文章编号:1004-0609(2008)04-0651-09
过冷熔体中球晶组织的形成规律
郭洪民1,杨湘杰2
(1. 南昌大学 材料科学与工程学院,南昌 330031;
2. 南昌大学 机电工程学院,南昌 330031)
摘 要:研究LSPSF工艺条件下Al-20%(质量分数)Cu合金的初生α(Al)的形貌演变,结合微观组织模拟技术和M-S界面形态稳定性理论,分析过冷熔体中球晶组织快速形成的基本规律。结果表明:合金熔体中自由晶数目和浆料冷却速度共同决定初生固相的尺寸和形态;最早(凝固发生3 s内)观察到的初生α(Al)呈细小球形,并在整个演变过程中始终保持球形不变,没有枝晶组织出现;晶粒周围溶质扩散层的叠加可明显降低固-液界面前沿的浓度梯度,提高固-液界面的稳定性;均匀化晶粒周围溶质分布,抑制晶粒的择优生长,促进初生α(Al)保持球形;由溶质扩散层的叠加和界面能引起的抑制和粗化效应可促使失稳的等轴晶粗化成球晶。
关键词:半固态成形;凝固;晶体生长;界面稳定性;微观组织模拟
中图分类号:TG 146.2 文献标识码:A
Formation mechanism of spherical particles in undercooled melt
GUO Hong-min1, YANG Xiang-jie2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330031, China;
2. School of Mechanical and Electronic Engineering, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330031, China)
Abstract: The microstructure evolution of Al-20%(mass fraction)Cu alloy under LSPSF (Low superheat pouring with a shear field) conditions was investigated. The quick formation mechanism of spherical particles in an undercooled melt was discussed by microstructure simulation technique and M-S interface stability theory. The results show that the morphology of primary α(Al) is determined by both the number of free crystals and the cooling intensity of melt. The first observable primary α(Al) of Al-20%Cu alloy is spherical shape, and grows spherically in subsequently lower cooling. The overlapping diffusion fields from adjacent growing crystals can induce a stabilizing effect on the morphological instability at the solid-liquid interface and promote the globular growth of primary α(Al). Restraining and coarsening caused by overlapping diffusion fields and Gibbs-Thomson effect are main dynamic conditions that promote the morphology transition of instabilized crystal from equiaxed shape into spherical shape.
Key words: semi-solid metal processing; solidification; crystal growth; interface stability; microstructure simulation
半固态成形是一种新型凝固组织控制技术,能够获得细小均匀分布的球形/近球形晶粒的半固态组 织。自该技术诞生之日起,国内外学者对搅拌条件下(机械搅拌、电磁搅拌)半固态组织的形成进行广泛深入的研究,提出许多机理和假说,其中颇具有影响力的有树枝晶破碎机制(认为球晶组织是由树枝晶破碎发展而来的)[1-4]和树枝晶抑制生长机制(认为球晶组织可以在液相中直接形成)[5-7]。提出这些机制所依赖的实验条件有如下特点:非常强烈的搅拌和高的剪切速率,如双螺旋搅拌可获得5 000~10 000 s-1的剪切速率[6];搅拌或剪切时间长,如电磁搅拌或机械搅拌的搅拌时间通常多于100 s[4],基本上作用于整个浆料制备过程。随着研究的深入,研究者又相继开发出液相线铸造[8]、NRC(New rheocasting)[9]、SLC(Sub liquidus casting)[10]、DTC (Direct thermal control)[11]和LSPSF[12]等一系列高效制备半固态组织的流变铸造工艺,并成为流变成形中半固态浆料制备的主流。这些工艺打破依靠机械搅拌和电磁搅拌等外场来获得球晶组织的传统思路,其球晶形成机理有别于强烈搅拌条件下的球晶形成,但尚缺乏系统的研究。
LSPSF工艺[12-13]可在15~25 s内制备出质量优异的半固态浆料,其中合金液流经输送管约用时2 s,其它时间半固态浆料处于静止状态;合金熔体的流动是在输送管转动和自身重力下实现的,是一种自发流动,流动强度比机械搅拌和电磁搅拌弱得多;合金熔体流经输送管时的温度在其液相线温度以下1~5 ℃,此时半固态浆料的固相率很低,流动性很好,合金液中存在的剪切力很小。这些特征为进一步研究半固态组织的形成创造条件。因此,本文作者以LSPSF为基 础,研究不同工艺条件下凝固组织的形成和球晶的演化过程,并结合理论分析试图解释过冷熔体中球晶组织快速形成的基本规律。
1 实验
实验合金为Al-20%(质量分数)Cu,经DTA分 析,其液相线温度为597 ℃,共晶温度为547 ℃,共晶温度对应的固相率为47%。该合金结晶区间较 宽,共晶温度对应的固相率低,有利于浆料固相率的控制和实验操作。本实验采用自制的相变致冷快速冷却装置,尽量减少冷淬过程对半固态浆料原始组织的影响。相变致冷,即是利用材料从固态到液态转变过程中吸收的热对熔体冷却的技术。本工作采用的相变致冷介质为纯锡,锡冷铜模冷淬实验装置如图1所示。
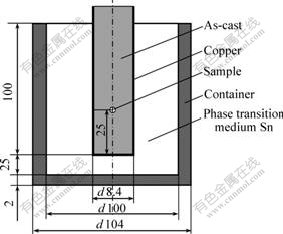
图1 锡冷铜模装置示意图和取样位置
Fig.1 Schematic illustration of geometry and dimensions of copper mould (mm)
将配制好的Al-20%Cu合金锭在坩埚电阻炉内加热到680 ℃,完全熔化后除气除渣,保温10 min使熔体均匀,进行浆料制备实验。晶粒细化剂为Al-5Ti-1B,以合金中含0.1%Ti为基准控制加入量,处理温度为680 ℃。
利用LSPSF工艺制备半固态浆料,其工艺原理和流程详见文献[13]。采用具有底部开口的中间包,每次实验的浇注量均为1 500 g,这样可保证浇注速度基本恒定。实验中输送管温度为400 ℃。通过调整浆料蓄积器的材质和预热温度来改变浆料在浆料蓄积器内的冷却速度,该冷却速度由温控系统测量,具体实验参数列于表1。考察球晶组织演变过程时,浆料蓄积器的预热温度为580 ℃,获得更慢的冷却速度便于冷淬控制,浆料在浆料蓄积器内冷却到不同温度,在此温度下倾入锡冷铜模,获得试样。利用配有定量金相分析系统的光学显微系统进行显微组织观察和分 析。用晶粒等效圆直径D = 2(A/π)1/2表征初生α(Al)的大小,用晶粒形状因子F = 4πA/P2表征初生α(Al)的形貌,其中A和P分别代表初生α(Al)晶粒的面积和周长。
表1 Al-20%Cu浆料制备的实验参数
Table 1 Experimental parameters used in preparation of semi-solid slurry for Al-20%Cu alloy
2 实验结果
2.1 晶粒数目与冷却速度的影响
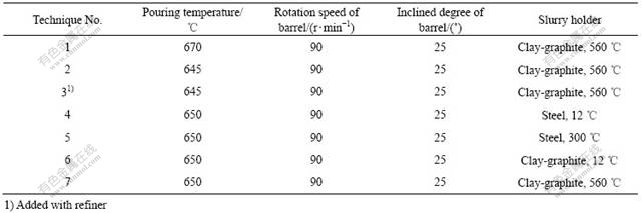
图2所示为表1中工艺1,2和3条件下Al-20%Cu合金的初生固相形态。由图可知,在相近的浆料冷却速度下,当浇注温度为670 ℃时,合金熔体的出口温度高于液相线温度,浆料中自由晶数量少,初生α(Al)尺寸粗大,形态为树枝状;当浇注温度为645 ℃时,合金熔体的出口温度低于液相线温度,自由晶数量大幅增多,初生α(Al)尺寸细小,形态为球状(形态因子0.87);在Al-5Ti-1B熔体处理条件下,异质形核得到加强,虽然在相同的浇注温度下,但浆料自由晶数量进一步增多,初生固相尺寸更加细小,形态因子0.88。研究表明[8-10, 12, 14-16],低过热浇注有利于获得球形或近球形的半固态组织,这与本研究的结果一致。但与液相线铸造、NRC、SLC和DTC等相比,LSPSF可以更多地提高浇注温度,这有利于实际生产中的浇注操作和温度控制。

图2 工艺1,2和3条件下Al-20%Cu合金的初生固相形态
Fig.2 Morphologies of primary α(Al) in Al-20%Cu alloy under technique No.1, 2 and 3 at different pouring temperatures: (a) 670 ℃; (b) 645 ℃; (c) 645 ℃, melt is refined with 0.1%Ti
在LSPSF工艺中,合金熔体流经输送管后,熔体的形核过程已经基本结束,浆料在浆料蓄积器内处于静止冷却过程。图3所示为表1中工艺4~7的实验结果。表明浆料的冷却速度极大地影响着初生固相的形态。随着冷却速度由0.42增到24.3 ℃/s,初生α(Al)尺寸变小,均匀性变差,其形态由球形晶粒→等轴晶→树枝晶,形状因子由0.89降为0.46。
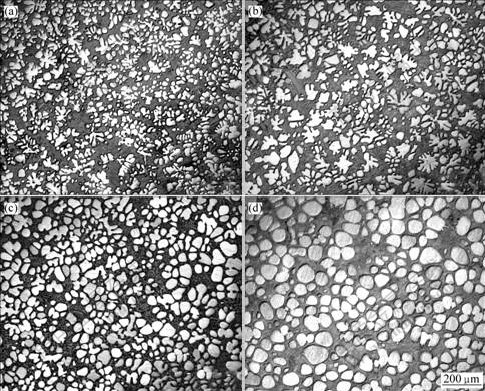
图3 不同冷却速度时Al-20%Cu合金初生固相的形貌
Fig.3 Morphologies of primary α(Al) in Al-20%Cu alloy poured at 650 ℃ and different cooling rates: (a) 24.3 ℃/s; (b) 11.2 ℃/s; (c) 2.8 ℃/s; (d) 0.42 ℃/s
2.2 初生α(Al)的形态演变过程
采用锡冷铜模快速冷却半固态浆料,获得该半固态浆料在缓慢冷却过程中的演变特征。具体实验条件为:浆料蓄积器预热温度580 ℃,浇注温度645 ℃,输 送管倾角25?,输送管转速90 r/min,浆料出口温度 595 ℃,浆料在浆料蓄积器内冷却速度为0.18 ℃/s。当浆料温度达到595~568 ℃时,迅速将半固态浆料倾入锡冷铜模,其微观组织如图4所示。表2所列为定量分析结果,其中固相率由Scheil公式获得。
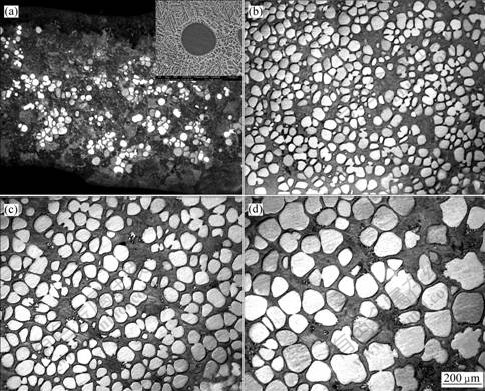
图4 熔体冷却速度0.18 ℃/s时连续冷却条件下Al-20%Cu合金半固态组织的演变过程
Fig.4 Microstructure evolutions of Al-20%Cu alloy during continuous cooling and average cooling rate of 0.18 ℃/s: (a) 595 ℃; (b) 592 ℃; (c) 584 ℃; (d) 568 ℃
 表2 Al-20%Cu在凝固初期不同时刻初生α(Al)的特征
表2 Al-20%Cu在凝固初期不同时刻初生α(Al)的特征
Table 2 Characteristics of primary α(Al) during different solidification stages corresponding to Fig.4
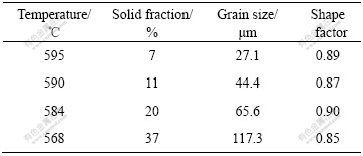
估算浆料在锡冷铜模内的冷却速度。利用Al-20%Cu合金液相线温度与共晶点间的温度差与凝固时间的比值来估算浆料的冷却速度。根据二次枝晶臂间距lDAS与凝固时间ts的关系[17],即
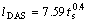 (1)
(1)
由图4(a)可知,二次枝晶臂间距确定为3~4 μm,取lDAS=3.5 μm,则浆料在锡冷铜模内凝固时间约为0.144 s,得浆料在锡冷铜模内的冷却速度约为346 ℃/s。如此高的冷却速度基本可以保持合金的半固态组织。
由于1 500 g Al-20%Cu合金流经输送管将历时约2 s,由图4可知,LSPSF工艺可以在凝固开始后3 s(操作过程的影响)获得球形的初生固相,并且球状形态可以在后续的缓慢冷却生长过程中得以保持。在整个演变过程中,初生α(Al)内部没有夹裹液相。随着冷却时间的延长,初生固相逐渐粗化,晶粒数目逐渐减 少,并出现一些形状不规则异常长大的晶粒,这可能是由于长大过程中晶粒相互合并形成的。
3 讨论
流出输送管的Al-20%Cu合金半固态浆料含有的固相率很低,约为7%。因此,初生α(Al)主要在静止状态下,即纯扩散条件下进行形态演变。在其它条件均固定的条件下,浇注温度决定着合金熔体的形核、晶粒游离和自由晶的存活,最终表现为半固态浆料中自由晶的数量[13]。以上实验结果表明,浆料冷却速度和浆料中自由晶数量共同决定着初生固相的生长形态;在高晶粒密度和缓慢冷却条件下,可以获得细小球形或近球形的半固态组织。这与NRC[9]和液相线铸造[14-16]获得的实验结果相同。从凝固形态学角度,晶粒球化的实质就是失稳到稳态转变以及稳态维持过程中固-液界面形态发生变化的结果。概括地讲,在纯扩散条件下,固-液界面的稳定性可以表示为经典M-S理论[18-19]:
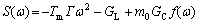 (2)
(2)
式中 Tm为合金熔点,Г为Gibbs-Thompson系数,m0为液相线斜率,ω为几何干扰频率,GL和GC分别为未扰动界面前沿的温度梯度和浓度梯度。根据M-S理论,函数S(ω)由如下3部分构成:第一项是由界面能决定的,由于任何频率的干扰总是趋于使界面面积增大,而界面能总是使界面面积缩小,因此界面能总是对界面稳定性有贡献的;第二项是由温度梯度决定的,由于在浆料制备工艺中,固-液界面前沿的温度梯度为负,所以浆料中的温度梯度促使界面失稳;第三项恒为正,表明界面前沿的浓度梯度总使界面不稳定。
按照经典M-S理论,当晶粒半径大于十几微米 时,球形界面将失稳,晶粒将以树枝形态生长,这无法解释本工作所观察到的直径达几十微米以上的球晶组织。经典M-S理论是建立在单个晶粒基础上的,即每个晶粒的生长互不影响。而在半固态浆料制备工艺中,浆料内含有一定数量的晶粒,当晶粒生长到一定程度时,晶粒间的相互作用必然对其生长形态产生影响。晶粒在发生碰撞(硬接触)前,主要通过各自的浓度场和温度场间的叠加(软接触,扩散场)发生相互作用。随着晶粒尺寸变大,界面能的作用逐渐变弱,而温度梯度和浓度梯度的负作用变强。如果维持晶粒继续以球晶方式生长,则必须尽可能地降低温度梯度和浓度梯度的负面作用。LSPSF工艺主要运用“缓慢冷却”。研究表明[14-16],缓慢冷却有利于球晶的形成。根据成分过冷理论,降低冷却速度可以使界面前沿的溶质和结晶潜热充分扩散,降低界面前沿的温度梯度和浓度梯度。但缓慢冷却并不是维持界面长期稳定的充要条件,上面实验表明,随着半固态浆料中自由晶数量的降低,初生α(Al)由球晶转变成蔷薇晶和树枝晶。本文作者认为,抑制自由晶以树枝晶形式生长必须具备两个条件:1) 缓慢冷却;2) 尽可能地提高浆料中自由晶的数量。下面以“扩散场叠加”进行解释。所谓“扩散场叠加”是:晶粒周围溶质扩散层的叠加影响着固-液界面处引起界面失稳的浓度梯度,影响着晶粒周围溶质浓度的分布,进而影响初生相的生长形态。
本文作者采用文献[20]建立的模拟流变铸造微观组织形成的元胞自动机模型分析LSPSF工艺中初生α(Al) 在浆料蓄积器内的形态演变过程。主要假设包括:由于温度扩散系数比溶质扩散系数大3~4个数量级,可假设相变驱动力由溶质扩散和Gibbs-Thomson效应决定;传热在微观尺度上扩散完全,即微观组织演变模拟空间内的温度可视为牛顿冷却;忽略凝固过程中对流的影响。
图5所示为Al-20%Cu合金5个晶粒共存,在不同条件下的形态,其中4个晶粒对称分布,第5个晶粒(称为中心晶粒)位于其它4个晶粒形成空间的中心,元胞尺寸为0.2 μm。图5(a)的条件为:熔体过冷度3 K,中心晶粒与其它晶粒间的距离为30个元胞;图5(c)的条件为熔体过冷度5 K,其它同图5(a);图5(e)的条件为:中心晶粒与其它晶粒间的距离为70个元胞,其它同于图5(a)。图5(b),(d),(f)为图5(a),(c),(e)的中心晶粒固-液界面处的溶质分布曲线。结果表明,晶粒浓度场间的相互叠加对中心晶粒的形貌及其周围的溶质分布具有严重的影响,且影响程度取决于冷却速度和晶粒间距。在低生长速度和晶粒间距小的情况下,中心晶粒由等轴晶转变为球晶,如图5(a)所示;在高生长速度和晶粒间距小的情况下,虽然中心晶粒仍为等轴晶,但其发达程度远不如其它4个晶粒的,如图5(c)所示;虽然同样在低生长速度条件下,如果晶粒间的距离增大,中心晶粒呈等轴晶状,其发达程度甚至比高生长速度短晶粒间距的情况下还要大,如图 5(e)所示。同时,降低冷却强度或减小晶粒间的距离均能够使溶质分布更为均匀;在短晶粒间距和低冷却强度下,晶粒周围固-液界面处的溶质分布呈“W”形,而其它情况下溶质分布呈“M”形。对于“M”形界面溶质分布,溶质浓度最低的部位是一次枝晶的枝晶尖端,而枝晶根部的溶质浓度最高,这正是晶粒择优生长的特征。与之相反,对于“W”型界面溶质分布,溶质浓度最低的部位是枝晶根部,而一次枝晶尖端的溶质浓度最高,这正是晶粒择优生长方向被抑制的主要特征,是晶粒浓度场强烈相互叠加的结果。
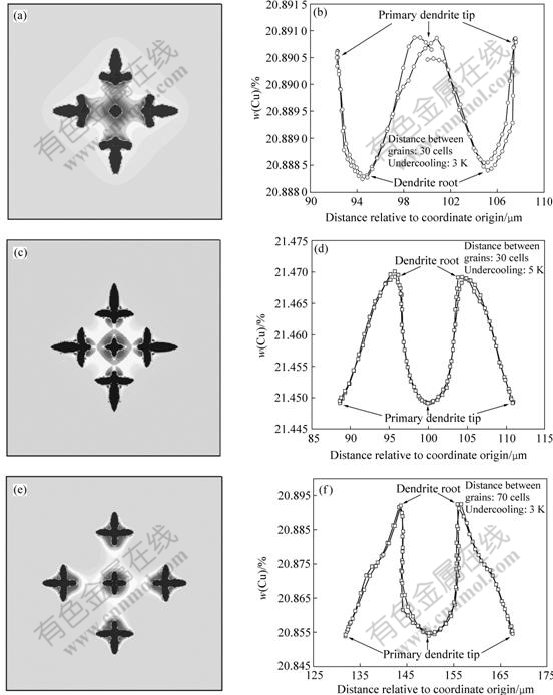
图5 过冷度和晶粒数目对Al-20%Cu合金初生固相的形态及固-液界面处的溶质Cu浓度分布曲线
Fig.5 Effects of undercooling and amount of grain on growth morphologies and Cu concentration field around grains: (a) Undercooling of 3 K, distance between grains is 30 cells; (c) Undercooling of 5 K, distance between grains is 30 cells; (e) Undercooling of 3 K, distance between grains is 70 cells; (b), (d), (f) Cu concentration distribution curves according to (a), (c) and (e), respectively
因此,在高晶粒密度、低冷却强度下,晶粒浓度场发生强烈而快速的相互叠加:1) 固-液界面前沿的溶质浓度梯度大大降低,浓度梯度对界面稳定性的负作用大大减弱,界面能的正面作用得到加强;2) 整个固-液界面上的溶质分布更为均匀,抑制枝晶尖端的生长,从而相对提高枝晶臂根部和侧面的生长速 度,晶粒在各方向上均匀生长,晶粒的择优生长受到强烈抑制;3) 固-液界面前沿液相浓度上升,使得相应液相线温度下将,过冷度减小,晶粒的生长速度下降,界面稳定性获得增强。在这3个方面的作用 下,初生α(Al)保持稳定球形生长的临界半径增大或在整个凝固过程中始终保持球形的生长方式。
而提高冷却强度或降低晶粒密度,晶粒周围浓度场叠加被推迟,导致液相中溶质浓度差别加大,增加固-液界面前沿的浓度梯度,当浓度梯度抵消界面能的作用力时,晶粒的球形生长条件被破坏,初生α(Al)的形态将向树枝晶或蔷薇晶方向发展。当冷却强度很高或晶粒密度很低时,枝晶尖端可以不受其它晶粒的影响而自由生长,只有当树枝晶较发达时,浓度场才发生相互叠加。图6所示的多粒子模拟结果进一步证实上述观点,图6(a)的模拟环境为:晶粒数目为50,冷却速度为0.5 K/s,元胞尺寸为1 μm;图6(b)的模拟环境为:晶粒数目7,冷却速度5 K/s,元胞尺寸1 μm。
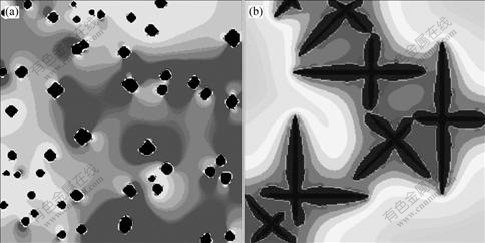
图6 多粒子条件下Al-20%Cu合金中初生α(Al)的形态和浓度场
Fig.6 Morphology evolutions and Cu concentration field during formation of primary α(Al) in Al-20%Cu alloy for two thermal and nucleation conditions: (a) Amount of nucleation 50, cooling rate 0.5 K/s, cell size 1 μm; (b) Amount of nucleation 7, cooling rate 5 K/s, cell size 1 μm
图7所示为Al-20%Cu合金5个晶粒共存,在4 K过冷度下的形态演变过程。中心晶粒与其它晶粒间的距离为30个元胞,元胞尺寸为0.2 μm。在较大过冷度下,晶粒很快发展成等轴晶,晶粒浓度场彼此还未发生相互作用,随着浓度场发生叠加,中心晶粒的择优生长被抑制,等轴晶根部的生长得到加强,最终中心晶粒演变成球形。因此,在缓慢冷却过程中,高晶粒密度还具有抑制和促进粗化的作用。晶粒密度高,晶粒间距越小,限制二次晶臂生长所需的热力学稳定性。晶粒周围浓度场的叠加,会抑制晶粒的生长,特别是等轴晶尖端的生长,晶粒择优生长的趋势受到抑制,促使各个方向生长几率相同。在界面能作用下,晶粒由曲率半径小向曲率半径大的方向演变。随着系统温度的降低,只有靠粗化一次晶臂来增加固相率,最终促使等轴晶粗化成球晶。因此可以认为,获得优质半固态浆料的首要条件是在合金熔体中获得最大数量的自由晶,即使其形态为树枝状或等轴状,这些细小的初生晶在后续的缓慢冷却过程中也可以快速演变成球晶。
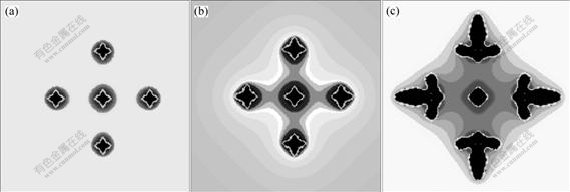
图7 4 K过冷度下Al-20%Cu固-液界面从失稳到稳态的转变过程
Fig.7 Evolution of solid-liquid surface from instability to stability in Al-20%Cu alloy at melt underdooling of 4 K
4 结论
1) 过冷熔体中自由晶数量及其冷却速度共同决定着初生固相的尺寸和形态。自由晶数量大,冷却速度低,球晶或近球晶形成的趋势大。获得优质半固态浆料的首要条件是在合金熔体中获得最大数量的自由晶。
2) Al-20%Cu合金中最早观察到的初生组织为细小球形(凝固后3 s),并在整个演变过程中始终保持球形,没有枝晶组织出现。
3) 微观组织模拟和凝固界面形态稳定性分析表明:在高晶粒密度和缓慢冷却条件下,晶粒周围溶质扩散层的叠加可明显降低固-液界面前沿的浓度梯度,提高固-液界面的稳定性;均匀化晶粒周围溶质分布,抑制晶粒的择优生长,使得晶粒在各个方向上几乎均匀生长,促进初生α(Al)保持球形。由溶质扩散层的叠加和界面能引起的抑制和粗化效应可促使失稳的等轴晶粗化成球晶。
REFERENCES
[1] FLEMINGS M C. Behavior of metal alloys in the semi-solid state[J]. Metall Trans A, 1991, 22(4): 957-981.
[2] DOHERTY R D, LEE H I, FEEST E A. Microstructure of stir-cast metals[J]. Mater Sci Eng, 1984, 65: 181-189.
[3] HELAWELL A. Grain evolution in conventional and rheocasting[C]//KIRKWOOD D H, KAPRANOS P. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Semi-Solid Processing of Alloys and Composites. England: The University of Sheffield, 1996: 60-65.
[4] 毛卫民, 赵爱民, 崔成林, 钟雪友. 电磁搅拌半固态AlSi7Mg合金初生α(Al)的影响规律[J]. 金属学报, 1999, 35(9): 971-974.
MAO Wei-min, ZHAO Ai-min, CUI Cheng-lin, ZHONG Xue-you. The formation mechanism of non-dentritic primary α(Al) phases in semi-solid AlSi7Mg alloy[J]. Acta Metallugica Sinica, 1999, 35(9): 971-974.
[5] MOLENAAR J M M, KATGERMAN L, KOOL W H. On the formation of the stir cast structure[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1986(21): 389-394.
[6] JI S, FAN Z. Solidification behavior of Sn-15 Wt pct Pb alloy under a high shear rate and high intensity of turbulence during semisolid processing[J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2002, 33(11): 3511-3520.
[7] 李 涛, 黄卫东, 林 鑫. 半固态处理中球晶形成与演化的直接观察[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2000, 10(5): 635-639.
LI Tao, HUANG Wei-dong, LIN Xin. Formation of globular structure in semisolid metal processing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2000, 10(5): 635-639.
[8] 董 杰, 路贵民, 任栖锋, 等. 液相线铸造法非枝晶半固态形成机理探讨[J]. 金属学报, 2002, 38(2): 203-207.
DONG Jie, LU Gui-min, REN Qi-feng, et al. Discussion on the formation mechanism of nondentritic semisolid microstructures during liquidus casting[J]. Acta Metallugica Sinica, 2002, 38(2): 203-207.
[9] KAUFMANN H, RANSHOFEN, WABUSSEG H, KAUFMANN H, WABUSSEG H, UGGOWITZER P J. Metallurgical and processing aspects of the NRC semi-solid casting technology[J]. Aluminum, 2000, 76(1/2): 70-75.
[10] JORSTAD J L. Interaction of key variables during rheocasting: importance of microstructure, fraction solid and flow velocity[J]. Solid State Phenomena, 2006(116/117): 24-33.
[11] LEE J K, YOON Y O, JO H H, et al. Development of in-ladle direct thermal control (DTC) rheocasting process[J]. Solid State Phenomina, 2006, 116/117: 518-521.
[12] GUO Hong-min, YANG Xiang-jie. Continuous fabrication of sound semi-solid slurry for rheoforming[J]. Solid State Phenomena, 2006, 116/117: 425-428.
[13] GUO H M, YANG X J. Efficient refinement of spherical grain by LSPSF rheocasting process[J]. Mater Sci Technol, 2008, 24(1): 55-63.
[14] PAN Y, AOYAMA S, LIU C. Spherical structure and formation conditions of semi-solid Al-Si-Mg alloy[C]//SUN G X, YUAN H. Proceedings of the 5th Asian Foundry Congress. Nanjing: Southeastern University Press, 1997: 443-451.
[15] MAO Wei-min, CUI Cheng-lin, ZHAO Ai-min. Effect of pouring process on the microstructures of semi-solid AlSi7Mg alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2001, 17(6): 515-519.
[16] 赵建新, 朱明芳, Kim J M, HONG C P. Al-Si合金在凝固过程中颗粒和枝晶组织的演变[J]. 理化检验: 物理分册, 2004, 40(9): 433-438.
ZHAO Jian-xin, ZHU Ming-fang, KIM J M, HONG C P. Evolution of globular and dendritic structures in solidification in Al-Si alloy[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis A: Physical Testing, 2004, 40(9): 433-438.
[17] SHIRAI Y, MORIYA T, YOSHIDA C. Heat transfer properties and solidification structure in the initial solidification of semi-solid metals[C]//KIRKWOOD D H, KAPRANOS P. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Semi-Solid Processing of Alloys and Composites. England: The University of Sheffield, 1996: 97-103.
[18] MULLINS W W, SEKERKA R F. Morphological stability of a particle growing by diffusion or heat flow[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1963, 34(2): 323-329.
[19] TRIVEDI R. Morphological stability of a solid particle growing from a binary alloy melt[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1980(48): 93-99.
[20] GUO Hong-min, YANG Xiang-jie. Morphology evolution of primary alpha phase in rotated duct process[C]//APELIAN D, ALEXANDROU A, GEORGIOU G, JORSTAD J, MAKHLOUF M. Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Semi-Solid Processing of Alloys and Composites. Limassol: The Worcester Polytechnic Institute and The Metals Processing Institute, 2004: 695-703.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50474007);江西省科技支撑计划资助项目;江西省教育厅科技资助项目(GJJ08006)
收稿日期:2007-07-28;修订日期:2007-12-24
通讯作者:郭洪民,博士;电话:0791-3969611;E-mail: guohongmin@ncu.edu.cn
(编辑 龙怀中)