文章编号:1004-0609(2014)11-2789-09
金属间化合物L10-TiAl点缺陷浓度的第一原理
陶辉锦1, 2,孙顺平3,张铖铖1,陈 图1,罗 伟1,江 勇1, 2
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 有色金属材料科学与工程教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083;
3. 江苏理工学院 材料工程学院,常州 213001)
摘 要:采用第一原理平面波赝势方法,结合Wagner-Schottky缺陷热力学模型,研究金属间化合物L10-TiAl中各种空位和反位点缺陷的形成焓、热力学平衡浓度及其相互作用等。结果表明:这些缺陷的热力学平衡浓度均随温度的升高而增大,其中反位缺陷浓度均高于空位缺陷浓度,Ti空位浓度高于Al空位浓度。在理想化学计量比成分下,Ti反位缺陷的浓度与Al反位缺陷的基本相当;在略偏离计量比的富Ti成分端,Ti反位缺陷的浓度高于Al反位缺陷的;在富Al成分端则相反。不同点缺陷之间均普遍存在相互排斥性,难以聚集,将倾向于向基体中分散和扩散。
关键词:L10-TiAl金属间化合物;点缺陷浓度;形成焓;第一原理;Wagner-Schottky模型
中图分类号:TG111 文献标志码:A
First principles of point defect concentrations in L10-TiAl intermetallic composite
TAO Hui-jin1, 2, SUN Shun-ping3, ZHANG Cheng-cheng1, CHEN Tu1, LUO Wei1, JIANG Yong1, 2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Nonferrous Metal Materials Science and Engineering,
Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. School of Materials Engineering, Jiangsu University of Technology, Changzhou 213001, China)
Abstract: Using the plane wave pseudopotential method in first-principles and Wagner-Schottky model, the formation enthalpies, equilibrium concentrations, and interaction of vacancies and anti-site point defects were assessed for L10-TiAl intermetallics. The results show that, in the whole composition range of interest, all the defect concentrations increase with increasing temperature. In particular, the anti-site defect concentrations are higher than the vacancy defect concentrations, and the Ti vacancy concentration is higher than the Al vacancy concentration. At the stoichiometric composition, the Ti anti-site defect concentration is comparable to that of Al anti-site defect. At the Ti-rich side, the Ti anti-site defect concentration is higher than that of Al anti-site defect, while at the Al-rich side, the Al anti-site defect concentration is higher than that of Ti anti-site defect. The interaction between these defects is essentially repulsive, which facilitates the defect distribution and diffusion in the matrix.
Key words: L10-TiAl intermetallic composite; point defect concentration; formation enthalpy; first principles; Wagner-Schottky model金属间化合物具有密度小、强度高和高温力学性能好等优点,是一类重要的航空航天用高温结构材料[1-2],特别是TiAl系金属间化合物已成功应用于飞机引擎、机体以及汽车阀摇杆等许多重要结构部件[3-4]。金属间化合物中存在多种类型的热力学点缺陷,其性质和行为比较复杂,其浓度受温度和材料成分的影响程度不同,对材料的热导、电导、光学和力学等重要性能有着较大影响[5-7]。单纯依赖实验方法开展点缺陷和点缺陷浓度的研究,技术难度较大,可靠性也不高。近年来,基于第一原理的材料缺陷计算研究方法逐渐成熟,已成为金属间化合物点缺陷的主要研究手段,如JIANG等[8-9]基于第一原理计算研究了B2型NiAl和C15型NbCr2中的点缺陷浓度与占位,发现Ni空位和Ni反位分别是富Al和富Ni的B2-NiAl热力学最稳定的点缺陷形式;过渡金属Zr、Hf和Ta在整个成分和温度范围内都优先占据C15型NbCr2的Nb亚点阵,而Ti、V、Mo和W的占位则取决于成分和温度。孙顺平等[10]计算了L12-Al3Li金属间化合物的点缺陷浓度随温度和成分的变化,发现Al和Li反位缺陷浓度较高,Li空位缺陷浓度较低,而Al空位浓度最小。温度升高,各种点缺陷的浓度增大。KORZHAVYI等[11]研究B2-NiAl中热力学点缺陷相互作用,发现Ni反位和Al反位之间以及Al空位和Al反位之间可能存在强烈的相互吸引,这些相互作用对缺陷平衡浓度影响较小,但有助于解释B2-NiAl中的亚稳缺陷组态。
在TiAl系金属间化合物方面,ZHU等[12]基于第一原理计算研究Al3Ti中点缺陷以及Si占位,发现在富Al成分下,Al反位的缺陷形成能最低,Si倾向于占据Al空位,导致Si在Al3Ti中存在有限固溶度。陈律等[13-14]研究预测和比较3d过渡金属元素在L10-TiAl中的占位倾向,发现d电子数较少的过渡元素(Sc、V和Cr)优先占据 Ti原子亚点阵, 而d电子数较多甚至是满d壳层的元素则优先占据 Al原子亚点阵。JIANG[15]借助参数化的Wagner-Schottky统计热 力学模型进一步比较3d、4d和5d过渡金属元素在L10-TiAl的选择占位,发现Zr和Hf优先占据Ti原子亚点阵,Co、Ru、Rh、Pd、Ag、Re、Os、Ir、Pt和Au优先占据Al原子亚点阵,V、Cr、Mn、Fe、Ni、Cu、Nb、Mo、Tc、Ta和W原子的占位倾向则强烈地依赖于合金成分的计量比和温度变化。LI等[16]采用第一原理平面波赝势方法研究掺Nb L10-TiAl合金中点缺陷之间的相互作用,发现占据Al原子亚格点上的最近邻两个Nb原子具有排斥作用,但次近邻Nb原子则相互吸引,表明Al原子亚格点上的Nb原子可能形成短程有序结构,这将有利于提高含NbTiAl合金的强度。WANG等[17]采用第一原理方法计算了Ti-Al二元系中有序B2相中不同点缺陷的形成焓,结果表明Al亚格点被Ti原子占据形成的反位缺陷和Ti亚格点被空位占据形成的空位缺陷在能量上更具优势,在此基础上对B2相的热力学模型进行的改进和重新优化得到了与实验值符合得更好的结果。
当前对L10-TiAl中第三组元原子的选择性占位已有较多计算预测,但对其本征点缺陷(Ti和Al的空位和各种反位)浓度随温度和成分的关系、本征点缺陷间的相互作用、以及点缺陷形成激活能等的研究却未见报道。因此,本文作者将采用第一原理方法计算L10-TiAl中各种主要点缺陷的形成焓,进一步结合Wagner-Schottky模型计算预测这些点缺陷的浓度随温度和成分的变化关系,评估这些点缺陷之间的可能相互作用,预测点缺陷形成激活能的可能值,为L10-TiAl金属间化合物的实验制备、缺陷分析和力学性能改进等提供有益的理论参考。
1 计算方法与参数
本研究中所有计算基于第一原理平面波赝势方法。电子与离子之间的相互作用采用投影缀加波方法(PAW)[18]来精确描述,电子之间的交换关联势采用广义梯度近似下的PBE方法来描述[19],Ti的3p4s3d和Al的3s3p电子作为Ti和Al元素的价电子,其余内层电子作为芯电子来考虑。晶胞模型简约布里渊的K点网格采用Monkhorst-Pack[20]方法来划分,系统总能量的计算采用BLOCHL等[21]修正的Linear-Tetrahedron方法。电子Kohn-Sham波函数用平面波基组展开,其数目由经过收敛性测试后的动能截断点来确定,在计算精度确定为1×10-3 eV的条件下,Ti、Al及TiAl超胞能量的动能截断点确定为400 eV,计算采用VASP(Vinena Ab-inito simulation package)总能计算程序进行。在计算含点缺陷的晶胞结构时构建了一个含有54个原子的超胞,倒易空间网格的划分取为4×4×3。图1所示为L10-TiAl金属间化合物及含有各种点缺陷的超胞结构示意图。
2 计算结果
2.1 Ti、Al及L10-TiAl的晶格常数和体弹性模量
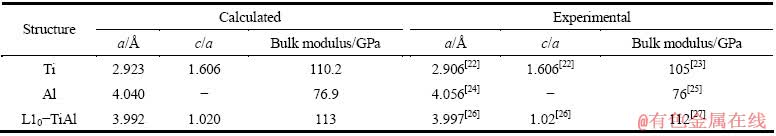
表1所列为计算得到的Ti、Al和L10-TiAl金属间化合物的体结构参数和弹性模量结果。与文献[20-27]中的实验值比较,晶格常数最大相对误差仅为0.58%(Ti),弹性模量仅为5%(Ti),理论结果总体上与实验结果符合较好。
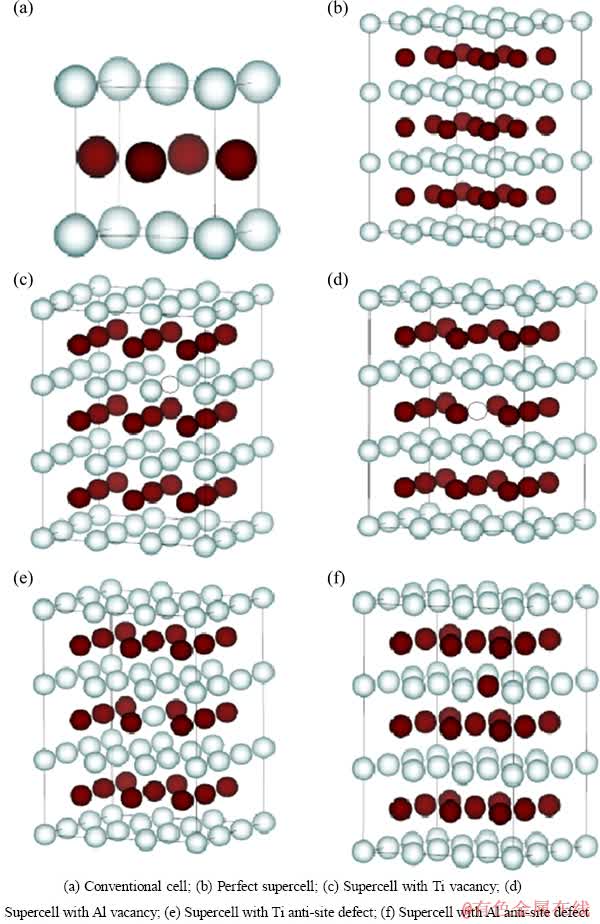
图1 L10-TiAl金属间化合物空位和反位点缺陷晶胞模型
Fig. 1 Supercell model of L10-TiAl intermetallics
表1 Ti、Al和L10-TiAl的计算值和实验值比较
Table 1 Comparison of calculated results with experimental data of Ti, Al, and L10-TiAl in comparison
2.2 L10-TiAl的点缺陷形成焓
当点缺陷的浓度足够稀时,可以采用Wagner-Schottky模型[10]来研究点缺陷浓度随成分和温度的变化关系。定义点缺陷浓度时采用的是原子浓度的形式,质点i(原子或空位)在α亚点阵位置的原子浓度可定义为
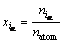 (1)
(1)
式中:natom为体系中原子的总数(不包含空位),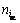 为质点i(原子或空位)占据α亚点阵位置的数目。在L10-TiAl金属间化合物中,质点i为{Ti,Al,V},而亚点阵α为{Ti,Al},其中V表示空位。在点缺陷(VAl,VTi,AlTi,TiAl)中,VAl表示占据Al亚点阵格点的空位(Al空位),VTi表示占据Ti亚点阵格点的空位(Ti空位),AlTi表示占据Ti亚点阵格点的Al原子(Al反位),TiAl表示占据Al亚点阵格点的Ti原子(Ti反位)。根据Wagner-Schottky模型,含点缺陷的L10-TiAl的形成焓与点缺陷浓度成正比,从而有
为质点i(原子或空位)占据α亚点阵位置的数目。在L10-TiAl金属间化合物中,质点i为{Ti,Al,V},而亚点阵α为{Ti,Al},其中V表示空位。在点缺陷(VAl,VTi,AlTi,TiAl)中,VAl表示占据Al亚点阵格点的空位(Al空位),VTi表示占据Ti亚点阵格点的空位(Ti空位),AlTi表示占据Ti亚点阵格点的Al原子(Al反位),TiAl表示占据Al亚点阵格点的Ti原子(Ti反位)。根据Wagner-Schottky模型,含点缺陷的L10-TiAl的形成焓与点缺陷浓度成正比,从而有
 (2)
(2)
式中:ΔHTiAl是符合化学计量比的完全有序的理想L10-TiAl的形成焓(以纯金属为参考态);xd为点缺陷(VAl,VTi,AlTi,TiAl)的原子浓度;Hd为单个点缺陷在L10-TiAl中的相对形成焓(以理想L10-TiAl为参考态)。
含缺陷L10-TiAl合金的形成焓可按下式计算:
 (3)
(3)
式中:m和n是晶胞中所含原子数目,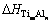 是晶胞
是晶胞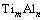 的形成焓,ETi和EAl为计算所得纯金属Ti和Al平均到每个原子的总能量,即化学势。
的形成焓,ETi和EAl为计算所得纯金属Ti和Al平均到每个原子的总能量,即化学势。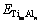 是晶胞
是晶胞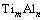 的总能量。其中,理想L10-TiAl的形成焓可按如下公式计算:
的总能量。其中,理想L10-TiAl的形成焓可按如下公式计算:
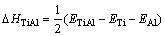 (4)
(4)
式中:ETiAl是L10-TiAl完整晶胞的能量。
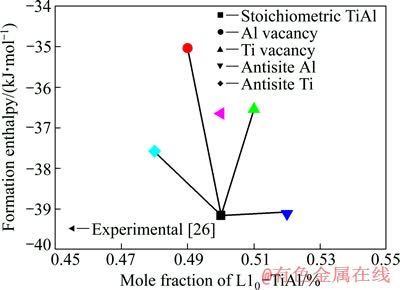
图2 L10-TiAl形成焓与成分之间的关系
Fig. 2 Relationship between of formation enthalpy and composition of L10-TiAl
根据式(3)和(4)可计算得到包含点缺陷(VAl,VTi,AlTi,TiAl)的L10-TiAl的形成焓,结果如图2所示。根据热力学可知,较低的形成焓意味着更加稳定的状态,从图2可以看出,含反位缺陷L10-TiAl的形成焓比空位缺陷的更低,表明反位缺陷在能量上可能是L10-TiAl中相对稳定的缺陷形式。本文计算所得理想L10-TiAl的形成焓与文献中报道的实验值相对误差小于7%,符合较好。
根据Wagner-Schottky模型所确定的公式(2)和图2的形成焓结果,得到以理想L10-TiAl为参考态的单个点缺陷(VAl,VTi,AlTi,TiAl)形成焓Hd[10]:
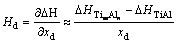 (5)
(5)
计算得到的空位和反位缺陷形成焓结果与其他计算结果和实验值对比见表2。
表2 L10-TiAl金属间化合物空位和反位形成焓
Table 2 Calculated formation enthalpy of vacancies and anti-site defects in L10-TiAl
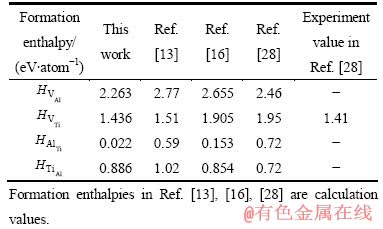
由表2可知,本文计算结果与文献[13,16,28-29]中报道过的计算和实验结果符合较好,只有Al反位缺陷的形成焓计算结果偏低。随后,通过增加Ti原子3s态电子作为价电子、提高K点网格密度、增加平面波动能截断等方法进行了重新计算,但结果均无明显改变。同时,表2显示的变化趋势与文献[13]和[16]一致,即L10-TiAl中Ti反位缺陷的形成焓值要大于Al反位缺陷的,Al空位的形成焓大于Ti空位的。据此可以估计,对于偏离理想化学计量比的富Al型TiAl化合物,可能的主要结构缺陷形式为Al反位和Ti空位,因前者的形成焓远小于后者的,Al反位缺陷的浓度将占绝对优势。同时,对于富Ti型TiAl化合物,可能出现的主要点缺陷形式为Ti反位和Al空位,且Ti反位缺陷的浓度将占绝对优势。因此,在偏离化学计量比的L10-TiAl金属间化合物中,总是更容易形成反位缺陷,富Ti或者富Al型L10-TiAl将分别以Ti反位或者Al反位为主要点缺陷形式而存在。
2.3 L10-TiAl的点缺陷浓度
在计算TiAl金属间化合物点缺陷浓度时需要考虑温度的因素,且不能忽略熵对系统的影响。简化起见,如果仅考虑组态熵的影响,可以通过平均场近似来计算组态熵:
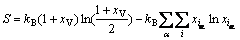 (6)
(6)
式中:kB为玻尔兹曼常数;xV为空位缺陷的浓度;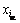 为公式(1)所定义的原子浓度。将式(6)代入吉布斯自由能公式,当吉布斯自由能达到最小值时可得到系统的稳定态或平衡态,此时对应的点缺陷浓度即为平衡浓度,因此,可以通过求
为公式(1)所定义的原子浓度。将式(6)代入吉布斯自由能公式,当吉布斯自由能达到最小值时可得到系统的稳定态或平衡态,此时对应的点缺陷浓度即为平衡浓度,因此,可以通过求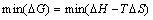 得到系统处于稳定态时的点缺陷平衡浓度的四元二次方程组:
得到系统处于稳定态时的点缺陷平衡浓度的四元二次方程组:
 (7)
(7)
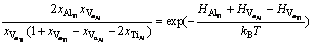 (8)
(8)
 (9)
(9)
 (10)
(10)
通过数值求解式(7)~(10)可以得到L10-TiAl金属间化合物点缺陷浓度随温度及成分变化的关系,如图3所示。考虑到L10-TiAl的相区成分主要在0.48~0.55(Al的摩尔分数)区间,图3所示为该成分区间的点缺陷浓度分别在973、1173、1373和1573 K温度下随成分的变化关系。
由图3可知:1) 点缺陷的浓度均随温度升高而增加;2) Al空位和Ti反位浓度随Al原子浓度的增加而下降,Ti空位和Al反位浓度随Al原子浓度的增加而增加;3) 不同温度下,反位缺陷的浓度总是大于空位缺陷的浓度;4) Ti空位浓度始终大于Al空位浓度,与表2点缺陷形成焓结果一致,即Ti空位形成焓更低,更容易形成;5) 在化学计量比处,Ti反位与Al反位缺陷浓度基本相当,但在富Ti端(xAl<50%),Ti反位浓度高于Al反位,在富Al端(xAl>50%)则相反。
为进一步研究点缺陷浓度与温度之间的关系,选取图3中满足化学计量比条件,即xAl=50%的L10-TiAl为研究对象,计算当成分固定时点缺陷浓度随温度变化的关系,其结果如图4所示。

图3 L10-TiAl金属间化合物的点缺陷浓度在不同温度下与成分之间的关系
Fig. 3 Relationship between point defect concentrations and composition of L10-TiAl intermetallic composite at different temperatures
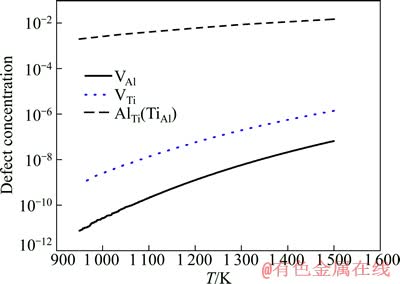
图4 理想化学计量比L10-TiAl点缺陷浓度与温度的关系
Fig. 4 Relationship between point defect concentration and temperature in stoichiometric L10-TiAl
由图4可知:1) 点缺陷浓度随温度升高而增大,在较低温下增长较快,在较高温度下增长变缓;2) Al反位缺陷和Ti反位缺陷的浓度几乎相同,但都高于空位浓度;3) Ti空位的浓度高于Al空位的。
2.4 L10-TiAl点缺陷形成激活能的实验值预测
图4所示为计算预测的理想化学计量比L10-TiAl中不同点缺陷浓度随温度的变化趋势。在实验研究中,实际测定点缺陷形成激活能通常都基于Arrhenius方程,即
 (8)
(8)
式中:c为点缺陷浓度,A为平衡常数,Q为点缺陷形成激活能(kJ·mol-1),R是摩尔气体常数,T为热力学温度。对式(8)取对数,可得
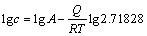 (9)
(9)
显然,lgc与1/T具有线性关系,即与T成反比关系。改变图4的横坐标为T的倒数(T -1),取点缺陷浓度c为纵坐标,重新绘制理想化学计量比L10-TiAl中点缺陷浓度与温度关系,得到结果如图5所示。
通过拟合各直线的斜率,可得到理想化学计量比L10-TiAl中不同点缺陷(VAl,VTi,AlTi,TiAl)对应的形成激活能(eV·atom-1)。其计算公式如下:
 (10)
(10)
式中:kB为玻尔兹曼常数,计算结果如表3所列。由表3可知,Al空位缺陷的形成激活能最大,Ti空位缺陷的次之,Al反位缺陷和Ti反位缺陷的形成激活能最小且相当。表3所预测的形成激活能实质上是一种表观激活能,可直接与实验结果直接对比,这为实验验证我们的理论计算结果提供了一种可能。
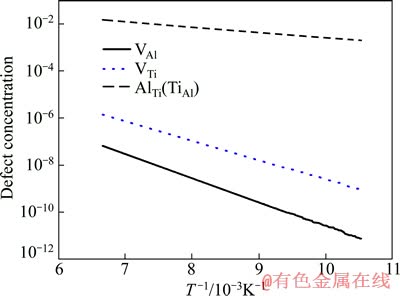
图5 L10-TiAl金属间化合物点缺陷浓度与温度之间的关系
Fig. 5 Relationship between point defect concentrations with temperature intermetallics composite of L10-TiAl
表3 L10-TiAl中空位和反位缺陷形成激活能的实验值预测
Table 3 Prediction of activation energy of vacancy and anti-site defects in intermetallics composite L10-TiAl (eV·atom-1)

2.5 L10-TiAl点缺陷对的形成焓
本研究计算了单个点缺陷(VAl,VTi,AlTi,TiAl)的形成焓,基于Wagner-Schottky模型研究点缺陷浓度随温度和成分的变化,并预测形成激活能的实验测量值。在此基础上,可以研究这些点缺陷之间的可能相互作用。现将这些点缺陷进行组合,得到6种可能的缺陷对(d-d′)结构,即VAl-VTi、VAl-AlTi、VTi-TiAl、AlTi-TiAl、VAl-TiAl和VTi-AlTi。图6所示为点缺陷对的超胞模型,根据这些模型计算这些点缺陷对的总能量,并与单个点缺陷进行能量对比,可以评估它们以理想L10-TiAl为参考态的形成焓和结合能,从而预测它们之间的吸引或排斥作用[30]。
以双空位点缺陷对(VAl-VTi)为例,其形成焓和结合能计算公式如下[31]:
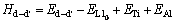 (11)
(11)
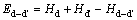 (12)
(12)
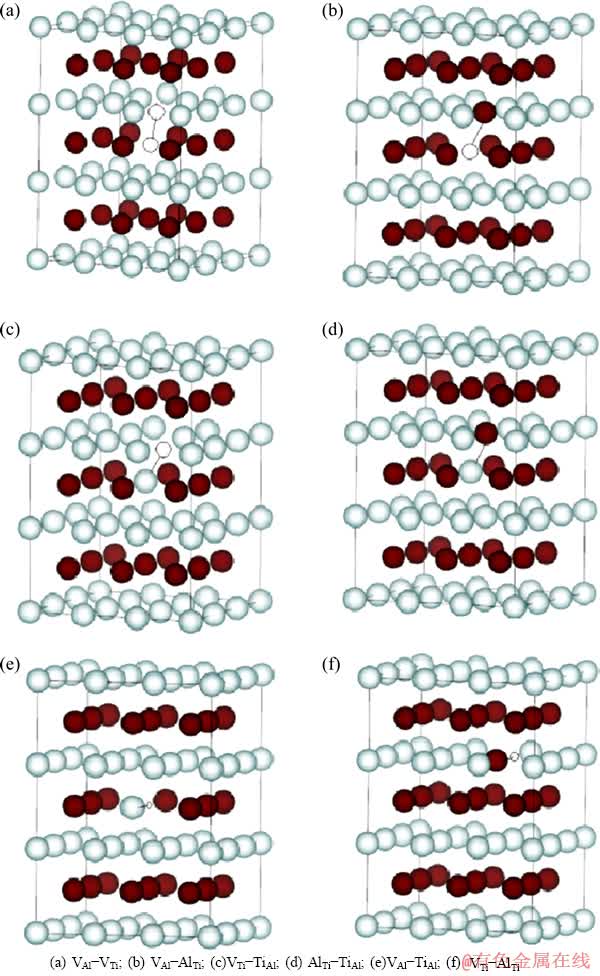
图6 L10-TiAl点缺陷对的晶胞模型
Fig. 6 Supercell model of point defect pairs in L10-TiAl
式(11)中的EAl、ETi与式(3)中的定义相同,分别表示纯Ti和纯Al的化学势。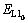 表示理想化学计量比的L10-TiAl超胞总能量,
表示理想化学计量比的L10-TiAl超胞总能量,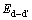 表示含有缺陷对(d-d′)的超胞总能量,
表示含有缺陷对(d-d′)的超胞总能量,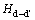 为点缺陷对的形成焓。式(12)中,
为点缺陷对的形成焓。式(12)中,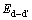 表示缺陷对(d-d′)的结合能,Hd和
表示缺陷对(d-d′)的结合能,Hd和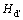 为单个点缺陷的形成焓(见表2)。所有计算结果可见表4。
为单个点缺陷的形成焓(见表2)。所有计算结果可见表4。
由表4可知:1) 点缺陷对形成焓的高低顺序依次为VAl-VTi、VAl-TiAl、VAl-AlTi、VTi-TiAl、VTi-AlTi、AlTi-TiAl,其中AlTi-TiAl缺陷对的形成焓值最低,相对而言最稳定;2) 所有点缺陷对的结合能均为负值,表明L10-TiAl中的这些点缺陷难以聚集,而是倾向于向基体分散和扩散。
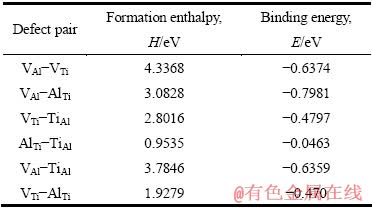
表4 L10-TiAl中点缺陷对的形成焓和结合能
Table 4 Formation enthalpies and binding energies of point defect pairs in L10-TiAl
3 结论
1) L10-TiAl金属间化合物中所有本征点缺陷的形成焓均为负值,其中Al和Ti反位缺陷的绝对值更大,表明反位缺陷在L10-TiAl中最为稳定;点缺陷浓度均随温度升高而增加,且反位缺陷浓度始终大于空位缺陷浓度,表明在不同温度下,反位缺陷始终是L10-TiAl中最主要的点缺陷形式。
2) 在整个L10-TiAl相区成分范围内(Al含量为48%~55%,摩尔分数),Al空位和Ti反位缺陷浓度均随Al含量增加而下降,而Ti空位和Al反位浓度变化趋势相反;在理想化学计量比(Al为50%)处,Ti反位与Al反位缺陷浓度基本相当,但在富Ti端,Ti反位浓度高于Al反位浓度,在富Al端,Al反位浓度高于Ti反位浓度。
3) 基于Arrhenius方程计算预测各种点缺陷的形成激活能,发现Al空位形成激活能最大,Ti空位次之,Al反位和Ti反位形成激活能较小且数值相当;通过对不同点缺陷之间亲和力的计算考察,发现点缺陷之间均存在相互排斥性,难以聚集,而是倾向于向基体分散与扩散。
致谢:感谢中南大学高性能计算中心为所有计算工作提供硬件管理支持。
REFERENCES
[1] 曹 阳, 李国俊. 金属间化合物高温结构材料的研究动向[J]. 材料导报, 1994(4): 14-18.
CAO Yang, LI Guo-jun. The recent development of high-temperature structural intermetallics[J]. Materials Review, 1994(4): 14-18.
[2] 周怀营, 湛永钟. TiAl金属间化合物的研究进展[J]. 广西大学学报, 1999, 24(4): 262-264.
ZHOU Huai-ying, ZHAN Yong-zhong. Development of studies on TiAl intermetallics[J]. Journal of Guangxi University, 1999, 24(4): 262-264.
[3] 冯旭东, 袁庆龙, 曹晶晶, 苏志俊. TiAl基合金研究进展[J]. 航天制造技术, 2009(3): 35-38.
FENG Xu-dong, YUAN Qing-long, CAO Jing-jing, SU Zhi-jun. Progress in TiAl-based alloys[J]. Aerospace Manufacturing Technology, 2009(3): 35-38.
[4] 李金山, 张铁邦, 常 辉, 寇宏超, 周 廉. TiAl基金属间化合物的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 中国材料进展, 2010, 29(3): 1-5.
LI Jin-shan, ZHANG Tie-bang, CHANG Hui, KOU Hong-chao, ZHOU Lian. Recent achievements and future directions of TiAl based intermetallic compounds[J]. Materials China, 2010, 29(3): 1-5.
[5] 张 静, 陈 铮, 杨 涛. 金属间化合物结构材料反位缺陷及其对性能的影响[J] .稀有金属材料与工程, 2013, 42(2): 429-434.
ZHANG Jing, CHEN Zheng, YANG Tao. Antisite defect in the intermetallic structural materials and its effect on the mechanical performance[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2013, 42(2): 429-434.
[6] 周立颖, 王福合. 点缺陷对γ-TiAl(100)表面O原子吸附和扩散影响的第一性原理研究[J]. 金属学报, 2013, 49(11): 1387-1391.
ZHOU Li-ying, WANG Fu-he. First-principles study of effect of point defect on adsorption and diffusion of oxygen at γ-TiAl (100) surface[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2013, 49(11): 1387-1391.
[7]  U, APPEL F.Strain ageing in γ(TiAl)-based titanium aluminides due to antisite atoms[J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50: 3693-3707.
U, APPEL F.Strain ageing in γ(TiAl)-based titanium aluminides due to antisite atoms[J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50: 3693-3707.
[8] JIANG C, CHEN L Q, LIU Z K.First-principles study of constitutional point defects in B2 NiAl using special quasirandom structures[J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53: 2643-2652.
[9] JIANG C. Site preference of early transition metal elements in C15 NbCr2[J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55(5): 1599-1605.
[10] 孙顺平, 李小平, 于 赟, 卢雅琳, 臧 冰, 易丹青, 江勇. L12-Al3Li金属间化合物点缺陷浓度的第一原理计算[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(2): 370-378.
SUN Sun-ping, LI Xiao-ping, YU Yun, LU Ya-lin, ZANG Bing, YI Dan-qing, JIANG Yong. First-principle calculation of point defects concentration in L12-Al3Li intermetallic[J]. The Chinese Journal ofNonferrousMetals, 2013, 23(2): 370-378.
[11] KORZHAVYI P A, RUBAN A V, LOZOVOI A Y, VEKILOV Y K, ABRIKOSOV I A, JOHANSSON B. Constitutional and thermal point defects in B2 NiAl[J]. Physical Review B, 2000, 61(9): 6003-6018.
[12] ZHU G L,DAI Y B, SHU D, XIAO Y P, YANG Y X, WANG J, SUN B D, BOOM R. First-principles study of point defects and Si site preference in Al3Ti[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2011, 50 (9): 2636-2639.
[13] 陈 律, 彭 平, 韩亚利. L10-TiAl基本物性的计算与比较研究[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2007, 15(1): 47-51.
CHEN Lü, PENG Ping, HAN Ya-li. A comparison on basic physical properties of L10-TiAlcalculatedby first-principles methods[J] MaterialsScienceandTechnology, 2007, 15(1): 47-51.
[14] 陈 律. 3d过渡金属在L10-TiAl中占位的第一原理计算[J]. 长沙航空职业技术学院学报, 2008, 8(3): 43-48.
CHEN Lü. First-principles calculation for site substitution of 3d transition metal elements in L10-TiAl intermetalliccompound[J]. Journal of Changsha Aeronautical Vocational and Technical College, 2008, 8(3): 43-48.
[15] JIANG C. First-principles study of site occupancy of dilute 3d, 4d and 5d transition metal solutes in L10 TiAl[J]. Acta Materialia, 2008, 56(20): 6224-6231.
[16] LI Yu-juan, HU Qing-miao, XU Dong-sheng, YANG Rui. Strengthening of g-TiAl-Nb by short-range ordering of point defects[J]. Intermetallics, 2011, 19: 793-796.
[17] WANG H, REED R C, GEBELIN J C, WARNKEN N. On the modelling of the point defects in the ordered B2 phase of the Ti-Al system: Combining CALPHAD with first-principles calculations[J]. Calphad: Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 2012, 39: 21-26.
[18] KRESSE G, JOUBERT J. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method[J]. Physical Review B, 1999, 59(3): 1758-1775.
[19] PERDEW J P, BURKE K M, EMZERHOF M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77(18): 3865-868.
[20] MONKHORST H J, PACK J D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations[J]. Physical Review B, 1976, 13(12): 5188-5192.
[21] BLOCHL P E, JEPSEN O, ANDERSEN O K. Improved tetrahedron method for Brillouin-zone integrations[J]. Physical Review B, 1994, 49(23): 16223-16233.
[22] NOVOSELOVA T, MALINOV S, SHA W, ZHECHEVA A. High-temperature synchrotron X-ray diffraction study of phases in a gamma TiAl alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 371(1): 103-112.
[23] 韩秀丽, 王 清, 孙东立, 孙 涛, 郭 强. 氢对钛晶体弹性模量影响的第一原理研究[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2009, 17(3): 305-310.
HAN Xiu-li, WANG Qing, SUN Dong-li, SUN Tao, GUO Qiang. First-principles study of the effect of hydrogen on the elastic moduli of titaniumcrystals[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2009, 17(3): 305-310.
[24] TOUGAIT O,  H. Stoichiometry of UAl4[J]. Intermetallics, 2004, 12(2): 219-223.
H. Stoichiometry of UAl4[J]. Intermetallics, 2004, 12(2): 219-223.
[25] SEITZ F, TURNBU D. Solid state physics: Advance in research and applications(Volume 16)[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1964.
[26] ZOPE R R, MISHIN Y. Interatomic potentials for atomistic simulations of the Ti-Al system[J]. Physical Review B, 2003, 68(2): 02402.
[27] DENIS M, SCHNEIDER J M. Effect of transition metal additives on electronic structure and elastic properties of TiAl and Ti3Al[J]. Physical Review B, 2006, 74(17): 174110-174114.
[28] YOO M H, FU C L. Physical constants, deformation twinning, and microcracking of titanium aluminides[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1998, 29(1): 49-63.
[29] BROSSMANN U, WüRSCHUM R, BADURA K, SCHAEFER H E. Thermal formation of vacancies in TiAl[J]. Physical Review B, 1994, 49(10): 6457-6466.
[30] FU C L, WANG X D. The effect of electronic structure on the defect properties of FeAl[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1997, 239/240: 761-768.
[31] PARLINSKI K, JOCHYM P T, KOZUBSKI, ORAMUS P. Atomic modelling of Co, Cr, Fe, antisite atoms and vacancies in B2–NiAl[J]. Intermetallics, 2003, 11(2): 157-160.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:湖南省科技计划项目(2013GK3010);国家基础研究发展计划资助项目(2014CB644001-2)
收稿日期:2014-05-13;修订日期:2014-09-11
通信作者:江 勇,教授,博士;电话:15111309497;E-mail:yjiang@csu.edu.cn