Al和Mo对难熔高熵合金高温氧化行为的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2019年第7期
论文作者:曹远奎 刘咏 刘彬 张卫东 王家文 杜萌
文章页码:1476 - 1483
关键词:高熵合金;难熔金属;高温氧化;氧化膜;显微组织
Key words:high entropy alloy; refractory metal; high temperature oxidation; oxide scale; microstructure
摘 要:难熔高熵合金在高温下具有优异的力学性能,其高温氧化行为非常重要。本文作者研究TiNbTa0.5Zr、TiNbTa0.5ZrAl 及 TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 3种合金的高温氧化行为,并讨论合金元素的影响。研究结果表明,TiNbTa0.5Zr及TiNbTa0.5ZrAl合金的氧化速率受扩散控制,符合指数型氧化规律。但TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5合金的氧化速率受界面反应控制,符合直线型氧化规律。添加Al可形成氧化保护膜从而提高合金的抗氧化性能;然而,添加Mo会破坏富Al保护膜。TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5合金的氧化膜中出现大量的孔洞和裂纹,导致其抗氧化性能明显下降。
Abstract: Refractory high entropy alloys have superior mechanical properties at high temperatures, and the oxidation behavior of these alloys is very important. The present work investigated the high temperature oxidation behavior of three alloys with compositions of TiNbTa0.5Zr, TiNbTa0.5ZrAl and TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5, and the effects of alloying elements were discussed. Results indicated that the oxidation rates of the TiNbTa0.5Zr and TiNbTa0.5ZrAl alloys are controlled by diffusion, and obey the exponential rule. However, the oxidation rate of the TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy is controlled by interface reaction, and obeys the linear rule. The addition of Al leads to a better oxidation resistance by forming a protective oxide scale. However, the protection of Al-rich scale is weakened by the addition of Mo. Extensive pores and cracks occur in the oxide scale of the TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy, resulting in a significant decrease in oxidation resistance.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 29(2019) 1476-1483
Yuan-kui CAO, Yong LIU, Bin LIU, Wei-dong ZHANG, Jia-wen WANG, Meng DU
State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 1 October 2018; accepted 21 May 2019
Abstract: Refractory high entropy alloys have superior mechanical properties at high temperatures, and the oxidation behavior of these alloys is very important. The present work investigated the high temperature oxidation behavior of three alloys with compositions of TiNbTa0.5Zr, TiNbTa0.5ZrAl and TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5, and the effects of alloying elements were discussed. Results indicated that the oxidation rates of the TiNbTa0.5Zr and TiNbTa0.5ZrAl alloys are controlled by diffusion, and obey the exponential rule. However, the oxidation rate of the TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy is controlled by interface reaction, and obeys the linear rule. The addition of Al leads to a better oxidation resistance by forming a protective oxide scale. However, the protection of Al-rich scale is weakened by the addition of Mo. Extensive pores and cracks occur in the oxide scale of the TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy, resulting in a significant decrease in oxidation resistance.
Key words: high entropy alloy; refractory metal; high temperature oxidation; oxide scale; microstructure
1 Introduction
Refractory high entropy alloys (HEAs) are the multi-principal component alloys based on refractory elements, such as W, Mo, Ta, Nb, V, Ti, Zr and Hf [1,2]. Refractory HEAs typically crystallize in the form of body centered cubic (BCC) [3]. Due to the high melting point and solid solution strengthening, refractory HEAs exhibit superior mechanical properties at high temperatures [4,5]. The effects of alloying elements on the mechanical properties have been reviewed in the literatures [6-8]. The addition of W or Mo can improve the high temperature strength and against softening even at temperatures higher than 1500 °C. For example, WMoTaNb and WMoTaNbV alloys show high compressive yield strength at 1600 °C [9], exceeding that of most of currant high temperature materials. The addition of Ti or Al can significantly decrease the density of the refractory HEAs, and thus gain a high specific strength [5,10]. SENKOV et al [11] have reported a promising refractory HEA with the composition of TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5, which has a yield strength of 745 MPa at 1000 °C and a density of 7.40 g/cm3. The specific strength of TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy is 1×105 Pa·m3/kg, almost the highest of metallic materials at 1000 °C.
The high temperature oxidation resistance is an important property for refractory metals. But, the oxidation mechanism is complex especially for multi-component alloys. In general, the oxidation behavior can be sorted into linear oxidation and exponential oxidation (including parabolic, cubical, and common exponential rules) [12,13]. The former usually leads to poor oxidation resistance due to the weak protection of oxide scales. The exponential oxidation usually results in high resistance in oxidation, due to multiple factors such as protective oxide scales and low solubility of oxygen. The alloying elements also affect the oxidation behavior. Elements such Al, Cr, Si, Y and Hf, can improve the oxidation resistant [14]. The addition of Al or Cr can lead to the formation of a continuous Al2O3 or Cr2O3 film that obstructs the direct diffusion of oxygen into the matrix [15]. Besides, Hf can enhance the bonding of oxide scale and matrix [16]. On the other hand, elements such as V, Mo and W, usually lead to fast oxidation. The main reasons are suggested to be the high solubility of oxygen and easy evaporation of oxide [17,18]. For traditional refractory alloys, it is clear to understand the oxidation mechanism. However, for refractory HEAs such as TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 and NbMoCrTiAl alloys, the oxidation behavior remains unclear due to their complex composition [19].
In this work, three refractory HEAs with compositions of TiNbTa0.5Zr, TiNbTa0.5ZrAl and TiNb- Ta0.5ZrAlMo0.5 were subjected to high temperature oxidation. The oxidation behavior and characteristics of oxide scales were investigated. The effects of alloying elements on oxidation mechanism were discussed.
2 Experimental
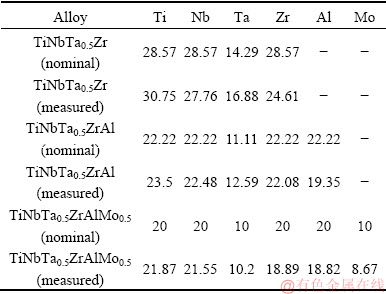
The HEAs with nominal compositions of TiNbTa0.5Zr, TiNbTa0.5ZrAl and TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 were vacuum arc melted under argon atmosphere in water-cooled copper crucible. The purities of Nb, Ta, Al, and Mo were 99.9%, while those for Ti and Zr were 99.6%. To avoid contamination from residual oxygen and nitrogen, high purity Ti was used as getter prior to melting. The alloys were remelted for at least five times to ensure homogeneity. The compositions of the alloy ingots determined with the use of an X-ray fluorescence (XRF) are given in Table 1.
Table 1 Compositions of refractory high entropy alloys (at.%)
The specimens for oxidation test were cut from the ingots with dimensions of 10 mm × 10 mm × 5 mm. Then, the specimens were polished and ultrasonically cleaned in ethanol. The cleaned specimens were put in corundum crucible and dried for 5 h in a vacuum drying. Isothermal oxidation tests were undertaken at 1000 °C in air with the exposure time of 5, 10, 15, 20 and 40 h. The heating rate was 20 °C/min. The mass of specimens was examined by using an electronic balance with a precision of 0.0001g.
The phase analysis was performed by X-ray diffraction (XRD, D8 ADVANCE) with Cu Kα radiation. The microstructures were observed by using a scanning electron microscope (SEM, Quanta 250 FEG) equipped with a backscatter electron (BSE) detector and an energy dispersive X-ray spectroscope (EDX). The elements distribution of oxide scales was analyzed by electron probe microanalysis (EPMA, JXA-8530F). Specimens for SEM and EPMA were obtained from cross-sections of the oxidized samples.
3 Results
3.1 Initial microstructures
The XRD patterns of the refractory HEAs are shown in Fig. 1. The three alloys present simple phase composition. BCC1 and BCC2 phases were detected in the refractory HEAs. With alloying elements increasing, the peaks of the two BCC phases separate gradually, and the diffraction peaks shift towards higher diffraction angles slightly. The dendritic microstructures of the refractory HEAs are shown in Fig. 2. The bright dendritic BCC1 phase is usually enriched with heavy elements such as Ta, Nb and Mo, while the dark interdendritic BCC2 phase is enriched with light elements such as Al, Ti and Zr [11,20].
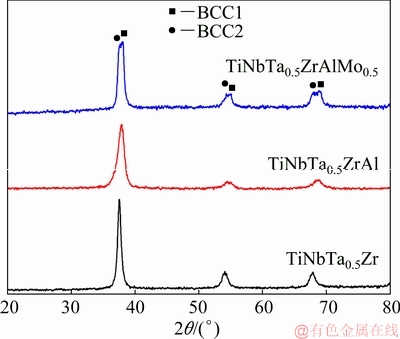
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of HEAs
3.2 Oxidation properties
The mass gain per unit area as a function of the exposure time for HEAs at 1000 °C is shown in Fig. 3. Both the TiNbTa0.5Zr and TiNbTa0.5ZrAl alloys exhibit exponential oxidation behavior. With Mo addition, the TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy presents linear oxidation behavior. The average oxidation rate k (given by k=Δm/t) for the TiNbTa0.5Zr alloy is 3.0 mg/(cm2·h). The addition of Al decreases the oxidation rate to k=1.1 mg/(cm2·h). However, the addition of Mo increases the oxidation rate to k=3.8 mg/(cm2·h). In the initial stage, the TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy shows a slow oxidation rate, and has almost the same mass gain to the TiNbTa0.5- ZrAl alloy at 10 h. After 10 h, the TiNbTa0.5ZrAl alloy exhibits a much slower oxidation rate, but the TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy presents a constant fast oxidation rate. The oxidized samples with exposure time of 10 h were analyzed to investigate the effects of the alloying elements.
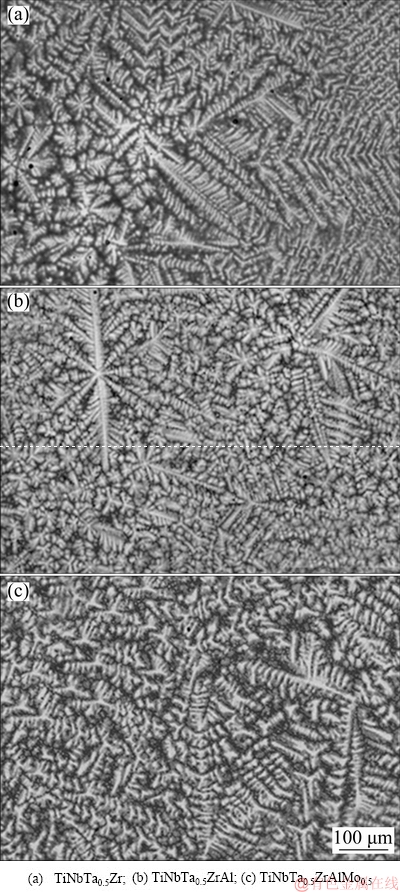
Fig. 2 BSE microstructures of HEAs
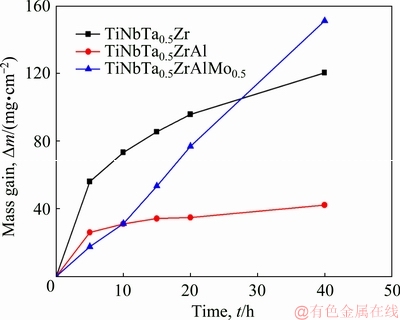
Fig. 3 Isothermal oxidation curves of HEAs at 1000 °C
3.3 Microstructures after oxidation
The XRD patterns of the oxide scales of the HEAs at 1000 °C for 10 h are shown in Fig. 4. Results show that the main oxides in the oxide scale of the TiNbTa0.5Zr alloy are TiO2, Nb2O5, Ti3O5 and ZrO2. With Al addition, an extra Al2O3 was found in the oxide scale of the TiNbTa0.5ZrAl alloy. And with Mo addition, both Al2O3 and MoO3 were found in the oxide scale of the TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy.
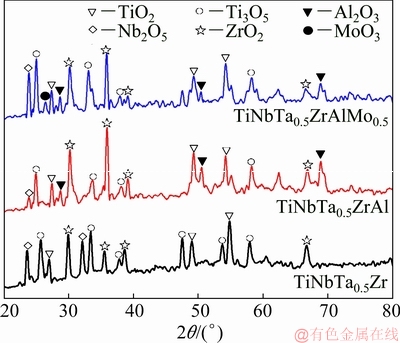
Fig. 4 XRD patterns of HEAs oxidized at 1000 °C for 10 h
The microstructures of oxide scale of the TiNbTa0.5Zr alloy are shown in Fig. 5. The scale is thick and the zone affected by oxidation is about 300 μm in thickness (Fig. 5(a)). A magnified view of the surface shows some cracks along the grain boundaries (Fig. 5(b)). A joint of grain boundaries is shown in Fig. 5(c), and the oxides at grain boundary present different features to the oxides inside grain. Fine oxides distribute homogeneously inside the grains, while coarse oxides and some pores locate at grain boundaries. The gray phase is detected as Ti-rich oxide, which is speculated as TiO2 according to the XRD results.
The microstructures of the oxide scale of the TiNbTa0.5ZrAl alloy are shown in Fig. 6. With Al addition, the oxide scale becomes thinner, and the zone affected by oxidation is about 150 μm in thickness (Fig. 6(a)). In the surface of the alloy, oxide scale is detected as Al-rich product, which can be speculated as Al2O3 according to the XRD results. Some Ti-rich particles, Zr-rich particles and small pores are also found in the oxide scale. The Al-rich oxide scale is fine and dense. The elemental distribution of the oxide scales is shown in Fig. 7. The surface of the oxide scale is enriched with oxygen and Al (Figs. 7(b) and (g)), which also indicates the existence of Al2O3. And from the O profile, the oxide scale is measured to be about 25 μm in thickness.
The microstructures of the oxide scale of the TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy are shown in Fig. 8. With Mo addition, the oxide scale becomes weak and separates from the substrate. Several cracks parallel to the surface are found. Perpendicular cracks are found through the oxide scale, which lead to a pathway for oxygen to diffuse into the substrate, as shown in Fig. 8(a). Extensive nano-scaled pores are found around the cracks. The dispersed bright phase which has the same size to the pores is detected as Mo-rich oxide. The Mo-rich oxide is speculated as MoO3 according to the XRD results. Figure 8(e) shows the details of the subsurface of the oxide scale. Three distinctive layers are detected. Layer 1 is a full oxide scale containing many pores and defects. Layer 2 is a transitional oxide scale, and the dispersive MoO3 and extensive nano-scaled pores are found in this layer. Layer 3 is detected as a Mo-rich scale. The elemental distributions of the surface and subsurface are shown in Figs. 9 and 10, respectively.
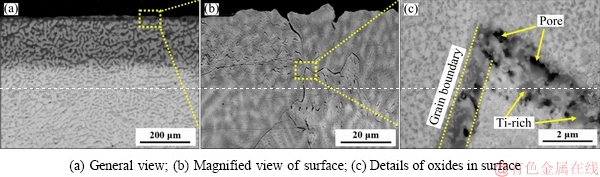
Fig. 5 Microstructures of oxide scale of TiNbTa0.5Zr alloy oxidized at 1000 °C for 10 h
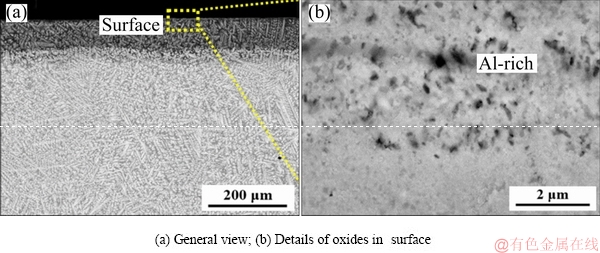
Fig. 6 Microstructures of oxide scales of TiNbTa0.5ZrAl alloy oxidized at 1000 °C for 10 h
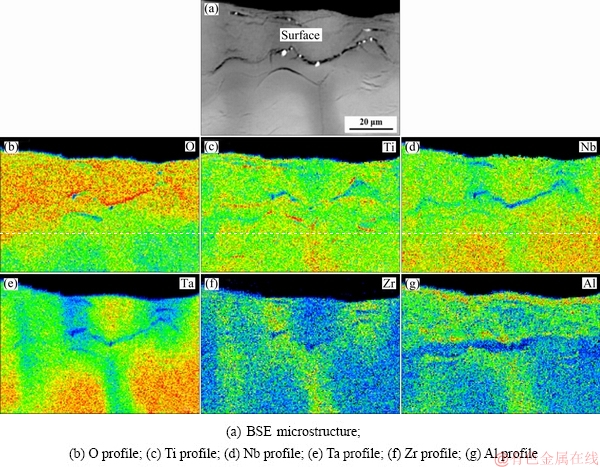
Fig. 7 EPMA elemental mappings of oxide scales of TiNbTa0.5ZrAl alloy oxidized at 1000 °C for 10 h
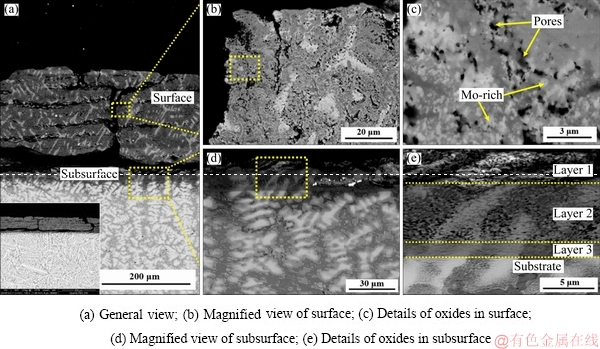
Fig. 8 Microstructures of oxide scales of TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy oxidized at 1000 °C for 10 h
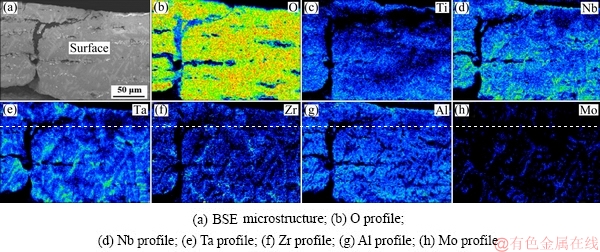
Fig. 9 EPMA elemental mappings of surface oxide scales of TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy oxidized at 1000 °C for 10 h

Fig. 10 EPMA elemental mappings of subsurface oxide scales of TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy oxidized at 1000 °C for 10 h
The surface presents characteristics of complete oxidation, containing a high content of oxygen. The Mo element is absent in the surface, which is related to the evaporation of the molybdenum oxides. The elemental distribution of the subsurface also shows layered oxidized features. Figure 10(b) presents the oxygen distribution, and a high content of oxygen is found in the upside of the subsurface (Layer 1 and Layer 2), indicating a serious oxidation. Between the subsurface and the substrate, a Mo-rich layer is detected (corresponding to Layer 3), as shown in Fig. 10(h). The content of Mo in Layer 3 is much higher than that in the substrate, which has not been reported in other literatures up to now.
4 Discussion
4.1 Oxidation kinetics
The oxidation behavior can be described by a power-law equation [12]:
△m=k1tn (1)
where Δm is the mass gain per unit area, t is the exposure time (in s), k1 is the oxidation rate constant, and n is the time exponent. There are two typical oxidation behaviors of metallic alloys [12,13]. The first is the linear oxidation behavior, which occurs when oxygen directly contacts the surface of the alloy. Thus, the oxidation rate is controlled by the interface reaction [21]. In this situation, the value of n in Eq. (1) is approximately 1. Alloys that exhibit linear oxidation behavior usually present: (a) a higher oxide density than the density of the alloy, (b) an oxide with high vapor pressure and easily evaporating from the oxide scale, and (c) spallation of the oxide scale [12,21,22]. The second is the exponential oxidation behavior, which occurs when oxygen is prevented from directly contacting the surface of the alloy. Thus, the oxidation rate is controlled by diffusion [12,16]. In this situation, the value of n in Eq. (1) is below 0.5. And for n=0.5, the alloy exhibits a typical parabolic oxidation behavior [18]. Alloys that exhibit exponential oxidation behavior usually present: (a) a lower oxide density than the density of the alloy, and (b) a continuous oxide scale well adhering to the substrate [12,18].
In this work, the oxidation kinetics of the three alloys was analyzed by the time exponent, as shown in Fig. 11. Both the TiNbTa0.5Zr and TiNbTa0.5ZrAl alloys exhibit exponential oxidation behavior since the values of n are 0.37 and 0.22, respectively. For TiNbTa0.5Zr alloy, the substrate is prevented from directly contacting the atmosphere due to the protection of the well-adhered oxide scale, and thus the oxidation rate is controlled by diffusion. Since diffusion is inversely proportional to the thickness of oxide scale, the oxidation rate decreases with the increase of the oxidation time, as shown in Fig. 3. With Al addition, the value of n decreases to 0.22, indicating the formation of a stronger protective oxide scale. Thus, the oxidation rate is also decreased with the addition of Al. However, with Mo addition, the value of n increases to 1.06, and the TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy exhibits linear oxidation behavior. This is mainly due to the spallation of the oxide scale, which leads to a direct contact of oxygen with the substrate, as shown in Fig. 8(a). Thus, the oxidation rate is controlled by the interface reaction. Since the concentration of oxygen in atmosphere is almost constant, the oxidation rate of the TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy is also constant (k=3.8 mg/(cm2·h).
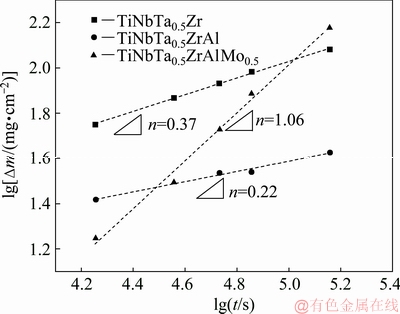
Fig. 11 Oxidation kinetics curves of HEAs at 1000 °C
It is necessary to point out that the above analysis did not take into account evaporation of some molybdenum oxides during the oxidation experiment. As for the TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy, indeed, the mass gain should contain both the mass gain caused by the formation of oxides and the mass loss caused by the evaporation of MoO3. However, it is reported that the mass change caused by the evaporation of molybdenum oxides is negligible [12]. SENKOV et al [12] have estimated the mass loss caused by the evaporation of molybdenum oxides in a TiNbTa0.5ZrCrMo0.5 alloy, and found that the total mass only increased by 3.8% after the oxide-loss correction. Furthermore, they also demonstrated that the mass loss caused by molybdenum oxides has little effect on the time exponent (n) and the oxidation rate constant (k1). Therefore, it is suggested that the mass change caused by the evaporation of MoO3 could not significantly influence the oxidation behavior of the TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy.
4.2 Effects of alloying elements on oxidation behavior
The oxidation resistance of the alloys is affected by the compactness of the oxide scale, which can be described through the Pilling-Bedworth ratio (PBR) [23]. The PBR is defined as the ratio of the oxide volume to the volume of the alloy from which the oxide forms [24,25]. For PBR<1, the oxide scale is discontinuous and porous, which cannot cover the substrate completely and further prevents direct connecting of the oxygen to the substrate. For PBR>2, the internal stress between oxides and matrix is high, and easily leads to the formation of pores and cracks around oxides. The pores and cracks will connect and cause a separation between the oxide scale and the substrate during high temperature oxidation. The best protection of the oxide scale occurs when PBR is between 1 and 1.5, in which the oxide scale is the densest [26].
In the TiNbTa0.5Zr alloy, the main oxide is TiO2, and the PBR for TiO2 is 1.95 [21]. Therefore, the internal stress between TiO2 and the TiNbTa0.5Zr substrate is high, which leads to the formation of pores and cracks around the oxides. The grain boundary acts as a weak region for oxidation resistance, since defects such as dislocations, pores and impurities gather here [27]. The defects lead to fast diffusion of oxygen, and result in coarse oxides around the grain boundary. Thus, the grain boundary becomes porous, and causes a fast oxidation of the alloy, as shown in Figs. 5(b) and (c). In the TiNbTa0.5ZrAl alloy, the main oxide is Al2O3. Since the PBR for Al2O3 is 1.28 [21], the Al-rich oxide scale presents a dense morphology without crack or spallation, and well-adhering with the TiNbTa0.5ZrAl substrate, as shown in Fig. 6(a). The oxidation rate of the TiNbTa0.5- ZrAl alloy in the initial 5 h is k=5.2 mg/(cm2·h), and then decreases to k=0.46 mg/(cm2·h) in the next 35 h, indicating the formation of Al2O3 scale after 5 h. The protective oxide scale of TiNbTa0.5ZrAl alloy leads to a better oxidation resistance than TiNbTa0.5Zr alloy, which agrees with the oxidation curves of the HEAs shown in Fig. 3. With the addition of Mo, the protection of Al-rich scale turns to be weakened, and the oxide scale of the TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy is mainly affected by MoO3. Table 2 presents the melting points of the oxides [18,22,28]. The MoO3 shows the lowest melting point (795 °C), which leads to a liquidation of the oxide during high temperature oxidation. The liquid MoO3 has a high saturated vapor pressure and evaporates fast [16]. Thus, the extensive nano-scaled pores were suggested to be an evidence of the evaporation of MoO3. Since the Mo-rich layer is parallel to the surface (Fig. 10(h)), the pores in Layer 2 (Fig. 8(e)) also distribute parallelly. During high temperature oxidation, the pores connect and cracks form, as shown in Fig. 8(a), which makes the scale porous and leads to a direct penetration of oxygen to the substrate. Therefore, the TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy shows a constant fast oxidation rate. Besides, in many traditional alloys, alloying elements can effectively influence the microstructures, and further affect the oxidation behavior of the samples [29,30]. For example, the addition of Si and B significantly affects the phase composition in molybdenum alloys. SUPATARAWANICH et al [29] examined the oxidation behavior of multiphase Mo-Si-B alloys with different starting microstructures, and found that the alloys with near-eutectic composition have a fine dispersion of T2, Mo, and Mo3Si phases, which results in the best overall oxidation resistance. Nevertheless, as for the current refractory HEAs, the addition of Al and Mo has limited effect on the microstructures (i.e. all the alloys present similar microstructures with dendritic BCC1 phase and interdendritic BCC2 phase as shown in Fig. 2), mainly due to the high entropy effect of the HEAs which can stabilize the BCC solid-solution phase [3]. Therefore, the oxidation behavior of the refractory HEAs depends more on the chemical compositions rather than the initial microstructures.
Table 2 Melting points of oxides [18,22,28]

5 Conclusions
(1) The TiNbTa0.5Zr and TiNbTa0.5ZrAl alloys exhibit exponential oxidation behavior, and the oxidation rates are controlled by diffusion. The TiNbTa0.5Zr- AlMo0.5 alloy exhibits linear oxidation behavior, and the oxidation rate is controlled by interface reaction.
(2) The addition of Al leads to a formation of Al2O3 oxide scale, which is dense and well adhered with the TiNbTa0.5ZrAl substrate. The protective Al2O3 scale results in a high oxidation resistance of the refractory HEAs.
(3) The addition of Mo causes a significant decrease in oxidation resistance, mainly due to the formation of MoO3 that evaporates during high temperature oxidation. The evaporative MoO3 oxides produce extensive pores in subsurface, and further form cracks, leading to a fast oxidation of the TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 alloy.
References
[1] SENKOV O N, WILKS G B, MIRACLE D B, CHUANG C P, LIAW P K. Refractory high-entropy alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2010, 18: 1758-1765.
[2] SENKOV O N, SCOTT J M, SENKOVA S V, MIRACLE D B, WOODWARD C F. Microstructure and room temperature properties of a high-entropy TaNbHfZrTi alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509: 6043-6048.
[3] MICHAEL C G, YEH J W, LIAW P K, ZHANG Y. High-entropy alloys: Fundamentals and applications [M]. Heidlburg: Springer, 2016.
[4] TODA C I, RIVERA D P. Modelling solid solution hardening in high entropy alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 85: 14-23.
[5] GORSSE S, MIRACLE D B, SENKOV O N. Mapping the world of complex concentrated alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2017, 135: 177-187.
[6] LIN C M, JUAN C C, CHANG C H, TSAI C W, YEH J W. Effect of Al addition on mechanical properties and microstructure of refractory AlxHfNbTaTiZr alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 624: 100-107.
[7] HAN Z D, CHEN N, ZHAO S F, FAN L W, YANG G N, SHAO Y, YAO K F. Effect of Ti additions on mechanical properties of NbMoTaW and VNbMoTaW refractory high entropy alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2017, 84: 153-157.
[8] FAZAKAS E, ZADOROZHNYY V, VARGA L K, INOUE A, LOUZGUINE L D, TIAN F, VITOS L. Experimental and theoretical study of Ti20Zr20Hf20Nb20X20 (X=V or Cr) refractory high-entropy alloys [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2014, 47: 131-138.
[9] SENKOV O N, WILKS G B, SCOTT J M, MIRACLE D B. Mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20- W20 refractory high entropy alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2011, 19: 698-706.
[10] FENG Rui, MICHAEL C G, CHANHO L, MICHAEL M, ZUO Ting-ting, CHEN Shu-ying, HAWK J, ZHANG Yong, LIAW P. Design of light-weight high-entropy alloys [J]. Entropy, 2016, 18: 1-21.
[11] SENKOV O N, SENKOVA S V, WOODWARD C. Effect of aluminum on the microstructure and properties of two refractory high-entropy alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 68: 214-228.
[12] SENKOV O N, SENKOVA S V, DIMIDUK D M, WOODWARD C, MIRACLE D B. Oxidation behavior of a refractory NbCrMo0.5Ta0.5- TiZr alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2012, 47: 6522-6534.
[13] KOFSTAD P. High-temperature oxidation of titanium [J]. Journal of the Less-Common Metals, 1967, 12: 449-464.
[14] JIANG H W, MA W, FENG X, DONG Z, ZHANG L, LIU Y. Effects of Nb and Si on high temperature oxidation of TiAl [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18: 512-517.
[15] YU H, UKAI S, HAYASHI S, OONO N. Effect of Al content on the high-temperature oxidation of Co-20Cr-(5,10)Al oxide dispersion strengthened superalloys [J]. Corrosion Science, 2017, 118: 49-59.
[16] HAN Bao-hong, MA Yue, PENG Hui, ZHENG Lei, GUO Hong-bo. Effect of Mo, Ta, and Re on high-temperature oxidation behavior of minor Hf doped β-NiAl alloy [J]. Corrosion Science, 2016, 102: 222-232.
[17] KARAHAN T, OUYANG Gao-yuan, RAY P K, KRAMER M J, AKINC M. Oxidation mechanism of W substituted Mo-Si-B alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2017, 87: 38-44.
[18] BUTLER T M, CHAPUT K J, DIETRICH J R, SENKOV O N. High temperature oxidation behaviors of equimolar NbTiZrV and NbTiZrCr refractory complex concentrated alloys (RCCAs) [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 729: 1004-1019.
[19] CHEN H, KAUFFMANN A, GORR B, SCHLIEPHAKE D, SEEMüLLER C, WAGNER J N, CHRIST S J, HEILMAIER M. Microstructure and mechanical properties at elevated temperatures of a new Al-containing refractory high-entropy alloy Nb-Mo-Cr- Ti-Al [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 661: 206-215.
[20] DIRRAS G, COUQUE H, LILENSTEN L, HECZEL A, TINGAUD D, COUZINIE J P, PERRIERE L, GUBICZA J, GUILLOT I. Mechanical behavior and microstructure of Ti20Hf20Zr20Ta20Nb20 high-entropy alloy loaded under quasi-static and dynamic compression conditions [J]. Materials Characterization, 2016, 111: 106-113.
[21] OSTROVSKAYA O, BADINI C, BAUDANA G, PADOVANO E, BIAMINO S. Thermogravimetric investigation on oxidation kinetics of complex Ti-Al alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2018, 93: 244-250.
[22] GORR B, MULLER F, AZIM M, CHRIST H J, MULLER T, CHEN H, KAUFFMANN A, HEILMAIER M. High-temperature oxidation behavior of refractory high-entropy alloys: Effect of alloy composition [J]. Oxidation of Metals, 2017, 88: 339-349.
[23] PROFF C, ABOLHASSANI S, LEMAIGNAN C. Oxidation behaviour of zirconium alloys and their precipitates—A mechanistic study [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2013, 432: 222-238.
[24] LI Ya-li, MORRAL J E. A local equilibrium model for internal oxidation [J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50: 3683-3691.
[25] REDDY A, HOVIS D B, HEUER A H, PAULIKAS A P, VEAL B W. In situ study of oxidation-induced growth strains in a model NiCrAlY bond-coat alloy [J]. Oxidation of Metals, 2007, 67: 153-177.
[26] XU J L, LIU F, WANG F P, YU D Z, ZHAO L C. The corrosion resistance behavior of Al2O3 coating prepared on NiTi alloy by micro-arc oxidation [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 472: 276-280.
[27] SUSHKO M L, ALEXANDROV V, SCHREIBER D K, ROSSO K M, BRUEMMER S M. Multiscale model of metal alloy oxidation at grain boundaries [J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2015, 142: 1-8.
[28] GORR B, MUELLER F, CHRIST H J, MUELLER T, CHEN H, KAUFFMANN A, HEILMAIER M. High temperature oxidation behavior of an equimolar refractory metal-based alloy 20Nb-20Mo- 20Cr-20Ti-20Al with and without Si addition [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 688: 468-477.
[29] SUPATARAWANICH V, JOHNSON D R, LIU C T. Effects of microstructure on the oxidation behavior of multiphase Mo-Si-B alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 344: 328-339.
[30] GENG J, TSAKIROPOULOS P. A study of the microstructures and oxidation of Nb-Si-Cr-Al-Mo in situ composites alloyed with Ti, Hf and Sn [J]. Intermetallics, 2007, 15: 382-395.
曹远奎,刘 咏,刘 彬,张卫东,王家文,杜 萌
中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083
摘 要:难熔高熵合金在高温下具有优异的力学性能,其高温氧化行为非常重要。本文作者研究TiNbTa0.5Zr、TiNbTa0.5ZrAl 及 TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5 3种合金的高温氧化行为,并讨论合金元素的影响。研究结果表明,TiNbTa0.5Zr及TiNbTa0.5ZrAl合金的氧化速率受扩散控制,符合指数型氧化规律。但TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5合金的氧化速率受界面反应控制,符合直线型氧化规律。添加Al可形成氧化保护膜从而提高合金的抗氧化性能;然而,添加Mo会破坏富Al保护膜。TiNbTa0.5ZrAlMo0.5合金的氧化膜中出现大量的孔洞和裂纹,导致其抗氧化性能明显下降。
关键词:高熵合金;难熔金属;高温氧化;氧化膜;显微组织
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (51671217) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (CX2017B047) supported by the Program of Innovation for Postgraduate of Hunan Province, China
Corresponding author: Yong LIU; Tel: +86-13307318308; E-mail: yonliu@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65054-5

