DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2020-37573
双模晶粒氧化物弥散强化合金的强化模型及热稳定性
展 鑫1, 2,王国伟1, 2,谭黎明1, 2,何武强1, 2,吴凯西1, 2,何英杰1, 2,刘 锋1, 2,黄 岚1, 2
(1. 中南大学 粉末冶金研究院,长沙 410083;
(2. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083)
摘 要:通过透射电子显微镜、电子背散射衍射、扫描电子显微镜和室温拉伸检测等手段,建立并验证双模晶粒尺寸分布氧化物弥散强化合金的室温强化预测模型。同时,通过在1150 ℃下进行不同时间的热处理试验,结合组织观察和显微硬度测试,研究合金的高温组织热稳定性。结果表明:室温强化预测模型通过叠加固溶强化(σss)、晶粒尺寸强化(σg)、位错强化(σd)与氧化物纳米粒子强化(σp)之和的平方根,模型预测结果与试验值十分接近。合金组织热稳定性研究结果表明,在1150 ℃热处理初期,晶粒长大迅速且合金硬度迅速降低;而当热处理时间延长到8 h之后,晶粒尺寸虽有变化但其长大速率明显放缓,且合金硬度在热处理8 h后趋于稳定。
关键词:双模分布;晶粒;氧化物弥散强化;强化模型;热稳定性
文章编号:1004-0609(2020)-03-0612-08 中图分类号:TG146.15 文献标志码:A
第四代裂变反应堆和聚变反应堆被认为是安全、经济、无污染的能源,是解决全球能源需求快速增长的理想能源[1]。反应堆中高温、高压、大剂量中子辐射的工作环境,对作为结构材料的综合性能提出严苛的要求。氧化物弥散强化(Oxide dispersion strengthened,ODS) 合金因其优异的高温性能和抗辐射性能,成为先进裂变反应堆燃料包层和聚变反应堆壁/包层应用的首选材料之一[2-4]。虽然ODS合金可以在高温下保持相对较高的强度,但铁基ODS合金的使用温度也只有700 ℃,特别是在高温下其强度迅速降低甚至失效。基于此,镍基ODS合金应运而生,其工作温度可以达到1000 ℃并保持优异的高温强度[5]。然而ODS合金作为一种纳米结构合金具有较高的强度,但其往往是以牺牲塑性为代价的。近年来,有学者提出在传统ODS合金中引入微米级粗晶粒的方法使合金在保持高强度的同时依然具有较高的塑性[6-7]。而在这种具有双模尺寸分布的ODS合金中,其强化模型相比传统ODS合金更为复杂。除此之外,ODS合金的力学性能与微观组织有着密不可分的联系,因此,合金在高温条件下的热稳定性对于作为核工业材料的ODS合金来说同样具有至关重要的意义。
在工程应用领域,通过合金的成分及微观组织建立相关的强化模型以预测合金性能可以很大程度上降低成本、缩短研发周期。为此,众多学者关于ODS合金的强化模型和组织热稳定性展开了初步研究。VAUCORBEIL等[8]通过模拟单个位错滑过一系列随机分布质点的过程,综合考虑了位错强化、固溶强化、沉淀强化的共同作用并建立强化模型,从而预测出一种铁基ODS合金的屈服强度。CASAS等[9]通过研究一种铁基ODS合金的强化机理,分别讨论了基于“粒子-晶界”强化的复杂强化模型和简单晶界强化模型的优缺点,并分析了各个强化模型的适用条件。CHAUHAN等[10]研究了两种铁素体ODS合金微观组织与屈服应力之间的关系,并表明纳米粒子强化、位错强化和晶粒尺寸强化是ODS合金主要的强化因素,通过预测模型可较为准确的计算出合金的屈服强度。在组织热稳定性研究方面,ZHAO等[11]研究了热处理工艺对14Cr-ODS合金微观组织及力学性能的影响,表明合金经过1000 ℃热处理5 h可以获得稳定的微观组织并保持最佳的拉伸性能。严菊杰等[12]研究了不同热处理温度对14YWT-ODS铁素体钢显微硬度的影响,并表明合金力学性能稳定的临界温度为1100 ℃。通过以上文献报道可以看出,近年来虽然关于ODS合金强化模型及组织热稳定性的报道层出不穷,但是大多数研究都基于铁基ODS合金,而关于镍基ODS合金强化模型的报道很少且现有文献报道大部分基于单模晶粒尺寸分布,双模晶粒尺寸ODS合金的强化模型及组织热稳定性研究更是鲜有报道。因此,研究双模晶粒尺寸分布的ODS合金强化模型和热稳定性具有重要的科学及工程意义。
本文通过分析一种双模晶粒尺寸分布ODS合金的微观组织特征,研究并建立了合金室温下的强化模型,并以拉伸检测验证了模型的可靠性。通过热处理实验结合组织观察和显微硬度研究了合金的组织热稳定性。
1 实验
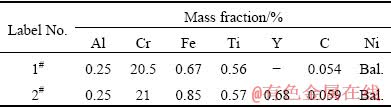
本实验采用氩气雾化的方法制得两种预合金粉末,其名义成分如表1所列。采用行星式球磨机将1#预合金粉末与YH2(≤75 μm)在高纯氩气保护的条件下进行机械合金化,从而得到与2#预合金粉成分相同的球磨粉。球料比为8:1,转速为350 r/min,球磨时间为24 h。将球磨粉末与2#预合金粉末按照质量比为1:2的比例在混料机中混合12 h得到混合粉末并装入不锈钢包套中,经过抽气、封焊后进行热挤压固结成型(HE, Hot Extrusion)得到致密的棒材。室温拉伸实验在动态疲劳试验机(MTS 370)上进行,拉伸速率为1×10-3 s-1。组织热稳定性实验在1150 ℃(±5 ℃)下进行,分别保温2、4、8、16、32、40、64、125、128 h后空冷至室温。
采用场发射扫描电镜(SEM, FEI Quanta 650 FEG)和电子背散射衍射(Electron backscatter diffraction, EBSD)观察粉末的微观形貌和合金组织,并使用HKL Channel 5软件分析所得数据。分别采用光学显微镜(OM, Leica/MeF3A)与透射电子显微镜(TEM, FEI Tecnai G2 F20)观察晶粒演化规律、位错和纳米氧化物粒子,并应用Image J软件统计晶粒及纳米粒子尺寸。硬度测试在维氏硬度计上进行,每个试样采集5个点后取平均值作为最终硬度值。EBSD检测时,加速电压为20 kV,扫描步长为0.5 μm。所采用的双喷液成分为80%乙醇和20%高氯酸(体积分数)。
表1 粉末名义成分
Table 1 Nominal composition of powder
2 结果与讨论
2.1 双模晶粒ODS合金的微观组织形貌
由于晶粒尺寸在2~5 μm分布的小晶粒不便于统计其平均晶粒尺寸,因此采用EBSD检测来研究其尺寸分布规律。合金EBSD图像及小晶粒尺寸统计如图1所示。两种尺寸分布的晶粒组织并不均匀,其小晶粒呈现聚集现象,这是由于球磨与混粉的不均匀性而引起的。热挤压后小晶粒晶粒尺寸分布如图1(b)所示,其平均晶粒尺寸为2.87 μm,大晶粒的平均晶粒尺寸为13.5 μm。
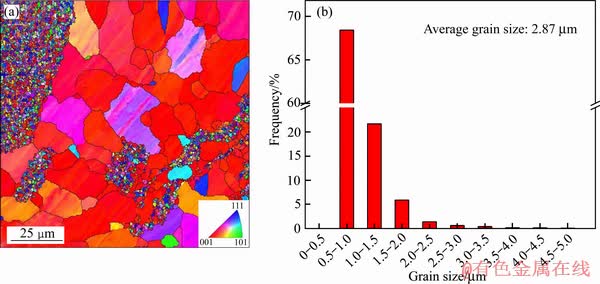
图1 热挤压态合金电子背散射衍射EBSD图像和小晶粒尺寸统计图
Fig. 1 EBSD image of hot extruded alloy(a) and statistical diagram of small grain size(b)
合金TEM像如图2所示。从图2(a)中可以清晰地看到合金经热挤压后发生大量高密度位错缠结、堆积。在热挤压过程中,大量位错发生运动,随着变形程度的逐渐增加,位错运动加剧从而产生位错网。当大量的位错运动到较小的晶粒时,位错发生堆积,并在晶界处形成位错堆积网。位错密度(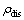 )的数值可由公式(1)计算得出[13]。
)的数值可由公式(1)计算得出[13]。
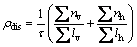 (1)
(1)
式中:t为TEM样品厚度;Lh和Lv分别为画在透射照片上的水平与垂直测试线的总长度;nh和nv分别指 位错与水平线和垂直线相交的个数。经计算,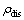 = 1.48×10-4/nm2。
= 1.48×10-4/nm2。
由图2(b)可看出,合金中的氧化物粒子细小、弥散的分布在晶粒内部和晶界上,经统计,其平均颗粒直径为11 nm。氧化物的体积分数可由公式(2)[14]得出。
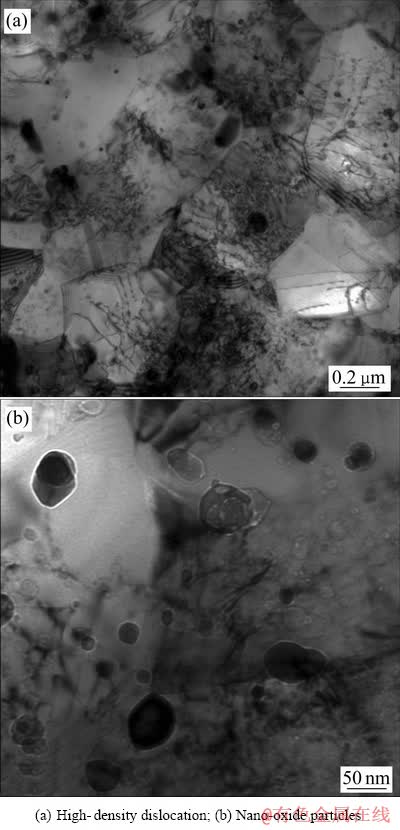
图2 合金热挤压态的TEM像
Fig. 2 TEM images of hot extrusion state of alloy
 (2)
(2)
式中:n和rp分别指氧化物粒子的个数和平均颗粒半径;S和D分别为TEM样品的面积和厚度。由公式(2)可得fv=0.007%。
2.2 强化预测模型与拉伸测试验证
在已知合金成分与组织形貌特征的情况下,通过强化模型来预测合金性能具有非常重要的工程意义。在以往关于ODS合金的预测模型研究中发现,影响屈服强度的因素主要有:固溶强化(σss),晶粒尺寸强化或Hall-Petch强化(σg),位错强化(σd),基于Orowan机制的氧化物纳米粒子强化(σp)。在室温下,合金屈服应力(σy)可以通过强化预测模型公式(3)[8, 15]得出:
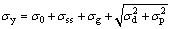 (3)
(3)
式中: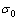 指晶格阻力或 Peierls-Nabarro 应力,通常应用公式(4)[16]计算。
指晶格阻力或 Peierls-Nabarro 应力,通常应用公式(4)[16]计算。
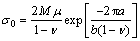 (4)
(4)
式中:M、μ、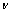 、b、a分别对应泰勒因子、剪切模量、泊松比、伯氏矢量、纯镍的晶格常数,其数值分别为2.45、80 GPa、0.32 nm、0.249 nm、0.35 nm。通过计算得出
、b、a分别对应泰勒因子、剪切模量、泊松比、伯氏矢量、纯镍的晶格常数,其数值分别为2.45、80 GPa、0.32 nm、0.249 nm、0.35 nm。通过计算得出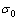 的数值为1.33 MPa,由于其数值相比于其他强化贡献值来说太小而通常忽略不计。
的数值为1.33 MPa,由于其数值相比于其他强化贡献值来说太小而通常忽略不计。
固溶强化(σss)包括以C为主的间隙固溶体强化和以Cr、W为主的置换固溶体强化。然而,就本文的合金而言,间隙固溶体强化的贡献是可以忽略不计的。因为其含量较低且大多数碳已经以碳化物的形式析出。通常情况下,固溶强化的贡献是以较为简单的公式(5)[17]计算。
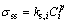 (5)
(5)
式中: 是指i元素的强化系数;Ci是元素i的原子分数。P为常数,且取值范围在1/2~1之间[18],在镍基合金中,P的值取1/2[19]。而GYPEN等[20]提出的公式(6) 综合计算了多组元合金中各个强化元素对合金固溶强化的贡献值,从而被广泛应用于ODS合金中。
是指i元素的强化系数;Ci是元素i的原子分数。P为常数,且取值范围在1/2~1之间[18],在镍基合金中,P的值取1/2[19]。而GYPEN等[20]提出的公式(6) 综合计算了多组元合金中各个强化元素对合金固溶强化的贡献值,从而被广泛应用于ODS合金中。
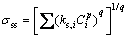 (6)
(6)
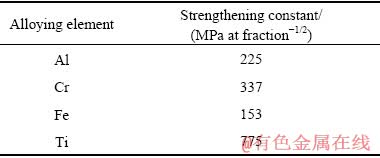
式中:q值为2。各个合金的强化系数ks,i如表2所列[21]。
表2 各强化元素在镍中的强化系数ks,i值[21]
Table 2 Strengthening coefficient ks,i value of each strengthening element in nickel[21]
晶粒尺寸强化或Hall-Petch (σg)强化反映了晶界对位错运动的影响。事实上,位错会逐渐运动在晶界处并形成堆积,直到位错驱动力达到越过下一个晶粒的临界值从而越过晶粒。这一观点是由Hall[22]阐述并扩展为公式(7)。
 (7)
(7)
式中: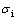 是指位错运动的晶格摩擦力;klock为常数;d 为平均晶粒尺寸。THOMPSON[23]研究表明,在镍基合金中,
是指位错运动的晶格摩擦力;klock为常数;d 为平均晶粒尺寸。THOMPSON[23]研究表明,在镍基合金中,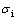 和klock分别为21.8 MPa和0.158 MPa·m1/2。
和klock分别为21.8 MPa和0.158 MPa·m1/2。
对于在微观组织中同时存在粗、细两种尺寸的合金体系,一般综合考虑两种晶粒的晶粒尺寸来计算双模合金的平均晶粒尺寸,其结果由公式(8)[24-25]得出:
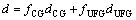 (8)
(8)
式中:fCG和fUFG分别指粗晶和细晶的体积分数;dCG和dUFG分别为粗晶和细晶的平均晶粒尺寸。经计算,双模合金的平均晶粒尺寸为10 μm,代入公式(7)得出晶粒尺寸强化(σg)的贡献值为72 MPa。
位错强化(σd)是位错之间相互作用的结果,其贡献值可以通过Bailey-Hirsch[26]公式(9)来计算。
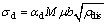 (9)
(9)
式中: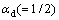 [27]指位错间的交互作用系数。经计算,位错强化(σd)的贡献值为196 MPa。
[27]指位错间的交互作用系数。经计算,位错强化(σd)的贡献值为196 MPa。
氧化物纳米粒子强化(σp)是指弥散分布的纳米氧化物粒子对位错滑移的阻碍作用产生的强化效果。基于对位错与氧化物粒子的交互作用机制,众多学者提出计算这一贡献的详细公式[28-29]。其中基于Orowan 机制的修正公式(10)[16]被认为普遍适用于ODS合金。
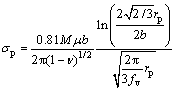 (10)
(10)
经公式(9)计算可得,氧化物纳米粒子强化(σp)的贡献值为233 MPa。
综合以上各个强化的计算值,代入公式(3)得出合金在室温下的屈服强度为551 MPa。为了验证此强化预测模型的正确与可靠性,对合金进行室温拉伸测试,所得拉伸曲线如图3所示。合金抗拉强度和屈服强度分别为824 MPa与542 MPa。
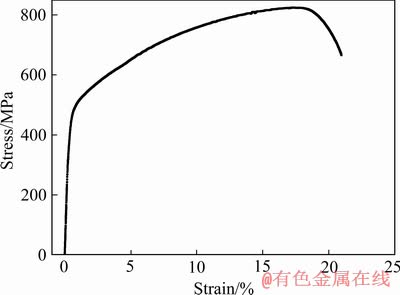
图3 合金室温拉伸应力-应变曲线
Fig. 3 Tensile stress-strain curve lf alloy at room temperature
各个强化因素对屈服强度的贡献值与试验值的对比结果如图4所示。预测模型的计算值与试验值非常接近,证明强化预测模型可由固溶强化(σss)、晶粒尺寸强化(σg)、位错强化(σd)与氧化物纳米粒子强化(σp)之和的平方根叠加。各个强化因素中氧化物纳米粒子强(σp)和位错强化(σd)的贡献最大,这是因为在球磨过程中形成的纳米氧化物粒子可以有效抑制位错运动和晶界迁移,从而提高合金强度。

图4 合金室温屈服强度实验值与计算值的对比
Fig. 4 Comparison between experimental data and calculation value of yield strength of alloy at room temperature
2.3 组织热稳定性研究
2.3.1 热处理后合金的微观组织
较为稳定的合金组织是获得稳定性能的前提。因此,通过在高温下长期热处理以研究合金组织热稳定性具有重要意义。合金组织在1150 ℃下热处理不同时间的晶粒形貌及尺寸演化规律如图5所示。热挤压态下,合金基体中存在两种明显不同尺寸的晶粒。数量较多的大尺寸晶粒均匀分布而小晶粒数量较少且呈“团状”分布。小晶粒的团状分布是球磨和混粉的不均匀性造成的,小晶粒由红色圆圈圈出(见图5(a))。热处理4 h后晶粒迅速长大(见图5(b)),当热处理时间延长到8 h,大晶粒进一步发生长大,但长大速率放缓。热处理32 h以后,大晶粒尺寸虽较8 h而言略微变大,但长大幅度不大。
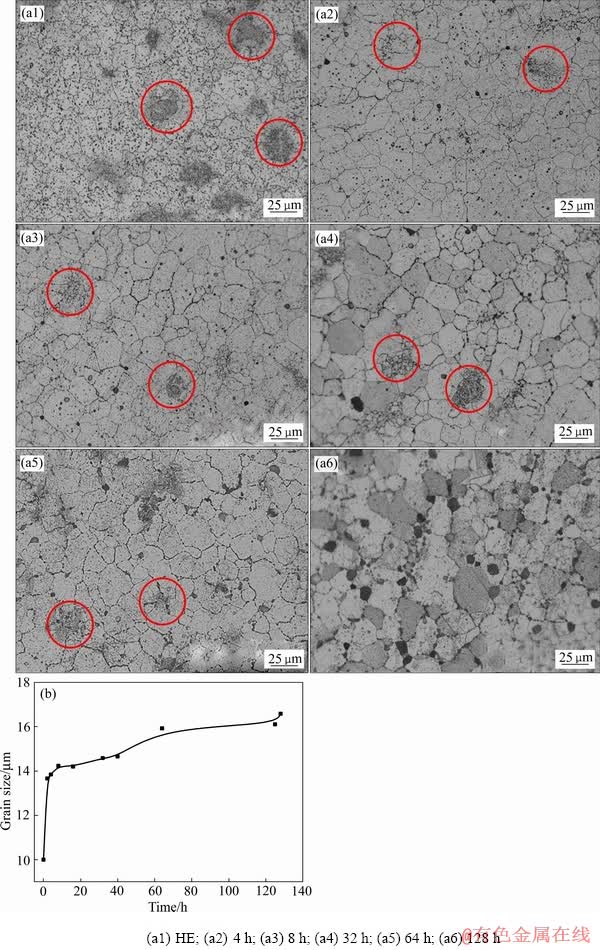
图5 1150 ℃热处理不同时间后的微观组织照片和晶粒尺寸统计图
Fig. 5 Pictures of microstructure after heat treatment at 1150 ℃ for different times(a) and statistical diagram of grain size(b)
统计得出热挤压态下合金平均晶粒尺寸为10 μm且在热处理前8 h晶粒长大较为迅速,而热处理8 h以后晶粒尺寸虽有变化但其长大速率明显放缓(见图5(b))。晶粒的长大是因为在高温下晶界的迁移速度加快从而致使晶粒间的互相合并,而总界面能的降低是晶界发生迁移的主要驱动力。在高温状态下,加速了原子克服一定位垒跳迁的热激活过程,从而导致界面迁移过程显著加快,因此晶粒始终发生不同程度的长大[30]。
2.3.2 热处理后纳米氧化物粒子演化
1150 ℃热处理后纳米粒子的TEM像如图6所示。热处理8 h后纳米粒子分布在晶粒内与晶界上,其平均尺寸长大为35.7 nm。当位错运动至不易变形的纳米粒子时,由于纳米粒子对位错的阻力较大,位错在粒子前运动受阻、弯曲,随着位错运动的进行,位错绕过粒子继续运动。如图6(a)中红色圆圈所示,位错正在绕过纳米粒子,这证明位错与纳米粒子的交互作用符合Orowan绕过机制,印证了强化模型中氧化物纳米粒子强化(σp)选择Orowan机制的正确性。热处理128 h后,纳米粒子相比8 h而言长大不明显,平均尺寸为37.3 nm。
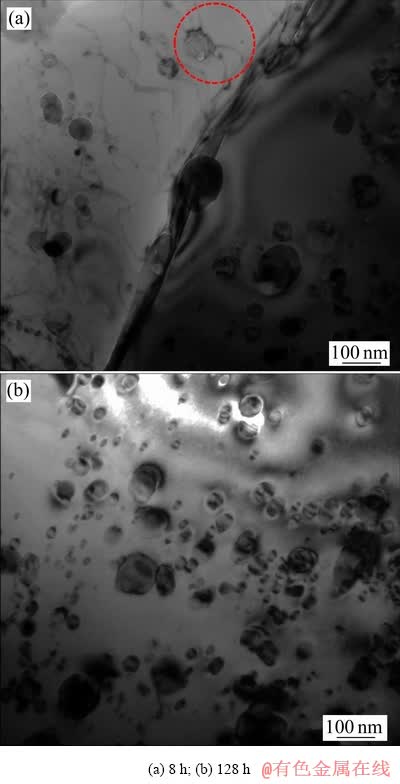
图6 1150 ℃热处理不同时间后的纳米粒子TEM像
Fig. 6 TEM images of nanoparticles after heat treatment at 1150 ℃ for different time
2.3.3 热处理后合金的硬度变化
1150 ℃下合金硬度随热处理时间的变化曲线如图7所示。热处理前合金的维氏硬度为225.1 HV,随着热处理时间的延长,合金硬度迅速降低。当热处理时间延长至8 h时合金硬度趋于稳定,并在热处理128 h时硬度值达到最低值,这一结果与合金组织演化规律相吻合。一方面,当晶粒较为细小并受到外部载荷发生塑性变形时,可分散至较多的晶粒内进行,从而使塑性变形较均匀和产生较小的应力集中。除此之外,晶粒越细小,总的晶界面积就越大,晶界越曲折,越不利于裂纹的扩展,从而表现为合金硬度越高。反之,晶粒越粗大,合金硬度值越低[31]。另一方面,由于热处理8 h后纳米粒子的快速长大直接导致其数量密度下降,削弱了对位错及晶界的钉扎作用,导致合金硬度的大幅下降[32]。
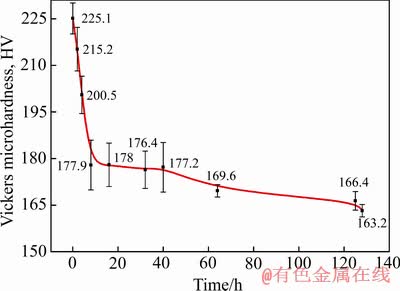
图7 热处理不同时间后合金的维氏硬度
Fig. 7 Vickers hardness of alloy after heat treatment for different times
3 结论
1) 通过耦合固溶强化(σss)、晶粒尺寸强化(σg)、位错强化(σd)与氧化物纳米粒子强化(σp)的作用,构建了合金室温屈服强度预测模型:
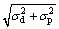 ,通过预测模型与拉伸试验得出合金室温下的屈服强度分别为542 MPa和551 MPa,二者非常接近,这表明了模型的可靠性。
,通过预测模型与拉伸试验得出合金室温下的屈服强度分别为542 MPa和551 MPa,二者非常接近,这表明了模型的可靠性。
2) 1150 ℃下热处理前4 h时晶粒长大较为迅速,而当热处理时间达到8 h后,晶粒尺寸虽有变化但其长大速率明显放缓。
3) 热处理初期,由于晶粒与纳米粒子的迅速长大使合金硬度突然下降,当热处理时间延长至8 h后合金硬度趋于稳定,并在热处理128 h时硬度值达到最低值。
REFERENCES
[1] LU C, LU Z, XIE R. Effect of Y/Ti atomic ratio on microstructure of oxide dispersion strengthened alloys[J]. Materials Characterization, 2017, 134: 35-40.
[2] ODETTE G R, HOELZER D T. Irradiation-tolerant nanostructured ferritic alloys: Transforming helium from a liability to an asset[J]. JOM, 2010, 62(9): 84-92.
[3] KIMURA A, KASADA R, IWATA N. Development of Al added high-Cr ODS steels for fuel cladding of next generation nuclear systems[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2011, 417(1): 176-179.
[4] LIU Dong-hua, LIU Yong, ZHAO Da-peng, LIU Zu-ming, HAN Yun-juan. Effect of addition manner of oxygen on mechanical properties of iron-based alloy 14YWT[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(5): 846-851.
[5] ZHANG Lin, QU Xuan-hui, HE Xin-bo, DUAN Bai-hua, QIN Ming-li. Research progress of ODS nickel based superalloy[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2010, 41(6): 90-96.
[6] DAPENG Z, YONG L, FENG L. ODS ferritic steel engineered with bimodal grain size for high strength and ductility[J]. Materials Letters, 2011, 65(11): 1672-1674.
[7] CHAUHAN A, LITVINOV D, AKTAA J. High temperature tensile properties and fracture characteristics of bimodal 12Cr-ODS steel[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2016, 468: 1-8.
[8] de VAUCORBEIL A, POOLE W J, SINCLAIR C W. The superposition of strengthening contributions in engineering alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 582: 147-154.
[9] CASAS C, TEJEDOR R, RODRiGUEZ-BARACALDO R. The effect of oxide particles on the strength and ductility of bulk iron with a bimodal grain size distribution[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 627: 205-216.
[10] CHAUHAN A, BERGNER F, ETIENNE A. Microstructure characterization and strengthening mechanisms of oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) Fe-9%Cr and Fe-14%Cr extruded bars[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2017, 495: 6-19.
[11] ZHAO Q, MA Z, YU L. Tailoring the secondary phases and mechanical properties of ODS steel by heat treatment[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2019, 35(6): 1064-1073.
[12] YAN Ju-jie,QIU Tao,SHEN Qin,WANG Xiao-jiao,LIU Wen-qing. High temperature stability of 14 YWT-ODS ferritic alloy[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2015, 36(7): 139-143.
[13] YAN P, YU L, LIU Y. Effects of Hf addition on the thermal stability of 16Cr-ODS steels at elevated aging temperatures[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 739: 368-379.
[14] TIAN D W, KARJALAINEN L P, QIAN B. Nonuniform distribution of carbonitride particles and its effect on prior austenite grain size in the simulated coarse-grained heat-affected zone of thermomechanical control-processed steels[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1996, 27(12): 4031-4038.
[15] DESCHAMPS A, BRECHET Y. Influence of predeformation and ageing of an Al-Zn-Mg alloy—Ⅱ. Modeling of precipitation kinetics and yield stress[J]. Acta Materialia, 1998, 47(1): 293-305.
[16] DADé M, MALAPLATE J, GARNIER J. Influence of microstructural parameters on the mechanical properties of oxide dispersion strengthened Fe-14Cr steels[J]. Acta Materialia, 2017, 127: 165-177.
[17] BUTT M Z, FELTHAM P. Solid-solution hardening[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1993, 28(10): 2557-2576.
[18] SUZUKI T. On the studies of solid solution hardening[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1981, 20(3): 449-462.
[19] AHMADI M R, POVODEN-KARADENIZ E, WHITMORE L. Yield strength prediction in Ni-base alloy 718Plus based on thermo-kinetic precipitation simulation[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 608: 114-122.
[20] GYPEN L A, DERUYTTERE A. Multi-component solid solution hardening[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1977, 12(5): 1028-1033.
[21] MISHIMA Y, OCHIAI S, HAMAO N. Solid Solution Hardening of Nickel — Role of Transition Metal and B-subgroup Solutes &mdash[J]. Transactions of the Japan Institute of Metals, 1986, 27(9): 656-664.
[22] HALL E O. The Deformation and ageing of mild steel: III Discussion of results[J]. Proceedings of the Physical Society Section B, 1951, 64(9): 747-753.
[23] THOMPSON A A W. Yielding in nickel as a function of grain or cell size[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1975, 23(11): 1337-1342.
[24] OSKOOIE M S, ASGHARZADEH H, KIM H S. Microstructure, plastic deformation and strengthening mechanisms of an Al-Mg-Si alloy with a bimodal grain structure[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 632: 540-548.
[25] PATRA S, HASAN S M, NARASAIAH N, et al. Effect of bimodal distribution in ferrite grain sizes on the tensile properties of low-carbon steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 538: 145-155.
[26] BAILEY J E, HIRSCH P B. The dislocation distribution, flow stress, and stored energy in cold-worked polycrystalline silver[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 1960, 5(53): 485-497.
[27] PRAUD M, MOMPIOU F, MALAPLATE J. Study of the deformation mechanisms in a Fe-14%Cr ODS alloy[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2012, 428(1): 90-97.
[28] BACON D J, KOCKS U F, SCATTERGOOD R O. The effect of dislocation self-interaction on the orowan stress[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 1973, 28(6): 1241-1263.
[29] RUSSELL K C, BROWN L M. A dispersion strengthening model based on differing elastic moduli applied to the iron-copper system[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1972, 20(7): 969-974.
[30] FENG-han, SONG Zhi-gang, ZHENG Wen-jie. Effect of solution treatment on microstructure and mechanical property of Inconel 690[J]. Journal of iron and steel research, 2009, 21(3): 46-50.
[31] YONG Qi-long. The second phase in steel[M]. Beijing: MetallurgicalIndustryPress, 2006.
[32] GRaNING T, KLIMENKOV M, RIETH M. Long-term stability of the microstructure of austenitic ODS steel rods produced with a carbon-containing process control agent[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2019, 523: 111-120.
Strengthening model and thermal stability of anoxide dispersion strengthened alloy with bimodal size distribution of grains
ZHAN Xin1, 2, WANG Guo-wei1, 2, TAN Li-ming1, 2, HE Wu-qiang1, 2, WU Kai-xi1, 2, HE Ying-jie1, 2, LIU Feng1, 2, HUAG Lan1, 2
(1. Powder Metallurgy Research Institute, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. State Key Laboratory for Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The yield strength model of oxide dispersion strengthened alloy with a bimodal size distribution of grain was established and verified via transmission electron microscope, electron backscatter diffraction, scanning electron microscope and tensile tests. In addition, the thermal stability of the alloy was investigated by heat treatment experiment, optical microscope observation and Vickers hardness. The results show that the yield strength model can be established by integrating solid solution strengthening (σss), grain size strengthening (σg), dislocation strengthening (σd) and oxide nanoparticle strengthening (σp), and the calculated values fit well with the experimental values. The research on thermal stability shows that the grains grow rapidly and the hardness decreases sharply at the early stage of heat treatment at 1150 ℃. However, after heat treatment for 8 h, the grain growth slows down and the hardness of the alloy keeps stable in response.
Key words: bimodal size distribution; grain; oxide dispersion strengthening; strengthening model; thermal stability
Foundation item: Project(2016YFB0701404) supported by the National Basic Research and Development Program of China; Project(91860105) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2019-07-09; Accepted date: 2019-10-08
Corresponding author: HUAG Lan; Tel: +86-15973118718; E-mail: lhuang@csu.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家重点研究发展计划资助项目(2016YFB0701404);国家自然科学基金资助项目(91860105)
收稿日期:2019-07-09;修订日期:2019-10-08
通信作者:黄 岚,教授,博士;电话:15973118718;E-mail:lhuang@csu.edu.cn