
DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2020.12.006
铝电解PFCs生成过程:F在炭阳极上吸附实验与第一性原理研究
孙珂娜1,张红亮1, 2,王景坤1, 3
(1. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 中南大学 难冶有色金属资源高效利用国家工程实验室,湖南 长沙,410083;
3. 中国宏桥集团有限公司,山东 滨州,256200)
摘要:通过对氟化物熔盐的电解,利用X线光电子能谱分析(XPS)和第一性原理对阳极表面反应层进行表征和计算,研究铝电解熔盐中的F在石墨表面的吸附行为,并指出F在不同石墨烯表面的最可能吸附位点,初步揭示阳极表面全氟化碳气体(PFCs)的微观形成机理。研究结果表明:电解后的阳极表面存在不同结构形式的C—F键,证明C和F在放电期间形成了中间产物CFx。F在本征石墨表面的最稳定吸附位为顶位,而覆盖度的不同并不影响稳定吸附位置。当F吸附在单空位缺陷石墨表面时,最稳定吸附位集中在距离单空位缺陷中心最近的3个C原子周围,包括3个顶位、6个桥位和空穴位。F在本征石墨烯和单空位缺陷石墨烯的吸附均属于化学吸附,并且缺陷可以促进F的吸附。
关键词:氟;石墨;吸附;第一性原理计算
中图分类号:TF821 文献标志码:A 开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID)
文章编号:1672-7207(2020)12-3321-10
PFCs formation process in aluminum electrolysis: experiment and First-principles study on adsorption of F on graphene
SUN Kena1, ZHANG Hongliang1, 2, WANG Jingkun1, 3
(1. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. National Engineering Laboratory for High Efficiency Recovery of Refractory Nonferrous Metals, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. China Hongqiao Group Limited, Binzhou 256200, China)
Abstract: Through the electrolysis of fluoride molten salt, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy(XPS) and first principles calculation were applied to characterize and calculate the anode surface reaction layer. The adsorption behavior of F in aluminum electrolysis molten salt on the graphite surface was studied. The most likely adsorption sites of F on different graphene surfaces, and the microscopic formation mechanism of perfluorocarbon gas(PFC) on the anode surface were revealed. The results show that there are C—F bonds with different structures on the anode surface after electrolysis, which proves that C and F form intermediate products CFx during discharge. The most stable adsorption position of F on the intrinsic graphite surface is the top position, and the different coverage of graphite layers does not affect the stable adsorption position. When F is adsorbed on the surface of single-vacancy defect graphite, the most stable adsorption sites are concentrated around the three C atoms closest to the single-vacancy defect center, including three top sites, six bridge sites and vacancy sites. In addition, the adsorption of F on intrinsic graphene and single-vacancy defect graphene is chemical adsorption, and defects can promote the adsorption of F.
Key words: fluorine; graphite; adsorption; First-principles calculation
目前工业铝电解槽使用炭素阳极,伴随着电解进程,电解质中氧化铝浓度不断降低,继而在阳极上发生阳极效应。阳极效应不仅会破坏正常电解,增加能耗,同时会产生大量全氟化碳(PFCs)气体。PFCs(主要包括CF4和C2F6)是高温室潜势气体,对环境影响巨大,铝电解工业是全球最大的全氟化碳气体排放源,约占总排放量的90%[1-2]。我国目前原铝产量居世界第1位,但是同工业发达国家相比还存在差距,主要体现在电解生产成本高,环境污染较重[3]。
针对PFCs的研究,早期主要集中在阳极效应的产生机理与消减方法,全氟化碳排放的定量评估与测量等,MARKS等[4-5]提供一种可精确测量CF4和C2F6排放量的方法,并将这些测量值与阳极相关联,从而指导生产;RHODERICK等[6]为确保空间测量的可比性,将开发的一套标准PFCs气体用于铝工业校准仪器从而检测和比较各厂的排放情况;邱竹贤等[7-8]通过电化学实验扫描出的3个电流峰,分别对应O2-放电,O2-与F-共同放电和F-放电,阳极效应就是阳极气体和表面化合物恶化了电极的湿润性,引发强电场把电介质击穿而形成的弧光放电;李劼等[9-10]将其团队开发的预焙铝电解槽阳极效应的预报算法应用于智能模糊控制系统中,从而降低阳极效应系数;秦庆东等[11-14]针对工业电解槽跟踪测试,发现PFCs排放量与效应电压和效应持续时间呈正比。而在非效应期间仅排放CF4,而不会产生C2F6,且持续时间短,强度低;CHEN等[15-16]针对实验室电解槽,采用气相色谱法分析阳极气体,采用电化学方法研究石墨电极在Na3A1F6-A12O3熔盐体系中的电化学行为,并通过气相色谱和XPS定性分析电极反应产物,证明反应后的电极表面有CFx生成。另外不少学者对完整、缺陷位或掺杂的石墨烯上吸附原子或分子进行过第一性原理计算,谭心等[17]发现双空位缺陷石墨烯比本征石墨烯更容易吸附碱金属原子,且最佳吸附位为H位;宋述鹏等[18]发现,C2H4在Fe,Co和Ni分别掺石墨烯的最佳吸附位为T位、H位和B位,掺杂后体系的吸附能力显著提高,且掺杂Ni时体系的吸附能力最强。不难看出,关于铝电解工业中PFCs的形成机制,目前国内外学者主要侧重于实验研究,但缺乏微观形成机理的探索,而石墨烯的微观计算研究也鲜少关于解决铝电解熔盐体系的具体问题。
为此,针对目前PFCs形成过程机制不明确、实验与微观计算缺乏关联的情况,本文作者采用实验与计算相结合的方式开展研究。首先,进行实验室熔盐电化学实验,为理论计算提供支撑;然后,采用第一性原理方法研究F在本征石墨和单空位缺陷石墨表面上的吸附行为,寻找最可能的稳定吸附位点,从而探索PFCs的形成机制,为工业生产中冶炼污染物的源头减排提供理论依据,降低实验研究的成本和周期。
1 材料与方法
以高纯石墨坩埚作为电解槽,反应电极由高纯石墨棒(d=5 mm)和热解氮化硼管(BN)构成,将裸露的电极底端浸入熔盐中作为电活性面。电解熔盐组成(质量分数)为54.8%NaF-44.7%AlF3-0.5%Al2O3。实验中使用的实验试剂均为高纯度等级,其中NaF和AlF3购买自上海麦克林生化科技有限公司,Al2O3购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
实验前将混合均匀的电解质装入石墨坩埚中并置于干燥箱中干燥24 h。实验准备完毕后将加入电解质的坩埚放入自制的井式炉中,配套CKW-3100温度控制器进行升温,选用MPS705直流稳流稳压电源(0~60 V/0~20 A)控制输入的恒定电压。本实验中电解温度为1 000 ℃,恒压2.5 V,电解2 h。
电解后的石墨阳极经空冷后切割表面,命名为样品A,将未使用的原始石墨电极作为空白对照组。采用X线光电子能谱法(XPS)分析原始石墨阳极表面和样品A表面,可以得到石墨电极的表面形貌与各元素的化学价态,为第一性原理计算提供实验支撑。
2 建模与计算方法
2.1 建立模型
2.1.1 不同覆盖度的本征石墨
LEI等[19-20]在研究H和O2等原子(或分子)在石墨表面的吸附时发现,石墨层间的范德华力相对于原子在石墨表面吸附作用的影响微弱,因此,在保证计算准确性的条件下,本文构建单层石墨烯代替实际片层状石墨结构,分别构建2×2,3×3,4×4,5×5, 共5种不同的超胞表面构型。
共5种不同的超胞表面构型。
本征石墨烯吸附单个F时,主要考虑3种高对称吸附位置,即顶位、桥位和空穴位(以下分别简写为T,B和H),分别位于石墨平面碳原子的正上方、C—C键的正上方以及碳环几何中心的正上方,如图1所示。定义覆盖度为被吸附原子个数与表面构型超胞原子个数之比,比值越大则相对应覆盖度越高。5种模型所对应的碳原子个数分别为8,18,32,50和54,按照每个模型吸附单个F来计算,则覆盖度分别为1/8,1/18,1/32,1/50和1/54。
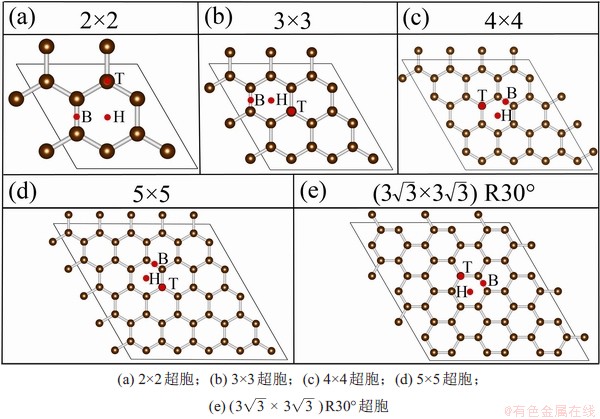
图1 优化后的不同晶胞大小的石墨烯构型及F可能吸附位
Fig. 1 Optimized graphene configurations with different cell sizes and possible F atom adsorption sites
2.1.2 单空位缺陷石墨
构建单空位缺陷石墨烯原胞再进行几何优化,其结构如图2所示。与原子数目接近的4×4本征石墨烯晶胞相比,单空位缺陷石墨少了1个碳原子,因此形成了1个空位,由于此单空位缺陷的存在,将F可能的吸附位细分为3类,其中,顶位12个:顶位-a~顶位-i;桥位12个:桥位-1~桥位-12;空穴位4个:空穴位H1~空穴位H4。
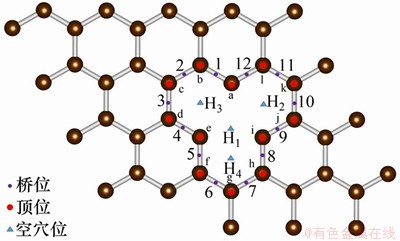
图2 单空位缺陷石墨烯构型及F可能吸附位
Fig. 2 Configuration of graphene with single vacancy and possible adsorption site of F atom
2.2 计算方法
以密度泛函理论为基础展开计算,采用Material studio软件中的Dmol3模块,根据模型特点和计算效率,计算选用GGA-PBE函数和DNP基组,K点设置为5×5×1,自洽收敛条件为:总能量收敛到2.721 14×10-4 eV以内,每个原子上的受力低于5.442 28 eV/m,位移的收敛精度标准为0.005×10-10 m。针对所建模型均进行K点的能量收敛性测试,测试表明上述所选取的参数值可使计算达到很好的收敛效果。为比较F单原子在石墨烯表面的吸附稳定性,本文计算F单原子在本征石墨和单空位缺陷石墨的不同位置的吸附能,吸附能(Eads)的计算公式定义为
 (1)
(1)
式中:Etot为F吸附后石墨烯体系的能量;EF为F单原子的能量;Egraphene为石墨烯晶胞的能量。当Eads>0为吸热反应,当Eads<0为放热反应,且Eads绝对值越大,相应的吸附结构越稳定。
3 实验结果
原始石墨的XPS谱如图3(a)所示,包括C 1s峰和O 1s峰。使用Thermo Avantage软件对高分辨的C 1s和O 1s峰进行拟合分析,获得各元素的详细化学价态和结构信息,分析结果如图4所示。C 1s高分辨谱中拟合出4个成分峰,其中C1和C2分别为石墨芳香环中非官能团化的sp2C和sp3C,为石墨的主要结构成分。在高结合能位置的C3和C4分别是C—O和C=O基团。O1s高分辨谱中拟合出4个成分峰,其中,C1是—OH基团,C2是—C=O双键结构,C3是—C—O单氧原子结构,C4是—C—O—桥式结构。而通过分析O 1s可知,样品中的氧主要来自有机污染物。
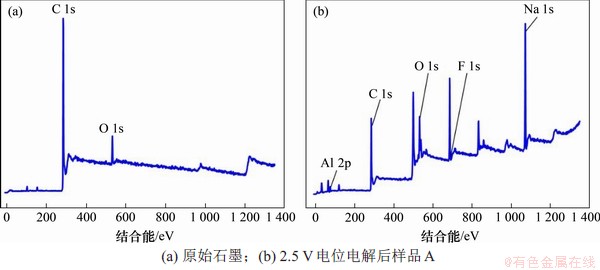
图3 电极表面XPS谱图
Fig. 3 XPS spectrum of electrode surface
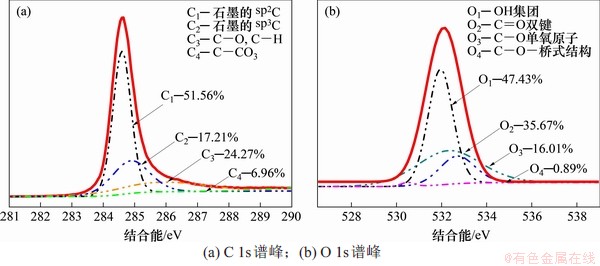
图4 原始石墨电极表面XPS高分辨C 1s与O 1s谱峰及其拟合结果
Fig. 4 High resolution XPS C 1s and O 1s peaks spectrum of graphite electrode without polarization and their fitting results
电解后样品A的石墨电极表层XPS谱图如图3(b)所示,经过分峰处理后得到图5所示的拟合结果。C 1s高分辨谱中拟合出7个成分峰,其中主要的C1,C2,C3和C4分别为石墨芳香环中非官能团化的sp2C和sp3C,C5为—C—O或—C—H结构,C6为—CF结构。从F 1s中可以,—CF结构又可以细分为离子、半离子、共价F—C键和其他种类。通过与图4空白组对比可知:电解后的石墨电极内表层存在F元素,C与F元素的化学价态发生变化,形成了C—F键,究其原因,可能是熔盐中铝-氟络合阴离子(如AlF63-)在电场作用下不断向石墨层靠近,并穿插在石墨层间,阳极电位达到F放电电位后,F靠近多层石墨中的C原子逐步放电形成C—F键。这证明了在冰晶石-氧化铝熔盐中,F会与碳放电形成中间产物CFx。通过高温熔盐实验证明电解后的石墨电极内表层存在C—F键,但微观反应机理还需要进一步探讨。
4 F在本征石墨烯上的吸附
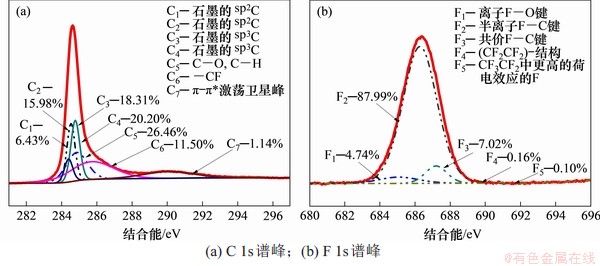
图5 样品A的XPS高分辨C 1s与F 1s谱峰及其拟合结果
Fig. 5 High resolution XPS C 1s and F 1s peaks spectrum of sample A and their fitting results
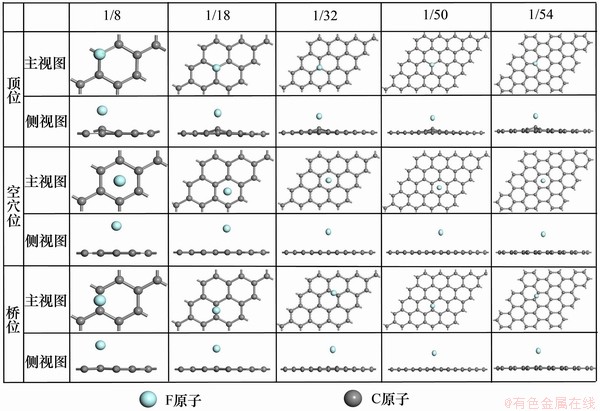
图6 F吸附在本征石墨表面的优化结构
Fig. 6 Optimized structure of F adsorbed on grapheme
计算F在不同晶胞大小(如图1所示5种不同覆盖度的超胞)石墨表面的不同吸附位置的吸附情况,优化后的吸附结构主视图和侧视图如图6所示。根据构建的吸附结构,分别计算不同覆盖度条件下,单个F在石墨表面经几何优化至稳定构型时,T,B和H这3类位置的吸附能、Mulliken电荷、垂直吸附高度和F处于吸附稳定位置时与最临近C原子的键长,计算结果如图7所示。
当覆盖度从1/8到1/54,F在本征石墨表面吸附时,在顶位的吸附能分别为-1.76,-1.90,-1.97,-2.05和-1.94 eV,桥位的吸附能分别为-1.37,-1.53,-1.60,-1.70和-1.62 eV,而空穴位的吸附能分别为-1.16,-1.44,-1.52,-1.66和-1.57 eV。根据吸附能的计算结构可知,F在本征石墨烯上的最稳定吸附位置为顶位(Top位),F吸附在所对应的C原子的上方,覆盖度并不影响稳定吸附位置。
从图6的侧视图可见:在顶位吸附引起的石墨表面畸变量最大,C原子向着F方向拱起,与桥位、空穴位吸附情况相比,在顶位的垂直吸附高度最低,吸附后F—C原子的键长最短。随着覆盖度降低,顶位处的吸附高度由1.721×10-10 m增加到2.021×10-10 m,而吸附后F—C原子的键长基本稳定在1.531×10-10 m。覆盖度由1/32向1/54变化过程中,体系吸附能绝对值的变化幅度降低到0.1 eV,而且体系的垂直吸附高度和F—C键长的增加值均很小,在0.11×10-10 m以下且逐渐趋于平稳,因此,覆盖度等于或小于1/32的石墨烯构型均可以作为石墨烯吸附单个F的稳定构型来进行模拟计算。
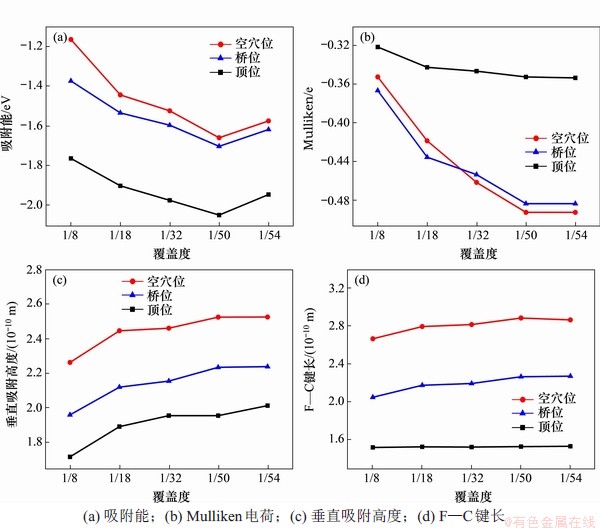
图7 F在本征石墨表面吸附的计算结果
Fig. 7 Calculation results of F adsorption on grapheme
5 F单空位缺陷石墨烯上的吸附
计算F在单空位缺陷石墨表面的不同吸附位置的吸附情况,优化后的吸附结构主视图和侧视图如图8~10所示,计算结果如图11所示。分别计算单个F在单空位缺陷石墨表面经结构弛豫至稳定构型时,顶位,桥位和空穴位这3类位置的吸附能、Mulliken电荷、垂直吸附高度和F处于吸附稳定位置时与最临近C原子的键长。图12标记出最可能吸附位置,根据C原子距离点缺陷中心的距离,将距离最近的3个C原子标记为C1,C2和C3。
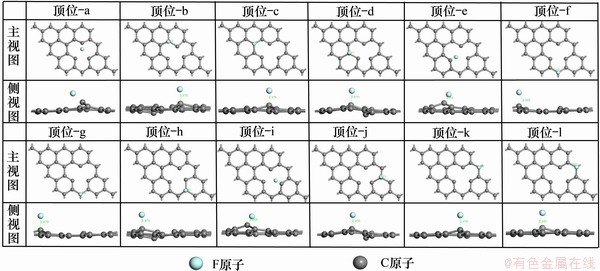
图8 F在单空位缺陷石墨烯的顶位吸附的结构优化图
Fig. 8 Structure optimization of F adsorption on top site of graphene with single vacancy
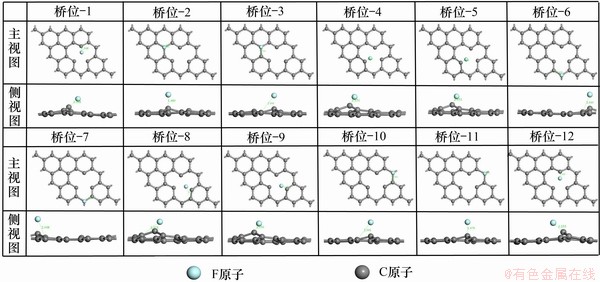
图9 F在单空位缺陷石墨烯的桥位吸附的结构优化图
Fig. 9 Structure optimization of F adsorption on site of graphene with single vacancy
从图8~10可见:F在不同位置的吸附均会引起石墨层较大的畸变。顶位-a~顶位-i这12个顶位,其中放在顶位-a、顶位-e和顶位-i上方初始位置的F在几何优化后会偏向单空位缺陷中间,而其余顶位的F原子依旧保持在原本对应的C原子上方。桥位-1、桥位-4、桥位-5、桥位-8、桥位-9、桥位-12上方的F在几何优化后也会偏向单空位缺陷中间。
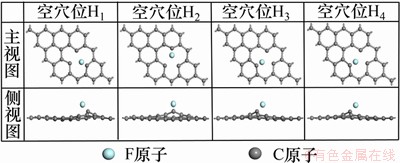
图10 F在单空位缺陷石墨烯的空穴位吸附的结构优化图
Fig. 10 Structure optimization of F adsorption on hollow site of graphene with single vacancy
从图11(a)可见:F在单空位缺陷石墨表面的顶位吸附时,最稳定吸附位置为顶位-a、顶位-e和顶位-i,吸附能均为-4.90 eV,从图8的侧视图可以看出,在这3个顶位吸附引起的石墨表面畸变量最大,垂直吸附高度分别为1.685×10-10,1.685×10-10和1.665×10-10 m,而F处于吸附稳定位置时与最临近C原子的键长均为1.35×10-10 m。F分别吸附在距离缺陷中心最近的C1,C2和C3上。其他顶位的F吸附能在-2.66~-2.79 eV之间,吸附后的F—C键长在1.47~1.48×10-10 m之间。
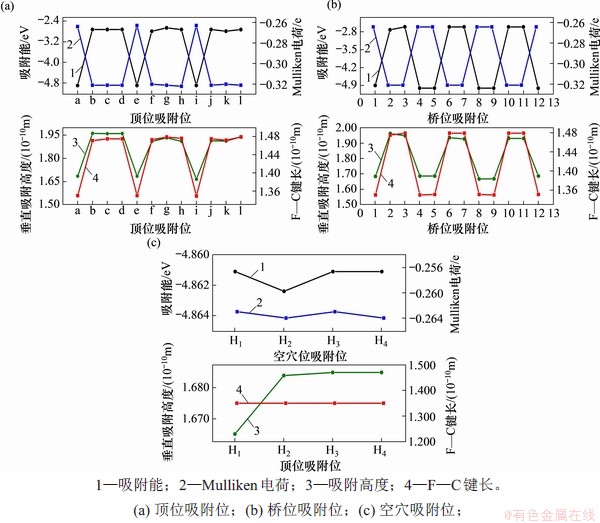
图11 F在缺陷石墨表面吸附的计算结果
Fig. 11 Calculation results of adsorption on surface of defective graphite
从图11(b)可见:F在单空位缺陷石墨表面的桥位吸附时,最稳定吸附位置为桥位-1、桥位-4、桥位-5、桥位-8、桥位-9和桥位-12,即C1,C2和C3周围的6个桥位,其吸附能均为-5.00 eV。桥位-1和桥位-12的F与C1吸附,桥位-4和桥位-5的F与C2吸附,桥位-8和桥位-9的F与C3吸附。与顶位吸附类似,在这6个桥位吸附引起的石墨表面畸变量最大,其他桥位的F吸附能为-2.61~-2.72 eV。
从图11(c)可见:F在单空位缺陷石墨表面的空穴位吸附时,H1位置是单空位缺陷的几何中心,而H2~H4可理解为本征石墨六元环的几何中心,这4个空穴位吸附情况一样,其吸附能均为-4.86 eV,即无论F放在空穴处的何处,都有利于F的吸附,而F会与临近的C1~C3吸附。
将顶位、桥位和空穴位计算出的最稳定吸附位见图12。从图12可以看出:距离单空位缺陷中心最近的3个C原子,C1~C3周围的位置都有利于F的吸附,即对应的3个顶位、6个桥位和空穴位。这些稳定吸附位的吸附能在-4.86~-5.00 eV之间,而Mulliken电荷均为-0.264 e,形成的F—C键长均为1.35×10-10 m。
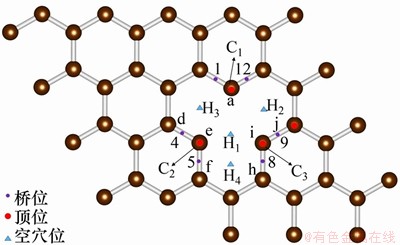
图12 F在缺陷石墨表面最稳定吸附位
Fig. 12 The most stable adsorption site of F on surface of defective graphite
相较于本征石墨烯结构,单空穴缺陷石墨烯对F的吸附能力有了很大提高,与C原子数接近的4×4本征石墨进行对比,顶位稳定吸附的吸附能由原本的-1.97 eV变为-4.90 eV,吸附引起的石墨表面畸变也更大,原子处于吸附稳定位置时与最临近C原子的键长也由1.96×10-10 m缩短为1.35×10-10 m,说明单空位缺陷的石墨烯对F的吸附属于相互作用较强的化学吸附。而除了靠近C1~C3的最稳定吸附位,其他吸附位置的吸附能也在-2.79~-2.60 eV,可以说明单空位缺陷的存在对F在石墨表面的吸附有很大影响,使之更有利于F在其表面吸附。
6 结论
1) XPS检测分析石墨电极表面的化学价态与成键信息,证实了电解后的阳极表面存在不同结构形式的C—F键,即F-与碳放电形成中间产物CFx。
2) F在不同覆盖度的本征石墨烯表面的最稳定吸附位均为顶位,覆盖度由1/32向1/54变化过程中,体系吸附能绝对值的变化幅度降低到0.1 eV以下,因此,覆盖度在1/32或低于1/32的石墨烯构型可作为石墨烯吸附单个F的稳定构型。
3) F在单空位缺陷石墨烯表面吸附时,最稳定吸附位集中在距离单空位缺陷中心最近的3个C原子周围,即C1~C3对应的3个顶位,6个桥位和空穴位。这些稳定吸附位的吸附能在-5.00~-4.86 eV之间,Mulliken电荷均为-0.264 e,形成的F—C键长均为1.35×10-10 m。
4) 本征石墨烯和单空位缺陷石墨烯对F的吸附都属于化学吸附,而F在单空位缺陷各处的吸附能都高于在本征石墨表面的吸附能,引起石墨表面畸变也更大,说明空位缺陷的存在会促进F的吸附。
参考文献:
[1] DANDO N R, SYLVAIN L, FLECKENSTEIN J, et al. Sustainable anode effect based perfluorocarbon emission reduction[J]. Light Metals 2011: 325-328.
[2] TABEREAUX A T. Anode effects, PFCs, global warming, and the aluminum industry[J]. Journal of Metals, 1994, 46(11): 30-34.
[3] LI Wangxing, CHEN Xiping, YANG Jianhong, et al. Latest results from PFC investigation in China[J] Light Metals 2012: 619-622.
[4] MARKS J, KANTAMANENI R, PAPE D, et al. Protocol for measurement of tetrafluoromethane and hexafluoroethane from primary aluminum production[J]. Light Metals, 2003:221-225.
[5] MARKS J, TABEREAUX A, PAPE D, et al. Factors affecting PFC emissions from commercial aluminum reduction cells[J]. Essential Readings in Light Metals, 2016: 295-302.
[6] RHODERICK G, CHU P, DOLIN E, et al. Development of perfluorocarbon (PFC) primary standards for monitoring of emissions from aluminum production[J]. Fresenius' Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2001, 370(7): 828-833.
[7] 邱竹贤. 论铝电解中阳极效应的机理[J]. 有色金属(选冶部分), 1978(7): 26-31.
QIU Zhuxian. On the mechanism of anode effect in aluminum electrolysis[J]. Nonferrous metals (smelting part) 1978(7): 26-31
[8] 张明杰, 邱竹贤, 王洪宽. 铝电解中的电极过程: Ⅰ阳极过程[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, 22(2): 123-126.
ZHANG Mingjie, QIU Zhuxian, WANG Hongkuan. Electrode processes in aluminium electrolysis: Ⅰ anodic process[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2001, 22(2): 123-126.
[9] 李劼, 丁凤其, 李民军, 等. 预焙铝电解槽阳极效应的智能预报方法[J]. 中南工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, 32(1): 29-32.
LI Jie, DING Fengqi, LI Minjun, et al. Intelligent anode effect prediction method for prebaked-anode aluminum reduction cells[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology(Natural Science), 2001, 32(1): 29-32.
[10] 李劼, 丁凤其, 邹忠, 等. 铝电解槽电流强化与高效节能综合技术的开发及应用[J]. 轻金属, 2011(2): 25-30.
LI Jie, DING Fengqi, ZOU Zhong, et al. Development and application of integrated technology of current-intensifying and high-efficiency energy-saving for aluminium reduction[J]. Light Metals, 2011(2): 25-30.
[11] 秦庆东, 柴登鹏, 邱仕麟, 等. 300 kA铝电解槽PFC排放特征研究[J]. 轻金属, 2012(1): 27-31.
QIN Qingdong, CHAI Dengpeng, QIU Shilin, et al. Study on PFC emission characteristics of 300 kA aluminium electrolysis cells[J]. Light Metals, 2012(1): 27-31.
[12] 秦庆东, 邱仕麟. 工业铝电解过程中PFC排放机理探讨[J]. 轻金属, 2015(6): 23-27.
QIN Qingdong, QIU Shilin. Study on the mechanism of PFC emission during the industrial aluminum electrolysis process[J]. Light Metals, 2015(6): 23-27.
[13] 秦庆东, 柴登鹏, 邱仕麟. 铝电解中非阳极效应过程全氟化碳的排放分析[J]. 有色金属工程, 2015, 5(6): 41-44.
QIN Qingdong, CHAI Dengpeng, QIU Shilin. Analysis of PFC emission in non-anode effect of aluminum electrolysis[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2015, 5(6): 41-44.
[14] LI Wangxing, ZHAO Qingyun, YANG Jianhong, et al. On continuous PFC emission unrelated to anode effects[J]. Light Metals 2011: 309-314.
[15] CHEN Gong, SHI Zhongning, GAO Bingliang, et al. Electrochemical behavior of graphite anode during anode effect in cryolite molten salts[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(9): 2306-2311.
[16] CHEN Gong, SHI Zhongning, WANG Zhaowen, et al. Mechanism of graphite electrode fluorinated in 2.4NaF/AlF3-Al2O3 melt at 1 373 K[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2014, 161(14): 587-593.
[17] 谭心, 陈路华, 刘尧尧, 等. 碱金属原子吸附在双空位缺陷石墨烯表面的第一性原理研究[J]. 功能材料, 2018, 49(10): 10098-10103.
TAN Xin, CHEN Luhua, LIU Yaoyao, et al. First-principles study on surface absorption of alkali metal atoms on double-vacancy defect graphene[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2018, 49(10): 10098-10103.
[18] 宋述鹏, 贾娜娜, 龚铁夫, 等. Fe, Co, Ni掺杂石墨烯表面吸附C2H4的第一性原理研究[J]. 原子与分子物理学报, 2019, 36(4): 710-716.
SONG Shupeng, JIA Nana, GONG Tiefu, et al. First-principles study of C2H4 adsorption on Fe-, Co- and Ni-doped graphene surface[J]. Journal of Atomic and Molecular Physics, 2019, 36(4): 710-716.
[19] LEI Yang, SHEVLIN S A, ZHU Wenguang, et al. Hydrogen-induced magnetization and tunable hydrogen storage in graphitic structures[J]. Physical Review B, 2008, 77(13): 212-219.
[20] LIU Juan, WANG Chen, LIANG Tongxiang, et al. Density functional theory investigation of oxygen interaction with boron-doped graphite[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 390: 273-282.
(编辑 秦明阳)
收稿日期: 2020 -06 -16; 修回日期: 2020 -08 -20
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51974373,51874365,51674300,61751312,61621062);山东省重大科技创新工程项目(2019JZZY020123);湖南省自然科学基金面上项目(2018JJ2521);中南大学中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(2019zzts242) (Projects(51974373, 51874365, 51674300, 61751312, 61621062) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2019JZZY020123) supported by the Major Scientific and Technological Innovation Program of Shandong Province; Project(2018JJ2521) supported by the General Program Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province; Project(2019zzts242) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University)
通信作者:张红亮,男,教授,博士生导师,从事冶金与材料多尺度仿真及工业过程智能制造研究;E-mail:csu13574831278@163.com