文章编号:1004-0609(2012)06-1747-07
基于有限元法压电纤维复合物结构的模拟优化
林秀娟,张 斗,张晓泳,李志友,周科朝
(中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083)
摘 要:利用有限元软件ANSYS模拟分析电极结构、压电陶瓷纤维厚度及体积分数等结构参数对纤维内部电场分布及复合物驱动应变性能的影响规律。结果表明:具有交叉指形电极结构的压电纤维复合物在纤维内部存在不均匀电场区域,其强度和体积分数共同制约着复合物的驱动应变性能。在恒定电场条件下,当交叉指形电极宽度为纤维厚度的一半时,复合物具有最大应变量;厚度较小的压电陶瓷纤维内部的均匀电场强度较高和体积分数较大,进而有利于提高复合物的驱动应变性能。在恒定电压条件下,电极指间距越大,复合物的驱动应变量越小。当指间距和指宽的比>10时,应变量可达到理想状态的90%。压电陶瓷纤维体积分数越高的复合物越容易获得较大的驱动应变性能。
关键词:压电纤维复合物;有限元法;电极结构;压电陶瓷纤维
中图分类号:TB34; TB332 文献标志码:A
Modeling and optimization of piezoelectric fiber composites based on finite element method
LIN Xiu-juan, ZHANG Dou, ZHANG Xiao-yong, LI Zhi-you, ZHOU Ke-chao
(State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The effect rules of electrode structure, piezoelectric ceramic fiber thickness and volume fraction on the electric field distribution in fiber and strain properties of composite were simulated and analyzed by finite element using ANSYS. The results show that the inhomogeneous zone exists in the fiber of piezoelectric fiber composites with interdigitated electrode. And the strain properties of composite are influenced simultaneously by the field strength and proportion of this zone. When the constant electric field is applied, the highest strain is generated when the electrode width is half of the fiber thickness. The field strength and proportion of the homogeneous zone in the thinner piezoelectric ceramic fiber are higher, which improves the strain properties of the composite. When the constant voltage is applied, the strain decreases with the increase of the electrode separation. 90% of ideal strain can be achieved with the electrode separation to the width larger than 10. The strain properties of the composite can be improved using the piezoelectric fiber with higher volume fraction.
Key words: piezoelectric fiber composites; finite element method (FEM); electrode structure; piezoelectric ceramic fiber
近十年来,智能材料及其与主体结构的集成已经成为感知和驱动主体结构的重要技术手段之一[1-2]。其中压电陶瓷因结构刚度高、驱动力大、机电响应转换快,并可与动态系统在宽频率范围内相互作用[3],成为应用最为广泛的一类智能材料,但陶瓷的脆性本质限制其在曲面控制等很多领域的应用。美国麻省理工学院智能材料和结构实验室于1993年首次提出的压电纤维复合物,由压电陶瓷纤维、聚合物基体和交叉指形电极(Interdigitated electrode,IDE)组成[4-5]。在该类复合物中,交叉指形电极结构有效利用了压电纤维的d33性能,具有较大的驱动应变,同时也降低了极化和驱动电压。此外,该复合物可进行大幅度弯曲和扭转,很容易应用于曲面结构,拓宽了压电器件的应用领域[6]。近几年来,压电纤维复合物在能量采集、智能结构控制、稳定状态的维护及结构健康监测等[7-9]领域的应用显示了广阔的应用前景。
以往对于压电纤维复合物的结构设计以经验为主,使得复合物的设计和制备过程存在很大盲目性。有限元模拟可获得复合物结构与性能之间的理论关系,为复合物设计提供重要的理论依据和强有力的技术支持,特别是自Bent创立以均匀场模型为理论基础,以具有代表性的结构单元为对象表征压电复合物的性能后[10],有限元模拟成为压电纤维复合物领域的一个研究热点。针对压电纤维复合物中结构参数对驱动应变性能的影响[11-13],许多研究工作者采用有限元法进行了分析。例如,HAGOOD等[4]和BOWEN等[14]以纯压电陶瓷为基体,研究结构单元中电极指宽等结构参数对驱动应变性能的影响;BECKERT和KREHER[13]、BELLOLI等[15]以及PARADIES和MELNYKOWYCZ[16]研究圆形压电纤维复合物结构单元中压电材料的极化状态及复合物的结构参数等与应力/应变性能之间的关系。但目前尚未见以均匀场模型为基础的方形压电纤维复合物结构与性能之间关系的相关报道。
本文作者以方形压电纤维复合物作为研究对象,利用有限元软件ANSYS进行模拟,系统地分析该结构中电极宽度、指间距、压电陶瓷纤维厚度及体积分数等对复合物驱动性能的影响,进而明确有效提高压电纤维复合物驱动性能的途径。
1 压电纤维复合物的有限元模拟
图1所示为压电纤维复合物结构示意图。其结构特点是沿纤维轴向正负分支电极交叉排列,各分支电极由一对异性主电极引出,上下表面电极结构完全对称。交叉指形电极结构在纤维轴向方向具有周期性,因而每对相邻异性电极之间的压电陶瓷纤维均应具有相同的电场、应力/应变场分布状态。因此,为简化分析过程,可以采用一对相邻异性电极之间的复合物作为最小结构单元(Representative volume element, RVE)进行研究(如图2所示),进而反映整个复合物的宏观驱动应变性能。在该最小结构单元中,主要的结构参数有压电纤维厚度H、电极宽度W、电极指间距P和电极长度L等。在此模拟分析中,对结构单元施加表1所示的边界条件[10]。

图1 压电纤维复合物结构示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of structure of piezoelectric fiber composites

图2 复合物结构单元结构示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of structure of representative volume element (RVE) of composite along fiber axis: (a) 3D model; (b) 2D cross-section
压电材料的电行为和力学行为之间的关系,即压电本构方程可以描述为[17]
 (1)
(1)
或
 (2)
(2)
式中: 表示极化方向为3的压电本构方程;
表示极化方向为3的压电本构方程; 表示矩阵的转置;
表示矩阵的转置; 表示常应变状态下的测量值;上标
表示常应变状态下的测量值;上标 表示常应力状态下的测量值;上标
表示常应力状态下的测量值;上标 表示电场强度E为常数下的测量值;T为应力;S为应变;e为压电应力常数;d为压电应变常数;c为弹性刚度系数;s为弹性柔顺系数;D为电位移。压电本构方程耦合的是压电应力常数e和施加的电场E,也可以耦合压电应变常数d和施加的电场E,压电应力常数e和压电应变常数d的关系是:
表示电场强度E为常数下的测量值;T为应力;S为应变;e为压电应力常数;d为压电应变常数;c为弹性刚度系数;s为弹性柔顺系数;D为电位移。压电本构方程耦合的是压电应力常数e和施加的电场E,也可以耦合压电应变常数d和施加的电场E,压电应力常数e和压电应变常数d的关系是:
 (3)
(3)
表1 结构单元所施加的位移、电压和电位移边界条件
Table 1 Boundary conditions of displacement (U), electrical potential (V) and electrical displacement (D) applied to RVE

根据式(1),压电材料的本构关系矩阵为
 (4)
(4)
根据均匀场理论设定结构单元中压电纤维的极化方向沿Z轴方向且极化强度均匀分布。其中,有限元模拟中所使用的材料参数列于表2[18]。
取结构单元中压电纤维中心线方向(即Z向)的静电场强度EZ以分析不同结构参数对复合物中静电场的影响,并规定图2(b)中压电纤维中心线与电极边缘交点为坐标原点。根据式(4)可得到结构单元的Z向平均自由应变SZ,以单位电压微应变量(SZ/V)对压电纤维复合物的驱动应变性能进行表征,并通过纤维中心线电场强度EZ的变化分析不均匀电场对复合物驱动应变性能的影响。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 电极宽度的影响
图3所示为压电纤维厚度H为120 μm、电极间距P为400 μm的条件下电极宽度W对复合物驱动应变性能的影响。从图3(a)可以发现,电极宽度W与结构单元应变量呈现先增大后减小的趋势;当电极宽度W为60 μm时,结构单元具有最大应变量,此时电极宽度W为压电纤维厚度H的一半,这与BOWEN等[14]报道的结果相同。由图3(b)结构单元中心线的Z向电场强度可以发现,结构单元内部存在电场强度变化不均匀的电场和电场强度恒定的均匀电场区域,且非均匀电场的Z向电场强度低于均匀电场的Z向电场强度。根据逆压电效应可以推知不均匀电场区域所产生的Z向应变量小于均匀电场区域的Z向应变量,因此,不均匀电场区域的存在对复合物的驱动应变性能产生了不利影响。此外,当电极宽度较小时,结构单元的Z向均匀电场强度较小,不均匀电场的体积分数也较小。随着电极宽度的增大,Z向均匀电场的强度增大,但不均匀电场的体积分数也随之增大。因此,结构单元具有最大应变量时的电极宽度W是均匀电场和不均匀电场相互平衡的结果。
表2 有限元模拟中所使用的材料参数[18]
Table 2 Material properties data used for finite element analysis[18]


图3 电极宽度对结构单元应变性能和电场分布的影响(H=120 μm, P=400 μm, V=400 V)
Fig. 3 Effect of electrode width on strain response of RVE(a) and electric field Z-direction at fiber centre axis(b) (H=120 μm, P=400 μm, V=400 V)
2.2 指间距的影响
图4所示为压电纤维厚度H为120 μm、电极宽度W为60 μm的条件下指间距P对复合物驱动应变性能的影响。图4(a)表征了指间距与结构单元应变量之间的关系。随着指间距的增大,结构单元的应变量减小。压电纤维复合物的驱动应变受均匀电场强度和体积分数的双重影响,且均呈正比例关系。为了进一步研究结构单元应变量减小的原因,将不同指间距下压电陶瓷纤维中心线的Z向电场强度列于图4(b),可以看到,在恒定指间距下,在距离电极边缘较近和较远的两端均呈现为电场强度逐渐变化的非均匀电场,而在两电极的中间区域则为电场强度恒定的均匀电场,且此两种电场的体积分数均可用其在中心线上的相对长度与指间距的比值来表示。由此可见,随着指间距的增大,均匀电场的体积分数逐渐增大,但强度却逐渐降低。在均匀电场体积分数随指间距增大而增大的情况下,结构单元应变量依然变小,说明均匀电场强度的降低起了主导作用。选取指间距较小的压电纤维复合物越易获得较大的驱动应变,但指间距过小,纤维内部最大电场强度过大,在施加极化电压和驱动电压时易引起击穿[13]。
图5(a)所示为压电纤维复合物中电场线分布,图5(b)所示为理想状态下的电场线分布,电场线沿纤维轴向平行分布且各处的电场强度相同,其中P*表示相邻异性电极之间的间距。SIDE和Sideal分别表示IDE结构和理想状态下结构单元的单位电压微应变量。用SIDE/Sideal反映IDE结构与理想状态之间的差异表征不均匀电场区域对驱动应变性能的影响。SIDE/Sideal越大,说明IDE结构中不均匀电场区域所占体积分数越小,对应变驱动性能的影响越小,电场线分布和应变驱动性能越接近于理想状态。
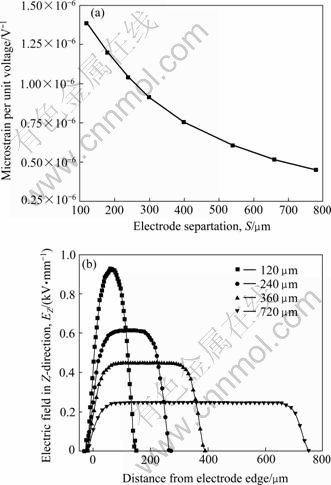
图4 指间距对结构单元应变性能和电场分布的影响(W= 60 μm, H=120 μm, V=100 V)
Fig. 4 Effect of electrode separation on strain response of RVE(a) and electric field in Z-direction at fiber centre axis(b) (W=60 μm, H=120 μm, V=100 V)

图5 压电纤维复合物的电场线示意图
Fig. 5 Schematic diagrams of electric field vector for piezoelectric fiber composites with interdigitated electrode(a) and ideal electric field(b)
图6所示为压电纤维厚度H为120 μm、电极宽度W为60 μm及指间距P为400 μm的条件下SIDE/Sideal与指间距之间的关系。从图6中可以发现,随着指间距的增大,SIDE/Sideal逐渐增大。当指间距为400 μm时, IDE结构的应变量可达到理想状态下的80%;当指间距为650 μm时,IDE结构的应变量可达到理想状态下的90%。因此,指间距越大,不均匀电场区域所占体积分数越小,对应变驱动性能的影响也越小,复合物的驱动应变越接近于理想值。

图6 SIDE/Sideal与指间距之间的关系(W=60 μm, S=400 μm, H=120 μm)
Fig. 6 Relationship between SIDE/Sideal and electrode separation (W=60 μm, S=400 μm, H=120 μm)
2.3 压电陶瓷纤维厚度的影响
图7所示为交叉指形电极的指间距P为400 μm、所施加的电压为400 V、同时保持压电陶瓷纤维厚度H与电极指宽W的比值为2的条件下纤维厚度H对复合物驱动性能的影响。图7(a)表征压电纤维厚度与结构单元应变量之间的关系,图7(b)所示为压电纤维厚度不同时纤维中心线的电场强度。由图7(a)可以发现,随着纤维厚度的增大,结构单元的应变量逐渐减小。当纤维厚度从80 μm增大到400 μm时,结构单元的应变量减小了74%。结合图7(b)的电场强度曲线可以发现,纤维厚度为400 μm时,均匀电场的体积分数非常小,且电场强度也较小;当纤维厚度减小到80 μm时,均匀电场强度显著增大且不均匀电场的体积分数也急剧减小。由此可知,压电纤维厚度减小使得均匀电场体积分数及电场强度增大,这均有利于结构单元应变量的增大。因此,可选用厚度较小的压电纤维制备具有较优驱动应变性能的压电纤维复合物。

图7 压电陶瓷纤维厚度对结构单元应变性能和电场分布的影响(P=400 μm, H/W=2, V=400 V)
Fig. 7 Effect of piezoelectric ceramic fiber thickness on strain response of RVE(a) and electric field in Z-direction at fiber centre axis(b) (P=400 μm, H/W=2, V=400 V)
2.4 压电陶瓷纤维体积分数的影响
图8所示为指间距P为400 μm,指宽W为60 μm及纤维厚度H为120 μm的条件下压电陶瓷纤维体积分数φ对复合物驱动性能的影响。由图8可以发现,随着复合物中压电陶瓷纤维体积分数φ的增大,结构单元的应变量增大。如需压电纤维复合物具有较大的驱动应变性能,可选取压电陶瓷纤维体积分数较高的复合物。但压电陶瓷纤维体积分数越大,陶瓷的脆性本质会使复合物的整体柔韧性相应地降低。因此,在实际使用时,应综合考虑驱动应变性和柔韧性的要求选择纤维体积分数合适的复合物。
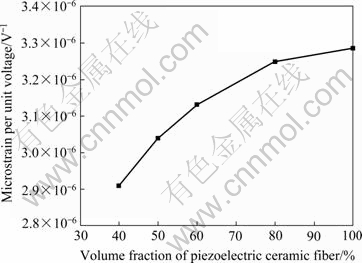
图8 压电陶瓷纤维体积分数与结构单元应变性能之间的关系(S=400 μm, W=60 μm, H=120 μm)
Fig. 8 Variation of strain response of RVE with volume fraction of piezoelectric ceramic fiber (S=400 μm, W=60 μm, H=120 μm)
3 结论
1) 压电纤维复合物中交叉指形电极结构使纤维内部存在不均匀电场区域,此区域对复合物的驱动应变性能产生了不利影响;不均匀电场和均匀电场的强度大小及体积分数共同制约着复合物的驱动应变 性能。
2) 在恒定电场强度条件下,受均匀电场和不均匀电场强度和体积分数相互制约的影响,当交叉指形电极宽度为压电纤维厚度的一半时,复合物具有最大驱动应变。减小压电纤维厚度可使纤维内部的均匀电场强度和体积分数都较高,这均有利于提高复合物的驱动应变性能。
3) 增大复合物中功能相即纤维的体积分数有利于增大复合物的驱动应变性能。
4) 指间距越大,IDE结构的压电纤维复合物应变量越接近于理想应变量。
REFERENCES
[1] TZOU H S, LEE H J, ARNOLD S M. Smart materials, precision sensors/actuators, smart structures, and structronic systems[J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2004, 11: 367-393.
[2] 芦 笙, 林萍华, 陈 静, 川岛弘一郎. 声发射在形状记忆合金研究中的应用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2001, 11(6): 1002-1008.
LU Sheng, LIN Ping-hua, CHEN Jing, KAWASHIMA K. Application of acoustic emission in research of shape memory alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2001, 11(6): 1002-1008.
[3] 贾菲 B. 压电陶瓷[M]. 林声和, 译. 北京: 科学出版社, 1979: 136-185.
JAFFE B. Piezoelectric ceramics[M]. LIN Sheng-he, tranls. Beijing: Science Press, 1979: 136-185.
[4] HAGOOD N, KINDEL R, GHANDI K, GAUDENZI P. Improving transverse actuation of piezoceramics using interdigitated surface electrodes[C]//Smart Structures and Materials 1993: Smart Structures and Intelligent Systems. Albuquerque: SPIE, 1993: 341-352.
[5] HAGOOD N, NESBITT W, BENT A A. Composites for structural control: USA, 6048622[P]. 2000-04-11.
[6] BENT A A, PIZZOCHERO A E. Recent advances in active fiber composites for structural control[C]//Smart Structures and Materials 2000: Industrial and Commercial Applications of Smart Structures Technologies. San Diego: SPIE, 2000: 244-254.
[7] TANG Li-hua, YANG Yao-wen, LI Hong-yun. Optimizing efficiency of energy harvesting by macro-fiber composites[C]// Smart Structures, Devices and Systems IV. Melbourne: SPIE, 2008: 7268081-7268089.
[8] PARK S, GRISSO B L, INMAN D J, YUN C. B. MFC-based structural health monitoring using a miniaturized impedance measuring chip for corrosion detection[J]. Research in Nondestructive Evaluation, 2007, 18: 139-150.
[9] MING Ai-guo, HUANG Ya-wen, FUKUSHIMA Y, SHIMOJO M. Development of an active flapping wing using piezoelectric fiber composites[J]. International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, 2008: 2144-2149.
[10] BENT A A. Active fiber composites for structural actuation[D]. Massachusetts: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1997.
[11] NELSON L J. Smart piezoelectric fibre composites[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2002, 18: 1245-1256.
[12] BOWEN C R, BOWLES A, DRAKE S, JOHNSON N, MAHON S. Fabrication and finite element modelling of interdigitated electrodes[J]. Ferroelectrics, 1999, 228: 257-269.
[13] BECKERT W, KREHER W S. Modelling piezoelectric modules with interdigitated electrode structures[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2003, 26: 36-45.
[14] BOWEN C R, NELSON L J, STEVENS R, CAIN M G, STEWART M. Optimisation of interdigitated electrodes for piezoelectric actuators and active fibre composites[J]. Journal of Electroceramics, 2006, 16: 263-269.
[15] BELLOLI A, CASTELLI B, KORNMANN X, HUBER C, ERMANNI P. Modeling and characterization of active fiber omposites[C]//Smart Structures and Materials 2004: Smart Structures and Integrated Systems. San Diego: SPIE, 2004: 78-88.
[16] PARADIES R, MELNYKOWYCZ M. Numerical stress investigation for piezoelectric elements with a circular cross section and interdigitated electrodes[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2007, 18: 963-972.
[17] IEEE Std 176—1987, IEEE Standard on piezoelectricity[S].
[18] MARTINEZ M, ARTEMEV A. Finite element analysis of broken fiber effects on the performance of active fiber composites[J]. Composite Structures, 2009, 88(3): 491-496.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51072235);中央高校基本科研业务费前沿研究计划(2010QZZD013);湖南省自然科学基金杰出青年资助项目(11JJ1008)
收稿日期:2011-05-23;修订日期:2011-10-10
通信作者:张 斗,教授,博士;电话:0731-88877196;E-mail: dzhang@csu.edu.cn