DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2019.02.04
微米/纳米SiC影响下非平衡凝固镁合金形核及组织细化
何 文1, 2,杨 伟2,王 祥2
(1. 南昌航空大学 江西省金属材料微结构调控重点实验室,南昌 330063;
2. 南昌航空大学 轻合金加工科学与技术国防重点学科实验室,南昌 330063)
摘 要:采用真空感应熔炼与阶梯铜模喷铸相结合,制备出微米/纳米SiC参与下快冷镁合金,研究SiC尺寸对非平衡凝固镁合金异质形核及组织细化的影响。结果表明:冷速的提高与SiC的添加共同促进镁合金的复合细化,其中铜模喷铸条件下微米SiC的细化效果更佳。当铜模内径di=4 mm,添加2%的微米SiC(质量分数)后快冷镁合金平均晶粒尺寸减小到5 μm以内。经(400 ℃, 2 h)等温固溶处理后,快冷合金晶界处的离异共晶β-Mg17Al12相消失,初生α-Mg晶粒由细小蔷薇状向多边形组织发生转变。通过枝晶生长与溶质截留模型的理论计算,铜模喷铸条件下获得的过冷度范围为67~80 K,所对应的临界形核半径为0.115~0.116 μm,因此,更有利于微米SiC对镁合金的组织细化。
关键词:非平衡凝固;异质形核;枝晶生长;组织细化;镁合金
文章编号:1004-0609(2019)-02-0248-07 中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
随着航空航天、国防科技和汽车工业可持续发展要求的提高,镁合金具有质轻、环境友好和资源丰富等突出优点而被誉为“绿色材料”,并被多国列为战略结构材料[1]。然而,镁合金普遍存在易氧化腐蚀、塑性和蠕变性能差等缺点,严重制约其在工程中的应用[2-4]。晶粒细化可有效减少缩孔及热裂倾向,缩短热处理周期,提高材料耐腐蚀性[5]。因此,镁合金晶粒细化已成为改善组织结构,获得高性能新材料的一种有效途径。
AZ91作为目前使用最广的铸造镁合金,具有良好的机械加工性能及均衡的力学性能,特别适合于制造复杂的薄壁零件[6]。然而该合金中的主要元素Al易与镁合金常用细化剂Zr发生反应,形成Al3Zr而弱化细化效果[7]。SiC与镁具有相似的晶体结构及良好的相容性,在AZ系列镁合金细化中发挥重要作用。LUO等[8]研究了AZ91/SiCP复合材料中的细化现象,并利用晶格错配度理论进行解释。CAI等[9]对SiC与镁晶体取向及界面相容性进行了表征。LELITO等[10]研究了镁合金晶粒尺寸随过冷度及SiC含量的变化,并采用统计学方法推导出形核过程中的关键参数。
快速凝固可以显著降低凝固潜热对形核的抑制影响,实现晶粒组织的细化[11-14]。GUPTA等[15]利用熔体喷射沉积技术制备出Mg/SiC复合材料,并获得良好的界面结合。MABUCHI等[16]采用单辊快冷技术制备出具有较高室温强度的Mg/Mg2Si复合材料。然而,有关快冷条件下细化剂尺寸对镁合金细化的影响研究尚未深入,非平衡条件下镁合金的异质形核机理仍需不断完善。根据GREER等[17]的非热形核理论,异质颗粒参与下的合金细化效果关键取决于外加颗粒的尺寸与凝固阶段的温度历程。因此,通过合金孕育与快速凝固相结合,系统研究非平衡效应作用下微米及纳米SiC对快冷镁合金的异质形核规律,对于镁合金细晶组织制备具有重要的指导意义。
1 实验
选用AZ91合金为原始材料,其成分为(质量分数,下同):Al 8.5%~9.5%, Zn 0.45%~0.9%, 其余为Mg。SiC颗粒的平均尺寸分别为2 μm和40 nm。实验合金成分为AZ91+2%SiC。
首先利用搅拌摩擦加工技术制备出含6%SiC的母合金,并实现其均匀分散。具体工艺步骤为:在厚度为12 mm的AZ91合金基板表面钻盲孔,其中基板尺寸为100 mm×15 mm×12 mm,孔间距为6 mm。SiC颗粒填入盲孔并压实后置于旋转搅拌摩擦设备型腔中进行挤压加工,其中机械旋转速度为300 r/min,挤压速度为15 mm/min。然后通过混合称重方式配比出所研究的AZ91+2%SiC目标合金。
铜模喷铸实验在高真空感应熔炼炉内进行。首先将实验合金装入石英坩埚内(坩埚尺寸:d 15 mm×150 mm,下方开有d 0.5 mm小孔),并置于内径为80 mm的水冷铜线圈内。调节支架位置确保坩埚底孔与铜模中心对齐,其中紫铜模具的外径80 mm,内径di由下至上依次为4、6、8 mm。为防止熔炼过程中镁合金氧化挥发,关闭舱体后首先预抽真空至5 Pa,然后返充高纯Ar气至炉内绝对压力为0.03 MPa。调节感应电源功率并采用标定后的双比色红外测温仪(美国雷泰,MM2MH)从坩埚侧壁进行实时测温。金属液经加热与散热达热平衡后在730 ℃保温5 min确保均匀混合,然后在坩埚上方通入绝对压力为0.12 MPa的高纯Ar气,金属液被垂直喷射入阶梯铜模内,从而制备出不同尺寸的快冷试样。为便于晶粒尺寸的统计分析,铜模喷铸试样随后进行(400 ℃, 2 h)的固溶处理。
试样经切割、镶嵌、打磨、抛光及腐蚀(腐蚀液为4%的柠檬酸)等标准金相制备步骤后,在VHX-600E三维超景深显微镜上进行光学显微组织分析,并利用Image-ProPlus软件通过截线法计算平均晶粒尺寸。采用FEI-Nova NanoSEM450场发射扫描电子显微镜和Quanta 200环境扫描电子显微镜进行高倍组织形貌分析,并利用INCA型能谱仪对微区成分进行测定。
2 结果与分析
2.1 SiC颗粒尺寸对快冷合金的组织细化
图1所示为铜模内径di=8 mm时快冷镁合金及其(400 ℃, 2 h)固溶处理后的光学显微组织,分别对应AZ91及其添加微米、纳米SiC后的合金。分析可知,铜模喷铸合金的原始非平衡凝固组织中初生相以细小蔷薇状为主,并且存在一定宽度的晶界(见图1(a)~ (c))。经400 ℃固溶处理后,晶粒形貌转变为多边形组织,晶界处第二相完全消失(见图1(d)~(f))。在未加细化剂的快冷合金中,晶粒较粗大且圆滑程度不高,局部存在不完整的枝晶组织(见图1(a)),所对应固溶组织中平均晶粒尺寸为34 μm(见图1(d))。添加2% SiC后,快冷AZ91合金的非平衡凝固组织得到显著细化,同时晶粒圆滑度明显提高。对比图1(b)和(c)可知,铜模喷铸条件下,微米SiC的细化效果要优于纳米颗粒的。结合固溶组织可进一步计算出微米和纳米颗粒参与下的快冷镁合金中平均晶粒尺寸分别为13 μm和22 μm (见图1(e)和(f))。
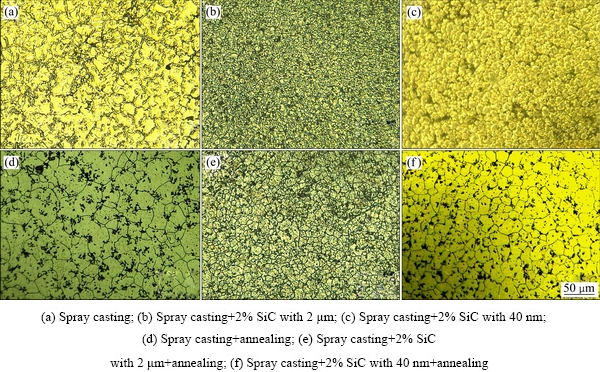
图1 铜模喷铸AZ91合金及其(400 ℃, 2 h)固溶处理后的光学显微组织(di=8 mm)
Fig. 1 Optical microstructures of spray casted AZ91 alloys and those after annealing at 400 ℃ for 2 h (di=8 mm)
图2所示为微米SiC作用下铜模喷铸镁合金SEM像及EDS能谱,其中铜模内径为8 mm。由AZ91凝固过程可知[18],该合金组织主要包括初生α-Mg基体和凝固末期溶质偏析形成的离异共晶β-Mg17Al12,分别对应图2中的黑色基体相和灰色网状晶界相。能谱分析表明,基体中主要溶质Al含量为4.9%,高于慢冷铸态含量,说明铜模快冷条件下,非平衡效应增强了溶质截留现象,提高了基体中溶质含量。通过对图2中颗粒物进行能谱分析可知,该相主要组成元素为C和Si,因此可判断为所添加的SiC细化剂。虽然原始颗粒平均尺寸为2 μm,然而在搅拌摩擦分散过程中,陶瓷颗粒的硬脆特征导致其在强机械摩擦力下发生破碎,因此除局部存在较大颗粒外,SiC的整体平均尺寸有所减小。
图3所示为纳米SiC作用下铜模喷铸镁合金SEM像及EDS能谱,其中铜模内径di为8 mm。对比图2可知,纳米颗粒影响下快冷合金的晶粒尺寸有所增加,平均大小约为18 μm,这与图1结果基本一致,说明铜模喷铸条件下,纳米颗粒的细化效果有所减弱。能谱分析结果表明,基体中Al元素含量为4.06%。根据溶质截留理论,快速凝固条件下当凝固界面迁移速度高于界面前方液相中溶质扩散速度时,溶质原子将由于扩散不及时而以过饱和固溶体形式存在,非平衡溶质分配系数也将随生长速度而变化[19]。由于图2和3中初生α-Mg的溶质含量相差不大,因此可推断二者生长速度基本接近。
2.2 铜模内径对快冷合金组织细化的影响
为进一步研究冷却速率对快冷镁合金组织细化的影响,图4所示为铜模内径6 mm和4 mm时快冷合金的固溶显微组织,其中均添加2%的微米SiC。对比可知,随着铜模内径的减小,合金细化效果增强,其中内径4 mm时平均晶粒尺寸已减小到5 μm以内(见图4(b))。这是由于铜模内径4 mm时所获得的激冷效果更佳,因此通过提高冷速与孕育剂相结合的复合细化方式,可以获得理想的细化效果。
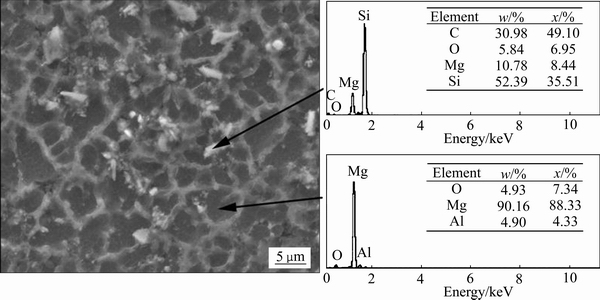
图2 添加2 μm SiC后铜模喷铸AZ91合金SEM像及EDS能谱(di=8 mm)
Fig. 2 SEM images and EDS spectra of spray casted AZ91 alloy after adding SiC particles with diameter of 2 μm (di=8 mm)
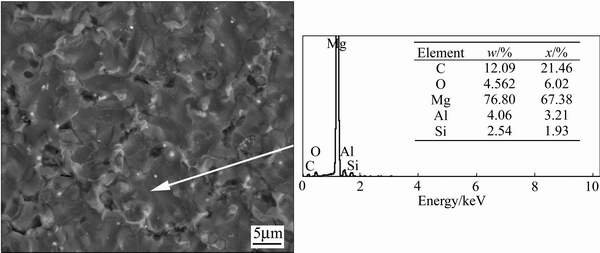
图3 添加40 nm SiC后铜模喷铸AZ91合金SEM像及EDS能谱(di=8 mm)
Fig. 3 SEM image and EDS spectra of spray casted AZ91 alloy after adding SiC particles with diameter of 40 nm (di=8 mm)
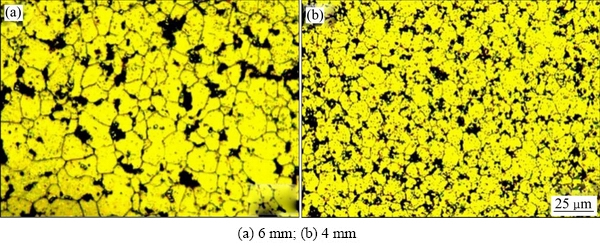
图4 不同铜模内径下添加2 μm SiC固溶(400 ℃, 2 h)后快冷AZ91合金的固溶光学组织
Fig. 4 Optical microstructures of spray casted AZ91 alloy with copper mould of different inner diameters after adding 2% SiC with 2 μm and annealing at 400 ℃ for 2 h
2.3 快冷合金凝固过程中的形核和生长分析
凝固过程涉及热力学、动力学、热/质传输及界面行为等诸多复杂现象。随冷速提高,非平衡效应的增强直接影响到具体的形核和生长过程。根据枝晶生长模型,晶体长大过程中的总过冷度ΔT由4部分组 成[20]:
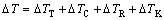 (1)
(1)
式中:ΔTT、ΔTC、ΔTR及ΔTK分别为热过冷、成分过冷、曲率过冷和动力学过冷。由于铜模喷铸属于正温度梯度下的非平衡凝固,凝固速度主要受凝固潜热的导出速率控制,因此,等式(1)中的热过冷度ΔTT可忽略不计,进而可整理为
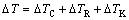 (2)
(2)
其中
 (3)
(3)
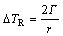 (4)
(4)
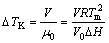 (5)
(5)
式中:m为平衡液相线斜率;c0为合金原始成分;ke为平衡分配系数;k为与生长速度V相关的非平衡分配系数;Γ为Gibbs-Thomson系数;r为枝晶尖端半径;Pc为溶质Peclet数;Iv为Ivantsor函数;V0为熔体中声速;Tm为纯熔剂熔点;R为气体常数;ΔH为熔化潜热。
基于LANGER和MULLER-KRUMBHAAR等界面稳定性研究,正温度梯度时枝晶尖端半径可由KGT模型来描述,具体表达式为[21]
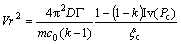 (6)
(6)
其中
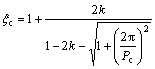 (7)
(7)
 (8)
(8)
根据传输动力学理论,当生长速度V与液相溶质扩散速度VD在数量级上相当时,扩散的非平衡效应,即弛豫效应在传输过程中将发挥重要作用,相应的溶质截留模型可表达为[22]:
 (9)
(9)
式中:VDI为界面处的溶质扩散系数。根据界面生长动力学理论(见式(1)~(5))及枝晶尖端稳定性判据(见式(6)~(8)),利用表1中所列AZ91合金的热物性参数[23-25],可计算出不同过冷度ΔT条件下的枝晶生长速度V。然后利用式(9)即可获得相应的溶质分配系数及固相中的主要溶质Al含量,具体结果如图5所示。当过冷度不是很大时,非平衡效应很弱,此时的过冷度主要为界面前方溶质过冷度,生长速度较慢,固相含量未发生明显变化,基本等于平衡溶质含量3.27%。随过冷度提高,枝晶生长动力学过冷度开始占据主体,生长速率加快,溶质截留现象趋于严重,导致初生相中溶质含量不断提高。结合图2和3中快冷合金固相含量的分析结果,可以推断出,铜模喷铸条件下的过冷度范围为67~80 K。
表1 AZ91合金的热物性参数[23-25]
Table 1 Physical parameters of AZ91 alloy[23-25]
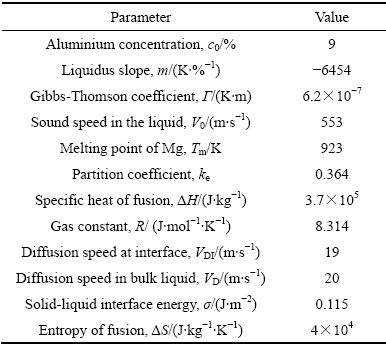
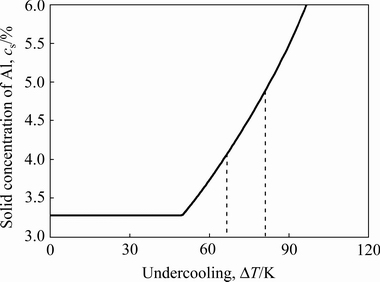
图5 不同过冷度时AZ91合金初生相中Al含量
Fig. 5 Calculated Al content in primary phase for AZ91 alloy with different undercoolings
根据GREER等[17]所提出的非热形核理论,形核事件的发生关键取决于临界形核半径与异质核心尺寸之间的相互竞争。因此,针对SiC颗粒参与下的镁合金晶粒细化,需要综合考虑颗粒特性与非平衡效应等因素,才能准确描述其形核规律。异质颗粒参与下的有效形核点尺寸r*可计算为
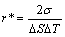 (10)
(10)
式中:σ为固/液界面能;ΔS为熔化熵。根据式(10)及表1中热物性参数,可以计算出不同过冷度条件下的有效形核尺寸,具体结果如图6所示。
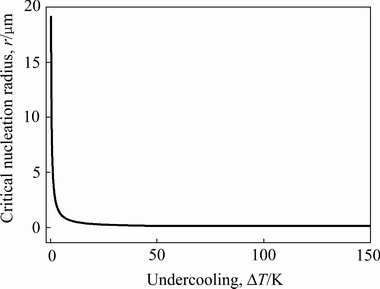
图6 不同过冷度时AZ91合金的有效形核尺寸
Fig. 6 Calculated effective nucleation size for AZ91 alloy with different undercoolings
当过冷度较小时,形核尺寸相应为微米级,这与GREER等[17]及LELITO等[10]的细化实验结果相吻合。随过冷度增加,有效形核尺寸急剧减小,其中铜模喷铸所获得的67~80 K过冷度范围内所对应的有效形核尺寸为0.115~0.116 μm。由非热形核理论可知,只有细化剂尺寸高于该尺寸时才能实现有效形核,而纳米颗粒平均尺寸仅为40 nm,低于该数值,不利于发挥其形核潜力。由于微米SiC尺寸高于该临界值,加之搅拌摩擦加工过程中颗粒的破碎还会进一步提高形核质点的数量(见图2),因此,能够获得最佳的细化效果。
3 结论
1) SiC的添加与冷速的提高可共同促进镁合金的复合细化,(400 ℃, 2 h)固溶处理后,快冷镁合金初生相形貌由细小蔷薇状向多边形组织发生转变。
2) 铜模喷铸条件下,微米SiC的细化效果优于纳米SiC的。当铜模内径4 mm时,2%的微米SiC可将AZ91镁合金晶粒尺寸细化到5 μm以内。
3) 铜模喷铸镁合金可获得67~80 K的过冷度,所对应的临界形核尺寸为0.115~0.116 μm,因此,更有利于微米SiC对镁合金的组织细化。
REFERENCES
[1] LUO A A. Magnesium casting technology for structural applications[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2013, 1(1): 2-22
[2] 杨文朋, 郭学锋, 梁世何. Ce对往复挤压—低温正挤压Mg-Zn-Ce合金组织与力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(12): 3336-3343.
YANG Wen-peng, GUO Xue-feng, LIANG Shi-he. Effects of Ce on microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Ce alloys processed by reciprocating extrusion and low-temperature forward extrusion[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(12): 3336-3343.
[3] 王长义. AZ91HP镁合金疲劳裂纹扩展行为与断裂机理[J]. 失效分析与预防, 2015, 10(2): 87-91.
WANG Chang-yi. Fatigue crack propagation behavior and mechanism of AZ91HP magnesium alloy[J]. Failure Analysis and Prevention, 2015, 10(2): 87-91.
[4] 梁键能, 林 翠. 温度对AZ91D镁合金初期大气腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 失效分析与预防, 2009, 4(1): 1-6.
LIANG Jian-neng, LIN Cui. Influence of temperature initial atmospheric corrosion behavior of AZ91D magnesium alloy[J]. Failure Analysis and Prevention, 2009, 4(1): 1-6.
[5] 王文礼, 张 薇, 雷宁宁, 王 杰. 稀土元素Sm、Ce对Mg-Y系合金组织和性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2016, 45(6): 1473-1476.
WANG Wen-li, ZHANG Wei, LEI Ning-ning, WANG Jie. Effect of Sm and Ce addition on microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg-Y series magnesium alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2016, 45(6): 1473-1476.
[6] 杨 伟, 殷海眯, 商景利, 王 祥, 刘吕果. SiC颗粒参与下快冷镁合金异质形核与高温晶粒长大[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2017, 27(2): 243-250.
YANG Wei, YIN Hai-mi, SHANG Jing-1i, WANG Xiang, LIU Lü-guo. Heterogeneous nucleation and grain growth at high temperature for quenched magnesium alloy containing SiC particle[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2017, 27(2): 243-250.
[7] GUNTHER R, HARTIG C, BORMANN R. Grain refinement of AZ31 by (SiC)P: Theoretical calculation and experiment[J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54(20): 5591-5597.
[8] LUO A. Processing, microstructure, and mechanical behavior of cast magnesium metal matrix composites[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1995, 26: 2445-2455.
[9] CAI Y, TAN M J, SHEN G J, SU H Q. Microstructure and heterogeneous nucleation phenomena in cast SiC particles reinforced magnesium composite[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 282(1/2): 232-239.
[10] LELITO J, ZAK P, SUCHY J S, KRAJEWSKI W, GREER A L, DARLAK P. 试验确定AZ91/SiC复合材料异质形核模型中决定于SiC质量分数和过冷度的晶粒密度函数[J]. 铸造, 2011, 60(3): 224-228.
LELITO J, ZAK P, SUCHY J S, KRAJEWSKI W, GREER A L,DARLAK P. Experimental determination of SiC and undercooling in AZ91/SiC composite heterogeneous nuclation model[J]. Foundry, 2011, 60(3): 224-228.
[11] 常亚涛, 郭学锋, 崔红保, 原志鹏, 朱攀攀. 冷却速度对B2-NiSc金属间化合物组织的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(7): 1444-1450.
CHANG Ya-tao, GUO Xue-feng, CUI Hong-bao, YUAN Zhi-peng, ZHU Pan-pan. Effect of cooling rate on microstructure evolution of alloy mainly consisted of B2-NiSc intermetallics[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(7): 1444-1450.
[12] LIU F, YANG G C. Rapid solidification of highly undercooled bulk liquid superalloy: Recent developments, future directions[J]. International Materials Reviews, 2006, 3: 146-170.
[13] 余 琨, 黎文献, 王日初, 冯 艳, 吴志文. 快速凝固镁合金开发原理及研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(7): 1025-1033.
YU Kun, LI Wen-xian, WANG Ri-chu, FENG Yan, WU Zhi-wen. Research theory and development of rapidly solidified magnesium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(7): 1025-1033.
[14] WANG W L, LI Z Q, WEI B. Macrosegregation pattern and microstructure feature of ternary Fe-Sn-Si immiscible alloy solidified under free fall condition[J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(14): 5482-5493.
[15] GUPTA M, LAI M. Synthesis, microstructure and properties characterization of disintegrated melt deposited Mg/SiC composite[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2000, 35: 2155-2165.
[16] MABUCHI M, KUBOTA K, HIGASHI K. High strength and high strain rate super plasticity in a Mg-Mg2Si composite[J]. Scripta Metallurgica et Material, 1995, 33(2): 331-335.
[17] QUESTED T E, GREER A L. Athermal heterogeneous nucleation of solidification[J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53: 2683-2692.
[18] 杨 伟, 陈寿辉, 张守银, 余 欢, 严青松, 蔡长春. 冷却速率对AZ91D镁合金非平衡凝固组织的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(3): 593-599.
YANG Wei, CHEN Shou-hui, ZHANG Shou-yin, YU Huan, YAN Qin-song, CAI Chang-chun. Effect of cooling rate on non-equilibrium solidified microstructure of AZ91D magnesium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(3): 593-599.
[19] LIU L, LI J F, ZHOU Y H. Solidification interface morphology pattern in the undercooled Co-24.0at.%Sn eutectic melt[J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(14): 5558-5567.
[20] WANG H P, YAO W J, WEI B. A remarkable solute trapping within rapidly growing dendrites[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 89(20): 201905.
[21] KURZ W, GIOVANOLA B, TRIVEDI R. Theory of microstructural development during rapid solidification[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1986, 34(5): 823-830.
[22] WANG H F, LIU F, CHEN Z, YANG G C, ZHOU Y H. Analysis of non-equilibrium dendrite growth in a bulk undercooled alloy melt: Model and application[J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55(2): 497-506.
[23] 胡耀波, 杨生伟, 姚青山, 潘复生. 挤压比及Mn含量对Mg-10Gd-6Y-1.6Zn-xMn镁合金组织和性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2017, 46(1): 135-142.
HU Yao-bo, YANG Sheng-wei, YAO Qing-shan. PAN Fu-sheng. Effects of extrusion ratio and Mn content on microstructure and properties of Mg-10Gd-6Y-1.6Zn-xMn magnesium alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2017, 46(1): 135-142.
[24] LI M, TAMURA T, MIWA K. Controlling microstructures of AZ31 magnesium alloys by an electromagnetic vibration technique during solidification: From experimental observation to theoretical understanding[J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55(14): 4635-4643.
[25] MONTIEL D, GUREVICH S, OFORI-OPOKU N, PROVATAS N. Characterization of late-stage equiaxed solidification of alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 77: 183-190.
Nucleation and microstructure refinement of non-equilibrium solidified magnesium alloy containing micro/nano SiC
HE Wen1, 2, YANG Wei2, WANG Xiang2
(1. Key Laboratory for Microstructural Control of Metallic Materials of Jiangxi Province, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China;
2. National Defence Key Discipline Laboratory of Light Alloy Processing Science and Technology, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China)
Abstract: With the combination of vacuum induction melting and spray casting by step copper mould, rapid cooled magnesium alloys containing micro/nano SiC were fabricated, and then the influence of particle size of SiC on heterogeneous nucleation and microstructure refinement was investigated. The results show that both the increase of cooling rate and the addition of SiC promote grain refinement of magnesium alloy, whereas, the effect of SiC with micron size is better than that with nano under spray casting condition. As for the copper mould with inner diameter di=4 mm, the addition of 2% micron SiC generates the reduction of average grain size within 5 μm. After solid solution treatment at 400 ℃ for 2 h, the grain morphology of primary α-Mg phase transits from fine rosette to polygon, accompanied by the disappearance of divorced eutectic β-Mg17Al12 phase at grain boundary. According to the theoretical calculation of dendrite growth and solute trapping model, the obtained undercooling range for spray casting is 67-80 K,which corresponds to the critical nucleation radius with 0.115-0.116 μm. Consequently, SiC particle with micron size is advantageous for microstructure refinement.
Key words: non-equilibrium solidification; heterogeneous nucleation; dendrite growth; microstructure refinement; magnesium alloy
Foundation item: Project(51461032) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China; Projects(GJJ14504, GJJ160715) supported by the Education Department of Jiangxi Province, China; Project (JW201523005) supported by the Open Project of Key Laboratory for Microstructural Control of Metallic Materials of Jiangxi Province, China
Received date: 2017-11-15; Accepted date: 2018-05-22
Corresponding author: YANG Wei; Tel: +86-791-86453167; E-mail: nchkyw@163.com
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51461032);江西省教育厅资助项目(GJJ14504,GJJ160715);江西省金属材料微结构调控重点实验室开放基金资助项目(JW201523005)
收稿日期:2017-11-15;修订日期:2018-05-22
通信作者:杨 伟,副教授,博士;电话:0791-86453167;E-mail:nchkyw@163.com