放电等离子烧结TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo复合材料的微观组织与力学性能
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2013年第9期
论文作者:张朝晖 神祥博 王富耻 魏 赛 李树奎 才鸿年
文章页码:2598 - 2604
关键词:TiB;钛基复合材料;放电等离子烧结;微观组织;力学性能
Key words:titanium boride (TiB); titanium matrix composites (TMCs); spark plasma sintering (SPS); microstructure; mechanical properties
摘 要:采用放电等离子烧结技术原位合成了TiB增强Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo复合材料,研究了烧结温度对复合材料微观组织和力学性能的影响规律。 结果表明,随着烧结温度的升高,钛合金中TiB晶须的长细比迅速减小;然而,复合材料的相对密度及TiB的体积含量随着烧结温度的升高而不断增大。由于TiB晶须长细比的减小会导致复合材料强度的降低,而复合材料的相对密度及TiB体积含量的增大又会带来复合材料强度的增加,因此,在这两种因素的共同作用下,最终导致TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo复合材料的弯曲强度随着烧结温度的升高而缓慢增大。 在烧结温度为1150 °C 时,TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo复合材料具有最大的弯曲强度1596 MPa。
Abstract: TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites were synthesized in situ using the spark plasma sintering (SPS) method at temperatures of 850-1150 °C. The effect of the sintering temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of the composites was investigated. The results indicate that the aspect ratio of the in situ synthesized TiB whiskers in Ti alloy matrix decreases rapidly with an increase in sintering temperature. However, both the relative density of the sintered specimens and the volume content of TiB whiskers in composites increase with increasing sintering temperature. Thus, the bending strength of the composites synthesized using SPS process increases slowly with increasing the sintering temperature from 850 to 1150 °C. TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composite synthesized at 1150 °C using SPS method exhibits the highest bending strength of 1596 MPa due to the formation of fine TiB whiskers in Ti alloy matrix and the dense microstructure of the composite.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 2598-2604
Zhao-hui ZHANG, Xiang-bo SHEN, Fu-chi WANG, Sai WEI, Shu-kui LI, Hong-nian CAI
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
Received 27 August 2012; accepted 15 October 2012
Abstract: TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites were synthesized in situ using the spark plasma sintering (SPS) method at temperatures of 850-1150 °C. The effect of the sintering temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of the composites was investigated. The results indicate that the aspect ratio of the in situ synthesized TiB whiskers in Ti alloy matrix decreases rapidly with an increase in sintering temperature. However, both the relative density of the sintered specimens and the volume content of TiB whiskers in composites increase with increasing sintering temperature. Thus, the bending strength of the composites synthesized using SPS process increases slowly with increasing the sintering temperature from 850 to 1150 °C. TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composite synthesized at 1150 °C using SPS method exhibits the highest bending strength of 1596 MPa due to the formation of fine TiB whiskers in Ti alloy matrix and the dense microstructure of the composite.
Key words: titanium boride (TiB); titanium matrix composites (TMCs); spark plasma sintering (SPS); microstructure; mechanical properties
1 Introduction
Titanium and its alloys have been noted as promising high-strength structural materials for aerospace, military and automotive applications owing to their superior physical and chemical properties, such as low density, high specific strength, oxidation resistance, and corrosion resistance [1-3]. However, conventional titanium alloys exhibit inferior wear resistance and suffer considerable loss in mechanical strength at high temperatures. Such drawbacks limit their full potential structural applications in many industrial sectors. In situ ceramic particles or whiskers reinforced titanium matrix composites (TMCs) offer a combination of good mechanical properties and high temperature durability such as high specific modulus, excellent high temperature strength and good heat resistance [4-6]. In the past decades, SiC, TiC, Al2O3, and TiB have been used to produce TMCs. Among these reinforcements, TiB is outstanding due to its high hardness and stiffness, excellent chemical and thermodynamical stability, good wear and heat resistance, strong interfacial bonding with titanium matrix, as well as the excellent whisker-induced strengthening effect [7-13]. Moreover, TiB reinforce- ment and Ti matrix have the similar thermal expansion coefficients (CTEs, 8.2×10-6 °C-1 for Ti and 7.2×10-6 °C-1 for TiB) [7,14-18]. Accordingly, the performance degradation induced by the large differences in the CTEs between other reinforcements and Ti matrix can be avoided [4]. In addition, TiB can be synthesized in situ through the reaction between Ti and boron or TiB2 particles, which produces a clean interface without the formation of any compound between TiB reinforcement and Ti matrix [19-23]. Thus, the excellent interfacial bonding can be obtained. Both the absence of intermediate phases between Ti and TiB and the possibility to grow TiB as high aspect ratio whiskers in Ti matrix contribute to improving mechanical properties of the TiB reinforced Ti or Ti alloy matrix composites.
Spark plasma sintering (SPS), also known as the field-assisted sintering technique (FAST), is a comparatively novel sintering process that allows the powders to be sintered at low temperatures, with short heating, holding, and cooling time [24-26]. These characteristics effectively prohibit the grain growth of materials during the sintering process. Our recent studies [14,27,28] showed that in SPS method, spark discharge, joule heating, and plastic deformation effects all contribute to densification of the powders. Moreover, the spark discharge effect between particles can easily puncture the oxide film on the surface of the particles. Thus, SPS process should be suitable to fabricate the hard-to-sinter materials such as most ceramics, amorphous materials and nanocrystalline materials [29-32]. In this study, the TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites were synthesized in situ using the SPS method and the microstructure characteristics of the composites were investigated.
2 Experimental
2.1 Starting powders and SPS process
Initial mixture was prepared by blending Ti and Fe-Mo powders (mean particle sizes were about 30 and 10 μm; Mengtai Powder Business Department, Beijing, China), together with TiB2 powder (mean particle size was about 4.5 μm; Ningxia Machinery Research Institute, Ningxia, China) in this investigation. Ti, Fe-Mo and TiB2 powders were mixed in the mean composition of 10% TiB/Ti-1.5% Fe-2.25%Mo in mass fraction. Here Fe-Mo was the alloying elemental powder. The chemical compositions of the Ti, Fe-Mo and TiB2 powders are summarized in Tables 1-3. The mixture was milled in a planetary mill at a rotation speed of 300 r/min for 60 min. Ethanol and agate balls were used as the milling medium. The mass ratio of agate balls to powder was fixed at 5:1. The resultant slurry was dried in a vacuum evaporator.
Table 1 Chemical compositions of Ti powders

Table 2 Chemical compositions of Fe-Mo powders

Table 3 Chemical compositions of TiB2 powders

2.2 SPS process
The SPS process was performed using a cylindrical graphite die (Sanye Carbon Group, Beijing, China) with external and internal diameters of 80 mm and 40 mm, respectively. A DR.SINTER type SPS-3.20 system (Sojitz Machinery Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) with a pulse pattern of 12:2 and pulse duration of 3.3 ms was used in the procedure. An infrared thermometer was used to measure the temperature. The final sintering temperatures were selected as 850, 950, 1050 and 1150 °C. The heating rate and holding time were 100 °C/min and 15 min, respectively. The applied initial and holding compressive pressure levels were 1 and 50 MPa, respectively. The uniaxial pressure was gradually applied up to 50 MPa within the first minute at the final sintering temperature and maintained at 50 MPa remaining 14 min.
2.3 Characterization tests
The bulk density was determined by the Archimedes method. Phase identification was performed using X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis (X’ Pert PRO MPD, PANalytical B.V., Netherlands). The polished specimens were etched with a solution of 5 mL HF, 10 mL HNO3 and 85 mL H2O. Microstructure investigation of the sintered composites was carried out using a scanning electron microscope (SEM; Hitachi S-4800, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). The bending strength of the composites was evaluated using the three-point bending method on an Instron instrument using 3 mm × 4 mm × 22 mm specimens. Fracture toughness was studied by the single-edge notched beam (SENB) method on notched 2 mm × 4 mm × 15 mm specimens using the same Instron equipment. At least six specimens were tested for each sintering temperature.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Phase identification
In the Ti-B binary system, following reactions may take place during heating the mixture of the elemental powders:
Ti+B=TiB, ΔG1000 K=-157 kJ/mol (1)
Ti+TiB2=2TiB, ΔG1000 K=-6.3 kJ/mol (2)
Ti+2B=TiB2, ΔG1000 K=-308 kJ/mol (3)
The Gibbs free energy change values ΔG of reactions (1)-(3) have been calculated using the thermodynamic data. The result shows that the ΔG values of the above reactions are negative, indicating that all the three reactions can take place under certain conditions. Although ΔG of reaction (3) is the most negative, Ti and TiB2 can further react to form TiB due to the negative value of the free energy of reaction (2). For this reason, TiB2 will be converted to TiB as long as the average B concentration in the reaction zone is less than 18% in mass fraction.
The XRD patterns of the TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites prepared by SPS process at different sintering temperatures are presented in Fig. 1. The image shows that Ti diffraction peaks are present in all of the diffraction patterns. No diffraction peaks of TiB and TiB2 are observed for the composites sintered at 850 °C and 1150 °C, respectively, indicating that the chemical reactions between Ti and TiB2 (shown in Eq. (2)) take place at 950 °C, and the reactions are nearly completed at 1150 °C. Thus, the composite sintered at 1150 °C only consists of Ti and TiB phases. In addition, Fig. 1 indicates that the composite matrix consists of a-Ti and b-Ti phases. Fe and Mo are b-Ti stabilizing elements and have high mutual soluble concentration in titanium. During the SPS process, Fe and Mo element diffused into titanium and formed a solid solution, which caused the b-Ti phase to be remained in the composite after the specimen was cooled to room temperature. Because the actual sintering temperature in specimen is higher than the testing temperature in the SPS process, b-Ti phase can be formed in the composite sintered at low temperatures (850 and 950 °C).
3.2 Microstructure characteristics
Figure 2 presents the scanning electronic microscopy (SEM) observations of polished and etched surfaces of the TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites synthesized at different sintering temperatures using SPS method. Obviously, the etched surfaces of the TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites sintered at 850 °C and 950 °C have a lot of pores, while few pores are observed on the surface of the composite sintered at 1150 °C, which indicates that the composite sintered at 1150 °C is nearly fully dense. Many unreacted TiB2 particles are detected on the surface of the composite sintered at 850 °C (Fig. 2(a)). Some in situ synthesized TiB whiskers are observed on the surface of the composite sintered at 1050 °C (Fig. 2(c)), and no unreacted TiB2 particles are detected on the surface of the composite sintered at 1150 °C (Fig. 2(d)), which reveal that the chemical reaction between Ti and TiB2 has been completed at 1150 °C during the SPS process. In addition, Fig. 2 also indicates that the Ti alloy matrix in the TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites is composed of a-Ti and b-Ti phases. The inset in Fig. 2(a) shows the typical microstructure of the b-Ti phase. The formation of the b-Ti phase is due to the solid solution of Fe and Mo element into titanium matrix.
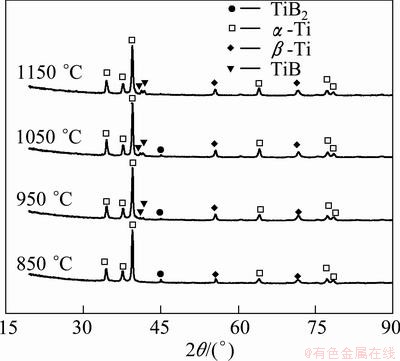
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites synthesized by SPS process
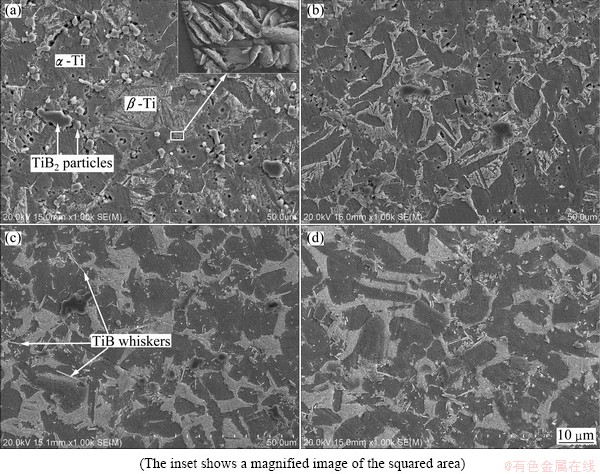
Fig. 2 SEM images of TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites spark plasma sintered at temperatures of 850 °C (a), 950 °C (b), 1050 °C (c), and 1150 °C (d)
Since TiB has a B27 crystal structure and the planes with a higher density of strong bonds tend to grow at a higher rate, TiB should grow along the [010] direction and develop a needle-shaped or rod-like morphology [33,34]. Figure 3 shows the SEM images of the TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites observed at high magnification. These images reveal that the in situ synthesized TiB phase has a needle-shaped or rod-like morphology with a high aspect ratio and is uniformly distributed in the Ti alloy matrix. A few nano-scale TiB needles with a mean diameter of 55 nm and a length of 5.1 μm are observed on the etched surface of the composite sintered at 850 °C, as shown in Fig. 3(a). Because the volume fraction of TiB is low, no diffraction peak of TiB is observed for the composite sintered at 850 °C in XRD patterns, as shown in Fig. 1(a). The chemical reaction temperature between Ti and TiB2 is about 950 °C. However, the local temperature in the sintered compact may be much higher than the average testing temperature due to the spark plasma discharge effect during the SPS process, the chemical reaction between Ti and TiB2 may take place in some micro-areas in the composite sintered at 850 °C. Figure 3(b) shows that a large number of TiB whiskers are synthesized in situ, which also reveals that the chemical reactions between Ti and TiB2 mainly began at 950 °C during the SPS process. The aspect ratio of the TiB whiskers decreases rapidly with an increase in sintering temperature (Figs. 3(c) and (d)). The average diameter of the in situ synthesized TiB whiskers increases from 0.18 μm to 1.55 μm with increasing sintered temperature from 950 °C to1150 °C, while the length of the whiskers has no obvious change.

Fig. 3 SEM images of TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites sintered at different temperatures

Fig. 4 Influence of sintering temperature on aspect ratio of TiB whiskers and relative density of composites
Figure 4 shows the influence of the sintering temperature on the aspect ratio of the TiB whiskers and the relative density of the composites. Obviously, the aspect ratio decreases rapidly with increasing sintering temperature, and the TiB whiskers in the composite sintered at 850 °C has the highest aspect ratio of 92.7. In addition, the TiB whiskers in the composites sintered at 1050 °C and 1150 °C have the similar low aspect ratio of 5.5 and 4.8, respectively. As noted above, TiB generally grows at a higher growth rate in the longitudinal direction than in the transverse direction. However, when the length of the TiB whiskers reaches about 10 μm (the value is related to the size of the initial powders), the growth of TiB whiskers toward the longitudinal direction is restricted. In addition, once the TiB whiskers are generated, they will grow rapidly in the longitudinal direction and reach a certain length. Then the TiB whiskers will stop growing in the longitudinal direction and only grow in the transverse direction. Therefore, the aspect ratio of the TiB whiskers decreases with increasing sintering temperature. Figure 4 also indicates that the relative density of the composites increases steadily with an increase in sintering temperature. KOO et al [4] reported that the aspect ratio of the TiB reinforcement is the main factor that influences the mechanical properties of the TMC when reinforced with TiB, and the strengthening efficiency of the TiB reinforcement can be improved remarkably when the aspect ratio of TiB is above 10. Thus, the composites sintered at 850 °C and 950 °C should have good mechanical properties according to the relation between aspect ratio of TiB and sintering temperature, as shown in Fig. 4. However, the volume content of the TiB reinforcement and the relative density of the composites sintered at 850 °C and 950 °C are relatively low, which may deteriorate the mechanical properties of the composites. Therefore, imaging that both a high relative density and a high volume content of TiB are achieved at 950 °C, the mechanical properties of the TMCs should be significantly improved. To increase the sintering pressure and decrease the sintering time during the SPS process may be a good choice.
Figure 5 shows the fracture surfaces of the TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites sintered at different temperatures. A porous and loose microstructure is presented in Figs. 5(a) and (b), and some unreacted TiB2 particles also can be observed on the fracture surfaces of the composites sintered at 850 °C and 950 °C. In comparison, the composites sintered at 1050 °C and 1150 °C by the SPS method have the dense microstructure, as shown in Figs. 5(c) and (d). In addition, Fig. 5(d) indicates that the main fracture modes for the TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites include the ductile fracture of Ti alloy matrix, the interface separation between TiB whiskers and Ti alloy matrix, and the cleavage of the TiB whiskers.
3.3 Mechanical properties
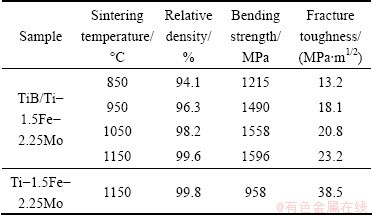
Table 4 presents the mechanical properties of the TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites and Ti-1.5Fe- 2.25Mo alloy spark plasma sintered at different temperatures. Obviously, both the bending strength and the fracture toughness of the TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites increase with an increase in sintering temperature, arising from an increase in the relative density of the composites and an increase in volume content of TiB whiskers in Ti alloy matrix. However, the increasing rate of the bending strength of the composites decreases sharply due to the rapid decrease in aspect ratio of the TiB whiskers, which indicates that the aspect ratio of the TiB whiskers has a significant influence on bending strength of the TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites. The TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composite synthesized by SPS method at 1150 °C exhibits the highest relative density of 99.6%, bending strength of 1596 MPa, and fracture toughness of 23.2 MPa·m1/2. By contrast, the bending strength of the TiB/Ti-1.5Fe- 2.25Mo composite is much higher than that of the Ti alloy prepared under the same conditions due to the strengthening effect of the in situ synthesized TiB whiskers. But on the other hand, the formation of the TiB whiskers in Ti alloy matrix clearly decreases the fracture toughness of the Ti alloy. In addition, the bending strength and the fracture toughness of the TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo sintered at 850 °C are much lower due to the relatively low relative density of the composite.
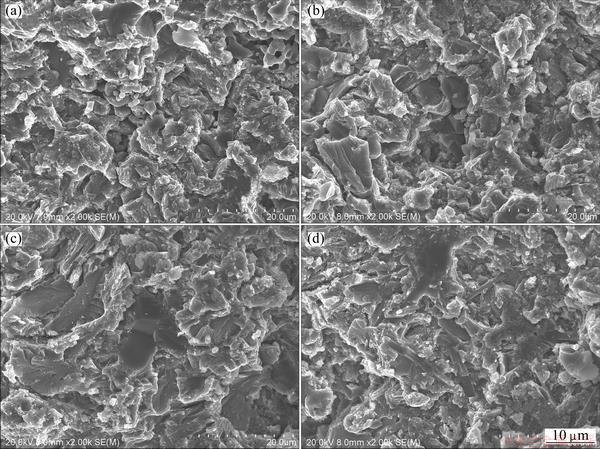
Fig. 5 Fracture surfaces of TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites sintered at temperatures of 850 °C (a), 950 °C (b), 1050 °C (c), and 1150 °C (d)
Table 4 Mechanical properties of TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites and Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo alloy
4 Conclusions
1) TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composites were in situ synthesized using SPS process at sintering temperatures between 850-1150 °C, heating rate of 100 °C/min, holding pressure of 50 MPa and holding time of 5 min.
2) The initial and final reaction temperatures between Ti and TiB2 during the SPS process are about 950 °C and 1150 °C, respectively.
3) The aspect ratio of the in situ synthesized TiB whiskers decreases rapidly with an increase in sintering temperature.
4) The in situ synthesized TiB whiskers mainly form along Ti alloy grain boundaries. Some TiB whiskers grow into inner of phases from boundaries, while others grow along the phase boundaries.
5) The TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo composite sintered at 1150 °C exhibits the highest relative density of 99.6%, bending strength of 1596 MPa, and fracture toughness of 23.2 MPa·m1/2.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. WANG Lin and Pro. CAI Hong-nian for their contributions to the investigation. In addition, the authors would also like to express gratitude to the unknown reviewers for their constructive comments on the original manuscript.
References
[1] BIROSCA S, BUFFIERE J Y, KARADGE M, PREUSS M. 3-D observations of short fatigue crack interaction with lamellar and duplex microstructure in a two-phase titanium alloy [J]. Acta Mater, 2011, 59(4): 1510-1522.
[2] FENG Shu-rong, TANG Hai-bo, ZHANG Shu-quan, WANG Hua-ming. Microstructure and wear resistance of laser clad TiB-TiC/TiNi-Ti2Ni intermetallic coating on titanium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(7): 1667-1673.
[3] WANG T, GUO H Z, WANG Y W, PENG X N, ZHAO Y, YAO Z K. The effect of microstructure on tensile properties, deformation mechanisms and fracture models of TG6 high temperature titanium alloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2011, 528(6): 2370-2379.
[4] KOO M Y, PARK J S, PARK M K, KIM K T, HONG S H. Effect of aspect rations of in situ formed TiB whiskers on the mechanical properties of TiBW/Ti-6Al-4V composites [J]. Scripta Mater, 2012, 66(7): 487-490.
[5] SHEN Xiang-bo, ZHANG Zhao-hui, WEN Sai, WANG Fu-chi, LEE Shu-kui. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the in situ TiB-Ti metal-matrix composites synthesized by spark plasma sintering process [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2011, 509(29): 7692-7696.
[6] TJGONG S C, MAI Y W. Processing-structure-property aspects of particulate- and whisker-reinforced titanium matrix composites [J]. Compos Sci Technol, 2008, 68(3-4): 583-601.
[7] DAS M, BALLA V K, BASU D, MANNA I, KUMAR T S S, BANDYOPADHYAY A. Laser processing of in situ synthesized TiB-TiN-reinforced Ti6Al4V alloy coatings [J]. Scripta Mater, 2012, 66(8): 578-581.
[8] ZHANG Zhao-hui, SHEN Xiang-bo, WANG Fu-chi, LEE Shu-kui. A new rapid route for in situ synthesizing monolithic TiB ceramic [J]. J Am Ceram Soc, 2011, 94(9): 2754-2756.
[9] BOEHLERT C J, TAMIRISAKANDALA S, CURTIN W A, MIRACLE D B. Assessment of in situ TiB whisker tensile strength and optimization of TiB-reinforced titanium alloy design [J]. Scripta Mater, 2009, 61(3): 245-248.
[10] MENG Qing-chang, FENG Hai-bo, CHEN Guang-chang, YU Rong-hai, JIA De-chang, ZHOU Yu. Defects formation of the in situ reaction synthesized TiB whiskers [J]. J Cryst Growth, 2009, 311(6): 1612-1615.
[11] PANDA K B, RAVI CHANDRAN K S. First principles determination of elastic constants and chemical bonding of titanium boride (TiB) on the basis of density functional theory [J]. Acta Mater, 2006, 54(6): 1641-1657.
[12] GENC A, BANERJEE R, HILL D, FRASER H L. Structure of TiB precipitates in laser deposited in situ Ti-6Al-4V-TiB composites [J]. Mater Lett, 2006, 60(7): 859-863.
[13] GORSSE S, MIRACLE D B. Mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V-TiB composites with randomly oriented and aligned TiB reinforcements [J]. Acta Mater, 2003, 51(9): 2427-2442.
[14] ZHANG Zhao-hui, SHEN Xiang-bo, WEN Sai, LUO Jie, LEE Shu-kui, WANG Fu-chi. In situ reaction synthesis of Ti-TiB composites containing high volume fraction of TiB by spark plasma sintering process [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2010, 503(1): 145-150.
[15] DUTTAMAJUMDAR J, LI L. Development of titanium boride (TiB) dispersed titanium (Ti) matrix composite by direct laser cladding [J]. Mater Lett, 2010, 64(9): 1010-1012.
[16] MADTHA S, LEE C, RAVI CHANDRAN K S. Physical and mechanical properties of nanostructured titanium boride (TiB) ceramic [J]. J Am Ceram Soc, 2008, 91(4): 1319-1321.
[17] QUAST J P, BOEHLERT C J, GARDNER R, TUEGEL E, WYEN T. A microstructure and sonic fatigue investigation of Ti-TiB functionally graded materials [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 497(1-2): 1-9.
[18] HILL D, BANERJEE R, HUBER D, TILEY J, FRASER H L. Formation of equiaxed alpha in TiB reinforced Ti alloy composites [J]. Scripta Mater, 2005, 52(5): 387-392.
[19] ZHANG Chang-jiang, KONG Fan-tao, XIAO Shu-long, NIU Hong-zhi, XU Li-juan, CHEN Yu-yong. Evolution of microstructural characteristic and tensile properties during preparation of TiB/Ti composite sheet [J]. Mater Des, 2012, 36: 505-510.
[20] MORSI K, PATEL V V. Processing and properties of titanium-titanium boride (TiBW) matrix composites-a review [J]. J Mater Sci, 2007, 42(6): 2037-2047.
[21] FENG Hai-bo, ZHOU Yu, JIA De-chang, MENG Qing-chang. Stacking faults formation mechanism of in situ synthesized TiB whiskers [J]. Scripta Mater, 2006, 55(8): 667-670.
[22] FENG Hai-bo, JIA De-chang, ZHOU Yu. Spark plasma sintering reaction synthesized TiB reinforced titanium matrix composites [J]. Compos Part A, 2005, 36(5): 558-563.
[23] BHAT B V R, SUBRAMANYAM J, PRASAD V V B. Preparation of Ti-TiB-TiC & Ti-TiB composites by in-situ reaction hot pressing [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, 325(1-2): 126-130.
[24] RONG Hui-yong, PENG Zhi-jian, REN Xiao-yong, PENG Ying, WANG Cheng-biao, FU Zhi-qiang, QI Long-hao, MIAO He-zhuo. Ultrafine WC-Ni cemented carbides fabricated by spark plasma sintering [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2012, 532: 543-547.
[25] RONG Hui-yong, PENG Zhi-jian, REN Xiao-yong, WANG Cheng-biao, FU Zhi-qiang, QI Long-hao, MIAO He-zhuo. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine WC-Ni-VC-TaC-cBN cemented carbides fabricated by spark plasma sintering [J]. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater, 2011, 29(6): 733-738.
[26] SANTANACH J G, WEIBEL A, ESTOUMES C, YANG Q, LAURENT C H, PEIGNEY A. Spark plasma sintering of alumia: Study of parameters, formal sintering analysis and hypotheses on the mechanism(s) involved in densification and grain growth [J]. Acta Mater, 2011, 59(4): 1400-1408.
[27] ZHANG Zhao-hui, WANG Fu-chi, WAN Lu, LEE Shu-kui. Ultrafine-grained copper prepared by spark plasma sintering process [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 476(1-2): 201-205.
[28] ZHANG Zhao-hui, SHEN Xiang-bo, WANG Fu-chi, LEE Shu-kui, FAN Qun-bo, CAO Mao-sheng. Low-temperature densification of TiB2 ceramic by the spark plasma sintering process with Ti as a sintering aid [J]. Scripta Mater, 2012, 66(3-4): 167-170.
[29] RAMOND L, BERNARD-GRANGER G, ADDAD A, GUIZARD C. Sintering of a quasi-crystalline power using spark plasma sintering and hot-pressing [J]. Acta Mater, 2010, 58(15): 5120-5128.
[30] KHALEGHI E, LIN Y S, MEYERSB M A, OLEVSKYAl E A. Spark plasma sintering of tantalum carbide [J]. Scripta Mater, 2010, 63(6): 577-580.
[31] XU Li-juan, XIAO Shu-long, CHEN Yu-yong, WANG Juan. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-43Al-9V alloy fabricated by spark plasma sintering [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(4): 768-772.
[32] BORRELL A, ALVAREZ I, TORRECILLAS R, ROCHA V G, FERNANDEZ A. Microstructural design for mechanical and electrical properties of spark plasma sintered Al2O3-SiC nanocomposites [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2011, 534: 693-698.
[33] KOOI B J, PEI Y T, de HOSSON J T M. The evolution of microstructure in a laser clad TiB-Ti composite coating [J]. Acta Mater, 2003, 51(3): 831-845.
[34] TIAN Y S. Growth mechanism of the tubular TiB crystals in situ formed in the coatings laser-borided on Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Mater Lett, 2010, 64(22): 2483-2486.
张朝晖,神祥博,王富耻,魏 赛,李树奎,才鸿年
北京理工大学 材料学院,北京 100081
摘 要:采用放电等离子烧结技术原位合成了TiB增强Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo复合材料,研究了烧结温度对复合材料微观组织和力学性能的影响规律。 结果表明,随着烧结温度的升高,钛合金中TiB晶须的长细比迅速减小;然而,复合材料的相对密度及TiB的体积含量随着烧结温度的升高而不断增大。由于TiB晶须长细比的减小会导致复合材料强度的降低,而复合材料的相对密度及TiB体积含量的增大又会带来复合材料强度的增加,因此,在这两种因素的共同作用下,最终导致TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo复合材料的弯曲强度随着烧结温度的升高而缓慢增大。 在烧结温度为1150 °C 时,TiB/Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo复合材料具有最大的弯曲强度1596 MPa。
关键词:TiB;钛基复合材料;放电等离子烧结;微观组织;力学性能
(Edited by Hua YANG)
Foundation item: Prject (20111D0503200316) supported by the Programme for Peking Excellent Talents in University, China; Project (613135) supported by 973 Defence Plan of China
Corresponding author: Zhao-hui ZHANG; Tel: +86-10-68912709; Fax: +86-10-68913951; E-mail: zhang@bit.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62773-9

