铝电解槽电热场计算精度与网格密度的关系
崔喜风,张红亮,邹忠,徐宇杰,李劼,张翮辉,赖延清
(中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:以某300 kA铝电解槽为实验对象,利用有限元商业软件ANSYS12.0建立其1/4槽电热模型,研究电热场计算精度与网格密度的关系。首先,通过在同一模型但不同网格划分策略下的计算结果和计算时间的实验比较,初步确定整体网格划分方案,再在模型局部区域进行网格疏密的探索研究。研究结果表明:对于铝电解槽电热场仿真精度而言,电流密度越大的区域受网格密度影响越大,应采用较细的网格;而电势梯度和温度梯度并非网格密度的决定性因素;最终确定所用算例模型的网格划分方案为:x和y方向单元尺寸均为30 mm,z方向阳极钢爪与阳极炭块接触部分取40 mm,z方向其余部分取70 mm,此时,计算精度高且计算效率最高。
关键词:铝电解槽;电热场;网格密度
中图分类号:TF821 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)03-0574-05
Relationship between thermal-electrical calculation accuracy of aluminum reduction cells and mesh density
CUI Xi-feng, ZHANG Hong-liang, ZOU Zhong, XU Yu-jie, LI Jie, ZHANG He-hui, LAI Yan-qing
(School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Taking a quarter model of 300 kA aluminum electrolysis cell as experimental subject, the impaction of mesh density on the thermal electrical calculation accuracy was discussed by the commercial software ANSYS12.0. Firstly, through the comparison of a series computing results and computing times of different grid segmenting strategies on the same model, the preliminary overall meshing policy was determined. Then local grid density was explored. The results show that the greater the current density, the more likely the calculation accuracy is influenced by the mesh density. However, the potential gradient as well as temperature gradient is less correlative. The final meshing strategy for the example in article is as follows: 30 mm for overall x and y coordinates element size, 40 mm for the coordinate on top layer, and 70 mm for z coordinate of rest parts, achieving high calculation accuracy with low time consumption.
Key words: aluminum electrolysis cell; thermal-electrical field; meshing density
有限元法是随着电子计算机的发展而迅速发展起来的一种现代计算方法,是以计算机和矩阵运算作为工具,对复杂工程问题或结构进行计算和分析的数值方法[1-2]。有限元方法的基本求解思想是把计算域划分为有限个互不重叠的单元,在每个单元内,选择一些合适的节点作为求解函数的插值点,将微分方程中的变量改写成由各变量或其导数的节点值与所选用的插值函数组成的线性表达式,借助于变分原理或加权余量法,将微分方程离散求解。在有限元方法中,在每个单元内选择基函数,用单元基函数的线性组合来逼近单元中的真解。整个计算域上总体的基函数可以认为由每个单元基函数组成的,因此,整个计算域内的解可以看作是由所有单元上的近似解构成[3]。由此可见,单元尺寸越小,计算结果越精确[4-5]。当网格数量增加到一定程度后,再继续细化,网格精度提高很小,而计算时间却大幅度增加。所以,应注意增加网格数量的经济性。实际应用时,可以比较2种网格划分的计算结果,若2次计算结果相差较大,则可以继续增加网格,若相反,则停止计算[6]。铝电解槽熔体温度高达960 ℃,腐蚀性强,很难进行温度和电流分布情况的测定。随着现代数学物理理论、数值模拟方法、计算机技术的发展,有限元计算方法以其适用于求解具有复杂几何形状和复杂边界条件的问题而得到迅速发展,目前在铝电解槽多物理场仿真计算中得到广泛的应用[7-8]。针对大型预焙铝电解槽这种大型模型,单元数高达百万数量级,很容易造成单元数超过硬件甚至软件的处理能力而无法计算。因此,在现有计算条件下,寻求既能够满足计算精度要求,又能够保证计算经济性的网格划分策略,显得尤为重要。在此,本文作者在HP高性能计算集群的计算节点HP ProLiant BL460c(CPU为 Intel E5430×2,内存DDR2-667 8GB)的硬件平台上,应用软件ANSYS12.0,建立300 kA铝电解槽1/4电热模型,并分别采用不同网格划分策略,分析电热计算结果与网格划分尺寸的关系,并以此来确定铝电解槽电热计算模型所采用的网格划分 策略。
1 实验模型
所研究的实验对象为某300 kA预焙铝电解槽,长度为7.536 m,宽度为2.036 m,高度为1.465 m。单元尺寸为70 mm时模型的网格划分图如图1所示。电解槽导电导热结构由阳极、电解质熔体、铝液、阴极和钢棒组成,采用SOLID69单元进行网格划分;其他部分如氧化铝覆盖料、电解质结壳、侧部炭块、槽帮伸腿、底部保温材料以及槽壳等仅导热但不导电部分
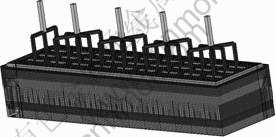
图1 模型网格划分图
Fig.1 Sketch of model mesh
采用SOLID70单元进行网格划分。阳极钢爪和阳极导杆结构简单,直接采用LINK68线单元建立。定义LINK68单元和炭阳极SOLID69单元间的电约束方程,以连接2种不同方式建立的结构实现电流的连续流动。
本模型将铝电解槽自上至下分为:氧化铝覆盖料层(含阳极),电解质结壳层(含阳极),含阳极电解质层,极间电解质层,铝液层,阴极炭块无钢棒层,阴极炭块含钢棒层以及底部保温结构层,如图2所示。划分网格时,定义单元尺寸,按照一定的顺序调用ANSYS结构化设计语言,自上往下分层划分网格。大部分体均可划分为六面体网格,但极少部分形状不规则体,无法扫过则划分为四面体网格。

(a) 氧化铝覆盖料层;(b) 电解质结壳层;(c) 含阳极电解质层;(d) 极间电解质层;(e) 铝液层;(f) 阴极炭块无钢棒层;(g) 阴极炭块含钢棒层;(h) 底部保温结构层
图2 模型分层示意图
Fig.2 Sketch map of model delamination
电流自阳极进入电解槽,流经电解质熔体和铝液,再经阴极炭块和钢棒流出。各导电部分特别是电解质熔体产生大量热量作为热源,再通过电解槽外表面与外部空气的热对流和热辐射作用将热量散失[9-10]。
在数值计算中,其电场和热场的控制方程分别如下:
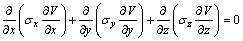 (1)
(1)
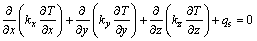 (2)
(2)
式中:V为电场强度;σ为电导率;T为热力学温度;k为导热系数;qs为热源强度;对于导电部分,qs等于控制单元的热量,对于非导电部分,qs等于0。通过电场产生的热量将电场和热场耦合起来进行计算。所采用电热计算方法见文献[11],本文所考察的重点为网格密度与计算结果(熔体温度、电压等)及计算效率(迭代次数、计算时间)的关系。
2 全局网格密度与仿真精度的关系
整体网格尺寸为70,60,50,40,35和30 mm时,计算得到的熔体温度和槽电压(槽内欧姆压降)以及计算时间如表1所示。
表1 采用不同全局网格尺寸的计算结果比较
Table 1 Comparison of calculated results for different overall element sizes
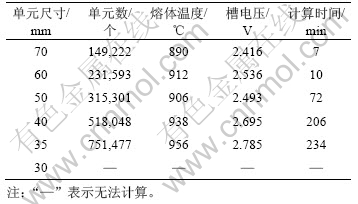
从表1可见:采用不同的单元尺寸进行网格划分所得的计算结果相差较大;随着单元尺寸变小,网格密度变大,网格数目急剧增加,计算得到的熔体温度与槽电压更加精确,但计算时间也大幅度增加。当单元尺寸为30 mm时,由于网格数量太多在所采用的软件及硬件平台上已经无法进行计算(硬件系统的内存分配及CPU资源已经无法满足要求,若进一步计算,则需要更加先进的软硬件平台),因此,暂时将35 mm确定为计算结果最接近实际值的单元尺寸。此时,电解质温度为956 ℃,槽电压为2.785 V,计算共耗时约4 h。
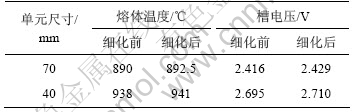
在计算数据变化梯度较大的部位要采用较大的网格密度[12],而铝电解槽底部、顶部和侧部温度梯度比较大。因此,分别在整体单元尺寸为70 mm和40 mm的基础上细化底部、顶部和侧部单元尺寸计算得到的结果如表2所示。从表2可以看出:细化保温结构前后计算结果相差很小。细化保温结构网格,仅仅使该部分的温度分布更加精确,但对该部分的散热量影响极小,并不是造成熔体温度和槽电压差异较大的主要原因。
为了考察导电部分的网格细化对于仿真结果的影响,采用4个方案进行网格划分:方案1令整体单元
表2 保温结构网格细化前后计算结果比较
Table 2 Comparison of calculated results before and after element refining in insulation constructions
尺寸为70 mm;方案2令x和y方向单元尺寸为35 mm,z方向70 mm;方案3令x和y方向单元尺寸为35 mm,z方向导电结构部分单元尺寸为35 mm,保温结构部分单元尺寸为70 mm;方案4令整体单元尺寸为35 mm。各方案的计算结果如表3所示。
表3 导电部分网格细化计算结果比较
Table 3 Comparison of calculated results different meshing strategies in conductive parts
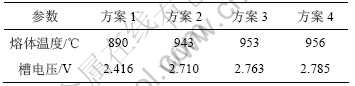
比较方案1和2的计算结果可知:x和y方向网格细化对计算结果有很大的影响;比较方案3和4的计算结果可知:导电部分z方向网格细化对计算结果也有一定影响,但影响较小,保温结构网格的细化对计算结果影响比较小,为保证计算时间的经济性,该部分可以忽略。因此,在确定了总体的网格密度之后,便可以对局部的网格密度(主要是整体x,y方向以及导电部分z方向单元尺寸)进行细致分析,以得到最优化的计算效率。
3 局部网格密度与仿真精度的关系
3.1 水平方向网格划分策略
保持导电部分z方向单元尺寸为35 mm,保温结构部分z方向为70 mm,分别取水平的x和y方向单元尺寸为35,30,25和20 mm,计算结果如表4所示。比较发现,当取单元尺寸为20 mm时由于网格数量过大计算机无法处理,而单元尺寸为30 mm与25 mm,熔体温度相差2 ℃,槽电压相差6 mV,都比较小。综合考虑计算精度以及计算时间经济性,水平x和y方向取单元尺寸为30 mm为宜。
表4 不同水平方向单元尺寸计算结果比较
Table 4 Results comparison of different xy coordinate element sizes
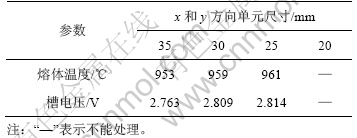
3.2 竖直方向导电部分整体网格划分策略
保持x和y方向单元尺寸30 mm,底部保温结构层z方向单元尺寸70 mm,分别取上部导电部分z方向单元尺寸30,35,40和50 mm,计算结果如表5所示。从表5可见:单元尺寸为35 mm和40 mm 时,计算结果相差不大,与单元尺寸为30 mm时的计算结果相比,熔体温度相差5 ℃,槽电压相差0.030 V,相对较小。因此,导电部分的竖直方向单元尺寸为 40 mm。
表5 不同导电部分竖直方向单元尺寸计算结果比较
Table 5 Comparison of calculated results different z coordinate element sizes in conductive parts
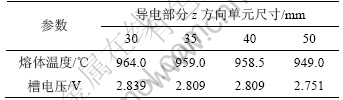
比较以上计算结果,取x和y方向整体单元尺寸30 mm,导电部分z方向单元尺寸40 mm,保温结构部分z方向单元尺寸70 mm。此时,共迭代10次,计算总耗时约4 h。
3.3 竖直方向局部网格划分策略
对以上确定的网格划分策略,虽然保证了计算精度,但计算时间比较长。由于网格划分的继承性,自上至下x和y方向单元尺寸不可变更。因此,可以采用分层稀疏化z方向网格的方法,以降低计算时间。
逐步将铝液层、阴极炭块含钢棒层、阴极炭块无钢棒层、电解质含阳极层、结壳层和上部氧化铝覆盖料层这些局部区域进行网格稀疏化,将其z方向单元尺寸设为70 mm。计算结果和计算时间如表6所示。
从表6可见:将铝液层、阴极层、电解质阳极层z方向网格逐步稀疏化之后计算结果变化很小,但计算时间降低了近2 h。结壳层单元尺寸变大后仍然划分为2层网格,所以计算结果及计算时间相同。上部氧
表6 竖直方向局部网格稀疏化后计算结果比较
Table 6 Comparison of calculated results before and after reducing local element density
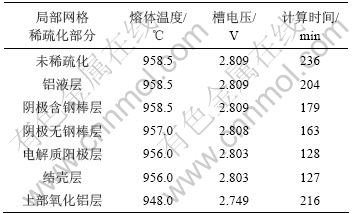
化铝层网格稀疏化之后,计算时间增至216 min,且计算精度降低,不可取。
极间电解质层厚度为50 mm,电势梯度大,网格划分时却仅为单层网格。将电解质层z方向网格细化为10 mm,计算得熔体温度957 ℃,槽电压2.809 V,细化电解质层前后计算结果变化很小。由此可见,电势梯度也不是网格细化与否的决定性因素。极间电解质层仍划分单层网格。
通过分析铝电解槽电流密度分布可知:在电流由阳极钢爪流向阳极炭块处,即上部氧化铝覆盖料层,是线单元与体单元的连接区域,有集中电流,电流密度很大。以上实验结果证明,计算结果主要受有电流集中的区域的网格密度的影响。因此,可以确定铝电解槽电热场计算精度与网格密度的关系为:电流分布受网格划分密度的影响很大,电流密度越大,越应将网格细化,所得电场精度越高,进而由电场影响其产生的热量,最终使得电解槽的热场精度越高,此时,热场又反过来通过材料非线性影响到电场,最终得到精度高的计算结果。
综合考虑计算精度、计算时间及硬件所能承受极限条件,最终将实验电解槽的底部保温结构部分以及阴极层、铝液层、电解质层和结壳层等无电流集中的区域z方向单元尺寸定为70 mm,氧化铝覆盖料层有电流集中的区域z方向单元尺寸设置为40 mm。此时,计算耗时127 min。
4 结论
(1) 温度梯度比较大的各部分保温结构以及电势梯度比较大的极间电解质层,网格划分尺寸对计算结果影响较小,无需划分过密的网格;而电流密度比较大的部位则受网格密度的影响很大,如钢爪与阳极的结合部位,此时,为获得准确的计算结果,应提高这部分的网格密度。因此,对于铝电解槽电热场计算,其计算精度主要受其电流集中区域的网格密度的影响,在网格划分上可遵循该思路适当调整全局和局部网格的密度。
(2) 对于本文的算例,上部氧化铝层处于阳极钢爪与阳极炭块的体单元的过渡区域,有很大的电流集中,故细化了该部分的网格,其x和y方向单元尺寸取30 mm,z方向取40 mm。由于网格划分的继承性,为划分六面体网格,其他部分x,y方向单元尺寸均取30 mm,z方向尺寸则可取70 mm,此时,在保证了计算精度的前提下,迭代次数最少,计算时间最短。
(3) 该网格划分思路及方法的确定可为提高铝电解槽电热仿真的精度和效率提供参考。
参考文献:
[1] 王瑞, 陈海霞, 王广峰. ANSYS有限元网格划分浅析[J]. 天津工业大学学报, 2001, 21(4): 8-11.
WANG Rui, CHEN Hai-xia, WANG Guang-feng. Analysis of ANSYS finite element mesh dividing[J]. Journal of Tianjin Institute of Textile Science and Technology, 2001, 21(4): 8-11.
[2] 李庆龄. ANSYS中网格划分方法研究[J]. 上海电机学院学报, 2006, 9(5): 28-30.
LI Qing-ling. Study of mesh dividing methods in ANSYS[J]. Journal of Shanghai Dianji University, 2006, 9(5): 28-30.
[3] 陶建华. 水波的数值模拟[M]. 天津: 天津大学出版社, 2005: 7-9.
TAO Jian-hua. Numerical simulation of water waves[M]. Tianjin: Tianjin University Press, 2005: 7-9.
[4] 金晶, 吴新跃. 有限元网格划分相关问题分析研究[J]. 计算机辅助工程, 2005, 14(2): 75-78.
JIN Jing, WU Xin-yue. Analysis of the finite element mesh problems[J]. Computer Aided Engineering, 2005, 14(2): 75-78.
[5] 古成中, 吴新跃. 有限元网格划分及发展趋势[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2008(3): 248-259.
GU Cheng-zhong, WU Xin-yue. A review of FEM and trend of development[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science & Technology, 2008(3): 248-259.
[6] 应世洲, 张建, 王国林, 等. 网格密度对全钢载重子午线轮胎有限元分析的影响[J]. 轮胎工业, 2008, 28(10): 579-582.
YING Shi-zhou, ZHANG Jian, WANG Guo-lin, et al. Effects of mesh density on finite element analysis for TBR tire[J]. 2008, 28(10): 579-582.
[7] 李劼, 程迎军, 赖延清, 等. 大型预焙铝电解槽电、热场的有限元计算[J]. 计算物理, 2003, 20(4): 351-355.
LI Jie, CHENG Ying-jun, LAI Yan-qing, et al. Numerical simulation of current and temperature fields of aluminum reduction cells based on ANSYS[J]. Chinese Journal of Computation Physics, 2003, 20(4): 351-355.
[8] 李劼, 邓星球, 赖延清, 等. 160 kA预焙铝电解槽在低分子比和低温条件下的三维电热场[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2004, 35(6): 875-879.
LI Jie, DENG Xing-qiu, LAI Yan-qing, et al. 3D Thermo-electric of 160 kA prebaked aluminum reduction cell at low cryolitic ratio and temperature[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology: Natural Science, 2004, 35(6): 875-879.
[9] Arkhipov G V. The mathematical modeling of aluminum reduction cells[J]. JOM, 2006, 58(2): 54-56.
[10] Dupuis M. Thermo-electric design of a 400 kA cell using mathematical models: A tutorial[C]//Peterson R D. Light Metals 2000. Nashville: TMS, 2000: 297-302.
[11] CUI Xi-feng, ZHANG Hong-liang, ZOU Zhong, et al. 3D freeze shape study of the aluminum electrolysis cells using finite element method[C]// Johnson J A. Light Metals 2010. San Diego: TMS, 2010: 447-452.
[12] 朱秀娟. 有限元分析网格划分的关键技巧[J]. 机械工程与自动化, 2009, 152(1): 185-186.
ZHU Xiu-juan. Pivotal skills in grid division in FEA[J]. Mechanical Engineering & Automation, 2009, 152(1): 185-186.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2010-08-10;修回日期:2010-10-13
基金项目:国家科技支撑计划项目(2009BAE85B03);国家高技术研究发展计划项目(2008AA030504);国家重点基础研究发展计划项目(2005CB623703);国家自然科学基金资助项目(50874120);国家自然科学基金资助项目(60634020)
通信作者:张红亮(1979-),男,湖南岳阳人,博士,讲师,从事冶金过程数值仿真及优化研究;电话:0731-88876454;E-mail: net_hotang@163.com