
DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.04.021
液固两相流体热毛细对流中颗粒动态积累结构研究
黄鑫1,梁儒全1, 2,范俊庚1
(1. 东北大学 材料电磁过程研究教育部重点实验室,辽宁 沈阳,110819;
2. 临沂大学 机械与车辆工程学院,山东 临沂,276000)
摘要:采用计算流体力学-离散元法(CFD-DEM)将流体与颗粒耦合,数值研究微重力下高径比对液固两相流体热毛细对流和液桥内颗粒动态积累结构(PAS)的影响。研究结果表明:水平面(z=0)上温度场旋转1周,监测点的温度周期性变化m次;随着高径比增加,方位角波数减少,水平面(z=0)上低温冷区的数目减少;沿着液桥的自由面,流体的速度由上至下先增加后减小,速度的振荡强度则由上至下逐渐增强;三向耦合下颗粒分布也呈现出PAS,液桥俯视图的中心区域出现不同形状的颗粒较少区域;所有颗粒按照近似的轨迹协同运动,使PAS随热毛细对流以相同的角速度旋转。
关键词:热毛细对流;振荡特性;功率谱密度;颗粒动态积累结构;计算流体力学-离散元法(CFD-DEM)
中图分类号:O782;TK121 文献标志码:A
文章编号:1672-7207(2021)04-1251-10
Study on dynamic particle accumulation structure in thermocapillary convection for liquid-solid two-phase flow
HUANG Xin1, LIANG Ruquan1, 2, FAN Jungeng1
(1. Key Laboratory of National Education Ministry for Electromagnetic Processes of Materials, Shengyang 110819, China;
2. School of Mechanical and Vehicle Engineering, Linyi University, Linyi 276000, China)
Abstract: The effects of aspect ratio on the thermocapillary convection and the particle dynamic accumulation structure(PAS) inside the liquid bridge were studied by using the coupled computational fluid dynamics and discrete element method(CFD-DEM). The results show that when the temperature field of the horizontal cross section z=0 rotates once, the temperature of the fixed points changes periodically m times. As the aspect ratio increases, the azimuthal wave number decreases, and the number of cold regions in horizontal cross section z=0 decreases. Along the free surface of the liquid bridge, the velocity of fluid increases first and then decreases from top to bottom, and the velocity oscillation strengthens from top to bottom. The PAS is also observed in simulations based on three-way coupling. There is a region with fewer particles in the center of the top view of a liquid bridge. All particles move together in an approximate pattern, which explains why the PAS rotates at the same angular velocity as the thermocapillary convection.
Key words: thermocapillary convection; oscillatory characteristics; power spectral density; particle dynamic accumulation structure; CFD-DEM
采用浮区法制备晶体过程中,在流体流动的驱动力为浮力、毛细力等。微重力环境下,浮力对流大大减弱,热毛细对流成为主导对流形式。研究表明,振荡热毛细对流会导致晶体表面和内部产生条纹,影响晶体的质量。因此,在微重力环境下,半导体熔体内热毛细对流及流动结构研究已成为空间材料生长的重要课题,对空间浮区法制备高质量晶体具有重要意义。
液桥是浮区法制备晶体简化模型。1979年,CHUN等[1]利用“光切割”技术,开展了半浮区液桥热毛细对流实验,发现了振荡热毛细对流。之后,针对液桥模型,国内外开展了线性稳定性分析[2-3]、三维数值模拟[4-6]和晶体生长实验[7-9]。ZENG等[10]数值研究了三维振荡热毛细对流,结果表明热毛细对流存在脉动振荡和旋转振荡两种不同的振荡模式,温度场随时间周期性变化。YASUHIRO等[11]通过数值模拟再现了实验观察到的不同频率的超临界熔体自由表面温度振荡,结果表明当温差达到一定的临界值时,表面温度振荡将向三维稳定周期振荡对流转变。当温差为更高的临界值时,表面温度振荡将会发生向三维振荡对流的第二次转变。
另外,浮区法制备晶体过程中浮区熔体中存在杂质,杂质颗粒具有动态积累特性,影响制备晶体质量。研究表明,在一定高径比条件下,稀密度的小颗粒在液桥中聚集,并具有时间依赖性。这些颗粒绕热毛细对流的轴旋转呈变形的螺旋,形成颗粒动态积累结构(PAS)[12]。SCHWABE等[13]发现了PAS。UENO等[14]也观察到了类似的结果,同时得到闭合螺旋绕组数等于方位角波数。SCHWABE等[15]通过改变等密度下的颗粒直径和等粒径下颗粒密度与流体密度的比值,测量PAS结构的形成时间,解释了PAS的形成机制,即颗粒与流体的密度差影响PAS的形成速度。 MULDOON等[16]的研究表明,密度差和颗粒-自由表面相互作用共同影响PSA的形成。
目前,对PAS的研究大多基于单向耦合,考虑三向耦合(同时考虑流体对颗粒的作用、颗粒对流体的反作用、颗粒之间的相互作用)的PAS研究缺乏,因此,对PAS的形成机制仍不清楚。另外,国内外关于热毛细对流的研究主要集中在单一流体热毛细对流研究,对夹杂颗粒的固液两相流体热毛细对流研究极其有限,对热毛细对流的周期性变化与热毛细对流中颗粒聚集规律之间相互关系的研究很少。采用浮区法制备单晶硅过程中熔区内不可避免含有杂质颗粒,针对这种夹杂颗粒的固液两相流体热毛细对流研究更具有理论意义与实际应用价值。
本文作者基于一种三向耦合的CFD-DEM方法,同时考虑流体对颗粒的作用、颗粒对流体的反作用、颗粒之间的相互作用,采用CFD方法计算流体的流动行为,利用DEM方法处理颗粒运动和颗粒间的碰撞,对夹杂颗粒流体热毛细对流进行了数值模拟,探究不同高径比下的热毛细对流和PAS,分析其形成原因。
1 物理与数学模型
本研究采用的物理模型如图1所示。2个半径相同的同心圆盘之间悬浮的是半浮区液桥,液桥的高度为L,半径为a,液桥高径比为L/a。上下圆盘之间存在温差,温度梯度的方向与重力的方向相反。
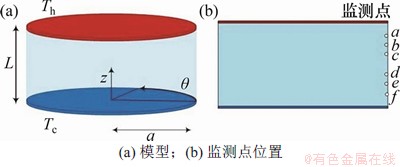
图1 液桥模型
Fig. 1 Liquid bridge model
考虑流体对颗粒的作用、颗粒对流体的反作用、颗粒之间的相互作用,三向耦合下液相的控制方程[17-23]如下。
连续性方程为
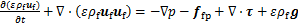 (1)
(1)
动量方程为
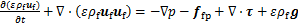 (2)
(2)
能量方程为
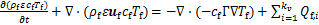 (3)
(3)
根据牛顿第二定律,单个颗粒的转动和平动方程分别为:
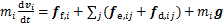 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
单个颗粒的能量守恒方程为
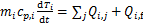 (6)
(6)
系统的边界条件为:下部圆盘(z=-L/2)处温度为T=Tc,上部圆盘(z=L/2)处温度为T=Th,上下圆盘绝热无滑移。自由面的径向温度梯度 T/
T/ r=0。在自由面(R=a)上,考虑热毛细效应,采用下列方程:
r=0。在自由面(R=a)上,考虑热毛细效应,采用下列方程:
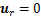 (7)
(7)
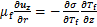 (8)
(8)
 (9)
(9)
式中:r,θ和z为坐标;ur,uθ和uz分别为r,θ和z这3个方向上的速度分量;ρf,uf,p,Tf,cf和Г分别为流体的密度、速度、压力、温度、比热容和热扩散系数;ε,t,τ,g和σ分别为孔隙率、时间、气相应力张量、重力加速度和表面张力;mi,vi,ωi,Ii,Ti和cp,i分别为颗粒i的质量、线速度、角速度、转动惯量、温度和比热容;ffp为颗粒-流体作用力;Qf,i为颗粒与流体间的热流量;ff,i为颗粒-流体作用力;fe,ij和fd,ij分别为弹性力矢量与黏性力矢量;Tn,ij,Tt,ij和Tr,ij分别为法向力矩、切向力矩和滚动摩擦力矩;Qi,j和Qi,f分别为颗粒间的换热量和颗粒与流体的换热量;MaT为热Marangoni数,MaT=rTTL/(μυ);Pr为普朗特数,Pr=υ/α;△T为上下板间的温差,△T=Th-Tc。
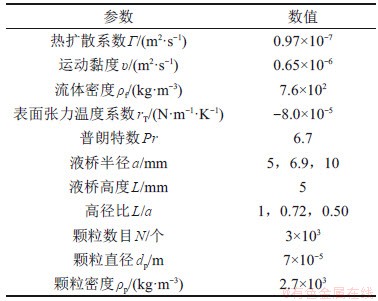
对3组不同高径比下的含夹杂物的两相流体热毛细对流进行模拟,所用的流体介质为0.65号硅油,Pr=6.7。采用有限体积法对控制方程进行离散,通过PISO算法求解控制方程。采用CFD-DEM下的Eulerian-Lagrangian模型,模拟含夹杂物的两相流。颗粒间的作用模型和颗粒与自由面的作用模型均为Ranz-Marshall模型,模拟所用的颗粒为直径70 μm的铝球。在计算的起始时刻,液桥中均匀注入所有颗粒。计算所需的参数见表1。3种高径比下均在液桥的(0.99a,0,0)处设置监测点。
表1 流体物理性质
Table 1 Fluid physical property
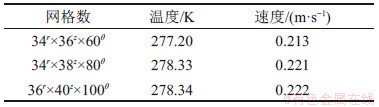
为了验证网格的相关性,在高径比为1,△T=10 K和MaT=12 457时,分别采用34r×36z×60θ,34r×38z×80θ和36r×40z×100θ这3种网格进行计算,监测点(0.99a,0,0)处计算结果如表2所示。当网格数为34r×38z×80θ和36r×40z×100θ时,监测点(0.99a,0,0)处温度和速度的相对误差均小于1%,因此,选用网格数更少的网格34r×38z×80θ作为数值计算网格。
表2 网格无关性检验
Table 2 Grid dependence test
2 结果与讨论
2.1 模拟结果验证
首先,将本研究的结果与SCHWABE等[12]的实验结果以及MELNIKOV等[24]的数值模拟结果进行比较验证。当△T=8.5 K,Pr=13.5,L/a=1时,在计算的起始时刻往液桥中均匀注入颗粒并施加温差,一段时间后液桥中出现稳定的温度和速度振荡,再经历一段时间后,颗粒呈现出动态积累,图2(a)所示为本研究模拟的液桥注入颗粒250 s后的俯视图。颗粒分布与图2(b)中SCHWABE等[12]的实验结果和图2(c)中MELNIKOV等[24]的模拟结果非常相似,也呈不对称的单环,PAS绕z轴逆时针旋转。图3所示为方位角波数模拟结果与SCHWABE等[12]的实验结果对比。当△T=10 K,Pr=8时,改变高径比,数值模拟测得对应的方位角波数。由图3可以看出:方位角波数数值模拟结果与实验结果相吻合,随着高径比增大,两者变化趋势相同,验证了本研究建立的模型与计算方法的有效性。
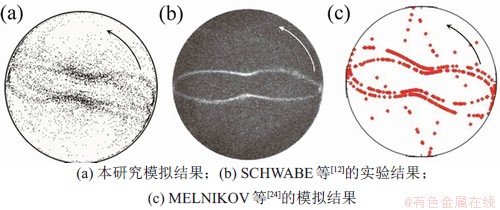
图2 颗粒动态积累结构对比
Fig. 2 Comparison of dynamic particle accumulation structure
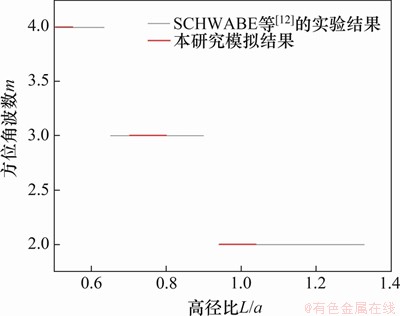
图3 方位角波数模拟结果与实验结果对比
Fig. 3 Comparison of azimuthal wave number between simulation results and experimental results
2.2 热毛细对流中颗粒动态聚集特性
图4所示为液桥模型中水平面(z=0)的温度分布。从图4可见:水平面中存在着2,3和4倍的对称结构,对称结构与方位角波数m对应;当上下圆盘的温差△T=10 K,高径比为0.50,0.72和1时,方位角波数m分别为4,3和2;随着高径比增大,方位角波数减少,水平面温度分布中低温冷区的数目减少,同时可以得到(L/a)·m≈2。图5所示为不同高径比液桥颗粒聚集结构的俯视图。从图5可见:中心出现颗粒较少区,形状分别为梭形(m=2)、三角形(m=3)、正方形(m=4);在这个中心区域,颗粒速度较低。这个区域绕z轴以恒定的角速度旋转,旋转过程中形状保持不变。这种粒子较少的多边形区域的形状也与液桥的高径比有关。粒子链组成了多边形的边,多边形的尖端连接液桥的顶部和底部m次。中心区域的形状对应着温度场中的m倍对称结构。图6所示为不同高径比液桥中颗粒分布的鸟瞰图。从图6可见:颗粒聚集结构并不局限于1个平面内,而是分布在整个三维空间;当PAS形成后,自由面和液桥体积的很大部分没有颗粒。颗粒沿闭合的环路积累,该环路在液桥中作三维螺旋运动,螺旋的形状不变;这个粒子链从热端开始,沿自由面向下,再随回流上升,直到再次接触到自由面;带着粒子的回流并没有穿过液桥中心,粒子链在自由面附近是陡峭的,在回流中则更加水平。粒子链不同的陡峭程度反映着颗粒不同的运动速度,即颗粒在自由表面附近速度更大,在回流中速度较小。
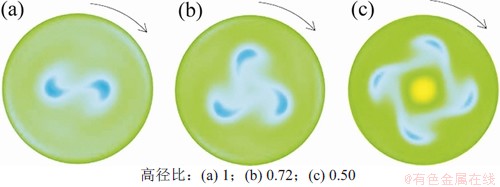
图4 △T=10 K和MaT=12 457时不同高径比液桥水平面温度分布
Fig. 4 Temperature distribution in horizontal cross section at different aspect ratios when △T=10 K and MaT=12 457

图5 △T=10 K和MaT=12 457时不同高径比的液桥颗粒聚集结构的俯视图
Fig. 5 Top view of PAS at different aspect ratios when △T=10 K and MaT=12 457
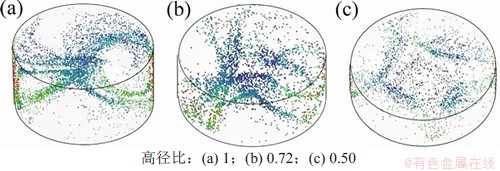
图6 △T=10 K和MaT=12 457时不同高径比下颗粒分布的鸟瞰图
Fig. 6 Bird′s-eye view of PAS at different aspect ratios when △T=10 K and MaT=12 457
2.3 热毛细对流旋转振荡特性
图7所示为L/a=0.72(m=3)时,1个周期内水平面z=0处温度云图和点(0.99a,0,0)处的温度变化曲线。从图7可见:水平面z=0处温度云图绕z轴旋转,旋转的周期Tmin=11.25 s。图7中的曲线为m=3时,监测点(0.99a,0,0)处温度变化曲线,振荡周期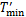 =3.75 s。可以得到Tmin=3·
=3.75 s。可以得到Tmin=3·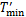 。当方位角波数m=2,3,4时,监测点处温度分别为T2,T3和T4,速度分别为u2,u3和u4。图8(a)所示为3种高径比液桥中监测点(0.99a,0,0)处温度变化曲线。可见3个监测点的温度出现了稳定的振荡,监测点温度T234,对于L/a=0.50(m=4)和L/a=1(m=2),也存在Tmin=m·
。当方位角波数m=2,3,4时,监测点处温度分别为T2,T3和T4,速度分别为u2,u3和u4。图8(a)所示为3种高径比液桥中监测点(0.99a,0,0)处温度变化曲线。可见3个监测点的温度出现了稳定的振荡,监测点温度T234,对于L/a=0.50(m=4)和L/a=1(m=2),也存在Tmin=m·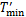 ,即温度云图旋转1周,液桥中固定点处温度周期性变化m次。同时,随着高径比减小,温度振荡周期变长。图8(b)所示为不同高径比下,监测点(0.99a,0,0)处速度变化曲线,可见3个监测点处速度u432,速度也呈周期性振荡,振荡周期与温度的变化周期一致。随着高径比减小,速度振荡周期变长,所以,速度与温度具有相同的变化趋势,这一特征表明整个液桥温度场与速度场之间存在强耦合,两者时空特性相似。高径比小的液桥水平面各点温度高,速度小。
,即温度云图旋转1周,液桥中固定点处温度周期性变化m次。同时,随着高径比减小,温度振荡周期变长。图8(b)所示为不同高径比下,监测点(0.99a,0,0)处速度变化曲线,可见3个监测点处速度u432,速度也呈周期性振荡,振荡周期与温度的变化周期一致。随着高径比减小,速度振荡周期变长,所以,速度与温度具有相同的变化趋势,这一特征表明整个液桥温度场与速度场之间存在强耦合,两者时空特性相似。高径比小的液桥水平面各点温度高,速度小。
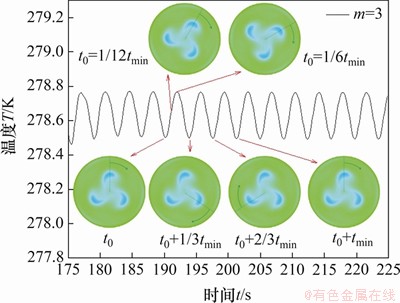
图7 L/a=0.72,△T=10 K和MaT=12 457时,1个周期内的温度云图和点(0.99a,0,0)处温度变化曲线
Fig. 7 Temperature field within one period and temperature-time curve at point(0.99a, 0, 0) when L/a=0.72, △T=10K and MaT=12 457
图8 △T=10 K和MaT=12 457时,不同高径比下点(0.99a,0,0)处温度-时间变化曲线和速度-时间变化曲线
Fig. 8 Temperature-time curves and velocity-time curves at points (0.99a, 0, 0) at different aspect ratios when △T=10 K and MaT=12 457
图9所示为高径比L/a=0.72(方位角波数m=3)时,1个周期内液桥中颗粒聚集结构的俯视图。在这个周期内,PAS绕z轴逆时针旋转。为清楚地展示PAS的旋转,三角形的1个顶点用圆点标记。旋转1周的时间为11.25 s,与液桥温度场的变化周期相同,所以,液桥的周期性旋转振荡与PAS的转动相对应,PAS的旋转周期与液桥温度场的旋转周期相同,但两者的旋转方向相反。所有颗粒协同运动,造成PAS随热毛细对流以相同的角速度旋转,这种运动趋势仅适用于整个PAS,与单个颗粒的运动轨迹有很大不同。
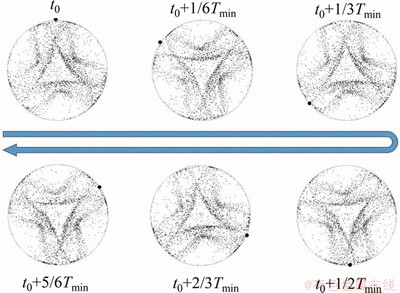
图9 L/a=0.72,△T=10 K和MaT=12 457时,1个周期内液桥俯视图
Fig. 9 Top view of liquid bridge within one period when L/a=0.72, △T=10 K and MaT=12 457
为了研究液桥中热毛细对流的速度振荡特性,图1所示的模型中设置了6个监测点,坐标见表3。图10(a)和图10(b)所示分别为L/a=1(m=2)时液桥上半部的3个监测点的速度变化和功率谱密度图(PSD)。图10(a)表明3个监测点的速度呈现稳定的振荡,监测点a,b和c的速度uabc,表明由于壁面和黏滞效应,越靠近上盘,流体的速度越来越小。从图10(b)可知:所有监测点的速度PSD有1个主要的波峰,这个波峰对应的频率和周期分别为f=0.3 Hz和T=3 s。这个主要波峰的峰值Wabc。因此,速度振荡的强度从热端到自由面中部逐渐增强。
表3 固定监测点的坐标
Table 3 Coordinates at fixed monitoring points
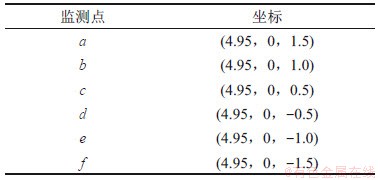
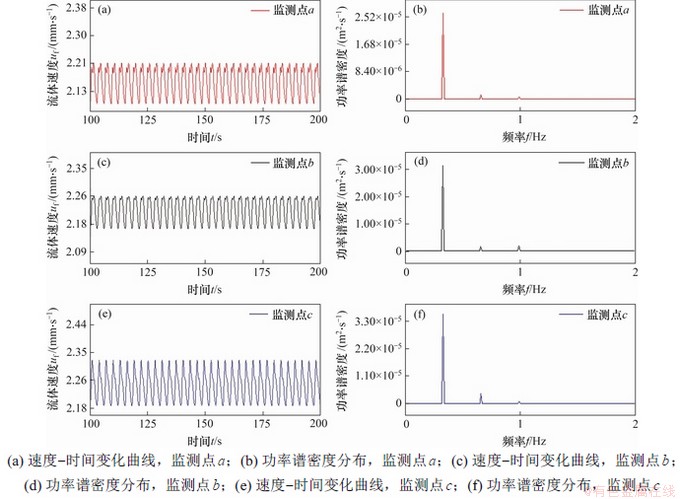
图10 L/a=1,△T=10 K和MaT=12 457时液桥上半部3个监测点的速度变化和这一阶段的功率谱密度
Fig. 10 Evolution of velocities at three monitoring points at the upper part and power spectral density (PSD) at this stage L/a=1, △T=10 K and MaT=12 457
图11(a)和图11(b)所示分别为L/a=1(m=2)时液桥下半部分的3个监测点的速度变化和功率谱密度图。图11(a)所示下部3个监测点的速度也呈现稳定振荡,但是,监测点d,e,f的速度ufed,表明在液桥下半部分,沿着自由面向下,流体的速度开始逐渐下降。从图11(b)可知:主要波峰的峰值Wdef,因此,速度振荡的强度从自由面中部到冷端逐渐增强。综上可知,从冷端到热端,自由面附近流体的速度先增加后减小,振荡强度则沿自由面向下逐渐增强。
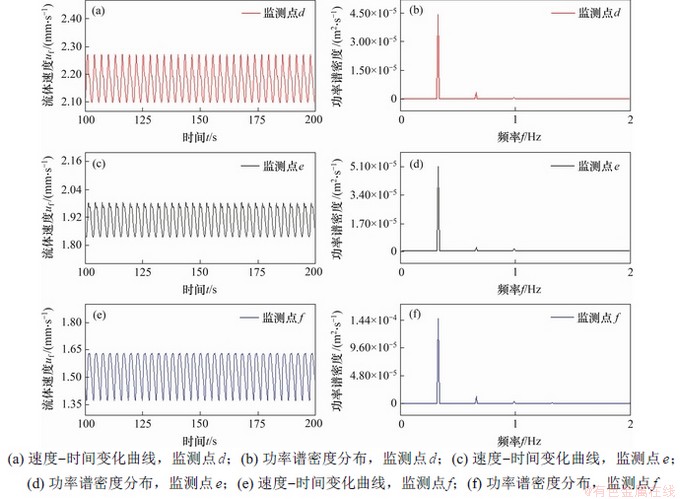
图11 L/a=1,△T=10 K和MaT=12 457时液桥下半部3个监测点的速度变化和这一阶段的功率谱密度
Fig. 11 Evolution of velocities at three monitoring points at the lower part and power spectral density (PSD) at this stage when L/a=1, △T=10 K and MaT=12 457
2.4 热毛细对流中颗粒振荡机理分析
图12所示为近似的m倍对称结构,速度矢量可以用m对扰动涡描述,自由面的流动沿方位角从热点流向冷点。当马赫数Ma足够大时(Ma>Mac,Mac为不稳定起点的马赫数),与热传导相比对流效应占主导地位,将产生“过冷或过热”并导致不稳定。由于自由表面存在温度梯度,局部冷点生成轴向扰动速度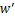 和方位角扰动速度
和方位角扰动速度 。流动从热点流向冷点。根据连续性原理,方位角扰动速度
。流动从热点流向冷点。根据连续性原理,方位角扰动速度 形成了1对扰动涡。轴向扰动速度
形成了1对扰动涡。轴向扰动速度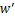 则从上盘带来热的流体来加热这个冷点。温度和速度扰动之间的相位差产生过热的热流,热流使局部冷点变为局部热点。新的局部热点也生成轴向扰动速度
则从上盘带来热的流体来加热这个冷点。温度和速度扰动之间的相位差产生过热的热流,热流使局部冷点变为局部热点。新的局部热点也生成轴向扰动速度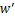 和方位角扰动速度
和方位角扰动速度 ,与冷点产生的扰动速度方向相反。局部热点产生的方位角扰动速度
,与冷点产生的扰动速度方向相反。局部热点产生的方位角扰动速度 也形成了1对扰动涡,内部的冷流通过这个涡被带到表面来冷却这个热点。温度和速度扰动之间的相位差产生过冷的冷流,冷流使局部热点变为局部冷点。当Ma>Mac时,这个过程交替进行,冷点和热点之间的振荡一直保持甚至加剧。这种持续的振荡是3种高径比液桥中监测点(0.99a,0,0)处温度与速度曲线保持振荡的原因。
也形成了1对扰动涡,内部的冷流通过这个涡被带到表面来冷却这个热点。温度和速度扰动之间的相位差产生过冷的冷流,冷流使局部热点变为局部冷点。当Ma>Mac时,这个过程交替进行,冷点和热点之间的振荡一直保持甚至加剧。这种持续的振荡是3种高径比液桥中监测点(0.99a,0,0)处温度与速度曲线保持振荡的原因。
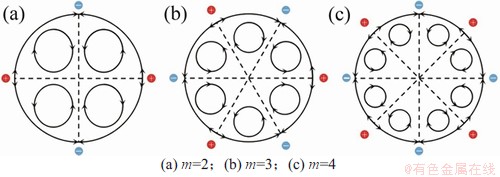
图12 扰动涡对模型
Fig. 12 Models of disturbance vortex pairs
若冷点(热点)继续保持或放大,则在方位角方向上,这个冷点(热点)发展成为m个冷热扰动,m取决于扰动涡的大小。以热点为例,3种高径比液桥中u432,当高径比很小时,速度也很小,速度扰动回流没有足够的能量穿过整个液桥,因此,被限制在一个局部区域内。假设自由表面存在1个局部热点,将产生1对扰动涡A和B,若这对扰动涡没有充满整个区域,则由于黏性效应会相应产生2个新的扰动涡A1和B1。若这4个扰动涡没有充满这个区域,则继续产生2个新的扰动涡A2和B2。这个过程一直进行,直到区域被m对扰动涡充满为止(见图13)。温度场的对称分布与m对扰动涡有关,涡对的数目与方位角波数相等。图4中的2,3和4倍温度对称分布结构分别对应着2,3和4对扰动涡。
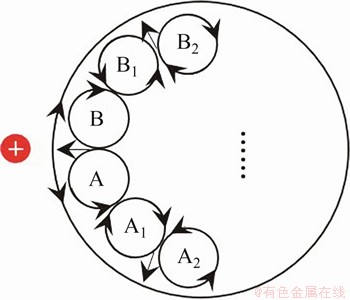
图13 覆盖整个区域的扰动涡对
Fig. 13 Vortex pairs formed in the whole circumference region
图14(a)所示为单个颗粒的运动轨迹图,单个粒子的轨迹不是圆形的,也不是闭合的,而为花朵状的连续曲线。独立运动的单个颗粒在自由面附近向下运动,在冷盘附近改变运动方向,然后随回流向上运动,在热的圆盘与自由面交界处再次向下运动。颗粒的运动轨迹可以看作在r-z平面的二维翻转和在方位角方向运动的叠加。粒子运动轨迹不是闭合的回路,颗粒的运动轨迹和PAS形状结构有很大的不同。在自由面附近B点,颗粒速度最大,轴向温度梯度使颗粒在自由面附近获得较大的速度;在热毛细对流的中心A点和C点,颗粒速度最小。所以,粒子链在自由面附近是陡峭的,回流中更加水平。图14(b)所示为颗粒(该颗粒与图14(a)中的颗粒相同)速度变化曲线。颗粒速度振荡变化,在自由面附近速度变化更为剧烈,在回流中速度变化较小。颗粒速度曲线中微小变化的部分对应颗粒和其他颗粒碰撞,速度曲线产生不规则变化。许多粒子沿与图示类似的轨迹运动,这是PSA形成的直接原因。
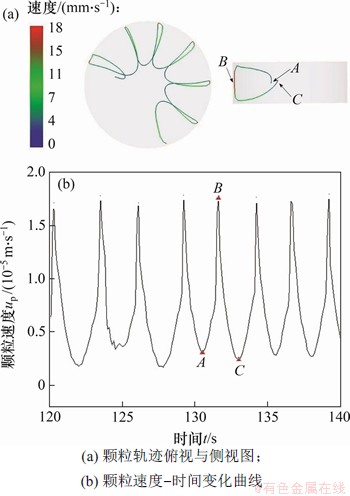
图14 L/a=0.72,△T=10 K和MaT=12 457时PAS组成颗粒的轨迹俯视图与侧视图和颗粒的速度变化曲线
Fig. 14 Top view and side view for path lines of PAS-forming particle and velocity-time curve of the particle when L/a=0.72, △T=10 K and MaT=12 457
3 结论
1) 热毛细对流的方位角波数m与液桥高径比L/a之间的关系为(L/a)·m≈2。三向耦合下的颗粒分布也显示出PAS。颗粒沿闭合环路积累,粒子链在空间做三维螺旋运动。
2) 内部流场呈周期性变化,温度场绕z轴顺时针旋转,PAS以相同的速度绕z轴旋转。水平面z=0处温度场旋转1周,液桥固定点处温度周期性变化m次。整个液桥内温度场与速度场之间存在强耦合,两者的时空特性相似。沿着液桥自由面,流体的速度从热端到冷端先增加后减小,速度的振荡强度则逐渐增强。
3) 冷点与热点的交替转换,使振荡保持甚至加剧,最后产生了覆盖整个液桥的m对扰动涡,这是温度场呈m倍对称分布的原因。所有颗粒按照近似的轨迹协同运动,使PAS随热毛细对流以相同的角速度旋转。
参考文献:
[1] CHUN C H, WUEST W. Experiments on the transition from the steady to the oscillatory Marangoni-convection of a floating zone under reduced gravity effect[J]. Acta Astronautica, 1979, 6(9): 1073-1082.
[2] YASUHIRO S, IMAISHI N, KUHLMANN H C, et al. Numerical simulation of three-dimensional oscillatory thermocapillary flow in a half zone of Pr=1 fluid[J]. Advances in Space Research, 1999, 24(10): 1385-1390.
[3] LAPPA M, SAVINO R. Parallel solution of three-dimensional Marangoni flow in liquid bridges[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 1999, 31(6): 911-935.
[4] LEYPOLDT J, KUHLMANN H C, RATH H J. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of thermocapillary flows in cylindrical liquid bridges[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2000, 414: 285-314.
[5] 李友荣, 刘英杰, 彭岚, 等. 液封液桥内振荡热毛细对流的三维数值模拟[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2006, 27(S2): 5-8.
LI Yourong, LIU Yingjie, PENG Lan, et al. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of thermocapillary convection in encapsulated liquid bridge[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2006, 27(S2): 5-8.
[6] 刘英杰. 液封液桥内振荡热毛细对流的三维数值模拟[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学动力工程学院, 2007: 10-46.
LIU Yingjie. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of oscillatory thermocapillary flow in encapsulated liquid bridge[J]. Chongqing: Chongqing University. College of Power Engineering, 2007: 10-46.
[7] SCHWEIZER M, CROLL A, DOLD P, et al. Measurement of temperature fluctuations and microscopic growth rates in a silicon floating zone under microgravity[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1999, 203(4): 500-510.
[8] 姚永龙, 解京昌, 束继祖, 等. 半浮区液桥振荡对流的微重力实验[J]. 力学学报, 1995, 27(6): 663-670.
YAO Yonglong, XIE Jingchang, SHU Jizu, et al. Microgravity experiment on oscillatory convection in liquid bridge of semi-floating zone[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 1995, 27(6): 663-670.
[9] 杨硕. 深空环境下高普朗特数流体热毛细对流研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学冶金学院, 2017: 140-165.
YANG Shuo. Study on thermocapillary convection for high Prandtl number fluid in deep space environment[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University. School of Metallurgy, 2017: 1-196.
[10] ZENG Zhong, MIZUSEKI H, SIMAMURA K, et al. Three-dimensional oscillatory thermocapillary convection in liquid bridge under microgravity[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2001, 44(19): 3765-3774.
[11] YASUHIRO S, LI K, IMAISHI N, et al. Oscillatory Marangoni flow in half-zone liquid bridge of molten tin[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2004, 266(1/2/3): 152-159.
[12] SCHWABE D, MIZEV A, TANAKA S, et al. Particle accumulation structures in time-dependent thermocapillary flow in a liquid bridge under microgravity[J]. Microgravity - Science and Technology, 2006, 18(3/4): 117-127.
[13] SCHWABE D. Particle accumulation structures(PAS) in thermocapillary flow in floating zones[C]// 2nd Europeam Symposium on Utilisation of the International Space Station. Paris, France: Europeam Space Agency, 1999: 233-240.
[14] UENO I, TANAKA S, KAWAMURA H. Oscillatory and chaotic thermocapillary convection in a half-zone liquid bridge[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2003, 15(2): 408-416.
[15] SCHWABE D, MIZEV A I, UDHAYASANKAR M, et al. Formation of dynamic particle accumulation structures in oscillatory thermocapillary flow in liquid bridges[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2007, 19(7): 072102.
[16] MULDOON F H, KUHLMANN H C. Origin of particle accumulation structures in liquid bridges: particle-boundary-interactions versus inertia[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2016, 28(7): 073305.
[17] WEI Guangchao, ZHANG Hao, AN Xizhong, et al. CFD-DEM study on heat transfer characteristics and microstructure of the blast furnace raceway with ellipsoidal particles[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 346: 350-362.
[18] GAN Jieqing, ZHOU Zongyan, YU Aibing. Effect of particle shape and size on effective thermal conductivity of packed beds[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 311: 157-166.
[19] ANDERSON T B, JACKSON R. Fluid mechanical description of fluidized beds: equations of motion[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals, 1967, 6(4): 527-539.
[20] ZHOU Y C, WRIGHT B D, YANG R Y, et al. Rolling friction in the dynamic simulation of sandpile formation[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 1999, 269(2/3/4): 536-553.
[21] ZHENG Q J, ZHU H P, YU A B. Finite element analysis of the rolling friction of a viscous particle on a rigid plane[J]. Powder Technology, 2011, 207(1/2/3): 401-406.
[22] GOU Dazhao, AN Xizhong, YANG Xiaohong, et al. CFD-DEM modeling on air impact densification of equal spheres: structure evolution, dynamics, and mechanism[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 322: 177-184.
[23] ZHAO Haiyang, AN Xizhong, GOU Dazhao, et al. Attenuation of pressure dips underneath piles of spherocylinders[J]. Soft Matter, 2018, 14(21): 4404-4410.
[24] MELNIKOV D E, SHEVTSOVA V. Different types of Lagrangian coherent structures formed by solid particles in three-dimensional time-periodic flows[J]. The European Physical Journal Special Topics, 2017, 226(6): 1239-1251.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期: 2020 -06 -07; 修回日期: 2020 -08 -23
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51676031,51976087) (Projects(51676031, 51976087) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:梁儒全,教授,博士生导师,从事多相流研究;E-mail:liang@epm.neu.edu.cn
引用格式: 黄鑫, 梁儒全, 范俊庚. 液固两相流体热毛细对流中颗粒动态积累结构研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(4): 1251-1260.
Citation: HUANG Xin, LIANG Ruquan, FAN Jungeng. Study on dynamic particle accumulation structure in thermocapillary convection for liquid-solid two-phase flow[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2021, 52(4): 1251-1260.