DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.07.051
pH对腐熟蓝藻微生物燃料电池产电性能的影响
陈桂顶,朱光灿,周越
(东南大学 能源与环境学院,环境医学工程教育部重点实验室,江苏 南京,210096)
摘要:采用双室微生物燃料电池(microbial fuel cell, MFC)装置,以腐熟蓝藻为阳极基质,以氧气为阴极电子受体,考察阳极基质初始pH对MFC产电性能和腐熟蓝藻降解效果的影响。研究结果表明:阳极基质为弱碱性时,可提高电子传递效率,有利于MFC产电。初始pH为8时,MFC最大输出功率密度为3.83 mW/m2,分别是初始pH为6,7和9时的1.46倍、1.18倍和1.58倍,并且pH为8时,COD的去除率达到89.8%。在稳定产电期间,由于阳极H+ 向阴极迁移的速率高于参与阴极还原反应的消耗速率,导致阴极室内H+ 积累,使pH持续下降。调控阳极基质pH、提高阴极还原反应速率,在有效降解蓝藻的同时实现电能输出,为蓝藻资源化利用提供了新的 途径。
关键词:微生物燃料电池;产电性能;pH;腐熟蓝藻液
中图分类号:X703 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2015)07-2757-05
Effect of pH on power generation in MFC fed with decomposed cyanobacteria at anode chamber
CHEN Guiding, ZHU Guangcan, ZHOU Yue
(Key Laboratory of Environmental Medicine Engineering of Ministry of Education,
School of Energy and Environment, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China)
Abstract: The effect of anodic pH on power generation of microbial fuel cell (MFC) and decomposed cyanobacteria treatment was investigated using a traditional two-chamber microbial fuel cell, and decomposed cyanobacteria and oxygen gas as anodic substrate and cathodic electron acceptor, respectively. The results show that the alkalescent anodic substrate is in favor for power generation of MFC due to an efficient electron transfer. Compared to that with the anodic pH of 6, 7 and 9, the maximum power output of 3.83 mW/m2 with anodic pH of 8 is increased by 1.46 times, 1.18 times and 1.58 times, respectively. Moreover, the COD removal rate of 89.6% is achieved with anodic pH of 8. During the stability of electricity generation, the transfer rate of H+ from anode to cathode is higher than the consumption rate of H+, which is responsible for accumulation of H+ in the cathode, resulting in continuous declination of cathodic pH. MFC could be a new approach to simultaneous power generation and decomposed cyanobacteria treatment by controlling the anodic pH and improving the reduction efficiency of cathode.
Key words: microbial fuel cell; performance of power generation; pH; decomposed cyanobacteria
微生物燃料电池(microbial fuel cell, MFC)是一种利用微生物的催化作用,将有机物的化学能转化为电能的装置,由于具有降解有机污染物的同时获得电能的特点而成为了研究热点[1]。目前,国内外研究者已证实多种有机物和污染物能够被微生物利用获得电能,包括葡萄糖[2]、海洋底泥[3]、食品废水[4]、养殖废水[5]、垃圾渗滤液[6]及蓝藻[7]等。其中蓝藻是水体富营养化的产物,在蓝藻爆发期每天近万t蓝藻从太湖打捞上岸,这些蓝藻如不妥善处理,容易通过渗透和径流重新回到太湖水域造成二次污染。蓝藻中有机质极为丰富,蛋白质质量分数达到38%~47%,是作为MFC阳极基质及回收能源的理想原料。陈辉等[7]利用沉积型微生物燃料电池,以蓝藻为阳极基质时获得最大输出功率密度为5.7 mW/m2。Yuan等[8]采用有效容积为170 mL的单室微生物燃料电池,以蓝藻为阳极基质,获得的最大输出功率密度为114 mW/m2,有机物的去除率高达78.9%。阳极基质pH是影响MFC产电性能的一个重要参数,它直接影响微生物的新陈代谢活性,从而影响电子和质子产生机制[9],因此受到较多的关注。Yuan等[10]以醋酸盐为阳极基质,发现阳极pH为9时可提高电子传递效率且获得的最大输出功率密度为(1 170±58) mW/m2,与阳极pH为7和5的电池相比,最大输出功率密度分别提高了29%和89%。Puig等[11]指出MFC中阳极碱性基质有利于电能的产生。Akiba等[12]利用纯菌种研究阳极pH在9~11之间MFC的产电性能,结果表明当阳极基质pH为10.5时得到最高输出电压和库仑效率。本文作者以腐熟蓝藻为阳极基质,以氧气为阴极电子受体,考察阳极基质的初始pH对微生物燃料电池产电性能和腐熟蓝藻降解效果的影响,为蓝藻资源化利用提供新的方向和途径。
1 试验材料与方法
1.1 试验装置
本试验采用传统的双室MFC装置,由有机玻璃制成。阴极室和阳极室有效容积均为3.6 L,采用表面积均为954.6 cm2的石墨毡为阴阳极的电极材料。采用面积为77.64 cm2的质子交换膜(PEM)(Nafion211, DuPont, America)分隔阴阳两极。阴阳两极均连接甘汞标准电极(212型,上海罗素科技有限公司)。
1.2 试验水质
本试验所用腐熟蓝藻液为宜兴市周铁镇符渎港蓝藻打捞站的富藻水在自然条件下腐熟所得,腐熟蓝藻富含氮磷有机质且因细胞死亡,氮磷等有机质均分布于水体中,蓝藻在腐熟的过程中,经各种物化及微生物作用,部分纤维素、蛋白质等大分子有机物降解为小分子有机物,有利于系统产电。初始蓝藻腐熟液中COD质量浓度为28 757.5 mg/L,用自来水稀释至1 g/L左右,并用1 mol/L NaOH和1 mol/L HCl调节pH,配成初始pH分别为6,7,8和9的阳极基质。
1.3 试验方法
阳极接种厌氧污泥,以稀释后的腐熟蓝藻为基质(COD质量浓度为1 g/L左右),阴极加入清水并曝气。阴阳极连接1 kΩ外电阻,启动反应装置,采用数据采集卡记录MFC的输出电压。当连续2个运行周期最高输出电压接近时,启动完成,进入稳定运行期。稳定运行期共3个周期,每个周期采用2个完全相同的反应器,3个周期的阳极基质初始pH分别为7和6,7和8以及7和9,考察pH对MFC产电性能和蓝藻降解效果的影响。实验期间,测定不同反应时间的阴阳极pH和阳极室COD的变化。
1.4 分析与计算方法
COD质量浓度采用密闭回流滴定法测定[13],氧化还原电位和pH采用便携式pH-ORP(PH100,YSI Co,America)测量仪,阴阳极电势采用甘汞标准电极测量。MFC的输出电压U由数据采集卡(iUSBDAQ- U120816,上海锐选自动化科技有限公司)自动读取,并连接电脑进行记录,数据记录的频率是1次/min。电流I由欧姆定律I=U/R计算,其中R为外电阻,1 kΩ。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 pH对MFC产电性能影响
MFC系统于2011-07-20开始启动,当连续2个运行周期最高电压接近时,启动完成,进入稳定运行期。从MFC启动到稳定运行所需时间为63 d,高于以猪粪废水为基质的MFC的启动时间(30 d)[5]。这可能是由于本实验采用的腐熟蓝藻比猪粪废水成分复杂,含有的纤维素等难以降解,导致启动时间较长。
图1所示为阳极基质初始pH分别为6,7,8和9时MFC输出电压随时间的变化情况。第1个周期,阳极pH为6和7,系统开始即获得较高的输出电压,其原因是经驯化培养后,阳极已获得活性较高的产电菌,更换基质后,能快速启动产电。在3个周期内,阳极基质pH为7时,系统的最高输出电压均稳定在500 mV左右,而当阳极pH为6,8和9时,最高输出电压分别约为470,550和 450 mV。因此当阳极基质初始pH为8时,MFC产电性能最佳。Behera等[14]研究表明pH影响阳极产电微生物的电化学活性和MFC的产电性能,pH为8时的产电性能优于pH为6时的性能,与本研究的结果一致。Gil等[15]采用双室MFC装置研究发现阳极基质的pH在7~8之间有利于MFC产电。Yuan等[10]以醋酸盐为基质,研究结果表明阳极基质为碱性(pH为9)时可提高电子传递效率,有利于MFC的产电。
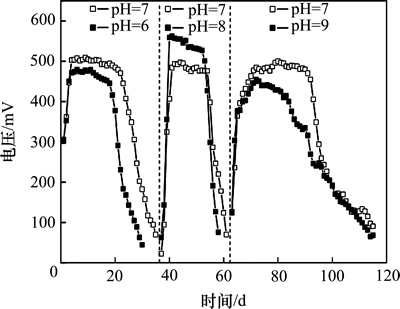
图1 阳极不同初始pH时输出电压随时间的变化
Fig. 1 Variation of cell voltage with time at different anodic initial pH
第3个周期为2011-11-26—2012-01-16,共52 d,期间试验水温为1~10 ℃。其中稳定运行时间达20 d左右,高于前2个周期,原因是试验进入第3周期后,水温较低,抑制了有机物的厌氧降解过程,导致周期时间增加。在第3个周期,pH为7时阳极的库仑效率为3.26%,高于pH为9时的库仑效率(2.48%),表明在低温条件下,碱性的蓝藻基质不利于系统产电。
阳极初始pH分别为6,7,8和9时,MFC的最大输出功率密度分别为2.63,3.25,3.83和2.42 mW/m2(图2),即阳极基质初始pH为8时,系统获得最佳的产电性能,最大输出功率密度分别是初始pH为6,7和9时的1.46倍、1.18倍和1.58倍,表明腐熟蓝藻基质偏碱性时,有利于产电微生物将有机物的化学能转化为电能,与叶晔捷等[16]的结果类似。Zhuang等[17]以啤酒废水为阳极基质,研究发现当阳极基质pH为10时,获得的MFC最大输出功率密度是pH为7时的2倍左右。郑宇等[18]以猪粪废水为阳极基质,研究结果表明阳极基质pH为10时,最大输出功率密度为2.1 W/m3,分别是pH为6和8时的2.7倍和1.9倍。采用不同阳极基质时,获得最高输出功率密度所需的基质pH不同,其原因可能是不同基质有不同的生化反应和反应产物。
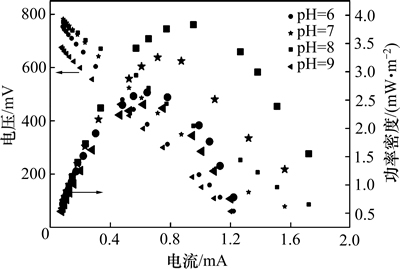
图2 阳极不同初始pH时MFC的极化曲线和功率密度曲线
Fig. 2 Polarization and power curves generated with different anodic initial pH
2.2 pH对腐熟蓝藻降解效果的影响
图3表明:在前2个周期,当pH为6,7和8时的COD去除率均为90%左右,获得45 mg/(L·d)的降解速率。在第3周期,实验进入12月份,水温较低,有机物降解速率明显降低,尤其在第3周期的后半期, COD质量浓度分别维持在270 mg/L(pH为7)和150 mg/L(pH为9)左右,有机物的厌氧降解几乎停滞。当pH为7和9时,COD去除率分别为80.7%和89.6%,降解速率分别仅为22 mg/(L·d)和24 mg/(L·d),库仑效率分别为3.26%和2.48%,表明低温时,碱性有利于腐熟蓝藻的厌氧降解而不利于产电。

图3 阳极不同初始pH时COD质量浓度随时间的变化
Fig. 3 Variation of COD with time at different anodic initial pH
2.3 电压与pH和COD关联性分析
图4和图5所示分别为阳极基质初始pH分别为7以及6,8和9时MFC输出电压、阳极室COD质量浓度、阳极室pH和阴极室pH的变化。当阳极基质初始pH为7时,3个周期的最高输出电压都稳定在500 mV左右,且能持续15 d以上。前2个周期的基质温度较高,当COD质量浓度高于100 mg/L时,输出电压可保持稳定,当COD质量浓度低于100 mg/L时,输出电压快速下降。而当基质温度较低时,需要更多的有机物参与产电反应,因此,在第3周期,COD质量浓度高于300 mg/L时才能维持稳定的输出电压。
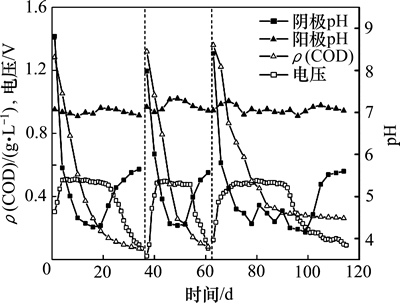
图4 阳极初始pH为7时不同周期内输出电压、COD质量浓度和pH随时间的变化
Fig. 4 Variation of cell voltage, COD mass concentration, pH of anode and cathode with time at anodic initial pH of 7 in different periods
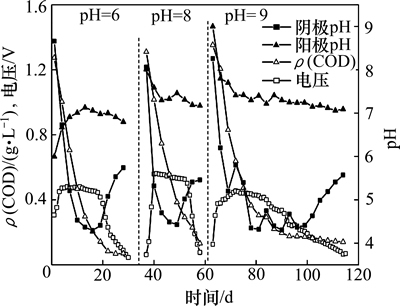
图5 阳极不同初始pH时不同周期内输出电压、COD质量浓度和pH随时间的变化
Fig. 5 Variation of cell voltage, COD mass concentration, pH of anode and cathode with time at different anodic initial pH in different periods
当阳极基质初始pH不同时,反应稳定后,pH均维持在7±0.3(图4和图5),然而系统产电稳定时,获得最大输出功率密度的阳极pH为8,表明阳极中产电菌与有机物厌氧降解菌具有不同适宜pH的生长环境,并且系统中有机物厌氧降解为主要反应。因此,若在反应过程中维持阳极pH在8~9,可提高用于产电反应的有机物比例,从而提高阳极库仑效率。而在反应周期中,随着产电反应的进行,阴极pH逐渐下降,在每个周期的后期,当输出电压开始下降时,即随着产电反应速率的下降,阴极的pH才逐渐上升。阴极pH的下降是由于阳极产电反应产生的H+透过质子交换膜进入阴极[19],H+的迁移速率大于参与阴极还原反应的速率,从而在阴极室内积累。H+从阳极室穿过质子交换膜到达阴极室的机制有2种:1) 浓度差。阳极室内的H+浓度高于阴极室,从而H+在浓度梯度的驱动下透过质子交换膜。2) 电位差。微生物燃料电池中阳极室电位较低,而阴极室内电位较高,电位差促使电子从阳极通过外电路到达阴极,导致H+穿过质子交换膜到达阴极参与反应。本实验中,由于阴极室内H+浓度高于阳极室内H+浓度,浓度差驱动机制不存在,因此,电位差才是质子传递的主要因素。并且,阴极室内溶解氧质量浓度始终高于5.5 mg/L,因此,溶解氧含量不是阴极反应的限制因素。实验中采用的电极材料是未加工的石墨毡,其表面氧气、质子和电子生成水的反应速率较低,造成较大的电荷迁移内阻,增加了微生物燃料电池的内阻。因此,改进电极材料的性能、提高阴极还原反应的速率,可提高MFC的产电性能,如以磷酸、硝酸和氯化锌等为活化剂活化石墨毡从而提高MFC的产电性能[20]。
3 结论
1) 阳极基质pH对MFC系统的产电性能有很大的影响,pH较高或较低都不同程度的抑制了阳极产电微生物的活性从而降低了MFC系统的产电性能。以腐熟蓝藻为双室MFC的阳极基质,初始pH为8时,MFC的产电性能最佳且蓝藻降解效果较好,最大输出功率密度为3.83 mW/m2,最大输出功率密度分别是初始pH为6,7和9时的1.46倍、1.18倍和1.58倍。
2) 阳极基质pH对腐熟蓝藻降解效果的影响较小,前2个周期内,基质温度较高,COD初始质量浓度为1.3 g/L左右,COD的去除率达到90%,进入第3个周期,基质温度较低,阳极基质初始pH为7和9时,库仑效率分别为3.26%和2.48%,COD去除率分别为80.7%和89.6%,且周期较长,表明低温抑制了有机物的厌氧降解过程,同时在低温条件下,碱性腐熟蓝藻有利于污染物的厌氧降解而不利于系统产电。
3) 阳极产电反应产生的H+透过质子交换膜进入阴极室,H+的迁移速率大于参与反应的速率,阴极材料表面较低的反应速率造成较大的电荷迁移内阻,增加了微生物燃料电池的内阻。因此,为进一步提高MFC产电性能,需改进电极材料的性能以此提高阴极还原反应的速率。
参考文献:
[1] Rabaey K, Verstraete W. Microbial fuel cells: Novel biotechnology for energy generation[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2005, 23(6): 291-298.
[2] Chaudhuri S K, Lovely D R. Electricity generation by direct oxidation of glucose in mediator less microbial fuel cells[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2003, 21(10): 1229-1232.
[3] Bond D R, Holmes D E, Tender L M, et al. Electrode-reducing microorganisms that harvest energy from marine sediments[J]. Science, 2002, 18(295): 483-485.
[4] Oh S E, Logan B E. Hydrogen and electricity production from a food processing wastewater using fermentation and microbial fuel cell technologies[J]. Water Res, 2005, 39(19): 4673-4682.
[5] Min B, Kim J, Oh S, et al. Electricity generation from swine wastewater using microbial fuel cells[J]. Water Res, 2005, 39(20): 4961-4968.
[6] 袁浩然, 邓丽芳, 王亚琢, 等. 垃圾预处理条件对渗滤液组分及其微生物燃料电池处理效果的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(10): 3237-3242.
YUAN Haoran, DENG Lifang, WANG Yazhuo, et al. Effects of pretreatment condition of MSW on components of leachate and result of MFC treatment[J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(10): 3237-3242.
[7] 陈辉, 赵娟, 吴瑾妤, 等. 可利用蓝藻产电的沉积型微生物[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2009, 9(4): 45-47.
CHEN Hui, ZHAO Juan, WU Jingyu, et al. Performance of power generation in sediment microbial fuel cell fed with cyanobacteria[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2009, 9(4): 45-47.
[8] YUAN Yong, CHEN Qing, ZHOU Shungui, et al. Bioelectricity generation and microcystins removal in a blue-green algae powered microbial fuel cell[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 187(1): 591-595.
[9] HE Zhen, HUANG Yuelong, Manohar A K, et al. Effect of electrolyte pH on the rate of the anodic and cathodic reactions in an air-cathode microbial fuel cell[J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2008, 74(1): 78-82.
[10] YUAN Yong, ZHAO Bo, ZHOU Shungui, et al. Electro catalytic activity of anodic biofilm responses to pH changes in microbial fuel cells[J]. Biores Technol, 2011, 102(13): 6887-6891.
[11] Puig S, Serra M, Coma M, et al. Effect of pH on nutrient dynamics and electricity production using microbial fuel cells[J]. Biores Technol, 2010, 101(24): 9594-9599.
[12] Akiba T, Bennetto H P, Stirling J L, et al. Eletricity production from alkalophilic organisms[J]. Biores Technol, 1987, 9 (9): 611-616.
[13] APHA. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater[M]. 19th ed. Washington, DC: American Public Health Association, 1995: 3-101.
[14] Behera M, Jana P S, More T T, et al. Rice mill wastewater treatment in microbial fuel cells fabricated using proton exchange membrane and earthen pot at different pH[J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2010, 79 (2): 228-233.
[15] Gil G C, Chang IS, Kim B H, et al. Operational parameters affecting the performance of a mediator-less microbial fuel cell Biosens[J]. Bioelectron, 2003, 18(4): 327-334.
[16] 叶晔捷, 宋天顺, 徐源, 等. 微生物燃料电池产电的影响因素[J]. 过程工程学报, 2009, 9(3): 527-530.
YE Yejie, SONG Tianshun, XU Yuan, et al. Influence factors of power generation in microbial fuel cell[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2009, 9(3): 527-530.
[17] ZHUANG Li, ZHOU Shungui, LI Yongtao. Enhanced performance of air-cathode two-chamber microbial fuel cells with high-pH anode and low-pH cathode[J]. Biores Technol, 2010, 101(10): 3514-3519
[18] 郑宇, 李天宏, 周顺桂, 等. pH值对猪粪废水微生物燃料电池产电性能的影响[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2010, 18(7): 2-9.
ZHENG Yu, LI Tianhong, ZHOU Shungui, et al . Effect of pH on power generation in microbial fuel cell fed with swine wastewater at the anode[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2010, 18(7): 2-9.
[19] Logan B E. Peer reviewed: Extracting energy from renewable resource[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2004, 38 (9): 160A-167A.
[20] 李冬梅. 化学活化石墨用于微生物燃料电池电极材料的研究[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学资源与环境工程学院, 2012: 1-65.
LI Dong-mei. Chemical activated graphite used as electrode materials in microbial fuel cells[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Technology. School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, 2012: 1-65.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2014-07-08;修回日期:2014-10-11
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(21277024) (Project(21277204) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:朱光灿,博士,教授,从事生活污水脱氮除磷技术与饮用水安全保障技术研究;E-mail: gc-zhu@seu.edu.cn