低气压室内环境传热传质的数值模拟
陈宁,廖胜明,饶政华
(中南大学 能源科学与工程学院,流程工业节能湖南省重点实验室,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:在考虑人的呼吸量及呼吸成分的前提下,采用RNG k-e湍流模型对低气压室内环境的传热传质进行数值模拟。对不同大气压下房间内的温度场、流场、氧气及二氧化碳气体的分布规律进行讨论,并对人体对流换热系数与经验值进行比较。研究结果表明:当大气压降低时,空气流速变化很小,房间的对流换热减弱,在稳定状态下温度略有上升;CO2体积分数增大,O2质量分数下降;但增加房间送风速度可以更好地排除CO2,有利于改善室内空气品质;混合对流时人体表面的对流换热能力减弱,减弱的趋势比强迫对流换热的小。
关键词:低气压;RNG k-e湍流模型;传热传质
中图分类号:TK124 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)01-0388-09
Numerical investigation of heat and mass transfer in hypobaric atmosphere
CHEN Ning, LIAO Shengming, RAO Zhenghua
(Hunan Key laboratory of Energy Conservation in Process Industry,School of Energy Science and Engineering,
Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Considering human’s respiration capacity and component, the RNG k-e turbulent model was developed to study the heat and mass transfer of indoor air in the hypobaric atmosphere. Distribution feature of temperature, velocity, O2 concentration and CO2 concentration was discussed. Body convective heat transfer coefficients were compared with those obtained by empirical formula. The results show that with the decrease of pressure, the convection heat transfer tends to be weak, causing the temperature to slightly increase, while CO2 concentration increases with the decrease of O2 concentration. But raising the supplied air-flow speed helps to exclude CO2 and hence indoor air quality. Body convective heat transfer under mix convection has gentler trend than that under forced heat convection.
Key words: hypobaric; RNG k-e turbulent model; heat and mass transfer
在低气压热环境研究中,有1个特殊的研究对象——青藏铁路客车。青藏铁路地处高海拔地区,乘客有许多来自于平原地区,很容易产生高原反应。车内的空气环境是低气压环境,低气压对人体生理的影响主要有2个方面:压力过低引起的压力效应和大气氧分压引起的低氧效应。在海拔3 km可以使大多数人在静息状态下出现不同程度的高原反应,而超过这个高度,其生理、生化、病理和临床方面的改变则明显加剧[1]。人们对低气压热环境进行的研究主要是对人体在低气压缺氧或供氧充足下的热反应及热感觉进行生理及心理测试[2-6],如:Blatteis等[2]测得高海拔地区人体的平均皮肤温度比平原地区的略高,说明在高海拔地区人体对冷产生的热量反应减少,同时也测得由于寒冷消耗的氧气增量在高原地区比平原地区的少;Ohno等[3]发现随着海拔高度的增加,心跳速率加快,这似乎与缺氧有关,脸和身体的热感觉增加,被测对象很难表述其热状态;崔代秀等[4]认为在氧气供给充足条件下航空座舱内温度、湿度及大气压力对人体皮肤蒸发散热及通过辐射和对流的非蒸发性散热均有显著影响,各单因素的作用是主要的,其中温度的影响为最大,其次是压力;人体的对流散热随大气压力减小而减小,而皮肤蒸发散热与大气压力成反比;Saito等[5]发现人体在不同海拔高度下冬季的心跳速率比夏季要快,与夏季时相比,人体生理反应在冬季更容易受低气压影响;Maland等[6]认为在高海拔低气压地区缺氧不影响皮肤的冷热感阈值。此外,Wang等[7]在低于大气压力20%~30%的低气压箱实验中也显示大气压力不影响平均皮肤温度;Kandjov[8]通过推导认为人体蒸发热阻随海拔增高而减小,人体的热稳定性及热舒适稳定性在高海拔地区比海平面的强。目前,车内采用弥散式供氧和分布式供氧相结合的供氧方式即增氧不增压的方式。弥散式供氧是指列车在海拔3 km以上运行时,空调系统供氧。王淼恒等[9]通过对青藏铁路客车进行全程或主要站点的高原反应生理检测,测得19%的人出现严重缺氧现象,认为弥散式供氧技术有待改进。在一般房间里,通风的主要目的之一是控制房间的二氧化碳气体含量在允许范围内。这是因为人体的呼吸会消耗氧气而增加二氧化碳气体,过量的二氧化碳气体和过少的氧气都会对人体生理产生负面影响。长期以来,数值计算是研究人员对室内热环境气流组织、空气品质及热舒适进行评价的主要方法之一。其中,Hyun等[10-13]在常压下建立了人体模型,考虑了人体的呼吸量,对房间内部人体周围的流场、温度场及污染物分布进行数值模拟。Hyun等[10]采用RNG k-e湍流模型模拟了站立人体瞬时呼吸对吸入污染物量的影响,比较了示踪污染气体在3个不同方位和高度的吸入污染物量。Tatsuya等[11]采用标准k-e湍流模型分别对站着、坐着和躺着3种姿势的人吸入污染物的情况进行了比较。Gao等[12]采用标准k-e湍流模型,建立仿真人体热模型对个性通风的品质进行评价。Zhu等[13]采用低k-e湍流模型模拟了房间下送风时人体鼻子周围呼吸区的瞬时流场分布情况。对于采用何种模型模拟人体传热,Jelina等[14]建议采用任一k-e湍流模型;Chen[15]则认为RNG k-e模型比标准k-e模型略好。这是因为室内空气被四周墙壁所包围,在近壁面区产生了低雷诺数流动区,而RNG k-e模型不仅适用于高雷诺数流动,也适用于低雷诺数流动[15]。在此,本文作者在前人研究的基础上,采用RNG k-e湍流模型对低气压室内环境的传热传质进行数值计算。本文考虑了人体呼气和吸气时不同的空气组分,对不同大气压下房间内的温度场、流场的分布规律、氧气及二氧化碳气体的运输规律进行探讨,研究温度、流速、气体含量与大气压力的关系,以便为低气压环境实现有效供氧和气流组织提供理论依据。
1 模型的建立
1.1 物理模型
本文研究的对象为1间热房间。房间的中央座椅上坐着1人,人体周期性地吸入和呼出组分不同的空气,其中吸入的氧气比呼出的氧气多,而吸入的二氧化碳气体比呼出的二氧化碳气体少。送风口位于顶部的中央,排风口位于一侧墙壁的底部中央。较低温空气从送风口送入房间,通过气流组织,将房间的余热和人体呼出的过多二氧化碳气体从排风口排走。
房间的长×宽×高为3 m×3 m×3 m,如图1所示。送回风口长×宽均为0.2 m×0.4 m,人和座椅高度均为1.0 m,人的膝盖高度为0.5 m,鼻子呼吸区的长×宽为0.1 m×0.1 m。
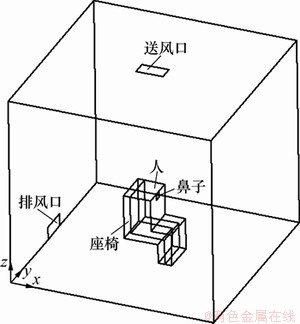
图1 三维低压房间模型
Fig.1 Three-dimensional room model in hypobaric condition
1.2 数学模型
1.2.1 假设条件
低气压房间内的空气为不可压非理想流体,空气各组分的密度计算均考虑Bossinesq近似; 流动为三维非稳态湍流,时间步长设为0.1 s;空气中的组分仅考虑有O2,CO2,H2O和N2。本文分别对青藏铁路客车经过的平原地区(1×105 Pa)、格尔木地区(0.707×105 Pa)、海拔最高的安多地区(0.556×105 Pa) 3种环境压力进行比较。
1.2.2 控制方程
控制方程包括连续方程、RNG k-e湍流模型[16-17]和组分输运方程。组分输运无量纲方程为:

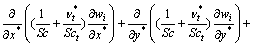
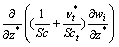 (1)
(1)
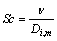 (2)
(2)
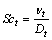 (3)
(3)
式中:上标“*”为变量的无量纲记号;变量v1,v2和v3分别为x,y和z 3个方向上的分速度;t为时间;Wi为组分的质量分数;Di,m为组分i的有效扩散系数(cm2/s),可由Stefen-Maxwell方程和Hougen-Watson方程联立求出;Dt为湍流扩散系数(cm2/s);νt为湍流黏性系数(cm2/s);Sc和Sct为分别为Schmidt数和湍流Schmidt数。一般地,在湍流流动中,质量扩散由湍流 Schmidt 数决定湍流输运控制。Sct规定了由于湍流而引起的动量和质量的相对扩散,它在所有湍流流动中一致相似。Sct相对于分子组成的湍流属于不敏感的经验常数,一般取0.7[18]。
1.2.3 主要边界条件
正常人体的呼吸频率为12~18次/min,呼吸量为6~8 L/min。在高原时,呼吸量增加[19]。假定不同海拔下人体呼吸过程中空气各组分保持与常压时的恒定值,人体呼吸量取12 L/min,呼吸次数为12次,每次5 s,人的呼吸量为0.2 L/s(呼气为负值,吸气为正值)。呼气和吸气的时间各占2.5 s。人的呼吸量随时间的变化曲线如图2所示。从图2可见:吸气时,吸走的空气量仅占排风口量的5/1 000,且空气成分与室内成分一致。为了便于计算收敛和简化问题,在吸气时,认为鼻子呼吸区仍为速度入口条件,但是,气流速度为0 m/s。各主要边界条件设定如表1所示。
图2 假想的人体呼吸过程
Fig.2 Assumption of transient respiration process
1.3 初始条件
初始温度为293 K,空气各组分O2,CO2,H2O和N2的质量分数的初始值分别为23%,0.06%,0.40%和76.54%(对应的体积分数分别为21.000%,0.040%,0.009%和78.951%)。
1.4 网格划分
对人、座椅、送回风口这些面,采用三角形非结构化面网格,间距为0.05 m。考虑人体附近的区域流动较复杂,将房间空间设置了2个疏密不同的体网格(如图3所示):第1个体网格间距为0.1 m,第2个体网格间距为0.2 m,共计217 859个网格。进行网格无关性验证,分别采用154 780,217 859和364 973个这3种网格进行稳态传热数值模拟,后两者结果误差不超过2%。考虑计算工作量,取217 859个网格。
表1 主要边界条件设定
Table 1 Boundary conditions
图3 低气压房间网格划分
Fig.3 Mesh generation for simulated room in hypobaric condition
1.5 求解方法
湍流模型采用RNG k-e 模型;控制方程组采用有限容积法离散交错网格。其中:对流-扩散方程采用一阶迎风格式;Navier-Stokes方程求解采用SIMPLE算法;方程组的迭代计算采用亚松弛法;时间步长取0.1 s。当各变量的残差均小于10-3及计算域能量平衡时,认为计算收敛。
2 模拟结果及讨论
2.1 达到稳定状态时各大气压力下排风口各参数的分布规律
2.1.1 排风口气流速度
排风口气流速度与时间的关系如图4(a)所示。从图4(a)可看出:从计算开始的最初阶段(0~2 500 s),不同环境压力下的速度都有些振荡;在3 000 s后,速度达到恒定值,3个环境压力下的速度曲线平行于横坐标而且重合,说明在送风速度一定、大气压力变小时,空气密度减小,使运动扩散能力增强,但同时雷诺数下降使空气的湍流减弱,这共同的作用结果使稳态下的速度不随环境压力变化而变化。
2.1.2 排风口气流温度
排风口气流温度与时间的关系如图4(b)所示。从图4(b)可见:在3 000 s后,气流温度达到恒定值,3个环境压力pa下的温度曲线平行于横坐标;随环境压力降低,气流温度则有所上升;当环境压力降至0.707× 105 Pa 时,房间温度从301 K升高至302 K;当环境压力继续降至0.556×105 Pa 时,房间温度升高至302.5 K,表征湍流空气运动扩散系数和热扩散系数之比的有效Pr数在3个环境压力下都为0.82。这说明在送风速度一定时,由于房间空气的运动扩散能力与热扩散能力相当,且不随压力变化而变化,房间温度达到稳定所需的时间与速度达到稳定的时间很接近;而由于热扩散系数随压力降低而略有增大,使空气在低压下的热扩散能力增强,稳态下房间温度随环境压力降低而略有升高。
2.1.3 排风口CO2体积分数
排风口CO2体积分数与时间的关系如图4(c)所示。从图4(c)可见:人体有规律的一呼一吸使得房间的CO2分布具有逐时变化的特征;在10 000 s时,排风口的CO2体积分数才达到恒定值,图中的曲线趋于水平;在1.000×105 Pa,0.707×105 Pa 和0.556×105 Pa 3个大气压下的CO2体积分数恒定值分别为730×10-6,773×10-6和800×10-6。表征湍流空气运动扩散系数和CO2质量扩散系数之比的有效Sc数在3个环境压力下都为0.5,说明尽管房间空气的运动扩散能力弱于质量扩散能力,但是,由于人体呼吸的周期性变化产生了大量的CO2,对房间CO2从初始状态达到稳定状态的过程造成了很大的干扰,从而使CO2达到稳定状态所需要的时比O2时间长。人体呼吸还使房间CO2体积分数变大,使得达到稳定状态的CO2体积分数增大。环境压力降低后,由于CO2在空气中的质量扩散系数系数增大,使稳态下房间CO2体积分数值随环境压力降低而略有升高。
2.1.4 排风口O2质量分数
排风口O2质量分数与时间的关系如图4(d)所示。从图4(d)可见:在将近10 000 s时,排风口的O2质量分数才趋于恒定值,在1×105,0.707×105和0.556×105 Pa这3个环境压力下的恒定值分别为2 295.6,2 295.2和2 295.0 mg/mg。说明由于人体呼吸使房间O2的质量分数变小,使得达到稳定状态的O2质量分数减小。环境压力降低后,尽管O2在空气中的扩散系数系数增大,但由于混合物气体的质量守恒,在CO2体积分数增加的同时,O2质量分数减小。
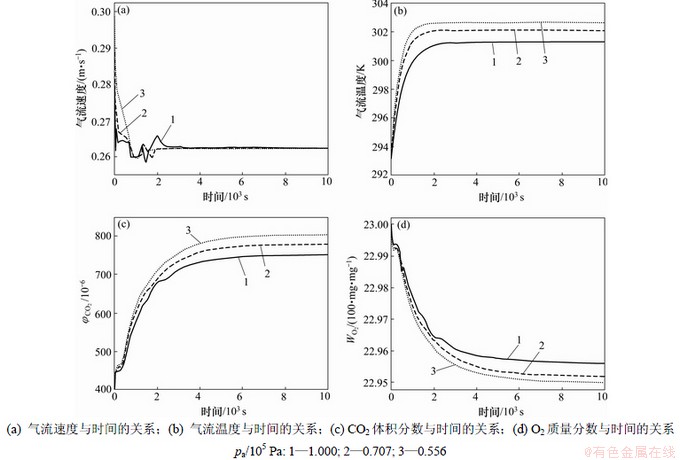
图4 vin为0.25 m/s时不同大气压下排风口4个参数(速度、温度、CO 2体积分数和O2质量分数)的瞬时值
Fig.4 Four transient parameters (velocity, temperature, CO2 concentration, O2 concentration) at exhaust opening when vin is 0.25 m/s
2.2 稳定状态时各大气压力下房间气体各参数的分布比较
在人体座位前方的位置(x=2.25 m,y=1.50 m),对4个参数(温度、速度、CO2体积分数、O2质量分数)在房间高度(z)上的分布进行比较,结果如图5所示(图中3个线型代表的大气压力与图4的相同),此时间为排风口的参数达到稳定后1个呼吸过程结束的时间。图5(a)~(d)中房间送风速度为0.25 m/s ;图5(e)~(h)中的房间送风速度为0.5 m/s。从图5可以看出:受人体及座位尺寸和人体呼吸的影响,CO2体积分数、O2质量分数和速度在人体腿部高度(z=0.5 m)以下的区域发生了变化:气流速度随高度降低而逐渐减小,人体呼吸产生的CO2在该高度之内聚集,O2质量分数则相应减少。而在这个高度以上的区域,3个参数均保持在某一个值附近。温度在房间高度上则呈某一梯度分布,在接近顶部的梯度明显大于其他高度的梯度。
当大气压力降低时,同一送风速度下的房间在同一位置上的CO2体积分数和温度增大,而O2质量分数减少,气流速度不变。
当送风速度由0.25 m/s增大到0.50 m/s时,同一位置上的CO2体积分数和温度减少,减少的幅度大于送风速度不变而压力由0.556×105 Pa增大至1.000×105 Pa 时的幅度;而O2质量分数则增大,其增大的幅度大于送风速度不变而压力由0.556×105 Pa增大至1.000×105 Pa时的幅度。位置上的气流速度则随送风速度增大而略增大。
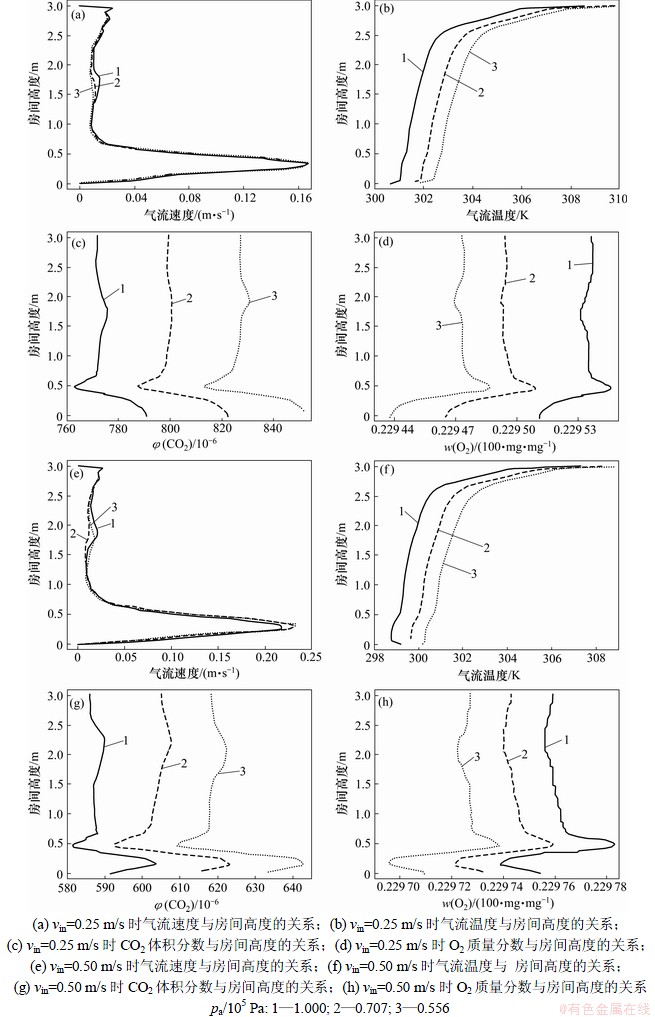
图5 不同大气压下房间内4个参数(速度、温度、CO2体积分数φ(CO2)和O2质量分数w(O2))的比较(x=2.25 m,y=1.5 m)
Fig.5 Comparison of four indoor parameters (velocity, temperature, CO2 volume concentration, O2 mass concentration) in different hypobaric conditions (x=2.25 m, y=1.5 m)
2.3 各大气压力下人体的对流换热系数
房间内的空气换热既包括强迫对流换热,也包括有浮升力产生的自然对流换热。当浮升力作用较小时,空气中的换热由强迫对流换热决定;而当浮升力作用较大时,空气中的换热由自然对流换热决定。当强迫对流和自然对流换热有明显的作用分界时,换热称为混合对流换热。通常,阿基米德数Ar作为评判这几种换热的准则数,当Ar<<1时,为强迫对流换热,忽略自然对流换热;当Ar>>1时,为自然对流换热,忽略强迫对流换热;当Ar>>1时,为混合对流换热[13]。对于人体对流换热,无量纲准则数Nub,Reb和Grb可以表达如下[20-21]:
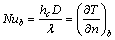 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
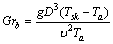 (6)
(6)
 (7)
(7)
其中:hc为对流换热系数(W/(m2·K));λ为导热系数(W/(m·K));v为气流速度(m/s);D为人体特征尺寸(m),本文取人体坐姿的高度;Tsk和Ta分别为人体皮肤和周围空气的温度(K)。ν与动力黏度μ及ρ有关。
在不同海拔(不同大气压力)、不同送风速度下房间内人体附近空气的Ar如表2所示。从表2可见:Ar都在1附近,说明房间内的人体对流换热应为混合对流换热。
2.3.1 人体对流换热系数的经验公式
对于自然对流,人体对流换热的无因次关联式为:
表2 不同海拔高度(不同大气压力)、不同送风速度下房间内的空气Re,Gr及Ar
Table 2 Re, Gr and Ar of indoor air in different inlet velocities and hyperbaric conditions
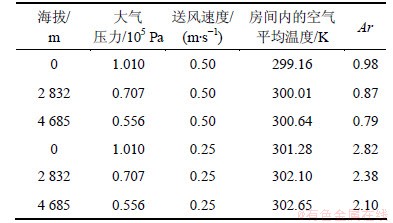
 (8)
(8)
式中:a和n为常数。当人体处于强迫对流的空气中时,人体对流换热的无因次关联式Nu可写为:
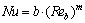 (9)
(9)
式中:b和m为常数。在各特性参数中,λ和μ随大气压力变化甚小,可忽略不计;ρ与大气压力有关。在一定的气流速度下, 海拔高度H引起大气压力降低和空气密度降低。不同海拔的人体对流换热系数hcH和1×105 Pa环境下,人体对流换热系数hc存在以下关系:
 (10)
(10)
2.3.2 本文数值模拟结果与经验公式所得结果比较
现有文献中尚未有混合对流换热的人体对流换热系数的报道。将本文根据式(4)计算所得的对流换热系数与文献[22-24]中明确为静坐的人的强迫对流换热系数进行比较,结果见图6。从图6可以看出:本文的计算结果在不同大气压下比文献[22]和[24]中的结果小,与文献[23]中的结果较接近。但人体对流换热系数随大气压降低的趋势比强迫对流经验公式所得的结果平缓。文献[22-24]中人体对流换热系数经验公式在强迫对流时比在自然对流受大气压力变化影响大,增幅明显。混合对流换热能力介于强迫对流与自然对流两者中间,其随大气压的降低趋势比强迫对流的降低趋势平缓,说明本文的计算模拟正确。
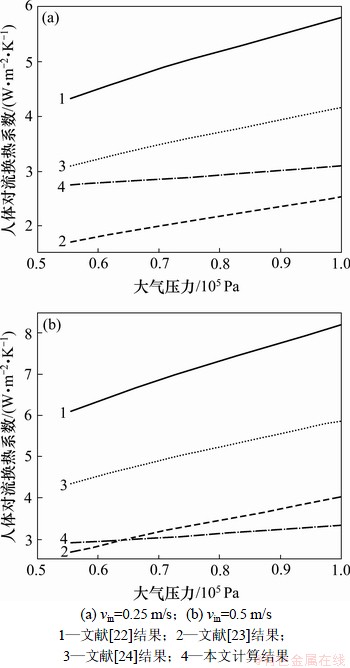
图6 vin为0.25 m/s时本文计算的人体对流换热系数与经验公式所得对流换热系数比较
Fig.6 Comparison of hcH deduced from simulation in this paper and empirical equations when vin is 0.25 m/s
3 结论
(1) 由于人体周期性地吸入或呼出成分含量不同的O2和CO2,房间内O2和CO2达到稳定状态的时间要远比温度、空气流速达到稳定状态的时间长。当大气压降低时,房间的对流换热减弱,稳定状态下的温度略上升;气体扩散能力增强,CO2体积分数增大,O2质量分数下降;空气流速变化很小。
(2) 人体周围的3个参数即CO2体积分数、O2气体质量分数、速度在人体腿部高度(z=0.5 m)以上的垂直分布几乎没有变化,而在腿部高度以下速度减缓,人体呼出的CO2大量聚集,此区域的O2质量分数也较小。温度则在垂直高度呈梯度分布。当送风速度增大1倍时,同一位置上的CO2体积分数和温度减少,减少的幅度大于送风速度不变而压力增大1倍时的幅度;而O2质量分数增加,其增加的幅度大于送风速度不变而压力减小1倍时的幅度;气流速度则随送风速度增加而略增加。说明在低气压环境可适当增加送风速度,减少房间的CO2体积分数。
(3) 房间内人体对流换热以混合对流换热为主。当大气压降低时,人体表面的对流换热能力减弱,减弱的趋势比强迫对流换热小。在同一大气压时,提高送风速度可以增强人的对流换热能力。因而,在低气压环境下,可适当增加送风速度以满足人体的热舒适,但也要考虑人体吹风感的影响。
参考文献:
[1] 李天麟. 高原与健康[M]. 北京: 北京科学技术出版社, 2001: 6-13.
LI Tianlin. High altitude and health[M]. Beijing: Beijing Science and Technology Press, 2001: 6-13.
[2] Blatteis M, Lutherer L O. Effect of altitude exposure on thermoregulatory response of man to cold[J]. Journal of Applied Physiology, 1976, 4(6): 848-858.
[3] Ohno H, Kuno S, Saito T, et al. The effects of hypobaric conditions on man’s thermal responses[J]. Energy and Buildings, 1991, 16(1/2): 755-763.
[4] 崔代秀, 祁章年, 王宪章, 等. 座舱温、湿度及压力改变对人体同环境热交换的影响[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 1996, 9(1): 42-48.
CUI Daixiu, QI Zhangnian, WANG Xianzhang, et al. Effect of temperature, humidity, pressure in cabin on heat exchange of human with environment[J]. Space Medicine & Medical Engineering, 1996, 9(1): 42-48.
[5] SaitoT, KunoS, Ohno H. The compound effect of hypobaric and warm conditions on physiological and psychological responses[C]//International Symposium on Air Conditioning in High Rise Buildings. Shanghai, 1997: 289-294.
[6] Malanda U L, Reulen J P, Saris W H, et al. Hypoxia induces no change in cutaneous thresholds for warmth and cold sensation[J]. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 2008, 104(2): 375-381.
[7] WANG Haiying, HU Songtao, LIU Guodan, et al. Experimental study of human thermal sensation under hypobaric conditions in winter clothes[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2010, 42: 2044-2048.
[8] Kandjov I M. Thermal stability of the human body under environmental air conditions[J]. Journal of Thermal Biology, 1998, 23(2): 117-121.
[9] 王淼恒, 王威, 张海峰, 等. 青藏列车中乘客的高原反应监测与分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2008, 35(9): 1704-1707.
WANG Miaoheng, WANG Wei, ZHANG Haifeng, et al. Monitoring and analysis of acute mountain sickness of train passengers on Qinghai—Tibet railway[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine, 2008, 35(9): 1704-1707.
[10] Hyun S, Kleinstreuer C. Numerical simulation of mixed convection heat and mass transfer in a human inhalation test chamber[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2001, 44: 2247-2260.
[11] Tatsuya H, Ashiaki Y I, Shinsuke K, et al. CFD analysis on characteristics of contaminated indoor air ventilation and its application in the evaluation of the effects of the contaminant inhalation by a human occupant[J]. Building and Environment, 2002, 37: 219-230.
[12] Gao N, Niu J. CFD study on micro-environment around human body and personalized ventilation[J]. Building and Environment, 2004, 39: 795-805.
[13] Zhu S, Kato S, Shuzo M, et al. Study on inhalation region by means of CFD analysis and experiment[J]. Building and Environment, 2005, 40: 1329-1336.
[14] Jelina S, Vladimir V, He G, et al. CFD boundary conditions for contaminant dispersion, heat transfer and airflow simulations around human occupants in indoor environments[J]. Building and Environment, 2008, 43: 294-303.
[15] CHEN Q. Comparison of different k-ε models for indoor air flow computations[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer, 1995, 28: 353-369.
[16] 陶文铨. 数值传热学[M]. 西安: 交通大学出版社, 2004: 347-370.
TAO Wenquan. Numerical heat transfer[M]. Xi’an: Xi’an Jiaotong University Press, 2004: 347-370.
[17] Fluent Inc. Fluent 6.3 user’s guide[M]. Lebanon: Fluent Inc, 2006: 834-927.
[18] 吕永达. 高原医学与生理学[M]. 天津: 天津科技翻译出版公司, 1995: 211-213.
L Yongda. High altitude medicine and physology[M]. Tianjin:Tianjin Science and Technology Translation and Publishing Corporation, 1995: 211-213.
Yongda. High altitude medicine and physology[M]. Tianjin:Tianjin Science and Technology Translation and Publishing Corporation, 1995: 211-213.
[19] Incropera F P, Dewitt D P. Introduction to heat transfer[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1996: 365-367.
[20] de Dear R J, Arens E, Hui Z, et al. Convective and radiative heat transfer coefficients for individual human body segments[J]. International Journal of Biometeorology, 1997, 40(3): 141-156.
[21] Clark R P. Human skin temperature and convective heat loss[C]// Cena K, Clark J A, ed. Bioengineering, Thermal Physiology and Comfort. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1981: 57-76.
[22] Winslow C E A, Gagge A P, Herrington L P. The influence of air movement on heat losses from the clothed human body[J]. Journal of Applied Physiology, 1939, 127(3): 505-518.
[23] Colin J, Houdas Y. Experimental determination of coefficient of heat exchange by convection of the human body[J]. Journal of applied Physiology, 1967, 22(1): 31-38.
[24] Mitchell D. Convective heat loss in man and other animals[C]// Montieth J L, Mount L E, ed. Heat loss from animals and man: assessment and control. London: Butterworths, 1974: 1-17.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2012-01-13;修回日期:2012-03-18
基金项目:广东省省部产学研结合引导项目(2011B090400338)
通信作者:廖胜明(1963-),男,湖南长沙人,教授,博士生导师,从事热能工程、热物理、暖通空调与制冷、新能源技术与政策等领域的研究;电话:13973186517;E-mail: smliao@csu.edu.cn