文章编号: 1004-0609(2005)04-0596 -07
多组分铜基金属粉末选区激光烧结致密化机理
顾冬冬1, 沈以赴1, 杨家林2, 王 洋2
(1. 南京航空航天大学 材料科学与技术学院, 南京 210016;2. 中国工程物理研究院 机械制造工艺研究所, 绵阳 621900)
摘 要: 研究了选区激光烧结专用多组分铜基金属粉末(组分包括纯Cu, 预合金CuSn, CuP)的烧结性能。 结果表明, 通过合理控制激光工艺参数(特别是激光功率和扫描速率), 能顺利实现粉末烧结成形, 且无明显的“球化”效应和翘曲变形。 扫描电镜和X射线衍射分析证实, 此组粉末体系的激光烧结是基于液相烧结机制, 其中熔点较低的CuSn充当粘结金属, 熔点较高的Cu充当结构金属; 而添加元素P则起稀释剂的作用, 能避免Cu颗粒表面氧化。 研究了粉末体系中粘结金属含量对粉末烧结致密化和烧结件微观组织的影响。 结果表明, 在一定范围内粘结金属含量的提高有利于改善烧结致密度; 但若粘结金属过量, 则会因“球化”效应而降低致密度。
关键词: 快速原型制造; 选区激光烧结; 铜基金属粉末; 液相烧结; 添加剂 中图分类号: TG14; TG665
文献标识码: A
Densification mechanism of multi-component Cu-based metal powder
in selective laser sintering process
GU Dong-dong1, SHEN Yi-fu1, YANG Jia-lin2, WANG Yang2
(1. College of Materials Science and Technology, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China;
2. Institute of Machinery Manufacturing Technology,China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China)
Abstract: Selective laser sintering of a special multi-component Cu-based metal powder which consists of high-purity Cu, pre-alloyed CuSn and CuP was processed. The experimental results show that choosing suitable laser processing parameters, especially laser power and scanning rate, can effectively control “balling” effect and curling deformation during laser sintering. The scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analyses show that the bonding mechanism of this process is liquid phase sintering, during which the Cu powder with higher melting point acts as the structure metal; while the CuSn powder with lower melting point acts as the binder. The element phosphorus acts as fluxing agent to react with oxygen, preventing the Cu particles form oxidation. The influence of the content of binder in powder system on the densification and attendant microstructural features of the sintered samples was investigated. It is found that with the increase of the binder content, the microstructures become denser; however, an excess of binder results in “balling” phenomena, hence damaging the densification.
Key words: rapid prototyping; selective laser sintering; Cu-based metal powder; liquid-phase sintering; additive
选区激光烧结(Selective laser sintering, SLS)作为快速原型制造技术的重要分支, 能直接烧结金属粉末, 成形高致密度三维零部件, 而一般不需要或很少需要炉中热处理强化和金属二次熔浸等辅助工艺手段, 故在缩短生产周期、 快速响应市场需求、 及削减生产成本方面具有显著优势[1, 2]。 目前, SLS技术正被广泛用于快速模具制造[3, 4], EDM电极制造[5], 梯度功能材料制造[6], 以及航空、 航天和其他装备用高性能关键金属零部件的集成制造领域[1, 7]。
液相烧结机制通常被认为是金属粉末选区激光烧结惟一可行机制[2, 8, 9]。 早先的研究集中于Ni, Cu, Pb, Sn, Zn[9, 10]等单组分金属粉末, 但因其在SLS过程中液相粘度较高、 表面张力效应明显, 故“球化”现象严重, 因而具有明显的工艺缺陷; 目前一般通过使用预合金粉末体系或多组分金属粉末体系来加以克服。 尽管如此, 金属粉末在采用SLS技术中普遍存在“球化”效应和翘曲变形, 使得精确成形形状复杂的金属零件仍有较大难度。 究其原因, 在材料方面, 目前的研究一般仅选用市售粉末冶金材料作为实验原材料, 因其并非专门为选区激光烧结而设计, 故其化学成分和物理性能一般难以满足SLS技术的特殊要求, 从而直接影响烧结过程和烧结质量[11]; 在激光工艺参数方面, 已有的研究[12, 13]一般是采用高功率激光(实际使用功率在1kW以上)对金属粉末进行多层熔覆而构建三维实体, 而高功率激光的引入不可避免地导致烧结过程中“球化”效应明显, 同时烧结件中过高的热应力导致翘曲变形严重, 甚至出现开裂。
金属粉末选区激光烧结涉及复杂的化学冶金和物理冶金过程, 原始粉末特性和激光工艺参数共同影响和决定烧结致密化过程和烧结件微观特征, 两者的作用相辅相成[3, 11]。 本文作者在制备SLS专用多组分铜基金属粉末的基础上, 选取合适的激光工艺参数对其进行烧结实验, 结合对烧结试样显微组织的分析, 优化粉末组分; 并探讨多组分金属粉末SLS致密化机理, 提出控制工艺缺陷、 改善烧结性的方法。
1 实验
1.1 材料
实验材料为多组分铜基金属粉末, 包括以下3种组分: 纯度为99%的电解铜粉, 其外形呈不规则状, 粒度为50~80μm; 水雾化CuSn预合金粉末(10%Sn), 粒度为10~40μm, 且呈高斯分布; 气雾化CuP预合金粉末(8.4%P), 其平均颗粒直径为20μm, 添加元素P以与基体元素Cu固溶的形态加入粉末体系, 作为稀释剂或脱氧剂而改善烧结性。 将Cu, CuSn和CuP按4组不同的质量比加以混合。
将满足质量配比的各组分粉末置于旋转式真空混粉设备的圆柱形型腔内加以混合, 通过调节设备旋转速度、 保证足够的混粉时间以实现混粉均匀性。
1.2 实验方法
使用北京隆源自动成型系统有限公司生产的激光快速成型机。 烧结系统主要包括连续CO2激光(λ=10.6μm), 最大输出功率为1kW, 且功率连续可调; 双缸自动铺粉装置, 即包括供粉缸和成形缸。 烧结过程中, 铺粉滚筒将供粉缸中的金属粉末均匀铺放于成形缸的基板上, 激光束根据零件第一层数据信息有选择地烧结粉层某一区域, 以形成零件的一个水平方向的二维截面; 随后成形缸活塞下降一定距离, 供粉缸活塞上升相同距离, 铺粉滚筒再次将粉末铺平, 激光束开始依照零件第二层信息扫描粉末; 如此反复叠加, 直至零件实体制造完毕。
激光烧结在室温下进行, 且不加保护气氛。 所用工艺参数为: 激光功率50~800W, 激光光斑直径0.3mm, 扫描速率0.01~0.10m/s, 扫描间距0.15mm, 铺粉厚度0.25mm。 实验中首先进行粉末单层烧结, 以确定合理的工艺参数, 进而制备多层烧结试样。 用于金相分析的试样依照规定程序制备, 腐蚀剂选用含FeCl3 5g, HCl 10mL, 蒸馏水100mL的溶液, 腐蚀时间30s。 原始粉末和烧结试样的物相利用BRVKER D8 ADVANCE型X射线衍射仪来表征。 试样的显微组织利用QUANTA 200型扫描电镜以及光学显微镜加以分析, 其元素分布利用EDAX型能谱来表征。 烧结件致密度利用阿基米德定律来测算。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 单层烧结及工艺参数确定
图1所示为激光功率在50~500W、 扫描速率在0.01~0.06m/s之间连续可调的条件下, 单层烧结粉末体系(Cu, CuSn, CuP质量比为60∶30∶10)所获得的工艺实验结果。 由于SLS是采用激光作为热源, 基于激光束的持续移动来逐行、 逐层烧结成形金属粉末, 故激光功率和扫描速率对烧结过程和成形质量影响尤为显著[9]。 根据工艺实验中单层烧结的熔凝特征, 可将整个激光功率-扫描速率变化区间分为下列5个区域:
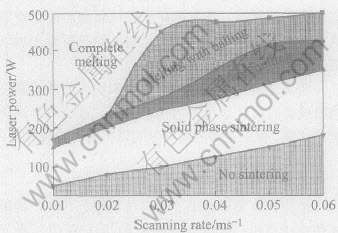
图1 一定激光功率和扫描速率下的工艺实验结果
Fig.1 Experimental results obtained within a range of laser powers and scanning rates
1)无烧结区: 即激光能量不足以对粉层产生任何影响。
2)固相烧结区: 即激光能量能对粉层产生影响, 但不足以使金属粉末发生熔化, 粉末之间仅发生部分微粘连。
3)部分熔化区: 即激光能量使金属粉末发生部分熔化而生成适量液相, 通过液相的“桥接”作用而粘结未熔固相颗粒实现烧结致密化(图2(a))。
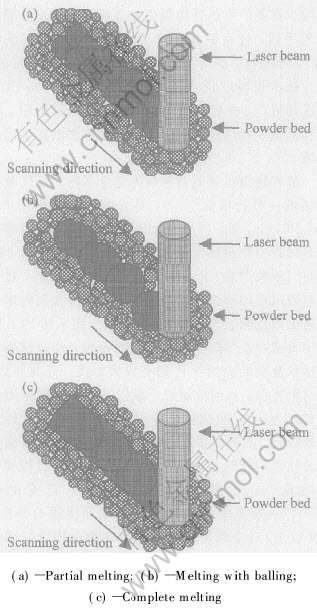
图2 激光烧结过程中粉末熔化方式
Fig.2 Melting of metal powder during laser processing
4)球化区: 即激光能量虽未使金属粉末完全熔化, 但生成过量的液相; 在较高的扫描速率下, 形成圆柱形金属熔化轨迹, 因表面能的降低所引起的液柱不稳定性会使其分裂成直径近似于光斑直径的球状, 即发生“球化”(图2(b))。
5)完全熔化区: 即激光能量使金属粉末完全熔化形成连续的液柱, 较之于球化区, 液柱在较长的间隔内发生断裂, 从而也形成非连续烧结线(图2(c))。
典型的粉末固相烧结一般涉及高温下原子沿颗粒表面、 晶界及其他途径的扩散传质等过程。 但因原子扩散速度缓慢, 欲实现粉末烧结致密化, 所需时间较长(一般需数小时)[9]。 而在SLS过程中, 激光在任一粉末颗粒上的持续辐照时间极短, 通常在0.5~25ms之间[9], 在如此短暂的热循环之下, 快速粘结机制是必需的, 这只能通过液相烧结来实现。 考虑到在球化区和完全熔化区内, 烧结件普遍具有孔隙率高、 微观裂纹明显、 氧化夹杂严重等工艺缺陷[11], 因此采取粉末部分熔化的方式, 并合理控制液相量, 是金属粉末SLS的惟一可行的机制。 对于多组分金属粉末, 一般由高熔点金属(结构金属)、 低熔点金属(粘结金属)及某些添加元素混合而成, SLS过程中仅有粘结金属熔化形成液相, 从而粘结未熔结构金属以实现烧结致密化。
当扫描速率较低时(0.01~0.03m/s), 欲仅使粉末体系中的粘结金属发生熔化, 对激光功率的控制极为严格; 而当扫描速率较高时, 激光功率变化区间则较宽, 烧结过程亦便于控制(图1)。 结果表明, 当扫描速率为0.04, 0.05和 0.06m/s时, 若对应的激光功率范围分别为275~350W, 315~400W和350~425W, 均能通过粉末部分熔化的液相烧结机制实现烧结致密化。
2.2 多层烧结及分析
2.2.1 烧结试样
基于工艺实验结果, 优化工艺参数(激光功率350W, 扫描速率0.05m/s), 对上述粉末体系进行多层(40层)烧结, 制备了尺寸为45mm×20mm×10mm的试样, 如图3所示。

图3 烧结试样实物图
Fig.3 Selective laser sintered sample
2.2.2 物相分析
图4所示为原始粉末体系和激光烧结试样的X射线衍射谱。 由图4(a)可见, 粉末体系中的物相主要包括Cu, Cu41Sn11和Cu3P。 Cu因其熔点相对较高, 能在SLS中保留其硬质核心, 故作为结构金属; Cu41Sn11的熔点相对较低, 则作为粘结金属; 而Cu3P则是预合金CuP的初始共晶组成相。
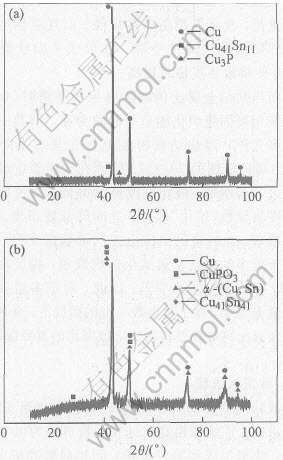
图4 原始粉末(a)和烧结试样(b)的X射线衍射谱
Fig.4 XRD pattern of starting powder(a) and laser-sintered sample(b)
由图4(b)可以看出, 在烧结试样中出现一种新物相α-(Cu, Sn), 而初始相Cu41Sn11仍存在。 这是由于SLS过程中激光能量与粉层的作用时间极其短暂, 原始粉末体系中的粘结金属Cu41Sn11未能完全熔化; 而熔化生成的液相则以α-(Cu, Sn)的形态析出。 图4(b)还表明, 添加元素P在烧结后以CuPO3的形态存在, 而铜的氧化物CuO或Cu2O并未出现。 这是因为P元素起稀释剂或脱氧剂的作用, 而优先与氧反应生成CuPO3。 此反应使得在液相烧结过程中金属颗粒表面能避免氧化, 进而能形成金属-金属接触界面, 显著改善液相对固相的润湿性, 提高烧结致密度。 X射线衍射分析结果表明, 由于原始粉末体系中加有合适的烧结添加元素, 实验中虽未通有保护气氛, 但对烧结质量无不利影响。
2.2.3 微观组织分析
图5所示为上述烧结试样典型的表面形貌。 由图可见, 未熔固相颗粒间通过液相凝固后生成的“烧结颈”而形成有效连接。 这是因为在SLS过程中, 激光能量使粘结金属发生熔化而形成液相, 液相包覆并润湿结构金属颗粒, 使其表面的棱角和凸出部位发生溶解, 并发生快速颗粒重排。 未熔固相颗粒核心通过液相的“桥接”作用而形成“烧结颈”, 以此实现颗粒间的粘结; 图5较好地验证了图2(a)提出的SLS成形机制。

图5 烧结试样的表面形貌
Fig.5 Surface morphology of sintered sample
图6所示为不同放大倍数下烧结试样的显微组织。 由图6(a)可见, 尽管图3显示烧结试样表面较为粗糙, 但其内部的显微组织则较为致密, 其中无明显的孔隙分布。 对图6(b)的能谱分析表明, 图中浅灰色部位(区域A)只分布有Cu元素, 而深灰色部位(区域B)则为Sn元素富集区。 可见, SLS过程中粘结金属CuSn熔化形成的液相已渗入结构金属Cu颗粒之间, 液相凝固组织成连续的网络状分布, 以此充分粘结未熔Cu颗粒。 这进一步说明液相烧结机制为此组铜基金属粉末SLS的可行机制。
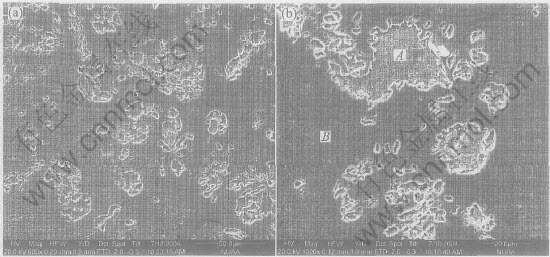
图6 不同放大倍数下烧结试样的显微组织
Fig.6 Microstructures of sintered sample with different magnifications
2.2.4 粘结金属含量对烧结致密化的影响
图7所示为不同粘结金属含量下烧结试样的显微组织。 制备各试样所用激光功率350W, 扫描速率0.05m/s, 而激光线扫描方式如图8所示。 图9所示为烧结试样的致密度随粘结金属含量的变化。 由于此组铜基金属粉末SLS沿用液相烧结机制, 因此生成的液相量(受粘结金属含量控制)将直接影响液相表面张力、 粘度、 润湿性等, 进而影响烧结致密度和烧结件微观组织(如孔隙形状和大小、 烧结线连续性等)。

图7 不同粘结金属含量下的烧结试样微观组织
Fig.7 Microstructures of sintered samples with variation of binder content

图8 激光扫描方式示意图
Fig.8 Schematic of scanning pattern used for laser sintering
当粘结金属含量较低时(10%), 单条扫描线中的液相凝固组织呈断续的窄条状分布, 而相邻两条烧结线之间几乎未有粘结, 其间充满大量连续分布的孔隙, 如图7(a)所示; 试样烧结致密度仅为理论密度的64.8%。 其原因在于, 由于粘结金属CuSn含量偏低, 其熔化形成的液相只能用于粘结在其周围的Cu颗粒, 故只能形成断续的凝固组织; 同时由于液相量偏少, 难以使得Cu颗粒发生重排, 导致大量孔隙存在于烧结件中。
随着粘结金属含量的增加(20%), 烧结试样中不存在连续分布的孔隙, 但整个凝固组织仍呈明显的条状分布。 单条烧结线的凝固组织连续性得以提高, 而相邻两条烧结线间的粘结性则较低, 其间仍分布有小尺寸的孔隙, 如图7(b)所示; 试样烧结致密度则增至理论密度的74.3%。 这是因为随着生成的液相量增加, 液相粘度降低, Cu颗粒位置发生重排, 并随液相迁移至激光扫描线的中心地带, 凝固后形成连续烧结线。
当粘结金属比例增至适量时(30%), 烧结试样中无明显的孔隙, 凝固组织中不再出现烧结线轨迹, 而是呈完整的平面状分布, 其组织均匀性显著提高, 如图7(c)所示; 烧结致密度达理论密度的83.6%。 此时由于生成足够的液相量, 液相不仅能完全包覆并润湿单条烧结线中的Cu颗粒, 加速其颗粒重排, 改善颗粒间的粘结性; 而且液相足以填充相邻烧结线之间的空隙, 以形成平面状凝固组织, 并使得致密度显著提高。
而当粘结金属比例继续增至较高量时(40%), 虽然液相凝固组织仍能呈平面状分布, 但其中分布有较多孔隙; 而烧结致密度也存在显示下降的趋势, 为理论密度的78.7%。 原因在于随着生成的液相量进一步增加, 液相粘度显著降低, 而过低的液相粘度将导致“球化”效应, 进而降低致密度。 实验中还发现, 此时烧结试样出现局部翘曲变形, 原因是由于更多的粘结金属熔化形成液相, 粉层收缩加剧, 故导致发生烧结变形。 因此, 对于多组分金属粉末激光烧结, 在工艺参数一定的前提下, 合理控制粘结金属比例是获得较高烧结致密化的重要保证。
2.3 致密化机理
液相烧结机制是多组分金属粉末体系SLS的可行机制。 传统液相烧结过程大致可分为以下3个阶段: 液相生成和颗粒重排; 固相溶解和析出; 固相骨架形成。 但因SLS热循环过程极为短暂, 液相的生成与凝固过程极快, 因此仅有传统液相烧结的第一阶段对金属粉末SLS致密化过程起主导作用[2, 9, 11]。 在SLS起始阶段, 随着激光能量注入某一烧结区域, 粉层内熔点较低的粘结金属即发生熔化。 随着更多的液相沿着粘结金属的晶界和颗粒间的接触面而生成, 原始粉末体系的刚性“骨架”即发生坍塌, 进而引起粉层收缩、 孔隙率降低。 当粘结金属完全熔化时, 液相包覆并润湿固相颗粒, 由于液相所施加的毛细管力及其自身的粘性流动, 结构金属颗粒重排加速, 这将引起粉层致密化程度进一步提高。
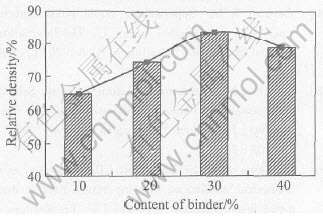
图9 烧结试样致密度随粘结金属含量的变化
Fig.9 Variation of density of laser-sintered samples with content of binder SLS
过程中生成的液相量将直接影响烧结热力学和动力学特征, 如液相粘度、 润湿性、 固液混合体系流动性等, 进而影响烧结件致密化程度[2, 9]。 若有足量液相生成, 且液相粘度较低, 固液体系具有良好的整体流动性, 则液相能均匀弥散在固相颗粒四周, 进而能显著改善润湿性、 提高颗粒重排率及最终致密化程度。 对于激光烧结件, 其最终的相对密度ds可表示为[14]

可见, 烧结件致密化程度随粉层相对密度dp和液相体积分数φl的增大而增大。 但需要指出的是, 液相体积分数不能过度增加, 否则固液混合体系粘度过低, 直接导致金属粉末SLS中的“球化”现象[15], 这将显著降低烧结致密度。
式(1)表明, 改善激光烧结致密度的途径有2种: 提高烧结前的粉层相对密度; 控制烧结过程中液相体积分数。 而有研究表明[2, 16], SLS过程中生成的液相体积分数取决于烧结温度, 在合理控制工艺参数的条件下, 则取决于粉末体系中粘结金属含量。 因此, 上述两方面问题均可在粉末制备过程中加以考虑。 在本实验中, 将各粉末组分置于真空混粉设备中长时间混合, 以获取足够的混粉均匀性, 进而提高粉末松装密度; 同时, 结合对烧结件显微组织的分析, 优化设计粉末体系中粘结金属含量。 本研究结果表明, 通过对以上两方面进行综合控制, 能使制备的激光烧结件获得较为理想的致密度。
3 结论
1)设计制备了选区激光烧结专用多组分铜基金属粉末, 组分主要包括纯Cu, 预合金CuSn和CuP。
2)通过合理控制激光工艺参数(特别是激光功率和扫描速率), 以液相烧结机制实现粉末烧结成形, 且无明显的“球化”效应和翘曲变形。
3)在一定范围内, 粘结金属含量的提高有利于改善烧结致密度和组织连续性; 但若粘结金属过量, 则会因“球化”效应而降低致密度。
REFERENCES
[1] Das S, Beaman J J, Wohlert M, et al. Direct laser freeform fabrication of high performance metal components[J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 1998, 4(3): 112-117.
[2] Zhu H H, Lu L, Fuh J Y H. Influence of binders liquid volume fraction on direct laser sintering of metallic powder[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 371(1-2): 170-177.
[3] Simchi A, Petzoldt F, Pohl H. On the development of direct metal laser sintering for rapid tooling[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 141(3): 319-328.
[4] Khaing M W, Fuh J Y H, Lu L. Direct metal laser sintering for rapid tooling: processing and characterisation of EOS parts[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2001, 113(1-3): 269-272.
[5] ZHAO Jian-feng, LI Yue, ZHANG Jian-hua, et al. Analysis of the wear characteristics of an EDM electrode made by selective laser sintering[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 138(1-3): 475-478.
[6] Pintsuk G, Brünings S E, Dring J E, et al. Development of W/Cu-functionally graded materials[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2003, 66-68: 237-240.
[7] Engel B, Bourell D L. Titanium alloy powder preparation for selective laser sintering[J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2000, 6(2): 97-106.
[8] Simchi A, Pelzoldt F, Pohl H. Direct metal laser sintering: material considerations and mechanisms of particle bonding[J]. The International Journal of Powder Metallurgy, 2001, 37(2): 49-61.
[9] Agarwala M, Bourell D, Beaman J, et al. Direct selective laser sintering of metals[J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 1995, 1(1): 26-36.
[10] Kathuria Y P. Microstructuring by selective laser sintering of metallic powder[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 1999, 116(119): 643-647.
[11] 顾冬冬, 沈以赴, 潘琰峰, 等. 直接金属粉末激光烧结成形机制的研究[J]. 材料工程, 2004, 5: 42-48.
GU Dong-dong, SHEN Yi-fu, PAN Yan-feng, et al. Research on mechanism of direct metal laser sintering[J]. Journal of Material Engineering, 2004, 5: 42-48.
[12] 张剑峰, 沈以赴, 赵剑峰, 等. Ni基金属粉末激光快速制造的研究[J]. 航空学报, 2002, 23(3): 221-225.
ZHANG Jian-feng, SHEN Yi-fu, ZHAO Jian-feng, et al. Study on laser sintering of Ni-based alloy powder[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2002, 23(3): 221-225.
[13] 张建华, 赵剑峰, 田宗军, 等. 镍基合金粉末的选择性激光烧结试验研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2004, 15(5): 431-434.
ZHANG Jian-hua, ZHAO Jian-feng, TIAN Zong-jun, et al. Experimental research on selective laser sintering of nickel-based alloy powder[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2004, 15(5): 431-434.
[14] German R M. Supersolidus liquid phase sintering(part Ⅱ): densification theory[J]. The International Journal of Powder Metallurgy, 1990, 26(1): 35-42.
[15] Tolochko N, Mozzharov S, Laoui T, et al. Selective laser sintering of single- and two-component metal powders[J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2003, 9(2): 68-78.
[16] GU Dong-dong, SHEN Yi-fu, LIU Man-cang, et al. Numerical simulations of temperature field in direct metal laser sintering process[J]. Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2004, 21(3): 225-233.
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金委员会-中国工程物理研究院联合基金资助项目(10276017);航空科学基金资助项目(04H52061);南京航空航天大学科研创新基金资助项目(S0403-061)
收稿日期: 2004-10-08; 修订日期: 2005-01-10
作者简介: 顾冬冬(1980-), 男, 博士研究生.
通讯作者: 沈以赴, 电话: 025-85687494; E-mail: yifushen@nuaa.edu.cn
(编辑 陈爱华)