中等嗜热菌群协同脱除高硫铝土矿中的硫
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报2016年第11期
论文作者:李寿朋 王瑞 郭玉婷 郭玉洁 王国华 刘新星 邱冠周
文章页码:2393 - 2403
关键词:高硫铝土矿;中等嗜热菌群;生物脱硫;协同作用;黄钾铁矾
Key words:high sulfur bauxite; moderately thermophilic consortia; bio-desulfurization; mutual effect; jarosite
摘 要:选用氧化特性不同的6株中等嗜热菌,构建4组共培养菌群,用于一水硬铝石型高硫铝土矿的摇瓶脱硫实验。对筛选出的高效菌群,分析其在高硫铝土矿脱硫过程中的脱硫行为,并采用SEM、XPS、XANES等技术手段分析含硫矿物氧化过程中的表面形貌和中间产物。结果表明:铁、硫氧化混合菌群比亚铁氧化菌群和硫氧化菌群具有更强的氧化能力,脱硫15d后矿石中硫含量下降到0.29%,满足拜耳法生产氧化铝的原料要求。在氧化过程中,含硫矿物表面出现单质硫和黄钾铁矾,但这些中间产物并未成为脱硫的阻止因素。最终氧化产物是硫 酸盐。
Abstract: Four microbial consortia were constructed using six moderately thermophilic and their ability to bio-desulfurization of high-sulfur bauxite were studied in flask scale. The most efficient consortia’s behavior during the process of high sulfur bauxite desulfurization was measured. The surface microcosmic appearance and speciation of bauxite were characterized by means of SEM, XPS and XANES. The results show that consortia containing sulfur- and iron-oxidizing moderately thermophilic acidophiles provide more rapid bio-oxidation rate than consortia containing iron-oxidizing or sulfur-oxidizing microorganisms only. After Bio-desulfurization 15 d, the sulfur content of bauxite decreases to 0.29%, then the bauxite can be used as raw material in Bayer process of alumina production. The mineral surface is partially covered by intermediate products of the elemental sulfur and jarosite, causing no passivation. The end product of pyrite oxidation is sulfate.
基金信息:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目
文章编号:1004-0609(2016)-11-2393-10
李寿朋1, 2,王 瑞1, 2,郭玉婷1, 2,郭玉洁1, 2,王国华1, 2,刘新星1, 2,邱冠周1, 2
(1. 中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 生物冶金教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083)
摘 要:选用氧化特性不同的6株中等嗜热菌,构建4组共培养菌群,用于一水硬铝石型高硫铝土矿的摇瓶脱硫实验。对筛选出的高效菌群,分析其在高硫铝土矿脱硫过程中的脱硫行为,并采用SEM、XPS、XANES等技术手段分析含硫矿物氧化过程中的表面形貌和中间产物。结果表明:铁、硫氧化混合菌群比亚铁氧化菌群和硫氧化菌群具有更强的氧化能力,脱硫15d后矿石中硫含量下降到0.29%,满足拜耳法生产氧化铝的原料要求。在氧化过程中,含硫矿物表面出现单质硫和黄钾铁矾,但这些中间产物并未成为脱硫的阻止因素。最终氧化产物是硫 酸盐。
关键词:高硫铝土矿;中等嗜热菌群;生物脱硫;协同作用;黄钾铁矾
中图分类号:Q939 文献标志码:A
截至2014年底,我国铝土矿查明资源储量为42.3亿t[1],其中一水硬铝石型高硫铝土矿5.6亿t,约占我国铝土矿资源总量11%[2]。据分析,高硫铝土矿中含硫矿物主要是黄铁矿(FeS2)及其异构体,占含硫矿物总量80%~90%,另有少量以黄铜矿(CuFeS2)和硫酸盐(如石膏(CaSO4·2H2O)和重晶石(BaSO4)),形式存在[3]。
目前,90%以上氧化铝采用拜耳法生产,当高硫铝土矿(硫含量≥0.7%)进入拜耳法高温溶出过程后,主要发生如下化学反应[4-5]:
8FeS2+30OH-→4Fe2O3+14S2-+S2O32-+15H2O (1)
4S22-+6OH-→6S2-+S2O32-+3H2O (2)
3S2O32-+6OH-→2S2-+4SO32-+3H2O (3)
S2O32-+2OH-→S2-+SO42-+H2O (4)
溶液中S22-含量提高,消耗母液中的碱,降低了溶出碱浓度从而降低氧化铝的溶出率;造成蒸发器组加热管和出料系统产生结疤,降低蒸发产能;硫以硫离子、羟基硫离子及配合物等形式溶解在铝酸钠溶液中,腐蚀蒸发和分解工序的钢制设备导致氧化铝品位因铁的污染而下降。因此,导致我国高达5.6亿t的高硫铝土矿资源被闲置。
近年来,随着我国氧化铝年产量的不断提高,优质资源越来越少,铝土矿资源供应日渐紧张。将高硫铝土矿应用于氧化铝生产中,为缓解供矿压力、增强在铝土矿进口贸易中的定价权具有巨大的经济和战略意义。为消除高硫铝土矿对氧化铝工业生产的负面影响,研究者主要从以下两个方向展开研究:1) 利用浮选[6]或焙烧[7]等方法预处理矿石脱硫,从源头控制硫的进入。浮选被认为是有前景的技术,中铝重庆分公司已建立浮选脱硫生产线,但浮选指标不够稳定,对细颗粒的硫脱除效果不佳;焙烧脱硫方法成本较高、需尾气脱硫等缺点,目前也无法工业应用。2) 在拜耳溶出过程中铝酸钠溶液中添加脱硫剂脱硫[8],消除硫的负面影响。因脱硫剂的成本较高,无法大规模工业应用。
高硫铝土矿生物氧化是近年来兴起的技术,通过微生物将高硫铝土矿中的含硫矿物氧化为硫酸盐,再通过固液分离,得到硫含量较低的铝土矿。此方法环境友好、成本较低,目前尚处于实验室内的中温菌的单菌株浸出阶段。王朋[9]从河南铝土矿矿区筛选到5株Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans用于脱除高硫铝土矿中的黄铁矿,在矿浆浓度10%(质量分数)、初始pH 2.0、摇床转速200 r/min、温度30 ℃、接种量1×108 mL-1时,摇瓶浸出20 d后脱硫率为72.54%。周吉奎等[10]等采用在山西某铝土矿区筛选的Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans SX-1,同样条件下对铝土矿脱硫21 d,最大脱硫率为83.57%。
单菌株生物氧化启动时间长、浸出周期时间长,生物氧化效率低。在矿山酸性水和工业运行的微生物氧化系统中,发挥作用的常常是以中等嗜热菌为主的菌群[11]。微生物之间存在协同作用,比中温菌单菌株表现出更高的脱硫效率[12]。跟中温菌相比,中等嗜热菌能耐受更高的温度,生长活性较高,酶活力较高,浸矿速度受温度影响较小;与嗜热古细菌相比,中等嗜热菌具有坚固的细胞壁结构,在高矿浆浓度、高金属离子浓度的情况下生长代谢的能力较强;另外,中等嗜热菌中存在兼性自养菌如Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans,添加有机物可提高细菌的生长和浸出速度,比中温菌和高温菌更易调控,脱硫过程强化更加简单。
因此,本课题组利用“Bottom up”[12]的菌群构建策略,基于高硫铝土矿的工艺矿物学性质,利用中等嗜热微生物构建具有不同代谢性质的菌群,并从中筛选具有高效脱硫能力的菌群,对其在脱硫过程中的行为进行测定。利用SEM、XPS、XANES等阐明其脱硫机理,为推动我国高硫铝土矿资源的工业应用进程提供理论指导和实验支持。
1 实验
1.1 矿样性质
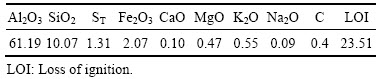
高硫铝土矿原矿来自重庆南川某一水硬铝石型高硫铝土矿。矿石主要化学成分见表1。
表1 高硫铝土矿的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical compositions of high-sulfur bauxite (mass fraction, %)
对铝土矿原矿进行硫的物相分析,结果如表2所列。硫化物是其主要的含硫相,占总硫的97.62%。对硫化物进行进一步的分析,主要以黄铁矿、白铁矿、胶黄铁矿的状态存在。其中黄铁矿占比77.38%,而胶黄铁矿占比20.24%。
所用矿样破碎到粒径小于0.075 mm的颗粒占总量95%以上,利用矿相显微镜分析其黄铁矿的单体解离度,黄铁矿单体占比仅88.37%。经MLA分析,除一部分以自形、半自形晶产出的黄铁矿外,大部分黄铁矿呈不规则粒状、脉状或微细粒浸染状等嵌布在一水硬铝石、硅酸盐矿物和脉石矿物中(见图1),属难浮选高硫铝土矿。
表2 高硫铝土矿中各矿物中硫的物相组成
Table 2 Phase distributions of sulfur presented in high-sulfur bauxite (mass fraction, %)

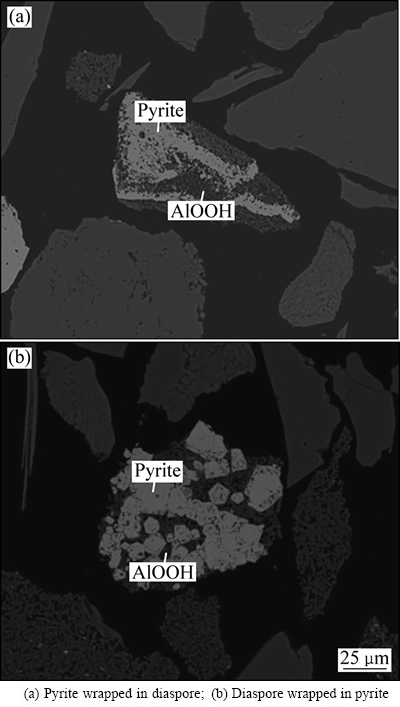
图1 高硫铝土原矿中黄铁矿与一水硬铝石赋存状态的SEM像
Fig. 1 SEM images showing relationship between pyrite and diaspore in high-sulfur bauxite
1.2 中等嗜热菌群的设计及脱硫实验
1.2.1 菌株的活化和驯化
本实验所用6种嗜酸微生物——嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌(Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans)、嗜酸氧化硫硫杆菌(Acidthiobacillus thiooxidans)、嗜铁钩端螺旋菌(Leptospirillum ferriphilum)、嗜酸喜温硫杆菌(Acidithiobacillus caldus)、嗜温硫氧化硫化杆菌(Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans)、铁质菌(Ferroplasma thermophilum),均来自生物冶金教育部重点实验室菌种保藏中心。在脱硫实验之前,6种嗜酸微生物以升华硫和硫酸亚铁为能源进行活化,然后以目标铝土矿为能源,逐渐增加矿浆浓度,在5%、10%、15%、20%浓度下进行驯化培养。
表3 9K基础培养基的主要成分
Table 3 Min components of 9K basal medium (g/L)
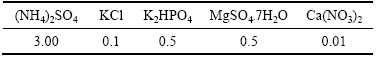
菌株的活化和驯化体系为100 mL,培养基成分如表3所列。培养条件和能源底物如表4所列,到达对数期后传代,每个梯度下传代2次。驯化的6种微生物分别以10000 r/min离心分离20 min,用9K培养基将微生物浓度稀释至均为4×108 mL-1,用于菌群的构建。
1.2.2 设计菌群的构建
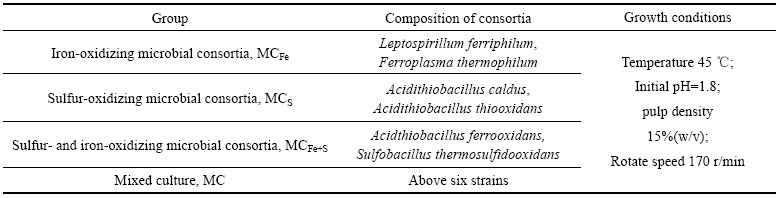
根据微生物的代谢特性[12],两两等比接种,构建了表5所列的亚铁氧化菌群MCFe、硫氧化菌群MCS、铁硫氧化菌群MCFe+S。另外,将组成3组菌群的6种菌等比混合,形成包含6株菌的菌群MC。共培养体系设为150 mL,初始pH=1.8,矿浆浓度15%,摇床转速170 r/min,接种后体系微生物浓度为5.0×106 mL-1,在恒温摇床内震荡培养。为便于比较,温度设为45 ℃,比Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans的最佳生长温度略高。
表4 微生物活化和驯化的培养条件
Table 4 Microorganisms and growth conditions
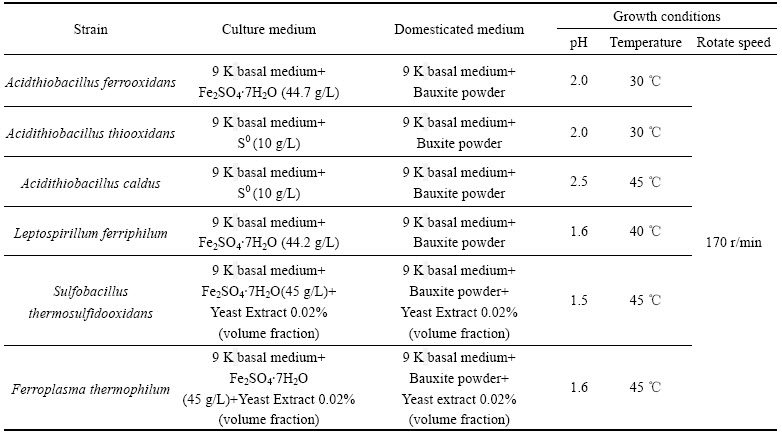
表5 人工组合菌群的构建及其培养条件
Table 5 Composition of designed microbial consortia and its growth conditions
1.2.3 设计菌群的脱硫实验
各设计菌群的脱硫实验在摇瓶中进行,采用150 mL体系,初始pH=1.8,矿浆浓度15%,摇床转速170 r/min,接种后初始微生物浓度为5.0×106 mL-1。每组实验设3个平行组。每天检测脱硫体系溶液中细菌数量、pH值、电位φ等参数,每3天取浸出渣检测硫含量。设置酸浸对照,体系中加入0.02%(体积分数)的百里香酚,以保证酸浸体系中无微生物生长。
1.2.4 实验表征
脱硫过程中的生物量的测定采用光学显微镜下的血球计数法。溶液pH值用PHSJ-5型pH计测量。溶液的氧化-还原电位φ利用电位计(铂电极-甘汞电极)进行测定,所测的溶液电位为相对于饱和甘汞电极的电位(vs SCE)。铝土矿的总硫含量使用重量法测定。利用X射线光电子能谱分析(XPS)、X射线吸收近边吸收光谱(XANES)分析脱硫过程中矿物表面产物成分。利用SEM观察脱硫前后矿石微观形貌以及微生物在矿物表面的吸附状态。
1.2.5 脱硫率的计算
硫的脱除率(Ei)按式(5)计算:
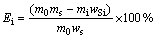 (5)
(5)
式中:m0表示氧化前高硫铝土矿原矿质量;mi表示铝土矿氧化渣的质量;ws表示原矿中硫的含量;wSi表示氧化渣中硫的含量。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 各组合菌群的脱硫效果及其对比
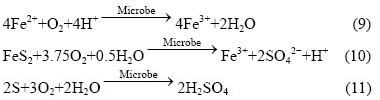
在无菌酸性条件下,黄铁矿的热力学研究和电化学研究表明,当溶液pH<4时,Fe3+溶解度高,是黄铁矿氧化的控速步骤[12]。酸浸对照的pH在1.8~2.34之间,Fe3+是起到主要作用的强氧化剂,溶解氧并非最关键因素[13]。发生的反应主要如下:
FeS2+2Fe3+→3Fe2++2S (6)
FeS2+14Fe3++8H2O→15Fe2++2SO42-+16H+ (7)
FeS2+O2+2H2SO4→2FeSO4+4S+2H2O (8)
而在有菌条件下,微生物在接种后0.5~2 h内即达到在矿物表面的最大吸附量[16]。其反应式与无菌条件下有所不同[16]:
4组混合菌和无菌酸浸对照组的脱硫率如图2所示。对照组在氧化过程中是缓慢的化学氧化,硫氧化菌群MCS与酸浸对照的氧化率类似,并不能直接对黄铁矿进行氧化[18];亚铁氧化菌群MCFe和氧化亚铁、硫的菌群MCFe+S对高硫铝土矿中含硫矿物均取得较高的氧化效果。与两种菌组成的菌群相比,由6种菌组成的菌群MC脱硫率最高,而氧化15 d后,矿石中硫含量仅为0.29%,已满足拜耳法生产需要。
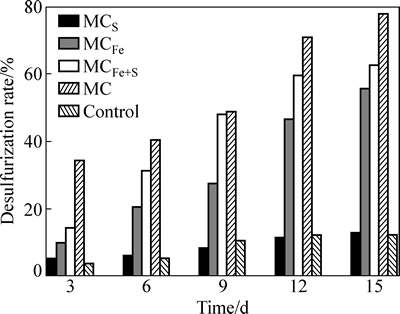
图2 高硫铝土矿微生物脱硫的脱硫率变化
Fig. 2 Desulfurization rate changing of high-sulfur bauxite during bio-desulfurization
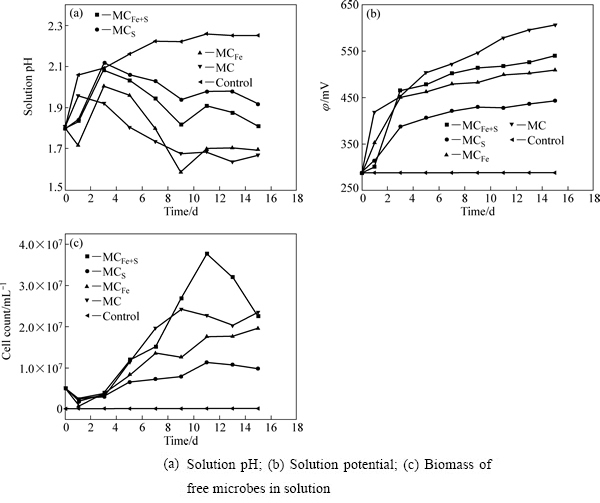
图3 脱硫过程中溶液中实验参数的变化
Fig. 3 Variations of different factors during bio-desulfurization of high-sulfur bauxite
pH、φ、细菌数量等变化趋势如图3所示。各组pH[19]总的趋势为先上升后下降,而酸浸对照的趋势则是一直上升。pH的变化与铝土矿中碱性脉石矿物耗酸直接相关。微生物的氧化产酸和碱性脉石耗酸彼此消长,由于主要含硫矿物黄铁矿的在铝土矿中的相对含量较低,各组pH维持在1.7~2.1之间,较为适宜菌群的生长,生物量在脱硫过程中都保持着上升的趋势。φ直接与[Fe3+]/[Fe2+]成正相关[19],微生物不断将Fe2+ 氧化成Fe3+,使脱硫体系中Fe3+的浓度逐步上升,φ在脱硫过程中逐步升高,前3 d各组电位升速较快,第3~9 d内电位增速下降,第9 d后除MC之外,电位逐渐维持在一个较小的区间内,MCS的φ维持在440 mV左右,MCFe的φ维持在500 mV左右,而MCFe+S的φ则维持在520 mV左右。而在酸浸对照组实验中,由于没有微生物将Fe2+ 氧化为Fe3+,φ几乎没有上升,保持在300 mV以下。
2.1.1 相同氧化特性菌株构成菌群的脱硫效果
硫氧化菌群MCS由嗜酸氧化硫硫杆菌(Acidthiobacillus thiooxidans)[21]和嗜酸喜温硫杆菌(Acidithiobacillus caldus)[22]等比组成。由图2可知,脱硫15 d后,其脱硫率仅为12.98%,与酸浸对照的数据相当,证实MCS并不能直接氧化黄铁矿,仅能利用黄铁矿表面自然氧化生成的单质硫,其反应式如式 (11)所示。MCS脱硫为间接作用[23]。
亚铁氧化菌群MCFe由嗜铁钩端螺旋菌(Leptospirillum ferriphilum)和铁质菌(Ferroplasma thermophilum)等比构成[16]。pH的变化趋势与其他菌群不同,先下降后上升。起始pH为这两种菌的最适生长pH,微生物的生长繁殖较快,此两种菌的作用均是将Fe2+氧化为Fe3+,Fe3+又发挥了其氧化剂作用,如式(9)和(10)所示,在脱硫过程中其pH最低。与铁硫氧化菌群MCFe+S相比,其生物量较低。推测其原因,应是随着Fe3+浓度的升高,存在对Leptospirillum ferriphilum菌的抑制作用[24]。脱硫15 d后,矿石中硫含量为0.58%。由脱硫率的结果来看,也表现出了与pH同样的趋势,可以佐证MCFe的脱硫以间接作用为主。
铁硫氧化菌群MCFe+S由嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌(Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans)和嗜温硫氧化硫化杆菌(Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans)[18]组成。由图4可知,脱硫第9 d时MCFe+S在黄铁矿表面形成胞外多聚物(EPS),吸附在矿物表面的菌体清晰可见。Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans要跟黄铁矿发生生化反应,第一步是要吸附在黄铁矿表面。K. Harneit、A. 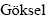 、D. Kock发现Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans吸附在纯黄铁矿表面的速度很快,30 min就可以达到最大吸附量,在90 min 左右就可达到吸附的临时平衡点[16]。GU等[25]发现Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans在吸附时优先吸附在黄铁矿表面有晶体缺陷和断裂面原子密度较低的位置。BLIGHT[26]对Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans氧化黄铁矿及浸出后的显微结构进行了研究,扫描电镜显示,浸出后的黄铁矿表面有广泛分布的蚀坑,刮下的浸渣中有黄钾铁矾,除渣后矿物表面有零星的微生物,可见细菌始终与矿物表面接触,认为细菌通过直接机理氧化黄铁矿。MCFe+S的数量高于MCFe和MCS,φ从289 mV上升到450 mV仅用了2 d的时间,之后电位维持在450~550 mV之间,pH维持在1.8左右。在酸性无菌条件下,对纯黄铁矿化学氧化的电化学研究发现,在450~600 mV(vs SCE)电位区间内,硫单质、缺铁硫化物(Fe1-xS2)和多硫化物(FeSn)等中间产物[27]覆盖在矿物表面,阻碍了黄铁矿的进一步氧化溶解,黄铁矿钝化。Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans和Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans均可消解覆盖在黄铁矿表面的氧化中间产物,促进黄铁矿的进一步溶解。因此在脱硫率方面表现出比MCFe和MCS更强的氧化能力,经15 d 氧化后,铝土矿中硫含量下降到0.49%,脱硫率为62.60%。在MCFe+S脱硫的过程中,既存在直接作用,又存在间接作用。
、D. Kock发现Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans吸附在纯黄铁矿表面的速度很快,30 min就可以达到最大吸附量,在90 min 左右就可达到吸附的临时平衡点[16]。GU等[25]发现Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans在吸附时优先吸附在黄铁矿表面有晶体缺陷和断裂面原子密度较低的位置。BLIGHT[26]对Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans氧化黄铁矿及浸出后的显微结构进行了研究,扫描电镜显示,浸出后的黄铁矿表面有广泛分布的蚀坑,刮下的浸渣中有黄钾铁矾,除渣后矿物表面有零星的微生物,可见细菌始终与矿物表面接触,认为细菌通过直接机理氧化黄铁矿。MCFe+S的数量高于MCFe和MCS,φ从289 mV上升到450 mV仅用了2 d的时间,之后电位维持在450~550 mV之间,pH维持在1.8左右。在酸性无菌条件下,对纯黄铁矿化学氧化的电化学研究发现,在450~600 mV(vs SCE)电位区间内,硫单质、缺铁硫化物(Fe1-xS2)和多硫化物(FeSn)等中间产物[27]覆盖在矿物表面,阻碍了黄铁矿的进一步氧化溶解,黄铁矿钝化。Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans和Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans均可消解覆盖在黄铁矿表面的氧化中间产物,促进黄铁矿的进一步溶解。因此在脱硫率方面表现出比MCFe和MCS更强的氧化能力,经15 d 氧化后,铝土矿中硫含量下降到0.49%,脱硫率为62.60%。在MCFe+S脱硫的过程中,既存在直接作用,又存在间接作用。
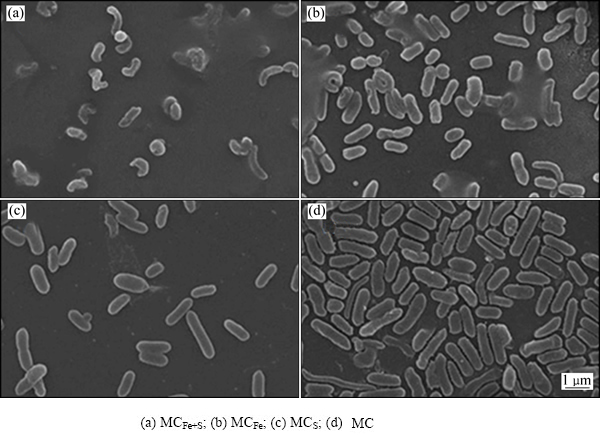
图4 浸出过程第9 d时吸附在矿物表面微生物的SEM像
Fig. 4 SEM images of attached microbes adsorbing on surface of high-sulfur bauxite at 9th day
由2种具有相同氧化特性的微生物组成的菌群,其脱硫能力由大到小的顺序为MCFe+S、MCFe、MCS。
2.1.2 不同氧化特性菌株构成菌群MC的脱硫效果
与MCFe+S、MCFe和MCS相比,由具有不同氧化特性的6种菌组成的菌群MC表现出更强的脱硫能力(见图3)。MC菌群在脱硫过程中电位升高较快,1 d后其电位就从289 mV上升到425 mV,3 d后其电位上升到450 mV左右,此时脱硫率为34.35%。脱硫12 d后,其脱硫率上升到70.99%。在450~600 mV范围内,黄铁矿化学氧化停滞,MC菌群的存在可氧化含硫矿物形成的钝化膜,直接导致脱硫率的上升。由图3可知,在脱硫过程体系的pH值稳定在1.8±0.1,微生物的氧化活性较强,生物量逐步上升,将Fe2+氧化成Fe3+(见式(9)~(11)),同时直接吸附在黄铁矿表面的晶格缺陷处,直接氧化黄铁矿。
首先,菌群MC中存在不同氧化特性的微生物,如硫氧化菌Acidithiobacillus caldus、Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans和亚铁氧化菌Leptospirillum ferriphilum。刘毅等将外来菌种Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans A01 加入土著混合菌群,生物氧化效果提高10.7%。功能基因分析表明,A01 加入使硫氧化菌(Acidithiobacillus caldus)的硫氧化相关基因表达下调,而亚铁氧化菌(如Leptospirilum ferriphilum)的铁氧化基因表达量上调,使得新菌群的铁、硫氧化基因表达总量上调,提高了黄铁矿的氧化效果[28]。SONG等[29]对Acidithiobacillus caldus和Leptospirilum ferriphilum在黄铁矿上竞争吸附的研究表明,菌群MC中的Acidithiobacillus caldus虽不能有效溶解黄铁矿,但其代谢物具有表面活性剂的作用,可以将不同形式的硫溶解,暴露出矿物表面,使其他微生物吸附在矿物表面并发挥作用[29]。其次,菌群MC中同时存在自养菌与异养菌,自养菌Acidithiobacillus caldus生长过程中产生有机物,可以促进异养菌Ferroplasma thermophilum或混合营养型菌如Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans的生长。当有机物浓度较高时,异养菌Ferroplasma spp.和兼养菌Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans又可以有效降低氧化体系的有机物浓度,提高自养菌的活性。由于菌群MC中各组成菌株的代谢可以互补,对环境压力的适应性较强,可以降低有害因子如较高浓度的有机物对微生物的抑制,群落的稳定性较高,使其氧化效果高于仅具有相同代谢特性的菌群。
2.2 高效脱硫菌群MC脱硫过程中矿物的表面形貌及中间产物
高硫铝土矿含硫矿物生物氧化机制,目前并无文献报道。高硫铝土矿主要含硫矿物是黄铁矿,黄铁矿的生物氧化机制方面的研究较多,黄铁矿氧化过程中存在多种氧化产物,如S0、连多硫酸盐(S2O32-等)、多硫化物[30]、FeSO4、Fe2(SO4)3、FeO、FeOOH、Fe2O3、Fe3O4 [31]等,硫代硫酸盐是不可缺少的中间产物。但对于6种菌组成的菌群MC,如何在脱硫过程中发挥作用,尚无文献报道。含硫矿物如何氧化,其他矿物如含铝矿物对黄铁矿的生物氧化有何影响,本文利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)[26]、X射线光电子能谱分析(XPS)[32]、X射线吸收近边吸收光谱(XANES)[33]等表面分析技术被应用于脱硫过程的研究,结果如图5~7所示。
XANES结果显示:在脱硫第3 d时,就在2.482 keV处出现明显的峰,经与参比化合物对比,确定为黄钾铁矾的峰。之后4次检测中均出现此峰。黄钾铁矾是生物氧化过程中常见的产物,其生成如反应式(12)所示[34],M为一价阳离子,如Na+,K+,NH4+。
M++3Fe3++2SO42-+6H2O→MFe3(SO4)2(OH)6+6H+ (12)
黄钾铁矾会降低EPS层的通透性,覆盖在矿物表面阻断微生物与矿物的接触,导致微生物氧化的停滞[35],当黄钾铁矾生成量较少,仅有部分矿物表面被遮盖,微生物会自由迁徙到无铁矾的位置,会减低微生物氧化的速度,但不会阻断微生物对高硫铝土矿中硫的持续浸出。
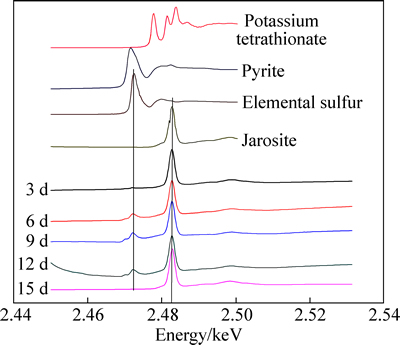
图5 MC浸出高硫铝土矿中硫的过程中矿物表面硫的K边XANES光谱
Fig. 5 Normalized sulfur K-edge XANES spectra of high sulfur bauxite surface during desulfurization processing with moderately thermophilic consortia MC
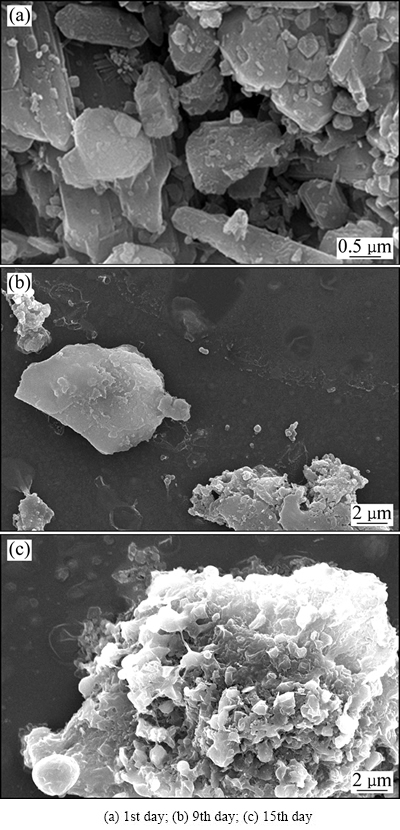

图6 菌群MC脱硫过程中铝土矿表面形貌变化的SEM像
Fig. 6 SEM images of high sulfur bauxite surface during desulfurization processing with moderately thermophilic consortia MC
在脱硫第6 d时,2.473 keV处出现了较为明显的波峰,对照参比化合物发现,为元素硫的峰。第9 d和第12 d的检测结果也显示有元素硫的生成,此时的溶液电位已到达600 mV。黄铁矿化学氧化渡过钝化期,进入过钝化期,发生如下的反应:
FeS2+8H2O→Fe3++2SO42-+16H++15e (13)
MC中的硫氧化菌如Acidthiobacillus thiooxidans和Acidithiobacillus caldus式(11)的反应,将元素硫氧化为硫酸根,到15 d时,元素硫的峰值消失。此时取矿样,利用SEM观察其表面形貌,结果显示,此时矿物表面已被黄钾铁矾包裹,氧化反应无法持续进行。
自脱硫体系中取得的氧化渣在进行XANES实验之前经过多次洗涤除去表面微生物,酸性环境下可溶性的硫酸铁从表面洗脱。另外,XANES的分析只能分析出硫的价态,通过与标准化合物的峰进行对比确定具体物质。当生成的硫酸铁水解,如式(12)所示,生成黄钾铁矾。此时硫的价态也为+6价,XANES并不能分辨出+6价的硫是以硫酸铁或黄钾铁矾的形式存在。因此,为验证黄铁矿的最终氧化产物,取15 d时的浸出渣另作XPS分析,其结果如图7所示。矿物表面存在黄钾铁矾和硫酸铁,对XANES的结果进行了修正。
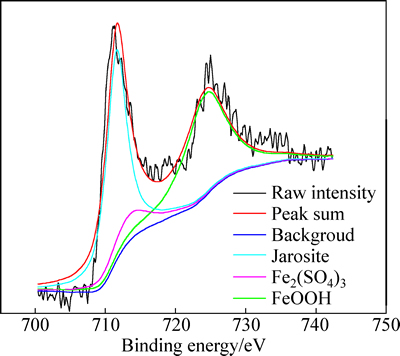
图7 高硫铝土矿氧化渣中铁的2p XPS结果
Fig. 7 Fe 2p XPS results of high-sulfur bauxite residue surface
3 结论
1) 代谢特性相同的菌群脱硫时,菌群代谢特性与高硫铝土矿的脱硫率直接相关。硫氧化菌群MCS无法直接脱硫;亚铁氧化菌群MCFe脱硫能力较强,硫含量降至0.58%;铁硫氧化菌群MCFe+S脱硫性能最强,硫含量降至0.49%。
2) 代谢特性不同的菌群脱硫时,MC各组成菌的代谢可以互补,对环境的适应性更强,活性较强。脱硫过程中pH值降低更快,φ升速较快,脱硫效率更高,最终硫含量0.29%,满足拜耳法氧化铝生产的需要。
3) 利用SEM、XANES、XPS分析混合菌群MC对高硫铝土矿的脱硫过程发现,含硫矿物在氧化过程中有单质硫出现,最终氧化产物为硫酸盐。当硫酸盐的水解产物黄钾铁矾未能包裹矿物表面时,会降低微生物脱硫的速度,但不会阻断微生物脱硫过程。
REFERENCES
[1] Ministry of Land and Resources People’s Republic of China. China Mineral Resources 2015[R]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2015.
[2] 彭 欣, 金立业. 高硫铝土矿生产氧化铝的开发与应用[J]. 轻金属, 2010, 11: 14-17.
PENG Xin, JIN Li-ye. Development and application of bauxite containing high sulfur[J]. Light Metals, 2010, 11: 14-17.
[3] HU X, CHEN W, XIE Q. Sulfur phase and sulfur removal in high sulfur-containing bauxite[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(7): 1641-1647.
[4] 李小斌, 李重洋, 齐天贵, 周秋生, 刘桂华, 彭志宏. 拜耳法高温溶出条件下黄铁矿的反应行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(3): 829-835.
LI Xiao-bin, LI Chong-yang, QI Tian-gui, ZHOU Qiu-sheng, LIU Gui-hua, PENG Zhi-hong. Reaction behavior of pyrite during Bayer digestion at high temperature[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(3): 829-835.
[5] LI X, LI C, PENG Z, LIU G, ZHOU Q, QI T. Interaction of sulfur with iron compounds in sodium aluminate solutions[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(2): 608-614.
[6] 王晓民, 张廷安, 吕国志, 鲍 丽, 吕 滨, 蒋孝丽. 高硫铝土矿浮选除硫的工艺[J]. 稀有金属, 2009, 33(5): 728-732.
WANG Xiao-min, ZHANG Ting-an,  Guo-zhi, BAO Li,
Guo-zhi, BAO Li,  Bin, JIANG Xiao-li. Flotation process for desulfurization of high sulfur bauxite[J]. Chinese Journal of Raremetals, 2009, 33(5): 728-732.
Bin, JIANG Xiao-li. Flotation process for desulfurization of high sulfur bauxite[J]. Chinese Journal of Raremetals, 2009, 33(5): 728-732.
[7] 吕国志, 张廷安, 鲍 丽, 豆志河, 赵爱春, 曲海翠, 倪培远. 高硫铝土矿的焙烧预处理及焙烧矿的溶出性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(9): 1684-1689.
 Guo-zhi, ZHANG Ting-an, BAO Li, DOU Zhi-he, ZHAO Ai-chun, QU Hai-cui, NI Pei-yuan. Roasting pretreatment of high sulfur bauxite and digestion performance of roasted ore[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(9): 1684-1689.
Guo-zhi, ZHANG Ting-an, BAO Li, DOU Zhi-he, ZHAO Ai-chun, QU Hai-cui, NI Pei-yuan. Roasting pretreatment of high sulfur bauxite and digestion performance of roasted ore[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(9): 1684-1689.
[8] 王 鹏, 魏徳洲. 高硫铝土矿脱硫技术[J]. 金属矿山, 2012(1): 108-110.
WANG Peng, WEI De-zhou. Desulfuration technique research of high-sulfur bauxite[J]. Metal Mine, 2012(1): 108-110.
[9] 王 朋. 铝土矿矿山微生物区系分析及浸矿微生物的筛选[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2006: 25-34.
WANG Peng. The microplora of the bauxite mine and the selecting of the metallurgical microorganisms[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2006: 25-34.
[10] 周吉奎, 李花霞. 高硫铝土矿中黄铁矿的细菌氧化试验研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2011, 40(12): 67-69.
ZHOU Ji-kui, LI Hua-xia. Experimental research on bacterial oxidation of pyrite in high sulfur bauxite[J]. Metal Mine, 2011, 40(12): 67-69.
[11] RAWLINGS D E, JOHNSON D B. The microbiology of biomining: Development and optimization of mineral-oxidizing microbial consortia[J]. Microbiology, 2007, 153(2): 315-324.
[12] 余润兰, 石丽娟, 周 丹, 邱冠周, 曾伟民. 生物浸出过程中微生物协同作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013(10): 3006-3014.
YU Run-lan, SHI Li-juan, ZHOU Dan, QIU Guan-zhou, ZENG Wei-min Research development of microorganism synergy mechanisms during bioleaching[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(3): 3006-3014.
[13] HOLMES P R, CRUNDWELL F K. The kinetics of the oxidation of pyrite by ferric ions and dissolved oxygen: an electrochemical study[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(2): 263-274.
[14] CHANDRA A P, GERSON A R. The mechanisms of pyrite oxidation and leaching: A fundamental perspective[J]. Surface Science Reports, 2010, 65(9): 293-315.
[15] LIU R, WOLFE A L, DZOMBAK D A, HORWITZ C P, STEWART B W, CAPO R C. Controlled electrochemical dissolution of hydrothermal and sedimentary pyrite[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2009, 24(5): 836-842.
[16] HARNEIT K,  A, KOCK D, KLOCK J H, GEHRKE T, SAND W. Adhesion to metal sulfide surfaces by cells of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 83(1/4): 245-254.
A, KOCK D, KLOCK J H, GEHRKE T, SAND W. Adhesion to metal sulfide surfaces by cells of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 83(1/4): 245-254.
[17] AFRICA C, van HILLE R P, SAND W, HARRISON S T L. Investigation and in situ visualisation of interfacial interactions of thermophilic microorganisms with metal-sulphides in a simulated heap environment[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2013, 48: 100-107.
[18] WATLING H R, PERROT F A, SHIERS D W. Comparison of selected characteristics of Sulfobacillus species and review of their occurrence in acidic and bioleaching environments[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 93(1/2): 57-65.
[19] PLUMB J J, MUDDLE R, FRANZMANN P D. Effect of pH on rates of iron and sulfur oxidation by bioleaching organisms[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2008, 21(1): 76-82.
[20] ZHAO H, WANG J, YANG C, HU M, GAN X, TAO L, QIN W, QIU G. Effect of redox potential on bioleaching of chalcopyrite by moderately thermophilic bacteria: An emphasis on solution compositions[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2015, 151: 141-150.
[21] SUZUKI I, CHAN C W, TAKEUCHI T L. Oxidation of elemental sulfur to sulfite by Acidthiobacillus thiooxidans cells[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1992, 58(11): 3767-3769.
[22] HE H, HONG F, TAO X, LI L, MA C, ZHAO Y. Biodesulfurization of coal with Acidithiobacillus caldus and analysis of the interfacial interaction between cells and pyrite[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2012, 101: 73-77.
[23] HAN Y, MA X, ZHAO W, CHANG Y, ZHANG X, WANG X, WANG J, HUANG Z. Sulfur-oxidizing bacteria dominate the microbial diversity shift during the pyrite and low-grade pyrolusite bioleaching process[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2013, 116(4): 465-471.
[24] 高 健, 康 健, 吴学玲, 徐 競, 李邦梅, 邱冠周. Fe2+对嗜铁钩端螺旋菌L.ferriphilum生长活性的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(1): 159-162.
GAO Jian, KANG Jian, WU Xue-ling, XU Jing, LI Bang-mei, QIU Guan-zhou. Effect of Fe2+ on growth activity of L. ferriphilum[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(1): 159-162.
[25] GU G, SUN X, HU K, LI J, QIU G. Electrochemical oxidation behavior of pyrite bioleaching by Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(5): 1250-1254.
[26] BLIGHT K, RALPH D E, THURGATE S. Pyrite surfaces after bio-leaching: A mechanism for bio-oxidation[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2000, 58(3): 227-237.
[27] SCHIPPERS A, ROHWERDER T, SAND W. Intermediary sulfur compounds in pyrite oxidation: Implications for bioleaching and biodepyritization of coal[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 1999, 52(1): 104-110.
[28] LIU Y, YIN H, ZENG W, LIANG Y, LIU Y, BABA N, QIU G, SHEN L, FU X, LIU X. The effect of the introduction of exogenous strain Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans A01 on functional gene expression, structure and function of indigenous consortium during pyrite bioleaching[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(17): 8092-8098.
[29] SONG J, LIN J, REN Y, LIN J. Competitive adsorption of binary mixture of Leptospirillum ferriphilum and Acidithiobacillus caldus onto pyrite[J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2010, 15(6): 923-930.
[30] HOLMES P R, CRUNDWELL F K. Polysulfides do not cause passivation: Results from the dissolution of pyrite and implications for other sulfide minerals[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013, 139: 101-110.
[31] SCHIPPERS A, JOZSA P, SAND W. Sulfur chemistry in bacterial leaching of pyrite[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1996, 62(9): 3424-3431.
[32] CAI Y, PAN Y, XUE J, SUN Q, SU G, LI X. Comparative XPS study between experimentally and naturally weathered pyrites[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2009, 255(21): 8750-8760.
[33] YANG Y, LIU W, BHARGAVA S K, ZENG W, CHEN M. A XANES and XRD study of chalcopyrite bioleaching with pyrite[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2016, 89: 157-162.
[34] WANG H, BIGHAM J M, JONES F S, TUOVINEN O H. Synthesis and properties of ammoniojarosites prepared with iron-oxidizing acidophilic microorganisms at 22-65 ℃[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(1): 155-164.
[35] SAND W, GEHRKE T. Extracellular polymeric substances mediate bioleaching/biocorrosion via interfacial processes involving iron(III) ions and acidophilic bacteria[J]. Research in Microbiology, 2006, 157(1): 49-56.
LI Shou-peng1, 2, WANG Rui1, 2, GUO Yu-ting1, 2, GUO Yu-jie1, 2,
WANG Guo-hua1, 2, LIU Xin-xing1, 2, QIU Guan-zhou1, 2
(1. School of Mineral Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Biological Metallurgy, Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Four microbial consortia were constructed using six moderately thermophilic and their ability to bio-desulfurization of high-sulfur bauxite were studied in flask scale. The most efficient consortia’s behavior during the process of high sulfur bauxite desulfurization was measured. The surface microcosmic appearance and speciation of bauxite were characterized by means of SEM, XPS and XANES. The results show that consortia containing sulfur- and iron-oxidizing moderately thermophilic acidophiles provide more rapid bio-oxidation rate than consortia containing iron-oxidizing or sulfur-oxidizing microorganisms only. After Bio-desulfurization 15 d, the sulfur content of bauxite decreases to 0.29%, then the bauxite can be used as raw material in Bayer process of alumina production. The mineral surface is partially covered by intermediate products of the elemental sulfur and jarosite, causing no passivation. The end product of pyrite oxidation is sulfate.
Key words: high sulfur bauxite; moderately thermophilic consortia; bio-desulfurization; mutual effect; jarosite
Foundation item: Project(2010CB630901) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Project (51320105006) supported by Projects of International Cooperation and Exchanges National Natural Science Foundation of China (Major Program)
Received date: 2016-05-03; Accepted date: 2016-10-19
Corresponding author: QIU Guan-zhou; Tel: +86-731-88716592; E-mail: qgzcsu@126.com
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2010CB630901);国家自然科学基金国际合作重大项目(51320105006)
收稿日期:2016-05-03;修订日期:2016-10-19
通信作者:邱冠周,教授,博士;电话:0731-88716592;E-mail:qgzcsu@126.com

