文章编号:1004-0609(2012)02-0337-06
强流脉冲离子束辐照镁合金微弧氧化膜的耐腐蚀性能
韩晓光1,雷明凯2,朱小鹏2,单英春1,徐久军1
(1. 大连海事大学 交通运输装备与海洋工程学院,大连 116026;
2. 大连理工大学 材料科学与工程学院 表面工程研究室,大连 116024)
摘 要:采用强流脉冲离子束在束流密度为200 A/cm2、辐照次数为1~10次条件下对AZ31镁合金微弧氧化膜进行辐照改性处理。采用扫描电子显微镜对氧化膜的表面及截面形貌进行表征;在Princeton Applied Research(PAR) 2273型电化学工作站测量氧化膜的极化曲线。结果表明:在束流密度200 A/cm2、5次辐照条件下氧化膜表面获得连续、致密的改性层;以3.5% NaCl溶液为腐蚀液,氧化膜表面发生的腐蚀过程由辐照前的活化溶解向辐照后的钝化-孔蚀击穿转变;在束流密度200 A/cm2、5次辐照条件下击穿电位提高到最大值-800 mV(vs SCE)。强流脉冲离子束辐照产生的连续致密改性层是氧化膜耐蚀性改善的主要原因。
关键词:镁合金;强流脉冲离子束;微弧氧化;腐蚀
中图分类号:TG156.95 文献标志码:A
Anti-corrosion properties of micro-arc oxidation films on
AZ31 magnesium alloy irradiated by high-intensity pulsed ion beam
HAN Xiao-guang1, LEI Ming-kai2, ZHU Xiao-peng2, SHAN Ying-chun1, XU Jiu-jun1
(1. College of Transportation Equipments and Ocean Engineering, Dalian Maritime University, Dalian 116026, China;
2. Surface Engineering Laboratory, School of Materials Science and Engineering,
Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China)
Abstract: The microarc oxidation (MAO) films on the AZ31 magnesium alloy were modified by high-intensity pulsed ion beam (HIPIB) at an ion current density of 200 A/cm2 with 1-10 shots. The surface and cross-section morphologies of the MAO films were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The polarization curves of the MAO films were measured by Princeton Applied Research 2273. The results show that a continuous and compact sealing layer forms on the MAO films by HIPIB with 5 shots. The polarization curves in 3.5% NaCl solution show that the corrosion behaviors of the MAO films transit from active dissolution of original films to pitting-breakdown of irradiated, and the breakdown potential achieves to -800 mV (vs SCE) at ion current density of 200 A/cm2 with 5 shots. The noticeable improvement in the corrosion properties of MAO films is attributed to the blocking effect of the sealing layer that hinders the process of electrolyte penetrating the MAO films to the magnesium alloy.
Key words: magnesium alloy; high-intensity pulsed ion beam; micro-arc oxidation; corrosion
镁合金是目前工业上可应用的最轻金属结构材料,因其比强度高、减振性好、耐热疲劳性好、不易老化,导热性良好、电磁屏蔽能力强、压铸工艺性能好、易加工、可再生利用而被誉为“21 世纪绿色工程金属结构材料”。目前镁合金主要应用在航空航天、汽车工业以及电子通讯等领域。但镁合金在应用中由于具有极高的化学和电化学活性极易受到周围环境的腐蚀,使镁合金的优良性能得不到充分发挥,极大地限制了镁合金在工程领域中的广泛应用。镁合金抗蚀性能差的主要原因有两个:一是镁的标准电极电位为-2.37 V,在常用金属结构材料中最低,当与其他金属材料接触形成腐蚀电偶时,镁均作为牺牲阳极而加速溶解。二是根据Pilling-Bedworth原理,当氧化过程中形成氧化物体积大于生成这些氧化物所消耗金属的体积即氧化膜致密系数(PB比)大于1时,氧化膜才具有保护作用。镁合金表面形成的氧化膜疏松多孔,致密系数为0.84,故不能形成稳定的保护膜。
为了改善镁合金的性能,进一步扩大镁合金的应用领域,各种表面改性技术被应用于改善镁合金的耐蚀性能。常用的方法主要有离子注入、激光表面处 理[1]、化学转化膜[2]和阳极氧化[3-8]等,其中微弧氧化方法[5-8]是一种基于阳极氧化发展起来的一种新的表面处理技术,应用成本与阳极氧化差不多,前处理简单,环境友好,氧化膜的硬度、致密性及耐腐蚀磨损性能较传统的阳极氧化膜均显著提高,但由于镁合金微弧氧化膜形成过程中,微弧放电会在氧化膜表面形成放电通道,同时氧化膜的致密系数较小使氧化膜表面存在孔隙,为腐蚀液通过氧化膜进入镁合金基体提供了通道,因而阻碍了镁合金耐蚀性能的进一步提高。
镁合金微弧氧化膜表面的孔隙是限制其耐蚀性进一步提高的主要因素,如何减少甚至消除氧化膜表面的孔隙成为提高镁合金耐磨抗蚀性能的关键问题。目前对氧化膜内的孔隙进行封孔处理方法主要有水合法、无机物封孔以及有机物封孔[9-12]等方法,这些方法均能够在一定程度上对氧化膜的孔隙进行封闭,提高镁合金的耐蚀性能,然而,上述方法均是采用其他物质对氧化膜内的孔隙进行填充,填充物与氧化膜性质上的差异使得这些封孔方法普遍存在改性效果有限、工艺效率不高的缺点,甚至在改善耐蚀性能的同时使氧化膜的硬度、刚度以及耐热性等均受到较大影响。
针对镁合金微弧氧化膜表面改性的难点问题,本文作者采用大面积强流脉冲离子束(High-intensity pulsed ion beam, HIPIB)技术对镁合金微弧氧化膜进行辐照改性处理,研究改性后氧化膜在3.5%NaCl溶液中的腐蚀行为,旨在发展出一种微弧氧化膜的冲击加工致密化技术。
1 实验
采用AZ31镁合金(Al 3.0, Zn 1.0, Mn 0.2, 其余为Mg,质量分数)作为基体,采用砂纸研磨至1000号后吹干、备用。以浓度分别为30~50 g/L Na2SiO3 和 5 g/L NaOH配制的碱性硅酸盐溶液为电解液在镁合金表面制备膜厚约为25 μm的微弧氧化膜。辐照实验在TEMP-6型强流脉冲离子束装置上在单极模式下进行,能量密度为 6 J/cm2,束流密度为200 A/cm2,辐照次数为1~10次,在真空度为3×10-3 Pa条件下对氧化膜进行辐照处理。辐照氧化膜的表面和截面形貌采用JSM-5600LV型扫描电子显微镜观察,SHIMADZU XRD-6000 型X射线衍射仪分析样品表面相结构。改性氧化膜的腐蚀性能测试在PAR 2273型电化学工作站上进行,工作站采用传统的三电极体系,饱合甘汞电极做参比电极,铂网做辅助电极,镁合金微弧氧化试样做工作电极,3.5% NaCl 溶液作为腐蚀液。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 辐照对氧化膜表截面形貌的影响
图1所示为原始及束流密度为200 A/cm2、辐照次数为1~10次条件下镁合金微弧氧化膜表面SEM像。由图1可见,原始氧化膜表面由许多大小不等的颗粒组成,颗粒熔化后连在一起,相连颗粒之间存在微孔,孔周围有熔化痕迹。微孔直径约几微米,大小不一且分布不均匀。微孔可能是由于微弧氧化过程中电弧放电造成的;同时氧化膜表面局部存在微裂纹,这是由于镁合金在微弧氧化过程中形成MgO与镁基体的致密系数为0.81(<1)[13],使形成的氧化膜内存在张应力产生的(见图1(a))。当采用束流密度为200 A/cm2的HIPIB对镁合金微弧氧化膜进行辐照处理时,在1次辐照条件下,氧化膜表面孔隙比原始氧化膜的孔隙略有增大。这可能是由于氧化膜表面存在孔隙,HIPIB辐照在孔隙边缘能量集中,产生选择性烧蚀造成的;氧化膜烧蚀表面发生重熔,颗粒的边缘变得圆滑,孔隙数量减少(见图1(b))。当辐照次数增加到3次时,表面重熔更为显著,孔隙尺寸减小,数量进一步减少,膜表面经历离子束的多次辐照,氧化膜表面反复重熔,膜表面出现面积约为50 μm×20 μm重熔区域(见图1(c))。当增加辐照到5次时,氧化膜表面变得更为致密,孔隙完全消失,表面重熔区域面积进一步增加到约100 μm×50 μm,重熔区域周围存在的小孔隙在离子束的作用下全部愈合,样品表面存在许多由于离子束的剧烈烧蚀作用产生的氧化膜颗粒(见图1(d))。在HIPIB的反复烧蚀作用下,HIPIB辐照氧化膜产生的等离子体向外扩展会在氧化膜表面产生向内传播的冲击波以及氧化膜表面升温不均匀产生的热应力对表面液相的扰动作用[14-15],这些因素均能推动熔融态的氧化膜向周围孔隙填充,使氧化膜表面的孔隙缩小甚至消失。继续增加辐照次数到10次,HIPIB对氧化膜表面烧蚀更为剧烈,与5次辐照相比,其表面形貌出现了明显变化,经过多次烧蚀,在膜表面形成许多圆形的凸台,重熔区域起伏较表面更高(见图1(e))。
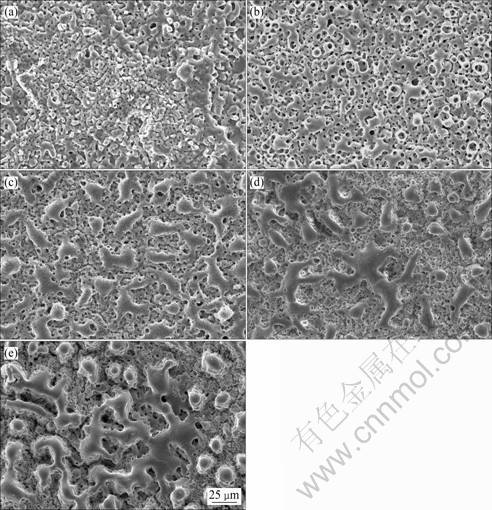
图1 经200 A/cm2、1~10次HIPIB辐照后镁合金微弧氧化膜表面的SEM像
Fig. 1 Surface SEM images of original and irradiated MAO films on AZ31 magnesium alloy by HIPIB at 200 A/cm2 with 1-10 shots: (a) Original; (b) 1 shot; (c) 3 shots; (d) 5 shots; (e) 10 shots
为了研究HIPIB辐照对镁合金微弧氧化膜膜层结构的影响,对氧化膜的横截面形貌进行观察。图2所示为原始及束流密度为200 A/cm2、辐照次数为1~10次时镁合金微弧氧化膜的横截面SEM像。由图2可见,原始氧化膜截面明显具有内、外亚层的双层结构,外亚层疏松多孔,厚度约为20 μm,内亚层较为致密,厚度约为5 μm(见图2(a));内亚层与基体结合良好,这主要是由于微弧氧化过程中火花放电使形成的氧化物膜层与基体烧结,形成微区冶金结合,避免了薄膜制备过程中常见的膜与基体结合力较差的问题。经HIPIB 1次辐照后,与原始氧化膜相比,横截面上的孔隙明显减少,整个氧化膜有致密化趋势(见图2(b));当辐照次数增加到3次时,在外亚层凸起的顶部出现较薄但不连续的熔化层,整个膜层变得更加致密(见图2(c));继续增加辐照次数到5次时,外亚层表层出现厚度约为10 μm的连续重熔层,几乎全部孔隙均消失,外亚层与内亚层界线不明显(见图2(d));当辐照次数增加到10次时,由于HIPIB极高的能量密度在膜表面产生强烈的烧蚀作用,外亚层横截面上出现波浪状的烧蚀形貌,波峰和波谷波动更为剧烈,高度差达到十几微米,尽管在波峰部分膜层形成厚度约为10 μm的重熔区,在波谷部分氧化膜内亚层被烧蚀变得很薄,厚度只有5 μm左右(见图2(e))。镁合金微弧氧化膜的选择性烧蚀形貌可能与氧化膜的特殊结构相关。在微弧氧化初始阶段,基体镁合金表面形成钝化膜的主要成份为MgO,在自腐蚀电位处发生溶解变成多孔MgO,随后在微弧氧化过程中由于基体镁合金的合金化作用使得在镁合金表面形成MgO与Mg2SiO4相间的氧化物膜。由于MgO与Mg2SiO4的汽化烧蚀温度相差较大,Mg2SiO4汽化烧蚀温度较低,由于强流脉冲离子束的选择性烧蚀作用[16],优先烧蚀低熔点元素。氧化膜的横截面上波浪状烧蚀形貌可能是由于离子束辐照过程中氧化膜表面Mg2SiO4被优先烧蚀掉而形成的。
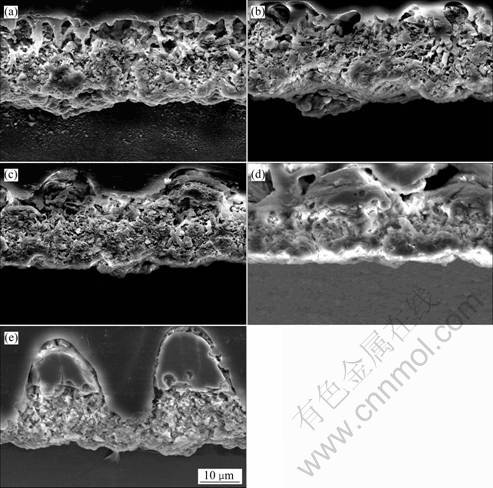
图2 束流密度200 A/cm2、1~10次HIPIB辐照后镁合金微弧氧化膜横截面的SEM像
Fig. 2 Cross-sectional SEM images of original and irradiated MAO films on AZ31 magnesium alloy by HIPIB at 200 A/cm2 with 1-10 shots: (a) Original; (b) 1 shot; (c) 3 shots; (d) 5 shots; (e) 10 shots
2.2 辐照对氧化膜表面相结构的影响
图3所示为镁合金AZ31基体、原始镁合金微弧氧化膜及束流密度为200 A/cm2,辐照次数分别为1~ 10次HIPIB处理后氧化膜的XRD谱。由图3可知,原始氧化膜主要由尖晶石相Mg2SiO4和MgO组成,氧化膜的XRD谱中存在多个镁合金基体的强峰,说明X射线能够很容易穿透氧化膜,这与氧化膜的多孔结构相关[5]。经HIPIB在束流密度为200 A/cm2辐照后,氧化膜表面XRD谱与原始氧化膜相比未发生明显变化,说明HIPIB辐照并没有改变镁合金微弧氧化膜的表面相结构,辐照后氧化膜保持原有的相结构。
2.3 辐照对氧化膜动电位极化性能的影响
为了研究HIPIB辐照镁合金微弧氧化膜的冲击加工致密化作用对氧化膜耐腐蚀性能的影响,对改性氧化膜在3.5% NaCl溶液中的动电位极化性能进行测试。图4所示为原始及束流密度为200 A/cm2、辐照次数1~10次条件下HIPIB辐照镁合金AZ31微弧氧化膜的动电位极化曲线。
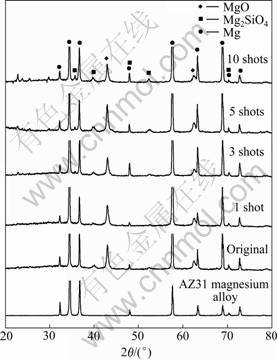
图3 AZ31镁合金及200 A/cm2、1~10次HIPIB辐照前后镁合金微弧氧化膜表层的XRD谱
Fig. 3 XRD patterns on surface layer of non-irradiated and irradiated MAO films on AZ31 magnesium alloy by HIPIB at 200 A/cm2 with 1-10 shots
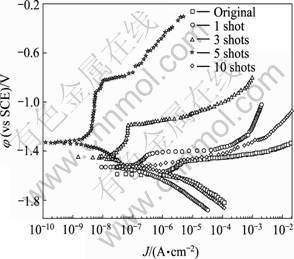
图4 束流密度为200 A/cm2、1~10次HIPIB辐照镁合金微弧氧化膜在3.5% NaCl溶液中的动电位极化曲线
Fig. 4 Polarization curves of MAO films on AZ31 magnesium alloy irradiated by HIPIB at 200 A/cm2 with 1-10 shots in 3.5% NaCl solution
由图4可见,原始镁合金AZ31微弧氧化膜一直处于活化溶解状态,经HIPIB辐照处理后,改性氧化膜的阳极极化行为由原始氧化膜的活化溶解转变为典型的钝化-孔蚀击穿过程。在外加阳极电流的作用下,镁合金AZ31表面发生反应Mg+2OH-=Mg(OH)2+2e,形成钝化膜。由于钝化过程是一个溶解-再钝化的平衡过程,当活性阴离子Cl-通过微弧氧化膜的孔隙到达基体合金表面时,由于Cl-与Mg2+的亲和力大于OH-和Mg2+的亲和力,形成可溶性的MgCl2,在钝化膜表面形成大阴极小阳极的腐蚀原电池,在极大的电流密度作用下,烧蚀改性氧化膜的孔蚀击穿电位随辐照次数增加呈先增加后减小过程,1次辐照时孔蚀击穿电位为-1 420 mV(vs SCE),在5次辐照条件下击穿电位提高到最大值-800 mV(vs SCE),而当辐照次数增加到10次,氧化膜的钝化不明显。钝化电流密度随辐照次数增加呈先减小后增大过程,1次辐照时钝化电流密度约为3×10-7 A/cm2,在5次辐照条件下钝化电流密度减小到最小值约为4×10-9 A/cm2,10次辐照时氧化膜的自腐蚀电流密度约为8×10-7 A/cm2。自腐蚀电位随辐照次数增加呈先增加后减小趋势,1次辐照时,微弧氧化膜的自腐蚀电位为-1 551 mV(vs SCE),当辐照次数增加到5次,氧化膜的自腐蚀电位增加到最大值-1 350 mV(vs SCE),进一步增加辐照次数到10次,自腐蚀电位反而下降到-1 530 mV(vs SCE)。烧蚀改性后氧化膜的自腐蚀电位及孔蚀击穿电位明显提高,自腐蚀电流显著减小,表明经200 A/cm2的HIPIB烧蚀改性后镁合金AZ31微弧氧化膜的抗均匀腐蚀性能、抗孔蚀性能和钝化性能得到明显改善。
3 结论
1) HIPIB烧蚀改性镁合金微弧氧化膜在束流密度200 A/cm2、5次辐照下形成连续、致密的烧蚀改性层。氧化膜表面在HIPIB高能量密度作用下,氧化膜表面急剧升温,发生熔融、蒸发/烧蚀,随着辐照次数增加,氧化膜表面熔融加剧,当辐照次数达到5次时,表面形成厚度约为10 μm的连续致密改性层,继续增加辐照次数到10次,氧化膜表面呈现波浪状烧蚀形貌。
2) 利用PAR 273型电化学工作站,采用动电位阳极极化测试HIPIB烧蚀改性镁合金AZ31微弧氧化膜在3.5% NaCl溶液中的腐蚀性能。烧蚀氧化膜表面发生的腐蚀过程由活化溶解向钝化-孔蚀击穿转变,孔蚀击穿电位随束流密度和辐照次数的增加呈先增加后减小的趋势。
致谢:
感谢朱雪梅教授、李朋、颜爱娟等的有益讨论和帮助。
REFERENCES
[1] MAJUMDAR J D, CHANDRA B R, GALUN R, MORDIKE B, MANNA I. Laser composite surfacing of a magnesium alloy with silicon carbide[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2003, 63(6): 771-778.
[2] HUO Hong-wei, LI Ying, WANG Fu-hui. Corrosion of AZ91D magnesium alloy with a chemical conversion coating and electroless nickel layer[J]. Corrosion Science, 2004, 46(6): 1467-1477.
[3] GRAY J E, LUAN B. Protective coatings on magnesium and its alloys—A critical review[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2002, 336(1/2): 88-113.
[4] FUKUDA H, MATSUMOTO Y. Effects of Na2SiO3 on anodization of Mg-Al-Zn alloy in 3 M KOH solution[J]. Corrosion Science, 2004, 46(9): 2135-2142.
[5] GUO Hong-fei, AN Mao-zhong, XU Shen, HUO Hui-bin. Microarc oxidation of corrosion resistant ceramic coating on a magnesium alloy[J]. Materials Letters, 2006, 60(12): 1538-1541.
[6] YEROKHIN A L, NIE X, LEYLAND A, MATTHEWS A, DOWEY S J. Plasma electrolysis for surface engineering[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 1999, 122(2/3): 73-93.
[7] MA Y, NIE X, NORTHWOOD D O, HU H. Systematic study of the electrolytic plasma oxidation process on a Mg alloy for corrosion protection[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2006, 494(1/2): 296-301.
[8] CHEN Fei, ZHOU Hai, YAO Bin, QIN Zhen, ZHANG Qing-feng. Corrosion resistance property of the ceramic coating obtained through microarc oxidation on the AZ31 magnesium alloy surfaces[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2007, 201(9/11): 4905-4908.
[9] DUAN Hong-ping, DU Ke-qin, YAN Chuan-wei, WANG Fu-hui. Electrochemical corrosion behavior of composite coatings of sealed MAO film on magnesium alloy AZ91D[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2006, 51(14/15): 2898-2908.
[10] 蔡启舟, 王 栋, 骆海贺, 魏伯康. 镁合金微弧氧化膜的SiO2溶胶封孔处理研究[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2006, 26: 612-614.
CAI Qi-zhou, WANG Dong, LUO Hai-he, WEI Bo-kang. Sealing of micro-arc oxidation coating on magnesium alloy by SiO2 sol sealing agent[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2006, 26: 612-614.
[11] 王天石, 何 劼, 夏乐洋, 陈科璞, 吾提库尔, 温 潇, 杜建成. 镁合金微弧氧化膜有机封孔耐腐蚀性能的研究[J]. 表面技术, 2006, 35(6): 8-10.
WANG Tian-shi, HE Jie, XIA Le-yang, CHEN Ke-pu, WU Ti-ku-er, WEN Xiao, DU Jian-cheng. Research on corrosion resistance of magnesium alloy with micro-arc oxidation film stuffed up with organic coating[J]. Surface Technology, 2006, 35(6): 8-10.
[12] 李 勇, 牛丽媛, 高光亮, 林继兴, 刘兰云. 微弧氧化工艺及封孔处理对镁合金耐蚀性能的影响[J]. 表面技术, 2008, 37(6): 14-17.
LI Yong, NIU Li-yuan, GAO Guang-liang, LIN Ji-xing, LIU Yun-lan. Effect of processing parameters of microarc oxidation and sealing treatment on corrosion resistance of magnesium alloy[J]. Surface Technology, 2008, 37(6): 14-17.
[13] ZHOU X, THOMPSON G E, SKELDON P, WOOD G C, SHIMIZU K, HABAZAKI H. Film formation and detachment during anodizing of Al-Mg alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 1999, 41(8): 1599-1613.
[14] LIU Chen, HAN Xiao-guang, ZHU Xiao-peng, LEI Ming-kai. Microstructural features of EB-PVD thermal barrier coatings irradiated by high-intensity pulsed ion beam[J]. Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology A, 2008, 26(6): 1439-1442.
[15] HAN Xiao-guang, MIAO Shou-mou, ZHU Xiao-peng, LEI Ming-kai. Phase transformation of graphite irradiated by high-intensity pulsed ion beams[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2007, 253(12): 5425-5430.
[16] ZHU Xiao-peng, LEI Ming-kai, DONG Zhi-hong, MIAO Shou-mou, MA Teng-tai. Crater formation on the surface of titanium irradiated by a high-intensity pulsed ion beam[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2003, 173: 105-110.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:高等学校博士学科点专项基金(20102125120008)
收稿日期:2011-05-20;修订日期:2011-07-09
通信作者:徐久军,教授,博士;电话/传真:0411-84723376;E-mail: xghan@dlmu.edu.cn