超慢速扩张脊地质特征与多金属硫化物成矿探讨
——以西南印度洋脊研究为例
叶俊,石学法,杨耀民,崔迎春
(国家海洋局 第一海洋研究所,海洋沉积与环境地质国家海洋局重点实验室,山东 青岛,266061)
摘要:以西南印度洋脊为例,从地形地貌、地幔性质与岩浆作用等方面分析了该超慢速扩张脊地质特征,并分别对西南印度洋洋脊西段、中段、东端热液活动及多金属硫化物成矿特征进行总结。结果表明:西南印度洋脊中间隆起段热液活动可能主要受深部岩浆热源控制,而东西两侧脊段热液活动可能主要受构造或基底岩石类型控制;地幔性质、岩浆作用与热液活动等方面仍是超慢速扩张洋脊今后研究的主要方向。
关键词:西南印度洋;超慢速扩张脊;地幔地球化学;热液活动
中图分类号:P736 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)S2-0034-05
Geological characteristics and mineralization of polymetallic sulfide in ultraslow-spreading ridges: Example as Southwest Indian Ridge
YE Jun, SHI Xue-fa, YANG Yao-min, CUI Ying-chun
(First Institute of Oceanography, SOA, Shangdong Qingdao, 266061)
Abstract: Taking Southwest Indian Ridge (SWIR) as an example, the geological characteristics in this typical ultraslow-spreading ridge were preliminarily analyzed in terms of morphology, mantle geochemistry and magmatism, and the hydrothermal activities and polymetallic sulfide mineralization were also summarized respectively from the western, middle and eastern of this ridge. The result shows that the hydrothermal activities in the middle swell part of the southwest Indian ridge are likely controlled by the deep magmatic heat source, whereas the hydrothermal activities in the western and eastern part of this ridge may well be constrained by the tectonics and/or substrate rock. The mantle characteristics, magmatism and hydrothermal activities are still the main direction in the future investigation on ultraslow-spreading ridges.
Key words: southwest indian ridge; ultraslow-spreading ridges; mantle geochemistry; polymetallic sulfide
超慢速扩张脊作为洋中脊体系的一个极端端元(全扩张速率<20 mm/a),是最近才认识的一种独特的新类型。该类型扩张脊包括西南印度洋脊(SWIR)、库克洋脊(Gakkel ridge)及一些小的洋脊段,总长度将近20 000 km,占大洋中脊体系总长度(55 000 km)近40%[1]。与快速扩张的东太平洋海隆(100~200 mm/a)、中速扩张的胡安德富卡脊(50~60 mm/a)、慢速扩张的大西洋脊(25~50 mm/a)等洋脊相比,超慢速扩张脊在地形地貌、玄武岩性质、重力、构造和热液活动分布特征等方面均表现出显著“异常”,现有的洋壳增生理论与标准模型不能够完全解释该“异常”[2]。而且超慢速扩张脊因地幔温度较低、火山活动较少,岩浆作用以低程度部分熔融为主,洋壳增生较薄,底辟作用导致地幔物质大量上涌,形成地幔橄榄岩在洋脊大面积出露,为直接研究地球深部的地幔性质与洋壳增生过程提供了很好的“窗口”。西南印度洋脊(SWIR)长约7 700 km,是一个典型的超慢速洋脊扩张脊。其西端为布维三联点(Bouvet Triple Junction, BTJ),东端为罗得里格斯三联点(Rodrigues Triple Junction, RTJ),构成了非洲板块和南极洲板块之间的边界,连接大西洋与印度洋。西南印度洋超慢速脊的全扩张速率为9~15 mm/a,显示崎岖多变的深海轴部裂谷,被一系列南北向的转换断层如Altantis Ⅱ和Melville等断裂带错断,最深处可达5 km[3],地幔物质如蛇纹石化橄榄岩在断裂带附近经常大范围出现[4],辉长岩、玄武岩等岩石在洋脊中常见。洋脊厚度为1~6 km,最薄处小于1 km。
1 西南印度洋超慢速扩张脊地质 特征
根据扩张速率的变化,全球洋中脊可划分为快速(全扩张速率>60 mm/a)、慢速(全扩张速率<60 mm/a)2种主要类型[2]。快、慢速扩张脊洋壳厚度大体相同(6~7 km);从平面图上看,快、慢速洋脊均被一些转换断层错开,形成阶梯状,沿脊轴方向常露出拉伸状的深海火山丘。2种不同类型扩张脊的差异主要有:快速扩张脊的轴部隆起,出现较窄的顶部地堑,地形受火山作用影响较大;慢速扩张脊轴部呈现较宽的裂谷,两壁为线状海山,地形受构造活动影响较大。在上述认识的基础上,建立了全球洋壳增生的蛇绿岩套标准模型,提出层状的枕状玄武岩、席状岩墙、辉长岩按一定的厚度比例构成洋壳,与下部的上地幔相接触。但对西南印度洋超慢速扩张脊的近期调查发现,洋脊火山活动地段与无岩浆作用地段相间出现。在无岩浆作用的洋脊段,海底大量地幔橄榄岩出露,伴随有零星玄武岩和辉长岩[1]。洋脊延伸方向并不与洋脊扩张方向垂直,可以形成任何方向的扩张。相比洋壳增生标准模型中以正断层出现的玄武岩块体,西南印度洋脊两壁主要为地幔橄榄岩墙,形成较长的倾斜断崖或显示不规则抬升[1, 5-6],部分洋中脊段展示为倾斜裂谷[1, 7],或出现独特“平坦”的海底[8]。
根据洋脊轴向相对扩张方向的倾斜度以及洋脊轴向裂谷深度,西南印度洋脊自西向东可被划分为一系列脊段,各段表现出不同的地形地貌特征(图1)[9]。BTJ-10°E脊段,转换断层密集发育;Shaka转换断层10°E~15°E脊段,洋脊轴向与扩张方向斜交,且洋脊轴向偏斜度可达51°,因此,也被称为“倾斜脊段”,轴部平均深度约4 km;16°E~25°E脊段,本段长约600 km,洋脊轴向与扩张方向近乎垂直,与倾斜脊段形成鲜明对比,被称为“垂向脊段”[1],其平均水深较倾斜脊段浅500 m;25°E~35°E脊段,被DT,Andrew Bain,Ma和PE等大型转换断层切割错断,并产生显著位移,使得该段长度达1 200 km;35°E~52°E 脊段,被Discovery,In和Gallieni等转换断层切割错断,整体较为连续,洋脊轴向略微倾斜(25°),轴部平均水深约3 200 m,为一个长约2 200 km的隆起脊段,该隆起脊段的中间部分(Discovery与In转换断层之间)水深达3 600 m,较周围两侧深。Gallieni(52°E )-64°E脊段,显著倾斜,被Atlantis II,Novara和Melville等转换断层和一系列延伸较长的非转换断层所切割;64°E~67.5°E脊段,洋脊轴向略微倾斜;61°E –RTJ脊段与9°E~25°E 相似,转换断层和非转换断层不发育。
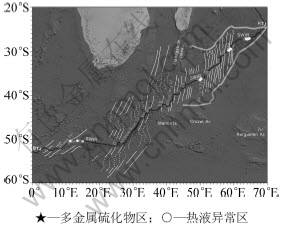
图1 西南印度洋脊构造地质简图
Fig.1 Scheme of geology and tectonics in Southwest Indian Ridge
SWIR附近有热点存在,一定程度上反映出地幔柱与洋中脊之间可能存在着某种必然的联系。如Marion岛,位于28 Ma的洋壳上,距离SWIR约250 km,标记着Marion/Prince Edward地幔柱的当前位置。Bouvet岛,位于7 Ma的洋壳上,距离BTJ东部约300 km,距离最近的SWIR约55 km,但是直到现在,到底是Bouvet到还是Spiess海山(位于BTJ和Bouvet岛之间),代表Bouvet地幔柱目前的位置,现在还不能确定。不过可以肯定,这2处的热点存在与SWIR的扩张有一定的联系。
总体看来,依据地质构造背景,西南印度洋脊可粗略划分为三段构造单元,分别为西段、中段、东段。西段(BTJ~35°E),以断裂构造较发育,断层位移较大,大规模地幔岩出露为特征;中段(35°E~52°E),洋脊显著隆起,岩浆活动发育,可能受Marion热点影响显著,基底以玄武岩为主;东段(52°E~RTJ),与西段类似,密级发育断裂构造,转换位移相对较小。
2 地幔性质与岩浆作用
洋中脊的岩浆活动占全球岩浆活动总量62%(包括侵入和喷出岩),占火山活动的73%,以岩浆冷凝和洋壳冷却等方式的热散失量接近地球内部热量散失的75%,洋中脊处岩石圈的增生率为18 km3/a[10]。对洋壳形成过程研究显示,洋中脊岩浆的减压部分熔融与分离结晶形成下地壳(熔体)和上地幔岩石圈(残余)。 火山岩壳(大洋中脊玄武岩、侵入岩墙和下地壳的辉长岩)主要为洋中脊岩浆熔体固化部分,而深海橄榄岩是岩浆的残余部分。洋中脊玄武岩的组成变化可反映整个熔融过程和地幔的熔融程度与熔融压力[11],深海橄榄岩主要反映地幔的组成,通过深海橄榄岩矿物组成和相平衡研究,可揭示洋中脊下部地幔最大的熔融程度和最后的熔融压力[12]。目前,有关超慢速扩张脊的数据少,岩浆活动期次还不能有效的确定。对这2类岩石的研究显示,地幔温度变化、板块扩张速率变化与地幔源区组成变化是控制岩浆熔融程度、洋中脊玄武岩组成与洋壳生成速率的主要控制因素,除地球物理与理论模式方法外,对岩石地球化学组成研究目前还是反映熔融程度的最直接手段和提供主要信息。对超慢速扩张脊, Bown等[13]预测地壳厚度随热传导的减少而减少,地球化学[14]和地震测量的资料显示超慢速西南印度洋脊存在有限的部分熔融。
超慢速扩张西南印度洋脊熔岩的元素与同位素地球化学特征与大西洋、太平洋的洋中脊玄武岩存在明显的差异[15],洋中脊玄武岩主要为碱性玄武岩[15],较正常MORB组成LREE明显富集,可能为地幔物质的较低部分熔融,形成富碱而贫硅的碱性岩浆的分离结晶作用所形成。如 SWIR (9°~25°E)玄武岩出现霞石(含量可达5.91%),中等程度K的富集(1.59%的K2O),显示为E-MORB[16]。但Seyler对西南印度洋脊(52°~ 68°E)13个站位的地幔斜方橄榄岩、二辉橄榄岩53个样品的岩石学、地球化学研究显示,残余地幔在区域或局部尺度上均存在明显的不均一性,部分岩浆也可形成于较高程度的部分熔融[17]。对49°E~ 70°E的研究显示,出现富Na玄武岩,特别是西南印度洋脊的东部,样品表现出高的Fe8和(La/Sm)N值。但总的来说,目前对西南印度洋脊的研究还比较零散,研究程度还较浅。
3 西南印度洋超慢速扩张脊热液活动及多金属硫化物成矿作用
在大西洋扩张脊热液活动发现之前,人们曾对较冷热结构的慢速扩张脊形成热液活动提出了质疑[18],认为慢速扩张脊较冷的地幔热状态对热液活动的形成极为不利。在20世纪90年代,基于快速扩张脊的扩张速率与发现的热液活动数量,建立了两者的线性关 系[19-20]。随后对上述线性关系进行了补充与拓展[21],并应用于慢速扩张脊,提出慢速扩张脊的构造裂隙为控制热液活动的重要因素并且限制了热液羽状流的扩散。尽管如此,仍然认为超慢速扩张脊的热液活动出现频率极低。随着对全球2 250 km超慢速扩张脊的联合调查与先进光学背散射传感探头的应用[22-25],发现超慢速扩张脊的高温热液活动极其普遍[7, 26],平均热液活动出现频率为每100 km出现1处,为快速扩张脊的2~4倍[24, 27]。
目前,西南印度洋脊已发现多金属硫化物区12处,热液活动异常11处[22-23, 28-30]。这些热液后动区分布于不同脊段构造单元。
3.1 西段洋脊热液活动与多金属硫化物成矿作用
在10°E ~16°E脊段发现6处热液异常,其中有5处的热液活动基底岩石为超铁镁质岩,主要是完全或部分蛇纹石化的方辉橄榄岩、二辉橄榄岩及纯橄榄岩等。热液活动均位于裂谷南、北两壁大于4 km的深水区。拖网样品显示有:(1) 块状硫化物;(2) 硅—海泡石;(3) 绿脱石—水纳锰矿等3种热液活动沉积类 型[24]。Bach等[23]对西南印度洋脊10°E~16°E的热液活动详细研究显示,构造活动是控制热液活动的主导因素,洋脊长期活动的断裂带是热液流体运移的通道,在超慢速扩张脊超铁镁质岩石赋存的热液体系中,橄榄岩与海水的水-岩放热反应(辉石、橄榄石蚀变形成蛇纹石、滑石、磁铁矿及水镁石),可形成中、低温热液成矿体系,而高温热液流体的形成可能还需其他热源来供应。
3.2 东段洋脊热液活动与多金属硫化物成矿作用
在西南印度洋脊东段(63°56′E)水深2 940 m,Melville断裂带附近的Jourdanne轴部火山上,发现数个已熄灭的热液活动的硫化物残余体[29],平均分布范围为5 m3。对硫化物矿物组合研究显示,从Fe的硫化物矿带可变化到富Zn,Cu,Pb的硫化物矿带,黄铁矿大范围交代磁黄铁矿,少量被白铁矿交代,个别样品可见胶状黄体矿和草莓状黄铁矿,硅及少量的硫酸盐矿物如重晶石等也普遍出现。Jourdanne火山热液区出现方铅矿和含Pb-As 的硫盐矿物,在碎屑矿石中出现少量的雄黄、硫锑铅矿,明显不同于无沉积物覆盖洋脊热液硫化物的矿物组合,可能反映超慢速扩张洋脊独特的硫化物成矿作用特征。
3.3 中段洋脊热液活动与多金属硫化物成矿作用
目前,我国在西南印度洋脊中段发现多金属硫化物区5处,热液异常区2处。5处热液区分别集中在49°E和51°E区域。49°E附近热液区主要为高温多金属硫化物区,而51°E附近区域目前发现大面积低温形成的蛋白石、碳酸盐等热液产物及少量多金属硫化物。
49°E附近热液区是我国在全球超慢速扩张脊发现的第一活动热液区。根据矿物组合[28, 31],硫化物矿石可划分出2种类型:其一为富Zn硫化物矿石,其二为富Fe硫化物矿石。富Zn硫化物矿石矿物组合主要为闪锌矿-黄铁矿-黄铜矿,闪锌矿集合体内普遍发育溶蚀孔洞构造及同质增生边结构;富Fe硫化物矿石矿物组合主要为黄铁矿-白铁矿-等轴古巴矿,具典型的等轴古巴矿固溶体分解结构,指示高温沉淀特征。2种硫化物矿石的矿物组合与结构构造特征表明该热液区硫化物成矿至少经历了2个阶段:第1阶段为中-低温富Zn硫化物沉积成矿阶段,第2阶段为高温富Fe硫化物沉积成矿阶段,成矿温度由低到高的转化说明热液体系存在幕式排泄特征,富Zn硫化物中可见自然金矿物产出。根据自然金主要赋存于闪锌矿中相对高Fe区域的特点,推测Au在热液流体中主要以Au(HS)0形式迁移。Au-As,Au-Pb的关系进一步指示该区至少存在两幕热液活动叠加改造过程。硫化物矿石的铂族元素总量较其他典型热液区低,且其球粒陨石配分模式与玄武岩相似,均无明显Rh异常,可能指示铂族元素主要来自流体对基底岩石的淋滤。S,Pb,Sr同位素研究显示,硫化物成矿物质主要来自热液流体对基底玄武岩的淋滤。结合区域地质背景资料,认为西南印度洋脊49.6oE热液区的热液活动可能受底部岩浆热源控制。
4 结论
超慢速扩张西南印度洋脊热液活动及多金属硫化物区的不断发现表明:岩浆供给量极低、超铁镁质岩大量出露的超慢速扩张脊也可形成大范围的热液活动。通过对西南印度洋脊地质特征及多金属硫化物成矿作用初步分析认为:不同洋脊区段,其热液成矿的主要控制因素可能存在差异。西南印度洋脊中间隆起段可能主要受深部岩浆热源控制,而洋脊东西两侧脊段则可能主要受构造或基底岩石类型控制。但目前对这一特征洋脊热液活动的动力学机制及多金属硫化物成矿的主要控制因素认识还不全面,因此,西南印度洋脊热液活动尚需进一步详细调查,多金属硫化物成矿控制因素也需进一步深入研究和验证,地幔性质、岩浆作用与热液活动等方面仍是超慢速扩张洋脊今后研究的主要方向。
参考文献:
[1] Dick H J B, Lin J, Schouten H. An ultraslow-spreading class of ocean ridge[J]. Nature, 2003, 426: 405-412.
[2] Snow J E, Edmonds H N. Ultraslow-spreading ridges: Rapid paradigm changes[J]. Oceanography-washington DC- Oceanography Society, 2007, 20(1): 90.
[3] Mendel V, Sauter D, Parson L, et al. Segmentation and morphotectonic variations along a super slow-spreading center: The southwest indian ridge (57° E-70° E) [J]. Marine Geophysical Researches, 1997, 19(6): 505-533.
[4] Fujimoto H, Cannat M, Fujioka K, et al. First submersible investigations of mid-ocean ridges in the Indian Ocean[J]. InterRidge News, 1999, 8(1): 22-24.
[5] Michael P J, Langumuir C H, Pick H J, et al. Magmatic and amagmatic seafloor generation at the ultraslow-spreading Gakkel ridge Arctic Ocean[J]. Nature, 2003, 423: 956-961.
[6] Okino K, Curewitz D, Asada M, et al. Preliminary analysis of the Knipovich Ridge segmentation: Influence of focused magmatism and ridge obliquity on an ultraslow spreading system[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 202(2): 275-288.
[7] Snow J, Jokat W, Hellebrand E, et al. Magmatic and Hydrothermal activity in Lena Trough Arctic Ocean[J]. Eos Trans. AGU, 2001, 82(17): 193.
[8] Cannat M, Sauter D, Mendel V, et al. Modes of seafloor generation at a melt-poor ultraslow-spreading ridge[J]. Geology, 2006, 34(7): 605-608.
[9] Rona P A. Diversity of hydrothermal systems on slow spreading ocean ridges[M]. Washington D C: American Geophysican Union, 2010: 153-173.
[10] Houghton B, McNutt S, Rymer H, et al. Encyclopedia of volcanoes[M]. SanDiego: Academic Press, 2000: 271-279.
[11] Langmuir C H, Klein E M, Plank T. Petrological systematics of mid-ocean ridge basalts: constraints on melt generation beneath ocean ridges[J]. Geophysical Monograph-American Geophysical Union, 1993, 71: 183-183.
[12] Niu Y. Bulk-rock major and trace element compositions of abyssal peridotites: implications for mantle melting, melt extraction and post-melting processes beneath mid-ocean ridges[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2004, 45(12): 2423.
[13] Bown J W, White R S. Variation with spreading rate of oceanic crustal thickness and geochemistry[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994, 121(3/4): 435-449.
[14] Robinson C J, White R S, Bickle M, et al. Restricted melting under the very slow-spreading Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. The Geological Society, 1996, 118(1): 131-141.
[15] Meyzen C M, Toplis M J, Humler E, et al. A discontinuity in mantle composition beneath the southwest Indian ridge[J]. Nature, 2003, 421(6924): 731-733.
[16] Standish J, Henry D, Anton P. The influence of Ridge Geometry on mantle melting: Basalt geochemistry along the SWIR(9°-25°E)[C]//Interrige Workshop: South West Indian Ridge, Southampton, 2002: 74.
[17] Cannat M, Rommevaux-Jestin C, Sauter D, et al. Formation of the axial relief at the very slow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge (49 to 69 E) [J]. J Geophys Res, 1999, 104(10): 22825-22843.
[18] Rona P A, Klinkhammer G, Nelsen T A, et al. Black smoker, massive sulfides and vent biota at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge[J]. Nature, 1986, 321: 33-37.
[19] Baker E T, Freely R A, Mottl M J, et al. Hydrothermal plumes along the East Pacific Rise, 8° 40’to 11° 50’N: Plume distribution and relationship to the apparent magmatic budget[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 1994, 128(1/2): 1-17.
[20] Baker E T, Chen Y J, Phipps M J. The relationship between near-axis hydrothermal cooling and the spreading rate of mid-ocean ridges[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1996, 142(1/2): 137-145.
[21] German C R, Parson L M. Distributions of hydrothermal activity along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge: interplay of magmatic and tectonic controls[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 160(3/4): 327-341.
[22] German C R, Baker E T, Mevel C, et al. Hydrothermal activity along the southwest Indian ridge[J]. Nature, 1998, 395(6701): 490-493.
[23] Bach W, Banerjee N K, Dick H J B, et al. Discovery of ancient and active hydrothermal systems along the ultra-slow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge 10°–16° E[J]. Geochem Geophys Geosyst, 2002, 3(7): 1044.
[24] Baker E T, Edmonds H N, Mickael P J, et al. Hydrothermal venting in magma deserts: the ultraslow-spreading Gakkel and Southwest Indian Ridges, 2004.
[25] Edmonds H N, Michael P J, Backer E T, et al. Discovery of abundant hydrothermal venting on the ultraslow-spreading Gakkel ridge in the Arctic Ocean[J]. Nature, 2003, 421(6920): 252-256.
[26] Petersen S, Kuhn T, Herzig P M, et al. Factors controlling precious and base-metal enrichments at the ultramafic-hosted Logatchev hydrothermal field, 14 4'5 N on the MAR: New insights from cruise M60/3//[J]. Mineral Peposit Research: Meeting the Global Challenge, 2005, 6: 679-682.
[27] Baker E T, German C R. On the global distribution of hydrothermal vent fields[J]. Geophysical monograph, 2004, 148: 245-266.
[28] 叶俊. 西南印度洋超慢速扩张脊49.6°E热液区热液硫化物成矿作用研究[D]. 青岛: 中科院海洋研究所, 2010: 1-120.
YE Jun. Mineralogy of sulfides from ultraslow spreading southwest indian ridge 49.6°E hydrothermal field[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2010: 1-120.
[29] Münch U, Lalou L, Halbach P, et al. Relict hydrothermal events along the super-slow Southwest Indian spreading ridge near 63° 56′ E—Mineralogy, chemistry and chronology of sulfide samples[J]. Chem. Geol, 2001, 177: 341-349.
[30] Tao C, Lin J, Guo S. Discovery of the first active hydrothermal vent field at the uhraslow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge: The Chinese DYIIS-19 Cruise[J]. Ridge Crest News, 2007, 16: 25-26.
[31] 叶俊, 石学法, 杨耀民, 等. 西南印度洋超慢速扩张脊 49.6°E 热液区硫化物矿物学特征及其意义[J]. 矿物学报, 2011, 31(1):17-29.
YE Jun, SHI Xue-fa, YANG Yao-min,et al. Mineralogy of sulfides from ultraslow spreading southwest indian ridge 49.6°E hydrothermal field and its metallogenic significance[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2011, 31(1):17-29.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2011-06-15;修回日期:2011-07-15
基金项目:国际海底区域研究开发“十一五”规划项目(DYXM115-01-2-01,DYXM115-02-1-04);海洋一所基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(2007T10)
通信作者:叶俊(1981-),女,湖北襄阳人,博士,助理研究员,从事海底成矿作用研究;E-mail: yejun@fio.org.cn