人工肌肉IPMC电致动响应特性及其模型
唐华平1,姜永正1,唐运军1,殷陈锋1,聂 拓1,王桥医2
( 中南大学 机电工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 湖南工业大学 机械工程学院,湖南 株洲,412008)
摘 要:采用自行设计的悬臂梁装置对人工肌肉IPMC的电致动响应特性进行测试,研究在直流电压作用下悬臂梁位移与电压的关系及在方波电压作用下位移与电压频率的关系,建立IPMC材料的力学模型;提出IPMC材料悬臂梁电致动挠曲线方程的大变形解法,导出作用于IPMC悬臂梁上的等效弯矩与电压、频率的函数。测试结果表明,在电压为5 V时位移达到最大值11.1 mm;当电压的频率大于30 mHz时,随着频率的增加,悬臂梁的位移逐渐减小,且在30~100 mHz时下降迅速。模型计算结果与测试结果最大相对误差在10%以内,证实了模型的准确性。
关键词:人工肌肉;离子交换树脂金属复合材料(IPMC);致动响应;悬臂模型
中图分类号:TH113.1 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2009)01-0153-06
Actuating response characteristics and model of
artificial muscles IPMC
TANG Hua-ping1, JIANG Yong-zheng1, TANG Yun-jun1, YIN Chen-feng1, NIE Tuo1, WANG Qiao-yi2
( School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Mechanical Engineering, Hunan University of Technology, Zhuzhou 412008, China)
Abstract: The actuating response characteristics of new artificial muscles ionic polymer metal composite (IPMC) and cantilever model were studied using the designed cantilever beams. The relationship between the displacement of cantilever beams and the voltage stimulated by DC voltage and that between the displacement and voltage frequency stimulated by square-wave voltage were studied. The mechanical model was established based on the test results. The function of voltage, frequency and equivalent moment which imposed on cantilever beams made by IPMC were derived, and large deformation solution for actuating deflection equation of cantilever beams was put forward. The testing results show that the maximum displacement is 11.1 mm when voltage value is 5 V. When voltage frequency is more than 30 mHz, the displacement of cantilever beams decreases gradually with the increase of the frequency, and it decreases dramatically when voltage frequency is 30-100 mHz. Compared with the testing results, the accuracy results of the model is validate, and the maximum error is within 10%.
Key words: artificial muscles; ionic polymer metal composites(IPMC); response of actuating; cantilever model
离子交换树脂金属复合材料(Ionic polymer metal composites, IPMC)是一种新型的电致形变高分子材料,在电场作用下呈现伸缩、弯曲等各种响应特 性,其特性参数与肌肉的接近,具有广阔应用前景。目前,有很多学者用它开展了仿生机器人、柔性低阻尼机器臂、传感器、微致动器件等方面的开发研究。Shahinpoor等[1-9]进行了一系列的试验研究,初步确定了悬臂IPMC材料的电压、频率响应特性,并得出IPMC在悬臂梁结构时的开环频率响应特性。Kaneda等[10]使用IPMC 材料开发了一种线性人工肌肉致动器,验证了此致动器位置控制的模拟结果和实验结果。Otero等[11]提出一种IPMC材料作为人工肌肉致动器的一种运动控制方法。谭湘强等[12]介绍了IPMC人工肌肉致动器的制备、致动特性和应用,并对IPMC人工肌肉致动器当前研究中存在的问题进行了分析阐述;罗玉元等[13]介绍了基于IPMC的柔性致动器的制备方法和关键技术,分析了致动机理,针对所构造的致动器样本初步研究了其机电特性。这些研究都没有建立人工肌肉材料IPMC材料本身的电致动力学模型,这给致动器的设计等带来了影响,在此,本文作者采用摄像非接触测试方法研究IPMC的电致动响应特性,建立相关力学模型。
1 实 验
实验中IPMC材料是采用从美国杜邦公司购买的Nafion 117薄膜进行表面镀铂处理得到的。使用的IPMC材料是悬臂长度为20 mm,截面为4 mm×0.18 mm(长×宽)的矩形。根据摄像非接触测量原理设计的摄像测量的实验装置如图1所示。
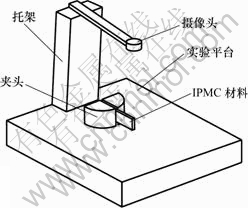
图1 摄像非接触测量实验台
Fig.1 Photograph test device
把IPMC材料夹持在夹头上,夹头两边通过导线与信号发生器正、负极连接,通电后人工肌肉变形,通过高清晰数码摄像机摄像获取变形后图像。在标定的基础上,应用图像分析方法计算出人工肌肉材料悬臂梁的位移。
人工肌肉悬臂梁通电后的位移S是与输入电压幅值V、频率P,材料的厚度d,悬臂长度d1相关的函数。因此有:
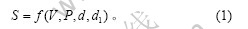
在进行实验时,通过改变V、P来研究位移S与输入电压幅值V、频率P的关系。使用编制的软件用摄像非接触测量方法测得的图像读取数据。数据获取时,首先设定标尺,如图2所示,右上角“标尺当量显示栏”中“标尺长度”后文本框中显示标尺的像数长度,图2中所示为342像数,等于20 mm,这是摄像前定的一个已知的参考长度,然后点击右上角的“确定”,计算出每像数得实际长度值,图2中显示为0.058 48 mm/像数。最后从悬臂的起始端依次取点做出数据轨迹,然后点击“输出”菜单中的“输出拟合点”将数据保存。
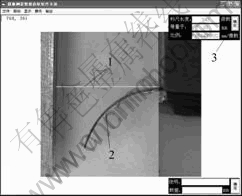
1—标尺线;2—悬臂端取数据轨迹;3—标尺当量显示栏
图2 数据获取界面
Fig.2 Surface of acquiring data
2 IPMC材料悬臂梁电致动特性
2.1 末端位移与刺激电压的关系
对于固定的频率及固定悬臂装置,悬臂梁的末端位移是输入电压的函数,因此,有:

对人工肌肉悬臂梁施加直流电压,将测得的实验数据采用最小二乘多项式拟合。经从线性最小二乘拟合到10次多项式最小二乘拟合,发现6次多项式最小二乘拟合与原始数据拟合得最好。因此,采用6次多项式拟合数据点。拟合曲线如图3所示,拟合曲线方程为:
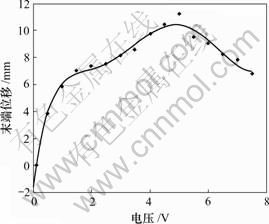
图3 末端位移与电压的关系
Fig.3 Relationship between tip displacement and voltage
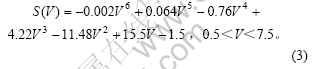
从位移与电压的关系曲线可以看出,当施加电压大小为5 V左右时,末端位移达到最大值。
2.2 末端位移与电压频率的关系
对于固定的电压及固定悬臂装置,悬臂梁的末端位移是输入刺激电压变化频率的函数,因此,有:

对人工肌肉悬臂梁施加不同频率的方波电压,将测得的实验数据采用3次多项式最小二乘多项式拟合,拟合曲线如图4所示,可得:
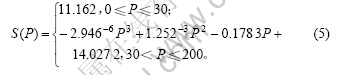
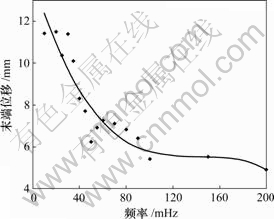
图4 末端位移与频率的关系
Fig.4 Relationship between tip displacement and frequency
从图4可以看出,当施加电压频率大于30 mHz时,末端位移会大幅度下降;在30~100 mHz时,位移下降比较迅速;在100~200 mHz时,位移变化已经比较小。这说明IPMC材料的电激反应特性具有频率低通性。
3 IPMC材料悬臂梁的电致动力学 模型
在人工肌肉应用中,有时要对设计的各种机构进行运动和动力学分析,这就需要建立人工肌肉的力学模型。根据前面测试的IPMC材料悬臂梁电致动位移特点,可以用几何非线性大变形梁来建立IPMC材料的电致动力学模型。
IPMC材料挠曲线示意图如图5所示。以变形前的梁轴线为x轴,垂直向上的轴为y轴,xy平面为梁的纵向对称面。在对称弯曲的情况下,变形后梁的轴线将成为xy平面内的1条曲线,称为挠曲线。挠曲线上横坐标为x的任意点的纵坐标,用 表示,代表坐标为x的横截面的形心沿y方向的位移,即为挠度,这样,挠曲线的方程式可以写成:
表示,代表坐标为x的横截面的形心沿y方向的位移,即为挠度,这样,挠曲线的方程式可以写成:

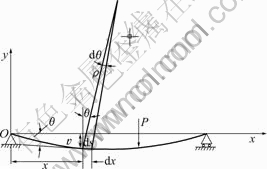
图5 挠曲线示意图
Fig.5 Schematic diagram of flexibility curve
在纯弯曲情况下,刘鸿文[14]导出其挠曲线微分方程为:

该方程适用于弯曲变形的任意情况。由于转角
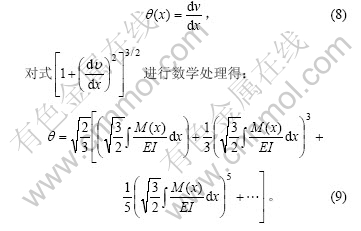
在本文设定的尺度下,事实上从第3项开始每项的值已经很小。为了便于求解,提高精度,去掉其高阶项,取前2项得:

电压为5 V时IPMC材料悬臂梁各点变形后的位移如表1所示。
表1 变形后各点位移
Table 1 Deform displacement of point
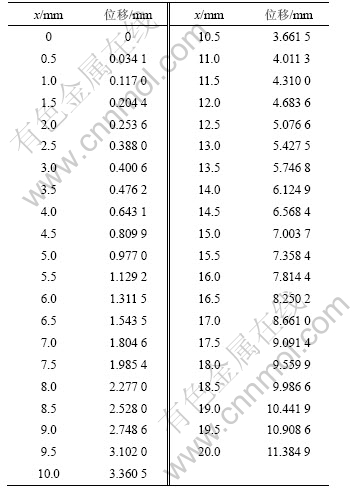
假设通电后相当于在IPMC材料悬臂梁上作用一个等效弯矩,则这个等效弯矩是通电电压的函数。实验中,使用的IPMC材料的悬臂模型的横截面惯性矩 I= 0.960×10-12 m4,材料弹性模量E=280×106 Pa[15]。采用末端位移拟合法,从表1可知,当在末端位移时,x=0.020 m,y=0.011 384 9 m,代入式(12)得关于M的一元三次方程,解得M=0.012 559 417 N?m。该弯矩非常小,这是合理的,因为IPMC材料是超弹性的,且使用的试样尺寸很小。
通过上面的分析,可以建立如下的IPMC材料悬臂梁电激力学模型:
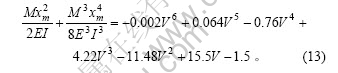
基于上面同样的方法,对于通电电压频率发生变化时,采用末端位移完全吻合法,由式(5)和式(12)得:

根据上式即可计算出在不同频率电压刺激下的当量弯矩M和位移,完成从电模型向机械力学模型的转化。
4 模型验证
为了验证IPMC材料悬臂梁电激响应方程(13)和(14)的正确性,将由式(13)和(14)计算所的悬臂模型的变形位移曲线与实测曲线进行比较。对于给定的电压V及悬臂长度xm,应用电压耦合方程(13)解出当量弯矩M。将计算出的当量弯矩代入式(14),就得到相应施加电压时的耦合悬臂梁大变形解法的方程。通过该方程计算出悬臂上各点的变形位移。然后,绘成曲线图。图6~9所示是直流电压为1,3,5和7 V时的由模型得出的悬臂端变形曲线与实测曲线。
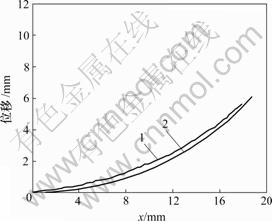
1—实测曲线;2—由模型建立的曲线
图6 电压为1 V时变形曲线
Fig.6 Deformation curves with voltage of 1 V
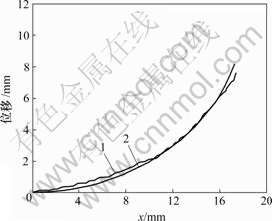
1—实测曲线;2—由模型建立的曲线
图7 电压为3 V时变形曲线
Fig.7 Deformation curves with voltage of 3 V
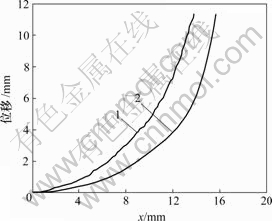
1—实测曲线;2—由模型建立的曲线
图8 电压为5 V时变形曲线
Fig.8 Deformation curves with voltage of 5 V
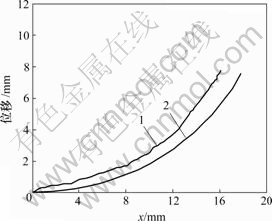
1—实测曲线;2—由模型建立的曲线
图9 电压为7 V时变形曲线
Fig.9 Deformation curves with voltage of 7 V
从图6~9可知,由电致动响应模型计算得出的IPMC材料悬臂梁变形位移曲线与实际测试的悬臂梁变形曲线的吻合程度是比较好的,这表明模型是合理的。从图6~9可以看出,变形越大,实际变形位移与由模型计算的变形位移误差就越大。其中,在施加5 V刺激电压时的实际变形位移与由模型计算的变形位移有较大误差。引起这种情况的主要原因可能是在建立模型方程非线性项展开项只取了2次项(见公式(7)~(10))。
为了验证频率耦合模型的有效性,将由模型方程(15)计算得出的变形位移曲线与实际测量的变形位移曲线进行对比,图10所示是电压为5 V,频率分别为20 mHz和100 mHz时由模型得出的悬臂端变形曲线与实测曲线对比结果。
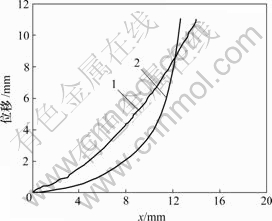
1—实测曲线;2—由模型所得的曲线
图10 电压为5 V、频率为20 mHz时变形曲线
Fig.10 Deformation curves with voltage of 5 V and frequency of 20 mHz
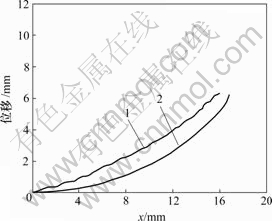
1—实测曲线;2—由模型所得的曲线
图11 电压为5 V、频率为100 mHz时变形曲线
Fig.11 Deformation curves with voltage of 5 V and frequency of 100 mHz
从图10~11可知,由频率耦合模型建立的IPMC材料悬臂梁的变形位移曲线与实际测试的悬臂梁变形位移曲线较吻合,特别是在末端位移和变形后在x方向上的缩短量上吻合得更好。由此说明模型方程(14)是合理的。
5 结 论
a. 人工肌肉IPMC材料电致动变形位移与施加电压有关,随着电压增加,变形位移增大,当电压增加到5 V时,变形位移达到最大;继续增加变形,则位移下降。
b. 当施加的电压的频率小于30 mHz时,IPMC材料能充分的变形,直到达到最大位移;当电压的频率大于30 mHz时,随着频率的增加,变形位移逐渐减小,且在30~100 mHz时位移下降迅速。
c. 施加于IPMC材料的电压等效于一个弯矩,等效弯矩是电压、频率的函数;应用等效弯矩和大变形梁能精确求解IPMC材料电致动变形位移,最大相对误差在10%以内。
参考文献:
[1] Shahinpoor M. Microelectro mechanics of ionic polymeric gels as artificial muscles for robotic applications[C]//Proceeding of the IEEE Conference Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE, 1993, 4: 380-385.
[2] Shahinpoor M. Continuum electro mechanics of ionic polymeric gels as artificial muscles for robotic applications[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 1994, 3(9): 367-372.
[3] Shahinpoor M, Bar-Cohen Y, XUE T, et al. Some experimental results on ion-exchange polymer-metal composites as bio- mimetic sensor and actuators[C]//Proceeding SPIE Smart Materials and Structures Conference. Bellingham: SPIE,1998, 3324: 251-267.
[4] Salehpoor K, Shahinpoor M. Role of ion transport in dynamic sensing and actuation of ionic polymeric platinum composites artificial muscles[C]//Proceeding SPIE Smart Materials and Structures Conference. Bellingham: SPIE, 1998: 3330-3309.
[5] Kim K J, Shahinpoor M. A novel method of manufacturing three-dimensional ionic polymer-metal composites (IPMCs) biomimetic sensors, actuators and artificial muscles[J]. Polymer, 2002, 43(3): 797-802.
[6] Shahinpoor M, Kim K J. Ionic polymer-metal composites (Ⅰ): Fundamentals[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2001, 10(4): 819-833.
[7] Shahinpoor M, Kim K J. Novel ionic polymer-metal composites equipped with physically loaded particulate electrodes as biomimetic, sensors, actuators and artificial muscles[J]. Sensors and Actuators, 2002, A96(2/3): 125-132.
[8] Kothfar C S, Leo D J. Bandwidth characterization in the micropositioning of ionic polymer actuators[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems, 2005, 16(1): 3-13.
[9] Kwangmok J, Jaedo N, Hyoukryeol C. Investigations on actuation characteristics of IPMC artifical muscle actuator[J]. Sensors and Actuators, 2003, A107(2): 183-192.
[10] Kaneda Y, Kamamichi N, Yamakita M, et al. Control of linear artificial muscle actuator using IPMC[C]//SICE 2003 Annual Conference. Tokyo: Soc of Instrum and Control Eng, 2003: 1650-1655.
[11] Otero T F, Cortes M T. Artificial muscle: Movement and position control[J]. Chem Commun, 2004(3): 284-285.
[12] 谭湘强, 钟映春, 杨宜民. IPMC人工肌肉的特性及其应用[J]. 高技术通讯, 2002, 12(1): 50-52.
TAN Xiang-qiang, ZHONG Ying-chun, YANG Yi-min. Property and application of IPMC artificial muscle[J]. Chinese High Technology Letters, 2002, 12(1): 50-52 .
[13] 罗玉元, 李朝东, 张国贤. 基于离子聚合物金属复合结构(IPMC)的柔性致动器研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2006, 17(4): 410-413.
LUO Yu-yuan, LI Chao-dong, ZHANG Guo-xian,Study on soft actuators based on ion-exchange polymer metal composites (IPMC)[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2006, 17(4): 410-413.
[14] 刘鸿文. 材料力学[M]. 3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1999: 212-216.
LIU Hong-wen. Material mechanics[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1999: 212-216.
[15] 唐运军, 唐华平, 殷陈锋. 一种离子交换树脂金属复合材料(IPMC)的力学参数测定[J]. 高技术通讯, 2007, 17(5): 508-511.
TANG Yun-jun, TANG Hua-ping, YIN Chen-feng. The mechanical parameter measurement of IPMC material[J]. Chinese High Technology Letters, 2007, 17(5): 508-511.
收稿日期:2008-06-10;修回日期:2008-10-31
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50575228);湖南省自然科学基金资助项目(07JJ3089)
通信作者:唐华平(1964-),男,湖南资兴人,教授,从事智能结构设计与控制、机械运动与振动控制、仿生机构设计研究;电话:0731-8831737;E-mail: huapingt@mail.csu.edu.cn