DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2019.02.19
钼(或铬,钒)原子替位掺杂对双相γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al界面的能量、延性和电子性质的影响
宋庆功1, 2,顾威风1,甄丹丹2,郭艳蕊1,胡雪兰2
(1. 中国民航大学 理学院低维材料与技术研究所,天津 300300;
2. 中国民航大学 中欧航空工程师学院,天津 300300)
摘 要:采用基于密度泛函理论计算研究了钼(或铬,钒)原子替位掺杂双相γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al界面体系的平均形成能、断裂功、电子结构等。结果显示:各个掺杂体系的总能量和平均形成能均为负值,表明它们可以由实验制备并能稳定存在。对代表性体系的断裂功和态密度分析表明,体系Mo-Sa5 (或Cr-Sa5)的结合强度减弱,同时体系Mo-Sa5的Mo-d和Ti-d电子态密度增加、相互作用增强,而Ti-d和Al-p轨道杂化键强度降低,位错运动的阻力减少,有利于改善TiAl合金材料的延性。对杂质原子所在(001)面电荷密度和布居数的分析发现,Mo(或V)的掺入会引起电子云在杂质原子周围的聚集效应,形成结合强度稍高的区域,该区域与周围其他区域结合的各向异性程度下降。这正是此类TiAl合金延性改善的内因。
关键词:双相γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al界面;能量性质;延性;电子性质;第一性原理
文章编号:1004-0609(2019)-02-0370-10 中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
TiAl合金由于其高熔点、低密度、高弹性模量,良好的抗氧化和抗蠕变性能,具有用于航空航天和汽车发动机领域的巨大潜力[1-2]。然而,室温下延展性和韧性较差,加工成型困难严重限制了它的广泛应用[3-5]。因此,目前研究的重点是在保持其优良性能的前提下,提高TiAl合金的室温延展性和韧性。作为γ-TiAl基合金第二相,α2-Ti3Al的添加能够改善其合金的延性[6-8]。双相TiAl-Ti3Al合金材料因其优异的强度和抗氧化性能备受关注[9-10]。这促使相关理论研究更加深入、实验探究更加细致,无疑对于揭示TiAl/Ti3Al界面的变形机理、提高TiAl合金的延性具有重要意义,也为研发性能更为优异的新材料提供了基础数据。
近年来,为了提高TiAl合金的综合性能,研究人员进行了大量的理论探索和实验研究,发现合金化和微合金化是降低该类合金脆性,提高延性和韧性的重要途径[11-14]。实验研究表明,对于γ-TiA相而言,在(111)平面上沿着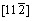 方向的滑移是最容易的;对于a2-Ti3Al相,在(0001)平面上沿着
方向的滑移是最容易的;对于a2-Ti3Al相,在(0001)平面上沿着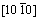 方向的滑移是最容易的[15-16]。祝莹莹等[17]用小型非自耗钨极电弧炉熔炼制备了Ti50Al48Cr2合金,用正电子湮没技术研究发现Cr掺杂使合金基体,特别是晶界处的电子态密度增加。并且由于Cr的加入使合金内d-d电子相互作用增强,从而改善了合金的延性。熊翔等[18]通过实验分析了添加Cr元素对TiAl合金室温延性和微观结构的影响,发现Cr元素的添加降低了TiAl合金的堆垛层错能,使得合金在位错滑移受阻时容易以孪生的形式产生塑性变形,从而获得较高的延性,且添加3% Cr的TiAl合金的室温延性最佳,同时发现合金的晶粒度以及Ti3Al第二相的含量对室温延性也有影响。理论上,王海燕等[19]研究了在γ-TiAl合金中加入Mo元素,当掺杂浓度为12.5%时,Mo掺杂能较好地改善TiAl合金的延性,并发现Ti原子的s、p和d电子与邻近的Mo原子发生了强烈的s-s、p-p和d-d电子相互作用,有效地束缚了合金中Ti和Al原子的迁移,有助于提高合金的稳定性和强度。魏强等[20]利用嵌入原子方法进行研究,发现低量掺杂Mo和W元素会减少Ti3Al合金的硬度,Cr替代Ti位后会增加合金的硬度。党宏丽等[21]研究了Nb和Mo合金化对γ-TiAl合金的影响,结果发现Nb和Mo可以提高杂质元素与其近邻基体各元素之间的相互作用以及相应原子之间的键合强度,导致较强的固溶强化效应,从而影响γ-TiAl的力学性质。MORINAGA等[22]研究表明,TiAl晶体中存在Al-p(Al原子的3p轨道)与Ti-d(Ti原子的3d轨道)轨道杂化的方向性键合, 使材料的剪切强度提高,进而造成其室温延性较差,并且通过掺杂第三元素来增强Ti—Ti键、减弱Al—Ti键,可以改善合金的延性。HAO等[23]利用第一性原理方法分析研究了γ-TiAl和α2-Ti3Al中V、Cr、Mn、Fe、Ni、Zr、Nb、Mo、Ta、Ga和Sn的位置占据情况。结果显示,在γ-TiAl相中,Zr、Nb和Ta原子优先占据Ti位,而Fe、Ni、Ga和Sn原子优先占据Al位,另一方面,V、Cr和Mn原子位置的选择取决于合金的组成。在α2-Ti3Al相中,Ga和Sn原子优先选择Al位,而V、Cr、Mn、Zr、Nb、Mo和Ta原子优先占据Ti位。上述工作大多着重于对于单相TiAl基合金结构与延性等性质的探索,对合金元素的占位情况也存在不一致的结论。再者,TiAl合金存在多种相结构,比较典型的是γ-TiAl相和α2-Ti3Al相共存,并且研究发现,少量α2相的存在能改善材料的延性或韧性[24-26]。WEI等[24]利用第一性原理方法结合经验判据,研究了过渡金属V、Cr、Nb、Ta、W和Re对双相TiAl-Ti3Al合金的界面性质的影响,发现增加了界面的解离能,降低了不稳定层错能,因而有助于改善TiAl/Ti3Al界面的延性。屈华等[25]从电子结构层次进行探索,认为相界面处的键结合强度弱化有利于增加界面稳定性与连续性、提高合金的韧性。刘伟东等[26]讨论了Mn添加到双相TiAl合金界面,对于层片状结构增加韧性的微观机制。但尚未见到关于合金元素对此类双相合金的界面的稳定性和电子性质的定量化研究与分析。众所周知,合金材料的性质取决于其微观结构,而微观结构与电子性质紧密相关。
方向的滑移是最容易的[15-16]。祝莹莹等[17]用小型非自耗钨极电弧炉熔炼制备了Ti50Al48Cr2合金,用正电子湮没技术研究发现Cr掺杂使合金基体,特别是晶界处的电子态密度增加。并且由于Cr的加入使合金内d-d电子相互作用增强,从而改善了合金的延性。熊翔等[18]通过实验分析了添加Cr元素对TiAl合金室温延性和微观结构的影响,发现Cr元素的添加降低了TiAl合金的堆垛层错能,使得合金在位错滑移受阻时容易以孪生的形式产生塑性变形,从而获得较高的延性,且添加3% Cr的TiAl合金的室温延性最佳,同时发现合金的晶粒度以及Ti3Al第二相的含量对室温延性也有影响。理论上,王海燕等[19]研究了在γ-TiAl合金中加入Mo元素,当掺杂浓度为12.5%时,Mo掺杂能较好地改善TiAl合金的延性,并发现Ti原子的s、p和d电子与邻近的Mo原子发生了强烈的s-s、p-p和d-d电子相互作用,有效地束缚了合金中Ti和Al原子的迁移,有助于提高合金的稳定性和强度。魏强等[20]利用嵌入原子方法进行研究,发现低量掺杂Mo和W元素会减少Ti3Al合金的硬度,Cr替代Ti位后会增加合金的硬度。党宏丽等[21]研究了Nb和Mo合金化对γ-TiAl合金的影响,结果发现Nb和Mo可以提高杂质元素与其近邻基体各元素之间的相互作用以及相应原子之间的键合强度,导致较强的固溶强化效应,从而影响γ-TiAl的力学性质。MORINAGA等[22]研究表明,TiAl晶体中存在Al-p(Al原子的3p轨道)与Ti-d(Ti原子的3d轨道)轨道杂化的方向性键合, 使材料的剪切强度提高,进而造成其室温延性较差,并且通过掺杂第三元素来增强Ti—Ti键、减弱Al—Ti键,可以改善合金的延性。HAO等[23]利用第一性原理方法分析研究了γ-TiAl和α2-Ti3Al中V、Cr、Mn、Fe、Ni、Zr、Nb、Mo、Ta、Ga和Sn的位置占据情况。结果显示,在γ-TiAl相中,Zr、Nb和Ta原子优先占据Ti位,而Fe、Ni、Ga和Sn原子优先占据Al位,另一方面,V、Cr和Mn原子位置的选择取决于合金的组成。在α2-Ti3Al相中,Ga和Sn原子优先选择Al位,而V、Cr、Mn、Zr、Nb、Mo和Ta原子优先占据Ti位。上述工作大多着重于对于单相TiAl基合金结构与延性等性质的探索,对合金元素的占位情况也存在不一致的结论。再者,TiAl合金存在多种相结构,比较典型的是γ-TiAl相和α2-Ti3Al相共存,并且研究发现,少量α2相的存在能改善材料的延性或韧性[24-26]。WEI等[24]利用第一性原理方法结合经验判据,研究了过渡金属V、Cr、Nb、Ta、W和Re对双相TiAl-Ti3Al合金的界面性质的影响,发现增加了界面的解离能,降低了不稳定层错能,因而有助于改善TiAl/Ti3Al界面的延性。屈华等[25]从电子结构层次进行探索,认为相界面处的键结合强度弱化有利于增加界面稳定性与连续性、提高合金的韧性。刘伟东等[26]讨论了Mn添加到双相TiAl合金界面,对于层片状结构增加韧性的微观机制。但尚未见到关于合金元素对此类双相合金的界面的稳定性和电子性质的定量化研究与分析。众所周知,合金材料的性质取决于其微观结构,而微观结构与电子性质紧密相关。
本文以Mo、Cr和V分别掺杂双相γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al界面体系作为研究对象,在密度泛函理论框架下研究合金体系的晶体结构、稳定性和延性,探索该类合金的延性与电子性质的内在关系,旨在揭示双相TiAl合金延性或韧性改善的微观机制、预测其宏观性能,为该类合金材料的实验研究提供理论依据。
1 理论模型与计算方法
1.1 理论模型及其选择
为了研究双相TiAl基合金体系,首先建立γ-TiAl和α2-Ti3Al的结构模型。γ-TiAl为L10型面心四方结构,空间群为P4/mmm,其晶胞中包含2个Ti原子和2个Al原子,晶格参量为a=b=0.400 nm,c=0.406 nm,如图1(a)所示。α2-Ti3Al为D019型晶体结构,晶格参量为a =b=0.576 nm,c=0.466 nm,如图1(b)所示。
对于双相TiAl/Ti3Al界面体系而言,其建立情况较为复杂。由于每种晶体的表面多种多样,γ-TiAl和α2-Ti3Al的表面两两结合,就存在多种可能的界面模型。由于密排面稳定性好,本文选择γ-TiAl 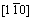 (111)及α2-Ti3Al
(111)及α2-Ti3Al 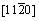 (0001)表面来构建界面模型。此TiAl合金中的取向关系已经被透射电子显微镜观测实验所证实[16]。为了尽量降低界面模型的错配度,以γ-TiAl (111) 4层表面结构单元和α2-Ti3Al (0001) 5层表面结构单元为基础,建立1×2×1的超胞结构,其中最上层包括10
(0001)表面来构建界面模型。此TiAl合金中的取向关系已经被透射电子显微镜观测实验所证实[16]。为了尽量降低界面模型的错配度,以γ-TiAl (111) 4层表面结构单元和α2-Ti3Al (0001) 5层表面结构单元为基础,建立1×2×1的超胞结构,其中最上层包括10 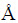 的真空层。该相界面系统包含Ti原子46个,Al原子26个。γ-TiAl (111)和α2-Ti3Al (0001)在形成相界面时会出现两种不同的结构,其对应的模型如图2所示。
的真空层。该相界面系统包含Ti原子46个,Al原子26个。γ-TiAl (111)和α2-Ti3Al (0001)在形成相界面时会出现两种不同的结构,其对应的模型如图2所示。
图1 γ-TiAl结构模型和α2-Ti3Al结构模型
Fig. 1 Structure models of TiAl
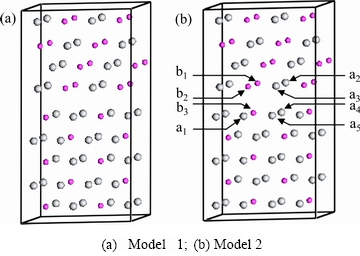
图2 γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al界面模型
Fig. 2 γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al interface models
为了选取合适的模型与计算方案,先对γ-TiAl和α2-Ti3Al模型单元进行优化,得到优化结果后再与报道的实验结果(对于γ-TiAl,a=b=0.400 nm,c0=0.408 nm;对于α2-Ti3Al,a=b=0.577 nm,c0=0.462 nm)[27-29]进行比较。计算结果与实验结果在一定的误差范围内吻合得很好,这表明使用的模型和计算方案可行。以此计算方案对图2所示的两个界面体系进行几何优化,得到总能量分别为-75233.8186 eV和-75234.1603 eV。可见,模型2的结合能更低,结构更稳定,后续的计算选用此模型。
为了研究Mo、Cr和V元素对S0(双相γ-TiAl/α2- Ti3Al)合金体系的结构和性质的影响,用Mo、Cr和V分别替代Ti(或Al)建立掺杂双相γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al合金体系模型。其中替代Ti的位置有5种,分别为a1、…、a5;替代Al的位置有3种,分别为b1、b2、b3,它们的位置如图2(b)所示。这样,每种合金元素掺杂,都会有8个掺杂双相γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al合金体系,即替代Ti原子的体系Sa1、…、Sa5,替代Al原子的体系Sb1、Sb2、Sb3,共24个掺杂双相γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al界面体系。
1.2 计算方法
采用基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理[30-31],并结合物理与化学理论方法进行研究。采用平面波赝势方法,选择广义梯度近似下PBE泛函描述交换关联作用;用超软赝势描述离子实与价电子之间的相互作用势。平面波截断能设置为350 eV,布里渊区k点设置为4×2×1,采用Pulay密度混合法进行自洽计算(SCF),迭代计算的收敛标准设为:原子的能量变化量为2.0×10-5 eV / atom;原子作用力为0.05 eV / nm;原子位移误差为0.002  ;应力偏差为0.1 GPa。
;应力偏差为0.1 GPa。
采用平面波赝势方法的CASTEP软件包,利用高性能计算机集群完成计算与研究。用拟牛顿算法对各个双相TiAl/Ti3Al界面体系进行几何优化,直至达到收敛标准,计算获得平衡状态下晶体的结构参量、总能量、电荷分布等物理量。在此基础上,依据物理、化学理论进行分析与讨论。
2 计算结果与分析
2.1 掺杂对相界面稳定性的影响
Mo、Cr和V元素替代界面上Ti原子或Al原子后,各个体系的晶格参量将发生变化。对体系的稳定性有一定的影响。为了分析晶格参量的变化对γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al界面体系稳定性的影响,在计算条件相同的情况下,对界面的结构模型进行了研究。表1列出了各个界面体系结构优化后的结果。
表1 Mo、Cr和V掺杂γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al界面体系的几何性质和能量性质
Table 1 Geometrical and energy properties of Mo, Cr and V-doping γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al interface systems
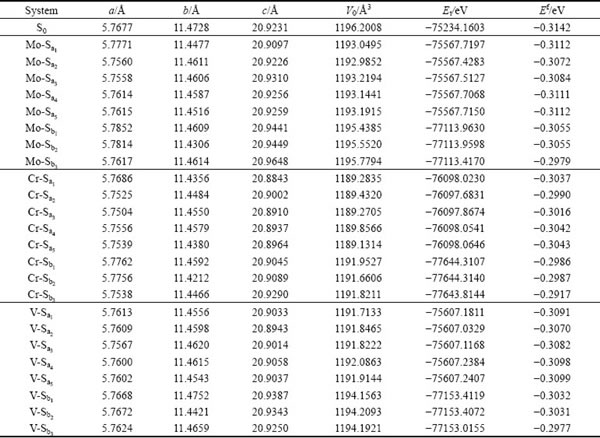
由表1可以看出,Mo、Cr和V元素分别替代γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al界面处的Ti原子或Al原子后,各个掺杂体系的晶格参量变化不一。对于Mo和V原子分别替代Ti原子,即体系Mo-Sa和V-Sa,a、b和c略有降低,体积稍微减少。这使体系的总能量变化不大。对于Cr原子替代Ti原子,即体系Cr-Sa,a、b和c均明显减小,体积明显减少。但由于Cr原子的共价半径(rCr=0.127 nm)明显小于Ti原子的共价半径(rTi=0.136 nm),占居Ti位的Cr原子具有较大的可移动性。这有利于位错滑移,进而有助于改善其延性。
对Mo原子替代Al原子,即体系Mo-Sb,a和c都略有所增加,b略有降低;对V原子替代Al原子,即体系V-Sb,a略有降低,b和c都略增加。总的说来,这两个体系的总体积稍微降低、释放出一定的能量,进而使体系的总能量降低。而对体系Cr-Sb,a增加,b和c都减小。这表明沿c轴方向的原子间距减小,有利于两相在界面处的结合,体系的体积稍有降低、释放出一定的能量,从而使得体系的总能量降低。
材料的能量稳定性可以用平均形成能表征。一般情况下,原子平均形成能越低,该材料的能量稳定性越好[32]。对于Mo、Cr和V掺杂双相γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al界面体系,平均形成能Ef计算公式可以表示为
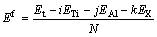 (1)
(1)
式中:Et表示优化后晶胞的总能量;ETi、EAl和EX分别表示Ti原子,Al原子和掺杂元素(Mo、Cr和V)在单质结构完全弛豫状态下的单原子能量;i、j和k分别表示各个元素在晶胞中的原子数;N表示晶胞中的总原子数。经计算,得到单质情况下Ti、Al、Mo、Cr和V原子的单原子能量分别为-1603.1192、-56.4638、-1936.8905、-2467.7351和-1976.5062 eV。优化后各个掺杂体系的总能量和形成能如表1所列。
从表1中可以看出,各个掺杂体系的原子平均形成能均为负值,表明它们均具有较好的能量稳定性,即在一定实验条件下掺杂双相界面体系是可以由实验制备并能稳定存在的。结果表明,对于Mo、Cr和V原子分别替代Ti原子和Al原子形成的体系,各个体系的平均形成能Ef相差不大,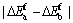 <0.014 eV,但
<0.014 eV,但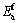 均略小于
均略小于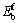 。这就表明Cr和V原子替位掺杂界面体系时,它们占居Ti位与占居Al位的概率差别不大。这一结论可与WEI等[24]研究结果相互佐证。对Mo元素替位掺杂的界面体系,Mo原子占居Ti位比占居Al位稍稳定,即Mo原子略微倾向于替代Ti原子。这一结论可与王海燕等[19]和HAO等[23]的研究结果可以相互佐证。但需要说明的是,王海燕等[19]研究的是单元素掺杂的γ-TiAl相;HAO等[23]研究的是α2-Ti3Al相。对于单元素掺杂的γ-TiAl相和α2-Ti3Al相,Mo原子倾向于替代Ti原子的原因主要在于Mo原子的共价半径(rMo=0.145 nm)与Ti原子的共价半径(rTi=0.136 nm)比较接近,而比Al原子的共价半径(rAl=0.118 nm)大得多。这使得Mo替代Ti原子后引起的晶格畸变小;相反,Mo替代Al原子后会引起较大的晶格畸变,造成体系的晶格能升高、稳定性降低。对于Mo原子掺杂双相TiAl/Ti3Al体系,γ-TiAl相与α2-Ti3Al相形成过渡区域,既非γ-TiAl相、也非α2-Ti3Al相,Mo原子恰好就在这个区域替代Ti或Al。因而,各个Mo掺杂双相γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al体系的能量差异变小,Mo原子占位的趋势随之发生了很大变化。这样,Mo占居Ti位与占居Al位的概率比较接近。相对而言,Cr和V原子的共价半径(rCr=0.127 nm,rV=0.125 nm)与Ti原子和Al原子相比变化不是很大,引起的畸变程度变化不是特别大,稳定性相近。尽管Cr和V原子替代Ti位与Al位的概率相近,Mo原子替代Ti位的概率稍微高一点,但是当通过实验进行元素掺杂时,合金元素替代哪种元素都有一定的概率。
。这就表明Cr和V原子替位掺杂界面体系时,它们占居Ti位与占居Al位的概率差别不大。这一结论可与WEI等[24]研究结果相互佐证。对Mo元素替位掺杂的界面体系,Mo原子占居Ti位比占居Al位稍稳定,即Mo原子略微倾向于替代Ti原子。这一结论可与王海燕等[19]和HAO等[23]的研究结果可以相互佐证。但需要说明的是,王海燕等[19]研究的是单元素掺杂的γ-TiAl相;HAO等[23]研究的是α2-Ti3Al相。对于单元素掺杂的γ-TiAl相和α2-Ti3Al相,Mo原子倾向于替代Ti原子的原因主要在于Mo原子的共价半径(rMo=0.145 nm)与Ti原子的共价半径(rTi=0.136 nm)比较接近,而比Al原子的共价半径(rAl=0.118 nm)大得多。这使得Mo替代Ti原子后引起的晶格畸变小;相反,Mo替代Al原子后会引起较大的晶格畸变,造成体系的晶格能升高、稳定性降低。对于Mo原子掺杂双相TiAl/Ti3Al体系,γ-TiAl相与α2-Ti3Al相形成过渡区域,既非γ-TiAl相、也非α2-Ti3Al相,Mo原子恰好就在这个区域替代Ti或Al。因而,各个Mo掺杂双相γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al体系的能量差异变小,Mo原子占位的趋势随之发生了很大变化。这样,Mo占居Ti位与占居Al位的概率比较接近。相对而言,Cr和V原子的共价半径(rCr=0.127 nm,rV=0.125 nm)与Ti原子和Al原子相比变化不是很大,引起的畸变程度变化不是特别大,稳定性相近。尽管Cr和V原子替代Ti位与Al位的概率相近,Mo原子替代Ti位的概率稍微高一点,但是当通过实验进行元素掺杂时,合金元素替代哪种元素都有一定的概率。
为了便于分析,将各个单原子掺杂双相γ-TiAl/α2- Ti3Al体系的平均形成能绘于图3中,依据各个体系的形成能差异确定较稳定的掺杂位置。由图3可以看出,在Mo、Cr和V替代Ti原子形成的体系中,体系Sa5的能量较低,或者说a5是比较稳定的位置。同理,在Mo、Cr和V替代替代Al原子的各个体系中,体系Sb1的能量较低,或者说b1是比较稳定的位置。因此,后续研究主要以体系Sa5和Sb1为对象。
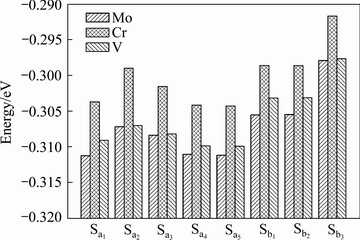
图3 Mo、Cr和V掺杂γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al界面体系的平均形成能
Fig. 3 Average formation energies of Mo, Cr and V-doping γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al interface systems
2.2 掺杂对界面结合强度及延性的影响
对于TiAl基合金,无论是穿晶断裂还是解理断裂,其裂纹扩展都必然穿过γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al相界面。当界面结合强度足够大时,就能够阻止裂纹的扩展,否则就不能阻止。因此,在一定程度上相界面的结合强度可以用断裂功来表征。各个相界面体系的Griffith断裂功W[33]可表示为
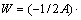
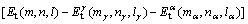 (2)
(2)
式中:A为界面模型的横截面积;Et (m, n, l)为优化后γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al相界面体系的总能量;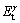 (mγ, nγ, lγ)和
(mγ, nγ, lγ)和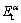 (mα, nα, lα)分别为形成界面前γ-TiAl (111)相和α2-Ti3Al (0001)相的总能量;m、n和l分别为Ti、Al和掺杂元素X的原子个数,且m=mγ+mα,n=nγ+nα,l=lγ+lα。
(mα, nα, lα)分别为形成界面前γ-TiAl (111)相和α2-Ti3Al (0001)相的总能量;m、n和l分别为Ti、Al和掺杂元素X的原子个数,且m=mγ+mα,n=nγ+nα,l=lγ+lα。
由表2中的晶格参量可得,体系S0、Mo-Sa5、Cr-Sa5、V-Sa5、Mo-Sb1、Cr-Sb1和V-Sb1共格界面的面积分别为0.6617、0.6598、0.6581、0.6598、0.6630、0.6619和0.6618 nm3。将它们代入式(2),计算得到相应的断裂功分别为3.22、3.18、3.19、3.22、3.27、3.26和3.28 J/m2。为便于比较,将各体系的断裂功绘于图4中。与体系S0相比较,体系Mo-Sa5和Cr-Sa5的断裂功均有不同程度的下降。这表明固溶于界面处的掺杂原子会导致结合强度降低。而体系V-Sa5的断裂功几乎不变,表明V占居Ti位时,对界面的结合强度影响较小。体系Mo-Sb1、Cr-Sb1和V-Sb1的断裂功均有不同程度的升高。这有利于提高界面的结合强度。这一结论可与魏强等[20]研究结果相互佐证。综上可知,体系Mo-Sa5和Cr-Sa5的结合强度减弱,有利于改善合金材料的延性;体系V-Sa5的结合强度变化不大,对延性改善贡献也小;体系Mo-Sb1、Cr-Sb1和V-Sb1的结合强度增大,不利于改善合金材料的延性。
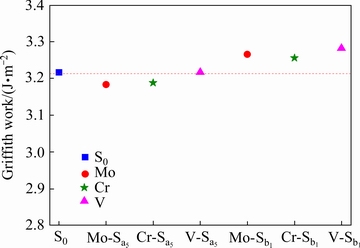
图4 Mo、Cr和V掺杂γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al界面体系的断裂功
Fig. 4 Griffith works of Mo, Cr and V-doping γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al interface systems
2.3 代表性掺杂体系的态密度与结合强度
为了进一步深入了解Mo、Cr和V元素掺杂对γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al合金界面延性改善的微观机制,选取断裂功最小、居中、最大的三个体系Mo-Sa5、V-Sa5和V-Sb1以及体系S0,绘制它们在相界面处的电子态密度(DOS)和分波态密度(PDOS),如图5所示,据此进行对比分析。
由图5的总态密度图可以看出,各个体系在费米能级处,电子浓度不为零。这说明掺杂前后的各个体系均呈现明显的金属性质。对于体系S0,总态密度在靠近费米能级附近出现了两个峰,即M0峰和N0峰。成键电子的能量区间主要分布在-9.59~1.0 eV。在此能量区间,Ti原子的3d电子和Al原子的3p电子相互重叠,电子轨道发生很强的杂化作用。Ti、Al原子的分波态密度显示,M0峰主要由Ti-d电子和Al-p电子贡献,即主要为p-d轨道杂化峰。这表明Ti原子和Al原子之间具有很强的共价键结合,从而使TiAl合金具有稳定的结构。根据Morinaga理论[22],Ti-d电子与Al-p电子形成的共价键具有较强的方向性。这是导致TiAl合金脆性的根本原因。N0峰主要由大量Ti-d电子和少量Al-p电子贡献,即主要为Ti—Ti键;同时含有少量的Ti—Al键。对于体系Mo-Sa5,成键电子能量主要分布在-9.61~1.0 eV,并且总态密度图上也出现了两个成键峰,即M1峰和N1峰。它们主要由Ti-3d电子,Al-3p电子和Mo-4d电子贡献。对比图5(b)与(a)可知,体系Mo-Sa5的p-d轨道杂化成键峰(M1, 24.22 eV-1)低于体系S0(M0, 25.14 eV-1),即体系Mo-Sa5的p-d轨道杂化键强度低于体系S0。这意味着Mo掺杂后,可使参与p-d轨道杂化的电子数减少,降低了共价键强度。相应地,位错运动的阻力减少,有利于延性的改善。这一分析可使HUANG等[34]关于Ti-Al-Mo三元体系的实验结果有了定量化依据。他们的实验研究表明,加入一定量的Mo元素,能够改变TiAl基合金中γ相和α2相的稳定性,使Ti-Al-Mo三元体系达到平衡。对于体系V-Sa5,成键电子的能量区间主要分布在-9.59~1.0 eV。它们主要由Ti-3d电子、Al-3p电子以及V-3d电子贡献。对比图5(c)与(a)可知,体系V-Sa5的p-d轨道杂化成键峰(M2,24.83 eV-1)低于体系S0。也就是说体系V-Sa5比体系S0的p-d轨道杂化键强度稍低。这意味着掺入杂质V,可使参与p-d轨道杂化的电子数稍有减少,对界面的结合强度影响较小。对于体系V-Sb1,对比图5(d)与(a)可知,成键峰M3和N3重叠。体系V-Sb1的p-d轨道杂化成键峰(M3, 19.45 eV-1)明显低于体系S0的p-d轨道杂化键峰;同时N3峰也明显降低。因此,单单由p-d轨道杂化键峰降低不能预测共价结合减弱,原因是形成Ti—Al、Ti—Ti和Al—Al键的电子数均在减少。然而综合图5可见,对于体系S0、Mo-Sa5和V-Sa5,Al-p电子与Ti-d电子的轨道杂化成键峰是明显低于Ti-d与Ti(Mo,V)-d电子的轨道杂化成键峰;而体系V-Sb1的p电子与d电子的轨道杂化成键峰已经与Ti(V)-d电子轨道杂化峰无差异,相对而言,实际是p-d轨道杂化的电子态密度大幅上升,各向异性程度增强。再者,在费米能级处,体系V-Sb1的电子态密度(15.74 eV-1)明显低于体系S0的(22.35 eV-1),也表明V替代Al原子后,使体系的总能量降低,增加了界面的结合强度,不利于改善体系的延性。
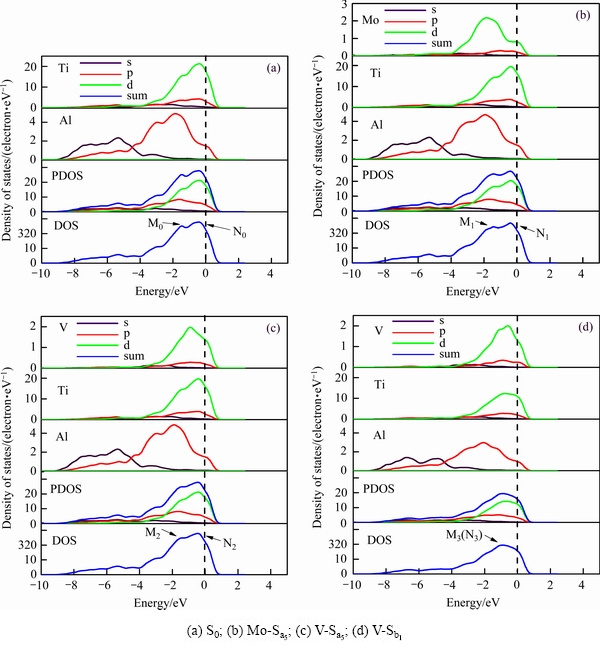
图5 界面体系的费米能级附近的电子态密度
Fig. 5 Densities of states of interface systems near Fermi level
2.4 代表性掺杂体系的电荷密度与化学键性质
虽然杂质Mo和V掺杂后会与其最近邻Ti或Al原子形成金属键、离子键,但合金中共价键Ti—Ti、Al—Al和Al—Ti仍占据主要部分[35]。为了进一步研究Mo和V掺杂后与周围原子的键合作用,图6分别绘制了体系S0、Mo-Sa5、V-Sa5和V-Sb1的具有代表性的(001)面的电荷密度。

图6 界面体系S0、Mo-Sa5、V-Sa5和V-Sb1中杂质原子所在(001)面的电荷密度分布
Fig. 6 Maps of charge density of crystal face (001) passing through impurity atom in interface systems
由图6可以看出,在体系S0中,Ti原子与Al原子通过共用电子对形成共价键,具有较强的方向性。对比图6(b)与(a)可以看出,在体系Mo-Sa5中,杂质原子Mo周围的电荷密度明显增加。在(001)面上,Mo原子与四个相邻的Ti原子之间的电子云“区域扩展、强度增加”。这表明当Mo替代Ti原子后,Mo-d电子与Ti-d电子杂化作用增强。类似地,Mo原子与两个相邻的Al原子之间的电子云,也具有“区域扩展、强度增加”的特点。这也表明Mo-d电子与Al-p电子的杂化作用增强。但仔细观察,发现在Al原子周围红色的低密度电子云形状发生了变化,在体系S0中其形状为“三角形”,而在体系Mo-Sa5中其形状更接近“圆形”。这也就是说,对体系Mo-Sa5而言,Al原子周围各向同性程度提高了,离子键、金属键特性增强了。为了使这一判断更有说服力,表2给出了(001)面上位置“0”处的Ti原子(或杂质Mo、V原子)和其最近邻的六个原子的Mulliken布居数;表3给出了位置“0”处的Ti原子(或杂质Mo、V原子)和其最近邻的六个原子之间的重叠布居数。由Mulliken布居数可知,在体系S0中界面处Ti(0)原子的总电荷数为0.06,在体系Mo-Sa5中Mo原子的总电荷数降低为-0.49。这表明Mo确实夺得了电子。Al(3, 6)的电荷数由-0.07变为-0.03。这表明参与s-p轨道杂化的电子数减少。由重叠布居数可知,Mo替代Ti原子掺杂后,Mo与Al原子之间的重叠布居数为0.17,低于体系S0中Ti与Al原子之间的重叠布居数0.20。这表明Mo与Al原子间的共价特性减弱。综合而言,Mo的掺入后,由于Mo原子实的吸引,使其邻近区域电子云分布发生明显的聚集效应;又因为周围的Ti原子核和Al原子实带正电,起到抗衡Mo原子实的吸引作用,最后达到平衡。综合效果就是,在Mo原子的周围形成结合强度稍高的区域。该区域与周围其他区域的结合的各向异性程度下降。这有利于改善材料的延性。上述分析结果与MANDA等[9]的实验分析相吻合。对比图6(c)与(a)可以发现,在体系V-Sa5中V原子周围情况与体系Mo-Sa5中Mo原子周围情况相似,即具有“区域扩展、强度增加”的特点,但程度稍低。这一判断得到原子电荷数和重叠布居数的支持。因此,综合效果也是在V原子的周围形成结合强度稍高的区域。该区域与周围其他区域相互作用的各向异性程度下降。这有利于改善材料的延性。对比图6(d)与(a)则发现,在体系V-Sb1中V原子掺杂似乎有引起向相反的方向发展的趋势,即电子云的反聚集效应。这导致该区域与周围其他区域相互作用的各向异性程度上升。这就不利于改善材料的延性。
表2 体系S0、Mo-Sa5和V-Sa5中原子的Mulliken布居数和电荷数
Table 2 Mulliken populations and charges numbers in system S0, Mo-Sa5 and V-Sa5
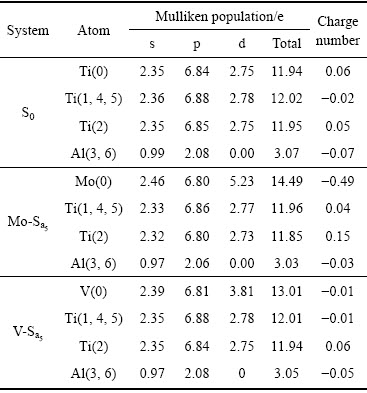
表3 体系S0、Mo-Sa5和V-Sa5中的重叠布居数
Table 3 Overlap populations of system S0, Mo-Sa5 and V-Sa5.

3 结论
1) Mo、Cr和V元素固溶于双相γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al界面后,各个掺杂体系的总能量和平均形成能均为负值,表明它们可以由实验制备并能稳定存在。对于Mo、Cr和V元素替代Ti或Al原子后,各个体系的平均形成能相差不大。这表明占居Ti位与占居Al位的概率差别不大。
2) 断裂功显示,体系Mo-Sa5和Cr-Sa5的结合强度减弱,有利于改善合金材料的延性;体系V-Sa5的结合强度变化不大,对延性改善贡献也小;体系Mo-Sb1、Cr-Sb1和V-Sb1的结合强度增大,不利于改善合金材料的延性。
3) 态密度显示,对体系Mo-Sa5 (或V-Sa5),Mo(或V)元素替代Ti原子掺杂使参与p-d轨道杂化的电子数减少,结合强度降低,降低了位错运动的阻碍阻力,有利于改善材料的延性;但V元素掺杂的影响较弱。对体系V-Sb1,V替代Al原子后,使体系的总能量降低,增加了界面的结合强度,不利于改善材料的延性。
4) 电荷密度显示,对体系Mo-Sa5(或V-Sa5),Mo(或V)的掺入使其周围形成结合强度稍高的区域。该区域与周围其他区域的结合的各向异性程度下降,这有利于改善材料的延性。而在体系V-Sb1中,V原子掺杂有引起电子云的反聚集效应的趋势,这就不利于改善材料的延性。
REFERENCES
[1] CLEMENS H, MAYER S. Design, processing, microstructure, properties, and applications of advanced intermetallic TiAl alloys [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2013, 15(4): 191-215.
[2] BEWLAY B P, NAG S, SUZUKI A, WEIMER M J. TiAl alloys in commercial aircraft engines[J]. Materials at High Temperatures, 2016, 33 (4/5): 549-559.
[3] WU X H. Review of alloy and process development of TiAl alloys[J]. Intermetallics, 2006, 14(10/11): 1114-1122.
[4] KANANI M, HARTMAIER A, JANISCH R. Stacking fault based analysis of shear mechanisms at interfaces in lamellar TiAl alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 106: 208-218.
[5] SHU S L, TONG C Z, QIU F, ZOU Q, JING Q C. Effects of ternary elements on the ductility of TiAl[J]. The Canadian Journal of Metallurgy and Materials Science, 2016, 55(2):156-160.
[6] 张建伟, 李世琼, 梁晓波, 程云君. Ti3A1和Ti2A1Nb基合金的研究与应用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(1): 336-341.
ZHANG Jian-wei, LI Shi-qiong, LIANG Xiao-bo, CHENG Yun-jun. Research and application of Ti3A1 and Ti2A1Nb based alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(1): 336-341.
[7] SASTRY S M L, LIPSITT H A. Fatigue deformation of TiAl base alloys[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1997, 8(2): 299-308.
[8] OEHRING M, APPEL F, ENNIS P J, WAGNER R, A TEM study of deformation processes and microstructural changes during long-term tension creep of a two-phase γ-titanium aluminide alloy[J]. Intermetallics, 1999, 7(3/4): 335-345.
[9] MANDA P, PATHAK A, MUKHOPADHYAY A, CHAKKINGAL U, SINGH A K. Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr and similar Mo equivalent alloys: First principles calculations and experimental investigations[J]. Journal of Applied Research and Technology, 2017, 15: 21-26.
[10] XI Y J, LIU Y J, WANG Z X, LIU J B. Oxidation and electrochemical corrosion performance of Ti3Al alloy with TiAl coating[J]. Anti-Corrosion Methods and Materials, 2010, 57(1): 13-17.
[11] 杨 锐. 钛铝金属间化合物的进展与挑战[J]. 金属学报, 2015, 51(2): 129-147.
YANG Rui. Advances and challenges of TiAl base alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2015, 51(2): 129-147.
[12] HU H, WU X Z, WANG R, LI W G, LIU Q. Phase stability, mechanical properties and electronic structure of TiAl alloying with W, Mo, Sc and Yb: First-principles study[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 658: 689-696.
[13] 宋庆功, 杨宝宝, 赵俊普, 秦国顺, 郭艳蕊, 胡雪兰. Zr和(或)Mn替位掺杂γ-TiAl基合金的延性与电子性质[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(11): 2309-2318.
SONG Qing-gong, YANG Bao-bao, ZHAO Jun-pu, QIN Guo-shun, GUO Yan-rui, HU Xun-lan. Investigations on ductibility and electronic property of Zr and (or) Mn doped γ-TiAl based alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(11): 2309-2318.
[14] 陈玉勇, 韩建超, 肖树龙, 徐丽娟, 田 竞. 稀土Y在γ-TiAl基合金及其精密热成形中应用的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(5): 1241-1251.
CHEN Yu-yong, HAN Jian-chao, XIAO Shu-long, XU Li-juan, TIAN Jing. Research progress of rare earth yttrium application in γ-TiAI based alloy and precision thermal forming[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(5): 1241-1251.
[15] WANG L, SHANG J X, WANG F H, ZHANG Y. First principles study of α2-Ti3Al (0001) surface and/γ-TiAl(111)/α2-Ti3Al (0001) interfaces[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2013, 276: 198-202.
[16] ZGHAL S, NAKA S, COURET A, A quantitative TEM analysis of the lamellar microstructure in TiAl based alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 1997, 45(7): 3005-3015.
[17] 祝莹莹, 邓 文, 孙顺平, 江海峰, 黄宇阳, 曹名洲, 熊良钺. 用正电子湮没技术研究Cr和Nb对TiAl合金中缺陷和d-d电子相互作用的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2009, 38(2): 271-274.
ZHU Ying-ying, DENG Wen, SUN Shun-ping, JIANG Hai-feng, HUANG Yu-yang, CAO Ming-zhou, XIONG Liang-yue. Influence of Cr and Nb on defects and d-d electron interactions in TiAl alloys researched by positron annihilation techniques[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2009, 38(2): 271-274.
[18] 熊 翔, 黄伯云, 雷长明, 吕海波. 添加铬元素对TiAl合金室温延性和微观结构的影响[J]. 中南矿冶学院学报, 1992, 23(5): 560-564.
XIONG Xiang, HUANG Bai-yun, LEI Chang-ming, Lü Hai-bo. Effect of Cr addition on room-temperature ductility and microstructure of TiAl alloy[J]. Journal of Central South Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 1992, 23(5): 560-564.
[19] 王海燕, 胡前库, 杨文朋, 李旭升. 金属元素掺杂对TiAl合金力学性能的影响[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65(7): 1-9.
WANG Hai-yan, HU Qian-ku, YANG Wen-peng, LI Xu-Sheng. Influence of metal element doping on the mechanical properties of TiAl alloy [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65(7): 1-9.
[20] 魏 强, 王 硕. 第三组元Cr, Mo, W掺杂对钛铝化合物脆性的影响[J]. 金属功能材料, 2014, 21(2): 26-31.
WEI Qing, WANG Shuo. Effect on brittle of titanium aluminum compound by doping Cr, Mo, W additions[J]. Metallic Functional Materials, 2014, 21(2): 26-31.
[21] 党宏丽, 王崇愚, 于 涛. γ-TiAl中Nb和Mo合金化效应的第一性原理研究[J]. 物理学报, 2007, 56(5): 2838-2844.
DANG Hong-li, WANG Chong-yu, YU Tao. First-principles investigation on alloying effect of Nb and Mo in γ-TiAl[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2007, 56(5): 2838-2844.
[22] MORINAGA M, SAITO J, YUKAWA N, ADACHI H. Electronic effect on the ductility of alloyed TiAl compound[J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1990, 38(1): 25-29.
[23] HAO Y L, XU D S, CUI Y Y, YANG R, LI D. The site occupancies of alloying elements in TiAl and Ti3Al alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 1999, 47(4): 1129-1139.
[24] WEI Y, ZHANG Y, LU G H, XU H B. Effects of transition metals in a binary-phase TiAl-Ti3Al alloy: From site occupancy, interfacial energetics to mechanical properties[J]. Intermetallics, 2012, 31: 105-113.
[25] 屈 华, 刘伟东, 张 坤, 刘志林. Ti3Al基合金(0001)α2//(110)β界面价电子结构分析[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2005, 34(10): 1569-1573.
QU Hua, LIU Wei-dong, ZHANG Kun, LIU Zhi-lin. Study on the valence electron structure of (0001)α2//(110)β interface in Ti3Al-based alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2005, 34(10): 1569-1573.
[26] 刘伟东, 屈 华, 刘志林. 双相TiAl合金α2/γ界面电子结构计算与增韧机制分析[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2005, 34(2): 199-204.
LIU Wei-dong, QU Hua, LIU Zhi-lin. Calculation of valence electron structures of α2/γ interface and toughening mechanism in two-phase TiAl-alloy[J]. Rare metal materials and engineering, 2005, 34(2): 199-204.
[27] WEI Y, ZHANG Y, ZHOU H B, LU G H, XU H B. First-principles investigation on shear deformation of a TiAl/Ti3Al interface and effects of oxygen[J]. Intermetallics, 2012, 22: 41-46.
[28] FISCHER F D, WAITZ T, SCHEU C, CHA L, DEHM G, ANTRETTER T, CLEMENS H. Study of nanometer-scaled lamellar microstructure in a Ti-45Al-7.5Nb alloy-experiments and modeling[J]. Intermetallics, 2010, 18: 509-517.
[29] KOIZUMI Y, FUJITA T, MINAMINO Y, HATA S. Effects of plastic deformation on lamellar structure formation in Ti-39 at.% Al single crystals[J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58: 1104-1115.
[30] 武佳佳, 马万坤, 焦 芬, 覃文庆. Cu、Ni 掺杂FeS2电子结构与光学性质的第一性原理计算[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2017, 27(3): 605-612.
WU Jia-jia, MA Wan-kun, JIAO Fen, QIN Wen-qing. First principle calculation of electronic structures and optical properties of copper and nickel doped FeS2[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2017, 27(3): 605-612.
[31] 刘 松, 王寅岗. 氢在钛晶体中扩散行为的第一性原理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(11): 3100-3106.
LIU Song, WANG Yin-gang. First-principles of hydrogen diffusion mechanism in titanium crystals[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(11): 3100-3106.
[32] 陶鹏程, 黄 燕, 周孝好, 陈效双, 陆 卫. 掺杂对金属-MoS2界面性质调制的第一性原理研究[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66(11): 11820.
TAO Peng-cheng, HUANG Yan, ZHOU Xiao-hao, CHEN Xiao-shuang, LU Wei. First principles investigation of the tuning in metal-MoS2 interface induced by doping[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(11): 11820/1-11820/8.
[33] 王小宏, 张彩丽, 户秀萍, 韩培德. Al、Zn 对Mg-Li相界合金化效应的第一性原理研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2014, 43(7): 1661-1665.
WANG Xiao-hong, ZHANG Cai-li, HU Xiu-ping, HAN Pei-de. First principle study on alloying effect of Al and Zn doping on Mg-Li phase interface[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2014, 43(7): 1661-1665.
[34] HUANG X M, ZHU L L, CAI G M, LIU H S, JIN Z P. Experimental investigation of phase equilibria in the Ti–Al–Mo ternary system[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2017, 52: 2270-2284.
[35] 宋庆功, 赵俊普, 顾威风, 甄丹丹, 郭艳蕊, 李泽朋. 基于密度泛函理论的La掺杂γ-TiAl体系结构延性与电子性质[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66(6): 066103.
SONG Qing-gong, ZHAO Jun-pu, GU Wei-feng, ZHEN Dan-dan, GUO Yan-rui, LI Ze-peng. Ductile and electronic properties of La-doped gamma-TiAl systems based on density functional theory[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(6): 066103.
Effect of Mo(or Cr, V) substitution doping on energy, ductility and electronic properties of dual-phase γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al interface
SONG Qing-gong1, 2, GU Wei-feng1, ZHEN Dan-dan2, GUO Yan-rui1, HU Xue-lan2
(1. Institute of Low Dimensional Materials and Technology, College of Science, Civil Aviation University of China, Tianjin 300300, China;
2. Sino-European Institute of Aviation Engineering, Civil Aviation University of China, Tianjin 300300, China)
Abstract: The average formation energies, Griffith fracture works and electronic structures of Mo (or Cr, V) doping of γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al interfacial systems were calculated with density functional theory. The results indicate that these systems possess energy stability and can be prepared by experiments and exist stably. The Griffith fracture work and density of the representative system show that the bonding strength of Mo-Sa5 (or Cr-Sa5) is weakened and the densities of state of Mo-d and Ti-d electrons of Mo-Sa5 are increased. The charge density map of the (001) plane passing through impurity atom and populations of the doping system show that, there is an electron cloud aggregation effect surrounding the dopant caused by the doping of Mo (or V) atom, which forms a region with a slightly higher bonding strength. As a result, the anisotropy degree of the combination of this region is reduced, which is the internal reason of the improved ductility for TiAl alloys.
Key words: dual-phase γ-TiAl/α2-Ti3Al interface; energy property; ductility; electronic property; first-principle
Foundation item: Project(51201181) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (3122016L012) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China
Received date: 2017-08-24; Accepted date: 2017-11-27
Corresponding author: SONG Qing-gong; Tel: +86-22-24092510; E-mail: qgsong@cauc.edu.cn
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51201181);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资助项目(3122016L012)
收稿日期:2017-08-24;修订日期:2017-11-24
通信作者:宋庆功,教授,博士;电话:022-24092510;E-mail:qgsong@cauc.edu.cn