文章编号:1004-0609(2015)02-0375-09
Zn在模拟酸雨大气环境中的腐蚀行为
刘雨薇1,王振尧1,曹公望1,吕旺燕2,苏 伟2
(1. 中国科学院 金属研究所,沈阳 110016;
2. 广东电网公司 电力科学研究院,广州 510080)
摘 要:利用自制的降雨喷淋装置模拟Zn在酸雨条件下的大气腐蚀行为,采用扫描电镜(SEM)、X 射线能谱(EDS)、X 射线衍射(XRD)和电化学测试技术分别研究Zn腐蚀48、96、144、192和240 h后的腐蚀产物成分、锈层截面形貌以及表面锈层的电化学特性,分析了锈层对Zn腐蚀行为的影响。结果表明:主要的腐蚀产物为Zn(OH)2、ZnSO4、Zn4SO4(OH)6·3H2O和Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O;腐蚀过程中,Zn的表面形成了具有较好保护性的锈层,随着腐蚀时间的延长,锈层对Zn的保护作用先增强后减弱。
关键词:模拟酸雨;大气腐蚀;腐蚀产物;电化学技术
中图分类号:TG172.3 文献标志码:A
Corrosion behavior of Zn in simulated acid rain atmospheric environment
LIU Yu-wei1, WANG Zhen-yao1, CAO Gong-wang1, L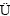 Wang-yan2, SU Wei2
Wang-yan2, SU Wei2
(1. Institute of Metals Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China;
2. Electric Power Research Institute, Guangdong Power Grid Corporation, Guangzhou 510080, China)
Abstract: The corrosion behavior of Zn in simulated acid rain atmospheric environment was studied with a simulating raining system self-designed, which can control rainfall and pressure close to the actual level. After zinc corroded in simulated acid rain atmospheric environment corrosion time of 48, 96, 144, 192 and 240 h, the morphologies and the composition of corrosion products, cross section of rust layers and the electrochemical characters of rust layers were investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), X-ray diffractometry (XRD) and electrochemical techniques. The results show that the corrosion products formed on the surface of zinc have good protection, but the degree of protection is limited, with the main product components for Zn(OH)2, ZnSO4, Zn4SO4(OH)6·3H2O and Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O. The protective effect of the rust layers is first enhanced, and then weakened as increasing the corrosion time.
Key words: simulated acid rain; atmospheric corrosion; corrosion products; electrochemical technique;
Zn由于良好的压延性、耐磨性和抗腐蚀性,在工业生产的诸多领域中都得到了广泛应用,其用量仅次于铁、铝、铜,其中约45%的初级产品用于钢铁表面镀层,以提高钢的耐蚀性。近些年,随着酸雨逐渐成为全球性问题[1-2],热镀锌钢作为一种经济有效的耐蚀材料[3-5],在建筑材料、航空配件、交通运输、电力通讯和家电家具等行业中,尤其在电力行业中都得到了更加广泛应用。随着我国经济建设的高速发展,电力负荷大幅度增加,镀锌钢作为输电线路中基础设施建设的主要材料,与输电网的安全运行密切相关[6-7]。因此,Zn及镀锌钢的大气腐蚀行为不仅得到了国内外学者的诸多关注,也受到了我国电力部门的重视[8]。20世纪80年代,国内外学者对Zn的腐蚀方面已经进行了大量研究[9-12],针对Zn及Zn涂层在污染环境中初期的腐蚀行为也给予了深入研究。QUINTANA等[13]、MORCILLO等[14-15]和ODNEVALL等[16-17]对Zn在不同室外暴露环境中的初期腐蚀产物以及对后期腐蚀行为的影响进行了分析和探讨,发现在海洋大气、工业大气、城市大气中腐蚀产物分别为Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O、Zn4Cl2(OH)4SO4·5H2O和Zn4SO4(OH)6·nH2O。AZMAT等[18]研究了酸性海洋环境下Zn的腐蚀行为,研究结果表明,酸化后Zn表面形成的腐蚀产物Zn5(OH)8(Cl)2·H2O 增大腐蚀质量损失速率,而NaZn4Cl(OH)6SO4·6H2O则降低腐蚀质量损失速率;王振尧等[19]研究了Zn在典型大气环境中的腐蚀行为,结果表明:Zn在沈阳、江津和青岛的大气暴露环境和室内模拟加速腐蚀试验环境中,表面形成的腐蚀产物均不能起到阻滞Zn腐蚀的作用;严川伟等[20]研究了Zn在SO2环境中大气腐蚀初期的腐蚀特性,在含 SO2 的较高湿度的空气环境中, Zn 具有一定的局部腐蚀倾向,SO2 能够将Zn 表面原有的富保护性的ZnO 膜转化成疏松多孔缺乏保护性的产物,SO2是对Zn有强烈破坏性的主要原因。安百刚等[21]主要以电化学手段研究了Zn在模拟酸雨溶液及薄液膜下的腐蚀行为;原徐杰等[6]采用动电位极化测试技术研究了沉积不同浓度NaCl和NaHSO3的镀锌钢在干湿交替作用下的腐蚀行为。DILER等[22]采用XRD和FTIR等分析手段,研究了纯锌在海洋大气环境中的腐蚀特点;谈天等[23]采用极化曲线的分析手段来研究不同服役环境中镀锌钢的腐蚀行为。目前,电化学实验结果与其他分析方法所得结果的相关性未得到深入研究,从而有待于进一步探讨。此外,尽管目前室内加速腐蚀实验方法较多,但设计新的更符合实际的腐蚀实验方法显得尤为必要。本文作者利用自制降雨装置来模拟喷淋环境,采用动电位极化测试技术和电化学阻抗测试技术来获得锈层的电化学性能,并结合成分与形貌分析,研究锈层对腐蚀的影响,分析不同实验结果之间的相关性,揭示Zn在模拟酸雨大气环境中的腐蚀机理。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料
实验材料为某厂提供的Zn2板材,其主要杂质成分为Fe 0.012,Cu 0.0005,Pb 0.040,Sn 0.0005,Ca 0.0005(质量分数,%)。形貌成分分析试样表面尺寸为15 mm×15 mm,分别用丙酮和酒精清洗后吹干备用。电化学试样表面尺寸为10 mm×10 mm,除工作表面外的其他面经蜡封后,清洗、吹干备用。
1.2 实验方法
采用自制模拟降雨仪器进行腐蚀实验,实验温度为室温,流量设定为6 L/h,压力为0.1 MPa。喷淋过程以3h为一个周期,喷淋10 min,干燥170 min, 腐蚀液采用模拟酸雨溶液(实际雨水浓度的200倍),溶液成分[24-26]为(NH4)2SO42.039、NaF 0.172、KNO31.178、MgSO4 0.330和CaCl2 3.633(浓度,g/L)。用 H2SO4将溶液pH值调为3,取样时间为48、96、144、192和240 h,每次取出2个形貌分析试样和3个电化学试样。
利用XL30FEG型扫描电子显微镜(SEM)对腐蚀试样的表面和截面微观形貌进行观察和分析。其中用于截面形貌观察的样品先用环氧树脂在室温下进行封闭,固化后用砂纸依次打磨至1000号,然后用1.5 W抛光膏抛光,最后用酒精清洗表面,吹干后进行喷碳处理。
X 射线衍射(X-ray Diffraction)分析,使用 Rigaku-D/max-2500PC 型衍射仪,采用 Cu Kα 靶,在 50 kV、250 mA 条件下以 2(°)/min的扫描速度对腐蚀产物进行测量,并用 PCPDF 和 Jade 软件进行 X 射线衍射结果的标定。
电化学测量采用PARSTAT2273设备和三电极体系来完成,饱和KCl甘汞电极(SCE)为参比电极,Pt 电极为对电极,工作电极为未腐蚀的纯锌或者不同腐蚀周期后的带锈试样。电解质为模拟酸雨溶液,在室温(20 ℃)下进行测量。阻抗测量扰动电位为10 mV,测试频率范围为1×10-2~1×105 Hz。极化曲线测量的扫描速率为0.3333 mV/s,扫描区间为-0.4~0.6 V(相对于开路电位)。电化学阻抗数据用ZSipWinV3.0 软件进行拟合。
2 结果与分析
2.1 腐蚀产物成分分析
图1所示为锌表面形成的腐蚀产物成分随时间演化的XRD谱。由图1可以看出,锈层的主要成分为Zn(OH)2,ZnSO4,Zn4SO4(OH)6·3H2O和Zn5(OH)8- Cl2·H2O。这些产物均是典型大气环境中常见的腐蚀产物,与很多研究结果[15, 27]一致,即在SO42-和Cl-同时存在的环境中,Zn的腐蚀产物主要是Zn5(OH)8- Cl2·H2O、ZnSO4·3Zn(OH)2·4H2O、Zn4Cl2(OH)4SO4·5H2O和Zn4SO4(OH)6·nH2O等。此外,在XRD分析结果中还可以看出,锈层成分随腐蚀时间的增加有明显的差异,腐蚀前期,Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O和Zn4SO4(OH)6·3H2O的相对含量较少;而腐蚀后期,二者的相对含量明显延长。由此可以推测,随腐蚀时间的延长,锈层主要成分的演化过程为由部分产物ZnSO4和Zn(OH)2逐渐的转化为Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O和Zn4SO4(OH)6·3H2O。
2.2 锈层形貌及元素分析
图2所示为不同周期Zn表面的腐蚀形貌以及腐蚀产物的成分。图2(a)~(e)反映腐蚀产物形貌随腐蚀时间的变化情况,图2(f)所示为图2(d)中产物的EDS谱。腐蚀初期,在Zn表面逐渐形成条束状结构的产物,附着在Zn基体表面,彼此成不同的角度(见图2(d))。这集片层,覆盖在Zn表面。平行于基体的产物形成后,条状腐蚀产物主要是Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O[28]。

图 1 腐蚀不同时间后Zn的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of Zn corroded for different times
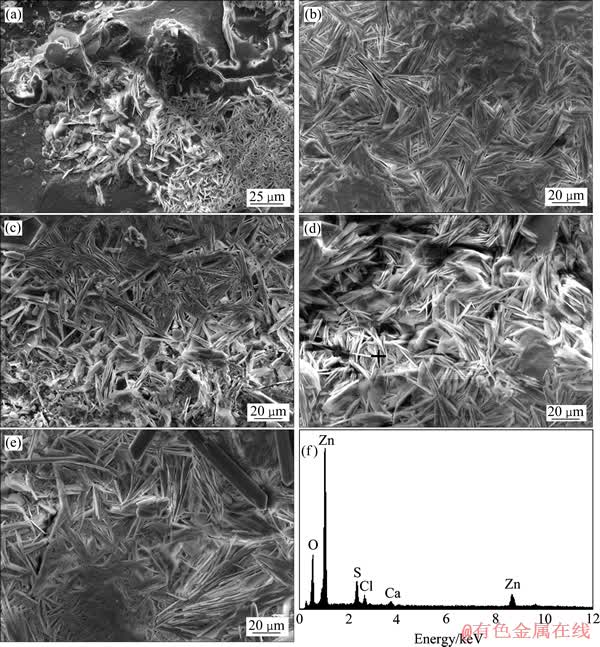
图2 Zn腐蚀不同时间后的SEM像及腐蚀产物的EDS谱
Fig. 2 SEM images of Zn after corrosion for 48 h (a), 96 h (b), 144 h (c), 192 h (d) and 240 h (e) and EDS spectrum of point in Fig. 2(d) (f)
随着腐蚀时间的延长,片状产物逐渐增加,并聚集成密随腐蚀时间的增加,新生成的腐蚀产物与先生成的产物之间呈一定的角度存在。腐蚀时间继续增加,产物形貌没有发生明显变化,但是条束之间逐渐出现缝隙,这可能是引起Zn耐蚀性下降的原因之一。
从截面形貌来看,腐蚀初期锈层比较致密,出现少量的片状结构产物(见图3(a)),由表1中EDS的结果可知,腐蚀48 h的主要腐蚀产物是ZnO。而随腐蚀时间的增加,锈层逐渐增厚,且产物成分发生变化,产物成分中有了S和Cl元素的存在,在腐蚀144 h时锈层达到最厚,锈层在邻近基体处比较致密,而再向外则变得疏松。当腐蚀时间再继续增加时,表面疏松的锈层开始脱落。由此可推测,锈层的逐渐增加使得Zn的耐蚀性逐渐增强,而锈层的脱落使得Zn耐蚀性减弱。
表 1 图3中不同点腐蚀产物元素的EDS结果
Table 1 EDS results of elements at different positions shown in Fig. 3

图4所示为去除腐蚀产物后锌表面的形貌。从图4中能够大致看出,点蚀坑密度的变化,前2个周期点蚀坑的密度较小,从第3个周期开始,点蚀坑密度有所增加,到第4周期时出现了一些较深的点蚀坑,最后一个周期大量的点蚀坑相互连接。从局部放大图中能够更加清晰地看到点蚀在前3个周期过程中形貌的变化。点蚀坑数量的逐渐增多和深度的逐渐加深使得锌的腐蚀容易在这些缺陷处发生,因而,点蚀坑的变化是引起Zn耐蚀性发生变化的原因之一。
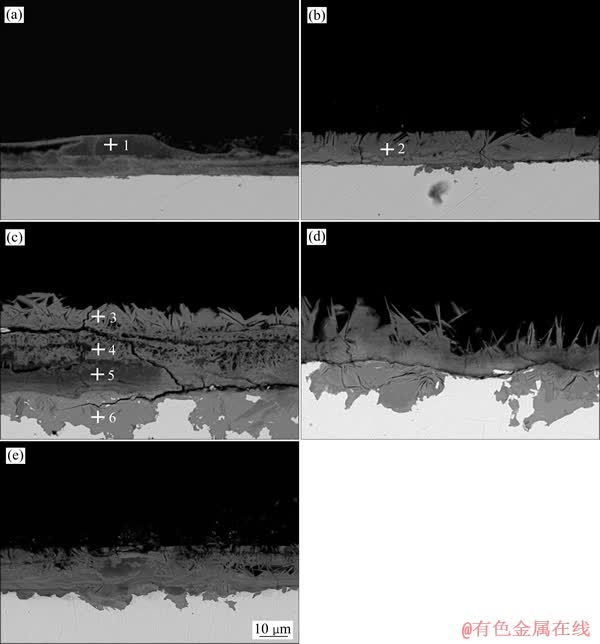
图3 腐蚀不同时间后Zn截面的形貌
Fig. 3 Cross section morphologies of rust layer of zinc after corrosion for 48 h (a), 96 h (b), 144 h (c), 192 h (d) and 240 h (e)
图 4 腐蚀不同时间去除腐蚀产物后Zn表面的SEM像
Fig.4 SEM images on surface of Zn after removing corrosion products at different corrosion times
2.3 电化学分析
大气腐蚀实质上是发生在薄液膜下的电化学反应,因而用电化学方法来分析大气腐蚀过程是合理可行的,极化曲线是应用最广泛的电化学测试方法之一。图5所示为Zn在不同腐蚀时间下的极化曲线。从图5中的极化曲线得到腐蚀电位(φcorr)、腐蚀电流密度(Jcorr)和阳极电流密度(Ja)(如表2所示),随腐蚀时间的增加,腐蚀电位先增大,后减小;腐蚀电流先减小后增大,这说明随着腐蚀时间的增加,材料的耐蚀性先增强,后减弱。
分析可能原因,未腐蚀试样(0 h)、腐蚀48 h和腐蚀96 h试样的阴极电流密度相近,阴极反应主要是 O2在Zn表面的还原,主要受氧扩散控制的过程。这是由于腐蚀初期产物比较致密,对O2扩散的阻碍作用比较大。而腐蚀144 h后,试样的阴极电流密度相近,均比腐蚀前期小得多。阴极反应受到电荷转移过程和O2扩散反应共同控制。这主要是由于随着腐蚀时间延长,试样表面沉积了一定的腐蚀产物,但产物变得疏松多孔,对O2扩散的阻碍减小。此外,不同腐蚀产物的形成使得阴极反应受到电荷转移过程和O2扩散反应共同控制。
阳极反应则主要是Zn的腐蚀溶解,阳极电流密度(Ja)越高,则基体材料越容易发生腐蚀,锈层的保护性能越差。由表2可知,在腐蚀过程中,阳极电流密度先减小,后增大,这表明锈层的保护性能先增强,后减弱。但是,经腐蚀后试样的阳极电流密度均不高于未腐蚀试样(0 h) 的阳极电流密度,即腐蚀产物对Zn的腐蚀一直具有抑制作用。

图 5 未腐蚀和带锈的Zn在不同腐蚀时间的极化曲线
Fig.5 Polarization curves of naked and rusted Zn at different corrosion times
表2 从极化曲线得到腐蚀电位、腐蚀电流密度和阳极电流密度
Table 2 Corrosion potential(φcorr), corrosion current density (Jcorr) and anode current density(Ja) as function of corrosion time from polarization curves

由腐蚀电流密度(Jcorr)和阳极电流密度(Ja)可知,未腐蚀试样(0 h)和腐蚀48 h后的试样,阳极电流密度与总的腐蚀电流密度差一个数量级,说明整个过程受阴极反应控制。而腐蚀96 h后的试样,反应过程则受阳极反应控制。
图6所示为Zn在不同腐蚀时间下的Nyquist 图。图中曲线反映了Zn在不同腐蚀时间下的演变过程,从腐蚀开始到144 h,容抗弧半径逐渐增大,继续腐蚀到240 h,容抗弧半径逐渐减小,并且出现两个明显的容抗弧。这一现象表明Zn的耐蚀性先增加后减小,与极化曲线的规律一致。
为了更好地解释Zn腐蚀不同时间后的电化学腐蚀行为,用图7所示的等效电路对电化学阻抗谱进行拟合,拟合结果如图6,拟合参数如表3所列。
拟合电路中,Rs是溶液电阻,Rr是锈层电阻,Q1是锈层电容,Rt是电荷转移电阻,Q2是双电层电容。极化电阻Rp可由下式表示:
Rp=Rs+Rt+Rr (1)

图6 腐蚀不同时间后Zn的电化学阻抗谱
Fig. 6 Nyquist plots of EIS results of Zn corroded for different time
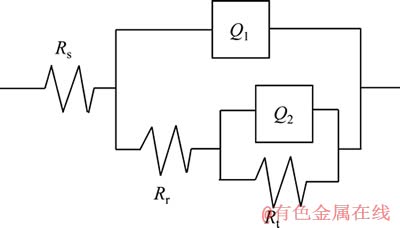
图 7 Zn的腐蚀等效拟合电路
Fig. 7 Equivalent circuit of fitting impedance of Zn
图8所示为Rr、Rt和Rp随腐蚀时间的变化情况。锈层电阻Rr随腐蚀时间的延长先增大,后减小。在腐蚀192 h达到最大值,因而,推测Rr的大小可能与锈层的厚度有关,即锈层越厚,Rr越大。电荷转移电阻Rt随腐蚀时间的增加先增大,后减小,引起Rt发生这种变化的原因可能为:腐蚀初期,Zn表面腐蚀产物少且表面状态均匀一致,反应极易进行,因而Rt较小。随着腐蚀时间的延长,腐蚀产物不断形成,对电极反应的阻碍作用逐渐增大,Rt不断增大,并在腐蚀144 h时,达到最大。之后由于表层疏松腐蚀产物的脱落,使得锈层变薄,阻碍作用减小,以及局部腐蚀坑的出现,Rt逐渐减小。通常情况下,Rp越大,耐蚀性越好。本研究中,随腐蚀时间的增加,极化电阻Rp先增大,后减小,表明随着腐蚀时间的增加,Zn耐蚀性先逐渐增强后减弱。这一结果与极化曲线得到的结果相一致。
表3 拟合后Zn的电化学阻抗谱参数
Table 3 Fitted EIS parameters of Zn

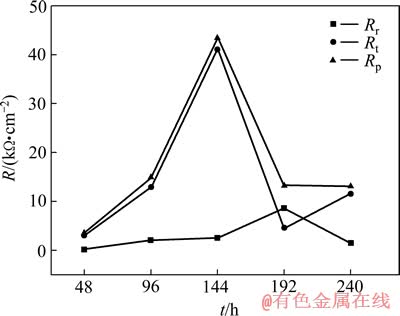
图8 电化学阻抗谱参数Rr、Rt和Rp随腐蚀时间的变化
Fig.8 EIS parameters of Rr, Rt and Rp as function of corrosion time
2.4 腐蚀机理分析
在模拟酸雨大气环境中,Zn的腐蚀过程表现为:反应初期,Zn首先和潮湿空气中的O2反应生成ZnO和Zn(OH)2,随着腐蚀时间的增加,由于模拟酸雨溶液中Cl-和SO42-的存在,使得Cl-和SO42-在氧化膜表面缺陷处吸附或者参与形成暂态中间化合物;随着腐蚀时间的延长,Cl-和SO42-与表面氧化膜不断反应,使得部分区域的氧化膜不断减薄,有利于O2的扩散并发生还原反应,促进基体阳极溶解反应的进行;吸附的Cl-和SO42-与Zn2+结合,形成中间产物或最终腐蚀产物。产物的形成过程为
酸性介质环境使样品的ZnO表面膜发生溶解
ZnO+2H+→Zn2++H2O (2)
Zn2+向阴极作电迁富集, 并在此形成难溶物 Zn4(SO4)(OH)6·3H2O 沉积下来
Zn2++SO42-→ZnSO4 (3)
Zn2++SO42-+xH2O→ZnSO4·xH2O (4)
3Zn(OH)2+ZnSO4+3H2O→Zn4(SO4)(OH)6·3H2O (5)
由于Zn2+和SO42-的电荷较高, 离子半径较大, 容易以离子对的形式存在, 其电迁移能力较差, 并且反应(2)~(4)消耗液层中的 Zn2+和SO42-离子, 导致阳极区与阴极区间的电导性显著下降, 使阳极与阴极间的腐蚀电池作用被削弱, 绝大部分的微电池不能在进一步的腐蚀过程中发展下去,导致腐蚀反应速度减慢。这一过程与前人所作的研究结果[20]相稳合。
Cl-吸附在Zn表面的主要反应过程是Cl-与Zn(OH)2的反应:
Zn(OH)2+ 4Zn2++6OH-+2Cl-→Zn5Cl2(OH)8·H2O (6)
GRAEDEL[29]表明,产物Zn5Cl2(OH)8·H2O具有较大的溶解性,在弱酸性雨水冲刷过程中极易溶解。因而在本实验环境下,当腐蚀时间增加到一定程度时,雨水的冲刷使得腐蚀产物Zn5Cl2(OH)8·H2O脱落,使得锈层厚度开始变薄,耐蚀性减弱。SO42-和Cl-两种离子对之间的相互作用也是腐蚀过程中,耐蚀性变化的原因之一,SVENSSON等[30]也证实了SO2和Cl-之间具有很强的协同效应。当大气环境中同时含有较高浓度的SO42-和Cl-时,随着液层酸性逐渐增强,Zn5Cl2(OH)8·H2O进一步发生溶解,导致液膜内出现大量的离子,电化学腐蚀的趋势增强,使得Zn的腐蚀明显加快,导致耐蚀性减弱。此外,锈层的成分[4]和腐蚀产物结构都直接影响着耐蚀性的大小。ODNEVALL等[31]也提出在含有SO2和Cl-的大气环境中,SO2和Cl-不同浓度配比条件下Zn表面主要腐蚀产物为Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O、Zn4Cl2(OH)4SO4·5H2O、NaZn4SO4Cl(OH)6·6H2O和Zn4SO4(OH)6·nH2O。腐蚀反应过程中SO42-和Cl-不断地参与反应,使得局部区域浓度配比不同,生成的产物也有所不同,导致Zn表面的耐蚀性发生变化。从电化学过程来看,腐蚀初期产生的锈层对Zn基体有保护作用,耐蚀性比Zn试样的强;继续增加腐蚀时间,耐蚀性较腐蚀前试样的要差。这是由于随着锈层的减薄,Zn5Cl2(OH)8·H2O的生成导致电极表面阴阳极出现pH梯度,更容易出现较深蚀孔[32]。研究发现[32-34],在Cl-存在的环境中,Cl-有促进点蚀发生的作用,导致点蚀继续发生,最终结果是蚀孔加深,使得Zn的耐蚀性比腐蚀前试样的耐蚀性差。因而,表面锈层对Zn具有一定的保护作用,但是这种保护作用是有限的。这与周学杰等[35]和FEDRIZZI等[36]的研究结果相一致。
3 结论
1) Zn在模拟酸雨大气环境中的腐蚀时,腐蚀产物的形状为片状,以不同的角度附着在基体表面。锈层的厚度则随着腐蚀时间的延长先增加后减小,锈层厚度减小后,Zn在含Cl-的环境中更易腐蚀,从而使得基体表面有点蚀坑的出现。
2) Zn在模拟酸雨大气环境中的腐蚀产物主要为Zn(OH)2、ZnSO4、Zn4SO4(OH)6·3H2O和Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O。随着腐蚀时间的延长,产物Zn4SO4(OH)6·3H2O和Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O的相对含量逐渐增加。
3) Zn的腐蚀电位和极化电阻都随腐蚀时间的延长先增大后减小;腐蚀电流密度随腐蚀时间的延长,先减小后增大;Zn表面锈层对Zn的保护性先增强后减弱。
REFERENCES
[1] 许新辉, 郜洪文. 中国南方酸雨的分布特征及其成因分析[J]. 四川环境, 2011, 30(4): 135-139.
XU Xin-hui, HAO Hong-wen. Analysis of the distribution and causes of acid rain in southern China[J]. Sichuan Environment, 2011, 30(4): 135-139.
[2] 张学元, 韩恩厚, 李洪锡. 中国的酸雨对材料腐蚀的经济损失估算[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2002, 22(5): 316-319.
ZHANG Xue-yuan, HAN En-hou, LI Hong-xi, Estimation of the corrosion losses by the acidic rain in China[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2002, 22(5): 316-319.
[3] EI-MAHDY G A. Advanced laboratory study on the atmospheric corrosion of zinc under thin electrolyte layers[J]. Corrosion, 2003, 59(6): 505-510.
[4] AZMAT N S, RALSTON K D, MUDDLE B C, COLE I S. Corrosion of Zn under fine size aerosols and droplets using inkjet printer deposition and optical profilometry quantification[J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(11): 1604-1615.
[5] THOMAS S, BIRBILIS N, VENKATRAMAN M S, COLE I S. Corrosion of zinc as a function of pH[J]. Corrosion, 2012, 68(1): 015009-1-015009-9.
[6] 原徐杰, 张俊喜, 季献武, 肖 嵘, 马行驰, 蒋 俊, 吕小增, 竺 欢. 镀锌层破损输电杆塔用镀锌钢在干湿交替作用下的腐蚀行为[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2013, 33(5): 395-399.
YUAN Xu-jie, ZHANG Jun-xi, JI Xian-wu, XIAO Rong, MA Xing-chi, JIANG Jun, L Xiao-zeng, ZHU Huan. Corrosion behavior of galvanized steel for power transmission tower with breakage of zinc coating in polluted environment[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2013, 33(5): 395-399.
Xiao-zeng, ZHU Huan. Corrosion behavior of galvanized steel for power transmission tower with breakage of zinc coating in polluted environment[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2013, 33(5): 395-399.
[7] 宋 卓, 郭军科, 郭锦龙. 环境对电网材料的腐蚀影响分析及评价[J]. 山西电力, 2008, 149(5): 7-9.
SONG Zhuo, GUO Jun-ke, GUO Jin-long. Analysis and evaluation of environment influence on network material corrosion[J]. Shanxi Electric Power, 2008, 149(5): 7-9.
[8] 默增禄, 程志云. 输电线路杆塔的腐蚀与防治对策[J]. 电力建设, 2004, 25(1): 22-23.
MO Zeng-lu, CHENG Zhi-yun. Corrosion and prevention of zinc deposit of transmission towers[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2004, 25(1): 22-23.
[9] KEITELMAN A D, GRAVANO S M, GALVELE J R. Localized acidification as the cause of passivity breakdown of high purity zinc[J]. Corrosion Science, 1984, 24(6): 535-545.
[10] SUXUKI I. The behavior of corrosion products on zinc in sodium chloride solution[J]. Corrosion Science, 1985, 25(11): 1029-1034.
[11] FIAUDA C, KEDDAMB M, KADRIA A. TAKENOUTIB H. Electrochemical impedance in a thin surface electrolyte layer influence of the potential probe location[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1987, 32(3): 445-448.
[12] DESLOUIS C, DUPRAT M, TOURNILLON C. The kinetics of zinc dissolution in aerated sodium sulfate solutions a measurement of the corrosion rate by impedance techniques[J]. Corrosion Science, 1989, 29(1): 13-30.
[13] QUINTANA P, VELEVA L, CAUICH W, POMES R, PENA J L. Study of the composition and morphology of initial stage of corrosion products formed on Zn plates exposed to the atmosphere of Southeast Mexico[J]. Applied Surface Science, 1996, 99(4): 325-334.
[14] ALEIDA E, MORCILLO M, ROSALES B. Atmospheric corrosion of zinc Part: Rural and urban atmospheres[J]. British Corrosion Journal, 2000, 35(4): 284-288.
[15] ALMEIDA E, MORCILLO M, ROSALES B. Atmospheric corrosion of zinc PartⅡ: Marine atmospheres[J]. British Corrosion Journal, 2000, 35(4): 289-296.
[16] ODNEVALL I, LEYGRAF C. Formation of Zn4SO4(OH)6·4H2O in a rural atmosphere[J]. Corrosion Science, 1994, 36(6): 1077-1091.
[17] ODNEVALL I, LEYGRAF C. Formation of NaZn2Cl(OH)6- SO4·6H2O in a marine atmosphere[J]. Corrosion Science, 1993, 34(7): 1213-1229.
[18] AZMAT N S, RALSTON K D, MUDDLE B C, COLE I S. Corrosion of Zn under acidified marine droplets[J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(4): 1604-1615.
[19] 王振尧, 于国才, 韩 薇. 我国若干典型大气环境中的锌腐蚀[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2003, 15(4): 191-195.
WANG Zhen-yao, YU Guo-cai, HAN Wei. Atmospheric corrosion performance of zinc at several selected test sits in China[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2003, 15(4): 191-195.
[20] 严川伟, 史志明, 林海潮, 曹楚南. Zn在SO2环境中大气腐蚀初期表面特性研究[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2000, 12(3): 151-153.
YAN Chuan-wei, SHI Zhi-ming, LIN Hai-chao, CAO Chu-nan. Laboratory investigation of the initially corroded zinc surfaces in air containing SO2[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2000, 12(3): 151-153.
[21] 安百刚, 张学元, 韩恩厚, 李洪锡. Zn在模拟酸雨溶液中及其液膜下的腐蚀[J]. 金属学报, 2004, 40(2): 202-206.
AN Bai-gang, ZHANG Xue-yuan, HAN En-hou, LI Hong-xi. Corrosion of zinc in simulated acid rain solution and under thin electrolyte layer formation by simulated acid rain solution[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2004, 40(2): 202-206.
[22] DILER E, ROUVELLOU B, RIOUAL S, LESCOP B, NGUYEN G, THIERRY D. Characterization of corrosion products of Zn and Zn-Mg-Al coated steel in a marine atmosphere[J]. Corrosion Science, 2014, 87: 111-117.
[23] 谈 天, 陈 彤, 张俊喜, 邢逸俊, 洪毅成. 镀锌钢在模拟不同服役环境中的腐蚀行为[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2014, 35(4): 307-320.
TAN Tian, CHEN Tong, ZHANG Jun-xi, XING Yi-jun, HONG Yi-cheng. Corrosion behavior of galvanized steel in different simulated service environments[J]. Corrosion and Protection, 2014, 35(4): 307-320.
[24] MAGAINO S, SOGA M, SOBUE K, KAWAGUCHI A, ISHIDA N, IMAI H. Zinc corrosion in simulated acid rain[J]. Electrochimical Acta, 1999, 44(24): 4307-4312.
[25] ZIN I M, HOWARD R L, BADGER S J, SCANTLEBURY J D, LYON S B. The mode of action of chromate inhibitor in epoxy primer on galvanized steel[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings, 1998, 33(3/4): 203-210.
[26] 黎学明, 刘 强, 孔令峰, 周建庭. 模拟酸雨溶液中应力对镀锌钢绞线腐蚀行为影响[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护, 2008, 20(1): 44-46.
LI Xue-ming, LIU Qiang, KONG Ling-feng, ZHOU Jian-ting. Corrosion behavior of galvanized steel under stress in simulated acid rain solution[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2008, 20(1): 44-46.
[27] YADAV A P, NISHIKATA A. TSURU T. Electrochemical impedance study on galvanized steel corrosion under cyclic wet-dry conditions-influence of time of wetness[J]. Corrosion Science, 2004, 46(1): 169-181.
[28] SERE P R, ZAPPONI M, ELSNER C I, DI SARLI A R. Comparative corrosion behavior or 55 aluminum-zinc alloy and zinc hot-dip coatings deposited on low carbon steel substrate[J]. Corrosion Science, 1998, 40(10): 1711-1723.
[29] GRAEDEL T E. Corrosion mechanisms for zinc exposed to the atmosphere[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1989, 136(4): C193-C203.
[30] SVENSSON J E, JOHANSSON L G. A laboratory study of the initial-stages of the atmospheric corrosion of zinc in the presence of NaCl-influence of SO2 and NO2[J]. Corrosion Science, 1993, 34(5): 721-740.
[31] ODNEVALL I, LEYGRAF C. Reaction sequences in atmospheric corrosion of zinc[C]// KIRK W W, LAWSON H H. American Society for Testing and Materials Special Technical Publication.Philadelphia: ASTM, 1995: 215-229.
[32] COLE I S, GANTHER W D,FURMAN S A, MUSTER T H, NEUFELD A K. Pitting of zinc: Observations on atmospheric corrosion in tropical countries[J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(3): 848-858.
[33] ZHANG H, LI X G, DU C W, QI H B. Corrosion behavior and mechanism of the automotive hot-dip galvanized steel with alkaline mud adhesion[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2009, 16(4): 414-421.
[34] ASSAF F H, ABD EI-REHIEM S S, ZAKY A M. Pitting corrosion of zinc in neutral halide solutions[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 1999, 58(1): 58-63.
[35] 周学杰, 张三平, 郑鹏华, 周 婵, 安江峰. 纯锌在水环境中腐蚀行为[J]. 装备环境工程, 2008, 5(5): 9-12.
ZHOU Xue-jie, ZHANG San-ping, ZHENG Peng-hua, ZHOU Chan, AN Jiang-feng. Corrosion behavior of pure Zn in water[J]. Equipment Environmental Engineering, 2008, 5(5): 9-12.
[36] FEDRIZZI L, CIAGHI L, BONORA P L, FRATESI R, ROVENTI G. Corrosion behavior of electrogalvanized steel in sodium-chloride and ammonium-sulfate solutions: A study by EIS[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1992, 22(3): 247-254.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:南网科技项目(K-GD2014-0532);国防技术资助项目(H102011B002)
收稿日期:2014-05-25;修订日期:2014-10-17
通信作者:王振尧,研究员,硕士;电话:024-23893544;E-mail: zhywang@imr.ac.cn