研究。
表2 初始条件与边界条件
Table 2 Initial and boundary conditions
地下水源热泵机组运行5 a后取水井井壁处孔隙率变化情况如图2所示。由图2可知:对于类型相同但厚度不同的含水层,即使运行期间压差保持不变,但对含水层孔隙率影响也不同。含水层厚度越小,压差越大,井壁处孔隙率的年变化率越明显。对于情况1,取水井井壁处运行5 a后的孔隙率为初始值的2.57倍;对于情况2,取水井井壁处运行5 a后的孔隙率为初始值的1.86倍。由上述分析可知:定压差取水方式对含水层影响很大,压差越大,孔隙率变化幅度越大,将孔隙率变化后的计算结果代入式(19)~(20),计算得到井壁处渗透系数的年变化情况,如图3所示。从图3可见:在地下水源热泵运行的第1年至第3年,随着孔隙率的增大(由式(19)和(20)可知,渗透系数是孔隙率的函数),3种情况的渗透系数并没有发生显著的变化。但从第3年开始,情况1井壁处的渗透系数开始明显增大,自第4年后,渗透系数急剧增大。而对于其他2种情况,渗透系数增幅并不明显。通过上述分析可知:取水压差越大,随着地下水源热泵运行时间的增加,含水层渗透性增加越明显;地下水源热泵运行5 a后,当含水层厚度分别为20,25和30 m时,这3种情况的渗透系数依次增大为初始值的156倍、16倍和7倍,差别十分显著。对于同一个含水层,地下水源热泵采用定压差方式取水,由式(18)可知,随着含水层渗透系数变大,渗透速度随之增大,结果如图4所示。
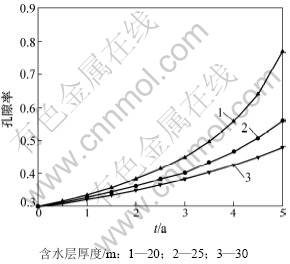
图2 地下水源热泵运行时井壁处孔隙率的变化
Fig.2 Porosity variation under GWSHP operating
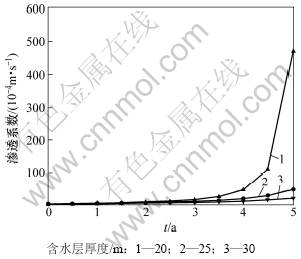
图3 地下水源热泵运行引起的井壁处渗透系数的变化
Fig.3 Hydraulic conductivity variation under GWSHP operating
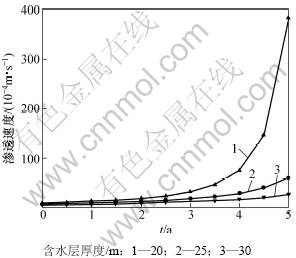
图4 地下水源热泵运行引起的井壁处渗透速度的变化
Fig.4 Seepage vetocity variation under GWSHP operating
通过上述分析可知:取水压差越大,对含水层渗透性影响越大;随着机组运行时间的增加尤为明显;含水层孔隙率增大后,含水层的渗透性明显增强,渗透速度逐渐变大,使得进入机组的实际流量大于其设计值,有利于提高地下水源机组的实际运行效率,减小抽取水与回灌水间的温差,地下水温度场波动范围变小,有利于保持地下空间的生态平衡。
4 结论
(1) 地下水源热泵定压差取水时,对于相同类型的含水层,取水压差越大,对含水层的渗透性影响越显著。在本文分析范围内,地下水源热泵运行5 a后不同厚度(20,25和30 m)含水层孔隙率依次增大到初始值的2.57,1.86和1.59倍;对应的渗透系数依次增大到初始值的156,16和7倍,差别十分显著。
(2) 随着地下水源热泵运行时间的增加,含水层渗透性在孔隙率达到某一值后急剧变大,而在热泵运行的前几年渗透性变化并不明显。
(3) 当热泵机组定压差取水时,随着热泵机组运行时间的增加,由于渗透速度变大,进入机组的实际水量大于其设计值,有利于提高热泵机组的实际运行效率。
参考文献:
[1] 杨昭, 张世钢, 孙政, 等. 地下水源热泵的最优化设计[J]. 太阳能学报, 2002, 23(6): 687-691.
YANG Zhao, ZHANG Shi-gang, SUN Zheng, et al. Optimization of a groundwater-source heat pump[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2002, 23(6): 687-691.
[2] 倪龙, 马最良. 同井回灌地下水源热泵地下水渗流理论研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2006, 27(12): 1219-1224.
NI Long, MA Zui-liang. Study on the seepage theory for groundwater source heat pump with pumping & recharge in the same well[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2006, 27(12): 1219-1224.
[3] 倪龙, 马最良. 含水层参数对同井回灌地下水源热泵的影响[J]. 天津大学学报, 2006, 39(2): 229-234.
NI Long, MA Zui-liang. Effect of aquifer parameters on groundwater heat pump with pumping and recharging in the same well[J]. Journal of Tianjin University, 2006, 39(2): 229-234.
[4] 李旻, 刁乃仁, 方肇洪. 单井回灌地源热泵承压含水层渗流解析解[J]. 山东建筑工程学院学报, 2006, 21(1): 1-5.
LI Min, DIAO Nai-ren, FANG Zhao-hong. Analytical solution of seepage flow in a confined aquifer with a standing column well[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Architecture and Engineering, 2006, 21(1): 1-5.
[5] 刘学玲, 朱家玲, 雷海燕. 地下水地源热泵夏季运行的测试与分析[J]. 暖通空调, 2006, 36(7): 110-111.
LIU Xue-ling, ZHU Jia-ling, LEI Hai-yan. Testing of ground water source heat pump systems in summer[J]. Journal of Heating Ventilation and Air Conditioning, 2006, 36(7): 110-111.
[6] 张远东, 魏加华, 李宇, 等. 地下水源热泵采能的水-热耦合数值模拟[J]. 天津大学学报, 2006, 39(8): 907-912.
ZHANG Yuan-dong, WEI Jia-hua, LI Yu, et al. Simulation of changes in geo-temperature field due to energy abstraction from underground aquifers[J]. Journal of Tianjin University, 2006, 39(8): 907-912.
[7] 杨清. 关于水源热泵水源问题的探讨[J]. 工程建设与设计, 2004, 52(6): 5-7.
YANG Qing. Study on water source of WSHP[J]. Engineering Construction and Design, 2004, 52(6): 5-7.
[8] Stavropoulou M, Papanastasiou P, Vardoulakis I. Coupled wellbore erosion and stability analysis[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 1998, 22(9): 749-769.
[9] wan Richard G, WANG Jin. Analysis of sand production in unconsolidated oil sand using a coupled erosional-stress- deformation model[J]. Journal of Canadian Petroleum Technology, 2004, 43(2): 47-53.
[10] XUE Shi-feng, YUAN Yan-guang. Sanding process and permeability change[J]. Journal of Canadian Petroleum Technology, 2007, 46(4): 33-39.
[11] 刘伟, 范爱武, 黄晓明. 多孔介质传热传质理论与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006: 5-7.
LIU Wei, FAN Ai-wu, HUANG Xiao-ming. Theory and application of heat and mass transfer in porous media[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006: 5-7.
[12] 李俊亭. 地下水动力学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987: 13-19.
LI Jun-ting. Groundwater dynamics[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 1987: 13-19.
[13] Papamichos E, Vardoulakis I.Sand erosion with a porosity diffusion law[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2005, 32(1): 47-58.
[14] 黄天荣, 徐照彪. 武汉市地下水源热泵应用情况分析[J]. 工程建设与设计, 2007, 55(7): 9-12.
HUANG Tian-rong, XU Zhao-biao. The analysis of groundwater heat pump application in Wuhan city[J]. Engineering Construction and Design, 2007, 55(7): 9-12.
[15] 周建伟, 谢先明, 周爱国, 等. 武汉市地下水源热泵应用现状及发展前景分析[J]. 工程建设与设计, 2007, 55(11): 9-13.
ZHOU Jian-wei, XIE Xian-ming, ZHOU Ai-guo, et al. The application actuality and developmental foreground of groundwater heat pump in Wuhan city[J]. Engineering Construction and Design, 2007, 55(11): 9-13.
[16] 陈焰华, 祁传斌. 武汉香榭里花园水源热泵空调系统设计[J].暖通空调, 2006, 36(3): 82-85.
CHEN Yan-hua, QI Chuan-bin. Water-source heat pump air conditioning system design for Wuhan Xiangxieli garden[J]. Journal of HV&AC, 2006, 36(3): 82-85.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2010-05-20;修回日期:2010-08-25
基金项目:国家“十一五”科技支撑计划项目(2006BAJ01B05)
通信作者:王松庆(1982-),男,黑龙江大庆人,博士研究生,从事地源热泵研究;电话:021-69583803;E-mail:wsq-hvac@163.com