文章编号:1004-0609(2009)06-1049-06
H65黄铜合金连续挤压过程中的组织和性能演变特征
隋 贤,宋宝韫,李 冰,运新兵,高 飞
(大连交通大学 连续挤压工程研究中心,大连 116028)
摘 要:采用金相显微镜、维氏硬度仪和万能实验机对H65黄铜合金连续挤压过程中的组织和性能演变特征进行研究。结果表明:连续挤压过程中合金发生了强烈的剪切变形,产生大量的位错和位错缠结,形成取向差较小的亚晶结构;随着变形程度的加剧,合金的温度升高,促进了动态再结晶的发生,小角度晶界通过吸收位错等方式长大成大角度晶界,使亚晶逐渐转变成细小均匀的等轴晶,有效地提高了材料的综合性能。这种组织的演变在力学实验中得到证明。
关键词:H65黄铜合金;连续挤压;组织演变;动态再结晶
中图分类号:TG 146.21 文献标识码:A
Characteristic of microstructure and properties evolution of H65 brass alloy during continuous extrusion process
SUI Xian, SONG Bao-yun, LI Bing, YUN Xin-bing, GAO Fei
(Engineering Research Center of Continuous Extrusion, Dalian Jiaotong University, Dalian 116028, China)
Abstract: The microstructure and properties evolution of H65 brass alloy during continuous extrusion were observed by OM, hardness-testing devices and universal-testing machine. The results show that severe plastic deformation (SPD) occurs in continuous extrusion of H65 brass alloy. A large number of dislocation and dislocation twins form. The sub-crystallization structure can be achieved. With increasing friction and temperature, the dynamic recrystallization occurs. After that, the low angle boundaries grow up to high angle boundaries through absorbing dislocation power. The homogeneous grain can be achieved. Continuous extrusion improves the properties of the material effectively. The microstructure evolution is demonstrated in the mechanical property experiments.
Key words: H65 brass alloy; continuous extrusion; microstructure evolution; dynamic recrystallization
连续挤压技术(Continuous extrusion forming, 简称Conform)是在20世纪70年代初期由英国Springfields核能研究所的GREEN先生提出的,作为一种新型的挤压技术,连续挤压有许多突出的优点,因此,得到企业界的极大关注,获得相当迅速的发展。20世纪80年代所出现的连续挤压技术的新颖之处在于将在压力加工中做无用功的摩擦力变为变形的驱动力和加热源,从而成为一种高效节能的加工新技术。该技术开始主要用于制造超长度的铝管,后来又进一步发展成连续挤压包覆技术,应用于铝包钢线、有线电视同轴电缆(CATV)和光纤复合架空地线(OPGW)领域。今天连续挤压已成为铝、铜及铜合金中小型材、铝及铝合金盘管、双金属导线和电缆包铝等材料生产的先进加工技术,应用十分广泛。
20世纪90年代宋宝韫等[1?2]对连续挤压塑变区速度场和连续挤压轮槽塑变区应力及几何参数进行了研究。储灿东等[3]对连续挤压成型过程的温度场进行了研究。运新兵等[4?7]介绍了一种制备超细晶材料的新技术?连续等径角挤压法。刘冬华等[8?9]对三辊行星轧制过程中ACR紫铜管的组织和性能演变进行了研究。2001年韩国的CHO和JEONG[10]利用三维有限元分析法对CONFORM连续挤压成型过程中的弯曲现象进行了大量的研究。2004年美国的RAAB等[11]对ECAP–Conform连续挤压进行了研究,该技术结合等径角挤压和连续挤压以连续的方式生产超细晶结构(UFG)材料。2006年MANNINEN等[12?13]对铜连续挤压过程中金属流动进行分析。但是对于黄铜连续挤压全过程组织演变还未见研究,本文作者结合自主研制的TLJ250连续挤压机的实际生产特点,对黄铜连续挤压的全过程进行组织和性能演变的分析,为黄铜合金连续挤压的实际生产提供了重要的指导意义。
1 实验
实验原材料采用H65黄铜合金,轧制为直径为d8 mm的杆料后进行退火处理。H65黄铜合金杆料经过预热处理在TLJ250连续挤压机上进行连续挤压试验,经挤压机挤压后水冷到室温,获得d3.6 mm圆形线材。TLJ250挤压机挤压轮直径为250 mm,轮槽的宽度为8 mm,模具为d3.6 mm的圆形模具。
连续挤压工艺原理为:挤压轮作旋转运动,在挤压轮圆周上有一环形沟槽,腔体工作圆弧与挤压轮的圆周相吻合,腔体内装有挤压模具[14]。铜杆料经压实轮压实,在摩擦力的作用下被连续送入挤压腔,坯料在腔体挡料块前面沿圆周运动,受阻进入腔体通过模具挤出产品。连续挤压原理图如图1所示。
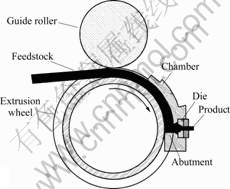
图1 连续挤压原理图
Fig.1 Principle of continuous extrusion
用线切割机沿试样纵向切割制成金相试样,然后,进行研磨、抛光、腐蚀,腐蚀剂为FeCl3(5g)+HCl(25 mL)+H2O(50 mL)溶液,用金相显微镜对H65黄铜合金的显微组织演变进行观察;用HVA-10A维氏硬度仪和万能实验机对H65黄铜合金连续挤压后不同区域的性能进行测定。
2 分析与讨论
2.1 原材料的显微组织
图2所示为H65黄铜合金连续挤压前的显微组织。由图2可见,H65黄铜合金退火后的显微组织由α和β两相组成,其中白色组织为α相,黑色组织为β相。轧制组织的晶粒大小不均,心部的晶粒较边缘粗大,这是因为心部和边缘的加工程度不同所致。退火后有许多退火孪晶,有些孪晶内还包括更细小的孪晶,并且有许多黑色点状组织,这是因为大量的铅聚集在一起而形成的,其平均晶粒尺寸约为60 μm。
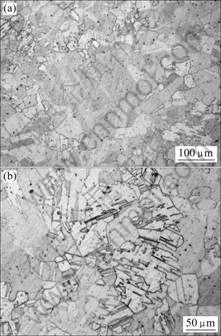
图2 H65黄铜合金连续挤压前的显微组织
Fig.2 Microstructures of H65 brass alloy before continuous extrusion: (a) Microstructure; (b) Twins microstructure
2.2 H65黄铜合金连续挤压后的显微组织
图3所示为H65黄铜合金连续挤压后的显微组织。由图3可见,经过连续挤压后,H65黄铜合金的显微组织由α和β两相组成,晶粒为等轴晶,整个横截面和纵截面的晶粒分布都很均匀,心部和边缘晶粒大小没有明显的区别,平均晶粒尺寸为20 μm左右,大约为原材料的1/3。因此,经过连续挤压后,H65黄铜合金的显微组织得到了很好的细化,没有挤压的方向性;并且由于聚集的铅溶解于β相中,所以聚集的杂质消除,H65黄铜合金中的黑色点状组织消失,性能得到改善。
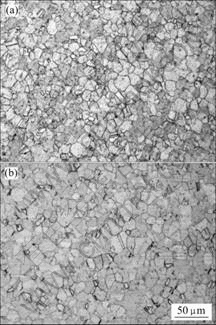
图3 H65黄铜合金连续挤压后的显微组织
Fig.3 Microstructures of H65 brass strip after continuous extrusion: (a) Cross section; (b) Longitudinal section
2.3 连续挤压过程中各塑性变形区的显微组织
连续挤压成型过程可以分为挤压型腔变形区和挤压模腔变形区,挤压型腔变形区是指轮槽和腔体前端圆弧面组成的变形区域,又可以分成4个区域,如图4所示:摩擦剪切变形区;镦粗变形区;粘着区;直角弯曲挤压区。图5所示为H65黄铜合金连续挤压型腔内不同区域的组织演变过程。
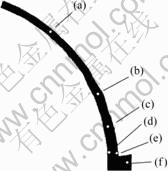
图4 H65黄铜合金连续挤压过程中各塑性变形区分布
Fig.4 Plastic deformation regions of H65 brass alloy in continuous extrusion process: (a) Friction-shearing deformation region; (b) Upsetting deformation region; (c), (d) Adhesion region; (e), (f) Right-angle bending region
在摩擦剪切变形区,坯料除了在压实轮压实过程中产生大量间距很小的变形带之外,金属基本上不再发生变形,只是紧紧粘在挤压轮槽底和轮槽壁上,随挤压轮旋转而向前运动。轮槽给予坯料的是有效摩擦力,用来提供坯料实现镦粗变形所需的力,而腔体和导板施予坯料的是摩擦阻力。在该区域内,晶粒沿着挤压轮转动方向变形,晶粒被拉长,在挤压轮旋转的方向可以看到少量的滑移线,如图5(a)所示。
在镦粗变形区,坯料在轮槽两侧摩擦力的作用下发生镦粗变形,逐渐充满整个挤压轮槽。镦粗变形区晶粒被镦粗,呈多边形,晶内存在着位错和滑移线,如图5(b)所示。
在粘着区,坯料在轮槽两侧摩擦力的作用下,继续随挤压轮向前运动,坯料粘着在挤压轮槽中形成了黄铜?黄铜的摩擦副。在该区内可以看见一种条带状的变形区,通常把这种条带状的变形组织称之为剪切变形带或剪切带[15],如图5(c)所示。剪切带变形区可以提供很好的形核条件,剪切带具有较高的储存能,有利于再结晶形核,此外,剪切带亚晶取向的多样性也为取向核的生长创造了条件。在粘着区下端(见图4(d)位置),剧烈的剪切变形在组织内部产生很大的应变,促使大量高密度缠结的位错生成。随着变形的继续,这些高能量的位错在应力作用下运动,逐渐在晶粒内部形成了胞状结构,部分晶粒内部位错反应较为完全,形成了亚晶,如图5(d)所示。
在直角弯曲挤压区,坯料在挡料块的作用下发生直角弯曲,进入模腔内挤压制品。 在该区内,坯料在摩擦力的作用下进入变形区,受到摩擦力剧烈作用,产生了较大的热量,使坯料温度升高,非常有利于位错的 运动与反应,极大促进了动态再结晶的发生,使能量得到了释放,小角度晶界通过吸收位错等方式长大成大角度晶界,使亚晶逐渐变成细小均匀的等轴晶,从而变形织构消失,该区域晶粒已经相当细小,组织比较均匀,平均晶粒尺寸在10 μm以下,如图5(e)和(f)所示。
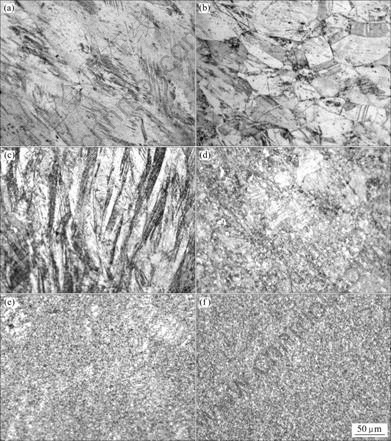
图5 H65黄铜合金连续挤压型腔内不同区域的组织演变过程
Fig.5 Microstructure evolution of H65 brass alloy at different parts in continuous extrusion cavity: (a) Microstructure of friction-shearing deformation region; (b) Microstructure of upsetting deformation region; (c), (d) Microstructure of adhesion region; (e), (f) Microstructure of right-angle bending region
2.4 硬度实验结果及分析
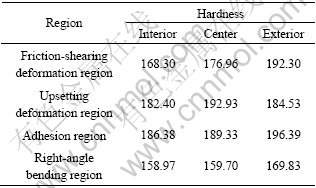
表1所列为H65黄铜合金连续挤压各变形区硬度的平均值,可以看出:内侧比中心和外侧的硬度高,粘着区的硬度最高。因为坯料外侧和导板、腔体接触,产生较高的摩擦力,温度升高,硬度下降。在直角弯曲挤压区内,由于温度升高,发生动态再结晶,晶粒细小,硬度低,在粘着区内受到的摩擦力最大,变形最为剧烈,硬度最高。以上结论和连续挤压型腔中的组织演变规律相吻合。
表1 H65黄铜合金硬度统计表
Table 1 Statistical table of hardness (HV) of H65 brass alloy
2.5 拉伸实验结果及分析
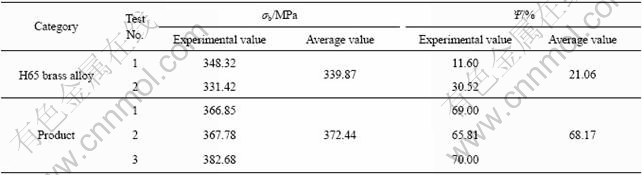
表2所列为H65黄铜合金的拉伸试验结果。由于H65黄铜合金经过连续挤压后的晶粒得到细化,组织均匀,抗拉强度增大,断面收缩率提高。从表2可以看出,断面收缩率提高了3倍,塑性明显提高。从总体上来说,产品的综合力学性能有所提高。
表2 H65黄铜合金拉伸试验结果
Table 2 Tensile test result of H65 brass alloy
3 结论
1) H65黄铜合金连续挤压过程中塑性变形区分为摩擦剪切变形区、镦粗变形区、粘着区、直角弯曲挤压区。
2) H65黄铜合金连续挤压过程中发生了强烈的剪切变形,产生大量的位错和位错缠结,形成取向差较小的亚晶结构;随着变形程度的增加,合金的温度升高,促进了动态再结晶的发生,小角度晶界通过吸收位错等方式长大成大角度晶界,使亚晶逐渐变成细小均匀的等轴晶。
3) H65黄铜合金经过连续挤压形成均匀、细小的组织,使黄铜线材的抗拉强度及塑性指标均有明显的提高,获得优良的综合力学性能。
REFERENCES
[1] 张新宇, 宋宝韫, 李明典, 高 飞. 连续挤压塑变区速度场分析及功率计算[J]. 中国机械工程, 1999, 10(1): 60?63.
ZHANG Xin-yu, SONG Bao-yun, LI Ming-dian, GAO Fei. Analysis of velocity field and calculation of power in continuous extrusion plastic zone[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 1999, 10(1): 60?63.
[2] 李明典, 宋宝韫, 杨新华, 李伟含. 连续挤压轮槽塑变区应力分析及几何参数的确定[J]. 塑性工程学报, 1999, 6(3): 25?30.
LI Ming-dian, SONG Bao-yun, YANG Xin-hua, LI Wei-han. Stress analysis and determination of geometry parameters in plastic zone of wheel groove[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 1999, 6(3): 25?30.
[3] 储灿东, 王东哲, 彭颖红, 阮雪榆. 连续挤压成型过程的温度场研究[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2001, 8(1): 9?12.
CHU Can-dong, WANG Dong-zhe, PENG Yi-hong, RUAN Xue-yu. Study on temperature field of continuous extrusion forming process[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2001, 8(1): 9?12.
[4] 运新兵, 宋宝韫, 陈 莉. 连续等径角挤压制备超细晶铜[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(9): 1563?1569.
YUN Xin-bing, SONG Bao-yun, CHEN Li. Ultra-fine grain copper prepared by continuous equal channel angular press[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(9): 1563?1569.
[5] 汪建敏, 许晓静, 石凤健, 姜银方. 等径角挤压获得超细晶铜的研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2004(7): 6?7.
WANG Jian-min, XU Xiao-jing, SHI Feng-jian, JIANG Yin-fang. Investigation on ultra-fine grain copper by equal channel angular pressing[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2004(7): 6?7.
[6] 陈彦博, 赵晶磊, 李英龙, 宋 丹, 温景林. 连续ECAP技术制备超细晶铝[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(12): 2054?2059.
CHEN Yan-bo, ZHAO Jing-lei, SONG Dan, WEN Jing-lin. Preparation of ultrafine grained aluminium by continuous equal channel angular pressing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(12): 2054?2059.
[7] 刘 咏, 唐志宏, 周科朝. 纯铝等径角挤技术(Ⅰ)—显微组织演化[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2003, 13(1): 21?26.
LIU Yong, TANG Zhi-hong, ZHOU Ke-chao. Equal channel angular pressing process (ECAP) of pure Al (Ⅰ)— Microstructure evolution[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 13(1): 21?26.
[8] 刘东华, 苏玉长, 邓楚平, 胡其平, 潘志勇. 三辊行星轧制过程中ACR紫铜管的组织和性能演变[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(5): 881?886.
LIU Dong-hua, SU Yu-chang, DENG Chu-ping, HU Qi-ping, PAN Zhi-yong. Microstructure and properties of ACR copper tube during three-roll planetary milling process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(5): 881?886.
[9] 李 冰, 杨 志, 刘化民, 张士宏, 张金利. 三辊行星轧制运动和管坯变形规律的仿真模拟[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2005, 12(5): 70?73.
LI Bing, YANG Zhi, LIU Hua-min, ZHANG Shi-hong, ZHANG Jin-li. Computer simulation on the movement and deformation rules of three-roll planetary rolling process of copper tube[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2005, 12(5): 70?73.
[10] CHO J R, JEONG H S. Parametric investigation on the curling phenomenon in CONFORM process by three-dimensional finite element analysis[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2001, 110: 53?60.
[11] RAAB G J, RUSLAN Z V, TERRY C L, YUNTIAN T Z. Continuous processing of ultrafine grained Al by ECAP-conform[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, 382: 30?34.
[12] MANNINEN T, KATAJARINNE T, RAMSAY P. Analysis of flash formation in continuous rotary extrusion of copper[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2006, 177: 600?603.
[13] KATAJARINNE T, MANNINEN T, RAMSAY P. Numerical simulation of flash formation in continuous rotary extrusion of copper[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2006, 177: 604-607.
[14] 宋宝韫. 连续挤压和连续包覆技术的理论研究与工程实践[J]. 中国机械工程, 1998, 9(8): 69?72.
SONG Bao-yun. Theoretical study and engineering practice in continuous extrusion and continuous cladding technology[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 1998, 9(8): 69?72.
[15] 毛卫民, 赵新兵. 金属的再结晶与晶粒长大[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1994: 14?28.
MAO Wei-min, ZHAO Xin-bing. Crystallization and grain growth of metals materials[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1994: 14?28.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金重点资助项目(50635020)
收稿日期:2008-06-19;修订日期:2008-06-10
通讯作者:宋宝韫,教授,博士;电话:13604241311;E-mail: songby@djtu.edu.cn
(编辑 何学锋)