文章编号:1004-0609(2012)03-0686-08
老挝纳勐铜多金属矿区
花岗岩地质地球化学特征及成因
张文山1, 2,郭 旻1, 2
(1. 中南大学 有色金属成矿预测教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 地球科学与信息物理学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:纳勐铜多金属矿区主要的花岗岩类为黑云母二长花岗岩和钾长花岗岩。岩体w(SiO2)为73.45%~77.46%;K2O/Na2O=0.73~1.40,属于准过铝质至弱过铝质富硅钙碱性系列;岩石稀土总量偏低,明显富集大离子亲石元素,亏损高场强元素,Rb/Sr=0.40~4.00。综合分析表明:纳勐矿区花岗岩岩石成因类型相当于Ⅰ型花岗岩,熔融温度较高,成岩过程与幔源岩浆的底侵作用有关,热的幔源不仅为地壳的部分熔融提供了热量,且与熔融的壳源岩浆发生了混合作用。
关键词:花岗岩;地质特征;地球化学
中图分类号:P588.12 文献标志码:A
Geological and geochemical characteristics and petrogenesis of granites in NaMeung copper polymetal deposit, Laos
ZHANG Wen-shan1, 2, GUO Min1, 2
(1. Key Laboratory of Metallogenic Prediction of Nonferrous Metals, Ministry of Education,
Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Geosciences and Info-Physics, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The outcropped rockbody is mainly biotite monzogranite, potassium granite in the NaMeung copper polymetal deposit, Laos. The main rocks belong to metaluminous to weakly peraluminous high Si calc-alkaline series, with w(SiO2) of 73.45%-77.46%, K2O/Na2O=0.73-1.40. It is obvious that the rocks are enriched in LILE and depleted in HFSE, with relatively low ∑REE contents, Rb/Sr=0.40-4.00. The analysis results show that the rockbody is similar withⅠtype, and its partially melting is in the high temperature. The formation of the granites is related to magmatic underplating. The hot mantle magma not only provides heat for the partial melting of crust, but also causes magma mixing with the crustalderived melts.
Key words: granites; geology characteristics; geochemistry
老挝纳勐铜多金属矿区位于老挝国万象省赛松奔县,大地构造位置位于我国兰坪—思茅地洼区的南延部分[1],区内经历了印支、燕山、喜山期构造运动。印支早期为地洼初动期,印支晚期、燕山期为地洼激烈期,喜山期为地洼余动期[2]。地洼激烈期主要为强烈的岩浆活动,为区内成矿作用提供了重要的物源和热源。因此,研究该时期形成的花岗岩类的地球化学特征,可进一步打开区内的找矿前景。
自2005年起,我国有色金属矿产地质调查中心和中色金地资源科技有限公司承担了纳勐矿区的找矿勘查工作,目前,已经完成了矿区的详查工作,发现Cu、Pb、Zn、Mo矿化分布面积约2.5 km2。但是,目前对矿区花岗岩的地质地球化学特征没有深入的研究,这严重制约了本矿区的进一步找矿工作。为此,本文作者旨在初步探讨本区花岗岩地质地球化学特征,为本矿区的成矿规律提供必要的佐证,指导进一步的找矿工作。
1 矿区地质背景及岩体地质
矿区出露的地层主要为石炭系、二叠系和侏罗系(见图1)。石炭系地层主要分布在矿区的西部和东部,岩性为灰白色细-粗晶大理岩、细粒结晶灰岩,局部夹薄层泥质灰岩。结晶灰岩中常含燧石结核、碎块和团块。二叠系地层出露在矿区的东部,岩性为砂岩、页岩、泥灰岩。侏罗系地层主要分布在矿区的西部和南部,岩性为砂岩、页岩和泥岩。
矿区位于老挝境内北东向琅勃拉邦构造成矿带和北西向长山构造成矿带的交接部位。东西向的普比亚山(Phu Bia)燕山期—喜马拉雅山期普比亚花岗岩隆起及近东西向纳勐弧形断裂带和北东向赛松奔构造控制了区域内构造格架,在北东和北西向的构造带之间,形成近东西向的构造格架。
矿区目前已发现Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ号蚀变矿化带,共有7个铜铅锌矿体和1个钼矿化体。矿体总体呈近东西向分布,主要赋存在花岗岩与灰岩的接触带上。矿石类型主要为矽卡岩型矿石、块状硫化物矿石和花岗岩型矿石。
矿区花岗岩分布面积约为13 km2,主要分布在矿区的东北部,主要呈岩基、岩株产出。根据野外产状以及岩性的不同,可划分如下不同的侵入单元。
黑云母二长花岗岩侵入体(ηr51):见于矿区中部, 是矿区面积最大的、较重要的侵入体之一,也是矿区最早期的花岗岩深成岩体,主要呈岩基产出。岩体内部分带现象明显,从岩体中心到两侧依次可分为中心相(中粗粒黑云母二长花岗岩)、过渡相(中粒黑云母二长花岗岩)及边缘相(细粒黑云母二长花岗岩)。其中,边缘相内内原生流动构造较发育,偶见有围岩的捕掳体及析离体。原生的层节理、横节理较为发育,常发育花岗伟晶岩脉、细晶岩脉。岩体侵入于石炭系地层中,又被侏罗系地层覆盖,故其侵位时代确定为印支晚期。

图1 纳勐铜多金属矿区地质图:1—第四系;2—中侏罗统上段;3—中侏罗统下段;4—二叠系上统;5—二叠系下统;6—石炭系上统;7—下石炭统上段;8—下石炭统中段;9—下石炭统下段;10—细粒黑云二长花岗岩;11—中-粗粒黑云二长花岗岩;12—矿体;13—地质界线;14—断层
Fig. 1 Geological sketch map of NaMeung copper polymetal deposit: 1—Quaternary; 2—Middle Jurassic upper member; 3—Middle Jurassic lower member; 4—Upper Permian; 5—Lower Permian; 6—Upper Carboniferous; 7—Lower Carboniferous upper member; 8—Lower Carboniferous middle member; 9—Lower Carboniferous lower member; 10—Fine grained biotite adamellite; 11—Medium-coarse grained biotite adamellite; 12—Ore body; 13—Geological boundary; 14—Fault
岩体的岩石学特征:灰白-浅肉红色,块状构造,中粗粒、似斑状结构。主要矿物为石英、钾长石、斜长石,次要矿物为黑云母,副矿物为磁铁矿、锆石等。石英:呈它形粒状,粒径为0.5~3.0 mm,含量30%左右。钾长石:主要为条纹长石,半自形-自形板状,细粒粒径为0.5 mm×1.0 mm左右,粗粒粒径为粒径1.2 mm×2.0 mm左右,含量约35%;斜长石:主要为奥-钠长石,自形-半自形短柱状,具钠长石双晶,长石牌号为5~30号,细粒粒径0.8 mm×1.5 mm左右,粗粒粒径为1.5 mm×2.5 mm左右,常见绢云母化、黏土化,含量30%左右;黑云母:片状,粒径 0.2 mm×0.6 mm左右,多氧化,析出铁质,含量5%左右。
钾长花岗岩(ξg51):分布于矿区东部,呈岩株产出,按粒度的渐变可分为粗粒钾长花岗岩和中粗粒钾长花岗岩两个相带。钾长花岗岩侵入于早期的二长花岗 岩,两者界线突变,可能为脉动式侵入接触关系。生成时代晚于黑云母二长花岗岩侵入体,确定为印支晚期产物。岩石常呈肉红色,致密块状、花岗结构、中粗粒结构。主要矿物成分为石英、钾长石、斜长石,次要矿物为黑云母,副矿物为磁铁矿等。石英:呈它形粒状,粒径0.5~2.0 mm,含量25%左右;钾长石:半自形板状,粒径0.2 mm×0.8 mm左右,高岭土化强烈,含量45%左右。斜长石:半自形板状,粒径0.2 mm×0.8 mm左右,常见聚片双晶,绢云母化发育,含量25%左右。黑云母:半自形片状,粒径0.2 mm×0.6 mm左右,含量5%左右。
2 样品和分析方法
本次花岗岩样品主要采自不同粒径的黑云母二长花岗岩以及钾长花岗岩,并选择新鲜样品测试,样品测试均由澳实分析检测(广州)有限公司完成。其中,主量元素分析方法为ME-XRF06,分析仪器为X荧光光谱仪。样品在煅烧后加入Li2B4O7-LiBO2助熔物,充分混合后,放置在自动熔炼仪中,使之在1 050~ 1 100 ℃熔融;熔融物倒出后形成扁平玻璃片,再用X荧光光谱仪分析。微量和稀土元素分析方法为ME-MS81,分析仪器为电感耦合等离子体质谱仪。样品首先加入到LiBO2熔剂中,混合均匀,在1 000 ℃以上的熔炉中熔化。熔液冷却后,用硝酸定容,再用等离子体质谱仪分析。
3 岩体地球化学特征
3.1 主量元素特征
矿区主要花岗岩的主量元素分析结果见表1,计算的CIPW标准矿物(分子个数)及有关岩石化学参数见表2。
从表1和2中可以看出,本区花岗岩主要元素具有以下特征:1) SiO2含量(质量分数)为73.45%~77.46%,高于中国花岗岩及世界花岗岩平均值[3](71.63%、71.30%),属于超酸性花岗岩。分异指数DI=88.93~ 93.22,说明本区花岗岩经历了高程度的分异演化。2)铝饱和指数变化不大,为不饱和或弱过饱和,w(Al2O3)为11.72%~13.76%,A/CNK值主要变化于1.042~ 1.101,大多数小于1.1,为弱过铝质。CIPW标准矿物中均出现刚玉分子,但大多数样品含量均低于1%,与典型的强过铝S型花岗岩(A/CNK>1.1,CIPW标 准矿物成分中刚玉分子的含量>1%[4])不太一致。3)碱含量变化不大,Alk含量偏低,主要集中在6.62%~ 8.06%之间,在MIDDLEMOST[5]全碱w(SiO2)(即TAS)图解上,都投影在亚碱性系列岩石范围(见图2);碱度率指数(AR)为2.85~4.05,碱铝指数(AKI)为0.73~ 0.85,平均值为0.80,低于典型的A型花岗岩平均 值[7](0.85)。按洪大卫等[8]提出的碱性、偏碱性和钙碱性岩的分界线(>1.0,0.9~1.0,<0.9),本区花岗岩属于钙碱性花岗岩。4) w(K2O)的含量变化规律性明显,与分异指数DI呈线性相关;在w(SiO2)—w(K2O)图解上(见图3),所有样品均投影在高钾钙碱性岩系内;w(Na2O)含量为3.05%~4.42%,绝大多数样品含量高 于3.2%,与典型的Ⅰ型花岗岩相当[8]。K2O/Na2O值变化范围比较大,其值为0.73~1.40,与徐克勤等[11-12]认为的过渡性地壳同熔型花岗岩特征相当。
表1 纳勐铜多金属矿区花岗岩岩石化学分析结果
Table 1 Chemical composition of granites in NaMeung copper polymetal deposit

表2 纳勐铜多金属矿区花岗岩CIPW标准矿物及参数表
Table 2 Parameters of granites in NaMeung copper polymetal deposit and CIPW standard minerals (molecule number)

3.2 稀土元素特征
从本区主要花岗岩样品的稀土元素分析结果(表3)及计算的一些参数值(表4)可以看出:
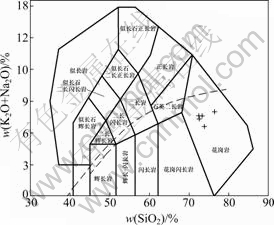
图2 TAS图据MIDDLEMOST[5](1994)(图中根据IRVINE and BARAGAR[6](1971)给出的曲线划分碱性、亚碱性系列)
Fig. 2 TAS diagram after MIDDLEMOST[5](1994) (Boundary between alkaline and subalkaline series after IRVINE and BARAGAR[6])
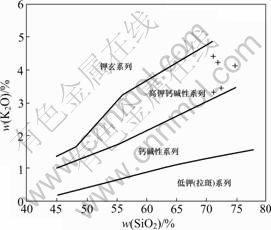
图3 w(K2O)—w(SiO2)图解(据PECCERILLO and TAYLOR[9])
Fig. 3 w(K2O)—w(SiO2) diagram (after PECCERILLO and TAYLOR[9])
表3 纳勐铜多金属矿区花岗岩稀土元素分析结果
Table 3 Results of REE analysis of granite in NaMeung copper polymetal deposit

表4 纳勐铜多金属矿区花岗岩稀土元素参数
Table 4 REE parameters of granites in NaMeung copper polymetal deposit

1) 本区花岗岩的稀土元素总量偏低,∑REE变化范围为70.69×10-6~118.63×10-6,反映了本区为稀土元素亏损区。2) 轻稀土含量远大于重稀土含量,LREE/HREE值为5.16~13.38,平均值为9.98,远高于一般花岗岩的平均值(1.0~1.2),具有明显的轻稀土富集特征。轻稀土分馏度LaN/SmN变化范围为2.26~ 0.92,指示轻稀土分馏程度较高;重稀土分馏度GdN/YbN变化范围为0.27~1.55,绝大多数样品的小于1,反映了本区花岗岩重稀土分馏明显偏低。3) D2花岗岩样品的δEu值为1.0,体现了幔源性质,反映了本区花岗岩成岩过程中有幔源物质加入的可能性;其他样品中δEu<0.6,体现出明显的Eu负异常,与典型的陆壳改造型花岗岩相当。δCe变化范围为0.68~ 0.97,显示出微弱的Ce负异常,属于Ce亏损型。4)区内花岗岩的稀土配分模式图(见图4)为向右倾斜的平滑曲线,反映区内岩浆演化程度较高。
3.3 微量元素特征
微量元素含量与组合特点可提供岩浆分异、演化程度、含矿潜力以及岩石所处的地球动力学背景等方面的重要信息。本区花岗岩微量元素含量见表5以及微量元素特征值见表6。

图4 纳勐矿区花岗岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式图(球粒陨石据WEDEPOHL[13], 1970)
Fig. 4 Chondrite-normalized REE distribution patterns of granites in NaMeung deposit (After WEDEPOHL[13],1970)
从表5和6中可以看出,本区花岗岩微量元素具有以下特征:1)本区花岗岩具有较低的Nb/Ta比值,Nb、Ta为一对互代元素,一般情况下不会发生分馏 (球粒陨石和原始地幔的Nb/Ta比值为17.5),壳幔分离时,Ta明显在地壳中富集而Nb亏损,因此,Nb/Ta比值可以指示岩浆形成时地壳组分的参与程度[14]。本区花岗岩Nb/Ta比值为4.95~6.70,明显低于后太古代大陆地壳的平均值11[14]。2) 高场强元素w(Zr+Nb+ Ce+Y)含量介于172.6×10-6~243.6×10-6,平均值为208.66×10-6,远低于A型花岗岩的含量下限[4] (350.6×10-6)。3) 岩浆结晶作用过程中,Rb主要代替钾长石中K,Sr则代替斜长石中的Ca。因而,当岩浆演化至晚阶段时,随着岩浆的演化和结晶分异作用的进行,岩浆越来越富钾贫钙,钾长石逐渐增多,斜长石明显减少。因而Rb越来越富集,Sr则强烈亏损。从表6中可以看出,区内花岗岩Rb/Sr比值为0.52~ 4.00,平均值为1.42,反映了岩体结晶分异彻底。与此同时,较低的Zr/Hf与Th/U比值,也反映了本区岩浆经历了高度的分异演化。
表5 纳勐矿区花岗岩微量元素含量
Table 5 Trace element compositions for granites in NaMeung deposit
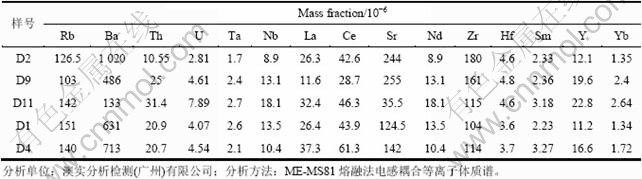
表6 纳勐矿区花岗岩微量元素参数
Table 6 Trace element parameters of granites in NaMeung deposit

矿区花岗岩微量元素蛛网图见图5。从图5中可以看出,花岗岩中明显富集Rb和Th等大离子亲石 元素,严重亏损Ba、Nb、Sr、P、Ti。Ba的亏损说明斜长石作为熔融残留相或结晶分离相存在。P、Ti的亏损与磷灰石、钛铁矿的分离结晶密切相关。Nb的亏损反映了源区岩石以陆壳岩石为主[15]。
4 讨论与结论
对于花岗岩的成因,BARBARIN[16]从不同的角度提出了不同的分类方案。英国学者PEARCE等[17]根据微量元素特征,将花岗岩形成的构造环境划分为洋脊花岗岩、火山弧花岗岩、板内花岗岩以及碰撞型花岗岩,并提出了Nb—Y、Ta—Yb、Rb—Y+Nb、Rb— Yb+Ta等判别图解。将本区花岗岩微量元素数据(见 表5)投影至Pearce提出的相关构造环境判别图解中(见图6),从图6可知,本区花岗岩数据均投影在火山弧花岗岩区内,反映了本区花岗岩形成环境为岛弧环境。
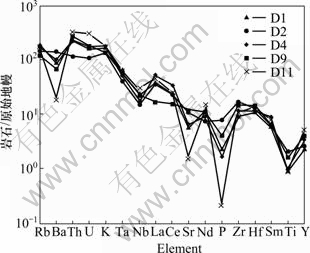
图5 纳勐矿区花岗岩微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图
Fig. 5 Primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider-web diagram for granites in NM deposit
花岗岩的Al2O3/TiO2比值可以作为源区部分熔融温度的标志,若Al2O3/TiO2<100,则部分熔融温度高于875 ℃;若Al2O3/TiO2>100,则部分熔融温度低于875 ℃[18]。本区花岗岩的Al2O3/TiO2比值变化范围为44.3~92.6,小于100,反映了本区花岗岩部分熔融的温度高于875 ℃,是在较高的温度下进行的。
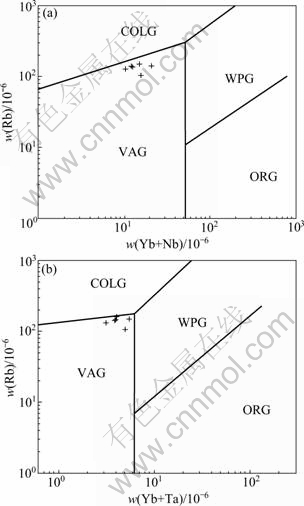
图6 花岗岩微量元素构造环境判别图解(据PEARCE, 1984[17]): VAG—火山弧花岗岩;ORG—洋脊花岗岩; WPG—板内花岗岩;COLG—碰撞型花岗岩
Fig. 6 Trace element diagrams for discrimination of structural environment of granites (after PEARCE, 1984[17]): VAG—Volcanic arc granite; ORG—Ocean ridge granite; WPG—Within plate granite; COLG—Collision granite
通过以上讨论得出如下结论:纳勐铜多金属矿区花岗岩类主要为黑云母二长花岗岩、钾长花岗岩,属于富硅钙碱性弱过铝质花岗岩类。岩体的岩石化学、地球化学特征均反映了本区花岗岩与我国华南过渡性地壳同熔型花岗岩特征相当。岩体形成于岛弧环境,并在较高的温度下部分熔融形成,其形成与幔源岩浆的底侵有关,热的幔源不仅为地壳的部分熔融提供了热量,而且与熔融的壳源岩浆发生了混合作用。
REFERENCES
[1] 陈国达. 中国大地构造问题[M]. 北京: 科学技术出版社, 1965: 1-184.
CHEN Guo-da. Tectonics of China [M]. Beijing: Science and Technology Press, 1965: 1-184.
[2] MANAKA T, ZAW K, MEFFRE S. Geological and tectonic setting of Cu-Au deposits in northern Lao PRD [J]. Proceedings of the International Symposia on Geoscience Resources and Environments of Asian Terranes, 2008, 24(11): 254-257.
[3] 迟清华, 鄢明才. 应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 1-148.
CHI Qing-hua, YAN Ming-cai. Handbook of elemental abundance for applied geochemistry [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007: 1-148.
[4] CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A J R. Two contrasting granite type: 25 years later [J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2001, 48(4): 489-499.
[5] MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4): 215- 224.
[6] IRVINE T N, BARAGAR W R A. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks [J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1971, 8(5): 532-548.
[7] WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis [J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-419.
[8] 洪大卫, 郭文岐, 李戈晶. 福建沿海晶洞花岗岩带的岩石学和成因演化[M]. 北京: 科学技术出版社, 1987: 1-132.
HONG Da-wei, GUO Wen-qi, LI Ge-jing. Petrology and genetic evolutions of miarolitic granite belts in Fujian coastal area [M]. Beijing: Science and Technology Press, 1987: 1-132.
[9] PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey [J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1): 63-81.
[10] 邱家骧, 林景仟. 岩石化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1991: 1-276.
QIU Jia-xiang, LIN Jing-qian. Petrochemistry [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1991: 1-276.
[11] 徐克勤, 胡受奚, 孙明志, 叶 俊. 华南两个成因系列花岗岩及其成矿特征[J]. 矿床地质, 1982, 1(2): 1-14.
XU Ke-qin, HU Shou-xi, SUN Ming-zhi, YE Jun. On the two genetic series of granites in southeastern China and their metallogenetic characteristics [J]. Mineral Deposits, 1982, 1(2): 1-14.
[12] 徐克勤, 胡受奚, 孙明志, 张景荣, 叶 俊. 论花岗岩的成因系列—以华南中生代花岗岩为例[J]. 地质学报, 1983(2): 107-118.
XU Ke-qin, HU Shou-xi, SUN Ming-zhi, ZHANG Jing-rong, YE Jun. On the genetic series of granites, as exemplified by the Mesozoic granites of south China [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1983(2): 107-118.
[13] WEDEPOHL K H. Handbook of Geochemistry (Vol Ⅱ) [M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1968: 1-405.
[14] GREEN T H. Significance of Nb/Ta as indicator of geochemical process in the crust-mantle system [J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3/4): 347-359.
[15] GREEN T H, PEARSON N J. An experimental study of Nb and Ta partitioning between Ti-rich minerals and silicate liquids at high pressure and temperature [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987, 51(1): 55-62.
[16] BARBARIN B. A review of the relationships between granitoid types, their origins and their geodynamic environments [J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3): 605-626.
[17] PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks [J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983.
[18] SYLVESTER P J. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites [J]. Lithos, 1998, 45(1/4): 29-44.
(编辑 李艳红)
收稿日期:2011-12-01;修订日期:2012-01-04
通信作者:张文山,副教授;电话:15111139188;E-mail: wszhang8888@yahoo.com.cn