
Microstructure evolution and deformation features of
single crystal nickel-based superalloy containing 4.2% Re during creep
TIAN Su-gui, LIANG Fu-shun, LI A-nan, LI Jing-jing, QIAN Ben-jiang
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shenyang University of Technology, Shenyang 110870, China
Received 18 October 2010; accepted 19 January 2011
Abstract: By means of microstructure observation and measurement of creep properties, the high temperature creep behaviors of a single crystal nickel-based superalloy containing Re were investigated. Results show that the single crystal nickel-based superalloy containing 4.2% Re possesses a better creep resistance at high temperature. After being crept up to fracture, the various morphologies are displayed in the different areas of the sample, and the γ′ phase is transformed into the rafted structure along the direction vertical to the applied stress axis in the regions far from the fracture. But the coarsening and twisting extents of the rafted γ′ phase increase in the regions near the fracture, which is attributed to the occurrence of the larger plastic deformation. In the later stage of creep, the deformation mechanism of the alloy is that the dislocations with 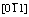 and [011] trace features shear into the rafted γ′ phase. The main/secondary slipping dislocations are alternately activated to twist the rafted γ′ phase up to the occurrence of creep fracture, which is thought to be the fracture mechanism of the alloy during creep.
and [011] trace features shear into the rafted γ′ phase. The main/secondary slipping dislocations are alternately activated to twist the rafted γ′ phase up to the occurrence of creep fracture, which is thought to be the fracture mechanism of the alloy during creep.
Key words: single crystal nickel-based superalloy; Re; creep; microstructure evolution; deformation mechanism
1 Introduction
Single crystal nickel-based superalloys have been widely used because of their high volume fraction of γ′ strengthening phase and good high temperature mechanical and creep properties, to make the blade parts of the advanced aeroengine [1-2]. With the increasing of service performance, such as the power of aeroengine and thermal efficiency, higher service temperature is required to increase the working efficiency of the aeroengine. Thus, it is very important to improve high temperature properties of superalloys [3-4]. Adding refractory elements, Re and W, can improve the high temperature properties of superalloys [5-6] because about 80% element Re is mainly distributed in the γ matrix to form the atomic group with short-range ordering structure of about several nm in size, which may reduce the diffusion rates of the elements and directional coarsening of γ′ phase during creep to improve the stability of the microstructure, and hinder the dislocation movement. Some literatures reported that the element Re may promote the precipitation of TCP phase [7-8], and the TCP phase precipitated in the superalloy with element Re may be transformed into the sphere-structure [9], which decreases only slightly the creep properties of alloy at high temperature. However, a few literatures reported the microstructure evolution feature and creep behaviors of Re-containing single crystal nickel-based superalloy at high temperature.
In the present work, the creep behaviors of 4.2% Re-containing single crystal nickel-based superalloy were investigated by microstructure observation and creep curves measuring of the alloy in the range of the applied stress and temperature, and deformation mechanism of the alloy during creep was briefly discussed.
2 Experimental
The single crystal nickel-based superalloy with [001] orientation has been produced with selecting crystal method in a vacuum directional solidification furnace under the condition of a high temperature gradient. The nominal chemical composition of the superalloy was Ni-Cr-Co-W-Mo-Al-Ta-4.2%Re (mass fraction). The heat treatment regimes of the single crystal nickel-based superalloy bars were given as follows: (1 280 °C, 2 h)+ (1 320 °C, 4 h, AC)+(1 120 °C, 4 h, AC)+(870 °C, 24 h, AC).
After fully heat treatment, the bars of the alloy were machined along the [001] orientation into the tensile creep samples with a cross-section of 4.5 mm×2.5 mm and gauge length of 20 mm. The uniaxial constant load tensile tests were conducted on a creep testing machine (GWT504 model). The creep curves of the alloy at different conditions were measured. The microstructures of the alloy at the different states were observed with SEM and TEM. The activation energy and stress exponent of the alloy during steady state creep were calculated according to the creep data.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Creep features of alloy
The creep curves of the single crystal nickel-based superalloy containing 4.2% Re under different conditions were measured, and are shown in Fig. 1. All of the creep curves display the obvious feature of three stages, initial creep, steady state creep and accelerated creep stages.
The creep curves of the alloy under the applied different stresses at 1 080 °C are shown in Fig. 1(a). It may be understood from Fig. 1(a) that the creep feature of the alloy under the applied stress of 120 MPa displays a shorter initial stage and longer steady state stage lasting for about 300 h, the creep lifetime of the alloy is measured to be 450.9 h. The strain rate of the alloy during steady state creep increases slightly as the applied stress enhances to 137 MPa, the creep lifetime of the alloy is measured to be about 200.6 h, and decreasing extent of the alloy lifetimes is about 55.4%. As the applied stress enhances to 150 MPa, the creep lifetime of the alloy decreases rapidly to 93.3 h, which indicates that the alloy during creep at 1 080 °C possesses an obvious sensibility to the applied stress.
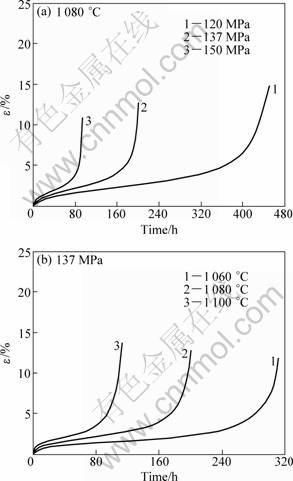
Fig. 1 Creep curves of 4.2%Re-containing single crystal nickel-based superalloy under different conditions: (a) Applied different stresses at 1 080 °C; (b) Applied stress of 137 MPa at different temperatures
The creep curves of the alloy under the applied stress of 137 MPa at different temperatures were measured, as shown in Fig. 1(b), indicating that the strain rate of the alloy during the steady state creep at 1 060 °C was measured to be 3.1×10-8 s-1, the time of the alloy during steady state creep lasts for about 240 h, and the creep lifetime of the alloy was measured to be 311.7 h. The strain rate of the alloy during the steady state creep was measured to be 5.8×10-8 s-1 as the temperature enhanced to 1 080 °C, the lifetime of the alloy was measured to be 200.6 h, decreasing extent of the alloy lifetimes is about 35.4%. With elevating the temperature to 1 100 °C, the creep lifetime of the alloy decreases to 113 h, indicating that the alloy during creep at 137 MPa displays a better resistance in the applied temperature range.
3.2 Constitutive equation and relative parameters
Transient strain is produced when load is applied at high temperature. Dislocations multiply rapidly and fill in the matrix channels between the cubical γ′ phases, which corresponds to the initial strain of the creep [10-11]. As the creep goes on, the creep rate is reduced while dislocations pile up in the channels to produce the strain strengthening. At the same time, the slipping and climbing of dislocations occur under the action of thermal activation, which releases the stress concentration in the local region [12-13]. And then the strain rate of the alloy during creep maintains constant for entering the steady-state stage when the equilibrium of the strain strengthening and recovery intenerating is obtained, and the strain rate of the alloy during steady state creep may be expressed by Dorn law as follows [14]:
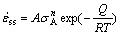 (1)
(1)
where  is the strain rate during the steady state creep; A is the constant related to material structure; σA is the applied stress; n is the apparent stress exponent; R is the mole gas constant; T is the thermodynamics temperature; Q is the apparent active energy.
is the strain rate during the steady state creep; A is the constant related to material structure; σA is the applied stress; n is the apparent stress exponent; R is the mole gas constant; T is the thermodynamics temperature; Q is the apparent active energy.
In the ranges of the applied temperature and stress, the dependences of the strain rates during steady-state creep on the applied temperatures and stresses are shown in Figs.2(a) and (b), respectively. According to the strain data during the steady-state creep, the creep activation energy and stress exponent of the alloy were calculated to be Q=483.5 kJ/mol and n=5.4, respectively.
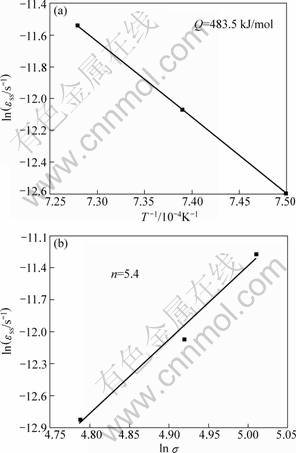
Fig. 2 Relationship between strain rates and applied temperature, stress during steady-state creep: (a) Strain rate and temperature; (b) Strain rate and applied stress
3.3 Microstructure evolution of alloy during creep
After fully heat treatment, the microstructure of the alloy consists of the cubical γ′ phase embedded coherent in the γ matrix phase. The morphology of the alloy on (001) plane is shown in Fig. 3, and the [100] and [010] directions on (001) plane are marked by arrows, which indicate that the cubical γ′ phase is regularly arranged along á100? orientation, and the average size of the cubical γ′ phase is about 0.45 μm, the width of the g matrix channel is about 100 nm.
After the alloy crept for 311.7 h up to fracture under the applied stress of 137 MPa at 1 060 °C, the morphologies in the different regions of the sample alloy are shown in Fig. 4. The normal of the observed sample is [100] orientation, the dark areas in the picture correspond to the γ′ phases, and the white areas correspond to the γ matrix phase. The various stresses are applied in the different regions far from the fracture in the creep sample, which results in the various microstructures displayed in the different regions. Therefore, the deformation extent of the alloy in the different regions may be analyzed according to the configuration of γ′ phase.
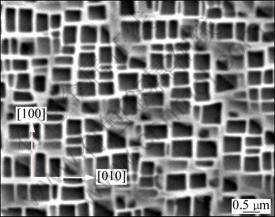
Fig. 3 Morphology on (001) plane of alloy after fully heat treatment
The γ′ phase with no strain in the region A displays the sphere-like morphology due to their coarsening under the condition of the thermal exposure for 311.7 h, as shown in Fig. 4(b). But the cubical γ′ phase in the region B has been transformed into the rafted structure along the direction vertical to the applied stress axis under the action of the applied tensile stress at high temperature, both rafted γ′ phase thickness and matrix channel thickness in the region B are about 0.7 ?m, as shown in Fig. 4(c). The morphology of the rafted γ′ phase in the region C is similar to the one in the region B, but the thickness of the rafted γ′ phase increases slightly, as shown in Fig. 4(d). But the twisted configuration of the rafted γ′ phase appears in the region D due to the larger plastic strain, the thickness of the rafted γ′ phase increases to 0.9 ?m, as shown in Fig. 4(e). The much more plastic strain occurs in the region E near the fracture, which results in the obvious twist of the rafted γ′ phase so that the orientation of the rafted γ′ phase has about 45° angle relative to the direction of the applied stress axis, as shown in Fig. 4(f). It may be considered by analysis that the coarsening and twist of the rafted γ′ phase in the region E are attributed to the severe plastic strain.
3.4 Deformation features of alloy during creep
During creep of the alloy at high temperature, a significant amount of dislocations are activated in the matrix, resulting in an obvious influence on the creep properties of the alloy [15-16]. Microstructures of the superalloy crept for 113 h up to fracture at 1 100 °C and 137 MPa are shown in Fig. 5. The orientation of applied stress is marked by arrow shown in Fig. 5(a). It may be understood from Fig. 5(a) that the orientation of the rafted γ′ phase is still vertical to the applied stress axis and displays the slight twisted configuration, and the thickness of the rafted γ′ phase is about 0.6 μm. Some dislocations are activated in the rafted γ′ phase marked by black arrow, and the rafted γ′ phase displays a slight twisted and broken configuration due to the plastic deformation marked by A in Fig. 5(a).
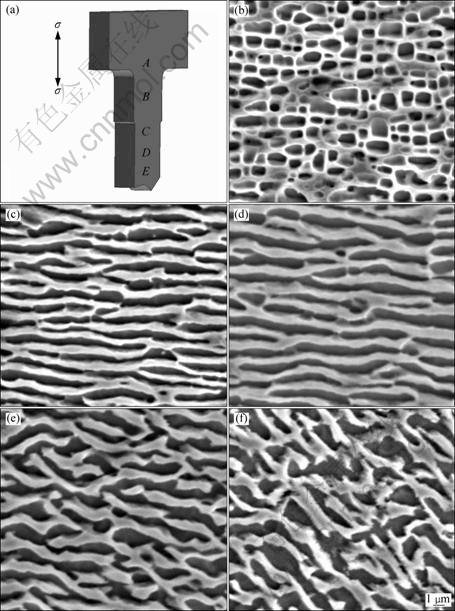
Fig. 4 Microstructures in different regions of alloy after being crept up to fracture at 1 060 °C and 137 MPa: (a) Schematic of marking locations in specimen; (b), (c), (d), (e) and (f) SEM images corresponding to regions A, B, C, D and E
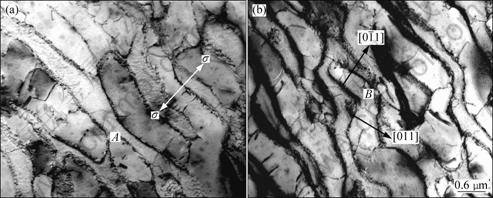
Fig. 5 Morphologies of alloy after being crept for 113 h up to fracture at 1 100 °C and 137 MPa: (a) Twisted rafted γ′ phase; (b) Alternated slipping of dislocations
After the alloy creeping for 113 h up to fracture, microstructure in the region near the fracture is shown in Fig. 5(b), and the normal of the film is [100] orientation. It may be understood from Fig. 5(b) that the orientation of the rafted γ′ phase is still vertical to the applied stress axis, and the twisted extent of the rafted γ′ phase increases. Some dislocation traces of 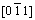 and [011] orientations with the feature of upright each other are activated within the twisted rafted γ′ phase marked by arrow. Thereinto, the direction of dislocations slipping is about 45° angle relative to the applied stress axis, which indicates that the slipping of the dislocation is activated along the direction with the maximum shearing stress during creep.
and [011] orientations with the feature of upright each other are activated within the twisted rafted γ′ phase marked by arrow. Thereinto, the direction of dislocations slipping is about 45° angle relative to the applied stress axis, which indicates that the slipping of the dislocation is activated along the direction with the maximum shearing stress during creep.
It is considered by analysis that the deformation mechanism of the alloy in the later stage of creep is that the super-dislocations with 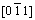 and [011] trace features shear into the rafted γ′ phase under the action of the maximum shearing stress. As creep goes on, the main slip system of the dislocations is firstly activated within the twisted rafted γ′ phase, and then secondary slipping dislocation is activated. The alternative operation of the main/secondary slipping dislocations results in the occurrence of the rafted γ′ phase twist. And the twisted extent of the rafted γ′ phase increases with the strain quantities of the alloy during creep, which makes the rafted γ′ phase transform into the irregular configuration marked by letter B in Fig. 5(b). The feature of the microstructure corresponds to the larger plastic deformation in the neck region. As creep goes on, the effective stress of the alloy during creep enhances and creep resistance of the alloy decreases. The alternative operation of the main/secondary slipping dislocations promotes the significant amount of dislocations shearing into the rafted γ′ phase up to the occurrence of creep fracture.
and [011] trace features shear into the rafted γ′ phase under the action of the maximum shearing stress. As creep goes on, the main slip system of the dislocations is firstly activated within the twisted rafted γ′ phase, and then secondary slipping dislocation is activated. The alternative operation of the main/secondary slipping dislocations results in the occurrence of the rafted γ′ phase twist. And the twisted extent of the rafted γ′ phase increases with the strain quantities of the alloy during creep, which makes the rafted γ′ phase transform into the irregular configuration marked by letter B in Fig. 5(b). The feature of the microstructure corresponds to the larger plastic deformation in the neck region. As creep goes on, the effective stress of the alloy during creep enhances and creep resistance of the alloy decreases. The alternative operation of the main/secondary slipping dislocations promotes the significant amount of dislocations shearing into the rafted γ′ phase up to the occurrence of creep fracture.
4 Conclusions
1) The 4.2% Re-containing single crystal nickel- based superalloy possesses a better creep resistance in the temperature ranges of 1 060-1 100 °C, but displays an obvious sensibility to the applied stress. In the ranges of the applied temperature and stress, the apparent creep active energy of the alloy was measured to be Q=483.5 kJ/mol.
2) After creeping for a longer time up to fracture, the various morphologies are displayed in different areas of the sample. The cubical γ′ phase is transformed into the sphere-like configuration in the no-strain regions. And the γ′ phase is transformed into the rafted structure along the direction vertical to the applied stress axis in the regions of the applied tensile stress. But the coarsening and twisting extents of the rafted γ′ phase in the region near the fracture increase, which is attributed to the larger plastic deformation.
3) The deformation mechanism of the alloy in the later stage of creep is that some dislocations with 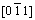 and [011] trace features shear into the rafted γ′ phase. The main/secondary slipping dislocations are alternately activated to twist the rafted γ′ phase up to the occurrence of creep fracture, which is thought to be the fracture mechanism of the alloy during creep.
and [011] trace features shear into the rafted γ′ phase. The main/secondary slipping dislocations are alternately activated to twist the rafted γ′ phase up to the occurrence of creep fracture, which is thought to be the fracture mechanism of the alloy during creep.
References
[1] MACKAY R A, NATHAL M V, PEARSON D D. Influence of molybdenum on the creep properties of nickle-base superalloy single crystals [J]. Metall Trans A, 1990, 21: 381-387.
[2] CHEN Rong-zhang, WANG Luo-bao, LI Jian-hua. Reviewand prospect on developments of cast superalloys [J]. Journal of Aeronautical Material, 2000, 20(1): 55-61.
[3] YEH A C, TIN S. Effects of Ru and Re additions on high temperature flow stresses of nickel-base single crystal supcralloys [J]. Scripta Material, 2005, 52: 519-526.
[4] LUO Yu-shi, LI Jia-rong, LIU Shi-zhong, HAN Mei, CAO Chun-xiao. Role of Re in stress rupture for single crystal superalloys [C]//The 11th Annual Meeting of China Superalloy Collection. Beijing: Metallurgical Press, 2007: 482-485.
[5] WANG Wen-zhen., JIN Tao, SUN Xiao-feng, GUAN Heng-rong, HU Zhuang-qi. Role of Re and Co on microstructures and γ′ coarsening in single crystal superalloys [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 479(2): 148-158.
[6] YU X H, YRO Y Y. Design of quaternary Ir-Nb-Ni-Al refractory superalloys [J]. Metall Trans, 2000(31): 173-181.
[7] TIAN Su-gui, QIAN Ben-jiang, LI Tang, YU Li-li, WANG Ming-gang. Precipitation behavior of TCP phase and its influence on stress rupture property of single crystal nickel-based superalloys [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(11): 2154-2161. (in Chinese)
[8] RAE C M F, REED R C. The precipitation of topologically close-packed phases in rhenium-containing superalloys [J]. Acta Mater, 2001, 49(19): 4113-4125.
[9] TIAN Su-gui, WANG Ming-gang, LI Tang, QIAN Ben-jiang, XIE Jun. Influence of TCP phase and its morphology on creep properties of single crystal nickel-based superalloys [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2010, 527: 5444-5451.
[10] YU Jin-jiang, SUN Xiao-feng, JING Tao, ZHAO Nai-ren, GUAN Heng-rong, HU Zhuang-qi. Effect of Re on deformation and slip systems of a Ni base single-crystal superalloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng, A, 2007, 458: 39-43.
[11] SHUI Li, HU Zhuang-qi. Creep characteristics of a Ni base single crystal superalloy along [001] direction [J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2010, 32(11): 1459-1463.
[12] TIAN Su-gui, ZHOU Hui-hua, ZHANG Jing-hua, YANG Hong-cai, XU Yong, HU Zhuang-qi. Formation and role of dislocation networks for a single crystal nickel-base superalloy during high temperature creep [J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 1999, 13(6): 632-636.
[13] YANG De-zhuang. Dislocation and strengthening mechanism of metal [M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 1990. (in Chinese)
[14] MUKHERJEE A K, BIRD J E, DORN J E. Experimental correlation for high-temperature creep [J]. Trans ASM, 1969, 62: 155-166.
[15] YIN Jiu-ren, ZHANG Ping, ZHANG Jun-yan. On the climb-controlled creep cavity nucleated time of alloy in high temperature [J]. Natural Science Journal of Xiangtan University, 2000, 22(4): 35-38. (in Chinese)
[16] ZHANG Ping, PENG Fan, MA Shi-cheng, LIU Zhong. Condensation-diffusion of vacancy condensation zone at high temperature [J]. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 1997, 18(3): 195-203.
一种含4.2%Re单晶镍基合金在蠕变期间的
组织演化与变形特征
田素贵,梁福顺,黎阿男,李晶晶,钱本江
沈阳工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,沈阳110870
摘 要:通过组织形貌观察及蠕变曲线测定,研究了一种含Re镍基单晶合金的高温蠕变行为。结果表明:含4.2%Re单晶合金在1 060-1 100 °C温度区间具有较好的承温能力,但表现出较强的施加应力敏感性。经高温蠕变断裂后,在试样不同区域γ′相具有不同的组织形貌,在远离断口区域γ′相形成的筏状组织与施加应力轴方向垂直,而在近断口区域,筏状γ′相的粗化及扭曲程度的增大为该区域发生较大塑性变形所致。在蠕变后期,合金的变形机制是迹线方向为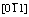 和[011]的滑移位错切入筏状γ′相,主、次滑移系交替开动,使筏状γ′相发生扭折形成不规则的扭曲形态,直至发生断裂是合金的蠕变断裂机制。
和[011]的滑移位错切入筏状γ′相,主、次滑移系交替开动,使筏状γ′相发生扭折形成不规则的扭曲形态,直至发生断裂是合金的蠕变断裂机制。
关键词:单晶镍基合金;Re;蠕变;组织演化;变形机制
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Foundation item: Project (50571070) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: TIAN Su-gui; Tel: +86-24-25494089; E-mail: tiansugui2003@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60892-3