文章编号:1004-0609(2013)08-2176-06
形变及热处理对白铜B10合金晶界特征分布的影响
茹祥坤1,刘廷光1,夏 爽1,周邦新1,马爱利2,郑玉贵2
(1. 上海大学 材料研究所,上海 200072;
2. 中国科学院 金属研究所 金属腐蚀与防护国家重点实验室,沈阳 110016)
摘 要:研究晶界工程处理过程中的冷轧变形量和再结晶退火对白铜B10合金晶界特征分布的影响,采用电子背散射衍射(EBSD)技术表征分析晶界网络的变化。结果表明:白铜B10合金经冷轧7%后在800 ℃退火10 min可使低Σ CSL(Coincidence site lattice,Σ≤29)晶界比例提高到75%以上,同时形成尺寸较大的“互有Σ3n取向关系晶粒的团簇”显微组织。当变形量小于7%时,经800 ℃退火后没有完全再结晶;当变形量大于7%时,低Σ CSL晶界比例和平均晶粒团簇的尺寸随冷轧变形量的增加而下降。
关键词:晶界工程;晶界特征分布;晶粒团簇;白铜合金
中图分类号:TG146.1+1;TG156.93;TG111 文献标志码:A
Effect of deformation and heat-treatment on grain boundary distribution character of cupronickel B10 alloy
RU Xiang-kun1, LIU Ting-guang1, XIA Shuang1, ZHOU Bang-xin1, MA Ai-li2, ZHENG Yu-gui2
(1. Institute of Materials, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China;
2. State Key Laboratory for Corrosion and Protection, Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China)
Abstract: The effects of cold rolling deformation and annealing on the grain boundary character distribution (GBCD) during grain boundary engineering (GBE) treatment were investigated by electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) in cupronickel B10 alloy. The results show that the proportion of low-Σ CSL (Coincidence site lattice, Σ≤29) grain boundaries increase to more than 75% by 7% cold rolling and subsequent annealing at 800 ℃. In this case, the grain boundary network (GBN) is featured by the formation of highly twinned large size grain-clusters produced by multiple twinning during recrystallization. When the cold rolling deformation amount is less than 7%, the 800 ℃ annealing can not induce perfect recrystallization. The perfect recrystallization occurs when the deformation amount is more than 7%, and the proportion of low-Σ CSL grain boundaries and the average size of grain-clusters decrease with the increase of the cold rolling reduction ratio.
Key words: grain boundary engineering; grain boundary distribution character; grain-cluster; cupronickel alloy
绝大多数工程应用金属材料都是多晶体材料。晶界相对于晶粒内部来说结构有序性差,具有更大的自由体积,更高的自由能,因此,晶界对材料的多种性能都有很大影响。KRONBERG等[1]于1949年提出局部原子回旋再结晶成核的模型,从定向成核的观点来说明再结晶织构与加工织构取向间的关系,这种取向关系可以构成特殊的重位点阵(CSL)晶界。重位点阵晶界常用Σn CSL晶界表示,其中n表示两个晶粒点阵构成的超点阵中有1/n的点阵位置相互重合。低Σ CSL晶界具有特殊的结构和性能,如抗晶界偏聚[2]、抗晶间腐蚀[3]、抗晶间应力腐蚀开裂[4]、抗蠕变[5]等。
1984年,WATANABE[6]提出“晶界设计”(Grain boundary design)的概念,其目的就是控制金属的晶界特征分布,增加低Σ CSL晶界的比例,从而改善其与晶界相关的性能。这一概念随后被PALUMBO等[3, 7]发展成为“晶界工程”(Grain boundary engineering, GBE)的研究领域,即通过适当的冷加工变形,并控制再结晶过程中热处理工艺参数,达到调整晶界特征分布的目的,从而提高材料与晶界有关的性能。晶界工程技术能够应用于多种低层错能面心立方结构的金属材料,如奥氏体不锈钢[8]、镍及其合金[8]、铅及其合金[7]、铜及其合金[9]等。
白铜是以镍为主要添加元素的铜基合金,具有低层错能面心立方结构,铜镍之间可无限固溶,形成连续固溶体[10]。白铜BFe10-1-1(简称白铜B10合金),由于其具有优良的导电性、导热性、耐腐蚀性和较好的加工性能、中等以上的强度等[11],因此,作为换热器冷凝管被广泛用于火力发电、核电、造船、海水淡化和海洋工程等行业[12]。在火电行业,白铜冷凝管的腐蚀问题一直没有得到彻底解决。作为发电机组的重要构件,其腐蚀泄漏是影响发电机组稳定运行的一大问题。它不仅会带来换管损失和停机损失,而且换管过程还可能会进一步污染水质,加速剩余白铜冷凝管的进一步腐蚀[13]。
本文作者借助EBSD技术研究形变及热处理工艺对白铜合金晶界特征分布的影响,得出控制白铜合金晶界特征分布的工艺,为通过晶界工程技术提高白铜B10合金的耐腐蚀性能提供可能的处理方法。
1 实验
本实验用材料为白铜B10合金,化学成分见表1。首先对原材料进行50%的冷轧变形,并在800 ℃下保温10 min后水淬,获得本实验的始态样品。然后对始态样品分别进行3%、5%、7%、10%、20%和50%的冷轧变形,在800 ℃保温10 min后进行水淬,得到样品S1、S2、S3、S4、S5和S6。样品制备工艺如表2所示。
表1 白铜B10合金的化学成分
Table 1 Composition of investigated cupronickel B10 alloy (mass fraction, %)

表2 样品的制备工艺
Table 2 Thermal-mechanical treatments of specimens

样品经过金相砂纸预磨后进行电解抛光,制备出适合EBSD检测的样品。电解液成分(体积分数):25% H3PO4 +25% C2H5OH +50% H2O,抛光电压为直流26 V,时间约为120 s。在相同电解液中进行电解蚀刻后进行金相观察,蚀刻电压为直流6 V,时间约为10 s,用于金相观察。采用KEYENCE-VHX数码显微镜对样品表面进行金相照片的拍摄。采用配备在CamScan Apollo 300型热场发射枪扫描电子显微镜上的Oxford/HKL-EBSD系统对样品表面选定微区进行EBSD测试,并采用Channel 5数据处理软件进行取向分析。采用Brandon标准(Δθmax= 15°Σ-1/2)[14]对CSL晶界类型进行判定,不同类型的晶界百分比例均为晶界长度百分比例。
2 结果与分析
图1所示为白铜B10合金始态样品的金相照片、不同类型晶界图、样品表面取向分布(IPF)图和(001)/(110)极图。利用Channel 5软件对始态样品的晶界特征分布进行统计,低Σ CSL的比例为53.2%,其中Σ3为46.6%,Σ9+Σ27为3.5%,其他低Σ CSL晶界比例为3.1%。利用等效圆直径法统计该样品的平均晶粒尺寸,如果将孪晶算为晶粒,那么晶粒平均尺寸为11.45 μm;如果不将孪晶算为晶粒,那么晶粒平均尺寸为26.01 μm。从(001)极图和(110)极图来看,材料有弱的(110)[001]织构,15°偏差范围内的织构含量为9.8%。
经过不同工艺的形变及退火处理得到样品S1~S6,并进行EBSD测定。图2(a)~(f)分别为样品S1~S6的不同类型晶界图。由图2可知,样品S1~S6的晶界网络有明显差异,样品S2~S5含有较高比例的孪晶界,构成大尺寸的晶粒团簇,尤其是样品S3,而样品S1和S6的孪晶界含量明显较低。

图1 白铜B10合金始态样品的金相照片、不同类型晶界图、表面取向分布(IPF)图和(001)/(110)极图
Fig. 1 Optical metallographs of starting-state specimen of cupronickel B10 alloy (a), OIM map of different types of gain boundaries (b), surface orientation distribution (IPF) map (c), (001) and (110) pole figures (d)

图2 经不同工艺形变及退火处理后各样品的不同类型晶界图
Fig. 2 Grain boundary networks of specimens after thermal-mechanical treatments
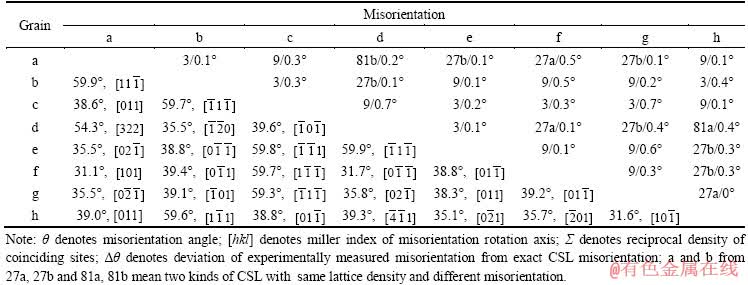
出现高比例的孪晶及其相关界面和大尺寸晶粒团簇是GBE处理后显微组织的重要特征[15-16],图2(c)中的阴影区域M就是一个晶粒团簇。团簇内部的晶界基本上全是Σ3、Σ9和Σ27类型晶界,边界全是随机晶界。对晶粒团簇M进行分析,如图3所示。该晶粒团簇的等效圆直径约为300 μm,包含88个晶粒,从中随机选取8个较大晶粒,对它们互相之间的取向关系进行分析[17],如表3所列。由此可以得出,晶粒团簇内任意两个晶粒之间互有Σ3n取向关系,无论它们是否相邻,这种互有Σ3n(n=1, 2, 3, …)取向关系的晶粒在团簇内部构成了大量的Σ3n类型的三叉界角(Triple junction)[15],如Σ3-Σ3-Σ9和Σ3-Σ9-Σ27等。这种大尺寸的晶粒团簇显微组织是GBE处理提高材料的耐腐蚀性能的原因[18]。下面对样品S1-S6的晶界网络特征进行统计,包括晶界特征分布、平均晶粒尺寸和晶粒团簇平均尺寸。
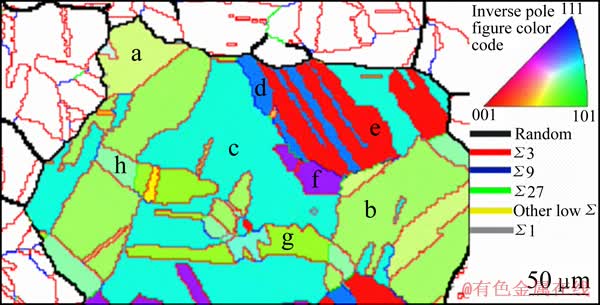
图3 图2(c)中晶粒团簇M中的晶粒取向在反极图(IPF)中的分布
Fig. 3 Orientations distributions of grains in grain-cluster M described by inverse pole figure (IPF) color code in Fig. 2(c)
图4(a)所示为样品S1~S6不同类型晶界比例。可见,S2~S5样品中形成了高比例的低Σ CSL晶界,明显高于始态样品的低Σ CSL晶界比例,尤其是样品S3的低Σ CSL晶界比例接近80%,达到了明显的GBE处理效果;而样品S1和S6的低Σ CSL晶界比例与始态样品基本相当,没有达到GBE处理的效果。图4(b)所示为各样品的平均晶粒尺寸和晶粒团簇平均尺寸,随GBE处理过程中的形变量变化趋势与低Σ CSL晶界比例的变化趋势相似。与始态样品相比,晶粒尺寸和晶粒团簇尺寸都有显著增加,尤其是晶粒团簇尺寸,其中样品S3中的晶粒团簇尺寸平均约为80 μm。
GBE处理后样品的晶界网络中,含有的大尺寸晶粒团簇是通过再结晶过程形成的[15],退火时再结晶晶核长大过程中发生多重孪晶(Multiple twinning)[19],依次形成了一代孪晶、二代孪晶、三代孪晶和更高代次的孪晶,构成孪晶链(Twin chain)[15],从而构成一个晶粒团簇。整个晶粒团簇由一个再结晶晶核通过多重孪晶形成,从晶粒团簇内部的晶粒产生过程可以看出,它们都与初始的再结晶晶核符合Σ3n的取向关系,从而晶粒团簇内部任意两个晶粒之间都具有Σ3n的取向关系。
表3 图3所示晶粒团簇M内随机选取的8个晶粒之间的取向关系
Table 3 Misorientations of eight randomly selected grains within grain-cluster M in Fig.3
晶粒团簇长大过程中发生多重孪晶,形成Σ3n(n=1, 2, 3, …)类型晶界,这是GBE处理后产生高比例低Σ CSL晶界的主要原因。因此,形成大尺寸的“互有Σ3n(n=1, 2, 3, …)取向关系晶粒的团簇”后,样品的低Σ CSL晶界比例才会明显提高[16]。GBE处理过程中,形变量越大的样品在随后的退火过程中再结晶形核密度就越高,可供晶核长大的潜在空间就越小,晶粒团簇尺寸就越小,不利于形成高比例的低Σ CSL晶界。因此,随GBE处理过程中的形变量增大,处理后样品S3~S6的低Σ CSL晶界比例降低。而样品S1和S2的低Σ CSL晶界比例反而比样品S3的低,原因是3%与5%的变形量太小,没有产生足够的形变储能,在随后的退火过程中没有发生再结晶或者没有完全再结晶。图4(a)中样品S1~S3,Σ1晶界(小角晶界,取向差2°~15°之间)比例随着冷轧变形量的增加而降低,说明样品S1和S2没有发生或没有完成再结晶。因此,GBE处理过程中需要合适的形变量,才能在随后的退火过程中形成高比例的低Σ CSL晶界。
Σ9和Σ27晶界是晶粒团簇长大过程中发生多重孪晶现象时[19]形成的,因此,Σ9和Σ27晶界比例之 和,与Σ3晶界比例变化趋势相似,如图4(a)所示。低Σ CSL晶界中基本上全是Σ3n晶界,其中,Σ3晶界占绝大多数,因此,总体低Σ CSL晶界比例也与样品的Σ3晶界比例变化趋势相同,在样品S3(冷轧变形量7%)处出现最大值,达到76.81%。
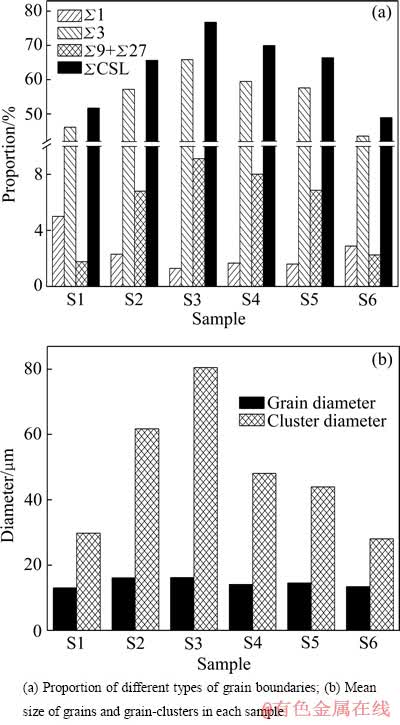
图4 晶界特征分布统计结果
Fig. 4 Statistics of grain boundary character distribution
从图4(b)中可以看出,平均晶粒尺寸和晶粒团簇平均尺寸同样随着冷轧压下量从3%逐渐增加,先增大,后减小,在样品S3(冷轧压下量7%)处出现最大值,分别为16.20 μm和80.49 μm。这说明,7%冷轧变形是本实验条件下GBE处理时的合适变形量。样品的低Σ CSL晶界比例与样品的晶粒团簇平均尺寸D和平均晶粒尺寸d之比的平方(D/d)2成正相关关系[16],如图5所示。因此,虽然平均晶粒尺寸和晶粒团簇平均尺寸的变化趋势相同,均在S3处达到最大值,但是平均晶粒尺寸变化幅度比晶粒团簇平均尺寸的变化幅度小得多,样品S3的晶粒团簇平均尺寸明显比其他样品的大,使得样品S3具有最高比例的低Σ CSL晶界和最大的晶粒团簇平均尺寸,形变量过大和过小都不利于获得好的GBE处理效果。

图5 各个样品的低Σ CSL晶界比例和(D/d)2值
Fig. 5 Proportion of low-Σ CSL boundary and value of (D/d)2 of each sample
3 结论
1) 固溶处理后的白铜B10合金,经过冷轧变形7%和800 ℃保温10 min退火处理,可以将低Σ CSL晶界比例提高到75%以上,同时形成大尺寸的“互有Σ3n取向关系晶粒的团簇”,并获得了最佳的“形变-热处理”工艺,为提高白铜B10合金的耐蚀性提供可能的处理方法。
2) 当冷轧变形量小于7%时,因为没有足够的形变储能,样品经800 ℃退火后没有完全再结晶。当冷轧变形量大于7%时,样品在随后的退火过程中能够发生再结晶,随着形变量增加,再结晶形核密度增加,可供晶核长大的潜在空间就越小,因而,冷轧变形量大于7%时,样品退火后的平均晶粒团簇尺寸和Σ3n晶界比例都会随着退火前变形量的增加而明显降低,致使低Σ CSL晶界比例也明显降低。
REFERENCES
[1] KRONBERG M L, WILSON F H. Secondary recrystallization in copper[J]. Trans AIME, 1949, 185(1): 501-514.
[2] KURBAN M, ERB U, AUST K T. A grain boundary characterization study of boron segregation and carbide precipitation in alloy 304 austenitic stainless steel[J]. Scr Mater, 2006, 54(6): 1053-1058.
[3] LIN P, PALUMBO G, ERB U, AUST K T. Influence of grain boundary character distribution on sensitization and intergranular corrosion of alloy 600[J]. Scr Metall Mater, 1995, 33(9): 1387-1392.
[4] WATANABE T, TSUREKAWA S, KOBAYASHI S, YAMAURA S I. Structure-dependent grain boundary deformation and fracture at high temperatures[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 420/411: 140-147.
[5] ALEXANDREANU B, WAS G S. The role of stress in the efficacy of coincident site lattice boundaries in improving creep and stress corrosion cracking[J]. Scr Mater, 2006, 54(6): 1047-1052.
[6] WATANABE T. Approach to grain boundary design for strong and ductile polycrystals[J]. Res Mechanica: International Journal of Structural Mechanics and Materials Science, 1984, 11(1): 47-84.
[7] PALUMBO G, ERB U. Enhancing the operating life and performance of lead-acid batteries via grain-boundary engineering[J]. MRS Bulletin, 1999, 24(11): 27-32.
[8] WEST E A, WAS G S. IGSCC of grain boundary engineered 316L and 690 in supercritical water[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2009, 392(2): 264-271.
[9] RANDLE V, OWEN G. Mechanisms of grain boundary engineering[J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54(7): 1777-1783.
[10] 《重有色金属材料加工手册》编写组. 重有色金属材料加工手册第1分册[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1979.
Edition Group of Heavy Non-ferrous Metal Materials Processing Manual. Book one of heavy non-ferrous metal materials processing manual[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1979.
[11] 李文生, 王智平, 路 阳, 徐建林, 杨德寿. 高强铜基合金材料的研究与应用现状[J]. 有色金属, 2002, 54(2): 30-34.
LI Wen-sheng, WANG Zhi-ping, LU Yang, XU Jian-lin, YANG De-shou. Review of high-strength copper-based alloy on application and research[J]. Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 54(2): 30-34.
[12] 陈 平, 付亚波. 铜镍合金冷凝管产品市场分析[J]. 上海有色金属, 2007, 28(4): 191-195.
CHEN Ping, FU Ya-bo. Market analysis of condensation tubes of Cu-Ni alloy[J]. Shanghai Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 28(4): 191-195.
[13] 邓楚平, 黄伯云, 李 卫, 潘志勇, 李宏英. 不同服役条件下冷凝器白铜管的腐蚀特性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(11): 1692-1698.
DENG Chu-ping, HUANG Bai-yun, LI Wei, PAN Zhi-yong, LI Hong-ying. Corrosion characteristics of white copper condenser tubes under different serving conditions[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(11): 1692-1698.
[14] LEHOCKEY E M,BRENNENSTUHL A M, THOMPSON I. On the relationship between grain boundary connectivity, coincident site lattice boundaries and intergranular stress corrosion cracking[J]. Corrosion Science, 2004, 46(10): 2383-2404.
[15] XIA Shuang, ZHOU Bang-xin, CHEN Wen-jue. Grain cluster microstructure and grain boundary character distribution in alloy 690[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2009, 40(12): 3016-3030.
[16] 刘廷光, 夏 爽, 李 慧, 周邦新, 陈文觉. 690合金原始晶粒尺寸对晶界工程处理后晶界网络的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2011, 47(7): 859-864.
LIU Ting-guang, XIA Shuang, LI Hui, ZHOU Bang-xin, CHEN Wen-jue. Effect of original grain size on the boundary network in alloy 690 treated by grain boundary engineering[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2011, 47(7): 859-864.
[17] HUMPHREYS F J, BATE P S, HURLEY P J. Orientation averaging of electron backscattered diffraction data[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 2001, 201(1): 50-58.
[18] XIA Shuang, LI Hui, LIU Ting-guang, ZHOU Bang-xin. Appling grain boundary engineering to Alloy 690 tube for enhancing intergranular corrosion resistance[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2011, 416(3): 303-310.
[19] GERTSMAN V Y, HENAGER C H. Grain boundary junctions in microstructure generated by multiple twinning[J]. Interface Science, 2003, 11(4): 403-415.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(50974148);上海市重点学科建设项目(S30107);国家自然科学基金重点项目(51131008)
收稿日期:2012-08-20;修订日期:2012-12-05
通信作者:夏 爽,副研究员,博士;电话:13817106410;E-mail: xs@shu.edu.cn