膜反应器结合离子交换法对镍钼矿的生物浸出
陈家武1, 2,肖连生1,高从堦1,张贵清1
(1. 中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 湖南生物机电职业技术学院 环境工程系,湖南 长沙,410127)
摘要:采用对钼有一定耐受性的金属硫叶菌,通过膜反应器结合离子交换吸附,除去钼以实现镍钼矿的浸出。研究结果表明:由于膜生物反应器(MBR)中膜的超滤作用,浸出液中的钼质量浓度保持在该菌可以承受的范围内,再通过离子交换将滤出液中的钼交换吸附,交换处理的浸出液返回浸出反应器,从而使MBR中钼保持很低的质量浓度而实现细菌对矿物高效浸出。浸出条件为:温度为65 ℃,接种量为10%,矿浆质量浓度为100 g/L,浸出时间20 d。在浸出过程中,当所超滤和离子交换的浸出液体积为35%左右时,MBR的Ni和Mo的浸出率分别为70.70%和46.92%;当所超滤和离子交换的浸出液体积为18%左右时,MBR的Ni 和 Mo 的浸出率分别为74.71%和50.97%;当所超滤和离子交换的浸出液体积为10%左右时,MBR的Ni和Mo的浸出率分别为79.53%和56.52%;而在相同条件下,柱浸镍和钼的浸出率则保持在75.59%和54.07%左右;可见,在浸出液的超滤和离子交换量较低(约10%)时,MBR中Ni和Mo浸出率比同条件下的柱浸浸出率高,达到了较好的浸出效果。
关键词:膜生物反应器;金属硫叶菌;超滤;离子交换;镍钼矿
中图分类号:TD925.5 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2012)07-2473-09
Bioleaching of nickel-molybdenum sulfide ores by reactor with membrane combined ion-exchange
CHEN Jia-wu1, 2, XIAO Lian-sheng1, GAO Cong-jie1, ZHANG Gui-qing1
(1. School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Department of Environmental Engineering, Hunan Biological and Electro-Mechanical Polytechnic,
Changsha 410127, China)
Abstract: The bioleaching of nickel-molybdenum sulfide ores with the Mo-resistant thermophilic bacterium sulfolobus metallics in a membrance biological reactor (MBR) with ion exchange was studied. The results show that the mass concentration of Mo can be controlled with filter of the membrane and the action of ion exchange. The toxicity of Mo to microorganism decreases and maintains at a low level in the bioleaching process. When the leaching solution is filtered at the 35%, 18% and 10%, the leaching percentage of Ni and Mo is respectively 70.70% and 46.92%, 74.71% and 50.97%, 79.53% and 56.52% after 20 d bioleaching in MBR at the condition of 65 ℃, 10% of inoculation and 100 g/L of ore pulp density. While 75.59% Ni and 54.07% Mo are leached out in column under the same condition. The leaching ratio of Ni and Mo of MBR exceeds that of the column leaching when the 10% of leaching solution is filtered and ion-exchanged.
Key words: membrane biological reactor (MBR); sulfolobus metallics; ultrafiltrateing; ion exchange; nickel- molybdenum sulfide ores
对于硫化钼矿,钼对微生物的毒性使该矿的细菌浸出非常困难,采用细菌浸出从钼矿中提取钼效果很差。耐钼菌浸出技术的研究与发展,是解决硫化钼矿高效生物浸出的关键步骤。吉兆宁等[1-4]采用常温菌对低品位钼矿浸出进行了探讨,但浸出率均不高,且浸出周期长,其原因之一在于常温菌的抗钼能力很弱。杨显万等[5]用氧化亚铁硫杆菌处理一种含Cu和Mo的低品位矿,在30 ℃条件下浸出60 d,Cu的浸出率为60%,而Mo的浸出率仅为0.34%。Donati等[6]发现氧化亚铁硫杆菌不被MoS3表面吸附,其原因在于Mo对细菌有毒性。在钼的毒性对细菌影响方面,Silverman等[7]的实验表明:在9 K培养基中,浓度为1 mmol/L的钼对Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans的铁氧化有抑制作用,浓度为2 mmol/L的钼则完全抑制铁的氧化。对黑色岩系镍钼矿的化学浸出,Zhao等[8-9]采用空气氧化法进行了探讨,但钼的浸出率不高。镍钼矿的生物浸出非常复杂,一方面,采用对钼具有一定耐受性的嗜热菌浸出镍钼矿,浸出速度比常温菌的快;另一方面,嗜热菌没有细胞壁,抗剪切力较低,普通条件的浸出不仅存在剪切力对细菌的伤害问题,而且当浸出液钼浓度超过一定值时,对细菌会产生抑 制[10],因此,只能在低矿浆浓度下浸出,这在工业应用中受到很大限制。耐钼菌结合良好的反应器是解决镍钼矿生物浸出的最佳途径。事实上,国内外一些研究者[11-16]采用反应器技术改进生物浸出,对黄铜矿、闪锌矿等矿物的嗜热菌槽浸、柱浸进行了研究,浸出效果比一般条件下的生物浸出效果好。而目前将膜技术及离子交换法引用到浸出反应器中以优化细菌生长环境的做法尚未见报道。为此,本文作者采用对钼有较好耐受性的金属硫叶菌,通过膜生物反应器(MBR)结合离子交换技术的浸出方式对硫化镍钼矿的生物浸出进行研究,以期较好地解决浸矿菌钼中毒对硫化镍钼矿生物浸出的干扰,降低浸出体系的剪切力,在较高矿浆浓度下获得较好的浸出效果。
1 实验
1.1 矿物、菌种及仪器
所用矿物为贵州镍钼矿,该矿物具有以下特点:含镍矿物主要为二硫镍矿(NiS2)、辉镍矿(Ni3S4)和辉砷镍矿(NiAsS),少量或微量针镍矿(NiS)、硫镍铁矿和含镍黄铁矿等;镍钼矿石平均含钼(质量分数,下同)达5%,其中,钼矿物是一种胶状集合体,称为胶硫钼矿,所以,采用X线衍射没有检测到硫化钼。矿物学研究表明:这种钼的集合体除了含硫与钼外,碳也是主要元素,因此,被称为“碳硫钼矿”。实验前矿样经烘干、细磨成粒径为0.048~0.077 mm。
菌种为金属硫叶菌,购于日本菌种保藏中心,属古生菌,好氧,兼性化能自养,既能氧化硫,又能氧化亚铁,最适温度为65 ℃。细菌在含0.5%镍钼矿的174型培养基中进行多次转移培养驯化,再用含1%镍钼矿和0.05%酵母的培养基中驯养5~7 d,作为以后的浸矿用菌。174型培养基的组分如下:硫酸铵130 mg,磷酸二氢钾280 mg,硫酸镁250 mg,氯化钙70 mg,三氯化铁20 mg,氯化锰1.8 mg,硼酸4.5 mg,硫酸锌0.22 mg,氯化铜0.05 mg,钼酸钠0.03 mg,硫酸氧钒0.03 mg,硫酸铬0.01 mg,酵母提取物1.00 g,蒸馏水1 L;用6 mol/L硫酸调pH至2。
仪器包括:F-2500分光光度计;XSP-24N-103生物显微镜;TZL16高速离心机;THZ-82振荡器;PE100原子吸收仪;膜生物反应器装置;离子交换柱。膜反应器中有3根高50 cm、直径为24 cm的塑料柱构成浸出反应池,中间1根柱子为膜池,配有膜装置,能通过过滤作用降低或控制钼浓度,而矿物和浸矿菌则被截留在池内。在反应池内配带有充气、控温和连续循环装置,以控制浸出过程中的氧气、恒温和浸出液的传质和传能,如图1所示。离子交换剂采用新合成的主要吸附钼的127型阴离子交换树脂。

图1 MBR结构图
Fig.1 Structure of MBR
1.2 实验方法
(1) 在装柱之前,先将阴离子交换树脂用pH=1.6的纯水浸泡2 d,将40 mL经过20 h纯水浸泡的树脂装入到交换柱中(离子交换柱不能有气泡和断层现象)。本实验共制离子交换柱2根,以供离子交换使用。上柱后再用pH=1.6的纯水平衡,使其pH稳定并与矿浆的pH基本一致。交换前用体积分数为1%的稀硫酸在交换柱中将树脂由OH型转为SO42-型,转型后用酸纯水平衡树脂至流出液pH等于浸出液的pH即可。
(2) 料液从交换柱的顶部进入,底部流出。
(3) 用纯水洗涤交换柱将柱内残留的料液洗涤干净,再用质量分数为0.5%的NaOH解吸。NaOH从柱子顶部进入,底部流出。
反应器运转前,先往反应池内定量注入含100 g/L镍钼矿的174型培养基,再接种驯化后扩大培养7 d左右的金属硫叶菌10%(体积分数)。然后,开启反应器,打开升温、充气、循环装置,使浸出液保持在温度65 ℃,充气速率为1.0 L/min。经膜生物反应器(MBR)浸出后,打开过滤泵,其滤出的浸出液进入离子交换柱进行吸附除钼,通过离子交换柱的过滤液再进入MBR反应槽。同时,用pH=2的蒸馏水补充浸出液蒸发,使浸出液在整个浸出期间体积保持恒定,如图2所示。膜交换浸出和柱浸分别在同一条件下同时进行,分别以3组不同过滤交换处理率进行浸出,在浸出过程中每组定期取样。经过20 d浸出,打开反应池底部的阀门,放出所有的浸出液,经过抽滤。然后,将浸出渣烘干,秤质量,测定渣样中Ni和Mo质量浓度。采用啉菲咯林法测定F2+和Fe3+的质量浓度,采用原子吸收法测定Ni,Mo,Cu,Zn和总Fe的质量浓度。

图2 MBR-离子交换树脂结构图
Fig.2 MBR combined with ion exchange structure
2 结果与分析
2.1 浸出液中浸出液中的Mo的存在形式及Fe(SO4)2-络合离子质量浓度
浸出液中的 Mo的存在形式非常复杂,主要为MoO22-,Mo8O264-,[PMo12O40]3-,[AsMo12O40]3-,[SiMo12O40]4-,MoO2Cl2和MoO2SO4。其中,Mo的络阴离子Mo8O264-,[PMo12O40]3-,[AsMo12O40]3-和[SiMo12O40]4-等离子能被实验所用的阴离子交换树脂吸附。根据配位化学理论[17],溶液中的Fe3+能与SO42-和Cl-形成配合物,其中Fe3+和SO42-配合成络阴离子FeL2的络合常数K稳很大,达到了105.4,因此,该络阴离子是很稳定的。而Fe3+与Cl-形成络阴离子的K稳很小,仅为100.01。通过采用离子色谱分析,细菌培养基母液中总SO42-和总Cl-质量浓度如图3所示。

图3 浸出液中的总SO42-和总Cl- 质量浓度
Fig.3 Total ion concentration of SO42- and Cl- in leaching liquid
在浸出时,该培养基母液被稀释25倍,稀释后的培养基(或浸出液中)总的SO42-质量浓度约为1 906.62 mg/L。在浸出过程中,实测的浸出液总Fe3+质量浓度都在100~500 mg/L范围变化,通过配位方程(1)~(4),可以求出Fe3+与SO42-配合形成的络阴离子FeL2的质量浓度及其变化,如表1所示。根据表1,Fe(SO4)2-络阴离子的质量浓度大约为总Fe3+的15%,在离子交换过程中被阴离子交换树脂吸附而离开浸出体系。
由Fe3++SO42-=FeSO4+可得出:
 (1)
(1)
由Fe3++2SO42-=Fe(SO4)2-可得出:
 (2)
(2)
由SO42-+H+=HSO4-可得出:
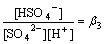 (3)
(3)
[Fe3+]T=[ Fe3+]+[FeL2]+[FeL] (4)
[SO42-]T=[ SO42-]+[HSO42-]+2[FeL2]+[FeL] (5)
式中:[ ]表示浓度,mol/L;β1,β2和β3为常数,分别为105.4,104.0和101.997。经过计算,Fe3+与络阴离子Fe(SO4)2-质量浓度的关系见表1。尽管上述络合平衡式的温度为25 ℃,但在本研究温度65 ℃下,随着浸出液Fe3+质量浓度的增大,其络合离子Fe(SO4)2-质量浓度也相应增大,可以通过上述配位方程得到具体的络合离子质量浓度。
表1 浸出液中Fe3+与Fe(SO4)2-质量浓度的关系
Table 1 Relationship between mass concentration of Fe3+ and Fe(SO4)2- in leaching liquid mg/L

2.2 对浸出液进行超滤-离子交换处理的浸出
本实验在浸出过程中对Mo的控制是通过MBR的超滤和离子交换作用,分别经高超滤-离子交换量、中等超滤-离子交换量和低超滤-离子交换量的处理后,观察3种情形的镍和钼的浸出率,从中得出对浸出液超滤-离子交换量与镍、钼浸出率的关系。
2.2.1 较高膜超滤量(35%左右)处理的浸出
本组浸出从浸出液中超滤、离子交换的浸出液体积较多,即交换量和交换率较高,使浸出液的钼质量浓度控制至很低,见表2。这样,在整个浸出过程中,每次超滤、离子交换处理的时间及处理前后的Ni,Mo和Fe质量浓度的变化如表3所示,20 d后的浸出率如表4所示。
从表2可以看出:从浸出的第6 d开始进行超滤交换处理,从第1次的1 200 mL到第7次的1 675 mL,交换率从26.37%逐渐递增,最高时达到第13 d的38.57%,总超滤量达到10 974 mL。每次超滤交换处理前后的Mo和Fe质量浓度都有较大变化,如表3所示。例如,第7 d超滤交换出理前的Mo质量浓度为0.107 g/L,而超滤和离子交换1 488 mL后,体系浸出液中的Mo质量浓度下降至0.076 g/L。通过7次间歇式处理,在整个浸出过程中,Mo质量浓度都维持在很低值。这种膜超滤-离子交换处理对浸出液中的总Fe 吸附较多,如第11 d超滤-交换前总Fe质量浓度为0.293 g/L,而交换处理后,总Fe质量浓度下降为0.231 g/L。只有Ni不被树脂吸附,交换前后的质量浓度变化不大。这是上述浸出液中存在的离子形态及络合质量浓度所致。此外,Mo8O264-和[PMo12O40]3-等多钼酸根离子能与Fe3+和Fe2+形成配合物,都影响Fe3+和Fe2+的质量浓度、对矿物的浸出能力以及浸出液的电位。Ni的存在形式为Ni2+,不能被阴离子交换树脂吸附。在该浸出液体系中,各种价位的Fe离子的氧化还原反应直接影响浸出液中Fe3+和Fe2+的质量浓度。因为两者都有可能被络合而成为络阴离子Fe(SO4)2-和 FeCl4-,其中Fe3+半径较大,所带电荷较多,比Fe2+更易被络合,这是浸出液中Fe3+与Fe2+质量浓度比的决定性因素之一,也是导致镍钼矿生物浸出中电位较低的原因之一。实验结果表明:在该矿的摇瓶细菌浸出时,电位总体不高,最高也没有超过500 mV。在这样的处理条件下,经过20 d的细菌浸出,其Ni和Mo的浸出率比在同一条件下柱浸的浸出率低,如表4所示。这说明尽管通过超滤和离子交换处理大量的浸出液,使浸出液中的Mo质量浓度保持在很低值,但在超滤和离子交换处理的同时,也吸附了一定量的Fe离子,从而影响了浸出液维持较高的电位。较高的电位对于Ni和Mo的浸出是必要的。
表2 35%超滤时膜超滤、离子交换处理时间与处理料液量情况
Table 2 Ultrafiltrated and ion-exchanged leaching liquid in different time at 35% ultrafiltration

表3 35%超滤时浸出液中超滤-交换处理前后Ni,Mo和Fe的质量浓度
Table 3 Mass concentration change of Ni,Mo and Fe before and after ultrafiltrated and ion-exchange at 35% ultrafiltration
g/L

表4 35%超滤时MBR和柱浸中镍和钼的浸出率
Table 4 Leaching rate of Ni and Mo in MBR and column at 35% ultrafiltration %

在35%超滤条件下,本研究将膜超滤-离子交换与另一组柱浸的Ni,Mo和Fe离子质量浓度变化进行比较,3种离子分别在膜浸出和柱浸出过程中的质量浓度变化情况如图4~6所示。从图4可以看出:MBR浸出和柱浸浸出液中的Ni质量浓度有差异,在超滤-交换处理条件下,MBR浸出液中的Ni质量浓度比柱浸的低。这可能是因为膜超滤和离子交换所吸附的Fe离子影响了浸出液中的Fe离子反应的平衡,最终使浸出液中的Fe3+质量浓度和体系的电位降低。而对于硫化镍的细菌浸出,主要是通过Fe3+和H+的作用所致。从图5可见:在MBR的浸出过程中,膜超滤和离子交换除去了大量的钼,使浸出液中的Mo质量浓度较低。第9 d时,MBR中的Mo质量浓度只有0.105 g/L,而同条件的柱浸9 d浸出液中的Mo质量浓度达到0.377 g/L;第11 d时,MBR浸出液中的Mo质量浓度仅为0.095 g/L,而这时的柱浸Mo质量浓度为0.409 g/L。此时,柱浸中细菌的代谢和氧化亚铁的能力受到了浸出液中Mo质量浓度的抑制,而MBR中的Mo由于质量浓度很低,远没有达到细菌的耐受程度。从这个意义上,膜超滤-离子交换达到了除钼的目的,对细菌的生长代谢很有利。但由于在膜超滤与离子交换的同时,也吸附走了大量的Fe离子,这对镍钼矿的Ni和Mo浸出是不利的。

图4 35%超滤时MBR和柱浸过程中Ni质量浓度的变化
Fig.4 Mass concentration of Ni in leaching process of MBR and column at 35% ultrafiltration

图5 35%超滤时MBR和柱浸过程中Mo质量浓度的变化
Fig.5 Mass concentration of Mo in leaching process of MBR and column at 35% ultrafiltration

图6 35%超滤时MBR和柱浸过程中Fe质量浓度的变化
Fig.6 Mass concentration of total Fe in leaching process of MBR and column at 35% ultrafiltration
2.2.2 中等膜超滤量(18%左右)处理的浸出
本实验的膜超滤和离子交换的浸出液体积比前面的小,浸出液中的钼质量浓度有所提高,在此条件下研究浸出过程中主要离子质量浓度的变化以及Ni和Mo的浸出率。在MBR浸出过程中,超滤和离子交换情况如表5所示。与表1相比,该实验过程中所超滤和离子交换量大大减小,其中交换量都在20%以下,总处理浸出液的量下降至5 710 mL。在浸出过程中,交换前后Ni,Mo的Fe的质量浓度以及Ni和Mo浸出率分别如表6和表7所示。从表6可以看出:除Ni外,Mo和Fe在交换前后的质量浓度变化比较明显。例如,第6 d交换处理前,Mo和Fe质量浓度分别为0.206 g/L和0.254 g/L,而离子交换处理后Mo和Fe质量浓度分别下降为0.189 g/L和0.185 g/L。而与同期相比,交换前后Mo,Ni和Fe的质量浓度与上一次相比均明显提高。以浸出过程中的第13 d为例,上一次交换处理前的Mo,Ni和Fe质量浓度分别为0.081,0.424和0.289g/L,而此次分别上升为0.244,0.499和0.363 g/L。20 d浸出结束时,MBR中Ni和Mo浸出率分别为74.70%和50.97%;柱浸中Ni和Mo的浸出率分别为75.59%和54.07%。MBR的Ni和Mo浸出率虽仍不及柱浸时的大,但比上一次的浸出率明显提高。
在浸出过程中,MBR以及柱浸的Ni,Mo和Fe离子质量浓度分别如图7~9所示。从图7可见:MBR和柱浸过程中浸出液的Ni质量浓度有差异,前者比后者的低,但两者差距比上一次高交换率的浸出明显缩小;浸出13 d时,MBR浸出液中Ni质量浓度为459.92 mg/L,而同条件下的柱浸浸出液中Ni质量浓度为493.05 mg/L。在浸出过程中,超滤-离子交换除去一部分钼后,MBR浸出液中的Mo质量浓度与上一次相比大大提高,如图8所示。当浸出13 d时,MBR浸出液中的钼质量浓度达到244.23 mg/L。而柱浸浸出液中的Mo质量浓度达到436 mg/L。MBR与柱浸相比,钼质量浓度低许多,对细菌的生长代谢比较有利,但同时被交换树脂吸附了较多的Fe (络合阴离子),影响了各种Fe离子的氧化还原反应平衡,促进了Fe3+向络合阴离子的转化,降低了MBR浸出液中总铁离子的质量浓度(如图9所示),从而降低了体系的电位,最终导致MBR浸出的Ni和Mo的浸出率比柱浸的低。
表5 18%超滤时膜超滤量、离子交换处理时间与处理料液体积的关系
Table 5 Relationship between ultrafiltratered and ion-exchanged leaching liquid and time at 18% ultrafiltration
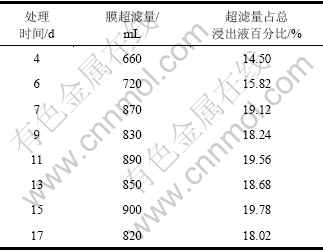
表6 18%超滤时MBR浸出过程中浸出液中交换处理前后的Ni,Mo和Fe的质量浓度
Table 6 Concentration change of Ni, Mo, Fe before and after ultrafiltrated and ion-exchange at 18% ultrafiltration g/L

表7 18%超滤时MBR和柱浸中镍和钼的浸出率
Table 7 Leaching percent of Ni and Mo in MBR and column at 18% ultrafiltration %


图7 18%超滤时MBR和柱浸浸出过程中Ni 质量浓度变化
Fig.7 Mass concentration of Ni in leaching process at 18% ultrafiltration

图8 18%超滤时MBR和柱浸浸出过程中Mo质量浓度变化
Fig.8 Mass concentration change of Mo in leaching process of MBR and column at 18% ultrafiltration
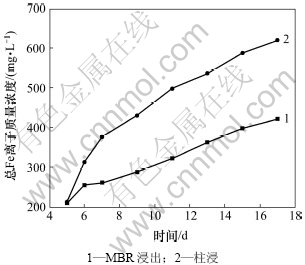
图9 18%超滤时MBR-离子交换处理和柱浸浸出过程中总Fe离子质量浓度变化
Fig.9 Mass concentration change of total Fe in leaching process of MBR and column at 18% ultrafiltration
2.2.3 低膜超滤量(10%左右)处理的浸出
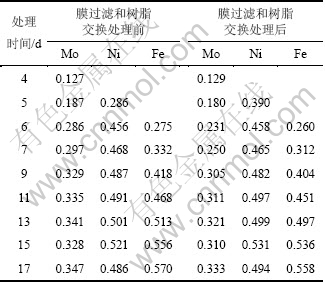
从前2次的浸出可以看出:在一定范围内,MBR方式的Ni和Mo浸出率与超滤-离子交换率成反比关系,即离子交换处理的浸出液较少,Ni和Mo的浸出率上升。本实验对MBR(膜生物反应器)浸出液采取更低的超滤和离子交换量,每次交换处理的浸出液大多在10%以下,处理的总浸出液为3 015 mL,每次处理量如表8所示。处理前后Ni,Mo和Fe的质量浓度及Ni和Mo的浸出率分别如表9和表10所示。从表9可见:浸出液中钼质量浓度与前2次的相比有所提高,浸出9 d时,钼质量浓度达到0.33 g/L,比上一次同期提高24.31%,超滤-交换处理的除钼效果仍然明显。如在浸出11 d交换处理前MBR中的Mo质量浓度为0.34 g/L,交换后为0.31 g/L;浸出17 d时,交换处理前的MBR中Mo质量浓度为0.35 g/L,交换后下降至0.33 g/L。此时,钼质量浓度还没有对细菌的代谢产生抑制,但浸出液中的总铁离子质量浓度进一步提高。10%超滤时MBR和柱浸中Ni和Mo的浸出率如表10所示,10%超滤时MBR和柱浸浸出过程中Ni 和Mo的质量浓度分别如表11和表12所示。从表10可以看出,在10%超滤和离子交换处理条件下,MBR的Ni和Mo浸出率均比柱浸的高,表明对MBR浸出液的处理控制了浸出液中的钼质量浓度,而Fe离子质量浓度减小较少,使MBR浸出体系的细菌生长环境和矿物的浸出环境和电位都处于比柱浸更有利的状态。
表8 10%超滤时膜过滤量和离子交换处理时间与处理料液体积的关系
Table 8 Relationship between ultrafiltrated and ion- exchanged leaching liquid volume and treating time at 10% ultrafiltration
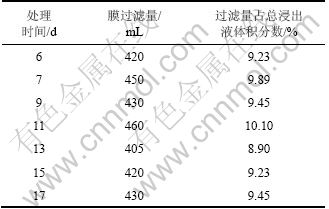
表9 10%超滤时MBR浸出过程中浸出液中交换处理前后Ni,Mo和Fe质量浓度
Table 9 Mass concentration change of Ni, Mo, Fe before and after ultrafiltrated and ion-exchange at 10% ultrafiltration
g/L
2.3 MBR和柱浸的电位变化
从表11和表12可见:在柱浸过程中,Ni和Mo的质量浓度都比MBR的高,当浸出 11 d时,柱浸浸出液中的Mo质量浓度达428.50 mg/L,而实验表明该菌所能耐受的最大钼质量浓度为395~400 mg/L,这对细菌的代谢产生了一定的抑制作用,细菌氧化亚铁的能力将开始下降。因此,当浸出13 d时,柱浸浸出液的电位开始下降,而MBR浸出的低交换处理浸出的电位一直上升,直到18 d才开始下降。而在MBR浸出中的高、中等程度的膜过滤和离子交换处理组浸出中,尽管细菌氧化亚铁的能力不受影响,但由于被吸附除去较多Fe络阴离子,这部分Fe络阴被离子交换作用所吸附而降低了Fe3+质量浓度。加之在浸出后期,细菌氧化亚铁的能力下降,导致Fe3+与Fe2+的质量浓度之比下降,因此,浸出液的电位一直变化较小而不利于Mo的浸出,各组的电位变化情况如图10所示。10%超滤时MBR-离子交换处理和柱浸浸出过程中总Fe离子质量浓度变化如表13所示。从表13可以看出:浸出液中的总Fe质量浓度与高、中交换处理量的相比明显提高,而且交换前后的差异比前2次减小。例如,浸出15 d交换前为0.56 g/L,交换后为0.54 g/L,这有利于浸出液保持相对较高的电位而促进Ni和Mo的浸出,因此,其Ni和Mo浸出率有所提高。
表10 10%超滤时MBR和柱浸中Ni和Mo的浸出率
Table 10 Leaching rate of Ni and Mo in MBR and column at 10% ultrafiltration %

表11 10%超滤时MBR和柱浸浸出过程中Ni 的质量浓度
Table 11 Concentration change of Ni in leaching process of MBR and column at 10% ultrafiltration mg/L
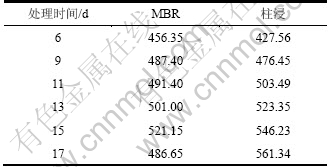
表12 10%超滤时MBR和柱浸浸出过程中Mo的质量浓度
Table 12 Mass concentration change of Mo in leaching process of MBR and column at 10% ultrafiltration mg/L

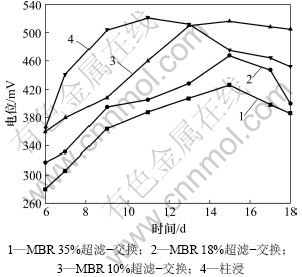
图10 MBR 和柱浸过程中的电位变化
Fig.10 Change of electric potential in leaching process of MBR and column
表13 10%超滤时MBR-离子交换处理和柱浸浸出过程中总Fe离子质量浓度变化
Table 13 Mass concentration change of total Fe ion in leaching process of MBR and column at 10% ultrafiltration
mg/L

3 结论
(1) 超滤和离子交换处理浸出液可以将钼质量浓度控制在较低值,有利于细菌的生长和代谢。但交换处理量必须适当,否则将因为吸附掉大量的铁络阴离子而影响总铁离子和Fe3+质量浓度,从而影响对镍和钼的浸出。将MBR浸出液离子交换率控制在10%左右时,镍和钼的浸出率较高,并超过了同条件下柱浸的浸出率。
(2) 超滤和离子交换处理的程度也影响浸出液中的电位变化。30%以上高离子交换率的电位明显比10%左右低交换处理率的电位低,可以断定:增大被树脂吸附的铁络阴离子质量浓度,改变了浸出液中铁的氧化还原反应的平衡,促进了Fe3+及Fe2+分别向Fe(SO4)2-和 FeCl4-的转化,降低了浸出液中的总铁质量浓度特别是Fe3+的质量浓度,降低了浸出液电位,从而降低了钼、铜和锌的浸出。因为这些离子的生物浸出都是通过细菌的间接作用完成的,故Fe3+是重要的氧化剂。
参考文献:
[1] 吉兆宁, 余斌, 刘坚, 等. 金堆城低品位钼矿石可浸性研究[J]. 有色金属, 2002(5): 15-19.
JI Zhao-ning, YU Bin, LIU Jian, et al. The leachable study on lower grade molydenum mineral of Jingduicheng[J]. Nonferrous Metal, 2002(5): 15-19.
[2] Mishra D, Kim D J, Ralph D E. Bioleaching of vanadium rich spent refinery catalysts using sulfur oxidizing lithotrophs[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2007, 88(1/2/3/4): 202-209.
[3] Nasernejad B, Kaghazchi T. Bioleaching of molybdenum from low-grade copper ore process[J]. Process Biochemistry, 1999, 35(5): 437-440.
[4] Zamani M A A, Hrroyoshi N, Tsunekawa M. Bioleaching of Sarcheshmeh molybdenite concentrate for extraction of rhenium[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2005, 80(1/2): 23-31.
[5] 杨显万, 沈庆峰, 郭玉霞. 微生物湿法冶金[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2003: 240-241.
YANG Xian-wang, SHEN Qin-feng, GUO Yu-xia. Microbe hydrometallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2003: 240-241.
[6] Donati E, Gurutchet G, Porro S, et al. Bioleaching of metallic sulfides with T. ferrooxidans in the absence of iron (Ⅱ)[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 1992, 98: 305-308.
[7] Silverman M P, Lundgren D G. Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium T. ferrooxidans (Ⅰ). An improved medium and harvesting procedure for securing high cell yield[J]. J Bacterial, 1959, 77: 642-647.
[8] ZHAO Zhong-wei, ZHANG Gang, HUO Guang-sheng, et al. Kinetics of atmospheric leaching molybdenum from metalliferous black shales by air oxidation in alkali solution[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 97: 233-236.
[9] ZHAO Zhong-wei, LI Jiang-tao, CAO Cai-fang, et al. Recovery and purification of molybdenum from Ni-Mo ore by direct air oxidation in alkaline solution[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 103: 68-73.
[10] 陈家武, 高从堦, 肖连生, 等. 硫化叶菌对镍钼硫化矿的浸出作用[J]. 过程工程学报, 2009(2): 257-263.
CHEN Jia-wu, GAO Cong-jie, XIAO Lian-sheng, et al. Leaching of nickel-molybenum with sulfolobus metallicus[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2009(2): 257-263.
[11] Yasuhiro K, Masshiko T, Satoru A, et al. Copper recovery from chalcopyrite concentrate by acidophilic thermophile Acidianus brierleyi in batch and continuous-flow stirred tank reactors[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2001, 59(2/3): 271-282.
[12] Yasuhiro K, Kouji K,Satoru A. Bioleaching of pyrite by Acidianus brierleyi in a continuous-flow stirred-tank reactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1997, 52(24): 4525-4532.
[13] Mark D, Lars L, Dan B. Silicate mineral dissolution in the presence of acidophilic microorganisms: Implications for heap bioleaching[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 96(4): 288-293.
[14] Astudillo C, Acevedo F. Adaptation of sulfolobus metallicus to high pulp densities in the biooxidation of a flotation gold concentrate[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 92(1/2): 11-15.
[15] Norris P R, Burton N P, Foulis N A M. Acidophiles in bioreactor mineral processing[J]. Extremophiles, 2000, 4(2): 71-76.
[16] Le L, Tang J, Ryan D, et al. Bioleaching nickel laterite ores using multi-metal tolerant Aspergillus foetidus organism[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 19(12): 1259-1265.
[17] 朱元保, 沈子琛, 张传福, 等. 电化学数据手册[M]. 北京: 中国教育出版社, 1984: 142-158.
ZHU Yuan-bao, SHEN Zi-chen, ZHANG Chuan-fu, et al. Electrochemistry data handbook[M]. Beijing: Education Industry Press of China, 1984: 142-158.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2011-08-15;修回日期:2011-10-22
基金项目:国家高技术研究发展计划(“863”计划)项目(2007AA06Z129)
通信作者:肖连生(1955-),男,湖南衡阳人,教授,从事冶金工程研究;电话:0731-88830143;E-mail: XLS1211@sina.com