电沉积镍钨合金的成核与生长机理
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2021年第6期
论文作者:叶猛超 丁婷婷 周浩 何凤姣
文章页码:1842 - 1852
关键词:Ni-W合金;电沉积;成核;生长;纳米晶
Key words:Ni-W alloy; electrodeposition; nucleation; growth; nano-crystalline
摘 要:研究电沉积镍钨合金的成核与生长机理。采用循环伏安法和计时电流法研究电沉积镍钨合金的电化学行为和成核机理。从计时电流法得到的结果可以得到电沉积镍钨合金的成核模型和动力学参数。同时,采用扫描电子显微镜、原子力显微镜和透射电子显微镜研究电沉积镍钨合金的成核与生长过程。结果发现,镍钨合金的成核与早期生长阶段经历原子、单晶和纳米团簇的形成、移动和聚集过程。当单晶尺寸长到10 nm左右和晶体颗粒平均尺寸长到68 nm左右后,都不再长大。随着施加电位增大,晶核数目增加,但不影响最终晶体颗粒的尺寸。因此,电沉积的镍钨合金具有纳米晶结构。
Abstract: The nucleation and growth mechanism of electrodeposited Ni-W alloy were investigated. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and chronoamperometry (CA) were used to examine the electrochemical behavior and nucleation mechanism of the electrodeposited Ni-W alloy. The nucleation type and kinetic parameters of the electrodeposited Ni-W alloy were obtained from the CA analysis results. SEM, AFM, and TEM were also used to investigate the nucleation and growth process of the electrodeposition of Ni-W alloy. The results demonstrate that the nucleation and initial stages of the growth phase of the Ni-W alloy undergo the formation, movement, and aggregation of atoms, single crystals, and nanoclusters. When the size of single crystal increases up to approximately 10 nm and the average size of the crystal granules is approximately 68 nm, they no longer grow. Increasing the applied potential increases the number of nuclei but does not affect the size of the final crystal granules. Therefore, the electrodeposited Ni-W alloy shows a nanocrystalline structure.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 31(2021) 1842-1852
Meng-chao YE1,2, Ting-ting DING1,2, Hao ZHOU1,2, Feng-jiao HE1,2
1. College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
Received 31 August 2020; accepted 25 March 2021
Abstract: The nucleation and growth mechanism of electrodeposited Ni-W alloy were investigated. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and chronoamperometry (CA) were used to examine the electrochemical behavior and nucleation mechanism of the electrodeposited Ni-W alloy. The nucleation type and kinetic parameters of the electrodeposited Ni-W alloy were obtained from the CA analysis results. SEM, AFM, and TEM were also used to investigate the nucleation and growth process of the electrodeposition of Ni-W alloy. The results demonstrate that the nucleation and initial stages of the growth phase of the Ni-W alloy undergo the formation, movement, and aggregation of atoms, single crystals, and nanoclusters. When the size of single crystal increases up to approximately 10 nm and the average size of the crystal granules is approximately 68 nm, they no longer grow. Increasing the applied potential increases the number of nuclei but does not affect the size of the final crystal granules. Therefore, the electrodeposited Ni-W alloy shows a nanocrystalline structure.
Key words: Ni-W alloy; electrodeposition; nucleation; growth; nano-crystalline
1 Introduction
Metal and metal alloy deposits have been widely used in the industry due to their excellent properties, such as corrosion resistance, and wear resistance [1-4]. The important method for preparing metal and metal alloy deposits is electrodeposition [5-8]. The morphology, structure, and properties of the electrodeposited metal or alloy deposits are determined by the initial stages of the electrochemical nucleation and growth process [9,10]. Many researchers have studied the nucleation and growth process of monometals in the initial stages of electrodeposition and obtained some valuable results [11-14]. HILLS et al [15] revealed the nucleation and growth mechanism of silver in the electrodeposition process. They proposed that in the early stage of the electro- deposited silver, silver ions were reduced to silver atoms, and the silver atoms gathered together to form independent nuclei by migration. The nuclei then grew by direct reduction of atoms on the surface of the nuclei or gathering of different nuclei via migration on the surface of the electrode [15,16]. SCHARIFKER and HILLS [17] studied the nucleation and growth of mercury and lead in the electrodeposition process. They proposed the Scharifker-Hills (SH) nucleation model, which is based on the analysis of potentiostatic current transients and describes a mechanism involving three-dimensional multiple nucleation with the growth rate of hemispherical nuclei controlled by semi-infinite linear diffusion. The current response during the electrodeposition process was described for two limiting cases: instantaneous nucleation and progressive nucleation. SCHARIFER et al [18] also studied the electrodeposition process of lead and proposed an expression for the current transient. They thought that instantaneous nucleation and continuous nucleation were only the two extreme cases in the lead electrodeposition process. MIRKIN and NILOV [19] proposed a three- dimensional nucleation and growth model of a monometal in the electrodeposition process by considering the effects of ion diffusion, quasi- reversible charge transfer, and adsorption atomic rearrangement.
The electrodeposition of some metal alloys was also reported. CAO et al [20] investigated the initial stages of As-Sb alloy electrodeposition and thought it followed the three-dimensional nucleation and growth model under diffusion control. AGUIRRE et al [21] studied the nucleation and growth mechanism of Cu-Co alloy and proposed that the electrodeposition process involved multiple nucleation stages, beginning with the three-dimensional instantaneous nucleation and then changing to continuous nucleation. Limited by the detection technique, they could only use traditional electrochemical techniques to conduct the study. They thought that the nucleation and growth were caused by the direct attachment of atoms to the nuclei through movement.
With the development of electron microscopes such as TEM, SEM and AFM, researchers can directly observe atoms, clusters and nanoparticles. USTARROZ et al [22-24] studied the initial stages of electrochemical nucleation and growth of silver and platinum by TEM. They observed that the nucleation and growth of metal caused by direct attachment as described by early researchers accounted for only a small part, most of which were completed by surface movement and polymerization of nanoclusters. Based on these observations, they proposed the mechanism of electrochemical agglomeration growth, which gave a new insight into the nucleation and crystal growth in the electrodeposition of metal.
So far, the study of early stages of electrochemical nucleation and growth of metal alloys by TEM, SEM and AFM has been less reported. Understanding the early stages of electrochemical nucleation and growth of metal alloys is very important to control the electro- deposition process and obtain the desired properties of metal alloys [25-28]. Ni-W alloys are important engineering materials [29]. In this work, we examined the early stages of electrochemical nucleation and the growth mechanism of electro- deposited Ni-W alloy via SEM, AFM, TEM and electrochemical detection methods.
2 Experimental
Ni-W alloy was electrodeposited from the bath consisting of 0.076 mol/L nickel sulfate hexahydrate (NiSO4·6H2O), 0.091 mol/L sodium tungstate dihydrate (Na2WO4·2H2O), 0.095 mol/L citric acid monohydrate (C6H8O7·H2O) and 0.076 mol/L sodium citrate tribasic dihydrate (C6H5Na3O7·2H2O). The pH of the solution was adjusted to 6.9 with ammonia. All reagents were of analytical grade and were used as received. The electrolytes were prepared using distilled water.
Cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry were carried out in a conventional three-electrode cell with CHI660B electrochemical workstation. Glassy carbon electrode with a diameter of 3 mm, platinum wire, and saturated calomel electrode (SCE) were used as the working electrode, counter electrode, and reference electrode, respectively. The scan rate was 10 mV/s and the scan potential region ranged from 0 to -1.55 V. The deposited samples were obtained by potentiostatic electrodeposition in the corresponding bath. Before each experiment, the glassy carbon electrode was polished successively with 0.3 and 0.05 μm alumina powders. Then, the electrode surface was rinsed thoroughly with distilled water and ultrasonically cleaned with distilled water, absolute ethanol, and distilled water for 3-5 min to remove surface impurities. Finally, the electrode surface was rinsed once again with distilled water and dried at room temperature. The TEM samples were directly deposited onto the carbon-coated copper TEM grids. The TEM grids were placed on the top of the glass carbon electrode and fixed to the grid by means of adhesive tape. In both cases, the electrolytes were previously deaerated by N2.
The surface morphology of Ni-W alloy at the early growth stages was determined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Hitachi S4800) and atomic force microscopy (AFM, Bruker MultiMode 8). Transition transmission electron microscope (TEM, JEOL JEM-2100plus) was used for the observation of the morphological and structure characterization of the electrodeposited Ni-W alloy at the early growth stages. An X-ray energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) equipped in the TEM was used to determine the composite of the electrodeposited nanoclusters. Ni-W alloy coated samples were analyzed using an X-ray diffractometer (XRD, Bruker D8-Advance) with Cu Kα radiation.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Electrodeposition of Ni-W alloy studied via CV and EDS
The cyclic voltammogram of the Ni-W alloy electrolyte bath is illustrated in Fig. 1. For comparison, the CV curve for the blank bath (the bath without metal ions) is also shown in Fig. 1. On Curve 2, no significant peak was shown. As seen on Curve 1, when the potential swept from 0 to -1.55 V, the current increased sharply at -1.18 V, and the characteristics of hysteresis were observed in the potential backward sweeping, which indicates that the deposits caused a change in the electrode surface properties. The anode dissolution peak at -0.4 V indicates that metal or metal alloy was deposited on the electrode surface. Moreover, the current of the anode peak was found lower than that of the cathode peak. This could be attributed to the production of hydrogen evolution when the potential increased negatively.
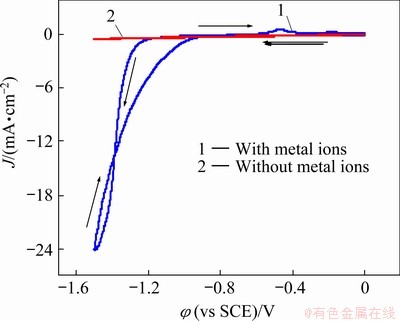
Fig. 1 Cyclic voltammograms of baths with and without metal ions (blank solution) at 298 K
The compositions of deposits obtained by potentiostatic electrodeposition at -1.30 V for 500 ms were tested by X-ray energy dispersive spectrometers (EDS), and the test results are shown in Fig. 2. The sample contained nickel and tungsten elements, which suggests that the nickel and tungsten were deposited on the electrode surface.
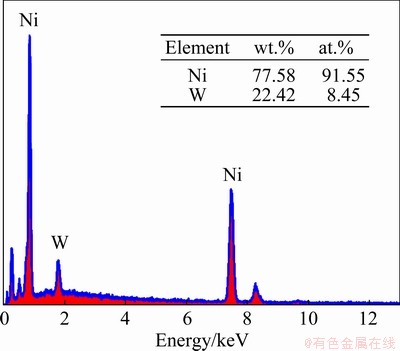
Fig. 2 EDS spectrum of electrodeposited Ni-W alloys at -1.30 V for 500 ms
3.2 Nucleation and growth process of electrodeposited Ni-W alloy
The electrochemical nucleation and growth process of electrodeposited Ni-W alloys can be monitored via SEM, AFM, TEM, and XRD.
The SEM morphologies of Ni-W alloys electrodeposited on glass carbon electrode at -1.30 V for 15, 20, 30 and 240 s are presented in Figs. 3(a, b, c, d), respectively, and morphologies of those alloys electrodeposited at -1.50 V for 5, 15 and 120 s are presented in Figs. 3(e, f, g), respectively. By comparing the deposits obtained at -1.30 V with electrodeposition time of 15, 20 and 30 s (Figs. 4(a, b, c)), the deposit size and amount increased with increasing electrodeposition time. By comparing the deposits obtained with electro- deposition time of 30 and 240 s, the crystal granule amount increased with increasing deposition time, but the average size of the crystal granules was the same, approximately 68 nm. For deposits obtained at a potential of -1.50 V (Figs. 4(e-g)), the size and the number of crystal granules increased with increasing deposition time up to 15 s. After 15 s, only the number of crystal granules increased with increasing deposition time, and the average size of the crystal granules remained approximately 68 nm.
According to a comparison between deposits obtained with deposition time of 15 s at -1.30 and -1.50 V (Figs. 4(a, f)), the number of crystal granules and their size under high overpotential were larger. These results demonstrate that a negative shift in the deposition potential could accelerate nucleation and growth but did not affect the average size of the final crystal granules. This may be due to the fact that the surface energy of the crystal granules decreases with increasing size and reaches a minimum when the average size of the crystal granules is approximately 68 nm; then, the crystal granules stop growing. The three- dimensional structure of the deposits is clearly shown in the inset images of Fig. 3(b), where the crystal granules were aggregated together. The results demonstrate that Ni-W alloy deposits exhibit a crystal granule microstructure.
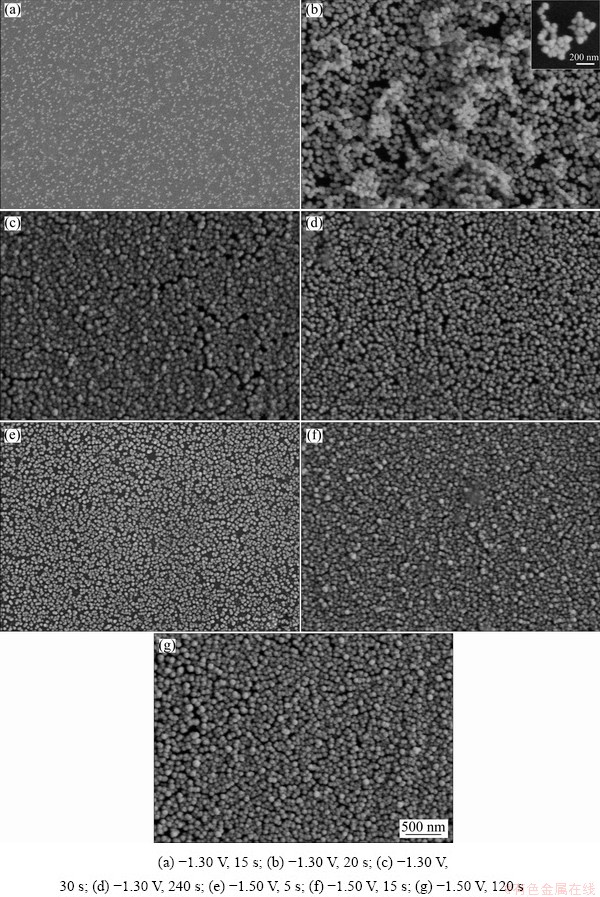
Fig. 3 SEM images of Ni-W alloys obtained under different conditions
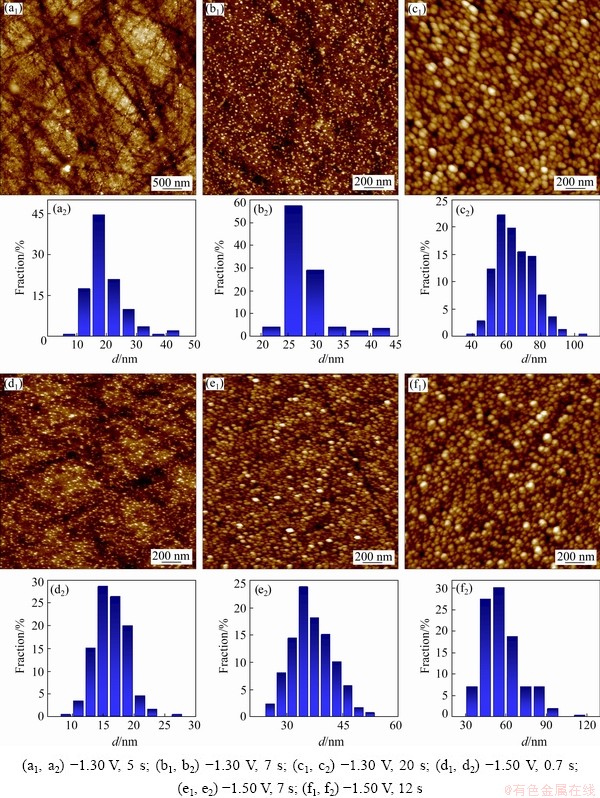
Fig. 4 AFM images (a1-f1) and corresponding size distribution histograms (a2-f2) of Ni-W alloy electrodeposited under different conditions
The AFM images of electrodeposits, obtained by potentiostatic electrodeposition on glass carbon electrode, are shown in Fig. 4, where Figs. 4(a, b, c) display the morphology and corresponding crystal granules size distribution of deposits obtained at -1.30 V with electrodeposition time of 5, 7 and 20 s, respectively. Likewise, Figs. 4(d, e, f) display the morphology and corresponding crystal granules size distribution of deposits obtained at -1.50 V with electrodeposition times of 0.7, 7 and 12 s, respectively. Figure 5 shows the morphology of the polished glass carbon electrode. The substrate surface roughness was 3.96 nm. For deposits obtained at -1.30 V and 5 s, a few of crystal granules with dimensions of 5-45 nm were randomly distributed on the electrode surface (Fig. 4(a)), where 15-30 nm crystal granules occupied 92%. For deposits obtained at -1.30 V and 7 s, numerous crystal granules with diameters of 20-45 nm formed on the electrode surface (Fig. 4(b)), and 25-40 nm crystal granules accounted for 93%; meanwhile, small-size crystal granules disappeared. The crystal granules obtained at -1.30 V and 20 s (Fig. 4(c)) were much more than those obtained under -1.30 V and 7 s (Fig. 4(b)). For the former, the crystal granules were in the range of 40-95 nm, where 50-80 nm crystal granules accounted for 92%. For deposits obtained at -1.50 V and 0.7 s (Fig. 4(d)), the crystal granules with 5-25 nm were randomly distributed on the electrode surface, and 10-20 nm crystal granules accounted for 90%. For deposits obtained at -1.50 V and 7 s (Fig. 4(e)), many crystal granules with diameters of 25-55 nm were formed on the electrode surface, and 25-45 nm crystal granules accounted for 95%. The crystal granules obtained at -1.50 V and 12 s (Fig. 4(f)) were more than those obtained at -1.50 V and 12 s (Fig. 4(e)), and the crystal granules were in the range of 35-95 nm, where 35-85 nm crystal granules accounted for 98%. The results are consistent with the SEM observation. During the electrodeposition process, the nuclei density increases with the increase of deposition time, and the size of crystal granules becomes larger. Moreover, with increasing overpotential, the number and the size of crystal granules increase in the nucleation and growth process. The increase in the overpotential can increase the free energy of metal ions to form new nuclei, resulting in increased nucleation rate and the size of crystal granules in the early stages of electrodeposition.
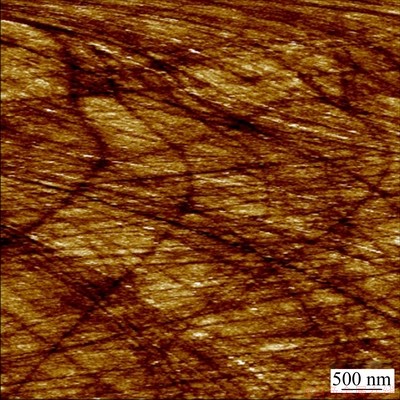
Fig. 5 AFM image of polished glass carbon electrode
TEM was also used to study the nucleation and early stages of growth process of electrodeposited Ni-W alloy. The TEM and corresponding HRTEM images of electrodeposits obtained by potentiostatic electrodeposition on copper grids at -1.30 V for 10, 50 and 500 ms are shown in Figs. 6(a, b, c), respectively. The size of the nanoclusters increased with the increase in electrodeposition time within 500 ms (Figs. 6(a1, b1, c1)). The HRTEM images (Figs. 6(a2, b2, c2)) showed single-crystal structure, whose diameter changed from approximately 2.5 to 10 nm with the increase in electrodeposition time from 10 to 50 ms, and the diameter remained at approximately 10 nm with a further increase in the electrodeposition time to 500 ms. The single crystal of the Ni-W alloy was observed in a short period, which indicates that the nucleation rate of Ni-W alloy was very fast. Moreover, the interplanar spacing of lattice fringes of the single crystal was 0.200 nm (Figs. 6(a2, b2)), which corresponds to the (111) crystal plane of the Ni-W alloy [30-32]. In Fig. 6(b3), single-crystal (green circle) and polycrystal nanoparticles (red circle) could be observed. In Fig. 6(b4), agglomerate could also be observed. Based on these results, the movement and aggregation of the nanocrystals and nanoclusters occurred in the early stage of electrodeposition process. Owing to the small size of the nanocrystals and nanoclusters, as well as the weak van der Waals force between Ni-W atoms and the substrate electrode, Ni-W nanocrystalline and nanoclusters could move on the electrode surface. In addition, they contacted each other and merged to form large-size nanocrystalline particles.
In the electrodeposition of Ni-W alloy, the maximum grain size was approximately 10 nm. The reason why it could not grow up may be related to the large difference between the atomic radii of Ni and W. The W atom replaced the Ni atom on the Ni lattice sites, resulting in a large distortion of the lattice.
In summary, in the early stages of electrochemical nucleation and growth of the electrodeposited Ni-W alloy, some single crystals with a diameter of 2.5 nm were immediately formed on the surface of the electrode, and then the single crystal grew to 10 nm by movement and aggregation of atoms and nanocrystals. And small- sized nanocrystals and nanoclusters continued to form crystal granules with a diameter of about 68 nm by movement and aggregation.
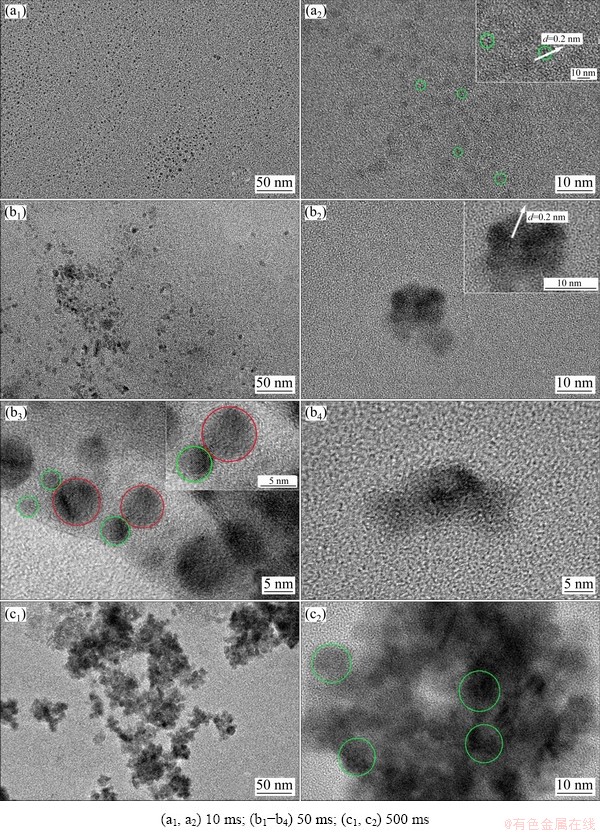
Fig. 6 TEM (a1-c1) and corresponding HRTEM (a2, b2-b4, c2) images of Ni-W alloys obtained at -1.30 V for various deposition time
X-ray diffraction was performed to evaluate the crystallographic texture and grain size of the electrodeposited Ni-W alloy. The XRD pattern of Ni-W alloys electrodeposited at -1.30 V is shown in Fig. 6. A sharp diffraction peak appeared at 2θ=44.3°, which was caused by the formation of a nanocrystalline solid solution of W in Ni [32-34]. The crystal lattice of Ni-W alloy calculated using Jade 6.0 software was 3.539 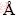 , which is larger than that of pure Ni (3.524
, which is larger than that of pure Ni (3.524 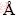 ). This result also indicates that the electrodeposited deposits were Ni-W alloy. The grain sizes of Ni-W alloys were calculated by the Scherrer equation:
). This result also indicates that the electrodeposited deposits were Ni-W alloy. The grain sizes of Ni-W alloys were calculated by the Scherrer equation:
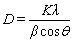 (1)
(1)
where D is grain size (nm), K is Scherrer constant (0.89), λ is wave length of X-ray (0.154056 nm), β is half peak width (rad) and θ is the diffraction angle [35]. The grain size was about 9.1 nm. This is consistent with the grain size calculated from TEM micrography.
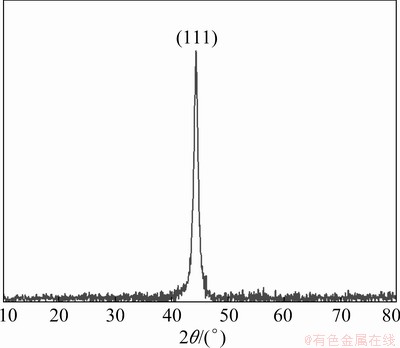
Fig. 7 X-ray diffraction pattern of electrodeposited Ni-W alloys
3.3 Nucleation mechanism of Ni-W alloy
To further investigate the electrochemical nucleation and growth mechanism of the electrodeposited Ni-W alloy and for comparison with the above results, the chronoamperometric test was performed. The results are presented in Fig. 8(a). It is observed that the current density dropped abruptly in the initial stage for all the curves, which was related to the charge of the electrode double layer [36]. After that, the current density increased with time, and a peak was observed, which corresponded to the nucleation and growth of the Ni-W alloy and an increase in the number of Ni-W nuclei. Finally, the current density decayed slowly from the peak to a steady state as the diffusion zones around the Ni-W nuclei overlapped. It is also found that the maximum current density increased with increasing applied potential, and the time required to reach the maximum current density decreased with increasing applied potential, due to the larger nucleation densities of Ni-W electrodeposited at high potential.
SCHARIFKER and HILLS [17] proposed a kinetic model (SH model) that divides nucleation into two limiting cases, namely, instantaneous nucleation and progressive nucleation, and can identify the nucleation/growth process of electrodeposition. Instantaneous nucleation and progressive nucleation are expressed as
Instantaneous nucleation:
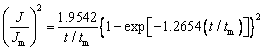 (2)
(2)
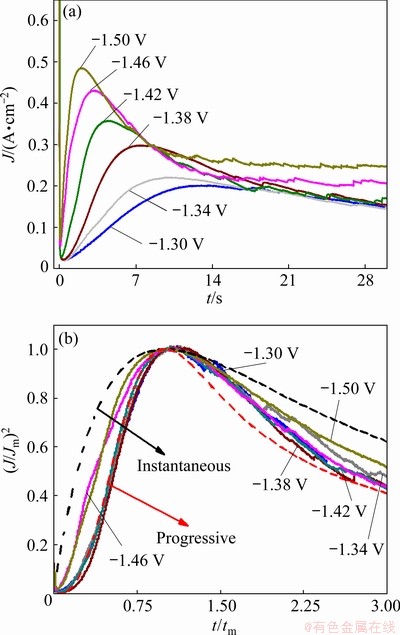
Fig. 8 Transient current density plots at various applied potentials (a) and nondimensional plots of experimental transients in comparison with theoretical curves for instantaneous and progressive cases (b)
Progressive nucleation:
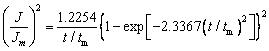 (3)
(3)
where J is the current density, Jm is the maximum current density, t is the time and tm is the time that corresponds to the maximum current density. A nondimensional treatment of the experimental data obtained via the CA and a comparison with the theoretical plot generated via Eqs. (1) and (2) are presented in Fig. 8(b). It can be observed that for potentials from -1.30 to -1.42 V, (J/Jm)2 vs t/tm experimental curves are close to the theoretical progress nucleation model; thus, the nucleation mechanism is based on the progressive formation of nuclei. For potentials from -1.46 to -1.50 V, (J/Jm)2 vs t/tm curves lie between the two theoretical nucleation models. This suggests that the nucleation mode of the Ni-W alloy changes with the negative shift of the applied potential. An increase in the overpotential can increase the free energy of nickel and tungsten ions to form new nuclei, thereby resulting in a deviation from progressive nucleation.
DIAZ-MORALES et al [37] developed a model for binary alloys and an expression for the current density transient that enables the determination of kinetic parameters, which is as follows:
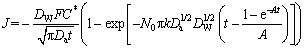 (3)
(3)
where C* is the bulk concentration of a pseudo-ion, DW is the mass and charge transport coefficient, F is the Faraday constant, Da is the apparent diffusion coefficient, k is a dimensionless constant, N0 is the number density of active sites, and A is the nucleation rate.
The values of C*, DW, Da and k can be calculated via the following equations:
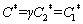 (4)
(4)
DW=(z1D1γ+z2D2)/(γ(z1x1+z2x2)) (5)
Da=(γD1+D2)/(γ+1) (6)
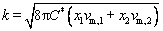 (7)
(7)
where C1* and C2* are the bulk concentrations of the two component species in the solution, z1 and z2 are the electron numbers of the two component species, with x1=C1*/(C1*+C2*) and x2=C2*/(C1*+C2*), D1 and D2 are the diffusion coefficients for these species, and vm,1 and vm,2 denote the molar volumes, respectively. The curves for the theoretical fits that were obtained via Eq. (3) are plotted in Fig. 9. The values of DWFC*/(πDa)0.5, N0πkDW0.5Da0.5 and A can be obtained from the fitting results. The relationships of D1 and D2 can be determined from the Cottrell equation as follows:
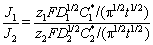 (8)
(8)
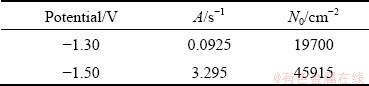
The mass ratios of Ni and W in alloy deposits were obtained via EDS analysis, and from the mass ratio, the value of J1/J2 was determined. The value of N0 was obtained through a combination of Eqs. (4)-(7). The values of kinetic parameters A and N0 are listed in Table 1, and both parameters increase with increasing overpotential. This is consistent with the results obtained from SEM and AFM, which demonstrates that the nucleation and growth rate of the Ni-W alloy are higher under high overpotential. However, the value of N0 is clearly lower than that directly observed from the SEM and AFM images.
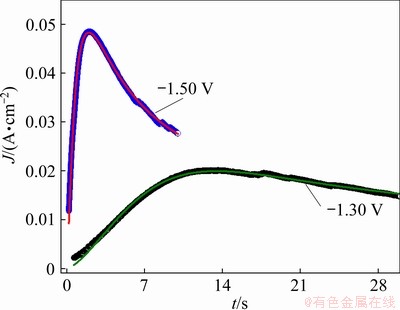
Fig. 9 Fitting of experimental current density transient curves of -1.30 and -1.50 V with Eq. (3)
Table 1 Kinetic parameters obtained from fitting results of experimental current density transients with Eq. (3)
4 Conclusions
(1) In the initial stages of the electrodeposited Ni-W alloy, some single crystals with a diameter of 2.5 nm were formed on the electrode surface; then, the single crystals grew via movement and aggregation of atoms and nanocrystals. The small-sized nanocrystals and nanoclusters continued to form large-sized crystal granules via movement and aggregation. The maximum size of the single crystals was approximately 10 nm, and the average size of the crystal granules was approximately 68 nm.
(2) Characterization of the electrodeposited Ni-W alloy revealed a nanocrystalline structure. The change in the overpotential of the electrode influenced only the nucleation rate but not the size of the electrodeposited crystal granules.
(3) The SH model was used to analyze the experimental current density transient curves. In a potential range from -1.30 to -1.42 V, the nucleation mechanism of the Ni-W alloy was close to progressive nucleation. When the applied potential was increased negatively, the nucleation mechanism varied between instantaneous nucleation and progressive nucleation. The current density transient curves were fitted with the model, and the kinetic parameters were obtained. The results demonstrated that the nucleation rate and nucleation density increased with increasing overpotential.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the Science and Technology Project of Hunan Province, China (No. 2018TP1012).
References
[1] ALESARY H F, CIHANGIR S, BALLANTYNE A D, HARRIS R C, WESTON D P, ABBOTT A P, RYDER K S. Influence of additives on the electrodeposition of zinc from a deep eutectic solvent [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 304: 118-130.
[2] UMRAO S, JEON J, JEON S M, CHOI Y J, LEE S. A homogeneous atomic layer MoS2(1-X)Se2X alloy prepared by low-pressure chemical vapor deposition, and its properties [J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9: 594-603.
[3] ABEDINI B, AHMADI N P, YAZDANI S, MAGAGNIN L. Electrodeposition and corrosion behavior of Zn-Ni-Mn alloy coatings deposited from alkaline solution [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30: 548-558.
[4] XU Yang, JIAO Han-dong, WANG Ming-yong, JIAO Shu-qiang. Direct preparation of V-Al alloy by molten salt electrolysis of soluble NaVO3 on a liquid Al cathode [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 779: 22-29.
[5] HNIDA K E, MARZEC M, WLAZLAK E, CHLEBDA D, SZACILOWSKI K, GILEK D, SULKA G D, PREZYBYLSKI M. Influence of pulse frequency on physicochemical properties of InSb films obtained via electrodeposition [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 304: 396-404.
[6] VIVEGNIS S, DELHALLE J, MEKHALIF Z, RENNER F U. Copper-zinc alloy electrodeposition mediated by triethanolamine as a complexing additive and chemical dealloying [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 319: 400-409.
[7] JIANG Jing-yun, ZHAO Wan-cheng, XUE Zhi-min, LI Qing-bo, YAN Chuan-yan, MU Tian-cheng. PEGylated quasi-ionic liquid electrolytes: Fundamental physiochemical properties and electrodeposition of aluminum [J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2016, 4(10): 5814-5819.
[8] BENGOA L N, PARY P, CONCONI M S, EGLI W A. Electrodeposition of Cu-Sn alloys from a methanesulfonic acid electrolyte containing benzyl alcohol [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 256: 211-219.
[9] XU Shao-hui, ZHU Yi-ping, XIONG Da-yuan, WANG Lian-wei, YANG Ping-xiong, CHU P K. Zinc electrodeposition on polycrystalline copper: Electrochemical study of early-stage growth mechanism [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121: 3938-3946.
[10] KIM Y R, LAI S C S, MCKELVEY K, ZHANG G, PERRY D, MILLER T S, UNWIN P R. Nucleation and aggregative growth of palladium nanoparticles on carbon electrodes: Experiment and kinetic model [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119: 17389-17397.
[11] VELMURUGAN J, NOEL J M, MIRKIN M V. Nucleation and growth of mercy on Pt nanoelectrodes at different overpotentials [J]. Chemical Science, 2014, 5: 189-194.
[12] JUNG H, LEE B, LENGYL M, AXELBAUM R, YOO J, KIM Y S, JUN Young-shin. Nanoscale in situ detection of nucleation and growth of Li electrodeposition at various current densities [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6: 4629-4635.
[13] AGUIRRE M C. Nucleation and growth mechanisms of palladium, nanoflower-shaped, and its performance as elecrocatalyst in the reduction of Cr(VI) [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2019, 49: 795-809.
[14] MONZON L M A, KLODT L, COEY J M D. Nucleation and electrochemical growth of zinc crystals on polyaniline films [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116: 18308-18317.
[15] HILLS G J, SCHIFFRIN D J, THOMPSON J. Electrochemical nucleation from molten salts—I. Diffusion controlled electrodeposition of silver from alkali molten nitrates [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1974, 19: 657-670.
[16] GUNAWARDENA G A, HILLS G J, MONTENEGRO I. Potentiostatic studies of electrochemical nucleation [J]. Electrochimica Acta,1978, 23: 693-697.
[17] SCHARIFKER B, HILLS G. Theoretical and experimental studies of multiple nucleation [J]. Electrochimica Acta,1983, 28: 879-889.
[18] SCHARIFKER B R, MOSTANY J, PALOMAR-PARDAVE M, GONZALEZ I. On the theory of the potentiostatic current transient for diffusion-controlled three-dimensional electrocrystallization processes [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1999, 146: 1005-1012.
[19] MIRKIN M V, NILOV A P. Three-dimensional nucleation and growth under controlled potential [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Electrochemistry, 1990, 283(1-2): 35-51.
[20] CAO Hua-zhen, ZHANG Yu-feng, WANG Qiang-qiang, WU Lian-kui, ZHENG Guo-qu. Nucleation/growth mechanism of electrocrystallization for As-Sb alloy in hydrochloric acid system [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 2291-2299.
[21] AGUIRRE M C, COAVAS H N, FABIETTI L M, URRETA S H. Nucleation and growth mechanisms in Cu-Co film [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120: 22142-22154.
[22] USTARROZ J, HAMMONS J A, ALTANTZIS T, HUBIN A, BALS S, TERRYN H. A generalized electrochemical aggregative growth mechanism [J]. Journal of American Chemical Society, 2013, 135: 11550-11561.
[23] USTARROZ J, KE X, HUBIN A, BALS S, TERRYN H. New insights into the early stages of nanoparticle electrodeposition [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116: 2322-2329.
[24] USTARROZ J, GUPTA U, HUBIN A, BALS S, TERRYN H. Electrodeposition of Ag nanoparticles onto carbon coated TEM grids: A direct approach to study early stages of nucleation [J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2010, 12: 1706-1709.
[25] ALLAHYARZADEH M H, ALIOFKHAZRAEI M, REZVANIAN A R, TORABINEJAD V, SABOUR ROUHAGHDAM A R. Ni-W electrodeposited coatings: Characterization, properties and applications [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2016, 307: 978-1010.
[26] LUKACZYNSKA M, CHERIGUI E A M, CEGLIA A, van den BERGH K, de STRYCKER J, TERRYN H, USTARROZ J. Influence of water content and applied potential on the electrodeposition of Ni coatings from deep eutectic solvents [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 319: 690-704.
[27] KONG De-long, ZHENG Zhen, MENG Fan-yu, LI Ning, LI De-yu. Electrochemical nucleation and growth of cobalt from methanesulfonic acid electrolyte [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2018, 165: D783-D789.
[28] RODRIGUEZ-CLEMENTE E, MANH T L, GUINTO- PANO C E, ROMERO-ROMO M, MEJIA-CABALLERO I, MORALES-GIL P, PALACIOS-GONZALEZ E, RAMIREZ- SILVA M T, PALOMAR-PARDAVE M. Aluminum electrochemical nucleation and growth onto a glassy carbon electrode from a deep eutectic solvent [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2019, 166: D3035-D3041.
[29] FENG Zhong-bao, WANG Lin, LI Da-gang, GAO Shuai-bo, SUN Qiang, LU Pai, XING Peng-fei, AN Mao-zhong. Nucleation and growth mechanism of a nanosheet-structured NiCoSe2 layer prepared by electrodeposition [J]. Nanotechnology, 2019, 30: 245602.
[30] AHMADI M, GUINEL M J F. Synthesis, characterization and understanding of the mechanisms of electroplating of nanocrystalline-amorphous nickel-tungsten alloys using in situ electrochemical impedance spectroscopy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 574: 196-205.
[31] LEE S, CHOI M, PARK S, JUNG H, YOO B. Mechanical properties of electrodeposited Ni-W thin films with alternate W-rich and W-poor multilayers [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 153: 225-231.
[32] BELTOWSKA-LEHMAN E, BIGOS A, INDYKA P, CHOJNACKA A, DREWIENKIEWICZ A, ZIMOWSKI S, KOT M, SZXZERBA M J. Optimisation of the electrodeposition process of Ni-W/ZrO2 nanocomposites [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2018, 813: 39-51.
[33] SALEHIKAHRIZSANGI P, RAEISSI K, KARIMZADEH F, CALABRESE L, PROVERBIO E. Highly hydrophobic Ni-W electrodeposited film with hierarchical structure [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2018, 344: 626-635.
[34] VAMSI M V N, WASEKAR N P, SUNDARARJAN G. Influence of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of pulse electrodeposited Ni-W alloy coatings [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2017, 319: 403-414.
[35] WANG Ming-yong, WANG Zhi, GUO Zhan-cheng. Electrodeposited free-crack Ni-W films under super gravity field: Structure and excellent corrosion property [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2014, 148: 245-252.
[36] NIKOLIC N D, STEVANOVIC S I, BRANKOVIC G. Nucleation and early stages of growth of lead onto copper electrodes from dilute electrolytes [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26: 3274-3282.
[37] DIAZ-MORALES O, MOSTANY J, BORRAS C, SCHARIFKER B R. Current transient study of the kinetics on nucleation and diffusion-controlled growth of bimetallic phases [J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2013, 17: 345-351.
叶猛超1,2,丁婷婷1,2,周 浩1,2,何凤姣1,2
1. 湖南大学 化学化工学院,长沙 410082;
2. 湖南大学 化学生物传感与计量学国家重点实验室,长沙 410082
摘 要:研究电沉积镍钨合金的成核与生长机理。采用循环伏安法和计时电流法研究电沉积镍钨合金的电化学行为和成核机理。从计时电流法得到的结果可以得到电沉积镍钨合金的成核模型和动力学参数。同时,采用扫描电子显微镜、原子力显微镜和透射电子显微镜研究电沉积镍钨合金的成核与生长过程。结果发现,镍钨合金的成核与早期生长阶段经历原子、单晶和纳米团簇的形成、移动和聚集过程。当单晶尺寸长到10 nm左右和晶体颗粒平均尺寸长到68 nm左右后,都不再长大。随着施加电位增大,晶核数目增加,但不影响最终晶体颗粒的尺寸。因此,电沉积的镍钨合金具有纳米晶结构。
关键词:Ni-W合金;电沉积;成核;生长;纳米晶
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Corresponding author: Feng-jiao HE, Fax: +86-731-88055818, E-mail: fengjiao87799232@hotmail.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(21)65621-2
1003-6326/ 2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press
2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press

