文章编号:1004-0609(2007)03-0384-06
Al-9.6%Mg合金高压凝固组织及稳定性
王振玲,王宏伟,魏尊杰,曹 磊
(哈尔滨工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,哈尔滨 150001)
摘 要:利用扫描电镜、X射线衍射仪和透射电镜对6 GPa高压下凝固的Al-9.6%Mg合金的显微组织以及组织的稳定性进行研究,对高压亚稳相形成机理进行探讨。结果表明:常压下枝晶间大量存在的Al3Mg2相在高压凝固时消失,形成另一密排六方结构相;经300 ℃, 11 h时效处理后,组织变得不稳定,六方结构相消失,转变成稳定的Al3Mg2相,但其形态由常压下三岔分界形式转变成团状,由此推断该六方结构相为亚稳相;在高压凝固条件下Mg在Al基体中的固溶度由7.74%增大到11.3%,Al相的晶格常数增加, 在XRD图中表现为Al相衍射峰左移,但经时效处理后,Al相衍射峰基体又回复到常压时的位置。
关键词:高压凝固组织;Al-Mg合金;时效处理
中图分类号:TG 113.12;TG 146.2 文献标识码:A
High pressure solidification microstructure and stability of Al-9.6%Mg alloy
WANG Zhen-ling, WANG Hong-wei, WEI Zun-jie, CAO Lei
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China)
Abstract: The microstructure and its stability were investigated when Al-9.6%Mg alloy was solidified under 6GPa high pressure using SEM, XRD and TEM. The formation mechanism of high pressure metastable phase was discussed. The results show that a hexagonal phase forms under high pressure solidification conditions instead of a great amount of interdendritic Al3Mg2 phases under normal pressure. This phase disappears after aging treatment (300 ℃, 11 h), and they are transformed into the stable Al3Mg2 phase, but its morphology changes from the branching to agglomerate. So it is deduced that the hexagonal phase formed at 6 GPa pressure is a metastable phase. In addition, the solid solubility of Mg in Al matrix increases from 7.74% to 11.3%, and the lattice constant of α(Al) phase also increases, the diffraction peaks of Al move to the left in XRD patterns. However, the position of the diffraction peaks of Al is almost the same as that of normal pressure after aging treatment.
Key words: high pressure solidification microstructure; Al-Mg alloy; aging treatment
金属的凝固过程对凝固组织形貌、相的组成及其大小和分布起着决定性作用,从而决定铸件的各种性能。传统的铸造过程主要是通过调整温度来控制凝固过程,而忽略压力对凝固过程的影响。随着高压设备及技术的改进,高压在材料科学领域的应用越来越广泛。尤其是压力达到GPa数量级时,极大地改变了合金的液/固相变过程。利用压力对相变点的影响,一些常压下的晶态材料在高压凝固后转变成纳米晶[1-3]及非晶材料[4-6],尤其是那些凝固过程体积膨胀的特殊合金系,如Cd-Sb,Cd-As和Cu-Ti等合金系在高压凝固后更容易转变成非晶合金。亚共晶Al-9.21%Si(质量分数,下同)合金在5.5 GPa高压下凝固时,初生α相由常压下枝状生长转为胞状生长,Si在α相中的固溶度增加[7-8]。当过共晶Al-26.6%Si合金在同样的高压下凝固时,过共晶合金成分中出现大量初生α相,并有α+β+(α+β)共晶的共生组织[9]。而与Al-Si合金类似的Al-Ge合金在高压下凝固时,不同Ge含量的过共晶合金中初生β相的形态不同。在常压下为过共晶的Al-60%Ge合金在高压凝固时也出现了大量的初生α相。另外,高压下Ge的生长方式发生改变,趋向于非小平面长大方式[10]。目前,人们对以上这些高压凝固研究主要集中于非晶、纳米晶等亚稳材料以及金属-半导体系简单二元合金,而对于金属-金属系合金的高压凝固研究较少。Al-Mg合金具有密度小、比强度高、室温力学性能较好、耐腐蚀性强等优点,多用作与液体相接触的器件,并在汽车与造船等领域也得到广泛的应用。由于该合金中Al和Mg都具有熔化过程体积膨胀性质,高压凝固时合金的熔点将大幅度增加,这势必对凝固组织和相变产生很大影响。在此,本文作者对高压下Al-Mg合金进行研究。
1 实验
用纯度为99.97%的纯铝和纯镁配制Al-12%Mg 合金。在金属型中浇成圆棒铸锭,化学分析结果显示 该合金成分为Al-9.6%Mg。将铸锭加工成高压试样,d5 mm×5 mm。高压凝固在CS-1B型高压六面顶压机上进行。
在本实验中,试样用BN粉末进行包裹,用叶腊石做密封兼传压材料。将压力升高到6 GPa后,开始加热到熔化温度1 000 ℃,保温保压6 min后停止加热,待试样冷却到室温,卸压,取出试样供测试分析用。
合金的显微组织及微区成分分别用 JEOL S-570 型扫描电镜及所附带的能谱进行分析。物相分析在Rigaku D/max-RB 型X射线衍射仪及CM12型透射电镜上进行。6 GPa高压凝固时的熔化冷却曲线用X-Y记录仪测量,如图1所示,根据冷却曲线估算,冷却速度大约为300 K/s,而常压下仅为100 K/s左右。
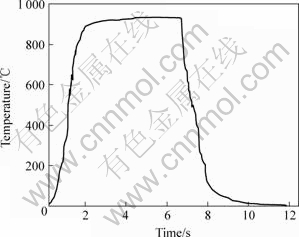
图1 Al-9.6%Mg合金在6 GPa高压凝固时的冷却曲线
Fig.1 Cooling curve of Al-9.6%Mg alloy solidified at 6 GPa pressure
2 结果与讨论
常压凝固的Al-9.6%Mg合金容易形成粗大的离异共晶组织,由初生α(Al)相和枝晶间的Al3Mg2相组成,如图2(a)所示。但在6 GPa高压凝固时,其组织与常压下的组织完全不同。图2(b)所示为Al-9.6Mg合金在6 GPa高压下的凝固组织,可见,枝晶间粗大的Al3Mg2相消失。除了少数的黑色腐蚀坑外,枝晶间为灰色相。微区成分分析结果表明,高压下Al基体中Mg原子的固溶度为11.3%,枝晶间灰色相的Mg含量为21.7%。而常压下Al基体中Mg的固溶度仅为7.74%,枝晶间Al3Mg2相中的Mg含量为36.19%。由此可见,高压凝固时,Mg在Al基体中的固溶度明显增加,枝晶间的灰色相中Mg的含量与Al3Mg2相中Mg的含量相比显著减小,但仍属于富Mg物质。很明显,高压增大了合金的固溶度,同时高压下相组成也发生了明显变化。高压下溶质原子在基体中的固溶度增加;另一方面,高压作用于熔体的凝固过程导致熔体粘度增加,原子扩散困难[11],即使在常压条件下冷速凝固,高压仍对固溶度的增加有一定贡献。图3所示为该合金的X射线衍射图,常压下凝固时合金由α-Al相与Al3Mg2相组成。 但是高压凝固试样的XRD图上,Al3Mg2相的衍射峰消失,只能看到Al相的衍射峰。这表明在高压凝固条件下,未产生Al3Mg2相,或者该相的数量太少,其衍射峰太弱,不能分辨。同时, Al相的衍射峰左移,这表明铝晶格常数增大。由于高压下Mg在Al基体中的固溶度增加,且Mg原子的共价半径为0.136 nm,大于Al原子的共价半径0.118 nm,结果造成α(Al)相的晶格常数增大。
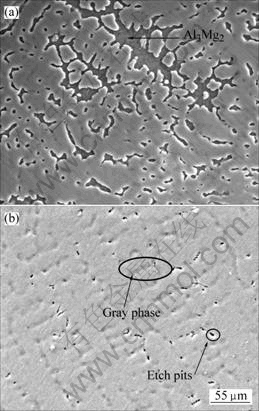
图2 Al-9.6%Mg合金凝固组织在不同压力下的SEM形貌
Fig.2 SEM morphologies of Al-9.6%Mg alloy solidified under different pressures: (a) Normal pressure; (b) 6 GPa
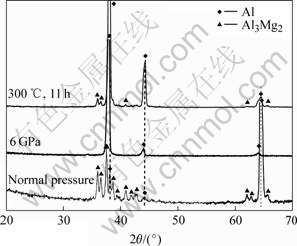
图3 合金在常压、高压及高压试样时效态的X射线衍射谱
Fig.3 XRD patterns of Al-9.6%Mg alloy solidified under normal pressure and high pressure as well as after aging for high pressure solidified sample
为进一步确定高压凝固条件下的物相组成,对高压凝固试样进行透射电镜观察,结果如图4(a)所示。可以看出,在Al基体上分布着大量暗衬度物相,不均匀地弥散在Al基体上。含暗衬度相的选区衍射(SAD)谱(见图4(b))共有2套衍射斑点,其中一套为Al 晶带,晶格常数为0.4 nm,比标准的Al的晶格常数小0.004 9 nm;另一套衍射斑点经标定为密排六方结构,由于第二相粒子尺寸很小且受透射电镜本身的限制,衍射斑点并不是很理想,因此,晶格常数未能标出,定义该相为AlxMgy相。此外,对合金的普通Al基体区域A(图4(a))也进行了选区衍射(见图4(c)),经计算其晶格常数为0.411 7 nm,远远大于与弥散相共存部分的Al相晶格常数(0.400 0 nm)。因此,可以推断高压下形成的AlxMgy相应该是从Mg含量很高的富Mg区析出,结果造成Al晶格常数急剧减小。由此可知,在6 GPa高压凝固条件下,Al3Mg2相消失,形成了另一密排六方结构相。
晶带,晶格常数为0.4 nm,比标准的Al的晶格常数小0.004 9 nm;另一套衍射斑点经标定为密排六方结构,由于第二相粒子尺寸很小且受透射电镜本身的限制,衍射斑点并不是很理想,因此,晶格常数未能标出,定义该相为AlxMgy相。此外,对合金的普通Al基体区域A(图4(a))也进行了选区衍射(见图4(c)),经计算其晶格常数为0.411 7 nm,远远大于与弥散相共存部分的Al相晶格常数(0.400 0 nm)。因此,可以推断高压下形成的AlxMgy相应该是从Mg含量很高的富Mg区析出,结果造成Al晶格常数急剧减小。由此可知,在6 GPa高压凝固条件下,Al3Mg2相消失,形成了另一密排六方结构相。
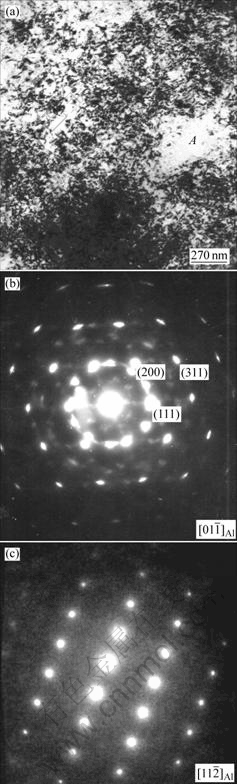
图4 Al-9.6%Mg合金在6 GPa高压下凝固后的TEM组织形貌及衍射斑点
Fig.4 TEM morphology and diffraction patterns of Al- 9.6%Mg alloy solidified under 6 GPa pressure: (a) Morphology of the second phase; (b) SAD pattern of the second phase; (c) SAD pattern of common Al matrix
据Ostwald台阶规律,液态凝固时要连续经历各种高温相,最后达到平衡相。压力作为热力学参数之一,通过改变原子间的相互作用而使液态相对稳定性发生变化。由于一般亚稳相具有单胞小、对称性强及原子真充率大的特点,亚稳相在高压下容易成核[12];此外,高压抑制原子扩散,对相结构演化起到一种延缓作用,而在高压下,凝固速度较快,这同样有利于高压亚稳相的形成[13]。在本实验中,为了考察高压凝固组织及相的稳定性,对高压凝固试样进行时效处理,时效工艺为300 ℃, 11 h。时效处理后的显微组织见图5。可以看出在高压凝固条件下溶质含量较高的枝晶间析出了大量的第二相,枝晶臂上也有少量析出。从图3所示的XRD可知,这些析出相是稳定的Al3Mg2相。另外,由于Al3Mg2相的析出,基体中Mg 的固溶度下降,导致Al的衍射峰重新向右偏移,基本上与常压下的衍射峰位置相当。同时,对时效处理的试样进行透射电镜观察,第二相的形态如图6(a)和(b)所示。该形态以团状形式分布在Al基体上,不同于常压下的三岔形态。这主要是该相通过时效析出形成所致。对图6(b)中的第二相(暗衬度部分)进行选区衍射,结果如图6(c)所示。经标定,该相属面心立方结构,晶格常数为2.801 nm,与Al3Mg2相的晶格一致[14]。较亮衬度的区域B的选区衍射见图6(d),标定后该部分为Al相。通过分析可知:高压下形成的密排六方结构的AlxMgy相为不稳定的亚稳相,经300 ℃, 11 h时效处理后消失,转变为稳定的Al3Mg2相。
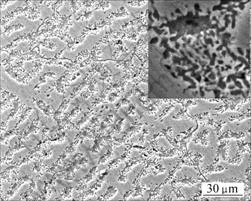
图5 Al-9.6%Mg合金高压凝固试样经300 ℃, 11 h时效处理后的SEM形貌
Fig.5 SEM morphologies of high pressure solidification sample Al-9.6%Mg alloy aged at 300℃ for 11 h
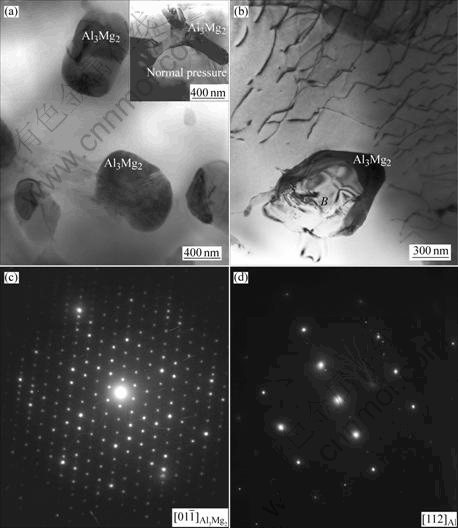
图6 Al-9.6%Mg合金高压凝固试样时效处理后TEM形貌
Fig.6 TEM morphologies of high pressure solidification sample after aging in Al-9.6%Mg alloy: (a), (b) Morphology of the second phase; (c) SAD pattern from dark area in Fig.5 (b); (d) SAD pattern from area “B” indicated in Fig.5(b)
Al-9.6Mg合金在高压凝固条件下形成亚稳相的机理可从形核的热力学角度进行解释。在最后凝固的枝晶间的富Mg熔体中形成稳定相还是亚稳相,主要取决于形核驱动力,为研究方便,假设冷却过程中形核为均匀形核,临界形核功可表示为

将?G* 对P求一阶偏导,因为σ随P的变化微小,可忽略不计,故[1]:

可见,无论增容反应(0<ΔV*≤1)还是减容反应(ΔV *<0),临界形核自由能ΔG都随着压力的增大而降低。一般亚稳相远偏离平衡态,具有更高的过剩能[13]。但在压力作用下,尤其是压力达到GPa数量级时,亚稳相的形核自由能将大大减小,当亚稳相的临界形核功小于稳定相的形核功时,亚稳相要优先于稳定相在组织中形核并长大。此外,在高压凝固条件下熔体的过冷度增大[15-16],在这种大的过冷度下,这对于密度较小的金属来说非常有利于亚稳相析出[17]。由此可见,高压凝固条件有利于亚稳相的形成。
3 结论
1) Al-9.6%Mg合金在6 GPa高压下凝固时,Al3Mg2相消失,形成尺寸极小的密排六方结构相,弥散分布在Al基体上。但该相是不稳定的,经300 ℃,11 h的时效处理后消失,重新形成稳定的Al3Mg2相。因此,Al-9.6%Mg合金的高压(6 GPa)凝固组织中形成亚稳相。
2) 在高压凝固条件下,Al基体中Mg的固溶度增加,由常压下的7.74%增加到高压下的11.3%,α(Al)相的晶格常数增加。
REFERENCES
[1] 李冬剑. 高压下亚稳相相变机制[D]. 沈阳:中国科学院金属研究所,1983.
LI Dong-jian. Mechanism of the phase transformation of the metastable phase under high pressure [D]. Shenyang: Institute of Metals Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1983.
[2] 刘浩哲,贺红亮,王鲁红,等. 高压下SiC增强Al基纳米复合材料[J]. 高压物理学报,1999,13(1):1-6.
LIU Hao-zhe, HE Hong-liang, WANG Lu-hong, et al. Synthesis of SiCp/Al nanocomposite under ultra-high pressure [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 1999,13(1):1-6.
[3] 刘建军,王爱民,张海峰,等. 高压原位合成块体纳米Mg-Zn合金[J]. 材料研究学报,2001,15(13):299-302.
LIU Jian-jun, WANG Ai-min, ZHANG Hai-feng, et al. In situ synthesis of bulk nanocrystalline magnesium-zinc under high pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2001, 15(13): 299-302.
[4] 李冬剑. 压力诱至非晶合金形成[J]. 高压物理学报,1994,8(1):73-79.
LI Dong-jian. Pressure-induced formation of amorphous alloys[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 1994, 8(1): 73-79.
[5] 刘惠莲,刘永胜,王佐成,等. Fe50Ti50非晶合金的高温高压研究[J]. 吉林师范大学学报: 自然科学版,2003,3:10-12.
LIU Hui-lian, LIU Yong-sheng, WANG Zuo-cheng, et al. High temperature and high pressure study of Fe50Ti50 amorphous alloys[J]. Journal of Jilin Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2003, 3: 10-12.
[6] Hu Z Q, Ding B Z, Zhang H F, Li D J, Yao B, Liu H Z, Wang A M. Formation of non-equilibrium alloys by high pressure melt quenching[J]. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2001, 2: 41-48.
[7] 于溪凤,张国志,肖汉杰,等. 高压凝固亚共晶Al-Si合金的组织变异及生长机制[J]. 材料研究学报,2000,14(增刊): 141-144.
YU Xi-feng, ZHANG Guo-zhi, XIAO Han-jie, et al. Microstructure changes and growth mechanism of hypoeutectic Al-Si alloy solidified at high pressure [J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2000, 14(Suppl): 141-144.
[8] 胡火生,于溪凤,张国志,等. 超高压条件下凝固界面的稳定性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2000, 10(4): 484-486.
HU Huo-sheng, YU Xi-feng, ZHAGN Guo-zhi, et al. stability of solidification interface at superhigh pressure [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2000, 10(4): 484-486.
[9] 张国志,于溪凤,王向阳,等. 超高压凝固Al-Si合金的非平衡组织[J]. 金属学报,1999,35(3):285-288.
ZHANG Guo-zhi, YU Xi-feng, WANG Xiang-yang, et al. Non-equilibrium microstructure of Al-Si alloy solidified at superhigh pressure [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1999, 35(3): 285-288.
[10] 赵海丽. 高压下Al-Ge合金的凝固[D]. 秦皇岛:燕山大学,2005.
ZHAO Hai-li. Solidification of Al-Ge alloy under high pressure [D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2005.
[11] Batashef A E. 金属和合金在压力下结晶[M].张锦升,罗守靖, 译. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社,1987: 23.
Batashef A E. Crystallization of Metal and Alloys at Pressure[M]. ZHANG Jin-sheng, LUO Shou-yi, transl. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 1987: 23.
[12] 秦志成. 高压下Pd82Si18合金凝固过程中形成的亚稳相[J]. 高压物理学报,1994,8(2):107-112.
QIN Zhi-cheng. Formation of the metastable phases in Pd-18at.%Si alloy solidified under high pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 1994, 8(2): 107-112.
[13] 王文魁. 亚稳相的高压暴露[J]. 高压物理学报,1989,3(4):257-268.
WANG Wen-kui. Exposure of the metastable phase under high pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 1989, 3(4): 257-268.
[14] Mondolfo L F. Aluminum Alloys: Structure and Properties [M]. London: Butterworth & Co Publishers Ltd, 1976: 313.
[15] 张国志,辛启斌,王向阳,等. 高压变熔点过冷大体积近快速凝固[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版,1998,19(5):479-481.
ZHANG Guo-zhi, XIN Qi-bin, WANG Xiang-yang, et al. Nearby rapid solidification of liquid metal in bulk at high pressure[J]. Journal of Northeastern University: Natural Science, 1998, 19(5): 479-481.
[16] 王海燕,刘日平,马明臻,等. FeSi2合金在高压下凝固[J]. 物理学报, 2004,53(7):2378-2383.
WANG Hai-yan, LIU Ri-ping, MA Ming-zhen, et al. Solidification of FeSi2 alloy under high pressure[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2004,53(7): 2378-2383.
[17] 胡汉起. 金属凝固原理[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社,2000: 58.
HU Han-qi. Solidification Theory of Metal[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2000: 58.
基金项目:哈尔滨工业大学科学基金资助项目(HIT.2002.29)
收稿日期:2006-08-30;修订日期:2007-01-12
通讯作者:王振玲,博士研究生;电话:+86-451-86400332; E-mail: wzlhit@gmail.com
(编辑 陈灿华)